Body temperature: Homeostasis and response: Biology: GCSE (9:1)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Homeostasis
The regulation of conditions in a cell or organism in order to optimally respond to internal and external changes
Body temperature
The amount of heat in the body which is controlled by homeostasis to ensure cells and enzymes function properly
Enzymes and colder temperatures
Enzymes work best at their optimum temperature, if it becomes too cold the enzymes will not have enough energy for successful reactions
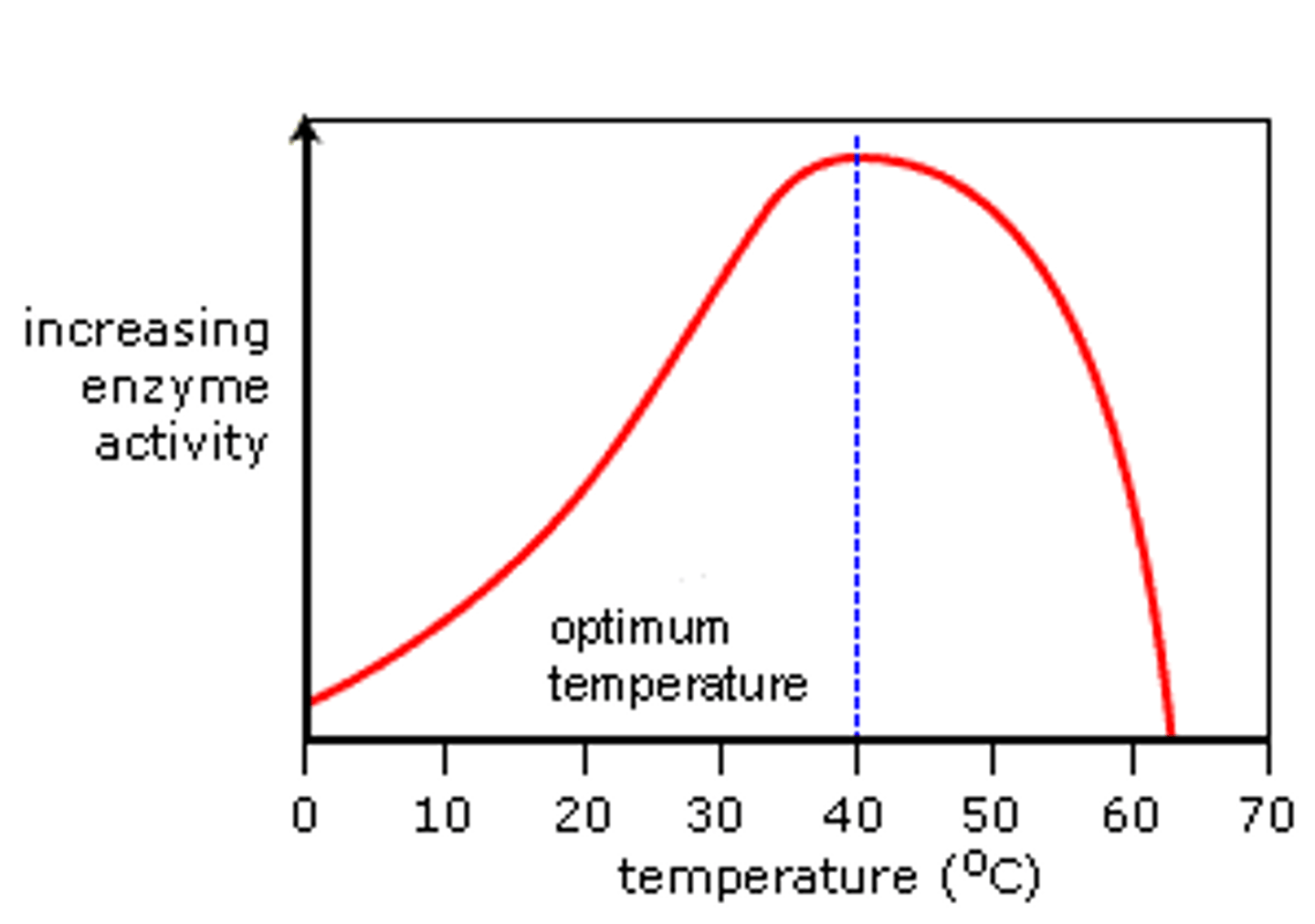
Enzymes and hotter temperatures
Enzymes work best at their optimum temperature, if it becomes too hot the enzymes will denature and be unable to function
Blood temperature
Temperature of the blood is normally around 37 degrees celsius, which is the optimal temperature for human enzyme activity
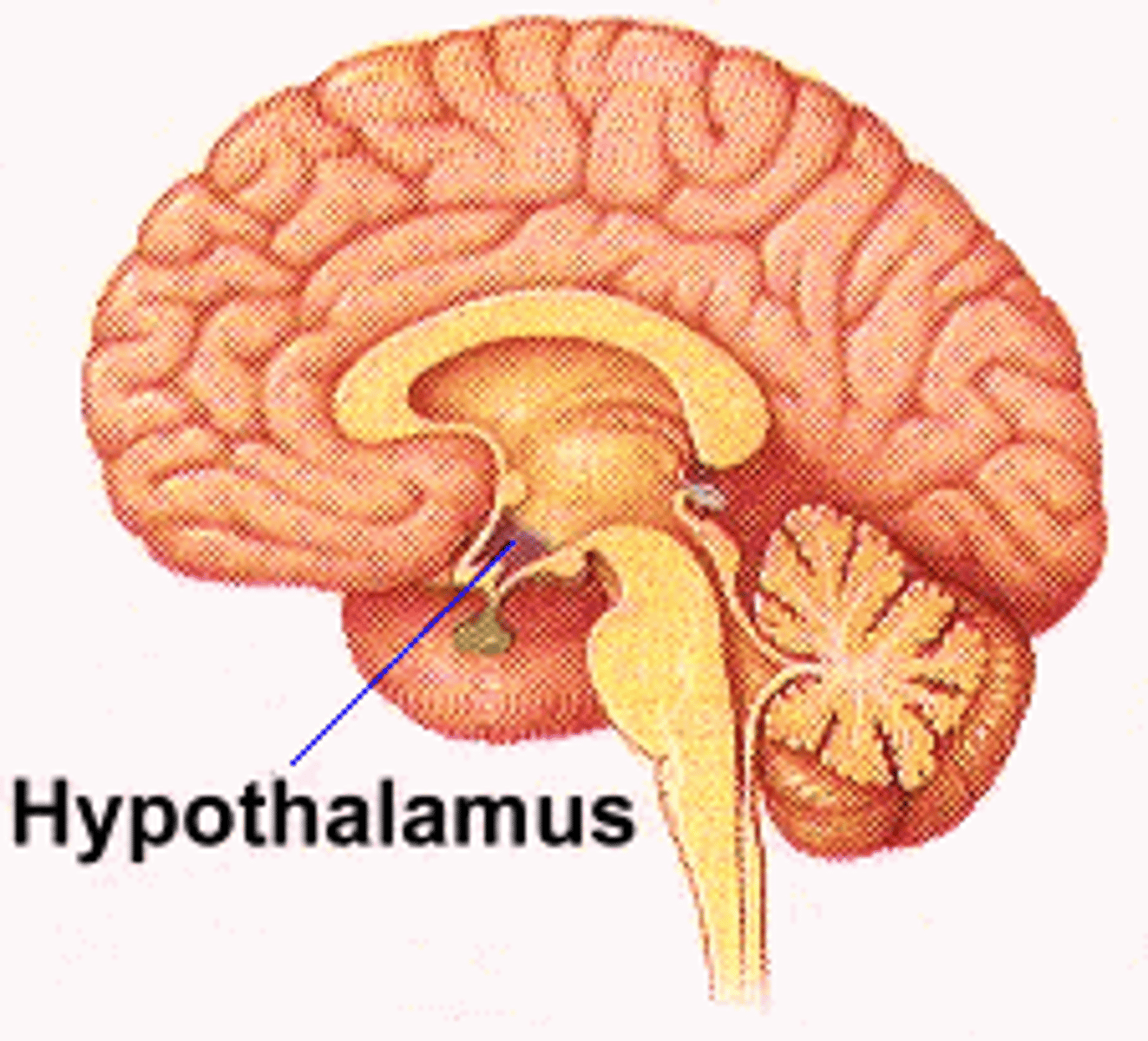
Thermoregulatory centre
The area of the brain that is sensitive to the temperature of the blood
Temperature receptors
Cells which respond to temperature changes in the skin and body
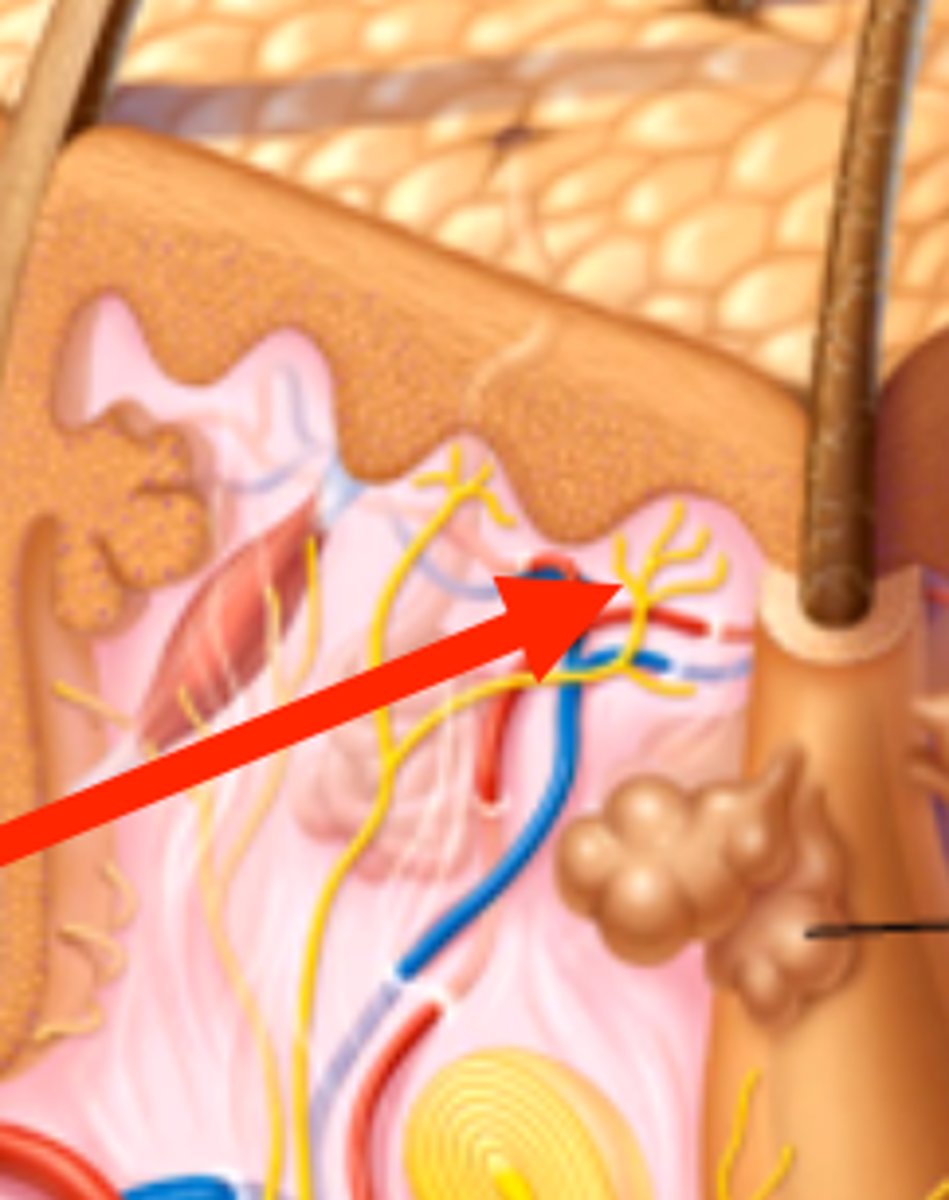
Nervous impulses
Electrical signals that are sent from temperature receptors to the thermoregulatory centre during a response to temperature change
Vasodilation
The widening of blood vessels which increases the amount of blood near the skin's surface, allowing more heat to be transferred to the surroundings
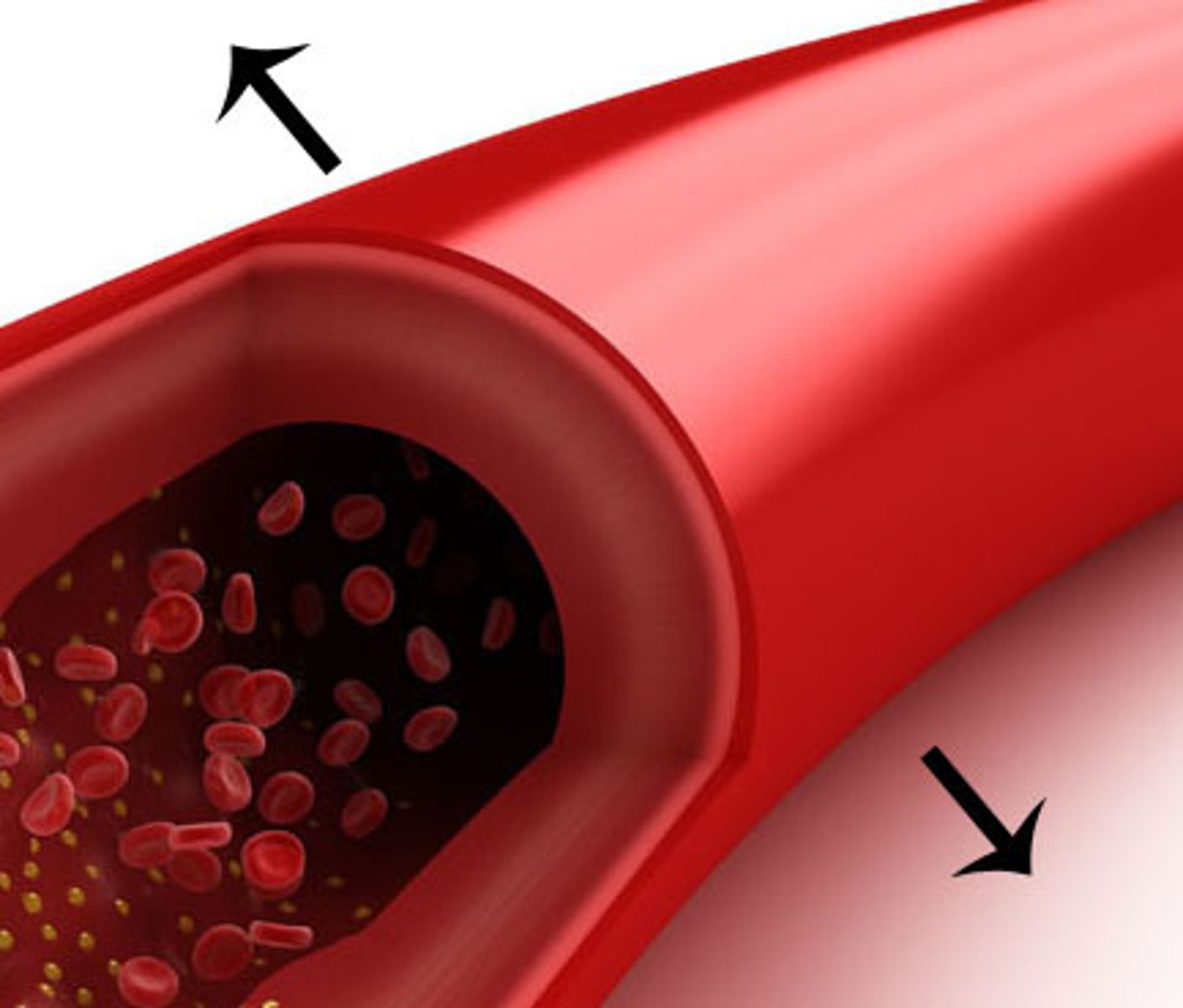
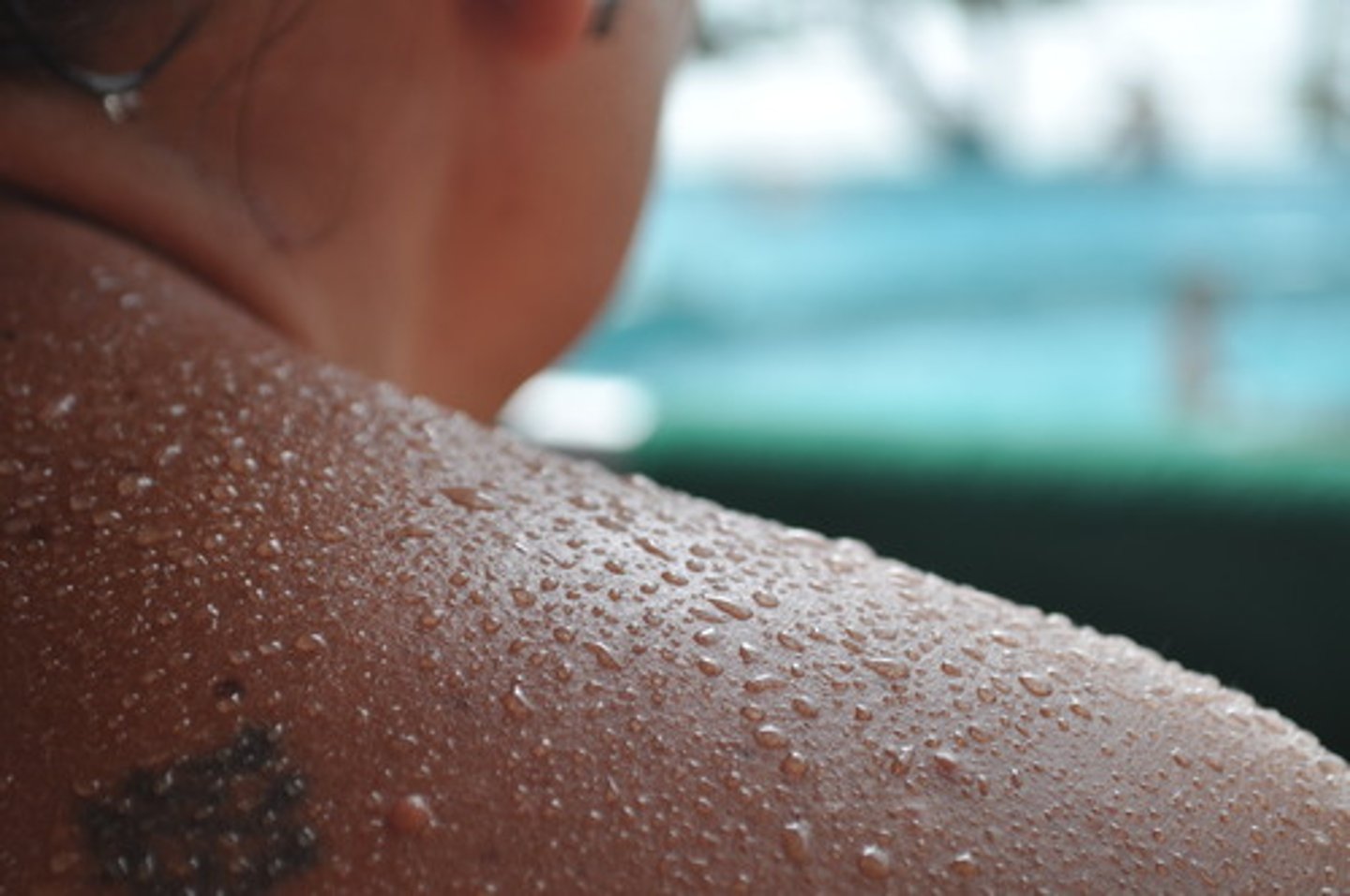
Sweat
The liquid produced by the sweat glands which reduces heat energy from the skin as it evaporates

Sweat glands
Glands located in the skin that are responsible for the production of sweat
Vasoconstriction
The narrowing of blood vessels that reduces the amount of blood near the skin's surface, allowing less heat to be transferred to the surroundings
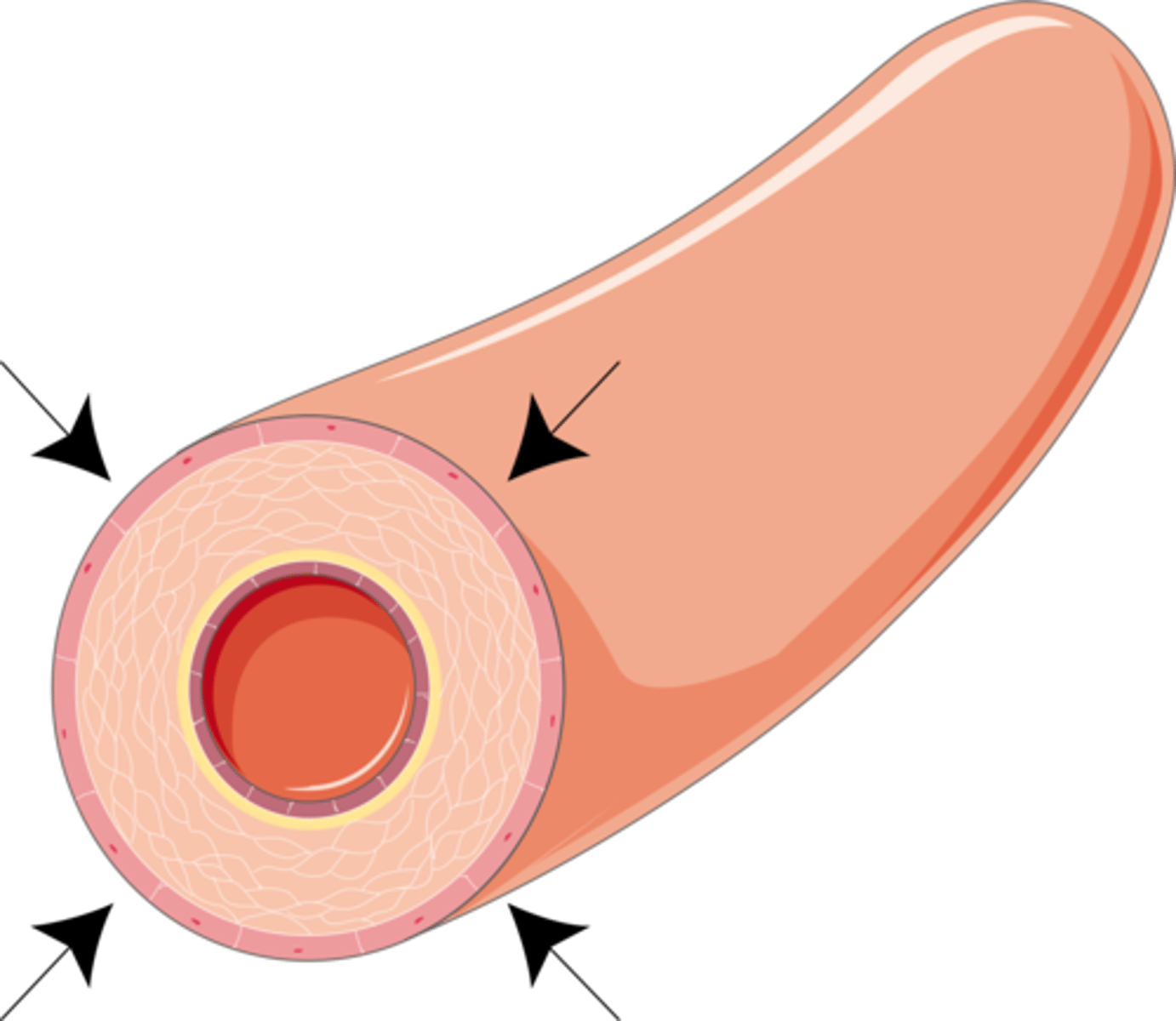
Shivering
The rapid involuntary contraction of skeletal muscle which leads to increased respiration rates and energy released as heat

If body temperature is too high
Blood vessels vasodilate and skin releases sweat
If body temperature is too low
Blood vessels vasoconstrict and shivering starts