Static Electricity
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is an electric field?
A region in which an electric charge experiences an electric force
In what direction are electric field lines drawn in?
Positive to negative
Direction of electric forces acting on a positive test charge
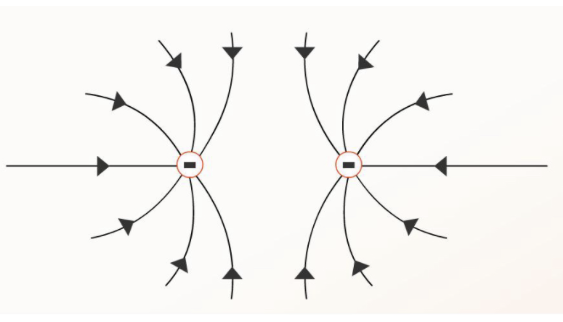
How do electric field lines look like for 2 negative charges in the same field?
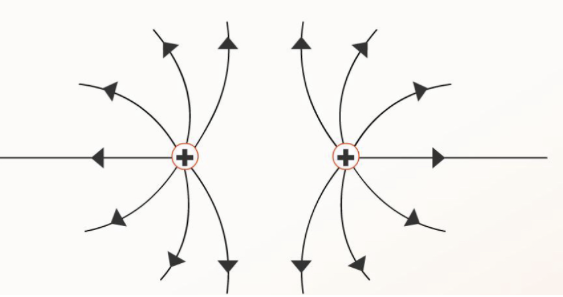
How do electric field lines look like for 2 positive charges in the same field?
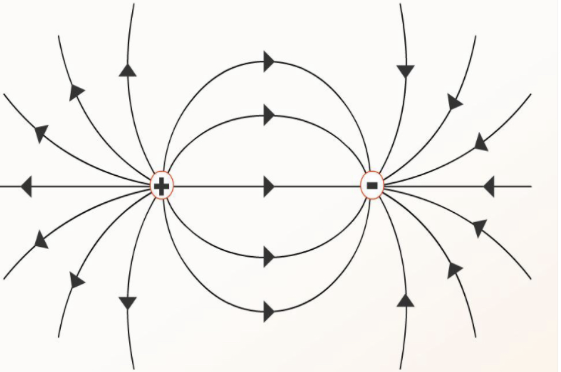
How do electric field lines look for 2 unlike charges in the same field?
Why do we charge insulators through rubbing?
Negative charges cannot move about freely
How is electrostatic charging by rubbing performed?
Before rubbing, 2 materials are electrically neutral, with an equal amount of positive and negative charges
During rubbing, some negative charges are transferred in the form of electrons from one material to another (usually from the better insulator)
The material that loses electrons becomes positively-charged while the substance that gains electrons becomes negatively-charged
Why must conductors be charged by induction?
Mobile electrons can easily be transferred to and away from them
What is induction?
Charging an electrical conductor without any form of contact between the charged body and conductor
What is earthing?
A process to discharge charged conductors by providing a path for excess electrons to flow out of the charged conductors
Neutralises excess charges unless charges are bound by an external charged object
Describe the 2-sphere method for inducing excess positive and negative charges
Bring 2 neutral conducting spheres, A and B together, with a positively or negatively charged rod near, but not touching A
The charged rod causes its opposite charges, O, on both spheres to be attracted towards it and they accumulate on the surface of A closest to the rod
Excess charges, E, that are of the same charge as that of the rod are repelled, and they accumulate surface of B furthest from the rod
Move both spheres apart while holding the rod in place
Remove the rod and excess charges will be evenly distributed in each sphere
Describe the single-sphere method for inducing excess positive charge
Bring a negatively-charged rod near a neutral-conducting sphere, but not touching the sphere
The rod repels negative charges to the side of the sphere furthest from the rod and attracts excess positive charges that remain nearest to the rod
While holding the rod in place, place an earth at the negatively-charged side of the sphere
Electrons flow out of the sphere to Earth, leaving excess positive charges
Remove the earth, then the rod
Charges redistribute themselves throughout the now positively-charged sphere
Describe the single-sphere method for inducing excess negative charge
Bring a positively-charged rod towards a neutral-conducting sphere but not touching the sphere
The rod repels positive charges to the side of the sphere furthest from the rod and attracts excess negative charges that remain nearest to the rod
While holding the rod in place, place an earth at the negatively-charged side of the sphere
Electrons flow out from the Earth to the sphere, neutralizing the positive charges and leaving excess negative charges in the sphere
Remove the earth, then remove the rod
Charges redistribute themselves throughout the now negatively-charged sphere
What is discharging?
A charged body is removed of excess charges
What is discharging via heating?
A positively / negatively charged insulator is brought near a flame
Intense heat from the flame ionises nearby air particles
Ions neutralise excess charges on the insulator and the insulator is discharged
What is discharging via humid conditions?
A positively / negatively charged insulator is placed in humid air
Water molecules in air are electrical conductors
Excess charges are transferred to the water molecules from the surface of the insulator
How is static electricity applied in lightning?
Charging by friction between water droplets and air molecules
Air ionises when charge buildup is large enough, allowing the charge to discharge to the ground
How do lightning rods provide protection from lightning strikes?
Electrons are repelled to the ground as storm clouds with negative charges pass by
Top of the rod is induced with positive charges and ionises the air
Positive ions are attracted to the negative part of the cloud, neutralizing partially and reducing chances of a strike
How is static electricity applied In fire and explosions?
Charge buildup on objects like planes and petrol tanks
If not carefully discharged, a spark (due to charge induced by friction) can start a fire or cause an explosion
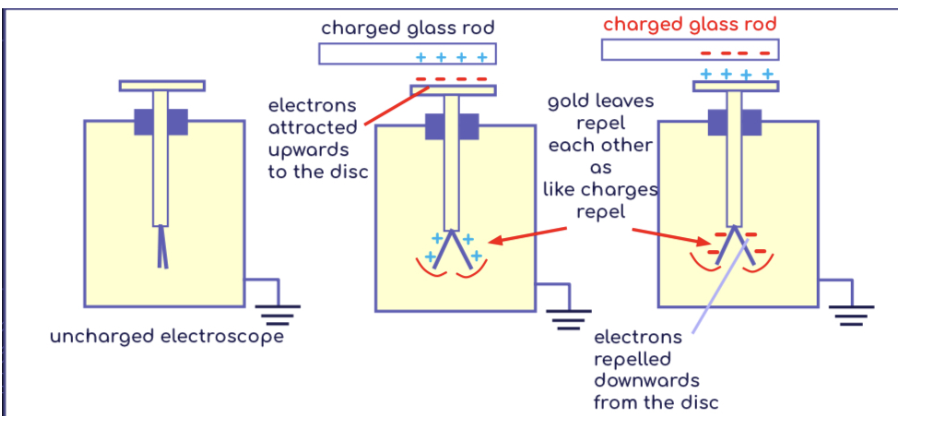
What is an electroscope?
Device that tests the presence of a positive or negative charge
Electroscope is first charged with either positive or negative charge through induction
Repulsion