1.3 AP Psych Quiz
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Nuerons
individual nerve cells that make up our entire nervous system
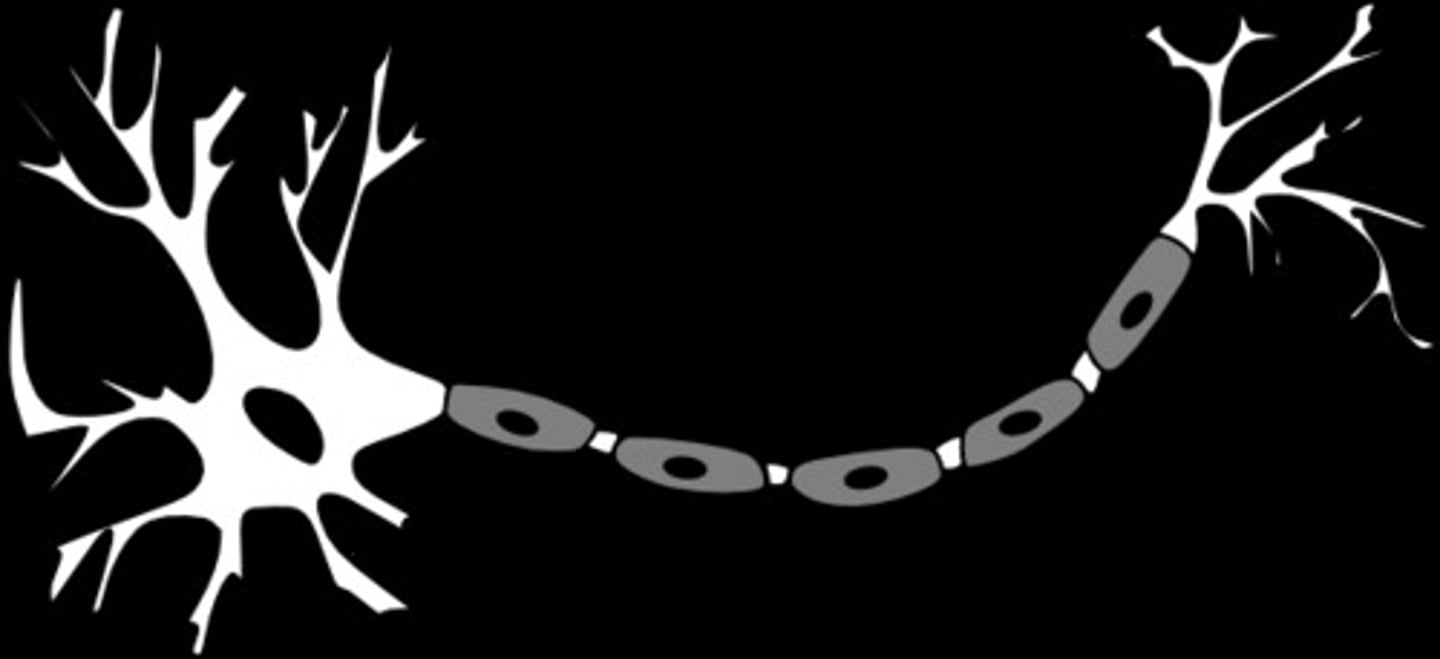
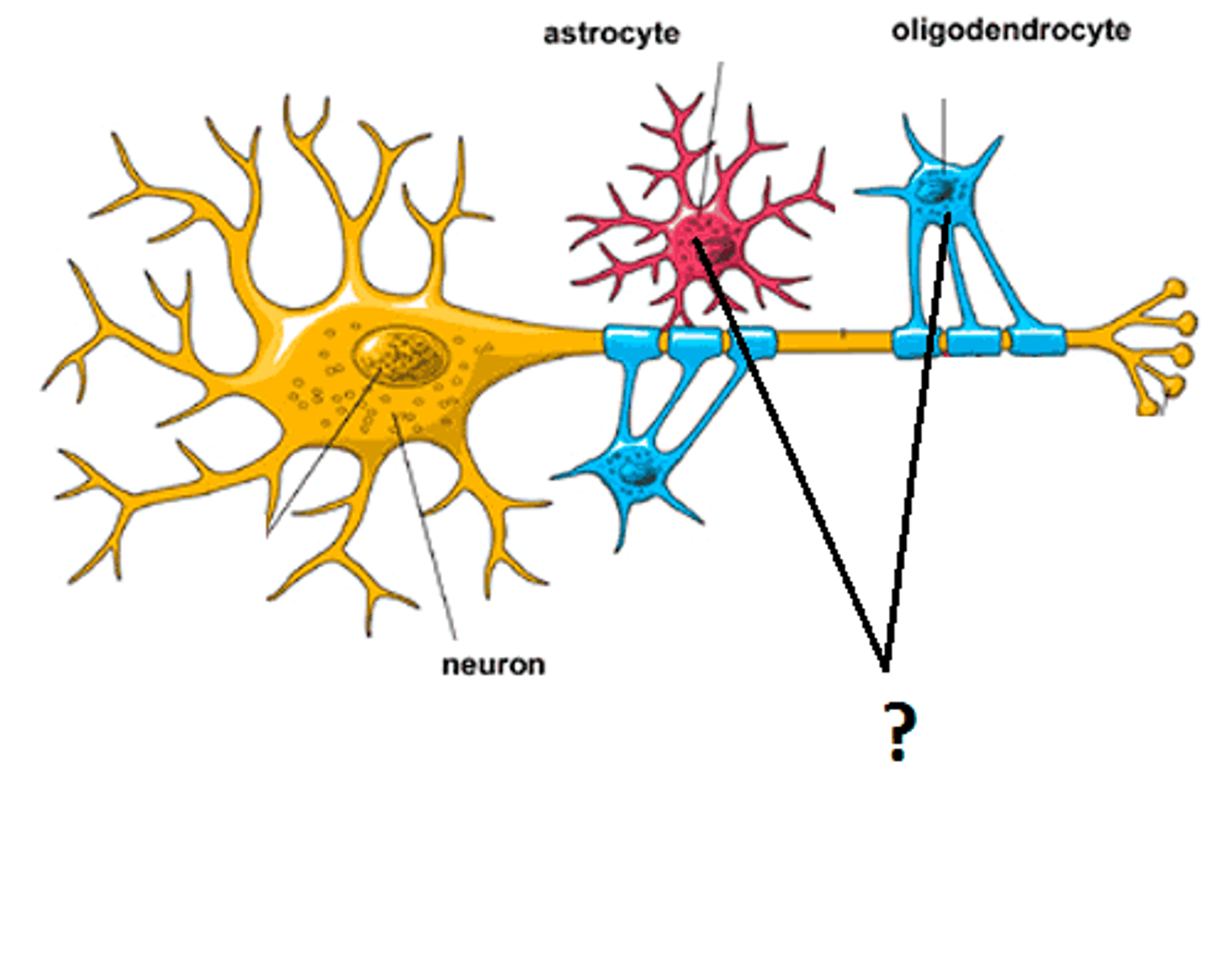
Glial Cells
Provides nutrition and protection for the neurons
Sensory neurons
neurons that take information from the senses ot the brain
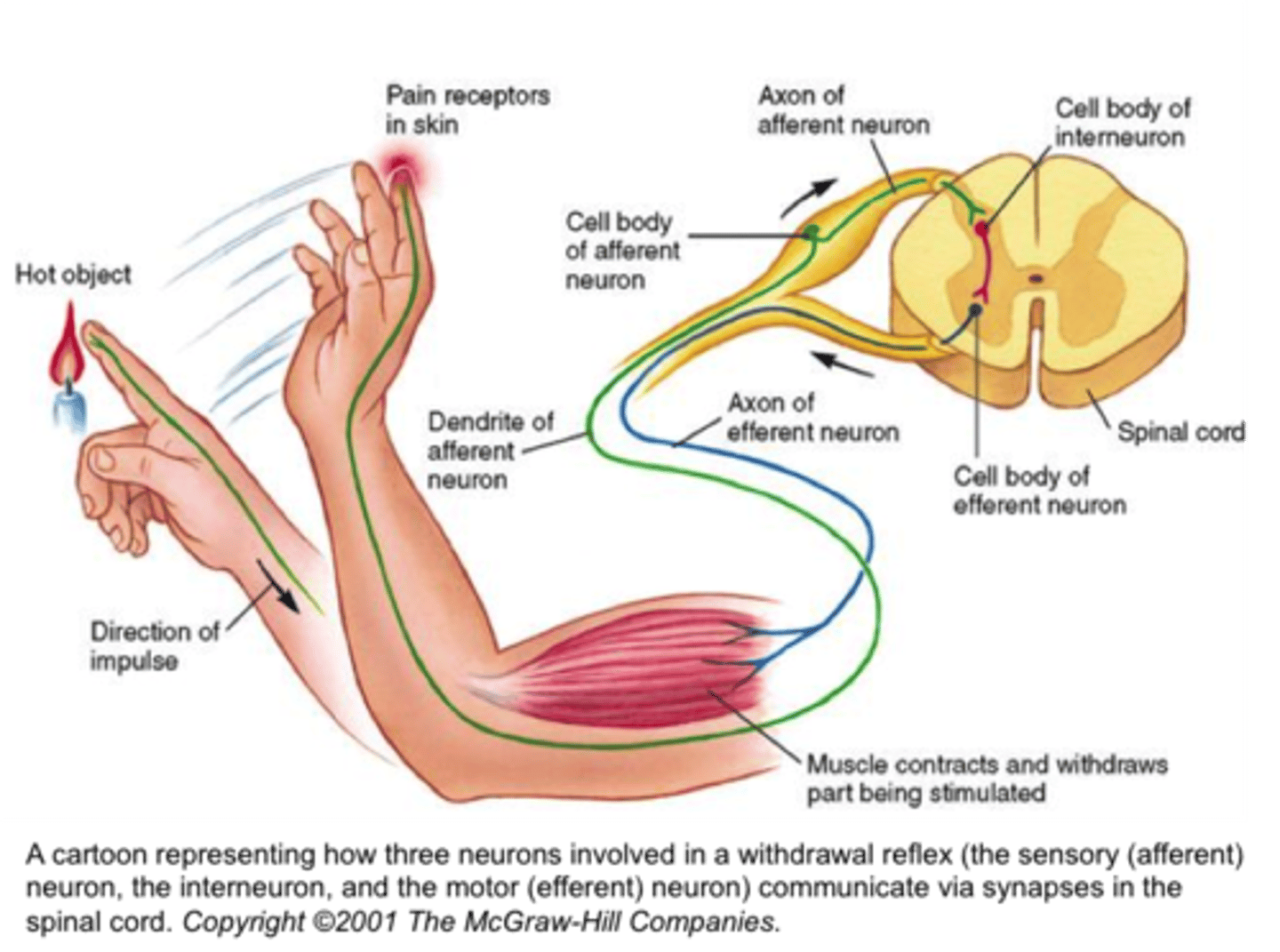
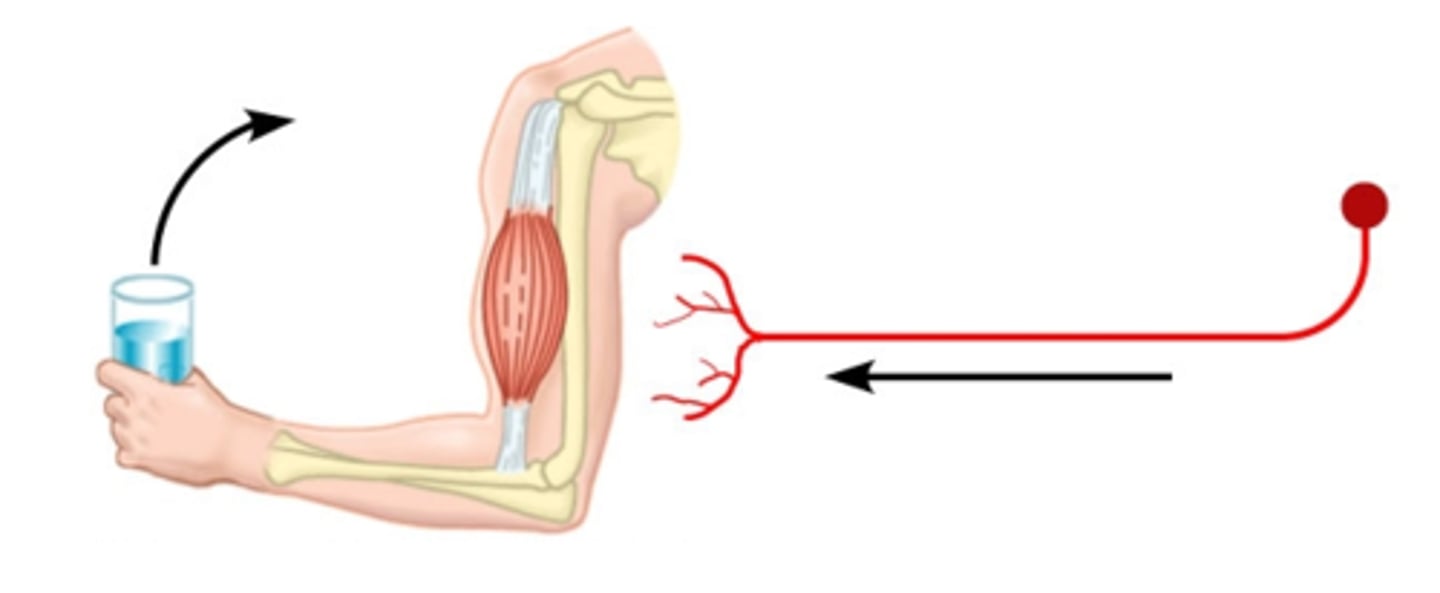
Motor neurons
neurons that take information from the brain to the rest of the body
Interneurons
in the brain or spinal cord, neurons that take messges and send them elsewhere in the brain or spinal cord
Spinal Reflex
an immediate response to external stimuli directed at the level of the spinal cord
Action potential
An impulse or brief electric charge that travels down the axon
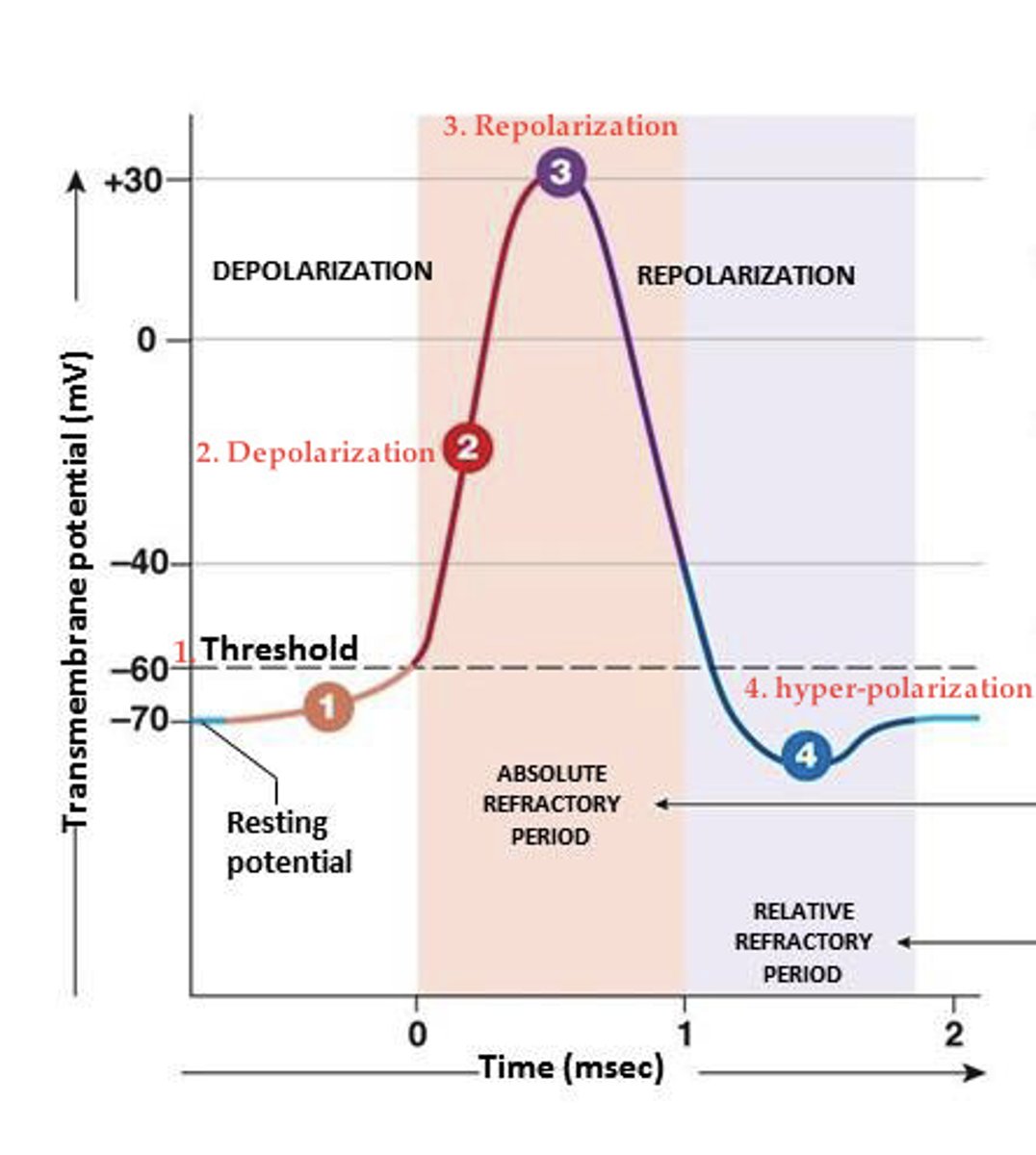
Threshold
the level of stimulation needed to trigger a neural impulse
All or None Response
A neuron either sends an impulse or it does not
Resting Potential
When a neuron does not have an action potential
Polarized
the state of a resting neuron; the outside of the membrane is positively charged, while the inside of the membrane is negatively
Depolarization
describes an axon that is firing. Positive ions enter the axon and cause other positive ions to move into the axon in the form of a neural impulse down the axon
Refractory Period
a resting pause, where neurons pump positively charged sodium ions back outside of the cell
Reuptake
The reabsorption of neurotransmitters by the sending neuron
Excitatory neurotransmitters
send signals that stimulate the brain
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
send signals to calm the brain down and create balance
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
the loss of muscle control resulting from a deterioration of the myelin sheath
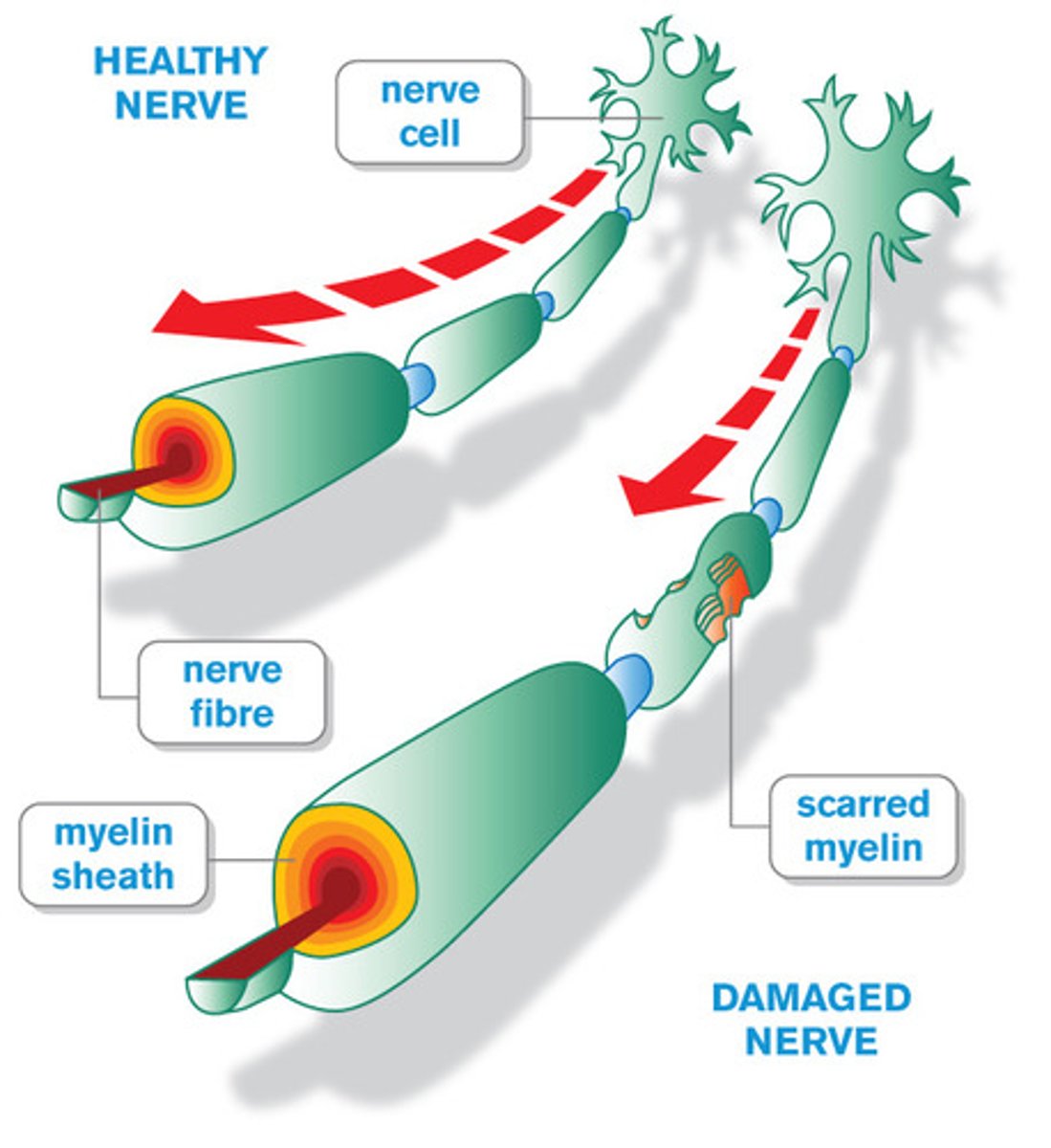
Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
a relatively rare acquired, autoimmune disorder caused by an antibody-mediated blockade of neuromuscular transmission, resulting in skeletal muscle weakness and rapid muscle fatigue (caused by a blockage of acetylcholine)
Nuerotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons that generate the next neural impulse, growth and development, tissue function, sexual function, reproduction, sleep, and mood, etc.
Hormone
a chemical messenger produced in the body that controls and regulates the activity of certain cells or organs (released in the bloodstream)
Adrenaline
a hormone that activates the sympathetic nervous system. This triggers our "fight or flight" response, which increases heart rate, dilates the pupil, increases blood flow to skeletal muscle, and reduces digestive and reproductive activity
Melatonin
a hormone known to regulate sleep and wake cycles
Ghrelin
increases hunger, secreted by an empty stomach
Leptin
Decreases hunger, a protein hormone secreted by fat cells
Oxytocin
is a hormone produced by the hypothalamus and released by the pituitary gland that plays a significant role in social bonding, sexual reproduction, childbirth, and the period after childbirth
Is acetylcholine (ACh) a neurotransmitter or a hormone
neurotransmitter
What is the function of acetylcholine
enables muscle action, learning, and memory
What is an example of a malfunction of acetylcholine
With alhiezmer's disease, ACh-producing neurons deteriorate
Is Dopamine a neurotransmitter or a hormone
neurotransmitter
What is dopamine's function
influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
What is an example of a malfunction of dopamine?
Oversupply linked to schizophrenia. Undersupply linked to tremors and decreased mobility in Parkinson's disease
Is serotonin a neurotransmitter or a hormone?
neurotransmitter
What is serotonin's function?
Affects mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
What is an example of a malfunction of serotonin?
undersupply linked to depression. Some drugs that raise serotonin levels are used to treat depression
Is Norepinephrine a neurotransmitter or a hormone?
neurotransmitter
What is norepinephrine's function?
helps to control alertness and arousal
Is GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) a neurotransmitter or a hormone
neurotransmitter
What is GABA's function?
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter
What is an example of GABA's malfunction
Undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, and insomnia
Is glutamate a neurotransmitter or a hormone
neurotransmitter
What is glutamate's function?
A major excitatory neurotransmitter; involved with memory
What is an example of glutamate's malfunction
Oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures
Are endorphins a neurotransmitter or a hormone
neurotransmitter
What is the endorphin's function
Neurotransmitters that influence the perception of pain or pleasure
What is an example of a malfunction of endorphins
Oversupply with opioid drugs can suppress the body's natural endorphin supply
Is Substance P a neurotransmitter or a hormone
neurotransmitter
What is Substance P's function
Involved in pain perception and immune response
What is an example of a malfunction for Substance P
Oversupply can lead to chronic pain
Psychoactive drugs
chemical substances that alter perceptions, mood, or behavior
Addiction
craving for a chemical substance despite its adverse effects
Tolerance
After long-term use, the brain then produces less of that specific neurotransmitter - this creates a need for increasing amounts of the drug to experience the same effect
Withdrawl
set of symptoms associated with discontinuing a drug - reverses neuroadaptation
Substance Abuse Disorder
continued substance craving and use despite significant life disruption and/or physical risk
Depressants
lowers neural activity and slows body functioning
What is alcohol
a depressant that slows neural processing and thinking and impairs physical activity
What are opiates
a depressant drug that reduces neurotransmission and temporarily lessens pain and anxiety
Stimulants
drugs that speed up the body's function
What are caffeine, nicotine, cocaine, meth, and amphetamines
stimulants
Hallucinogens (psychedelics)
drugs that distort perceptions of reality
What are LSD and marijuana
hallucinogens (psychedelics)
Agonists
chemicals that activate the receptors for certain neurotransmitters and make the effects of neurotransmitters stronger
What is caffeine specifically
agonist for ACH
What are Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
agonists for serotonin. They also increase the amount of serotonin available to the brain, and are commonly prescribed for depression
Adderall, methamphetamine, cocaine, and speed are all...
agonsists for norepinephrine. When these drugs increase the excitatory effects of norepinephrine, they create feelings of euphoria and extreme alertness
Benzodiazepines and alcohol are...
agonists of GABA
Opiates (morphine, oxycodone, heroin, etc.)
agonists of enorphins
Antagonists
chemicals that inhibit the actions of neurotransmitters
LSD is
an antagonist for serotonin
What are some diseases dopamine antagonist drugs are used to treat
psychosis, schizophrenia, and bipolar disorder
Reuptake inhibitors
drugs that prevent the axon terminals from engaging in the reuptake of neurotransmitters
What is an example of a reuptake inhibitor for dopamine
cocaine