Surface Water 2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
fill and spill hydrology
where there are many depressions in a watershed, a rainfall will replenish groundwater - needs enough volume to spill over in order before connecting to downstream parts of catchment
in prairies, bedrock, etc - praire potholes
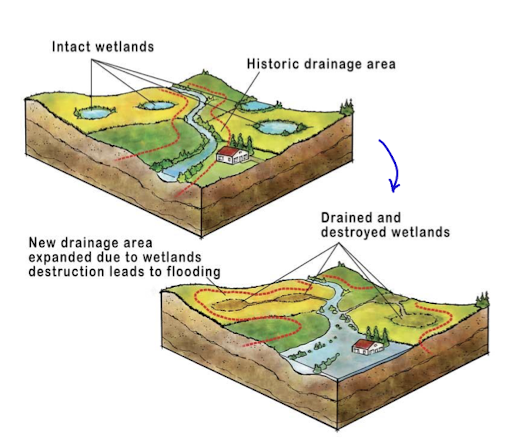
how does changes in a wetland impact hydrological regime
draining wetlands alongside other changes will alter the natural drainage area to be larger and encompass a larger area etc
storage decreases which increases runoff
flooding
can be fluvial (overflows over banks), pluvial (rain), coastal (storm surge, tsunami)
knowing risks is very important with land use etc of floodplains
flood frequency, changing risk, erc
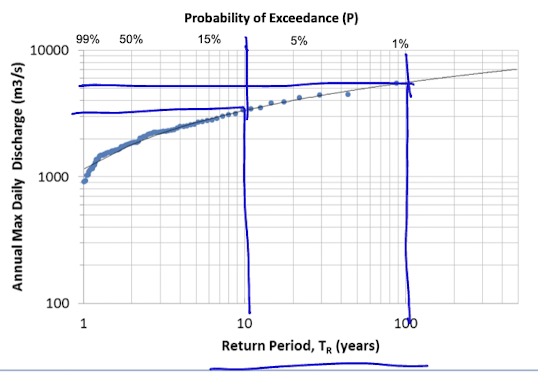
flood frequency
understanding frequency and magnitude based on historical methods
return period - how often can we expect a flood greater than a specific discharge
exceedance probability of the large flood in a given year
important to understand how parts of a flood plain will be flooded - city planning, insurance, etc
return period equation
= (n+1)/Rank
(n - years of record)
probability equation
Rank/ (n+1)
probability of a flood of a certain amount occuring
levees
constructed to prevent/protect against flooding
BUT can increase further downstream and runoff is faster
and also can be catastrophic when it fails
calgary flood control
2013 flood was extremely costly
additional control needed in bow and elbow rivers, springbank reservoir added storage
glenmore reservoir also added storage
dam under assessment, additional levees built, dry dam created
non-stationary flood frequency
future =/ the past
need to account for climate change, land use/management (ag, forestry, etc), fires, dams/diversions/drainage, and alteration of river channel
need to account for these in modelling and projections
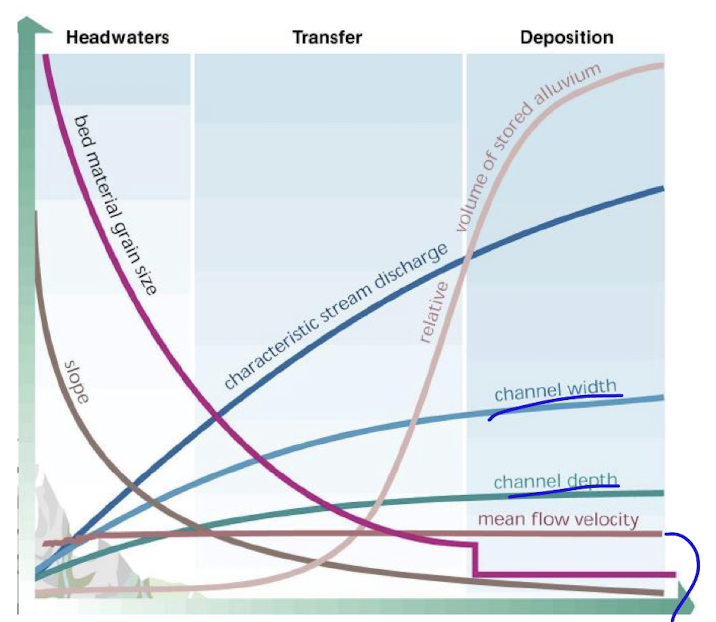
river morphology
headwaters (in the mountains), transfer zone comes next where lower elevation streams merge in lower slopes
in the depositional zones meandering streams flows maybe into delta, maybe sea, etc
stream power
rate of energy dissipation against the bed and banks of a river per unit downstream in length
work done by a stream to move sediment
so for example a river flowing at a constant speed which does not gain any kinetic energy needs to dissipate energy in some way and so it does as kinetic energy for sediment, ______
stream power equation (Ω)
Ω = p*g*Q*S
p = density of water, g = acceleration due to gravity, Q=discharge, S = slope
stream power interpretation
steep rivers with a higher discharge will have greater stream power therefore a higher power to transport/erode sediments
with no sediment stream power is instead dissipated as heat vs kinetic energy
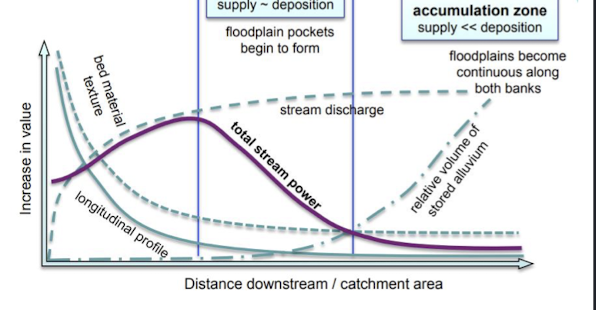
river zones and sedimentation
in the headwaters usually supply of sediment is higher than the rate of deposition, therefore stream power acts on the supply
in the transfer zone floodplain pockets begin to form, supply/sedimentation and deposition are more equal
in the depositional zone the supply is less than, therefore floodplains are continuous and deposition is constant
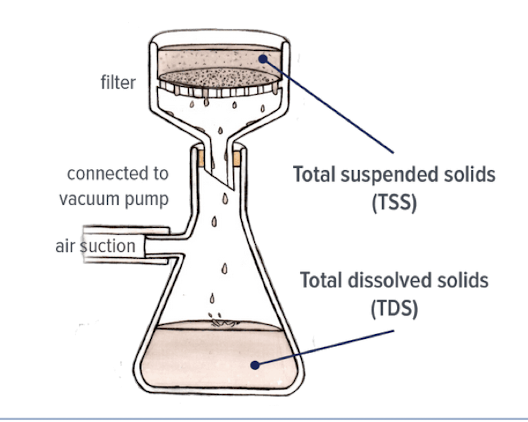
total suspended solids
measured by filtration and weighing of the filter before and after
filter pore size determines difference between a dissolved and suspended solids
dominated by silt, clay, sand but can also include organic material
increases with higher stream velocity
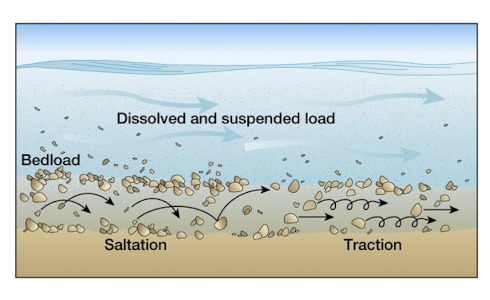
bedload
sediment particles which are too heavy to be suspended
move by rolling, sliding, and saltation
needs stream depth 10x sediment diameter
increases with higher stream velocity
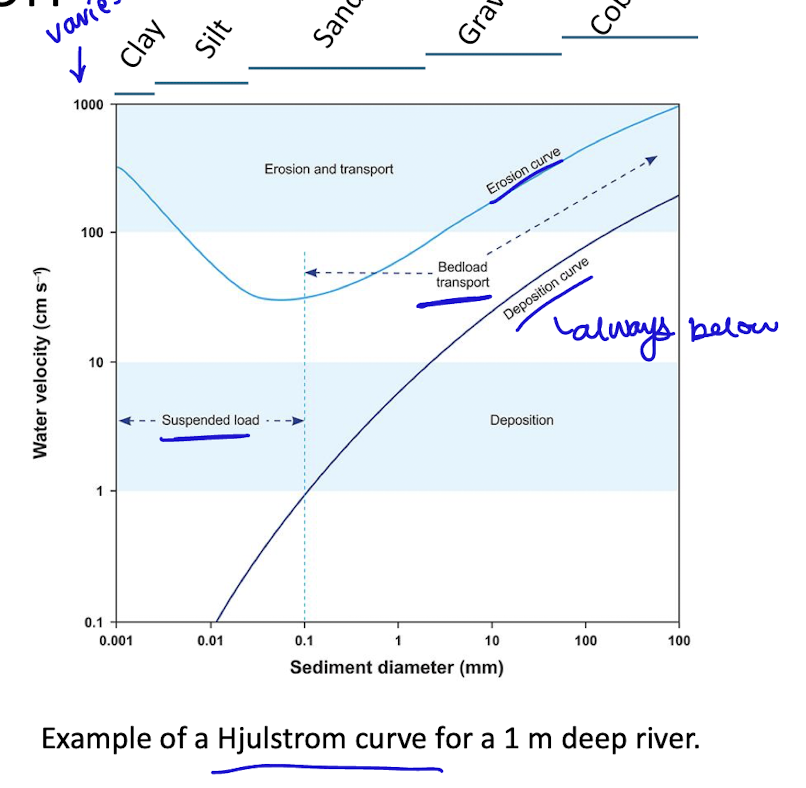
entrainment and deposition
higher velocity needed to entrain (erode) than to keep sediment in suspension
smaller particles easier to keep in suspension, easier to erode (exception of clay/silt)
deposition caused by lower stream velocities, TSS and bedload increased with higher V
larger rivers able to transport more TSS and bedload
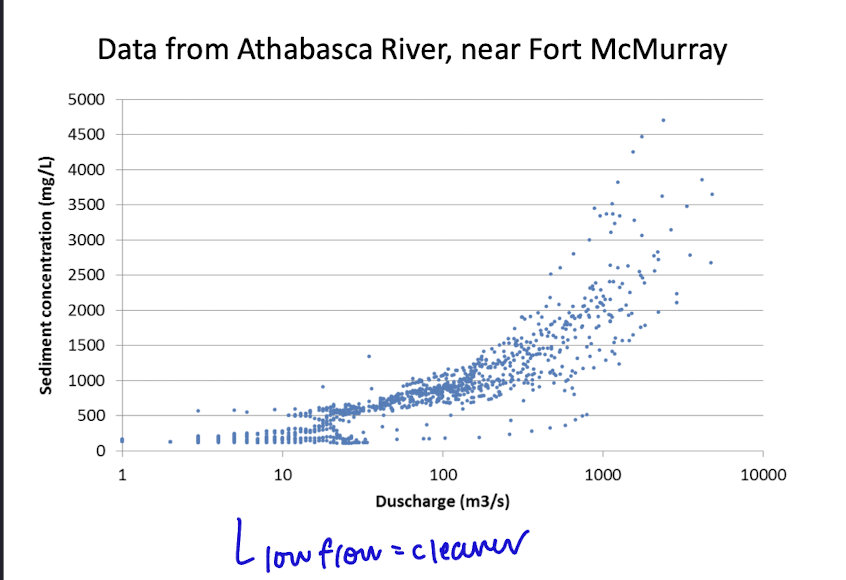
yield
total amount of sediment or other dissolved transported in a river over time, largely during high flow as Q increases with C
ex tonnes/year
= D*C (discharge * concentration)
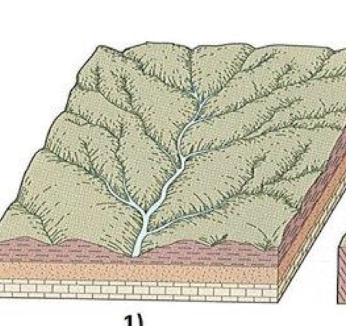
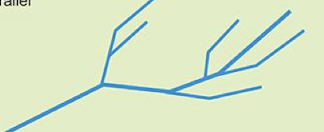
dendritic
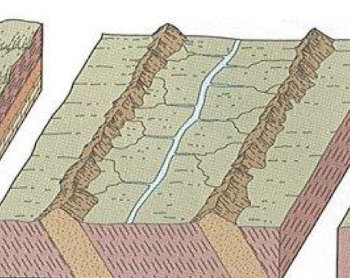
trellis
rockies
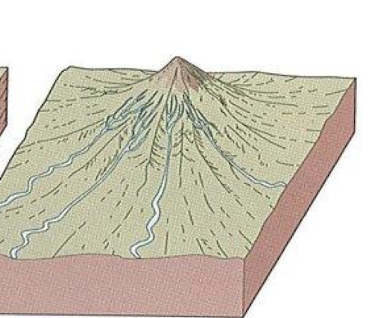
radial
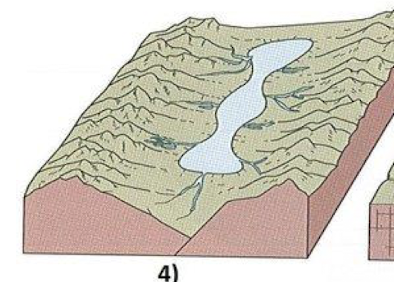
centripetal
rectangular
cracking landscape
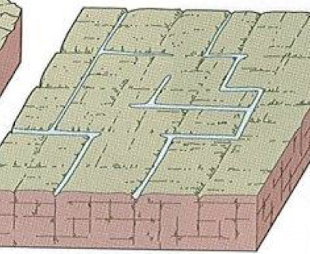
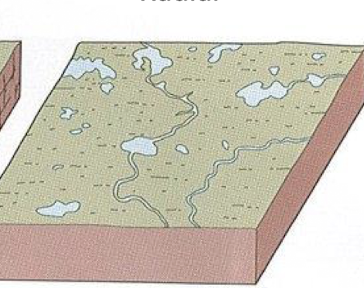
deranged
prairies, depressions
parallel
braided river
higher bedload, more grained sediment, decreasing bank stability, high discharge variability, high slope
channel type in the transfer zone

meandering pattern
more suspended load, finer grain sediments, increasing bank stability, low variability discharge, low channel slope
sinuosity >1.5
channel type in the transfer zone

sinuosity
length of thalweg / distance along valley
meandering river will have >1.5
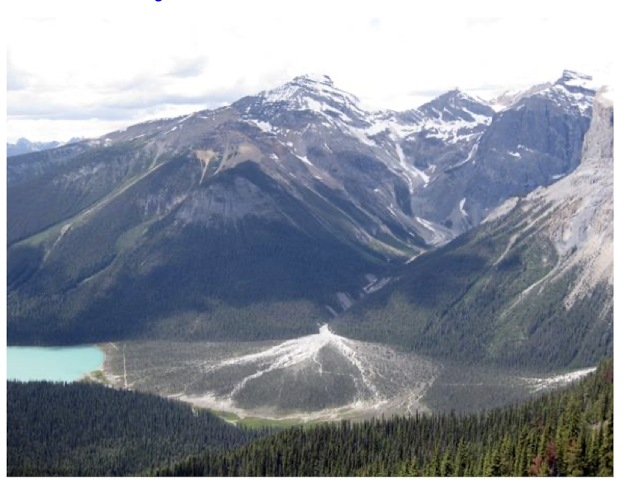
alluvial fans
base of mountain
deposition when river slows down - less slope and loss of stream power

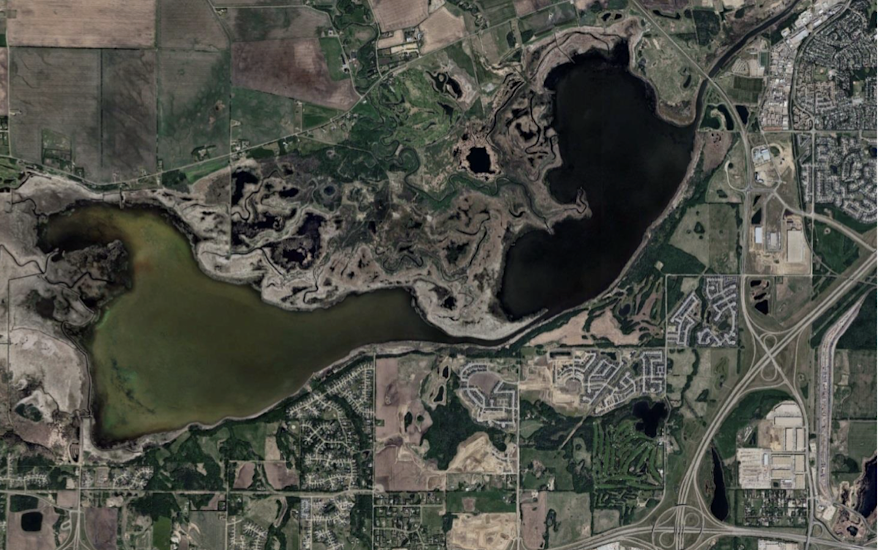
deltas
in lakes or oceans, lots of sediments - silts and clays
deposition when river slows down - less slope and loss of stream power
sediment trapping in dams can reduce sediment load here, when wave erosion>deposition then they will shrink

human modifications of sediment transport
urbanization increases runoff, increases erosion and river incision ex in the mill creek ravine
reservoirs trap sediments, and when there is less in water downstream then increases erosion and stream incision
this can also reduce sediments in deltas which causes them to shrink (when wave erosion>deposition)