Exercise Physiology Exam 1
1/197
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
198 Terms
What are examples of physical activity?
Washing the dishes, cleaning the house
What are examples of exercise?
Running, Walking, Lifting
What are examples of sports?
Hockey, Football, Soccer
What's the difference between sports and exercise?
In sports you have competition and exercise you just complete your program
What are the three different types of muscles?
Smooth, Cardiac, Skeletal
What is smooth muscles sometimes called?
Involuntary muscle
Where is smooth muscle found?
In the wall of most blood vessels, and wall of internal organs
Where is cardiac muscle found?
The heart
Is cardiac muscle under conscious control?
No
Are skeletal muscles under conscious control?
Yes
Together with bones the skeletal muscles make up the what?
Musculoskeletal system
The human body has more than _____ skeletal muscles?
The human body has more than 600 skeletal muscles
What are the three different layers of connective tissue?
Epimysium, Perimysium, Endomysium
Where's the epimysium located?
Tissue around entire muscle belly
Where's the perimysium located?
Tissue around a bundle of muscle fibers
Where's the endomysium located?
Tissue around one muscle cell
What surrounds an individual muscle fiber?
Plasmalemma
What is the plasmalemma part of?
The sarcolemma
Inside the plasmalemma there are myo-fibrils what's inside the myo-fibrils?
The sarcoplasm
What does the sarcoplasm house?
Transverse tubules (T-tubules)
What do the t-tubules provide?
They provide pathways for waste to leave the cells and substances to enter the cells
A network of tubules is known as?
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum (SR)
The sarcoplasmic reticulum serves as a storage unit for what?
Calcium
What is the stored form of glucose called?
Glycogen
What's inside a muscle fiber?
Filaments (Thick and Thin)
What do thick filaments contain?
Myosin, titin
What is myosin?
Protein that binds and moves actin
What is titin's role in the muscle?
Center myosin, provide force when muscles are stretched, prevent overstretching and damage to the sarcomere
What do thin filaments contain?
Actin, Troponin, Tropomyosin
What does tropomyosin do?
It's a tube-shaped protein that twists around the actin strand
What does troponin do?
A protein that's attached at intervals to both the actin and tropomyosin
What's nebulin?
An anchoring protein for actin
What's this called? (picture on answer slide)
Motor unit
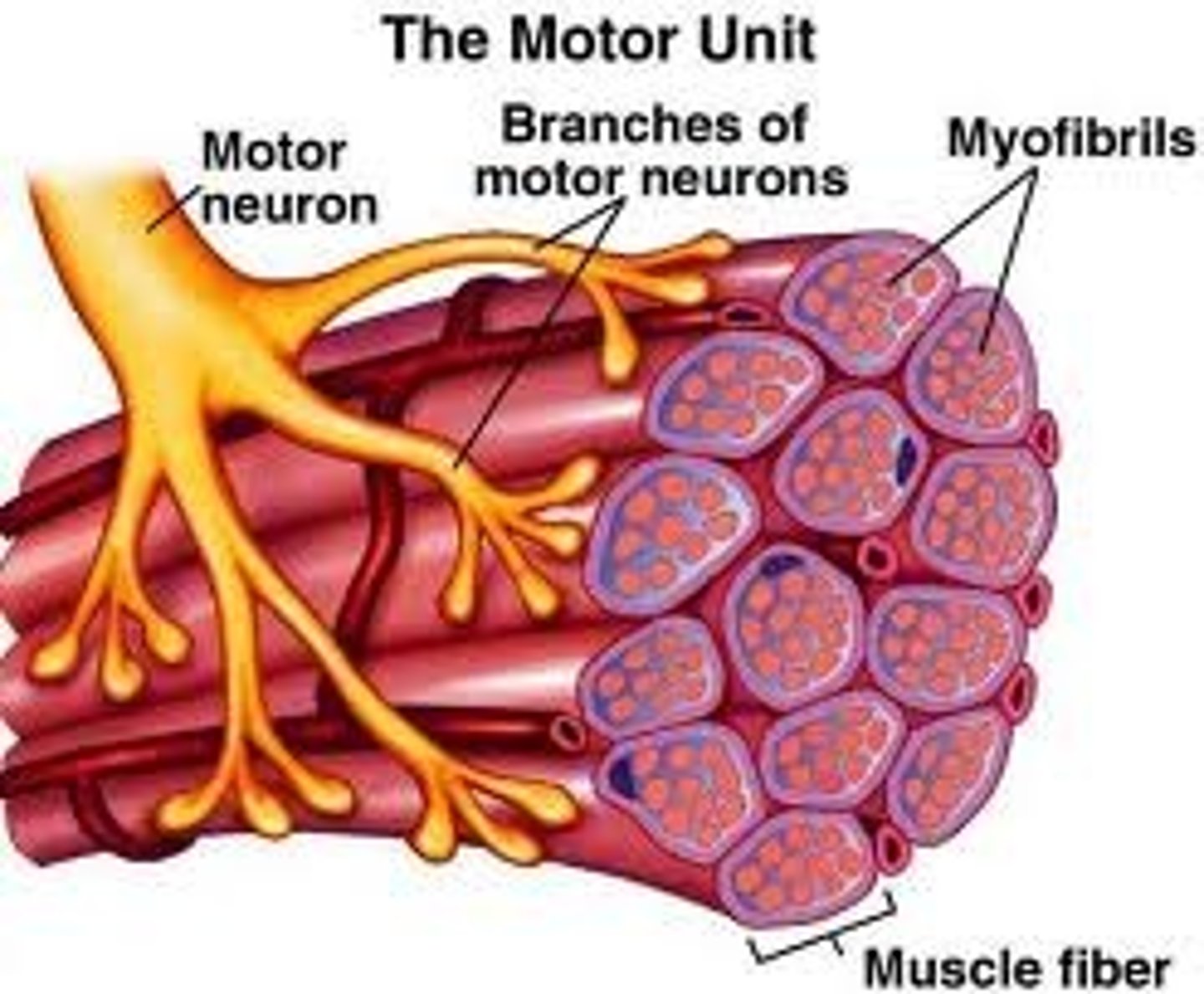
An α-motor neuron is a nerve cell that connects with many muscle fibers. A single α-motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it directly signals are collectively termed a
Motor unit
In a motor unit what occurs between the muscle fibers and the axon terminal?
Neuromuscular junction
What's excitation contraction coupling in simple terms?
Muscle contraction
What does the hemoglobin do?
Carries oxygen in the blood
What does the myoglobin do?
Transfers oxygen in the cell
ATP can be hydrolyzed by what process?
ATPase
After the ATP process has occurred what is made?
ADP, and Inorganic Phosphate
At -90mv what's this called? (In the muscle)
Resting Membrane Potential
At -55mv what's this called? (In the muscle)
Threshold Potential
At +30mv what's this called? (In the muscle)
Action Potential
What are the two types of muscle fibers?
Type I (slow twitch)
Type II (fast twitch)
What are the extra Type II muscle fibers?
Type IIa, Type IIb/x
What's it called when fibers are activated upon recruitment?
Principle of orderly recruitment
A sprint is using what muscle fiber type?
A marathon is using what muscle fiber type?
Type II
Type I
What's the all or none response?
All muscle fibers activate or none do
What are the three types of muscle contractions?
Concentric, Eccentric, Isometric
What is happening to the muscle during concentric, eccentric, and isometric contractions?
Concentric - Shortening of the muscle
Eccentric - Lengthening of the muscle
Isometric - Muscle stays at the same length
Are muscles always contracting during contractions?
Yes
More force can be generated when _____ is activated?
More motor units
What's a single electrical stimulus called?
Twitch
What are three stimuli called?
Summation
What is continuous stimulation called?
Tetanus
What is hypertrophy/atrophy?
Hypertrophy is when the muscle fibers grow/Atrophy is when the muscle fibers shrink
Most muscles are composed roughly of what?
50% type I fibers, 25% type IIa fibers, 25% type IIb
Type I has a ____ form of myosin ATPase
Slow
Type II has a ____ form of myosin ATPase
Fast
Which muscle fibers have a more developed sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Type II
A type I motor unit has a smaller cell body and innervates <____ muscle fibers?
300
A type II motor unit has a larger cell body and innervates >____ muscle fibers?
300
What exercises coincide with type I muscle fibers?
Aerobic and endurance training
What exercises coincide with type II muscle fibers?
Anaerobic and force training
As we grow older muscles tend to lose which type of muscle fibers?
Type II
What are the three energy substrates?
Carbohydrates, Fats, Proteins
What are substrates mostly made out of?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen and (in the case of protein) nitrogen
Where are carbs normally stored?
Muscle and Liver
How many grams can the muscle and liver store?
Muscle (500g) Liver (110g)
Where is glycogen stored in muscle cells?
Cytoplasm
Glucose can be found in what?
The blood
Can glycogen be found in the blood?
No
What breaks down creatine phosphate into creatine and inorganic phosphate?
Creatine Kinase (CK)
Muscle and liver glycogen stores are what?
Limited
Carbs are the only energy source used by what?
Brain tissue
When does fat get used for energy?
During prolonged less intense exercise
What's glycogenesis?
Glucose converted to glycogen
What's glycogenolysis?
Glycogen converted to glucose
What's gluconeogenesis?
Protein or fat is converted to glucose
What's lipogenesis?
Formation of fat
What do enzymes control?
Rate of chemical reactions
Going from ADP and inorganic phosphate to ATP is called what?
Phosphorylation
Glycolysis is the process of turning _____ into _____?
Turning glucose into pyruvate
How many pyruvate do you make in glycolysis?
2
In anaerobic glycolysis what is produced?
Lactate
The rate limiting enzyme is called what?
Phosphofructokinase (PFK)
In anaerobic glycolysis how many ATP are made?
4
In anaerobic glycolysis how many net ATP are made?
2
In anaerobic glycolysis how many NADH are made?
2
In aerobic glycolysis how many ATP are made?
38
Prolonged exercise relies on what system?
Oxidative System
Anaerobic production of ATP takes place in what?
Cytoplasm
In the oxidative system, production of ATP occurs where?
Mitochondria
When is lactate good?
When it goes through a buffer system
When is lactate bad?
When it doesn't go through a buffer system
If you buffer lactate, what does it make?
ATP and NADH in glycolysis
What does FFA stand for?
Free Fatty Acids
One molecule of glycerol makes how many FFA's?
Three
What's the process of converting FFA to Acetyl CoA?
β-oxidation
β-oxidation yields how many molecules of acetyl CoA?
8 molecules