SQ10 - 🗣️ Cerebral Cortex (Lang & Higher Cortical Relations; Dr. Rivera)
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
fibers :: hemispheres connected, Brodmann areas # :: location, Layers of cortex :: #, Cortical structure :: typic dose
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Gray matter, cortex
90% of the cerebrum is comprised by the X matter, aka cerebral Y.
Limbic, cingulate, parahippocampal, dentate; central
The cerebrum has 4 major lobes. It also has 2 minor lobes:
X lobe: composed of X gyrus (sagittal section), Y gyrus (at the base of the brain), Z gyrus (hidden)
X lobe / Island of Reil / Insula: located inside Sylvian fissure.
Gray matter, gyrus, sulcus
What layer / matter of cerebrum?
Consists predominantly of cell bodies
aka Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is thrown into folds (X), which are separated from each other by fissures (Y), to Increases its surface area and enables more cerebral cortex matter to fit inside the skull
White matter, nucleus
What layer of cerebrum / matter?
Composed of nerve fibers and axons
Interspersed with darker areas called X
Caudate x
Putamen
Globus pallidus
Thalamus
Internal capsule
ID: White matter between thalamus and globus pallidus
(seen in transverse and coronal section)
Axons,
Since white matter is made of nerve fibers:
What is the structure of neurons that mainly comprise white matter?
CoMMiSSural, Association, Projection
WHITE MATTER’S FIBERS:
X fibers: connects homologous areas of the 2 hemispheres (L/R)🔛
Y fibers: connects within the same hemisphere (Back/Front) 🔙
Z fibers: connects cortex to subcortical nuclei (Up/Down) ↕
Commissural Fissure
ID fiber:
Examples:
→ Corpus callosum
→ Anterior commissure
→ Posterior commissure
→ Commissure/Crura of the fornix
→ Habenular commissure
Corpus Callosum, r/l hemisphere
Found at the bottom of the longitudinal fissure
Largest commissure of the brain
It connects the XX.
Rostrum, frontal
Thin part of the anterior end of the corpus callosum
Prolonged posteriorly to be continuous with the upper end of the lamina terminalis (kasi nasa harap siya)
Interconnects the anterior part of the X lobe
Genu, Temporal
Curved (baluktot=bading=…?) anterior end of the corpus callosum that bends inferiorly (ay bottomesa) in front of the septum pellucidum 🏳🌈👋🍑
Connects the anterior part of the X lobe
Body, frontal, Parietal, Temporal
Arches posteriorly and ends as the thickened posterior portion called splenium (body tea ni selena)
Connects the posterior parts of the X and Y lobes and superior part of the Z lobe
Splenium, occipital
Thicked and most posterior part of the corpus callosum
Interconnects the X lobe
Anterior commissure, inferior & middle
● Small bundle of nerve fibers that crosses the midline in the lamina terminalis (karugtong ng Rostrum)
● Interconnects the X and Y temporal gyri
● When traced laterally, a smaller or anterior bundle curves forward on each side toward the anterior perforated substance on each side , and grooves the inferior surface of the lentiform nucleus to reach the temporal lobes
● Found in front of the columns of the fornix and above the hypothalamus
Posterior commissure, visual
Rounded band of white fibers crossing the midline on the dorsal aspect of the rostral end of the cerebral aqueduct
● Found at the posterior floor of the diencephalon, related w/ pineal gland (inf stalk), behind thalamus
Carries decussating fibers of the superior colliculi and pretectum which is concerned in the X reflex (light), going to the parasympathetic part of the oculomotor nuclei
Commissure of the fornix,
Flattened transverse fibers that connects the two crura of the fornix
→ Closely attached to the bottom of the corpus callosum
● Fx: is to connect the hippocampal formations of the 2 sides (attach the two fornices)
Fornix
is a bundle of nerve fibers that acts as the major EFFerent system of the hippocampus
→ Bilateral structure, present in each hemisphere of the Brain
→ Also carries some afferent fibers from the diencephalon & basal forebrain
→ Part of the limbic system
Habenular nuclei
Receive many Afferent from the amygdaloid nuclei and hippocampus
Afferent fibers pass here, via the striA medullaris thalami
Habenular commissure
Consists of stria medullaris fibers crossing over to the contralateral habenular nuclei
Small bundle of nerve fibers that crosses the midline in the superior part of the root of the pineal stalk
Short association fiber
Lie immediately beneath the cortex and connect adjacent gyri
Fibers run transversely to the long axis of the sulci
Example: Arcuate Loop/Fibers
superior longitudinal fasciculus, Frontal, Parietal, Occipital, ARCUATE
→ Largest bundle of nerve fibers
→ Located above the insula
→ Connects the X, X, & X lobes (has 3 names, kaya 3 lobes kinoconnect)
→ Gives rise to the X fasciculus
Arcuate fasciculus
▪ Has a role in language development
▪ Located posterior to the insula and arches from the
superior longitudinal into the temporal lobe
▪ Connects the frontal and temporal lobes
Inferior occipitofrontal fasciculus
→ Located below the insula
→ Connects the frontal lobe to the occipital and temporal lobes
→ Situated deep within the cerebral hemisphere
→ Related to the X border of the caudate nucleus
Inferior longitudinal fasciculus
→ Runs anteriorly from the occipital lobe
→ Passes lateral to the optic radiation
→ Distributed to the temporal lobe
Uncinate fasciculus
→ Connects the first motor speech area and the gyri on the inferior surface of the frontal lobe with the cortex of the pole of the temporal lobe
→ Joins the orbital part of frontal lobe to temporal lobe
Cingulum
→ Long, curved fasciculus lying within the white matter of the circulate gyrus
▪ Beneath the cingulate and parahippocampal gyri
→Connects the frontal and parietal lobes with parahippocampal and adjacent temporal cortical regions
→ Forms part of the Limbic System
Posterior, anterior
The internal capsule has 3 parts:
X limb: between the thalamus and globus pallidus
Y limb: located between the caudate nucleus, and, globus pallidus and putamen
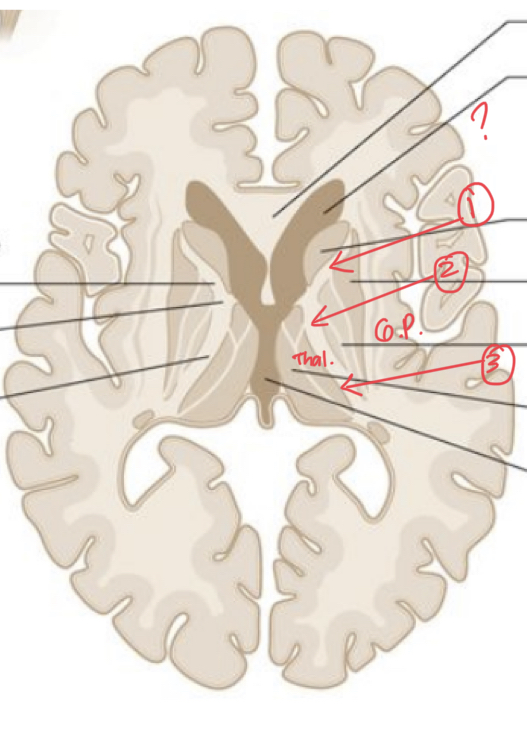
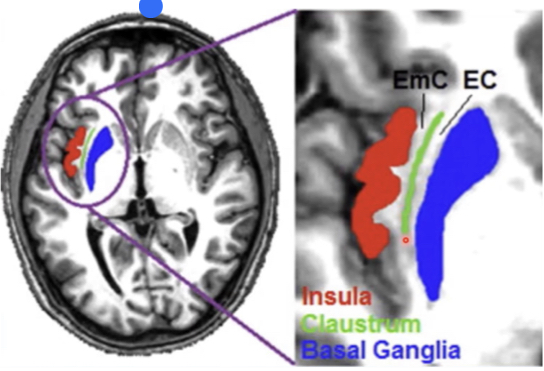
External capsule
iseries of white matter fiber tracts in the brain
Run from the most lateral segment of the lentiform nucleus and the claustrum
Leni is an EVP who Likes (lateral) Santa Claus
Internal capsule, Corona radiata
While it is at the level of lentiform/lenticular nuclei, it is called the XX
Once the fibers are located above lenticular nuclei, it is called YY
Optic radiations
On the occipital part (posterior part), the corona radiata is called the XX
→ project into the visual cortex
Cortex, gray, neocortex, paleocortex, olfactory, Archicortex, hippocampal
The X (Y matter) is subdivided based on the order of development of the brain.
● X
→ “New”
→ Last in evolution and it is 90% of the cortex
● Y
→ Restricted to the base of the hemisphere
→ Associated with the Y system
● Z
→ Oldest/first to develop
→ Make up the Z formation
T
T/F? The limbic system is composed of paleocortex and the archicortex
Isocortex
The prototype cortex
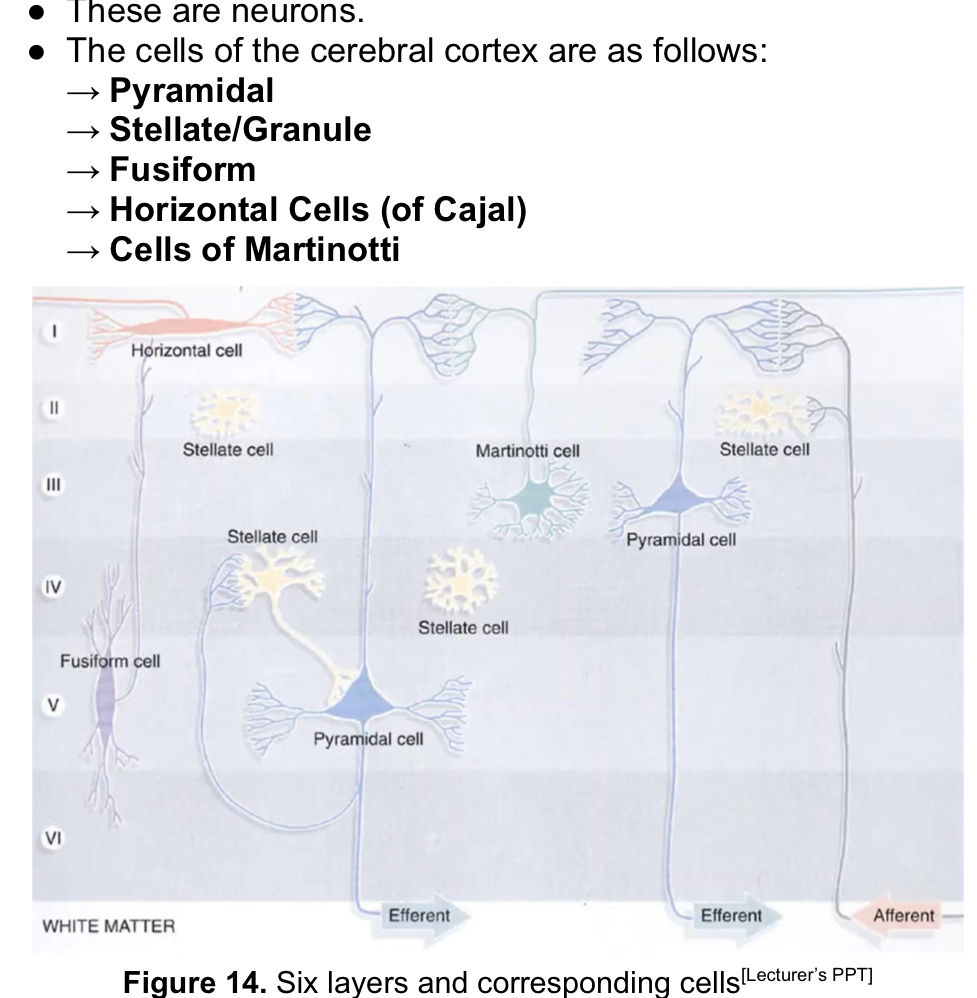
Molecular, external Granular, external pyramidal, INTERNAL granular, Internal Pyramidal, Multiform
The Isocortex has 6 layers.
X layer: horizontal cells of cajal
X layer: stellate cells
X layer: Martinotti cell, Pyramidal cell
layer: Stellate cells
ganglionic layer: fusiform & pyramidal cell
Fusiform layer: n/a
Mesocortex
● Area between isocortex and allocortex
● Paralimbic areas
● The number of layer varies from 3-6 layers depending on location
→ Nearer the Isocortex: 5 or 6 layers
→ Nearer the Allocortex: 3 to 4 layers
ALLocortex
Gray matter region:
Composed of 3 layers
● Found in the hippocampal formation and the piriform / primary olfactory cortex
Corticoid region
● “Cortex-like”
● Regions that have neurochemical features and neuronal connections characteristic of the cortex but the layers are not discernable
● Found in the septal region in substantia innominata and are part of the amygdaloid complex
● No layering but components are of the same cells that the other regions have
Horizontal cells of cajal
● Small and fusiform in shape
● Horizontally-oriented/parallel to the surface
● Dendrites emerges from each end like the fusiform
● Axon runs parallel to the surface and synapse with
dendrites of pyramidal cells
Pyramidal cell
Largest neuron in the cortex
● Large apical dendrite with dendritic spines
→Directed toward a surface and several large basal dendrites that pass horizontally
● The axons proceeds from the base and leaves the cortex to reach other cortical areas as commissural, association, or projection fibers
Betz cells
→ Largest pyramidal cell
→ Reach 150 micrometers
Stellate cell
● Polygonal interneurons
● Has numerous short dendrites that extend in all directions
● Short axon that terminates on nearby neurons
● Cell body is small (~8 micrometers)
● Numerous in sensory and association areas
Fusiform cell, inferior dendrites, superior dendrites
● Long axis is vertical to the surface
● Concentrated in the deepest layers of the cortex
● Dendrites arise from each pole
● X dendrites branches within the same cellular layer
● Y dendrites ascends towards the surface and
branch in the superficial layers
Cells of martinotti
● Multipolar neurons present in all layers (marami)
● Short dendrites
● Axon is directed toward the surface and ends in the most
superficial layer as origin of few short collateral branches
F
The cortex layers have a definite boundary between layers. T/F"?
Vertical cortical column
● Functional unit of the cortex/cortical activity
→ Organized in groups of neurons perpendicularly oriented to the surface
→ Contains 1000s of neurons interconnected in a vertical direction
● Cannot be delineated
● Needed in order to process information, stimulus, or modality
Cortical structure can be further classified according to how well a layer is developed.
● Xtypical
→ All layers are equally developed
→ Seen in association areas of the brain
Granular, II & IV
Hets are idiots!
→ X 👀⭐️
▪ Well developed layers X&Y
▪ Located in sensory areas (postcentral gyrus, superior
temporal gyrus, parts of hippocampal gyrus)
▪ Predominant cells are stellate cells
▪ Receive thalamocortical fibers (sensory functions)
Agranular, III & V
→ X 🏍🔺
▪ Well developed layers Z&A
▪ Located in motor areas of the brain (precentral gyrus,
other areas of frontal lobe)
▪ Predominant cells are pyramidal cells (motor
functions)
▪ These cells send efferent fibers
Primary area, association area
FUNCTIONAL CORTICAL AREAS:
X receives the stimulus/modality, idiotypic isocortex
Y interprets stimulus received, adjacent to X areas, external, homotypic isocortex
Heteromodel association area
Receives input from multiple unimodal areas
● Deals with sensory/sensorimotor contingencies
● In some cases, it fires only in response to stimuli of
motivational significance
Prefrontal cortex
→ This is what makes humans more superior than our closest kin
→ Largest part of the frontal lobe and located rostral to the motor areas
→ Integrate motivational events with complex sensory stimuli
→ Processing site of attention, behavior, judgment, and decision-making
Prefrontal cortex
If there is a lesion in this area, patient may be:
▪ Unconcerned with illness & appear depressed
▪ Ignore ordinary standards of cleanliness, like eating
from the floor
▪ Essentially having no insight
Wernicke area
Part of the temporoparietal association area (Specifically, in the posterior part of the superior temporal gyrus or BA 22)
Important in language formation
Motor, somaesthetic, vision, auditory
Generalizations of Area
● Frontal lobe- X
● Parietal lobe- X
● Occipital lobe- X
● Temporal lobe- X
41
● Organ of Corti
→ Receptor for sound
▪ located in inner ear
→ Contains hair cells with spiral ganglion
▪ Sends its fibers to vestibular tract going to the
primary auditory cortex (BA ??)
LANGUAGE FORMATION
Organ of Corti > Spiral Ganglion > projet to Primary Auditory Cortex (Area 41 in Ant. Transverse Temporal gyrus) > 2ndary Auditory Area (Area 42 in Post. Transverse temporal gyrus) > assoc fibers > BA 22 (Wernicke / speech sensory / comprehension) > arcuate fasciculus > broca:s area (BA 44, 45 in Opercular & Triangular of inf. Frontal Gyrus / speech motion area / architect of ms movement) > primary motor area (BA 4 / precentral gyrus > subcortical nuclei > larynx
VISION LANGUAGE:
rods and cones > primary visual area (BA 17 in Lips of Calcarine Fissure) > 2ndary visual area (BA 18, 19) > Angular gyrus (reading: dyslexia / aslexia) > wernickes area (comprehend) > brocas area (loud wide) > primary motor area (produce sound)
Broca, motor
Lesion?
Type of aphasia?
Motor
Speech sensory
Conduction
Global

Wernicke, speech sensory
Lesion
Type of aphasia

Arcuate fasciculus, conduction
Says 21 instead of correct 25, repeating til he says it right. Gets niyang mali siya.
Lesion?
Type of aphasia?

T
Certain nervous activity is predominantly performed by one of the two cerebral hemispheres. T/F?
Dominant
Dominant/nondominant?
controls
behavior, analytical thinking,
verbalizations
T
In fetuses and neonates, more descending fibers in left pyramid crossover to the right than vice versa. T/F?
Left, Handedness
left hemisphere (think, intellectual) controls right side of ur body, right hemisphere controls left side.
most ppl are X hemisphere dominant and just so happen to be right handed. but handedness is NOT determined by your hemisphere dominance,
CHOOSE: Handedness / Cerebral dominance?
is determined by the number of fibers crossing over from one side to another.
T
Handedness and language dominance develop before a child has learned to speak. T/F?
Dominant side = subject proficiency ng NMAT = Intellectual, Language, behavior, analytical thinking, verbalizations
Non dominant = perceptual acuity ng NMAT = spatial perception, recognition of faces, and music