Mid Term case studies
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
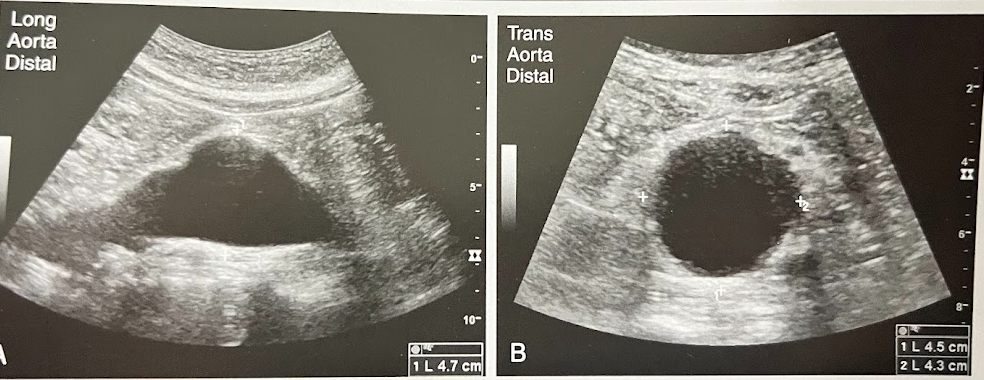
A 63 year old man is seen for evaluation of a possible renal mass seen on a radiograph. The sonogram reveals a rt renal cyst. Incidentally noted are the findings in the Ao images. The aorta measured 4.7cm in AP diameter. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Aortic aneurysm w/thrombus
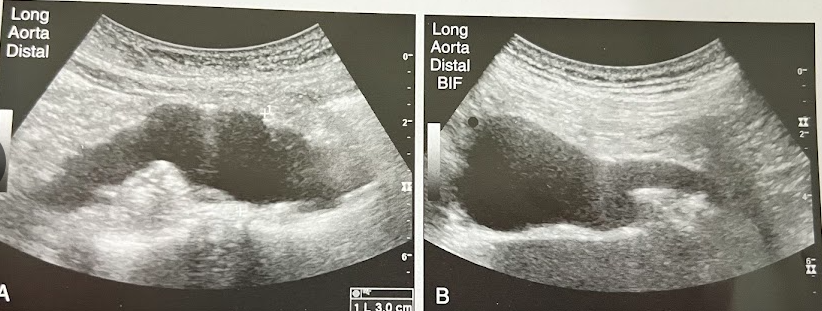
A 55 year old man w/Hx of cigarette smoking undergoes sonography of the Ao b/c of a pulsatile mass over the area of the umbilicus on physical examination. The distal Ao is shown. What is the most likely diagnosis?
AAA
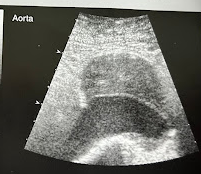
A 70 year old man collapsed at a shopping mall and was transferred to the ED at the nearest hospital. The pt is hypotensive, is in shock, and has pulsatile abd. mass. A portable sonogram is requested immediately and reveals a dilated Ao that measures 8.5cm in AP diameter. What diagnosis do the clinical and sonographic findings suggest? How do the clinical findings contribute to the diagnosis?
Ruptured Ao aneurysm. The diagnosis is supported by the clinical symptoms. The classical presentation of a ruptured AAA includes the triad of hypotension, abdominal or back pain, and a pulsatile abd. mass.
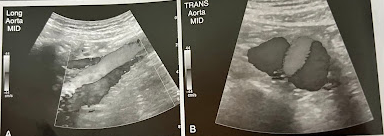
A 60 year old woman undergoes sonography of the Ao. She reports recent episodes of fainting and abd. back pain. She has a hx of poorly controlled hypertension and aortic aneurysm. An abd. sonogram is performed to check the status of the aneurysm. A new finding of linear echo is identified w/in the Ao, and color confirms flow on both sides of this flap. What is the most likely diagnosis? What symptoms, risk factors, and clinical presentation does she have to support the findings?
Aortic dissection. The clinical presentation is usually onset of severe chest pain.
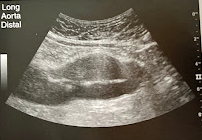
A 75 year old man is seen for f/u of a known AAA. The sonogram reveals a dilated distal Ao that measures 3.9 cm in AP diameter. Mural thrombus is seen in the aneurysm. No increase in size is noted from a sonogram performed 6 months prior. Considering the size of aneurysm and the thrombus that is present, what is the recommended schedule of sonographic surveillance>
No further testing for pt’s w/abdominal Ao aneurysms less than 3cm and annual sonography for pt’s w/aneurysms measuring 3-4cm
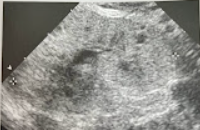
A 10 year old child presented w/hx of enlarged echogenic kidneys, hepatosplenomegaly, and evidence of portal hypertension. Renal function tests reveal the child is in moderate renal failure. Discuss the clinical findings and significance of the appearance of the kidney and the associated liver abnormalities.
These findings are consistent w/juvenile presentation of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), also known as infantile polycystic kidney disease. ARPKD can manifest in various forms that range in severity.
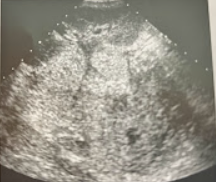
A 3 day old infant presents w/a palpable abd. mass that was also on a prenatal sonogram; the origin of the mass could not be determined. Postnatal sonography reveals a large heterogeneous. The child has no other symptoms. What are the differential diagnoses for this mass? What lab values could aid in making a more definitive diagnosis?
Hepatic or adrenal masses. Determining the organ of origin and lab findings should be considered in this case. If the mass is assumed to be adrenal, catecholamine levels can help with the diagnosis.
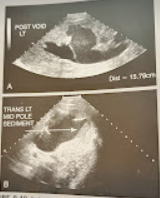
A 6 year child w/fever, chills, and back pain was seen for a renal sonogram. The kidneys were markedly enlarged, and the findings in the image were noted. What is the most likely diagnosis.
Pyelonephritis w/moderate hydronephrosis and enlargement of the kidneys
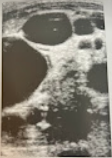
A 4 year old girl is seen by the pediatrician for an abd. mass discovered by the parent. The child is in no physical distress, and mother reports no illness. On questioning family hx, the physician learns that the mother has epilepsy and has been on long term antiseizure meds. The child is referred for a sonogram of the RUQ. The rt kidney was not identified. Discuss the palpable nature of this mass and how the family hx is significant.
Multicystic dysplastic kidney may manifest as palpable abd. mass. The sonographic findings of the multicystic dysplastic kidney are multiple noncommunicating cysts in the renal bed. This cause is poorly understood but can be the result of an obstructive process. Antiseizure meds can cause this disease.
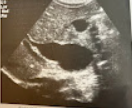
A 6 month old boy of Asian ethnicity is seen by the pediatrician for abd. pain and vomiting. The physician notes physical signs of jaundice, and on questioning, the parent reports this has been present since birth. The physician is also able to palpate a RUQ mass. A sonogram is performed, and a balloon-like dilation of the CBD and mild intrahepatic ductal dilation are seen. Discuss the likely cause of this mass and the significance of the clinical findings.
The sonographic findings are consistent w/type 1 choledochal cyst, the most common type. Clinical findings include jaundice and pain.
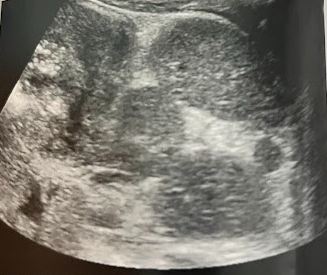
A 5 month old girl w/clinical suspicion of splenomegaly undergoes an abdominal sonogram. Her clinical hx included an echo reporting an atrioventricular canal defect, chest x-ray illustrating an interrupted IVC, and possible situs ambiguous. The sonogram revealed the liver to be located more central midline and the spleen to be abnormal in location and appearance. This image was obtained in trans to the lf of the midline in the region of the spleen. Describe the sonographic findings and congenital associations for this appearance
The sonogram reveals multiple splenules consistent w/polysplenia. This is mostly associated w/heterotaxy syndrome, which can include partial situs inversus.
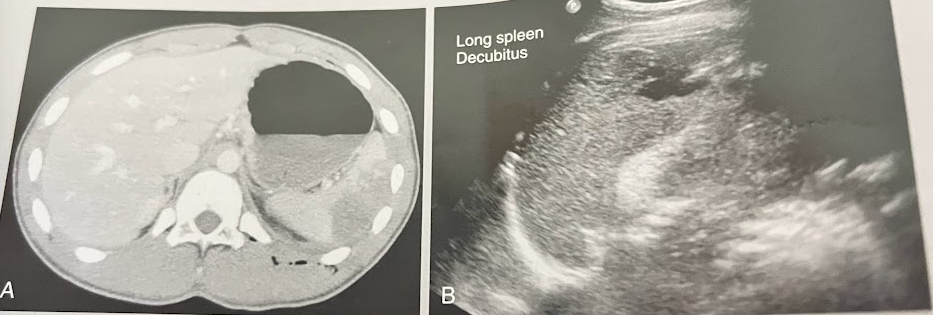
A 16 year old pt presents to the ED w/a gunshot wound to the LUQ. A focused assessment by sonography for trauma (FAST) sonogram performed in the ED did not reveal peritoneal fluid or bleeding. A complete blood count indicated normal values w/the exception of a decreased hematocrit. The BP was stable. The pt was referred for a CT, which demonstrated a subcapsular splenic abnormality; the remainder of the study was normal. The sonogram identified the findings in the image as the absence of free peritoneal fluid. Discuss these findings.
Spleen images reveal an anechoic to hypoechoic striated lesion in the lateral portion of the spleen. Clinical hx indicates a diagnosis of subcapsular hematoma
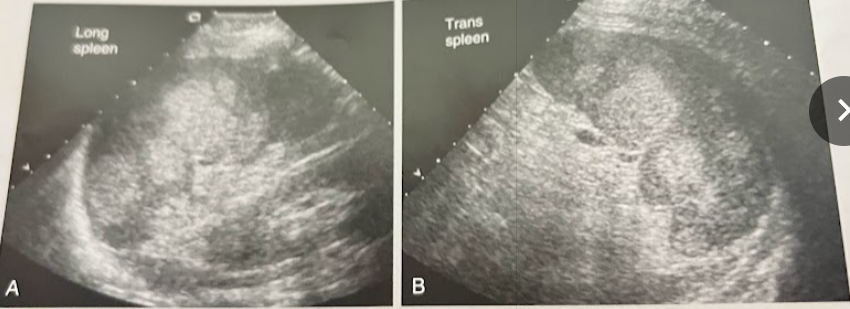
A 44 year old woman presents w/RUQ discomfort and is referred for an abd. sonogram. Lab values were normal for hematocrit, RBC, WBC and platelet values. The pt reported absence of pain or discomfort on the lt side. This image demonstrates heterogeneity of the spleen owing to multiple hyperechoic lesions. What are the sonographic appearances and clinical hx most suggestive of?
Hemangiomas
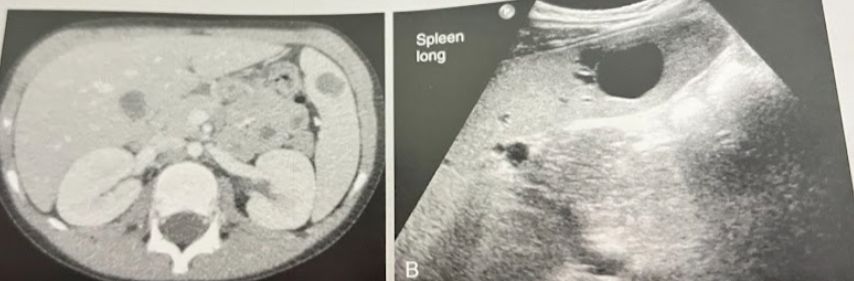
A 22 year old man w/hx of multiple sclerosis and neurogenic bladder has undergone multiple CT scans and sonograms over the years. This image demonstrates a solitary splenic lesion that has been stable in size and appearance across the pt’s imaging hx. What is the most likely nature of this finding?
Cyst
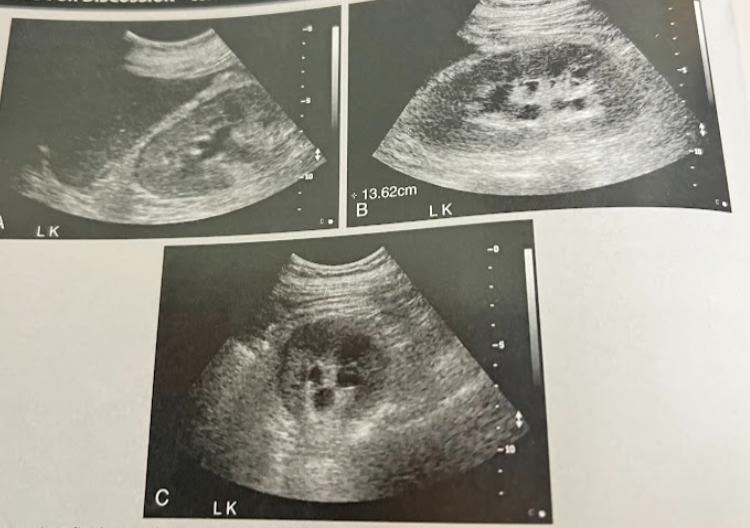
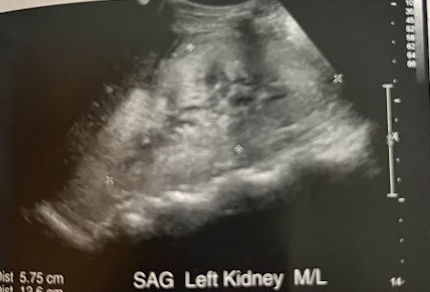
A 45 year old woman presents to the ED w/severe back pain. The requisition states “abnormal renal function - r/o obstruction.” What clinical findings indicate an acute rather than chronic condition. Are these findings consistent w/an obstructive cause of renal impairment? What do the fluid filled structures in the kidney likely represent? Are they related to renal function?
This is acute renal failure indicated by the presence of an enlarged echogenic lt kidney w/trace amounts of perirenal fluid. This is an obstructive cause of renal impairment. The fluid filled structures are multiple parapelvic cysts. Parapelvic cysts are typically asymptomatic and are noted incidentally in this case.
A 50 year old man is sent from the ED for a renal sonogram. He c/o not feeling well and says his hands and feet are swollen and urine was smoky-colored. He recently was treated for strep throat. Vital signs are normal w/a blood pressure of 150/110mmhg. The renal sonogram reveals prominent pyramids w/an increase in the cortical echogenicity. What is the likely diagnosis for this pt?
Acute glomerulonephritis
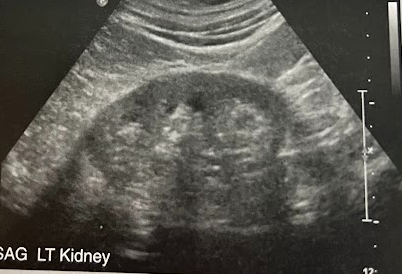
A 65 year old man undergoes a renal sonogram b/c of proteinuria and hematuria. He was diagnosed w/diabetes 12 yrs ago and has has a 15 yr hx of hypertension. He admits not taking his meds like he should and c/o being overly tired. Sonographically, the kidneys have thinned cortex and demonstrate a slight increase in cortical echogenicity. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Chronic kidney disease
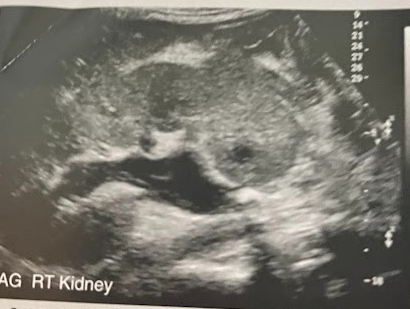
A 30 year old woman arrives from the ED for a renal sonogram. She presents w/fever, nausea, and a sudden sharp pain on the rt side and back. This is the 1st time she has ever experienced this type of pain and reports being otherwise healthy. The renal sonogram shows an echogenic calculus w/posterior acoustic shadowing in the prox rt ureter causing obstructive hydro. w/in the dilated, primarily anechoic collecting system are low-level echoes that show a layering effect. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Pyonephritis
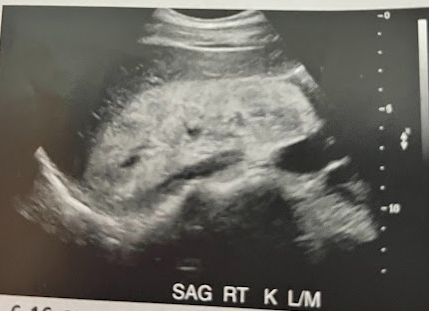
A 25 year old man was admitted after a serious automobile accident has a portable renal US performed in the ICU. He is recovering from a surgery repair for a fractured pelvis and femur. The pt has remained hypotensive w/decreased urine output despite being given fluid and medications. The renal sonogram reveals appropriately sized but echogenic kidneys bilaterally. What is the likely diagnosis for this pt?
Acute kidney injury
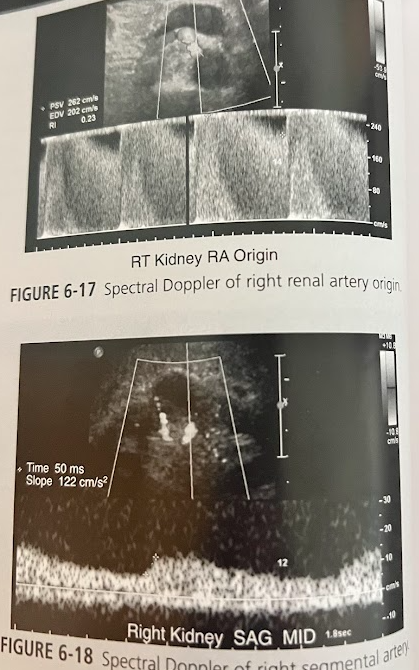
A 62 year old man w/a hx of hypertension and increased BUN and creatinine presents for a renal sonogram. He has a 40-pack per year of tobacco use and c/o pain in his buttocks with walking. Sonographically there is no signs of stone, cysts, masses, or hydro. The rt kidney measures 8cm in length and the lt measures 12cm in length. Doppler eval. reveals a velocity too high to measure accurately at the origin of the rt renal artery. There is a lengthened systolic peak in the rt intrarenal segmental arteries. What is the likely diagnosis?
Renal artery stenosis
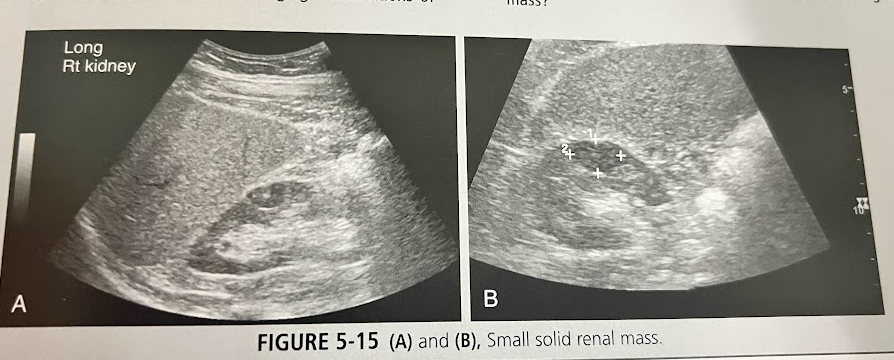
A 60 year old man is seen by his doctor for a routine exam. A routine lab work-up is performed, and microscopic hematuria is found. The pt has mild hypertension and hx of cigarette smoking. A UT sonogram is requested to help find the cause of the hematuria. These findings are seen in this image. What is the most likely diagnosis and how does pt hx contribute?
RCC, male pts of increasing age are more likely to develop this. Hematuria and hypertension are associated signs.
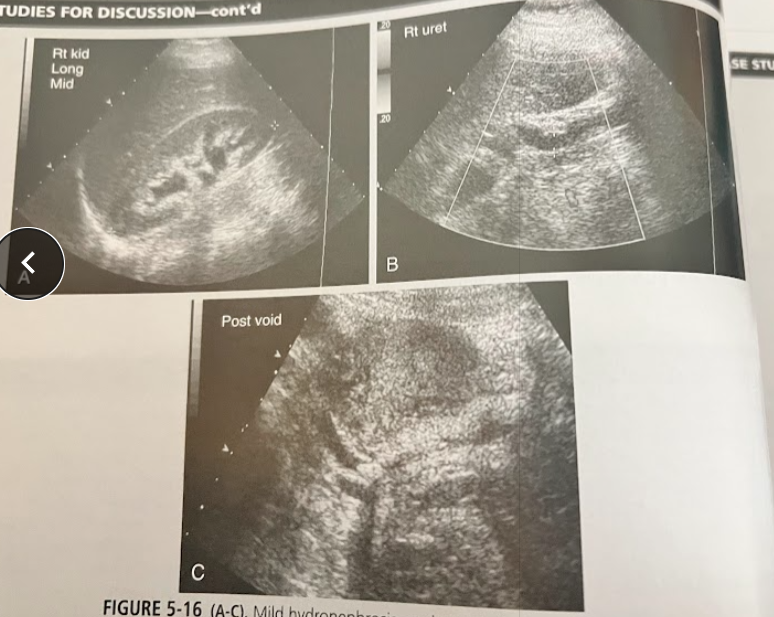
A middle aged woman presents to the ED w/flank pain, N/V and a low grade fever. Urinalysis reveals microscopic hematuria and she is referred for a urinary tract sonogram. The findings are in these images. What is the most likely diagnosis and what scanning techniques should the sonographer employ in completing this exam?
Ureteral caliculi causing partial obstruction at the ureterovesicle junction (UVJ). Using tissue harmonics and doppler can help detect it. Look for shadowing
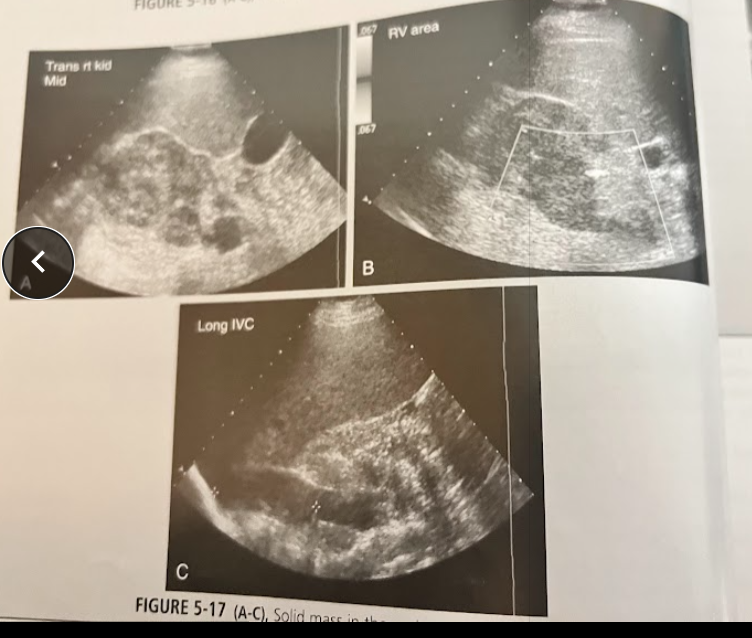
A 40 year old man w/clinical hx of gross hematuria is seen for a UT sonogram. No priors. A mass is seen in these images. Where is the mass located and discuss the diagnosis.
Transitional cell carcinoma, it is located in the renal sinus
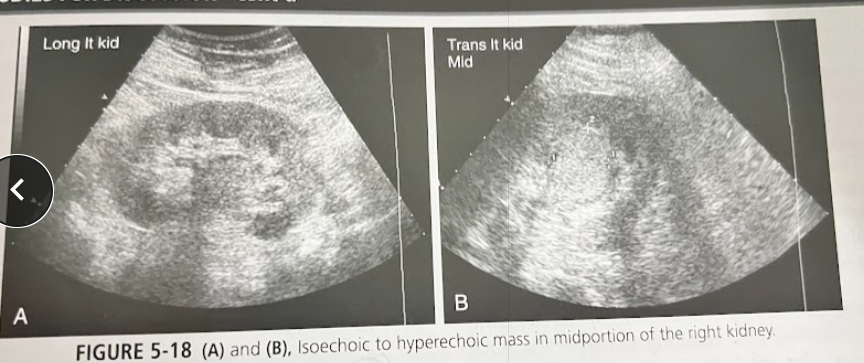
A 45 year old, mildly obese woman sees her doctor w/ complaints of RUQ pain, N/V after eating. Lab analysis reveals elevated cholesterol levels and microscopic hematuria. The exam is positive for gallstones. During the course of the exam, the sonographer discovers an incidental solid, well-defined iso/hyperechoic mass. There is a central scar w/in mass (shown on CT). What is the most likely diagnosis?
Oncocytoma
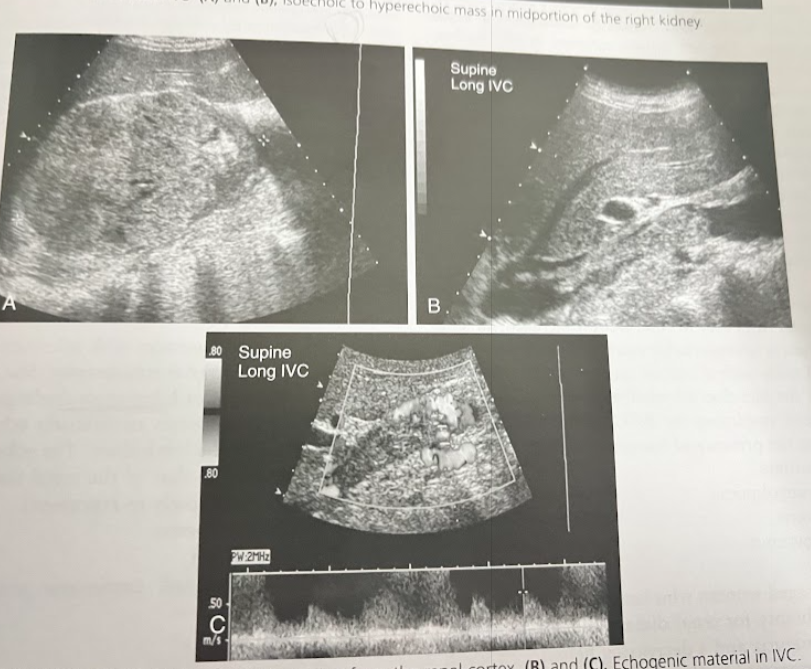
A 65 year old man w/hx of painless hematuria is referred for renal sonography. A solid mass is identified. What possible neoplasms might this mass be? What stage is this mass?
The most likely differential diagnosis are RCC, transitional cell carcinoma, or oncocytoma. Stage 3
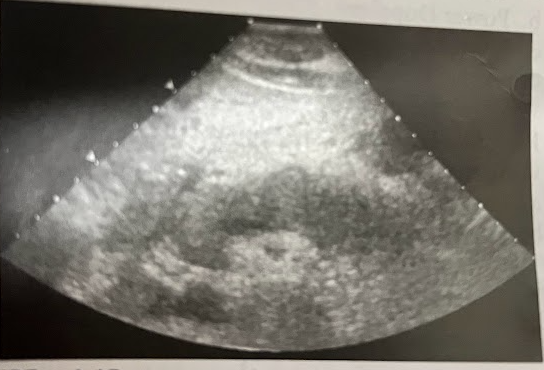
A 33 year old man w/a hx of alcoholism presents w/acute onset of epigastric pain, N/V, elevated WBC, elevated serum amylase, and increasing lipase level. The entire pancreas is enlarged and hypoechoic w/well-defined borders. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute pancreatitis
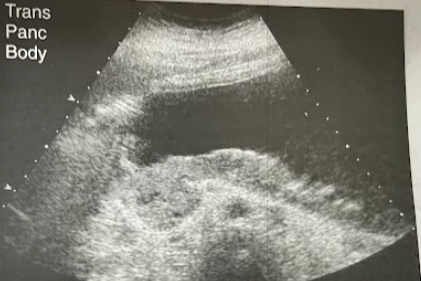
A 55 year old, moderately obese woman w/previous cholelithiasis returns to her Dr. for a 6 month f/u exam after cholecystectomy. She now has mild to moderate, intermittent epigastric pain and occasional fever. Sonographic results show choledocholithiasis, a dilated pancreatic duct, and a fluid collection anterior to the tail of the pancreas. What is the cause for the sonographic findings?
Pseudocyst
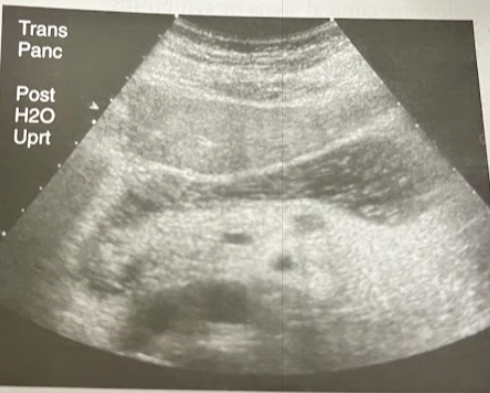
A 41 year old obese woman presents in acute distress. The family member accompanying her reports that her initial symptoms were mild and included hunger and anxiety. Earlier in the day, she began to have what appears to have been seizures. Imaging studies are ordered, the sonogram reveals a small hypoechoic lesion that measures approximately 1cm. Discuss the pt hx and likely reason for sonographic finding.
Functioning islet cell tumor (an insulinoma) which occur in obese pt’s w/hypoglycemic episodes
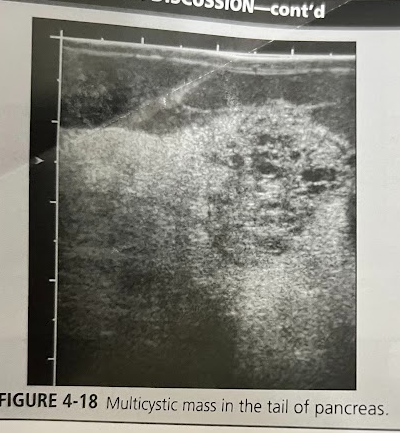
A 50 year old woman undergoes a sonogram for nonspecific abd. pain and a feeling of general malaise. While scanning the upper abd., the sonographer notices a multicystic mass in the tail of the pancreas. The pt denies any hx of smoking or alcohol abuse. Lab tests are unremarkable. A CT scan was performed and confirmed that the multicystic lesion was arising from the pancreas. Discuss the diagnostic possibilities.
Csytadenoma, cystadenocarcinoma
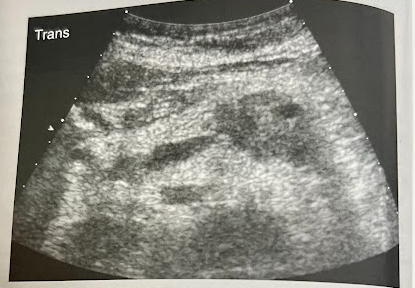
A 75 year old man is referred for an abd. sonogram to r/o gallstones and biliary disease. He reports recent significant wt. loss and epigastric pain. Sonogram reveals findings in this image. What is the most likely diagnosis?
This represents adenocarcinoma, the most common solid pancreatic neoplasm. Men are more effected btw 60-80 yrs.
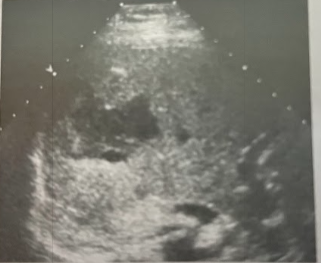
A 38 year old woman undergoes a sonogram of the liver. She was seen in the ED 3 days earlier for severe RUQ pain. At that time CT scan was done, which showed a liver lesion that contained fresh blood. The pt had been taking oral contraceptives. Today’s exam shows a 6.5 × 5.5 cm heterogeneous, complex, cystic-appearing mass. Given pt hx and clinical presentation, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Hemorrhagic hepatocellular adenoma
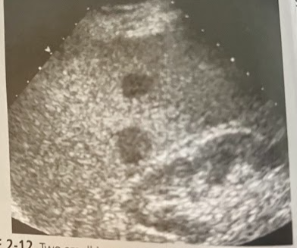
A 77 year old man undergoes a sonography-guided bx after a CT scan. His hx includes a complete gastrectomy 8 months prior for grade IV gastric cancer, and the CT scan today shows multiple liver lesions. The sonogram reveals hypoechoic lesions in both lobes of the liver. What is the bx most likely to show?
Metastatic gastric cancer
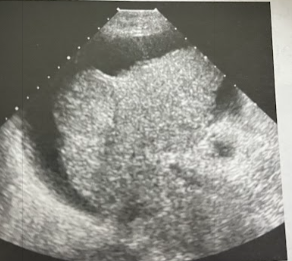
A 77 year old woman undergoes an abdominal sonogram. She is known to have hepatitis C, presumably contracted from a blood transfusion during coronary artery bypass surgery in the 1970s. The sonogram reveals a cirrhotic-appearing, heterogeneous liver. A 1.6cm mass is seen at the periphery of the rt lobe. A large amount of ascites is present. Given the pt’s hx of hepatitis C and the cirrhotic appearance of the liver, what is the most likely diagnosis?
HCC
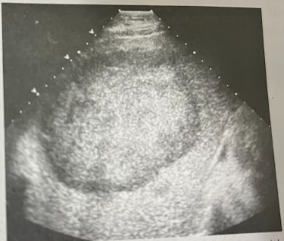
A 66 year old man undergoes a sonographic guided bx of a large liver mass previously discovered on CT. He has a hx of persistent cough, SOB, unexplained wt loss, low-grade fever, and abd. wall discomfort. Two large hyperechoic lesions w/peripheral halos are seen in the rt lobe, the largest measuring 12.6 × 13.2cm. What will the bx confirm?
Primary lung cancer w/mets to liver
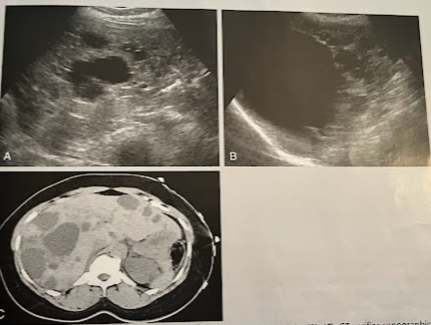
A 55 year old woman underwent an abd. sonogram b/c of a feeling of fullness in her abd. The liver demonstrated multiple anechoic lesions, some w/irregular walls and many w/acoustic enhancement. A f/u CT was ordered that confirmed the sonographic findings. A couple cystic lesions identified arising from the rt and lt kidneys. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Polycystic kidney disease of the liver and kidneys
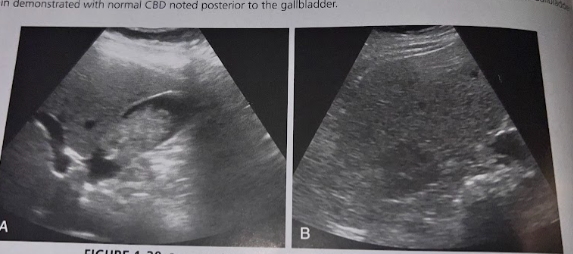
A 78 year old man presents w/ RUQ pain, malaise, and wt loss. A RUQ sonogram reveals irregular echoes w/in the GB wall and hypoechoic lesion in the rt love of the liver. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Gallbladder carcinoma w/mets to the liver