AP Bio Macromolecules (1.2-1.6)
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
macromolecule
large molecule necessary for life built from smaller organic molecules
monomer
single subunit or building block
polymer
2+ monomers covalently bonded
dehydration synthesis
hydrogen and hydroxide separate from monomers forming water, and polymer covalent bonded together, uses enzymes
hydrolysis
breaking down of polymer into two monomers by adding water, uses enzymes
product of dehydration synthesis
polymers and water
product of hydrolysis
monomer
carbohydrates elements
C1:H2:O1
glucose chem formula
C6H12O6
carb monomer
monosaccharide
carb polymer
polysaccharides
bonds between monosaccharides (carbs)
glycosidic bond
examples of monosaccharides
fructose, glucose, galactose
disaccharides examples
lactose and sucrose
polysaccharides
long monosaccharide chains, can be branched or unbranched
glycogen
stores extra glucose in animals
cellulose
structural plant cell wall, glucose chained together
starch
stores extra glucose in plants
compare and contrast starch and cellulose
both made up of glucose, cellulose is arranged in 180 degree rotations forming tight wall
function of carbs
energy, structure, storing, or transporting energy
lipids elements
CHO, sometimes P
monomer of lipids
fatty acids and glycerol (not true monomer)
bonds between lipids
ester linkages
lipids relationship to water
all nonpolar and hydrophobic
fat molecule/triglyceride
glycerol bound to 3 fatty acids
glycerol
3 carbon molecule with 3 -OH groups
fatty acid
hydrocarbon chains with carboxyl group
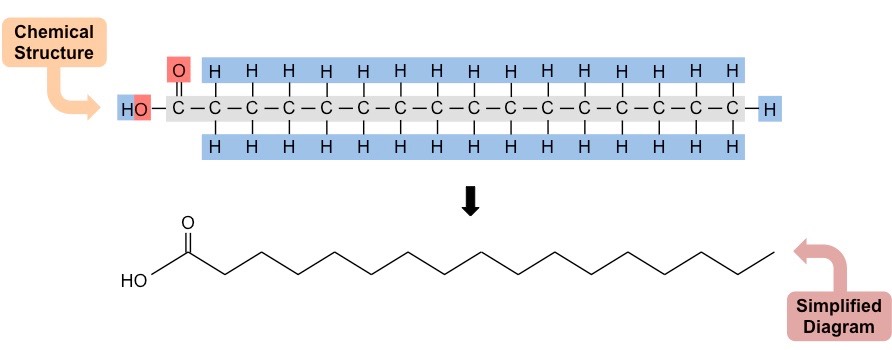
saturated fatty acid defintion
single bond
flexible hydrocarbon tails
known as “fats”
every backbone saturated with hydrogen atoms
can stack up (solid at room temp)
saturated fatty acid diagram
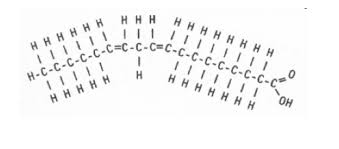
unsaturated fatty acid defintion
double bonded
less flexible due to kinks
known as “oils’
cant stack (liquid at room temp)
unsaturated fatty acid diagram
wax
long fatty acid tails bonded to long alcohols or carbon rings, packed tightly to be water resistant
phospholipids found in
plasma membrane
phospholipids structure
glycerol attached to 2 fatty acids and polar group
phospholipid bilayer
hydrophilic heads face water while hydrophobic tails in middle
steroids
lipids w rigid backbone bc 4 fused hydrocarbon rings
example of steroid
cholesterol forming bile salts
proteins elements
CHONS
proteins monomer
amino acid
structure of amino acid
amine attached to carboxyl group, r group differs characteristics
how do amino acids r groups fold
exterior if hydrophilic, interior if hydrophobic
bonds between amino acids
peptide bonds (between carboxyl of one w amine of another)
covalent
protein function
structure, nutrition, defense, enzymes, communication
important thing to remember about proteins
shape determines function
enzymes
catalysts in biochem reactions
what macromolecules make up hormones
proteins or lipids (steroids)
denaturation
protein loses function from change in ph, temp, or salts
how does denaturing break proteins
disrupt hydrogen bonds and proteins cant fit in enzymes
primary structure
amino acid polypeptide chain
consists of N terminus (amino group) and C terminus (carboxyl group)
secondary structure
hydrogen bonds create folds in polypeptide
r groups role in secondary structure
none, r groups protrude out or above
2 outcomes of secondary structure in proteins
alpha helix or beta pleated sheets
tertiary structure
interaction of r groups creates 3-dimensions
types of r group interactions in tertiary structure
-repel or attract (ionic) each other based on charge
-hydrophobic folds inside away from water
-hydrophilic stays on outside towards water
-disulfide linkages (only covalent)
quaternary structure
r group interaction but DIFFERENT polypeptide chains
is denaturing reversible
sometimes, if agent is removed
chaperones
protein helpers that aid in folding process
where is dna found
nucleus of eukaryotes + chloroplasts and mitochondria
role of rna
protein synthesis
monomer of nucleic acids
nucelotides
bonds between nucleic acids
phosphodiester
structure of nucelotides
nitrogen base
5-carbon sugar
phosphate group
elements found in nucleic acids
CHONP
purines
double ring (AG)
pyrimidines
single ring (CTU)
how to identify r group polarity (amino acids)
hydrocarbon (hydrogen or carbon)=nonpolar
oxygen, nitrogen, or other electronegative-polar
which part of a nucleotide is charged
phosphate group
how are carbons counted
clockwise
what is held on 1 prime of deoxyribose
nitrogenous base
what is held onto 3 prime of deoxyribose
phosphate group of ANOTHER nucleotide
what is held onto 5 prime of deoxyribose
phopshate group of own nucelotide
how to tell which direction nucleotide strand is in
O on sugar always points towards 5 end
bonds between bases in double helix
hydrogen bonds (easy to separate)