Ch. 2 atomic structure EVERYTHING
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
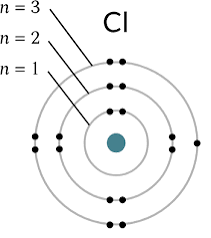
what is Bohrs Model?
Atomic mass?
A set of # due to total of isotope
Atomic number?
# of protons
Isotope?
Protons with different number as neutrons
Abundant isotope?
They appear the most (for example highway in the graph.)
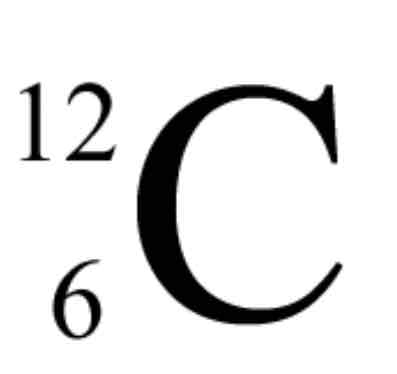
What is the top?
Mass #
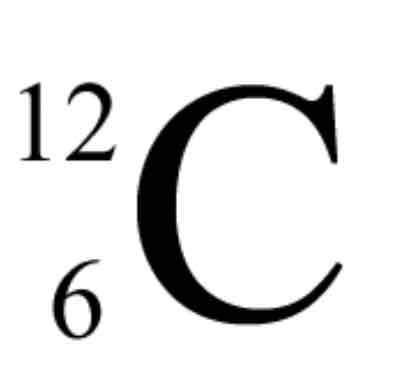
What is the bottom?
Atomic #
Why is protons and electrons the same #?
For they can stay neutral
What is the equation to find atomic mass?
Atomic # x % = atomic mass (amu)
How do you find a mass number? (Out of a lot of isotopes)
Do ur normal thing but set it up like an equation with the total mass out (seen in the periodic table)
Who created Bohrs Model?
Bohr
Who created Plum Pudding model?
Thompson
What did Rutherford find?
A nucleus in the center, where the proton is found. Did this by Gold foil.
What did Aristole do?
That atoms moved through a empty space, everything is made up of earth air Fire and Water
What did democritus do?
Made up of tiny particles, but could not prove it
What are the scientists discoveries in order?
Dulton
Thompson
Rutherford
Bohr
What did Dulton do?
Came up with the Dulton Atomic Theory
What is the Dulton Atomic Theory
All mater is made of atoms
Same items are identical
Atoms are indestructible
How do you find Mass Number?
Protons + neutrons
Radioactivity =
Nuclear Energy
Radioactivity does NOT =
Chemical reaction
Each orbital has a what?
Fixed amount of energy
What did Aufbau say?
Electrons should be placed at its lowest orbital
What did Paulixclusion say?
must have 2 electrons in the opposite side (like facing opposite direction)
What does Hunz Say?
Electrons in each orbital before paring
What is Electron configuration (definition)?
Arrangement of Electrons
What is electron configuration (write it down)
Ex: 1s²2s²
What is the electron dot structure?
( With X’s in Cambridge )

How do you release energy?
Jumping electrons release energy due to being excited, but then going to grown level. They release this in forms of waves.
What do protons determine?
type of Element
Atomic # =
Protons
What does electron determine?
Chemical Property
What does Neutrons determine?
It helps keep the protons in place and keeping it from moving
Smallest particle of an element?
Atom
lowest energy in orbital?
Ground state
Smallest particle in a atom?
Electrons
Greatest to least mass
Protons and neutrons are the same
electrons are least
What is an Atom?
A basic unit of of matter, a building block, consisting of protons, electrons, and neutrons
FREBIE
FREBIE

label all of these top to bottom
Atomic #
Element symbol
Element name
Mass #
What do the parts of the atom tell us about each element?
The number of protons in an atom defines the element's identity and atomic number, neutrons contribute to its atomic mass and create isotopes, and electrons determine its chemical behavior and bonding properties, influencing how it interacts with other elements.
What is radioactivity
Radioactivity is the physical phenomenon of certain elements emitting energy in the form of radiation
What are the uses of radioactivity?
In Nuclear energy, cancer treatment
types of radiation.
▪ Identify their symbols.
Alpha (B)
Beta (a)
Gamma (y)
What is Alpha (a)
a helium nucleus with 2 protons and 2 neutrons. Paper blocks this. This also has a positive charge. Less than Beta, which is deflected by a magnetic field.
What is Beta (B)
a high energy electron which is blocked by 3mm aluminium. It has a charge of negative. It is in the opposite direction and has a higher charge than Alpha, being deflected by manetic field.
What is Gamma (Y)
This is apart of a electromagnetic spectrum, which is blocked by several m of concrete or lead. It has no charge and is not deflected by a magnetic field.
How is the periodic table aranged by?
Atomic number / protons
a neutral atom is …
same number of protons and electrons
How was the nucleus found?
In the gold foil experiment
What are valence electrons?
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom that participate in chemical bonding, determining the element's reactivity and properties.
How many total valance electron can be In mass?
8
Why was Aristole more believed rather than democritus?
Due to being able to see it