articulation test
1/235
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
236 Terms
resonance
Fundamental in speech production
is an acoustic response of air molecules within the oral, nasal, and pharyngeal cavities to some source of sound
Air can be set into vibration in response to a sound from the larynx
resonating cavities
are pharyngeal, oral, nasal, air spaces between lips, teeth, cheeks
Movement of articulators change the shape of these resonators
act on sound at larynx
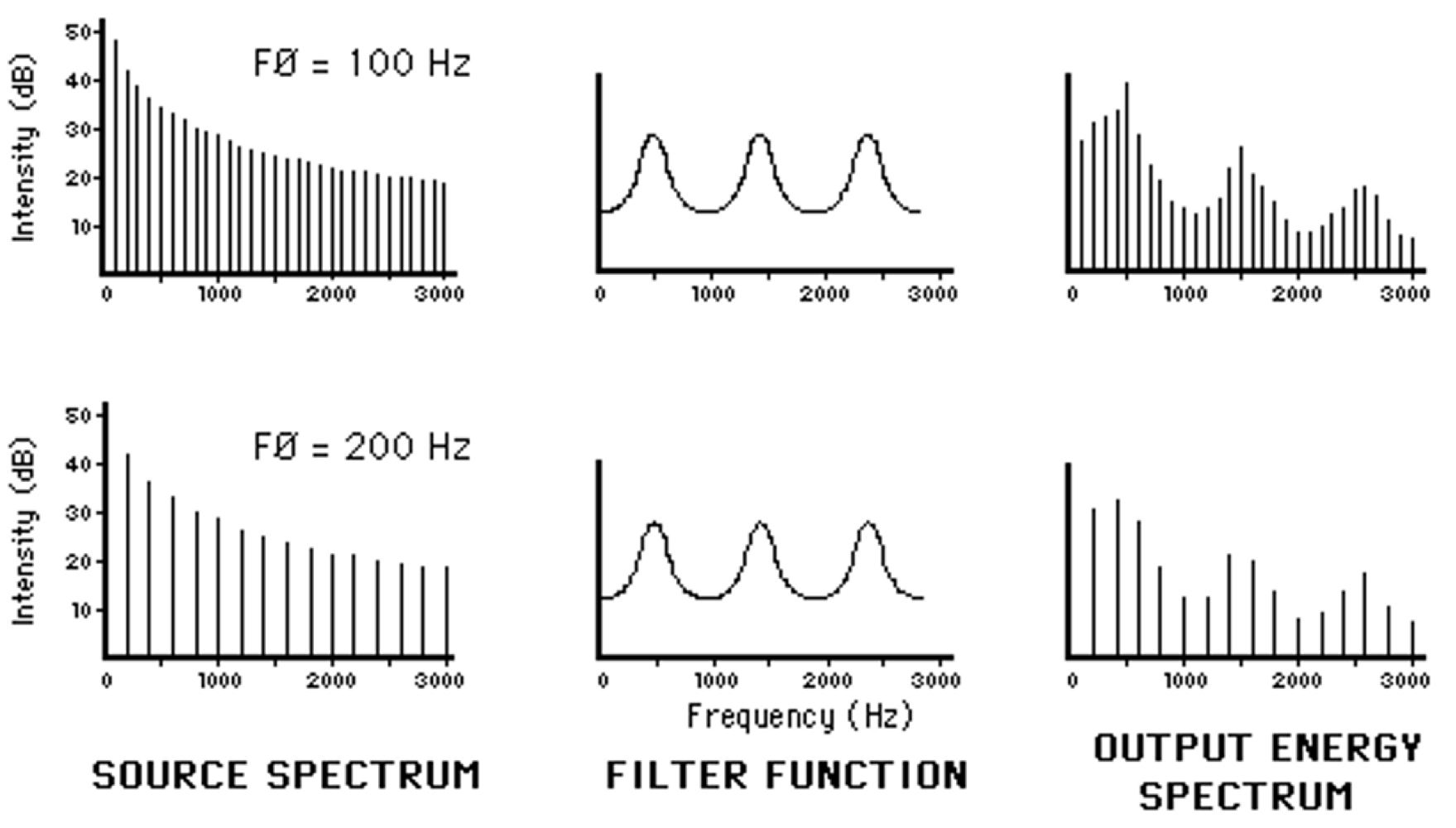
source filter theory
The combination of sound energy and the resonating cavity results in a shaped spectrum with broadband energy peaks. (forks)
Acoustic speech output results from a combination of:
A source of sound energy
Energy modulated by a transfer filter function
Determined by the shape/characteristics of the filter
whatever shape that energy is moving through dictates how energy will come out looking like
vocal tract
a series of tubes : pharynx, oral cavity(most important bc moveable articulators) and nasal cavity
sound
Shaping the vocal tract differently causes change in….
Tongue
Lower jaw (mandible)
Velum (soft palate)
Lips
Cheeks
Fauces and pharynx
Larynx and hyoid bone
what are the mobile articulators
Upper jaw (maxilla)
Alveolar ridge
Hard palate
Teeth
what are the immobile articulators
Mandible (lower jaw)
Unpaired bone (one bone)
Fuses at midline by 1 year of age
largest and strongest
holds teeth
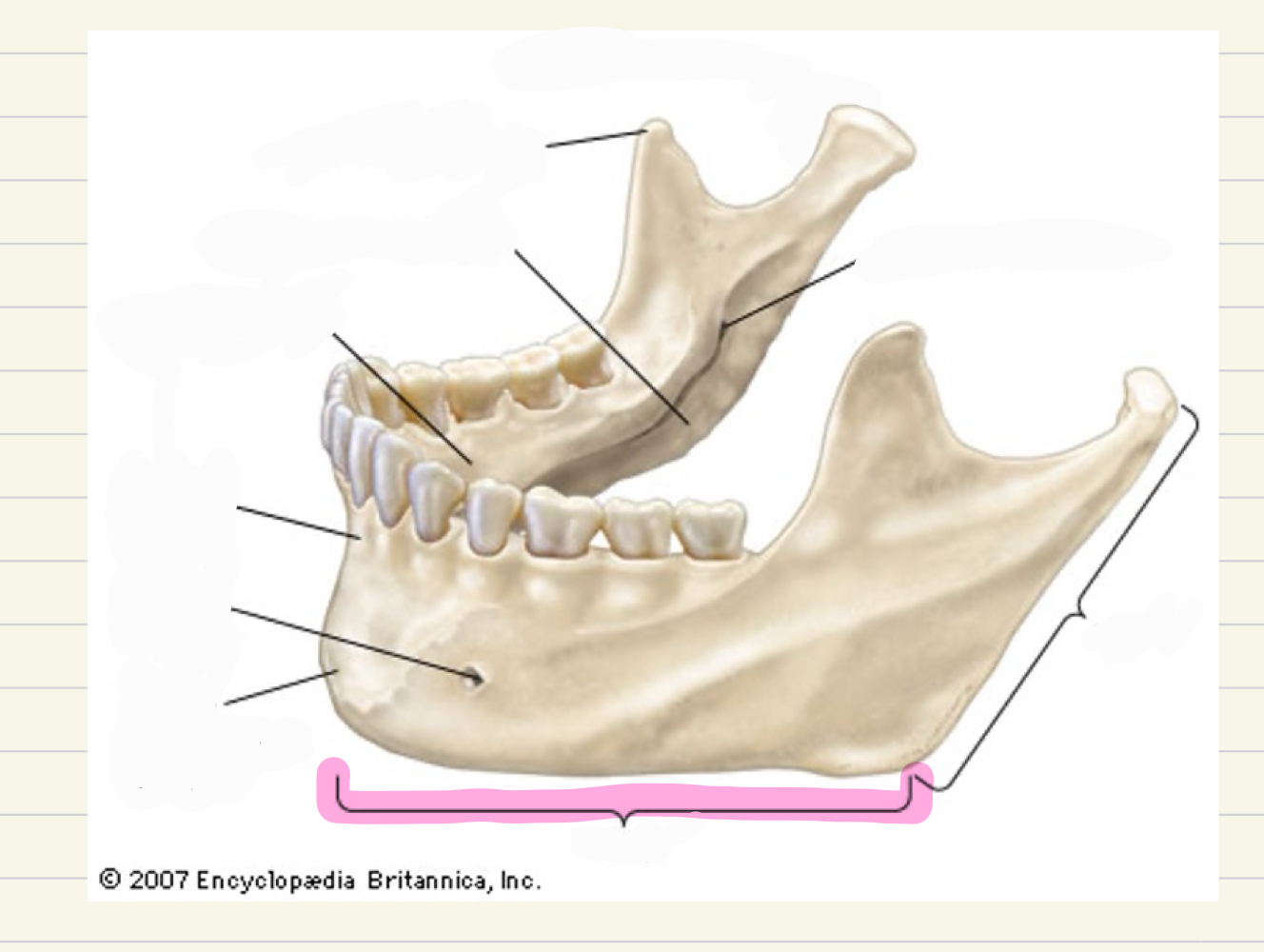
Mandible (lower jaw)
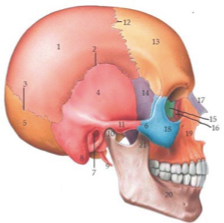
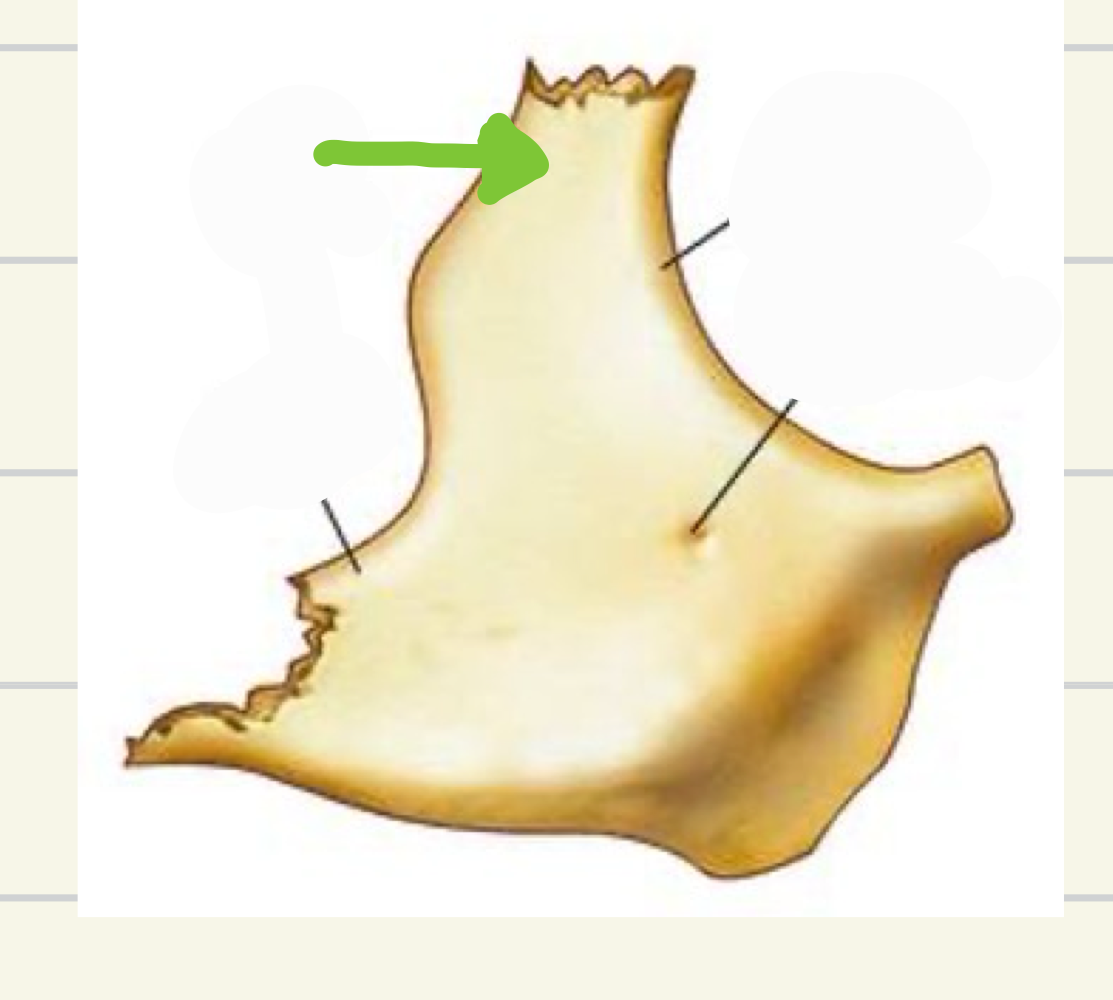
what bone of the face is this?
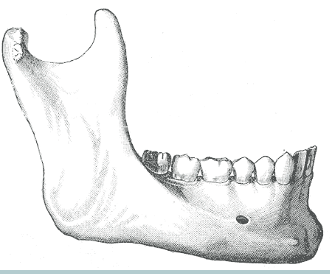
symphysis mente or mental symphysis - where 2 halves combine
what is this landmark ?
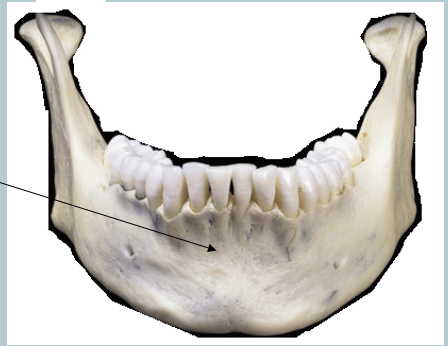
corpus or body
what is this mandibular landmark
ramus
what is this mandibular landmark
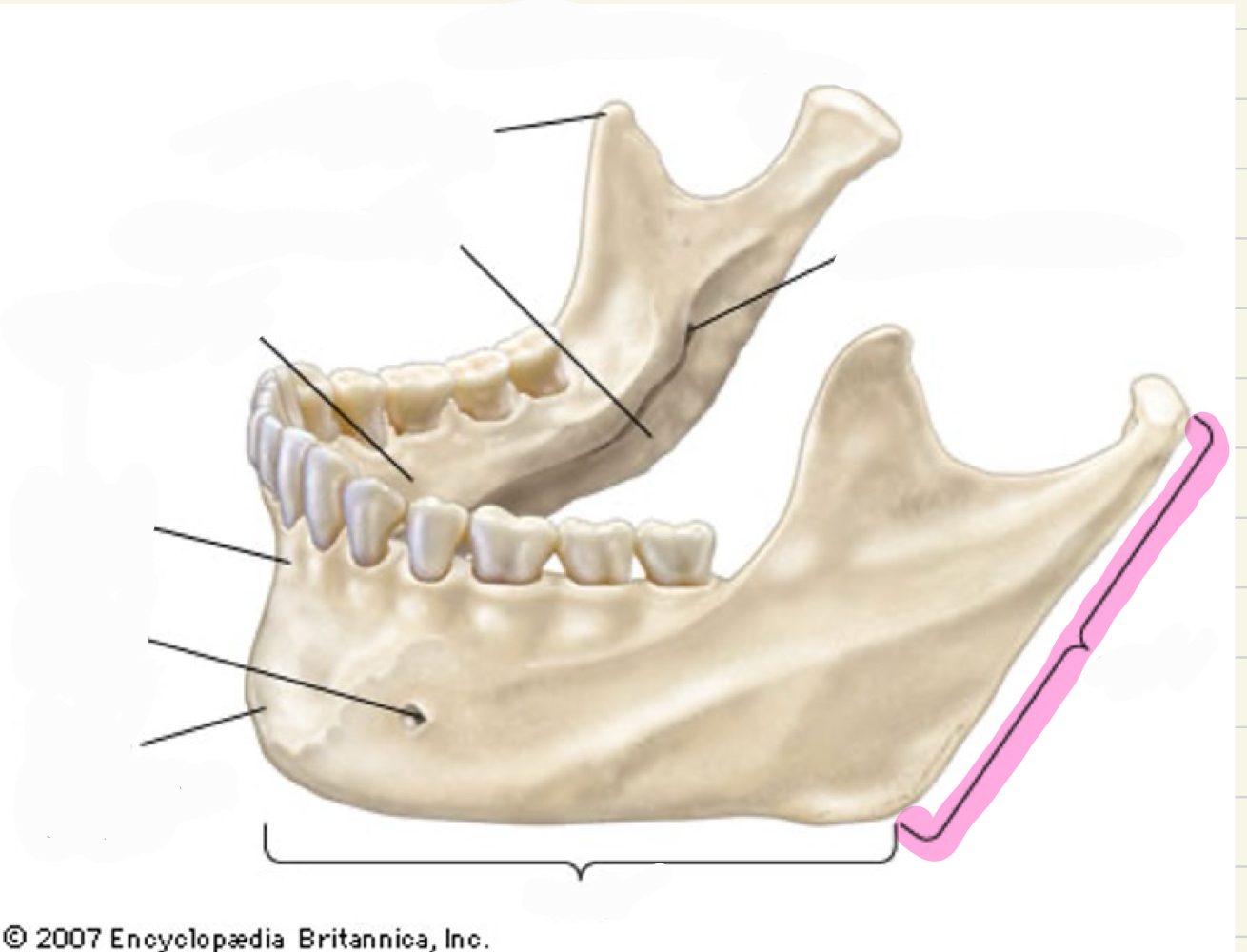
ramus
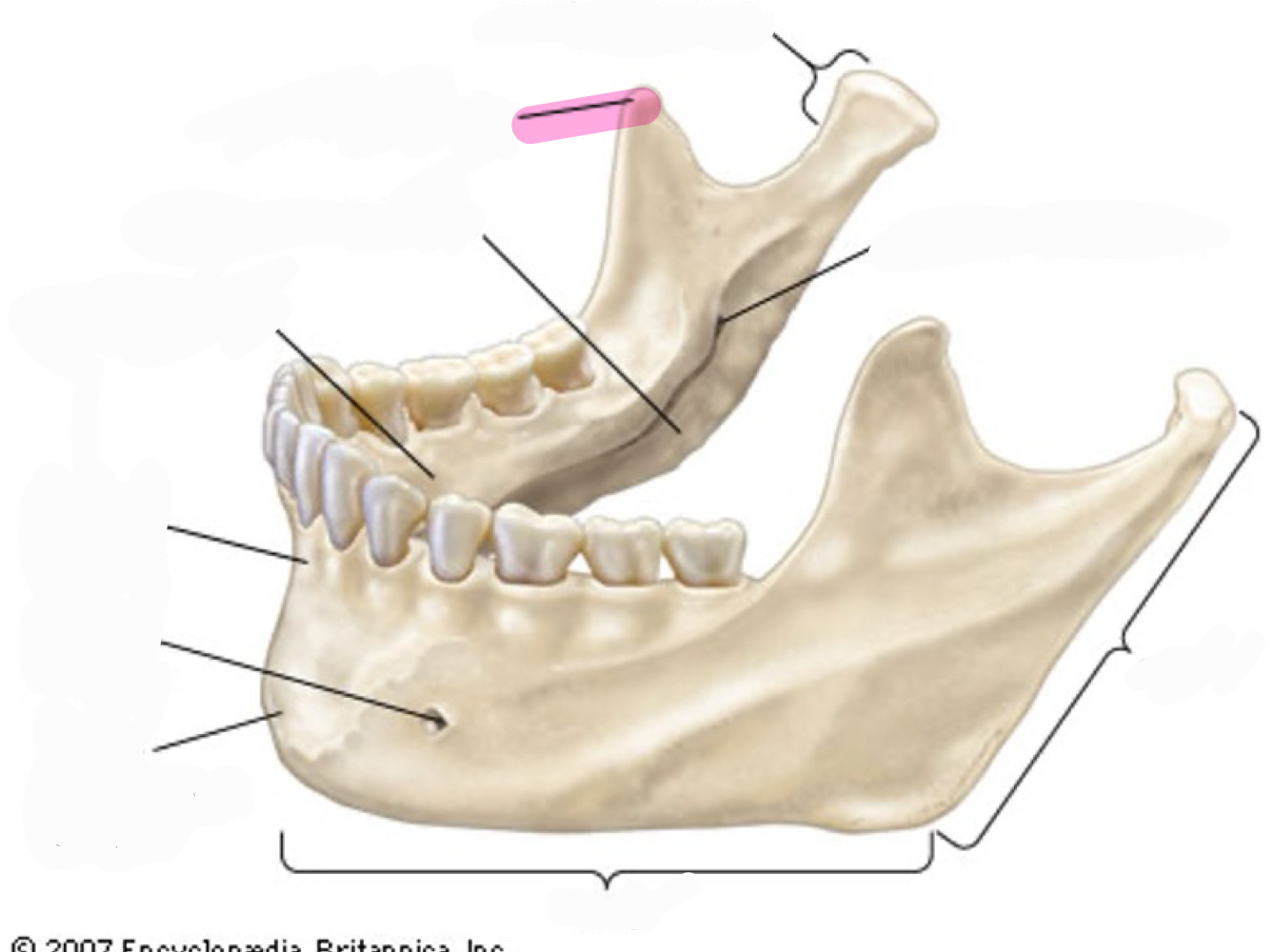
Superior border of each of these separated by the mandibular notch
coronoid process- point of attachement for muscles
what is this mandibular landmark
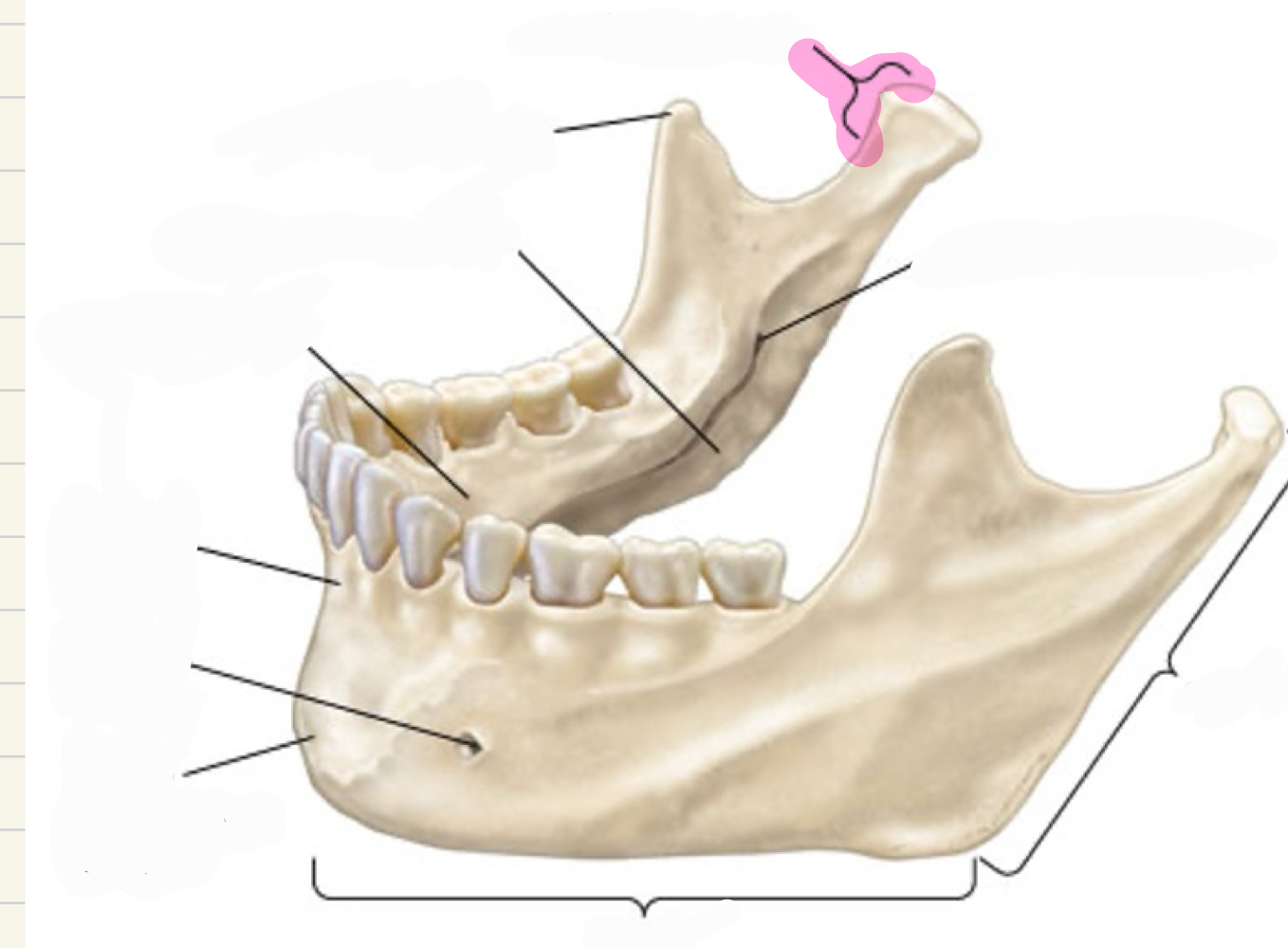
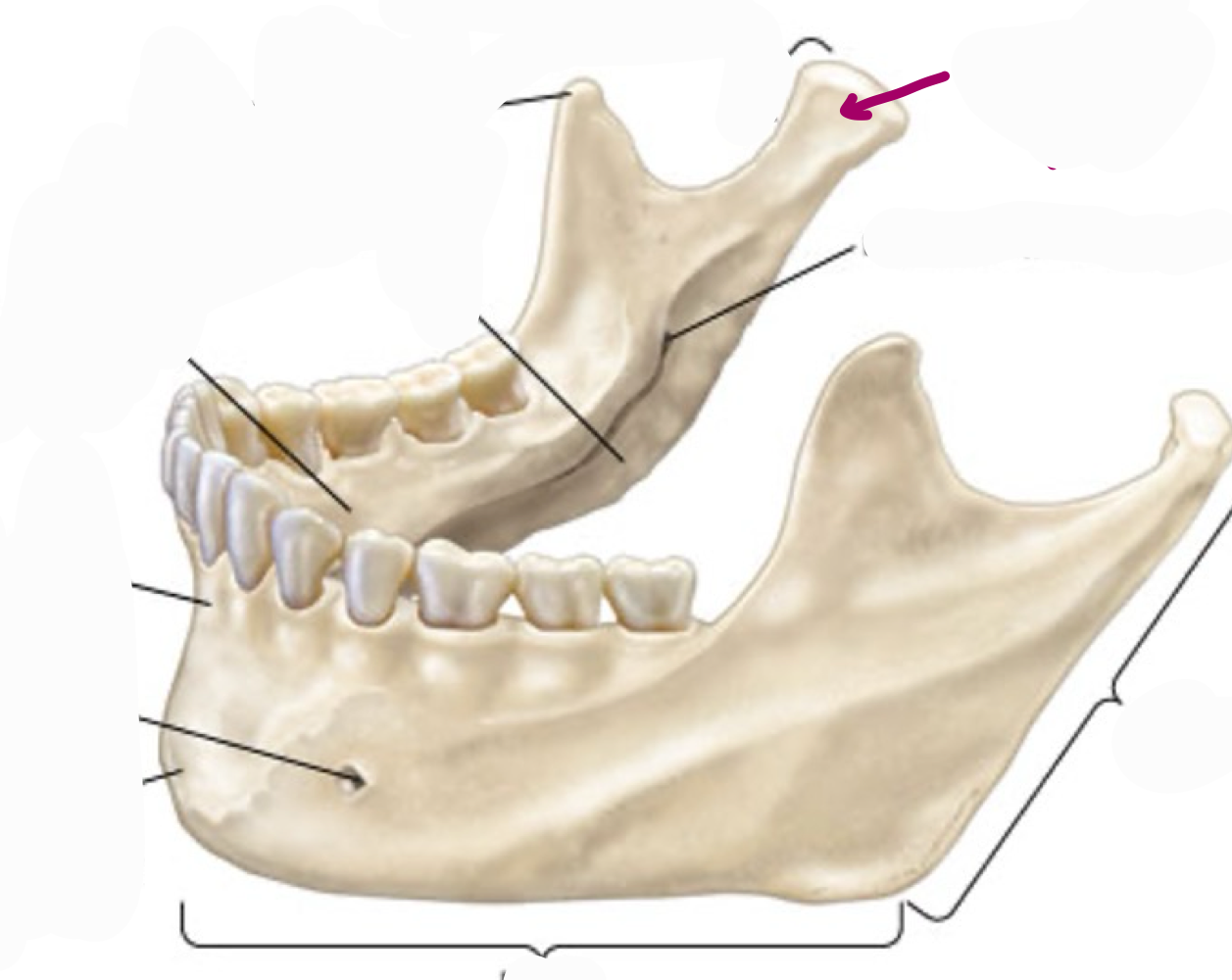
condylar process- head articulates with cranial bones (TMJ)
what is this mandibular landmark
mylohyoid line
what is this mandibular landmark
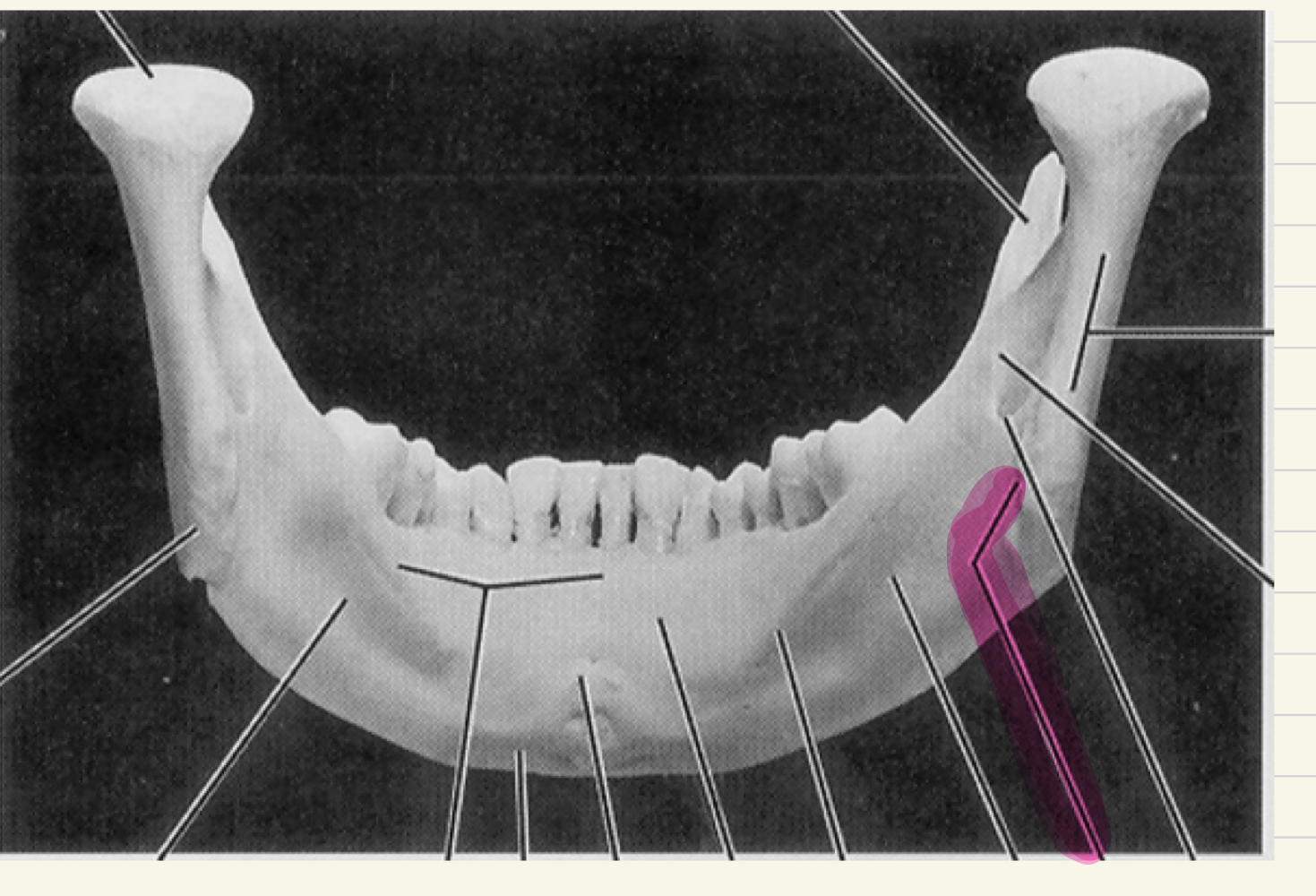
angle
what is this mandibular landmark
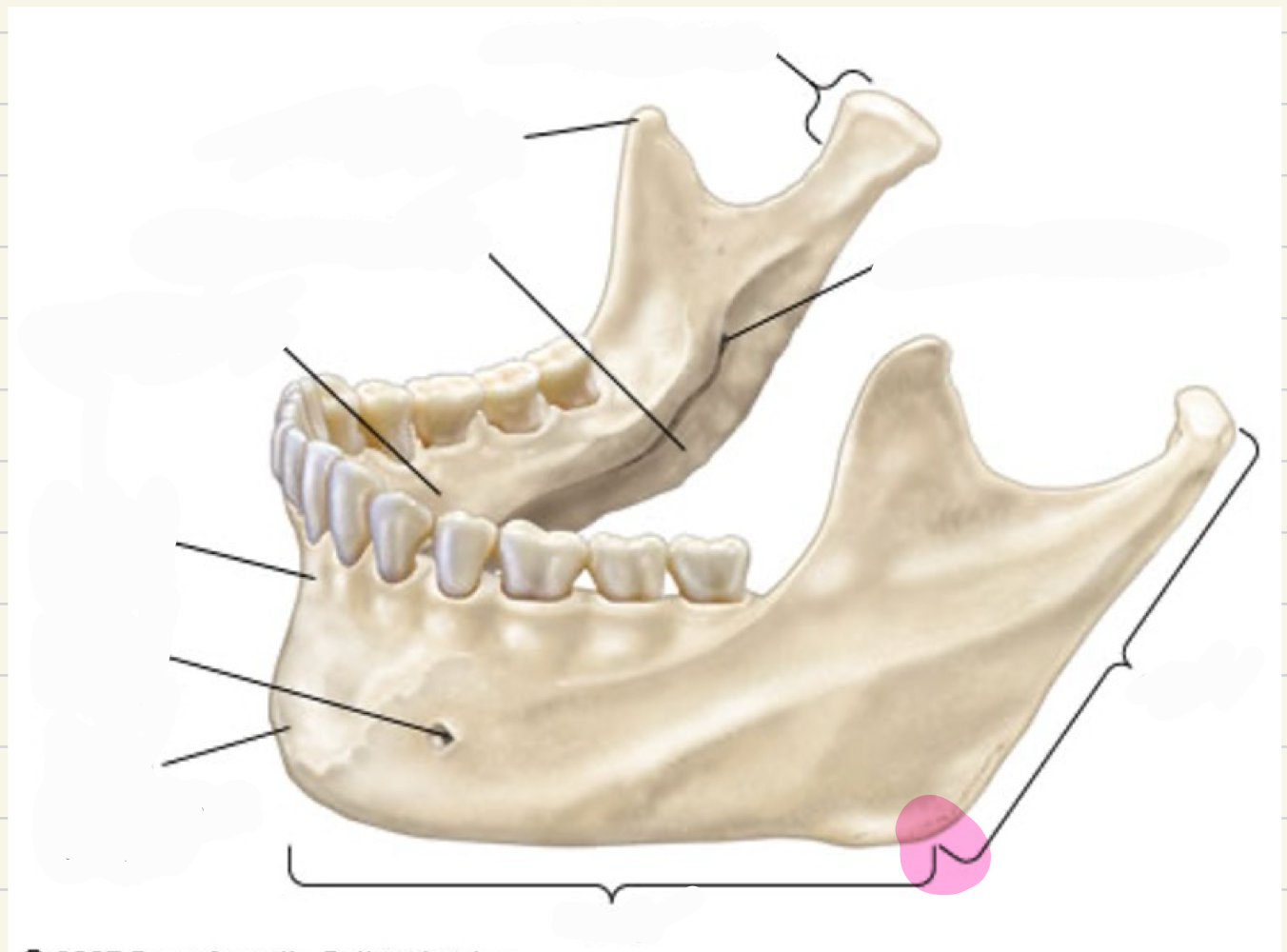
Movements of the mandible and tongue result in modification of the size and acoustic characteristics of the oral cavity
houses lower teeth
point of attachement
foundation for tongue movement
mandible contributions to speech
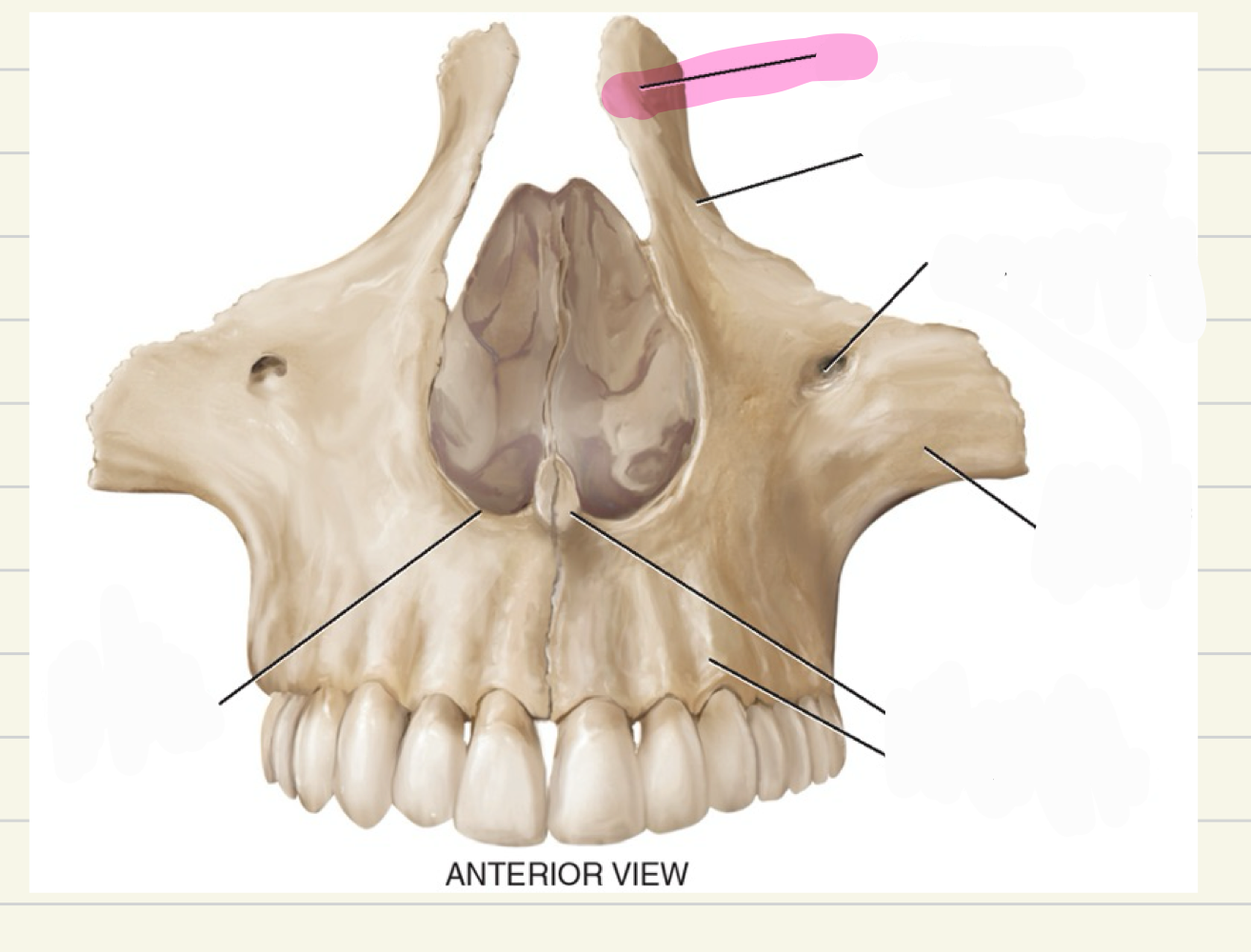
Maxillae
Paired bones making the upper jaw
Also make up most of the hard palate, nose, and upper dental ridge
zygomatic process
what is this maxillae landmark
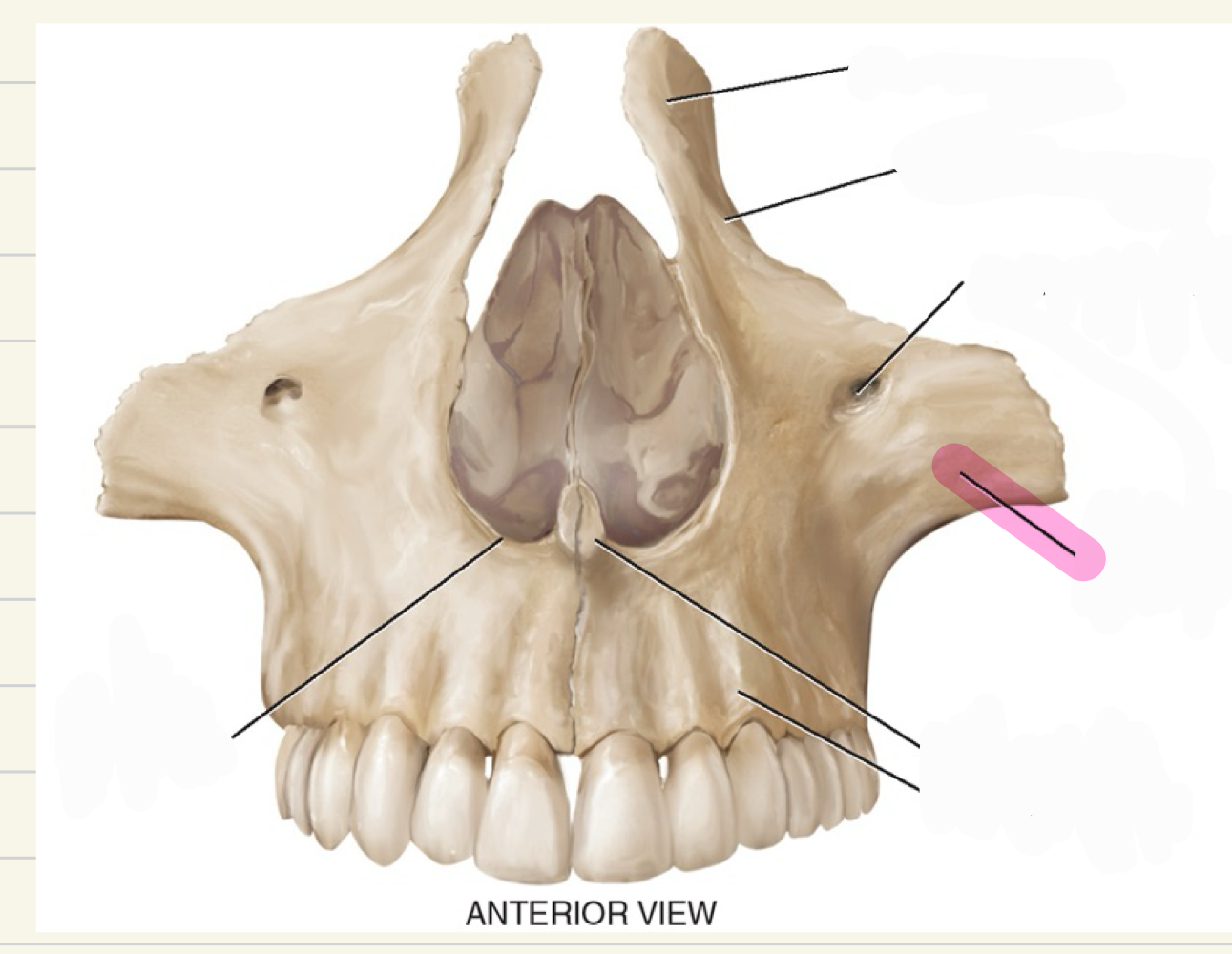
frontal process
what is this maxillae landmark
orbital process
what is this maxillae landmark
anterior nasal spine
what is this maxillae landmark
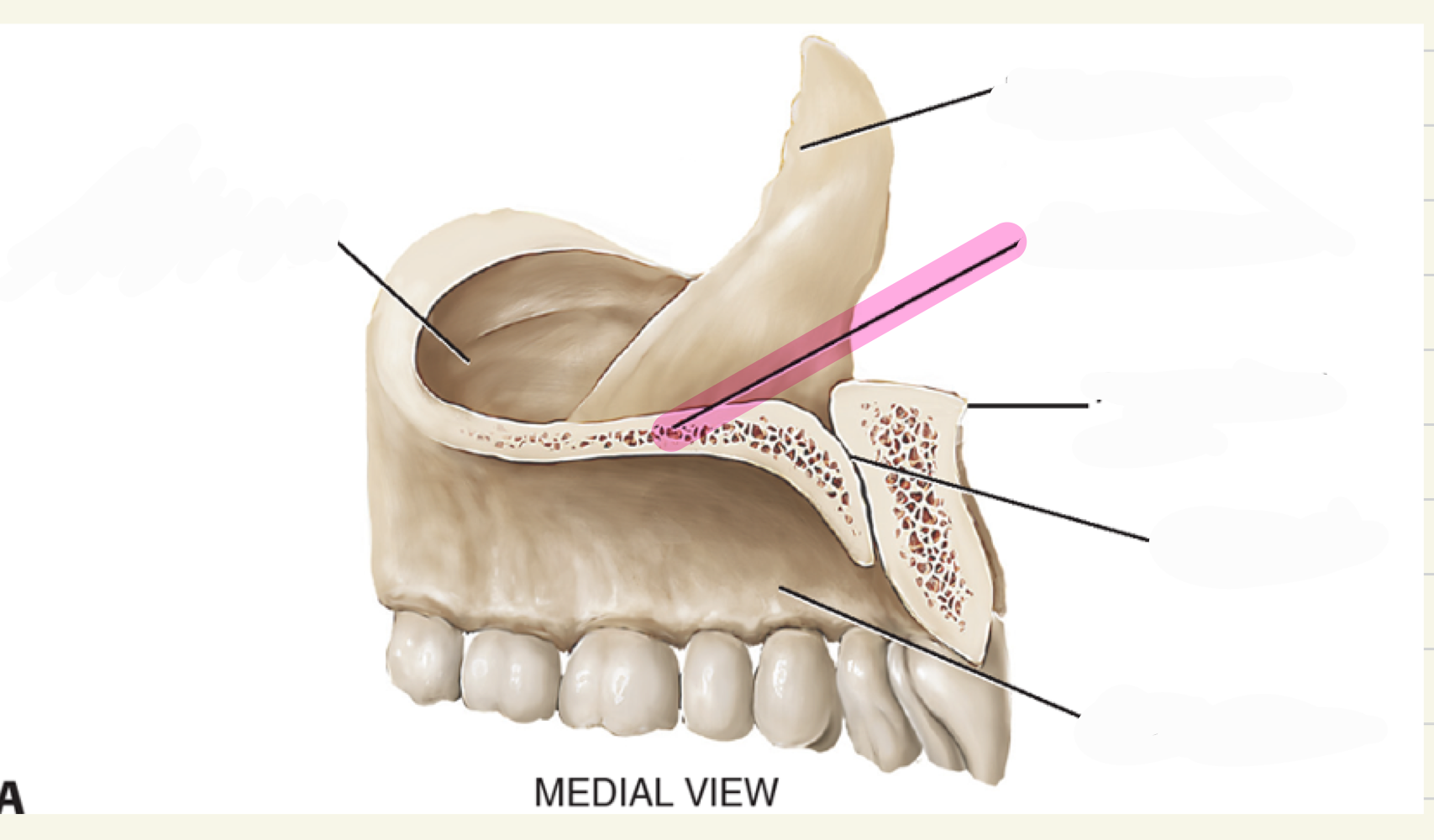
alveolar process
what is this maxillae landmark
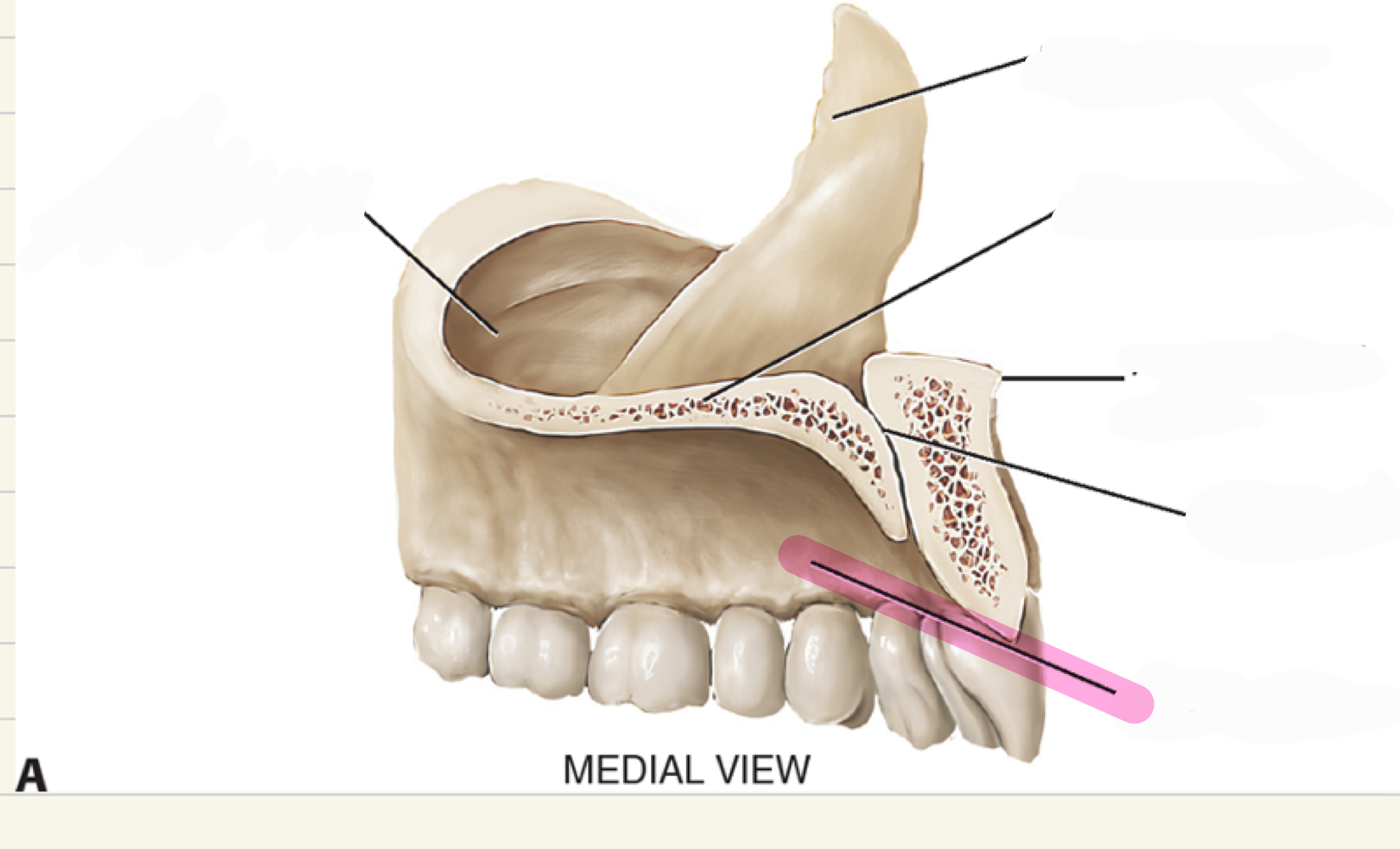
palatine process
what is this maxillae landmark
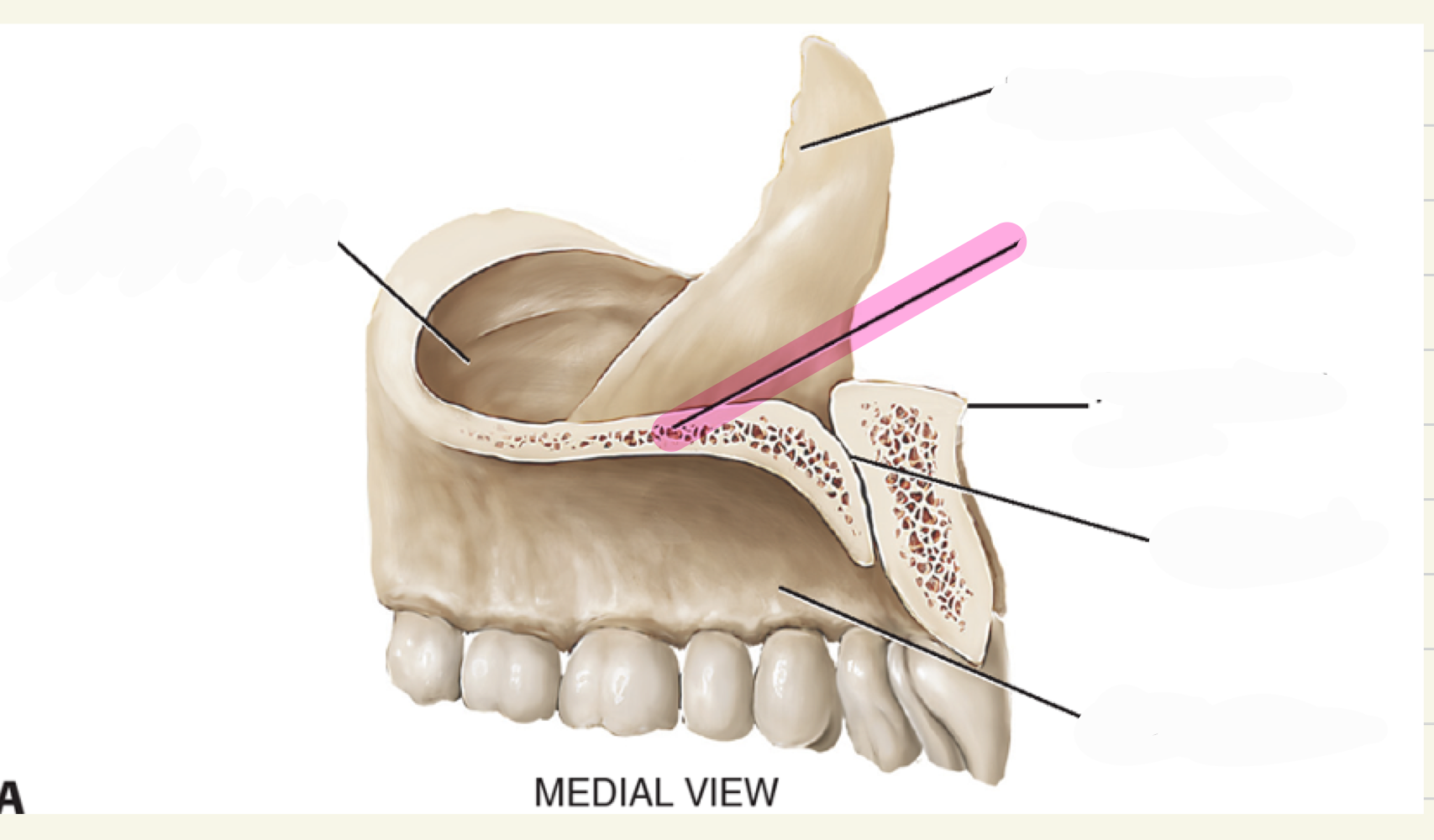
intermaxillary suture(where two bones come together)
what is this maxillae landmark
palatine process
what is this maxillae landmark
premaxila, premaxillary suture
what is this maxillae landmark
nasal bones
located at the superior bridge of the nose
frontal bone
what bone is this
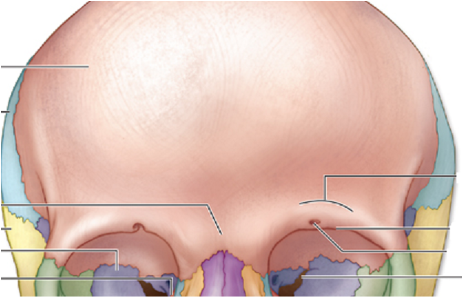
frontal bone
make up the forehead, bridge of eyebrows and superior portion of orbit
articulate with maxilla, nasal, zygomatic and parietal
orbital portion
parietal bone
Paired bones which overlay the parietal lobes
Form the middle portion of the brain case
Sagittal suture
Lamboidal suture
Squamosal/lateral suture
Coronal suture
parietal bone
what bone is this
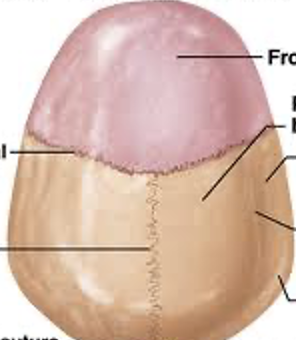
sagittal suture
what is this
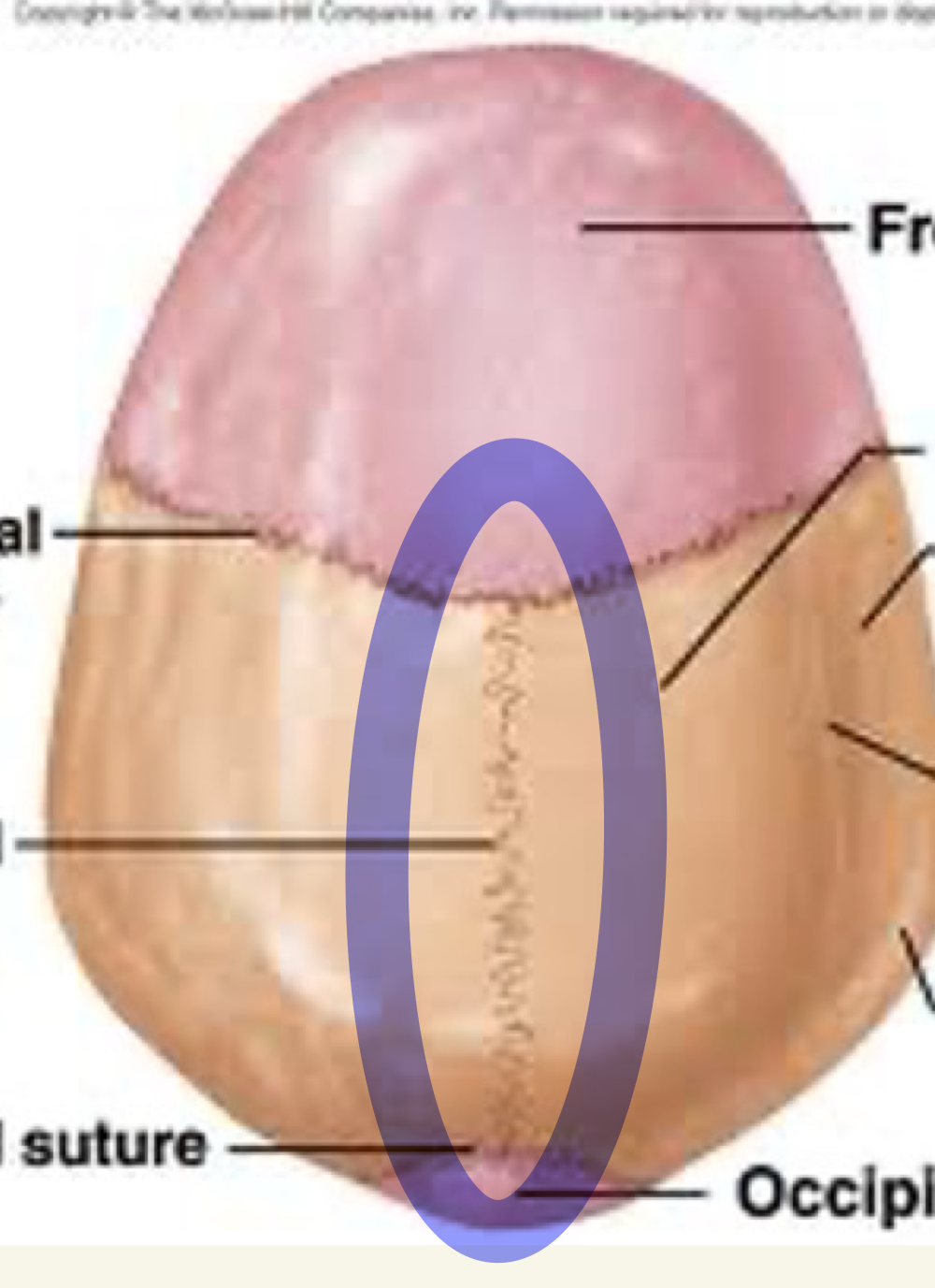
occipital bone
what bone is this
occipital bone
overlies the occipital lobe
makes up the posterior brain case
articulates with parietal, temporal and sphenoid
External occipital protuberance
Cerebral and cerebellar fossa
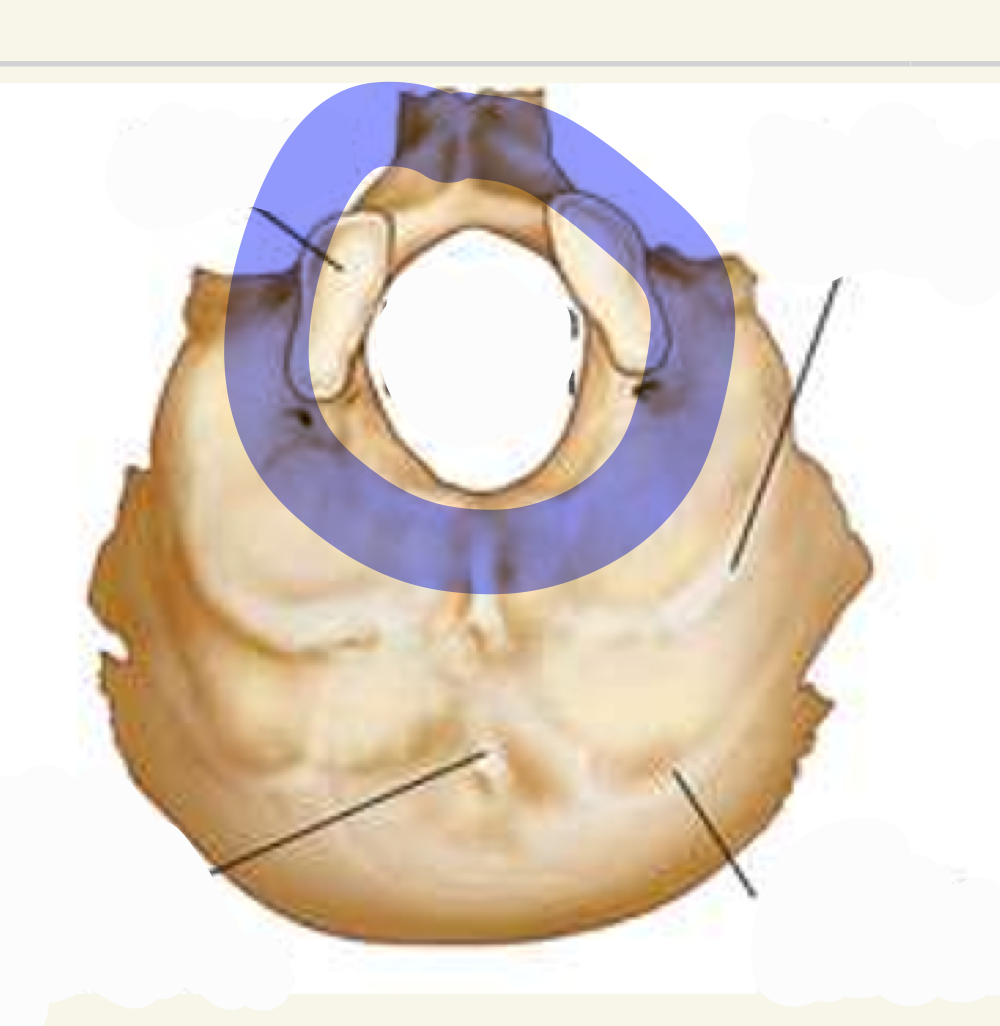
Foramen magnum
Condyles
Basilar part
foramen magnum
what is this
temporal bone
Covers the temporal lobe, which is extremely important for speech and language
Squamosal suture
Occipitomastoid suture
Temporal fossa
Divided into four segments
1.Squamous portion
- Zygomatic process
2.Mastoid portion
- Mastoid process
3.Tympanic portion
- Styloid process
4.Petrous portion
temporal bone
what bone is this
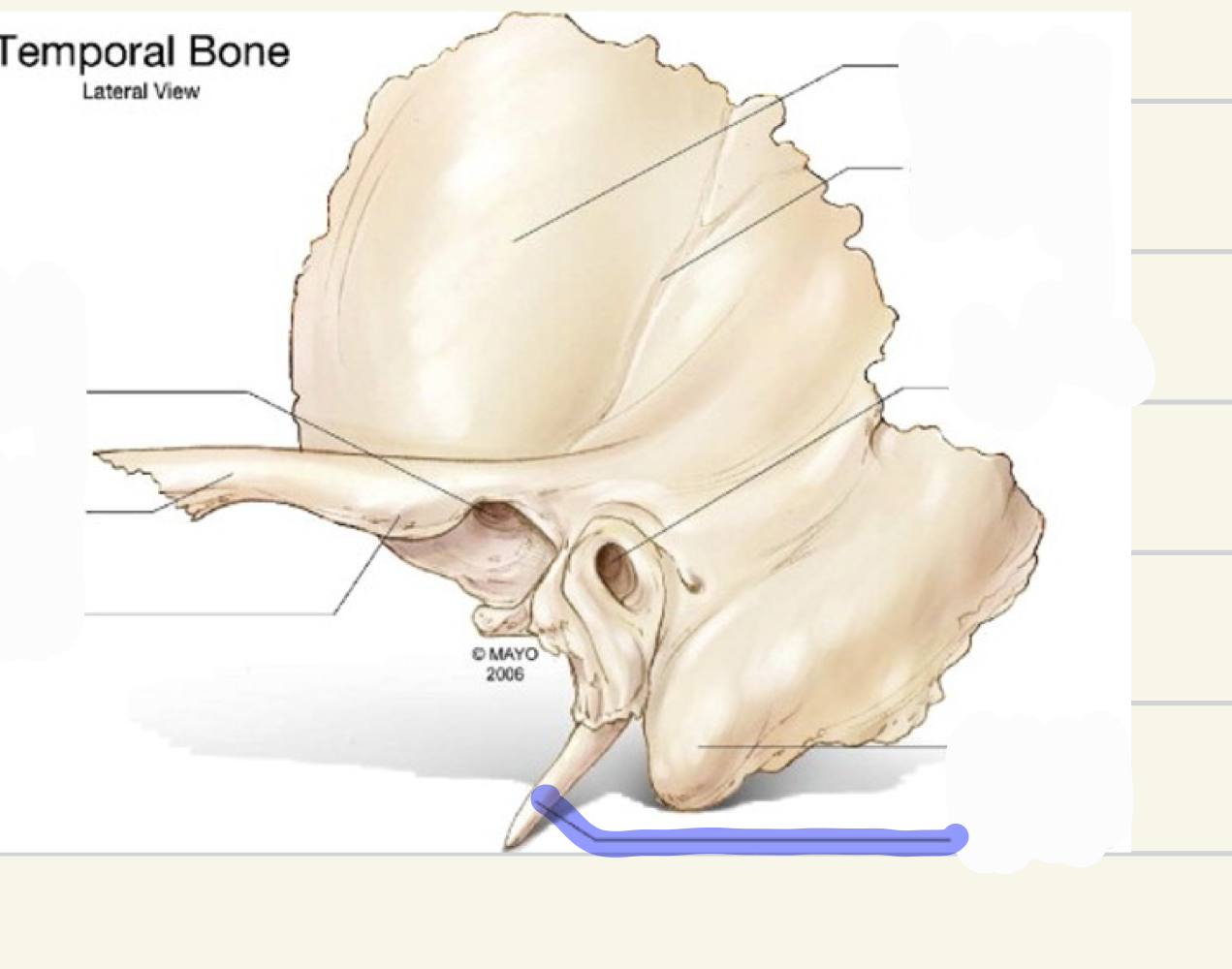
styloid process
what is this
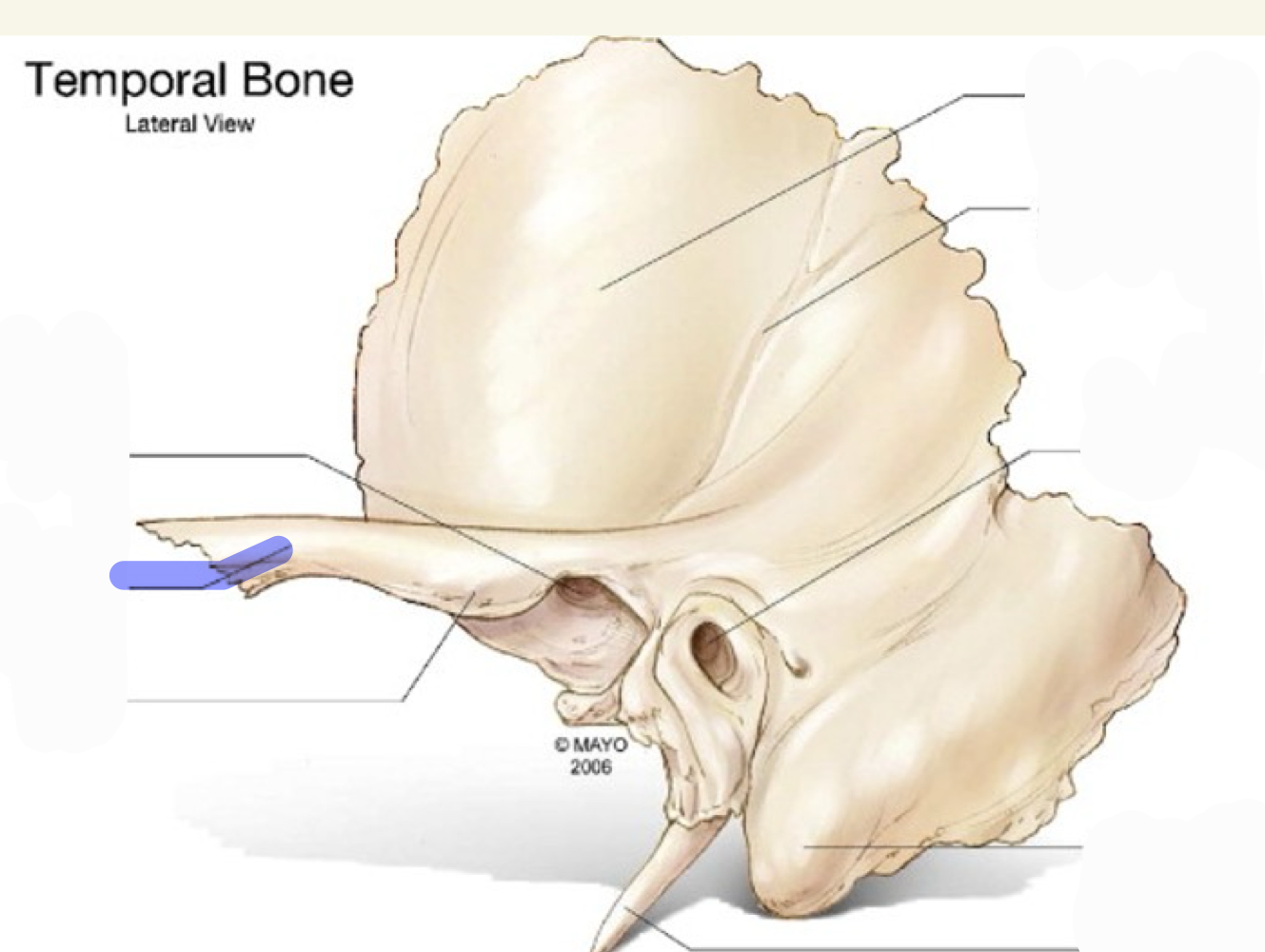
zygomatic process
what is this
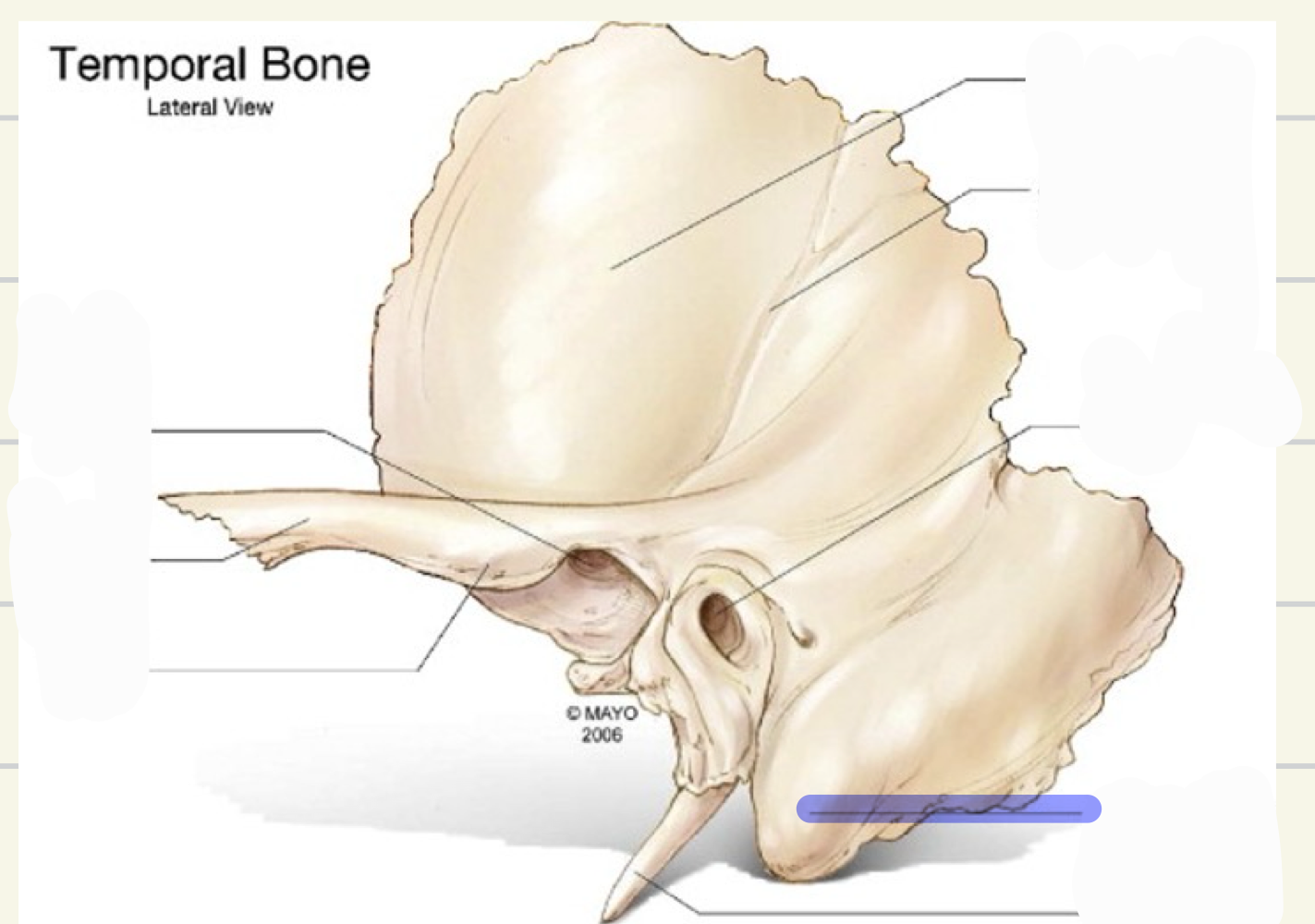
mastoid process
what is this
articulation
bringing two things together
articulatory system
system of mobile and immobile articulators and you bring them close together in order to shape or produce speech sounds
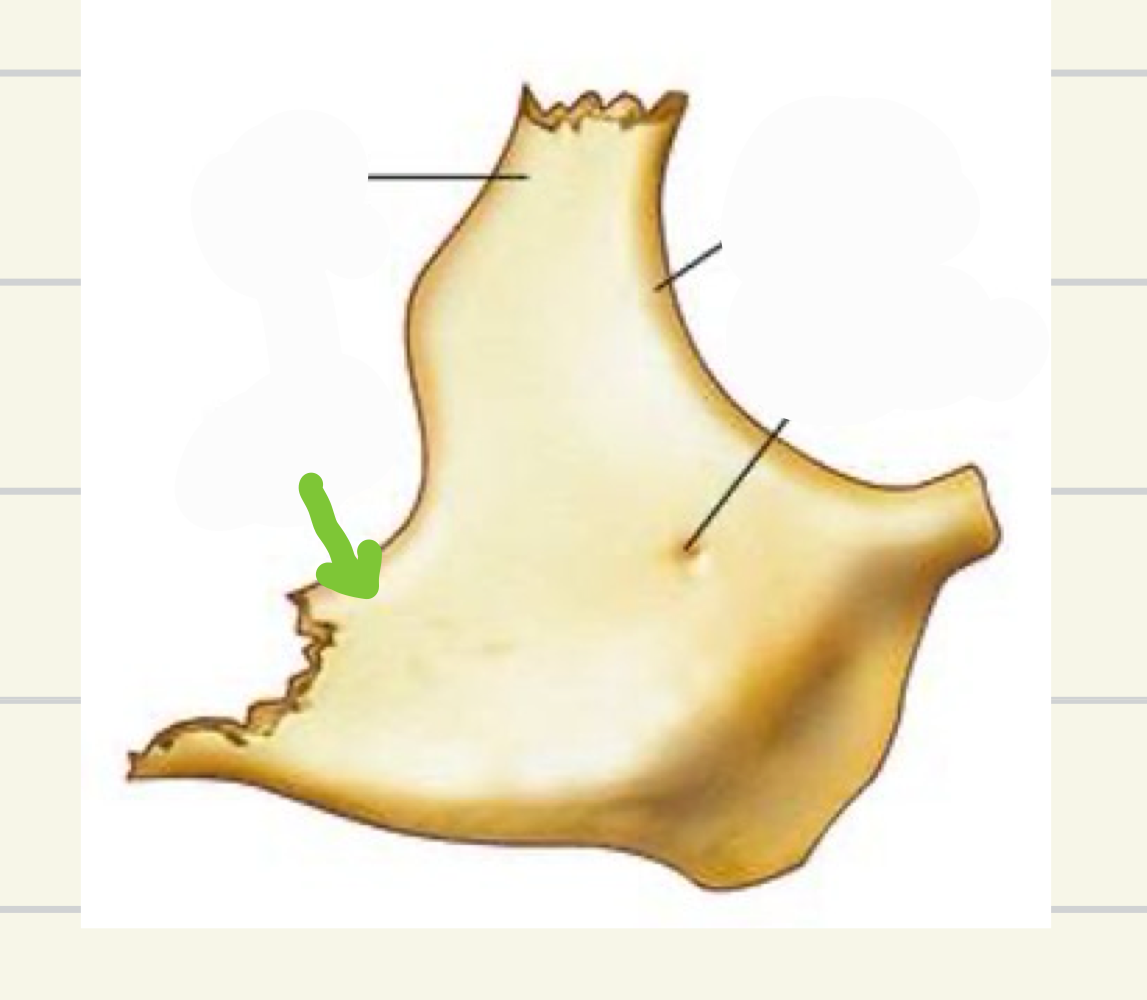
pterygoid fovea
what landmark is this
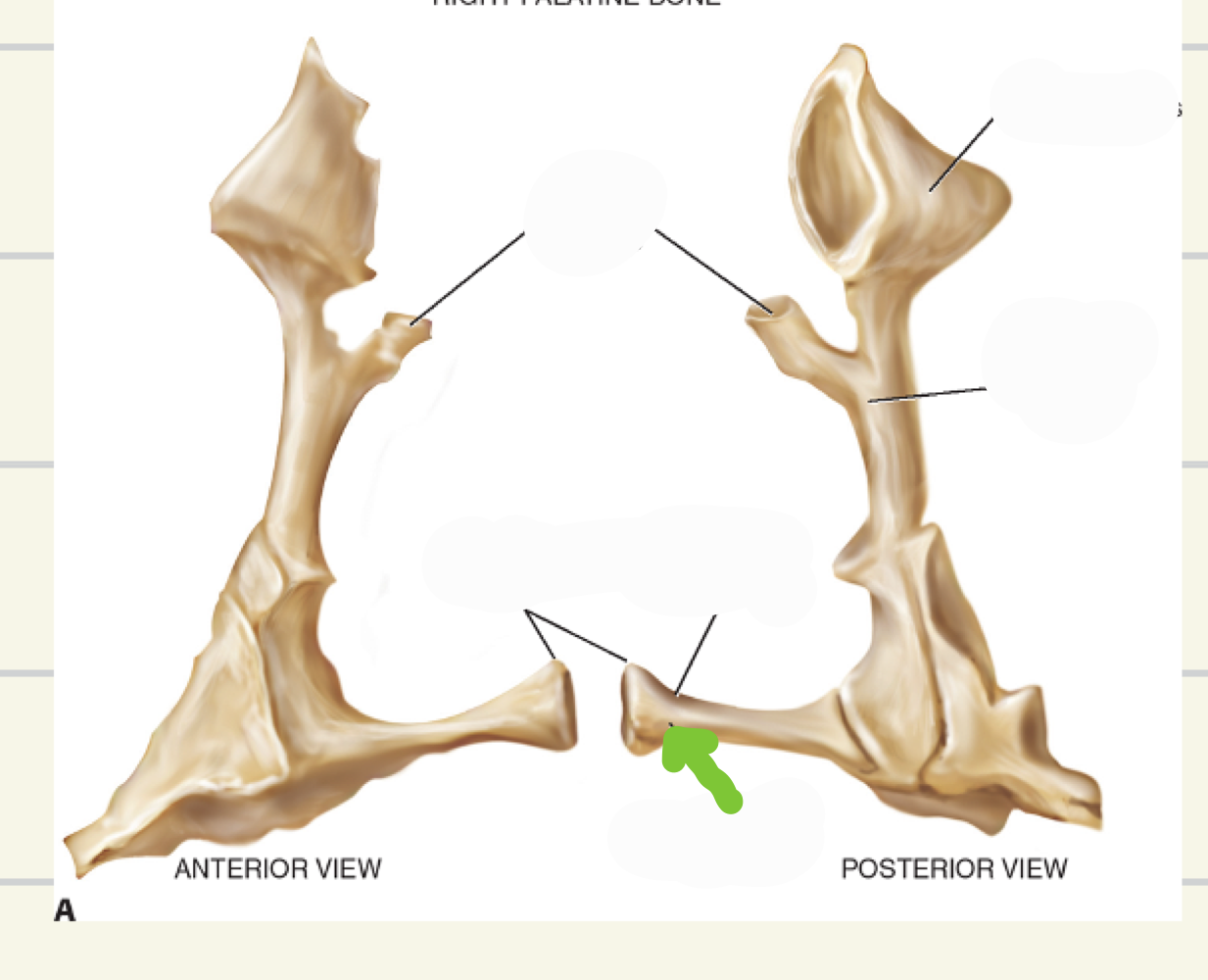
palatine bones
1/4th of the hard palate is made up of the horizontal plate of the palatine bone
Contributes to formation of 3 cavities: Nasal cavity, Oral cavity, Orbital cavity
Posterior nasal spine and Nasal crest
Perpendicular plate
Horizontal Plate
Orbital process
palatine
what bone is this
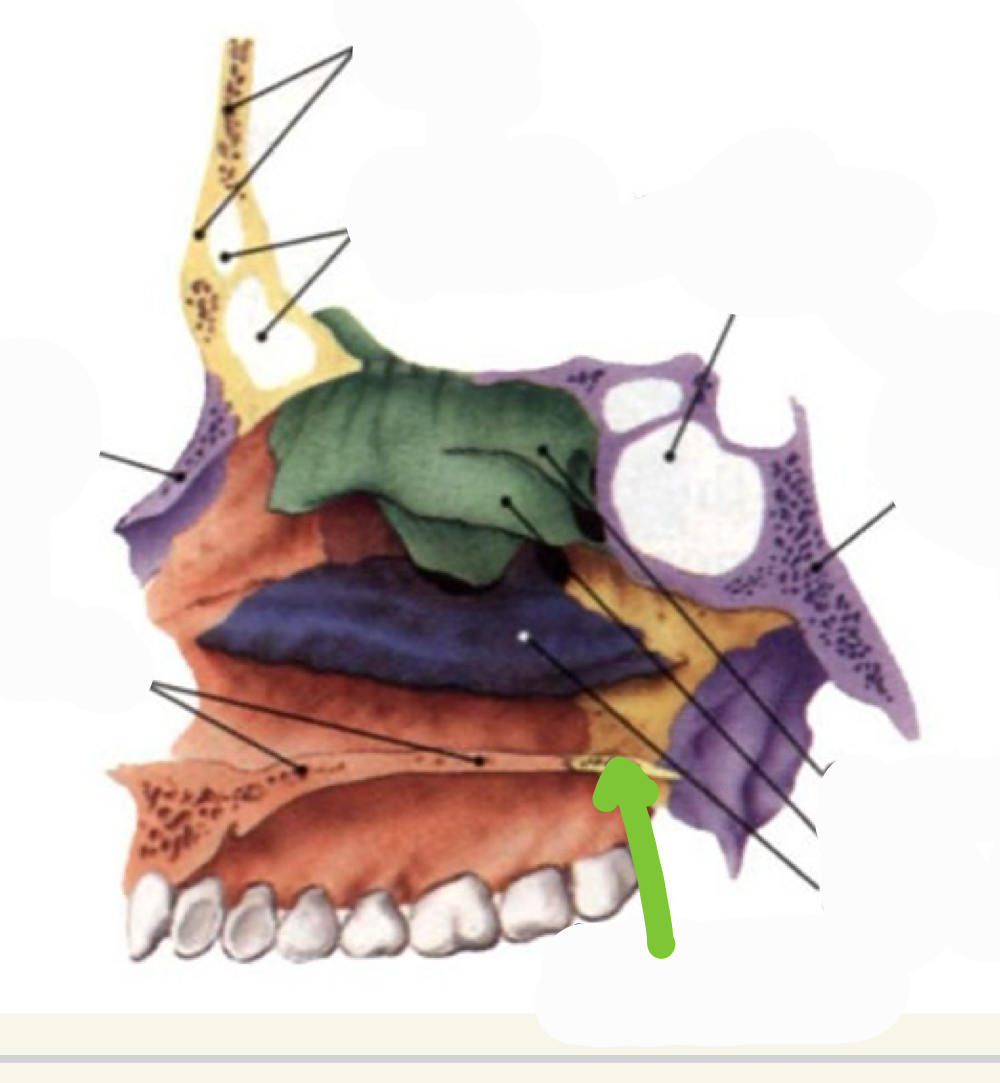
perpendicular plate- projects upwards, lateral walls of posterior nasal cavity
what landmark is this
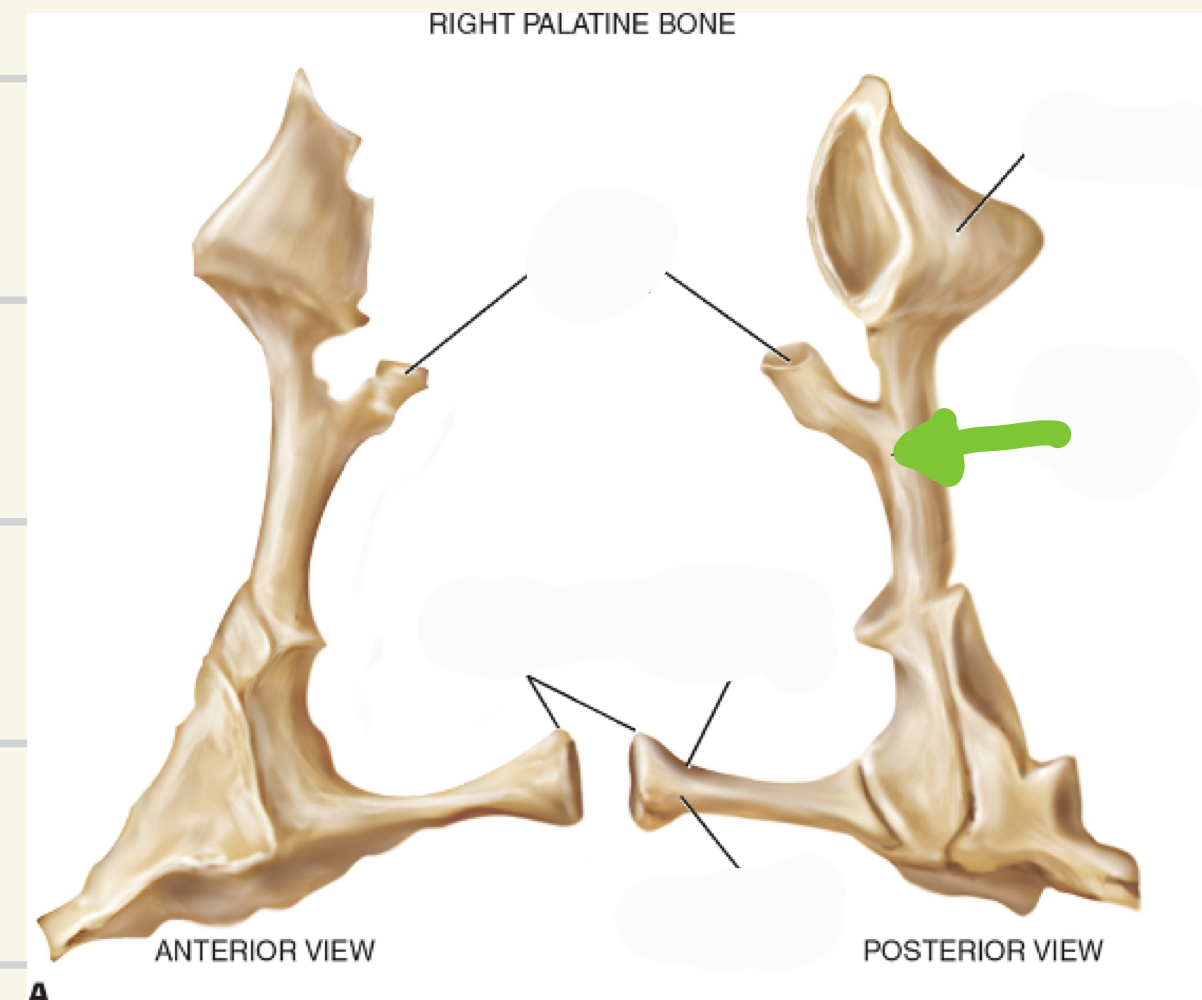
horizontal plate- run medially and come together at medial floor of nasal cavity
what landmark is this
vomer
Midline bone making up the inferior and posterior nasal septum
if broken its a deviated septum
vomer-
what bone is this
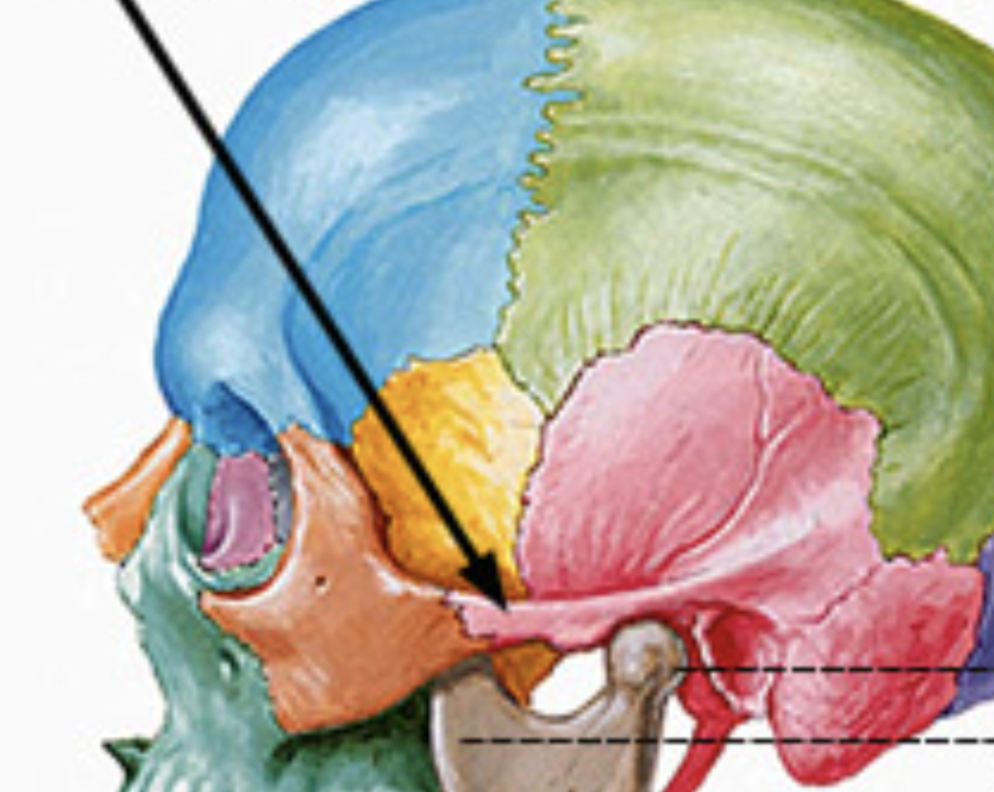
zygomatic bone
Commonly referred to as the ‘cheek bones’
Articulates with the maxillae, fontal bone, and temporal bone and makes up the lateral orbit
Maxillary process
Temporal process
Zygomatic arch
Frontal process
zygomatic bone
what bone is blue
temporal process
what landmark is this
zygomatic arch
what landmark is this
frontal process
what landmark is this
lacrimal bones- smallest and close to tearducts. make up part of orbital cavity
what bone is this
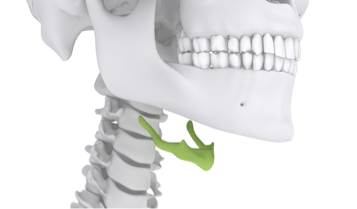
hyoid- connects phonatory and articulatory system
what bone is this
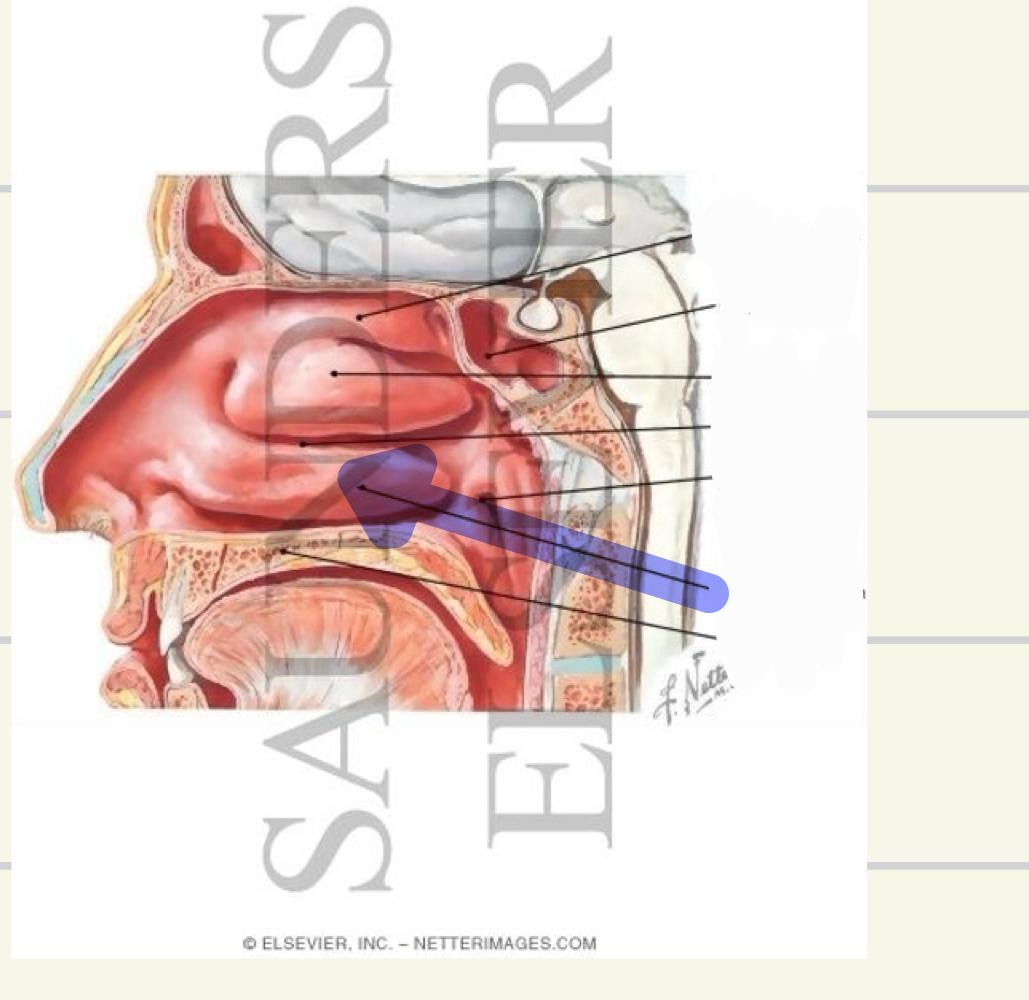
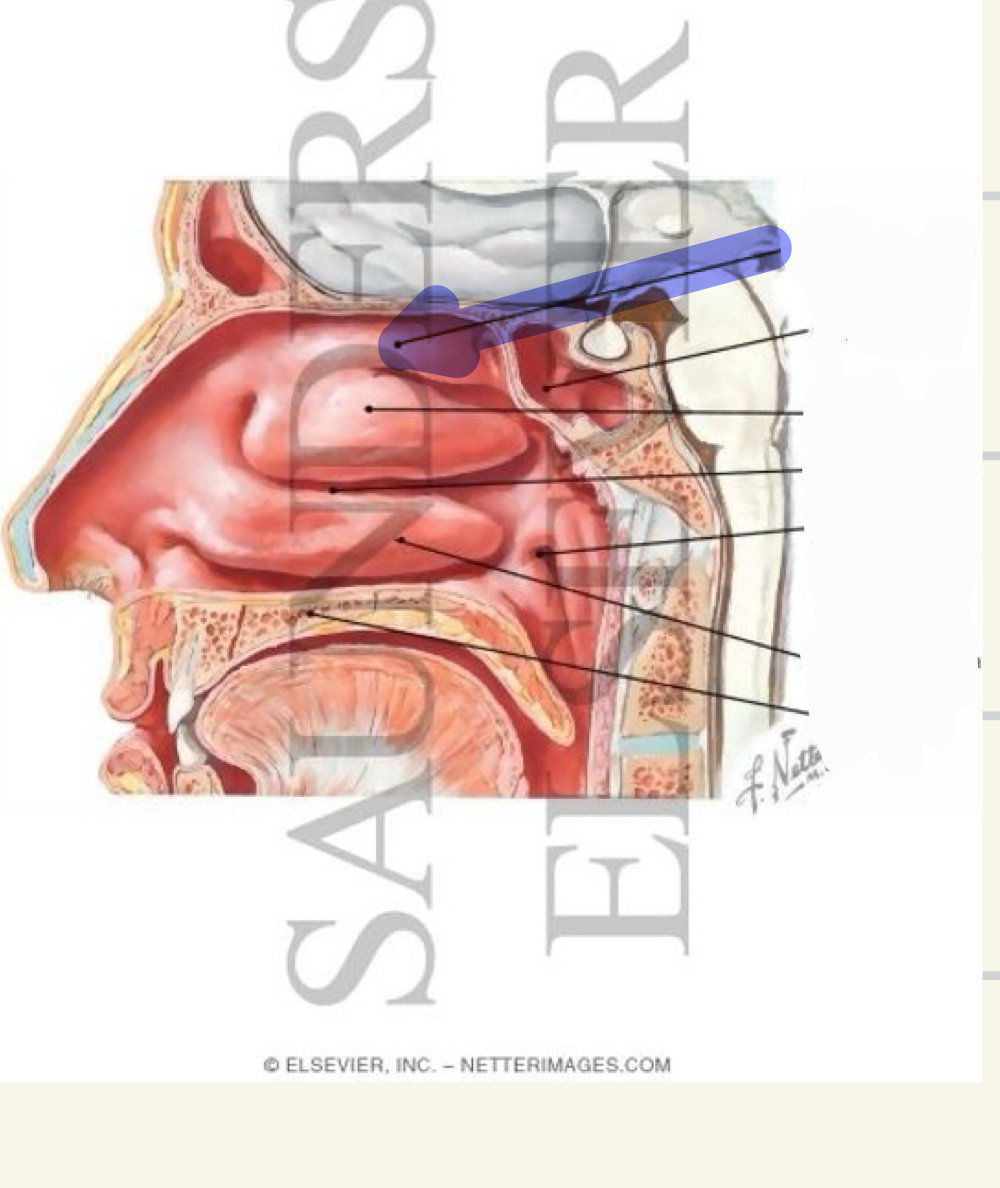
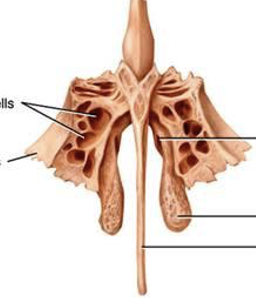
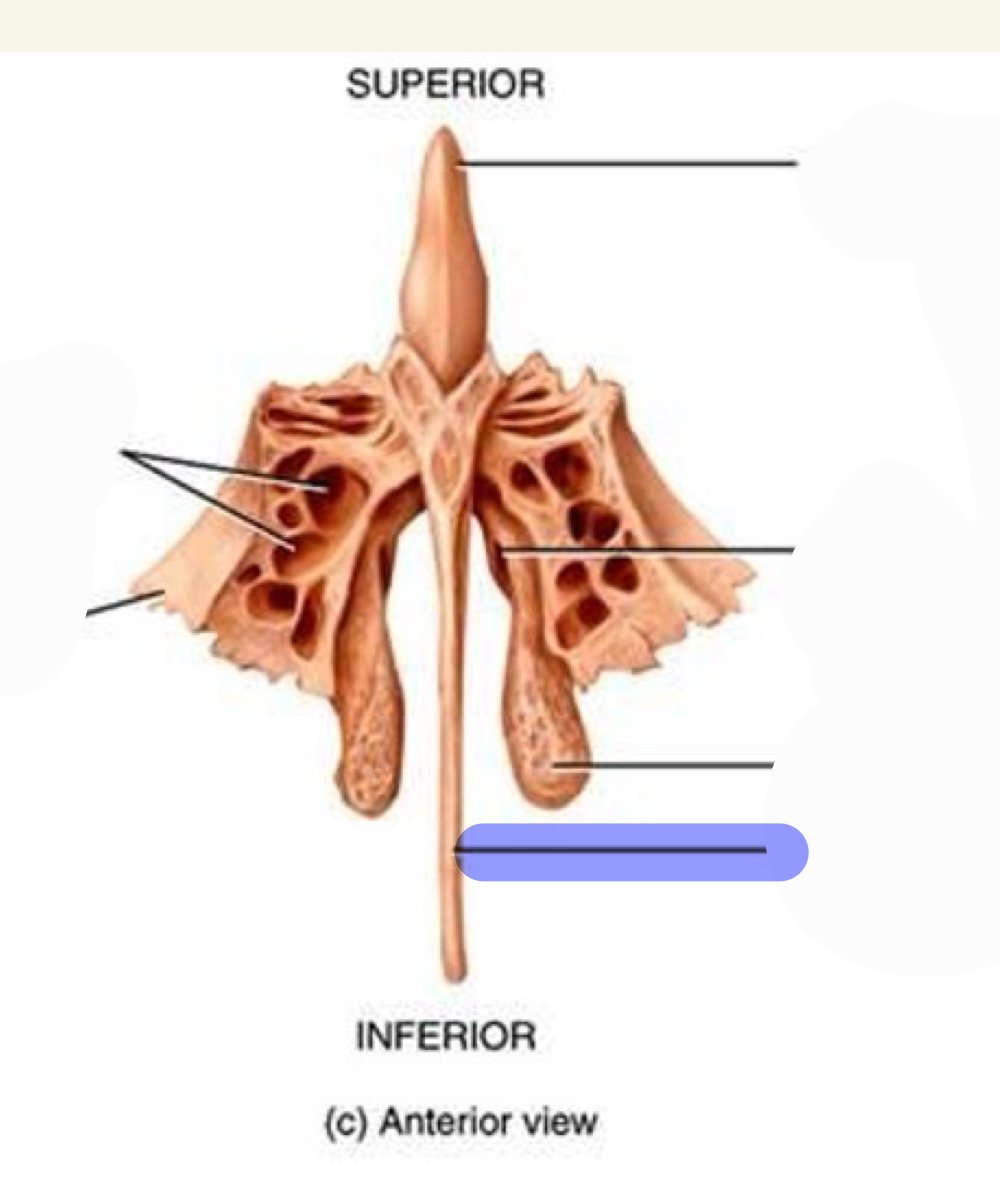
nasal conchae
Inferior nasal concha (inferior turbinates)- attached to maxilla
Middle nasal concha – attached to ethmoid
Superior nasal concha- attached to ethmoid
Inferior nasal concha
what landmark is this
Middle nasal concha
what landmark is this
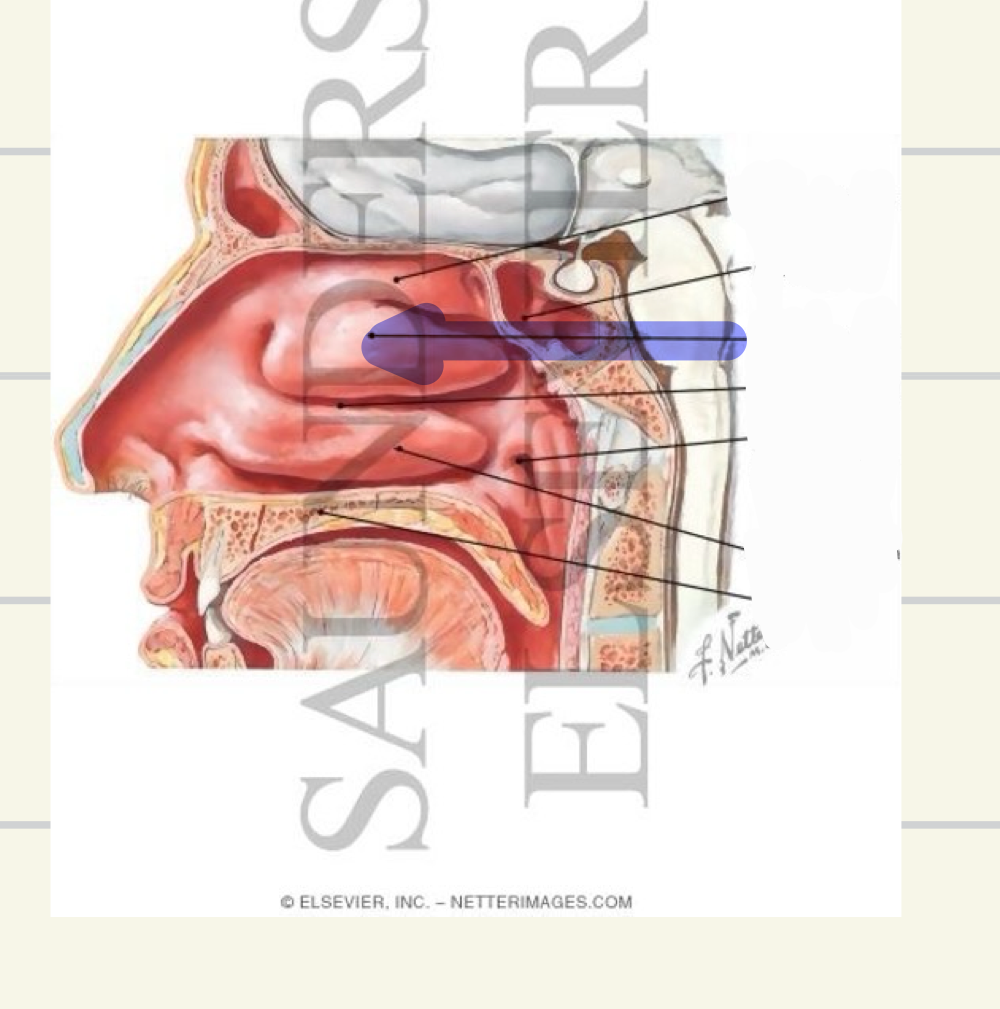
Superior nasal concha
what landmark is this
ethmoid bone
what bone is this
perpendicular plate
what landmark is this
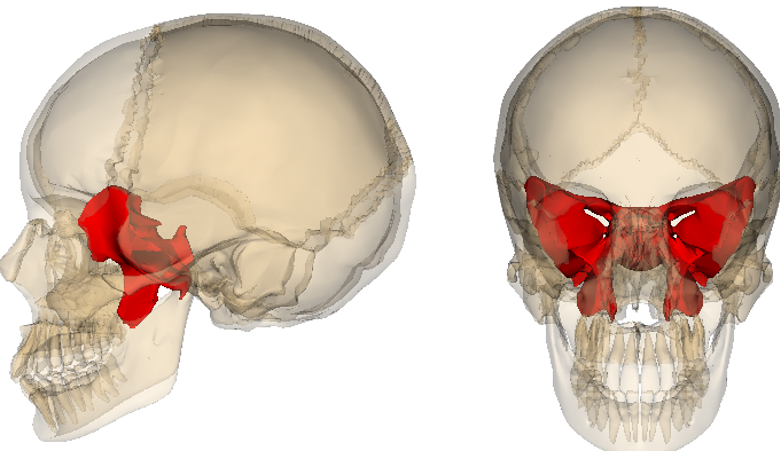
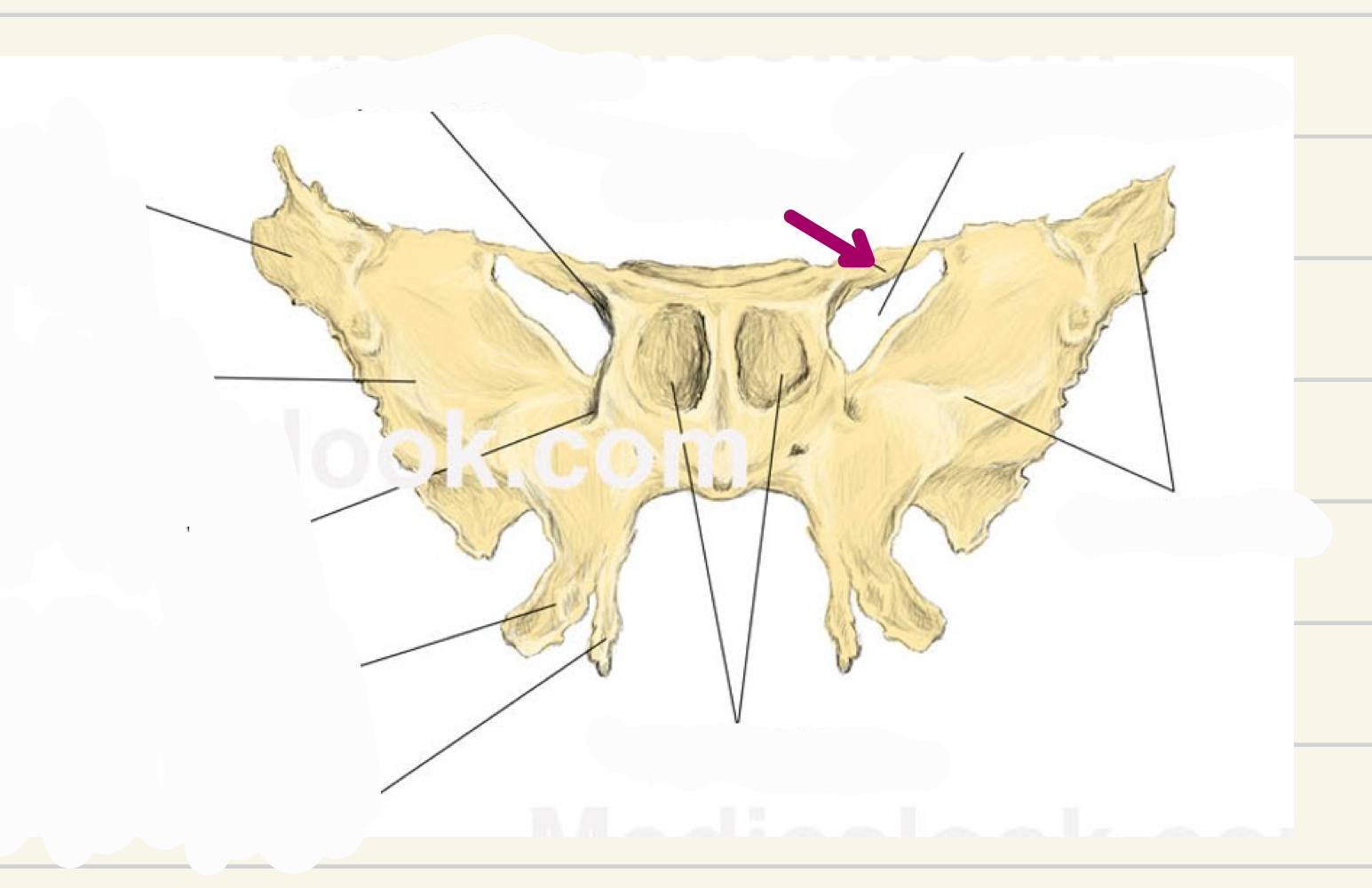
sphenoid bone
anterior to foramen magnum
one of the most complex bones in the skull
Contains:
Sphenoid sinuses
Lesser wings
Greater wings
Pterygoid processes
sphenoid
what bone is this
lesser wings
what landmark is this
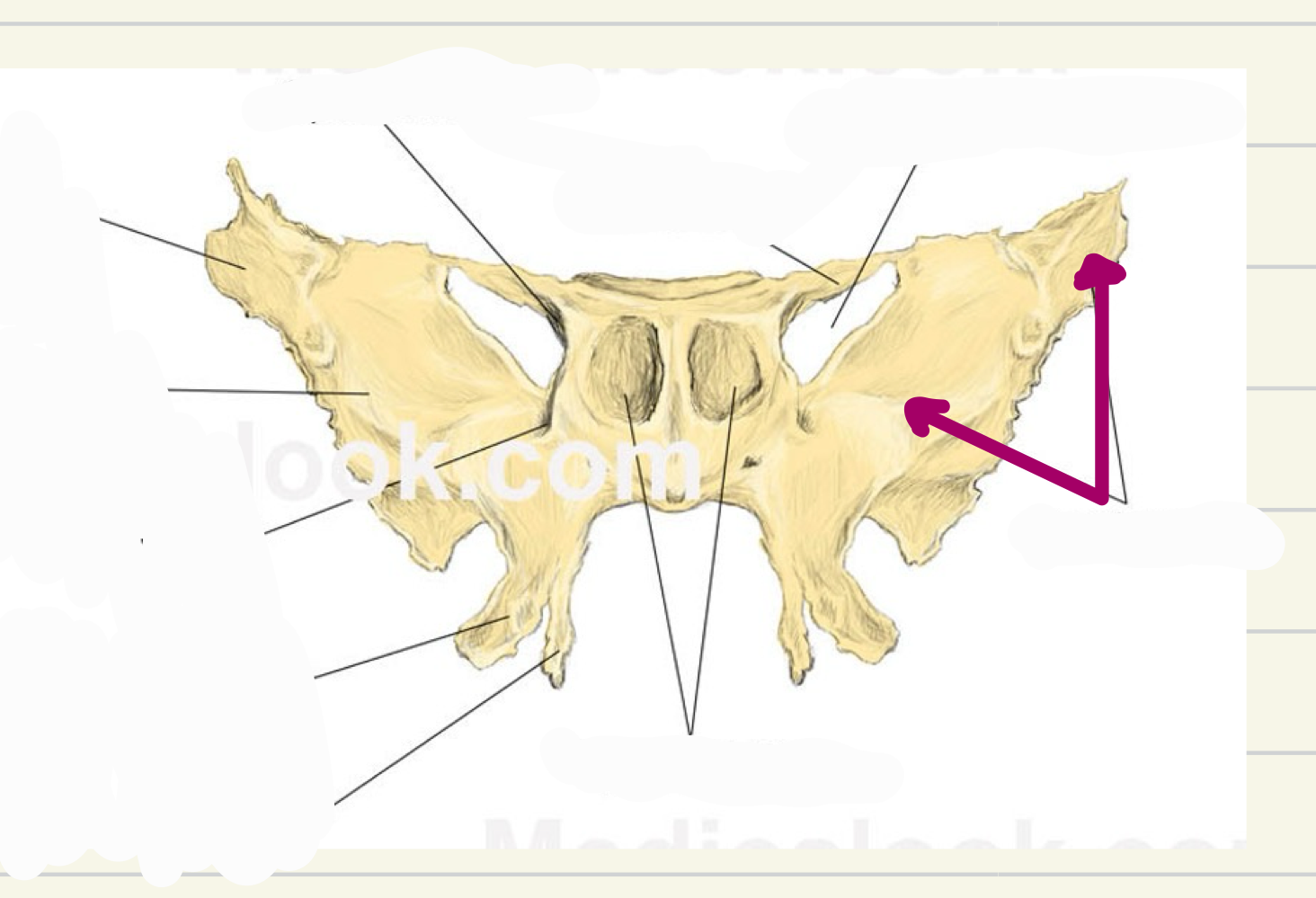
greater wings
what landmark is this
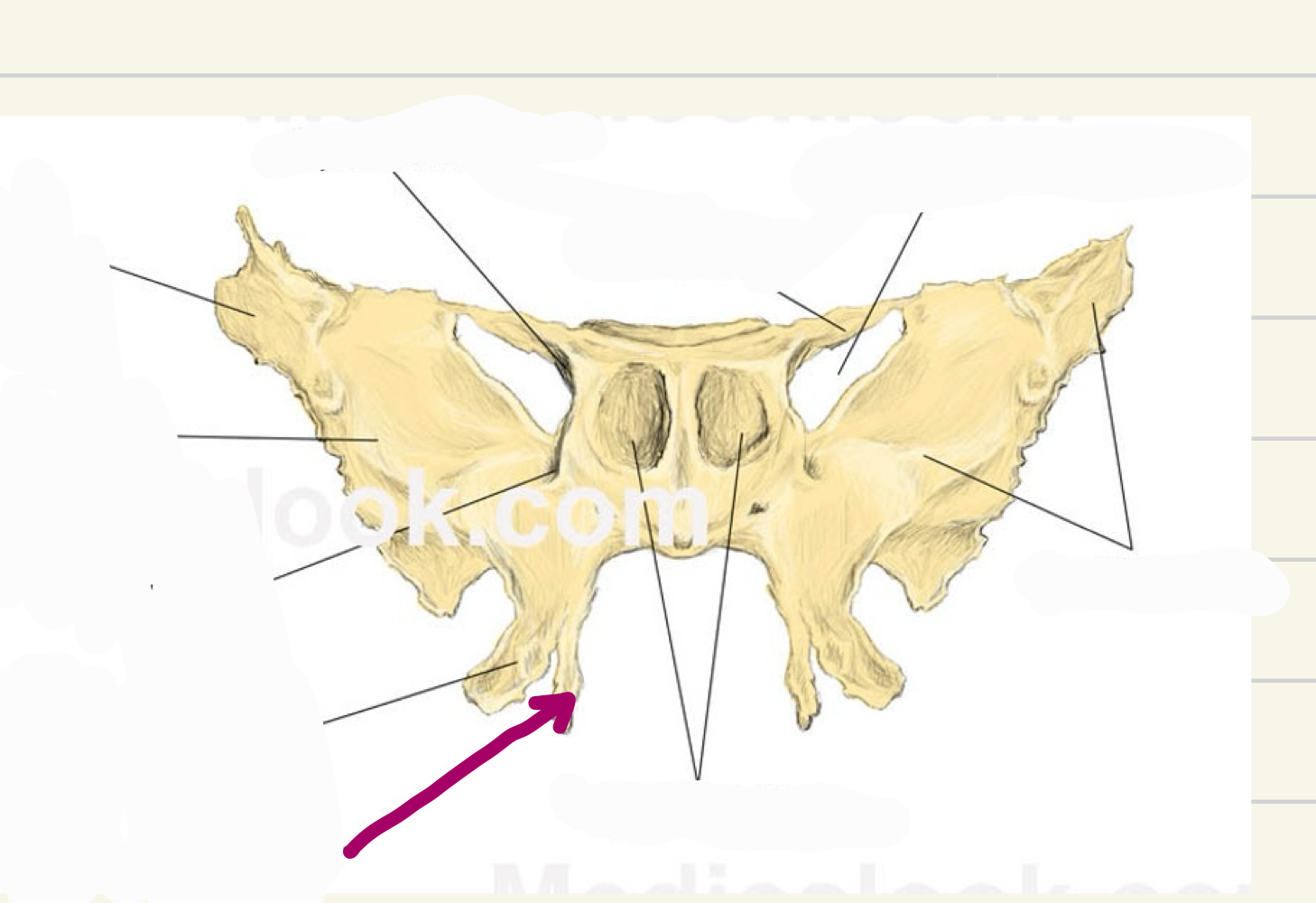
medial pterygoid plate
what landmark is this
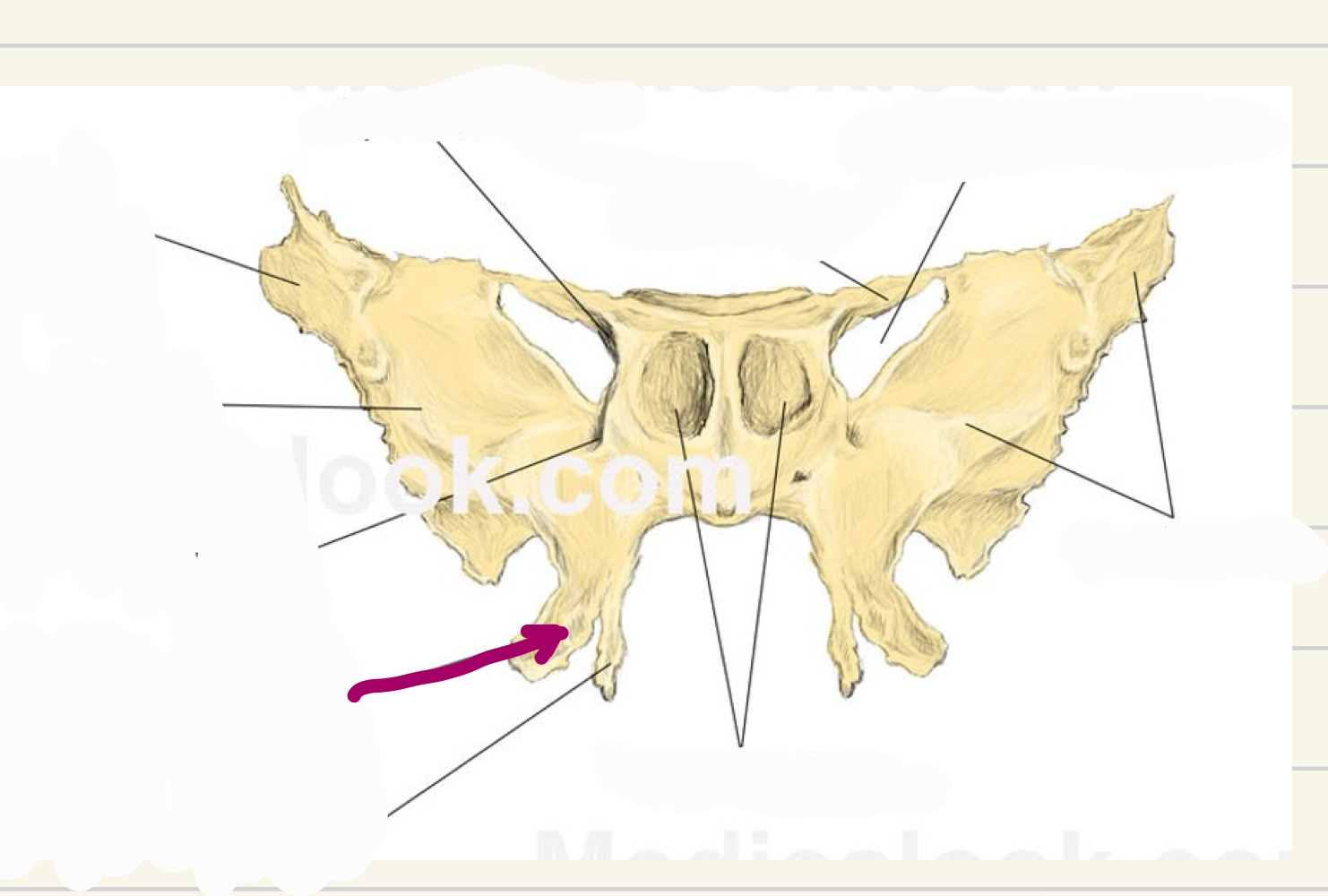
lateral pterygoid plate
what landmark is this
-Nasal
-Pharyngeal
-Oral
Buccal
what are the Cavities of the Upper Vocal Tract
nasal cavity
Contained by the paired maxilla, palatine, ethmoid, and nasal bones
Divided by the nasal septum (vomer bone)
Contains:
Turbinates covered with mucous membrane
Beating and secreting epithelia
Rich vascular supply
Nares (nostrils)
nasopharynx
oropharynx
laryngopharynx
what is the order of the 3 parts of the pharyngeal cavity
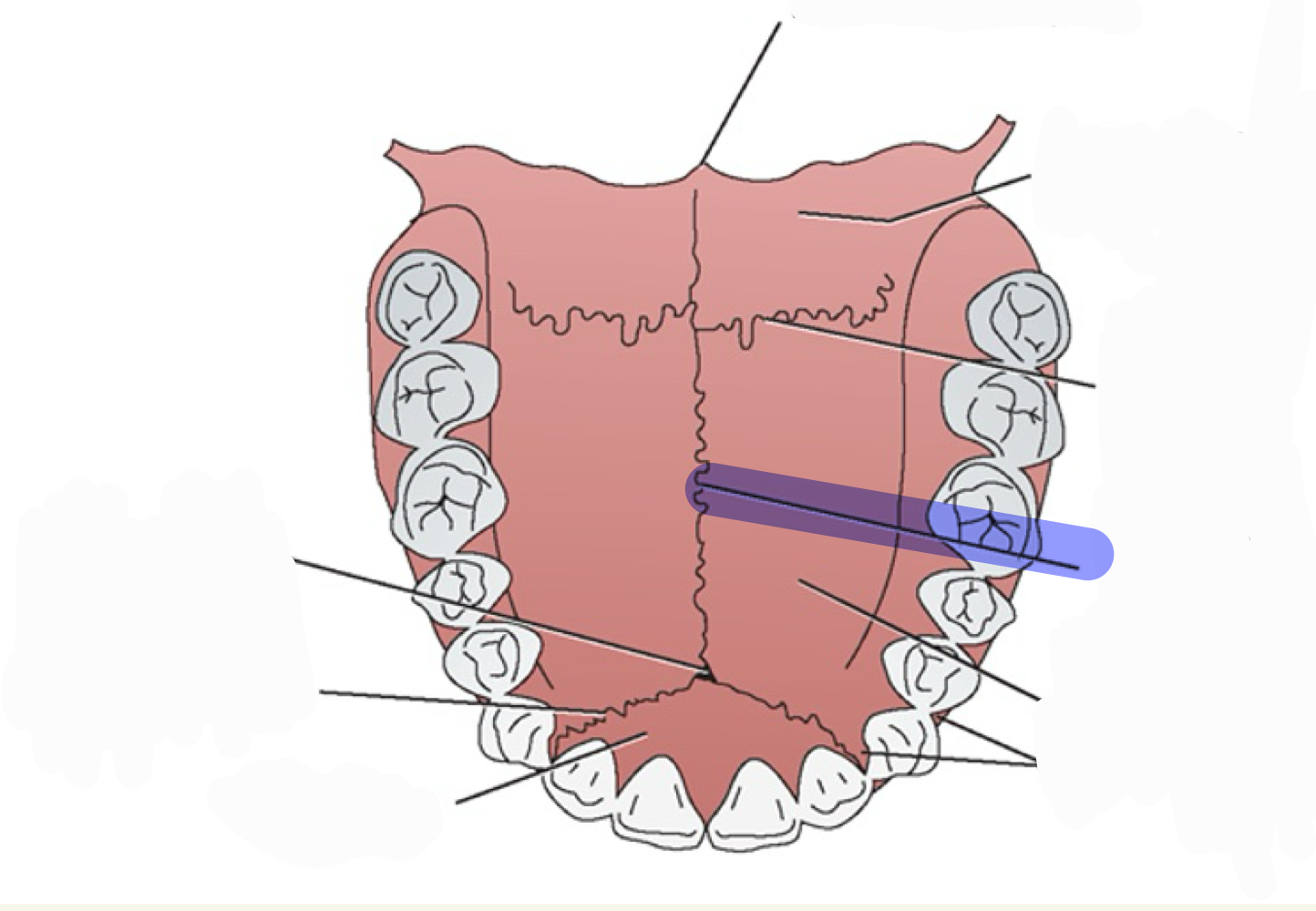
oral cavity
Hard palate:
Rugae:
Median raphe:
Soft palate (velum)
Anterior faucial pillars
Posterior faucial pillars
Palatine tonsils
Buccal Cavity (between teeth and cheeks/lips)
hard palate
what is this
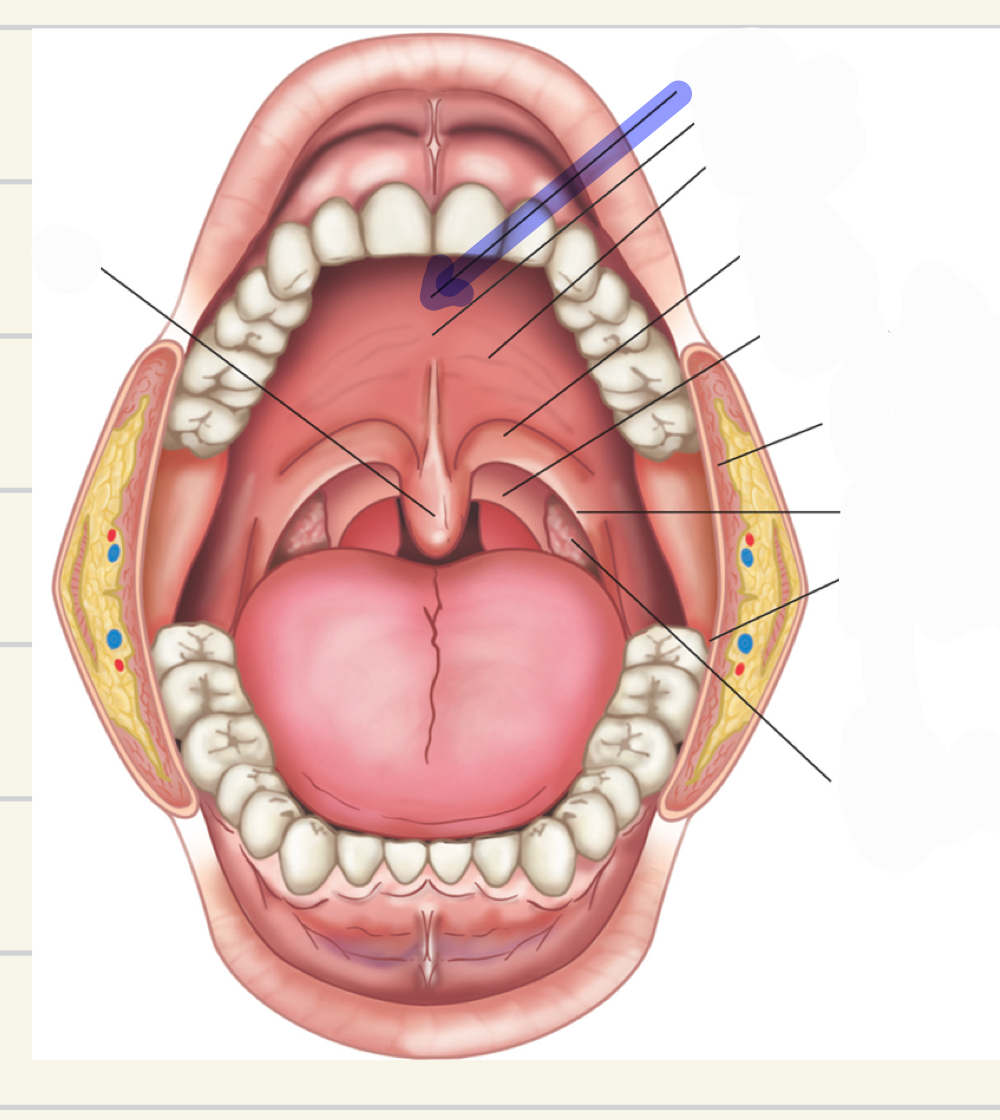
rugae
what is this
median raphe
what is this
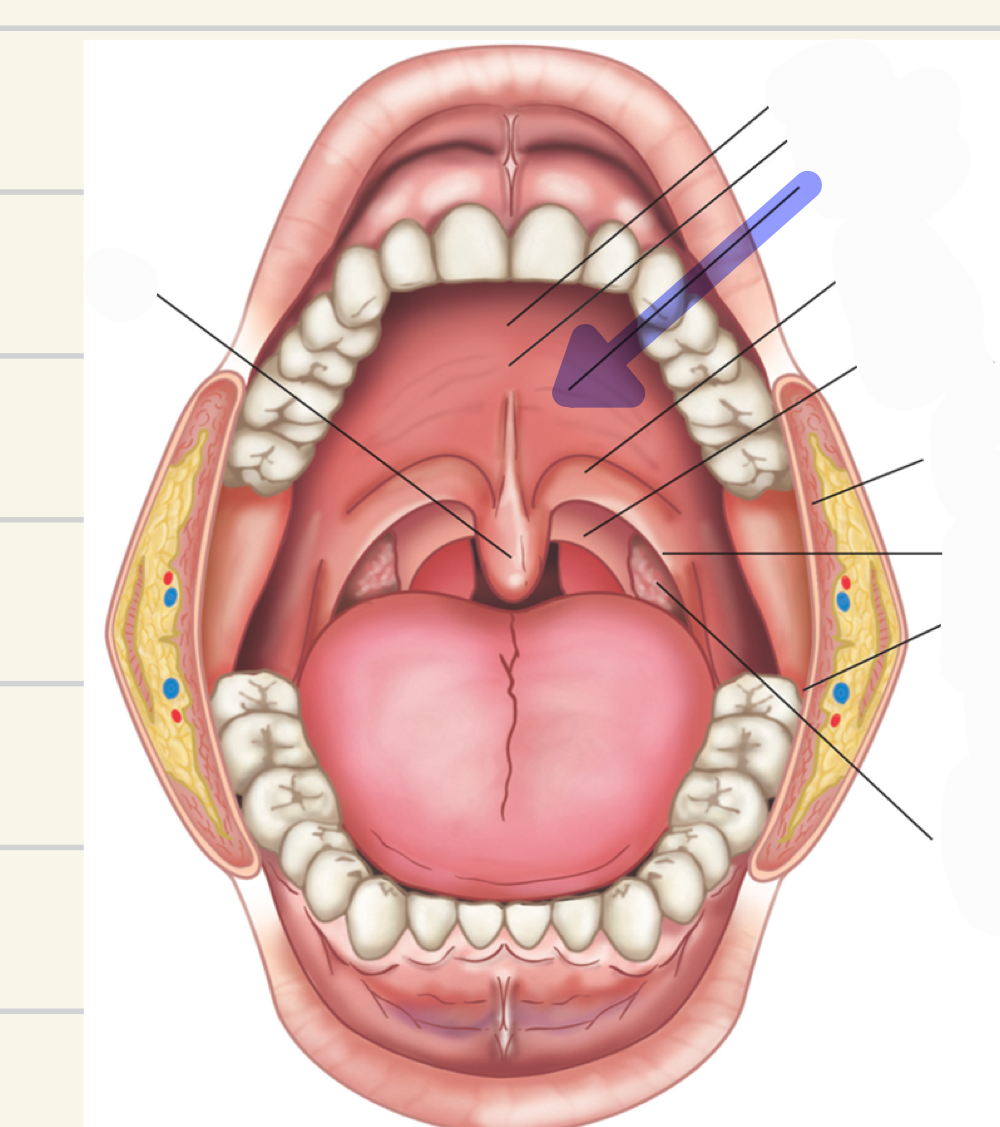
soft palate (velum)
what is this
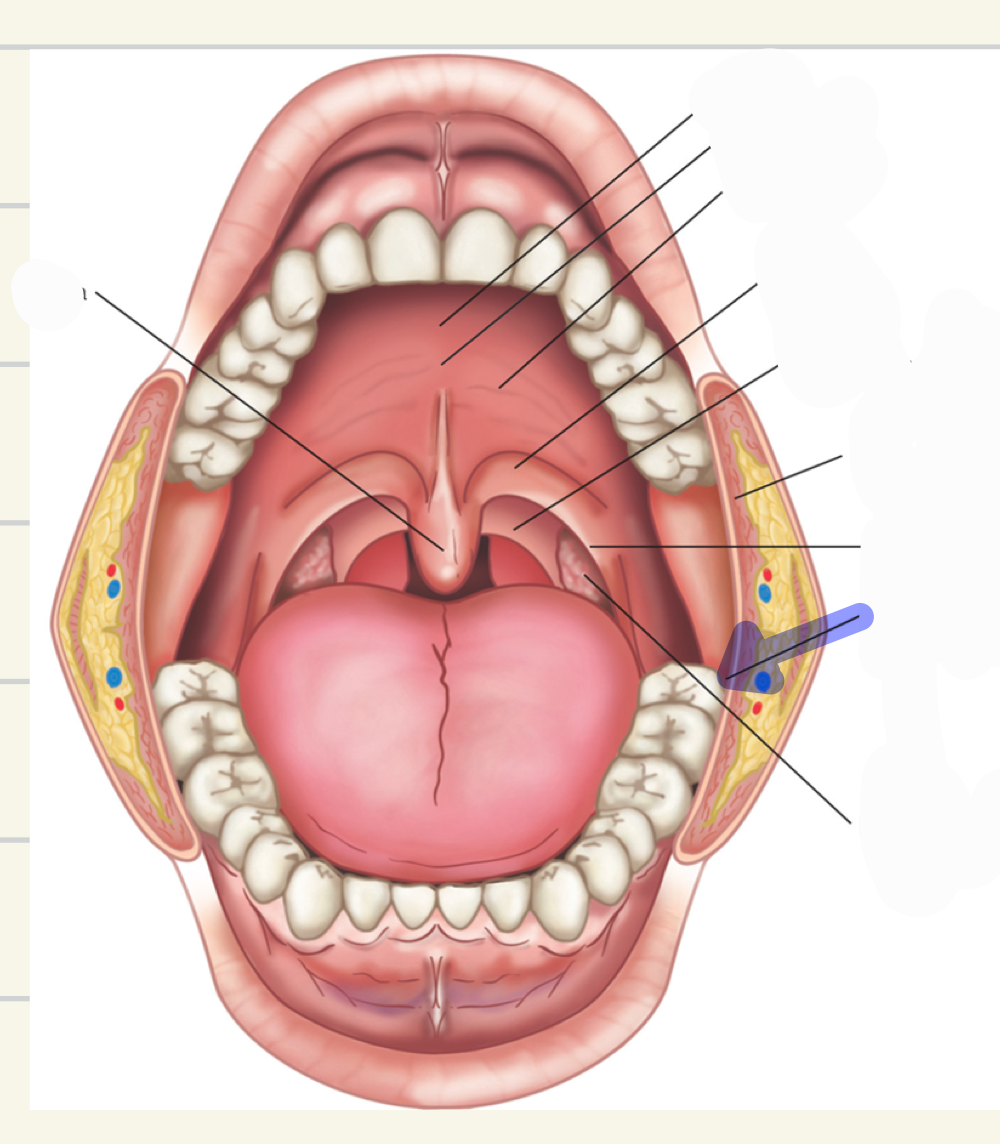
anterior faucial pillars
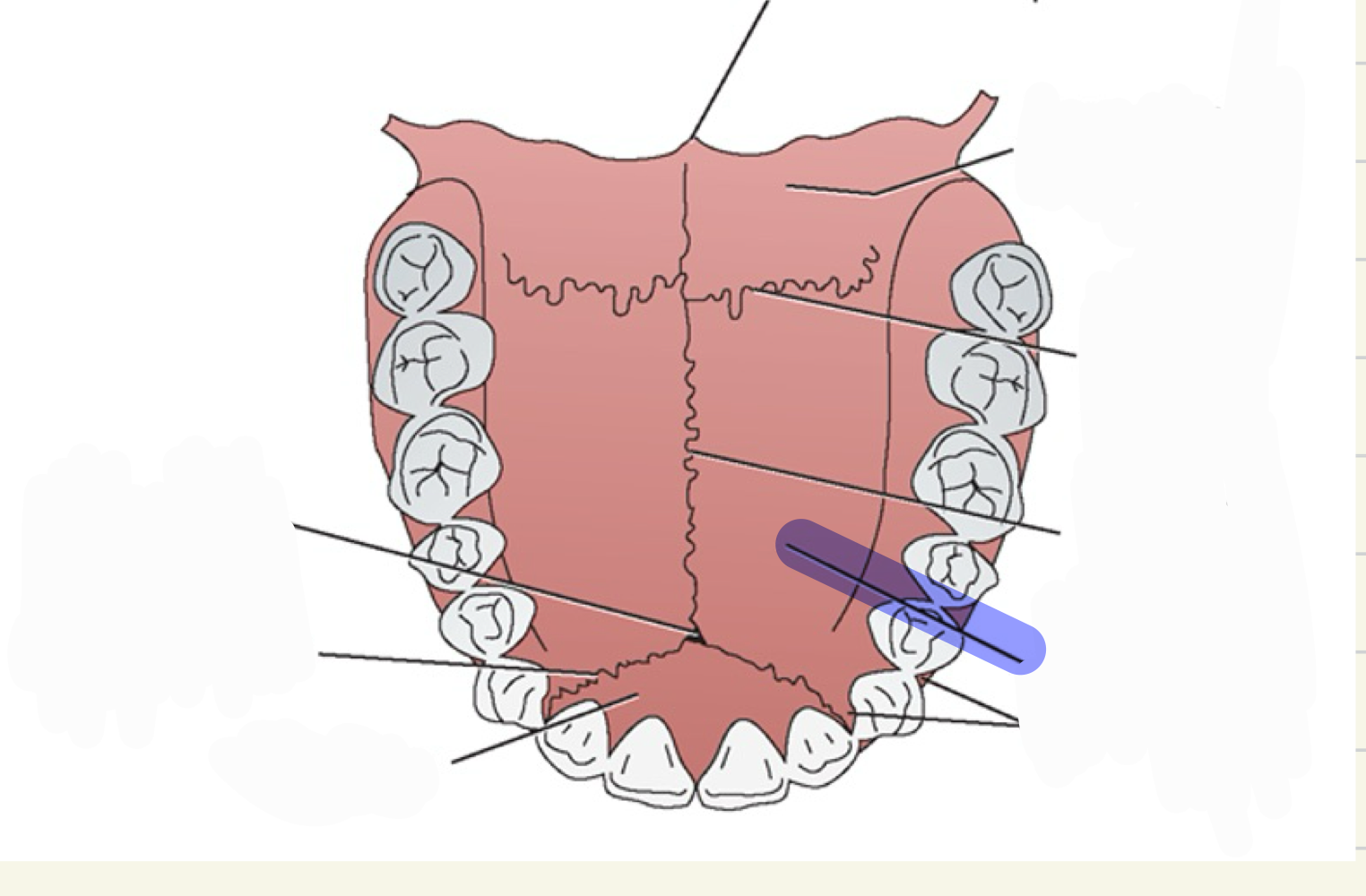
what is this
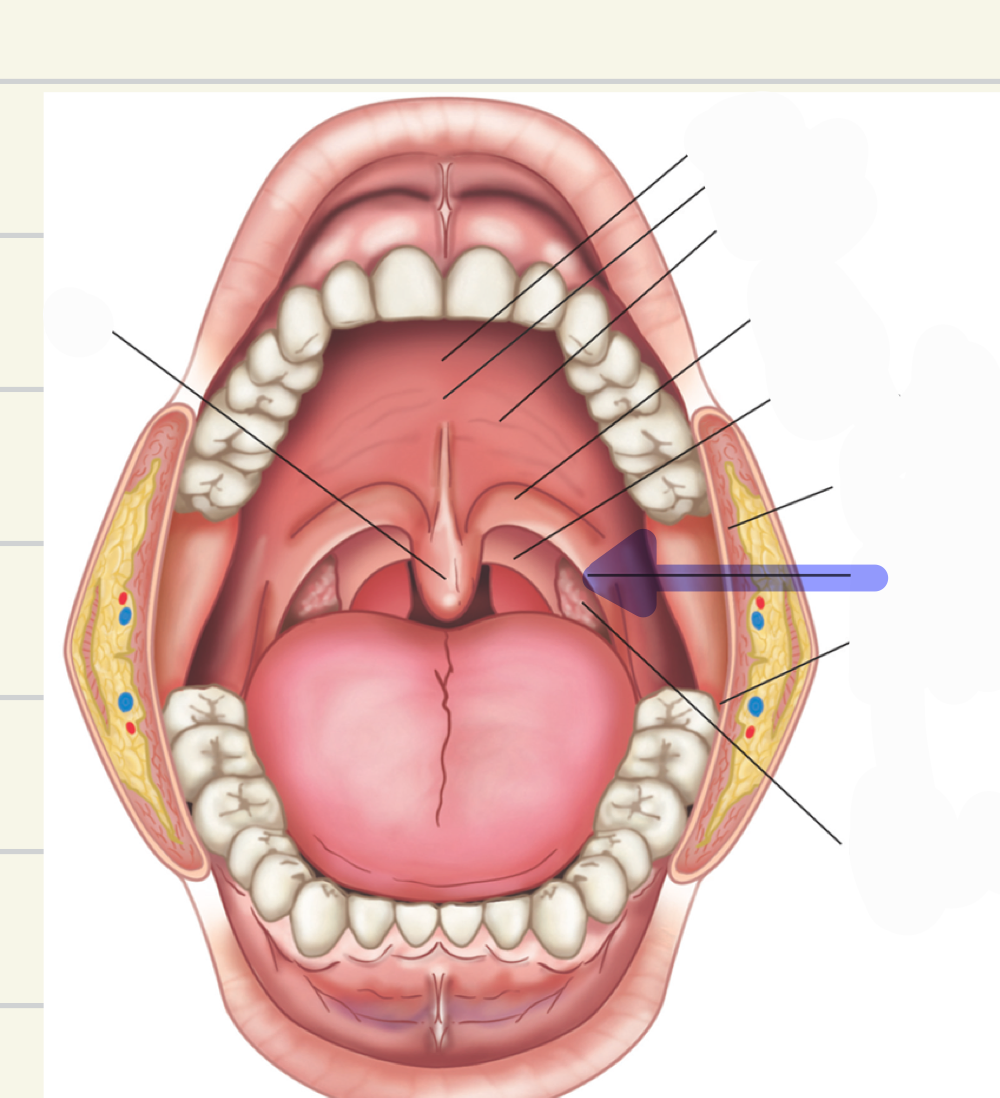
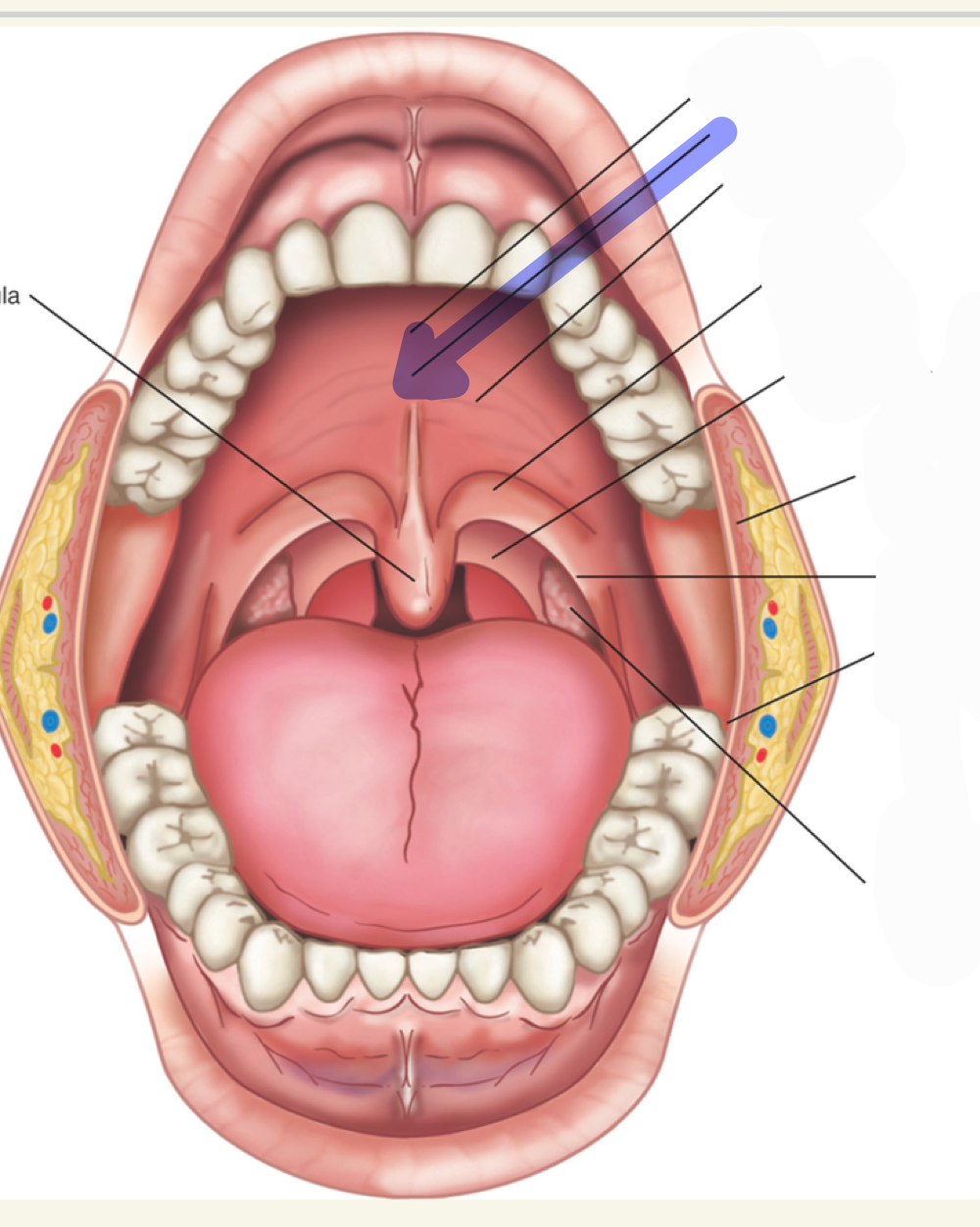
posterior faucial pillars
what is this
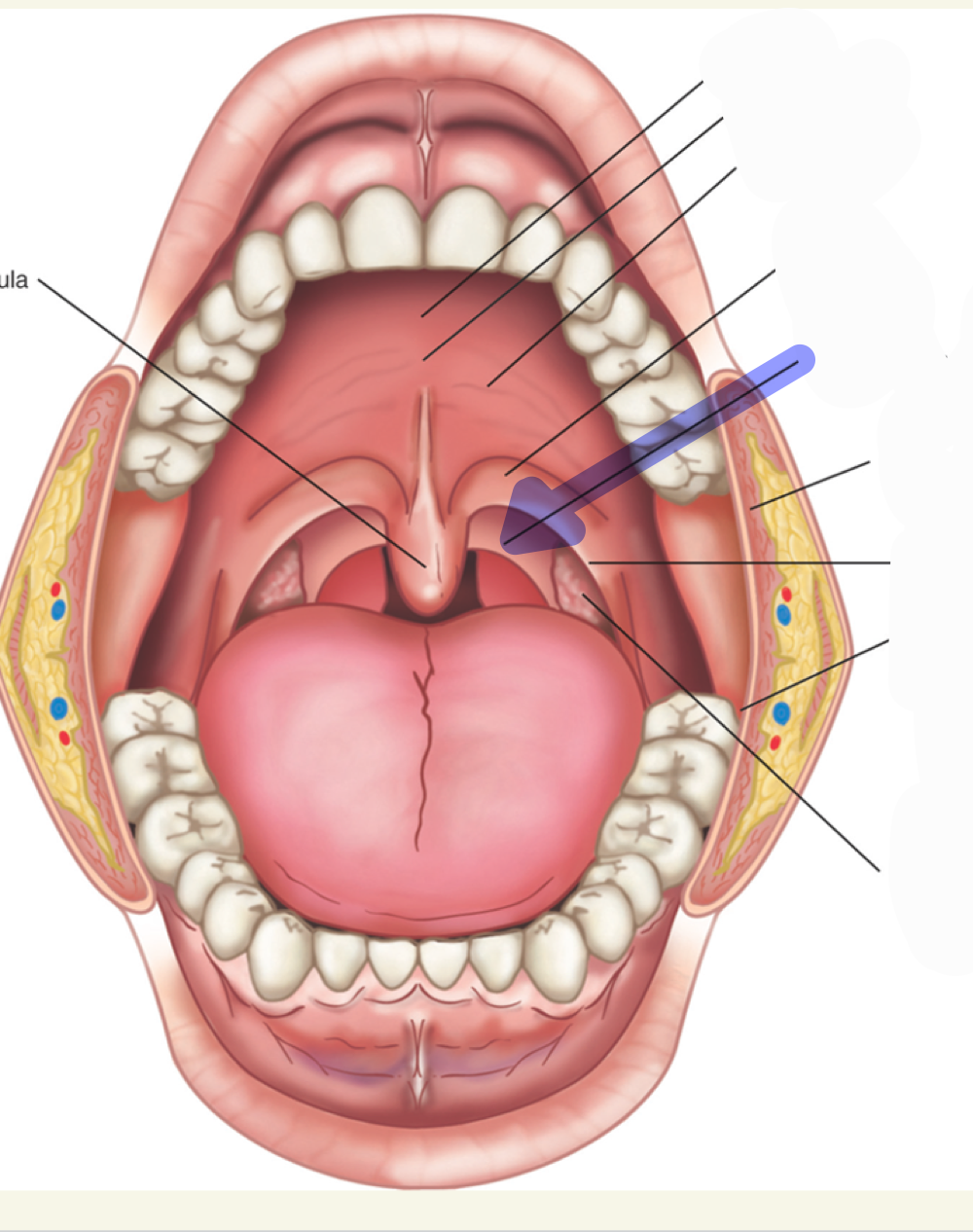
palatine tonsils
what is this
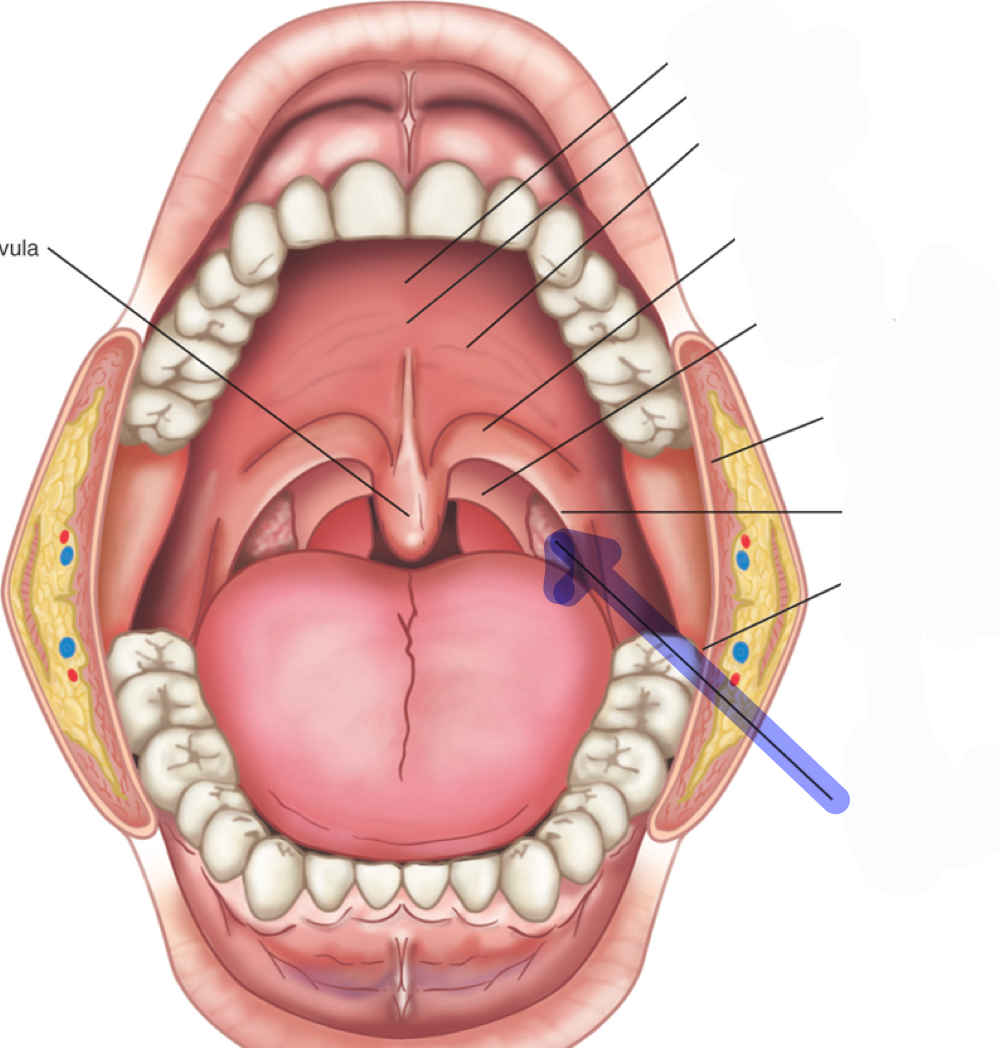
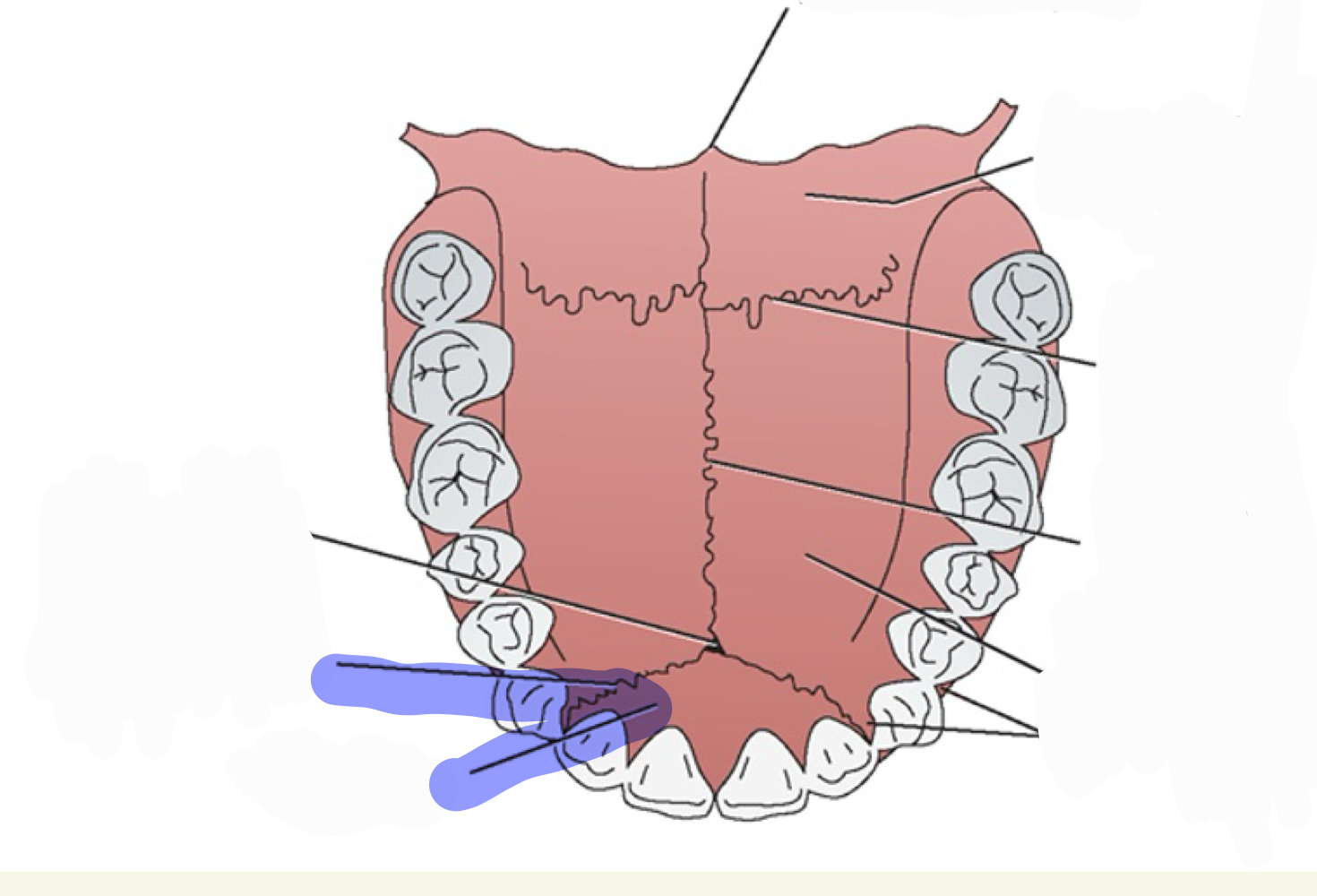
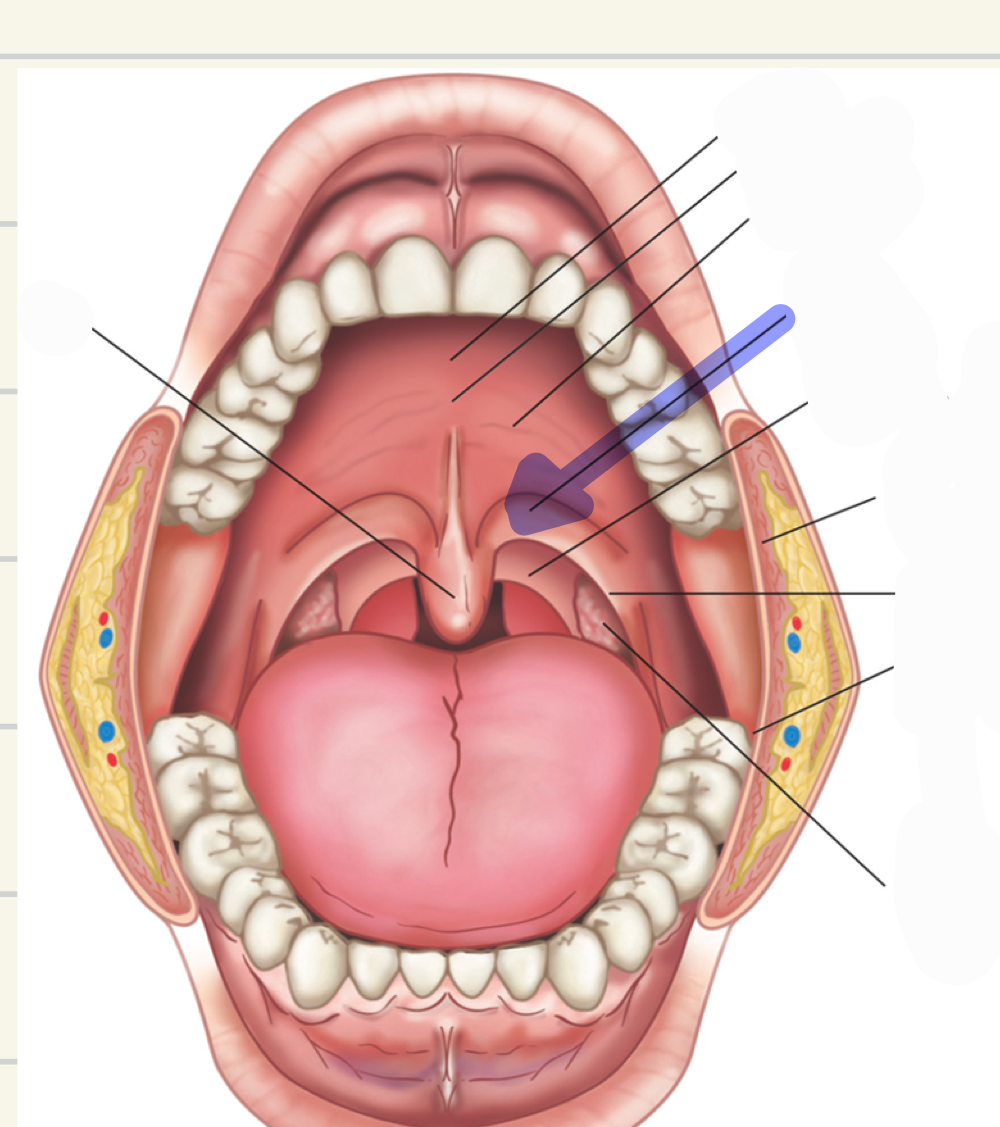
buccal cavity
what is this
dentition
Housed in the alveoli of the maxillae and mandible
Incisors (2 pairs)
Cuspids (1 pair)
Bicuspids (2 pairs)
Molars (3 pairs)
four types of teeth are:
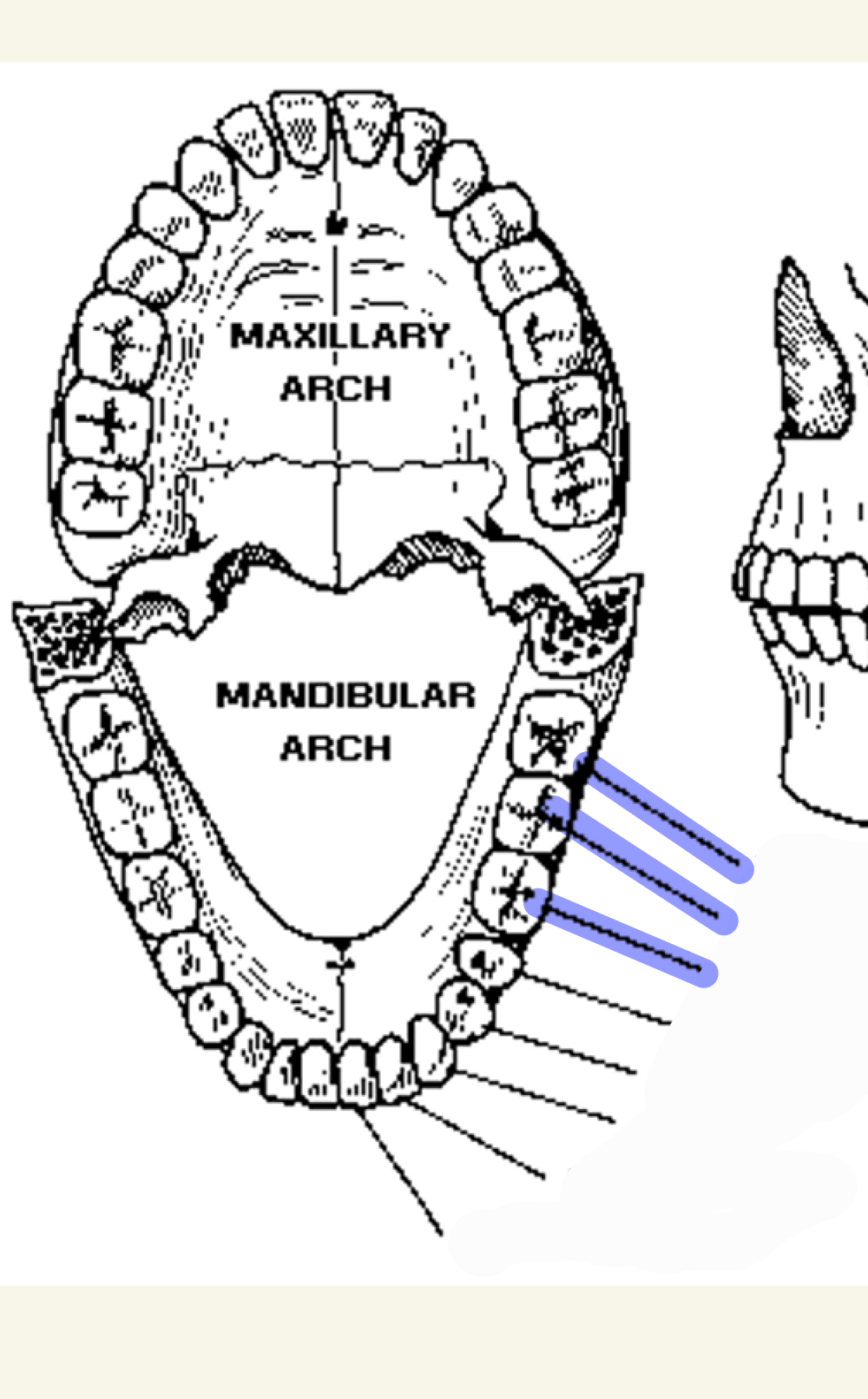
molars (3)
which teeth are these
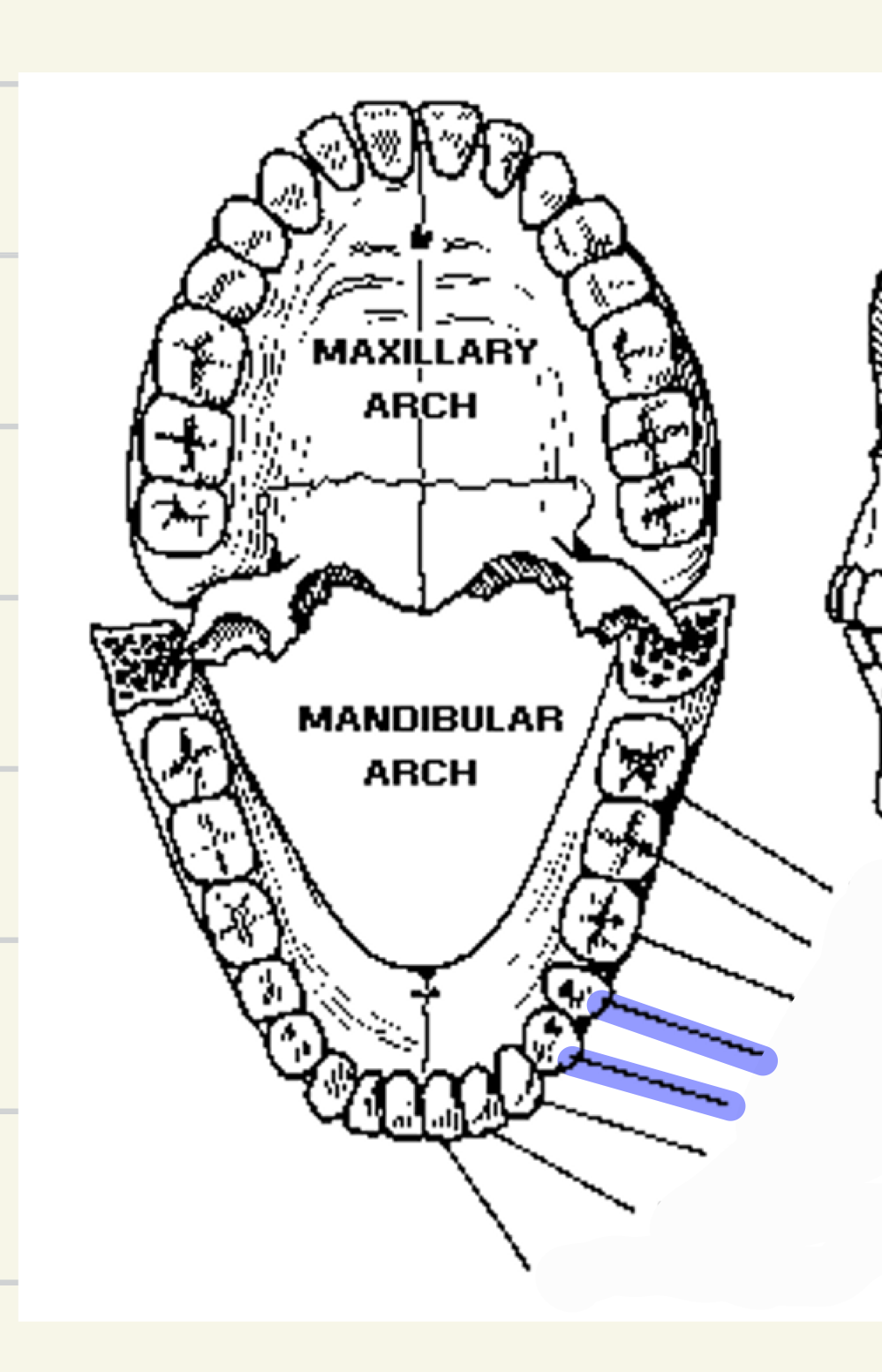
bicuspids (2)
which teeth are these
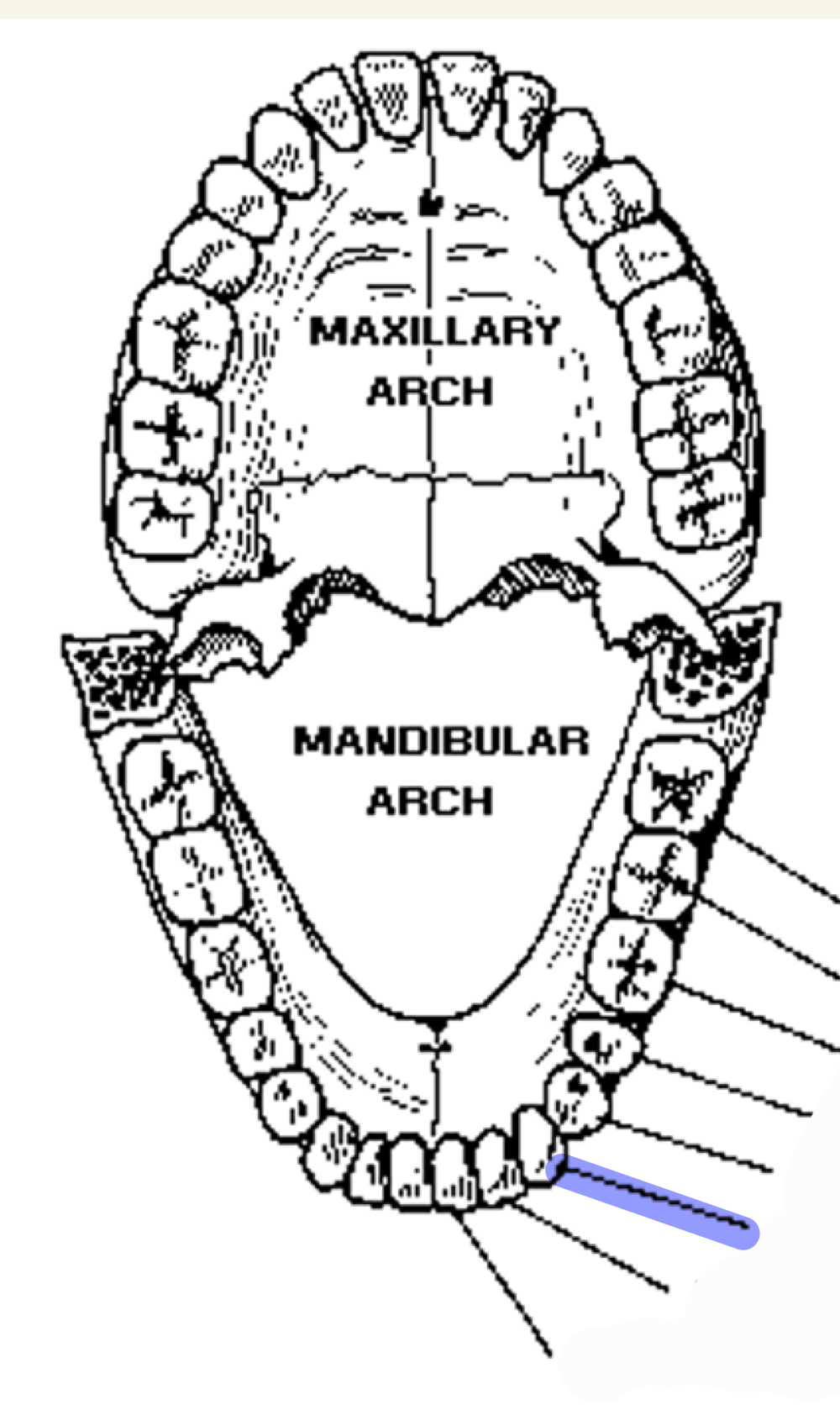
cuspids (1)
which teeth are these
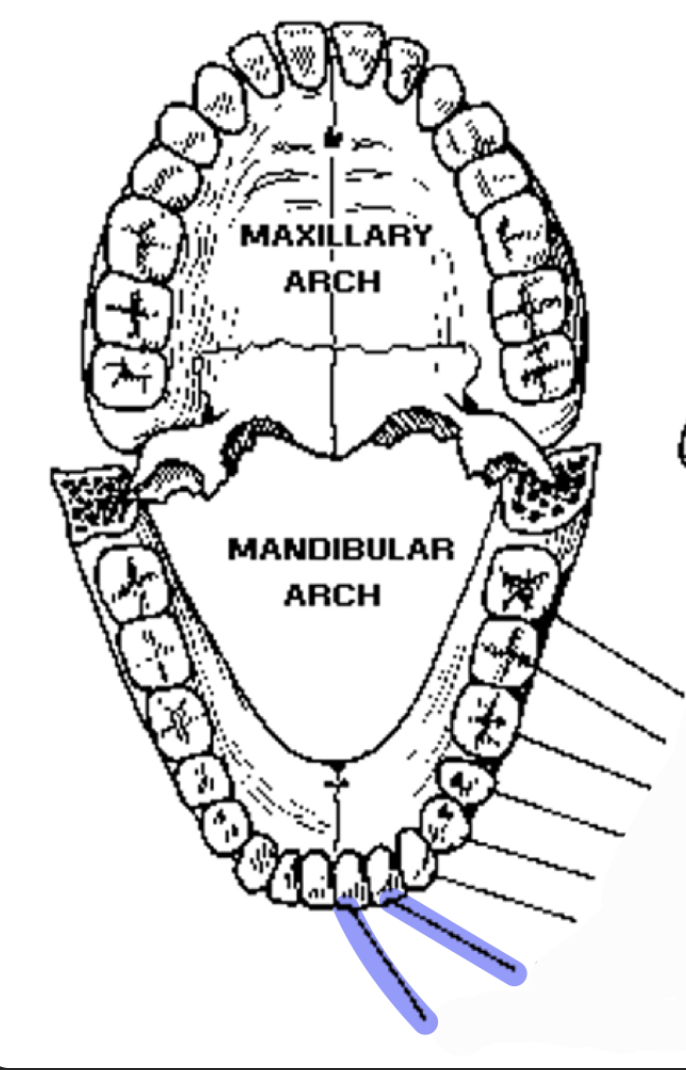
incisors (2)
which teeth are these
root
what is this
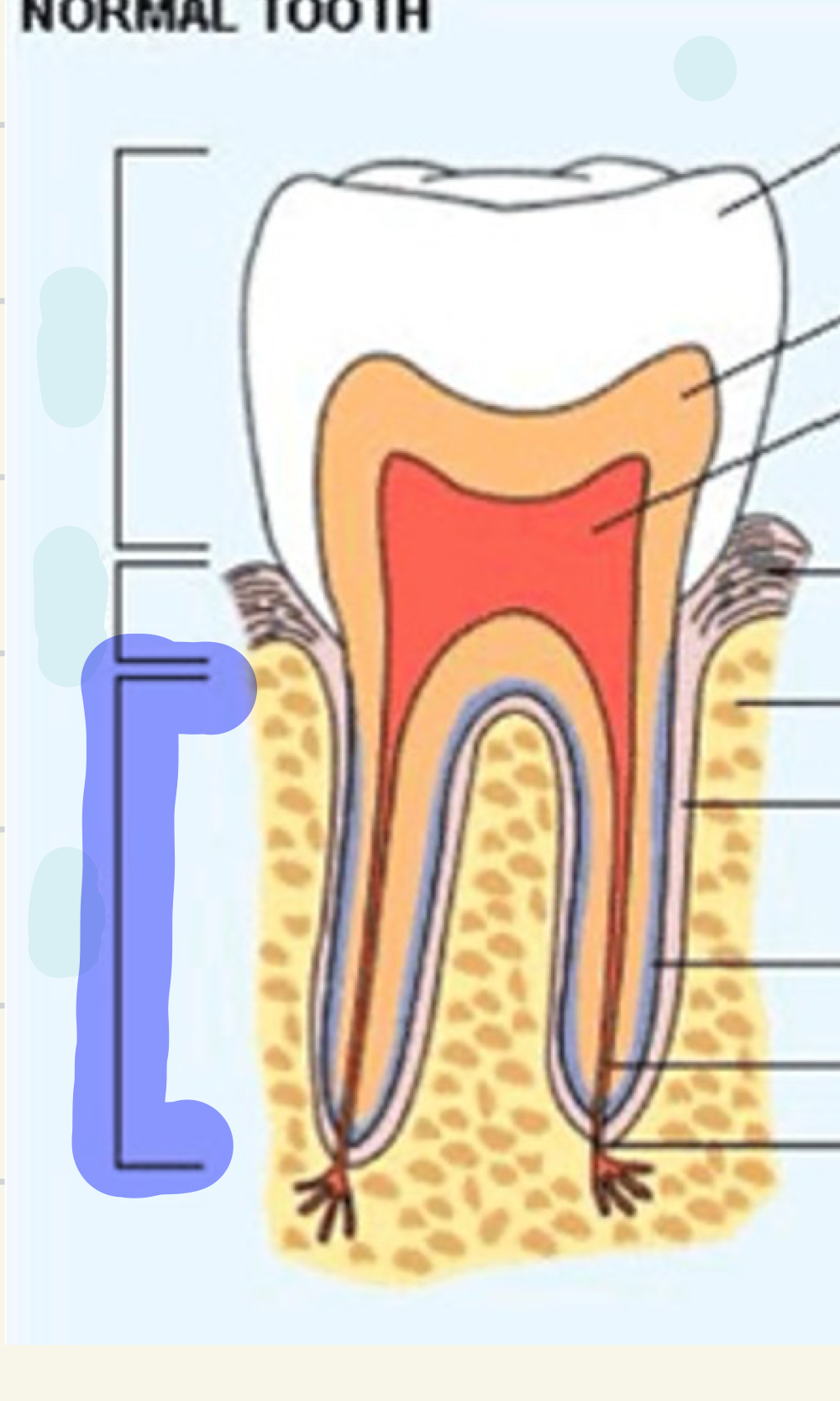
neck
what is this
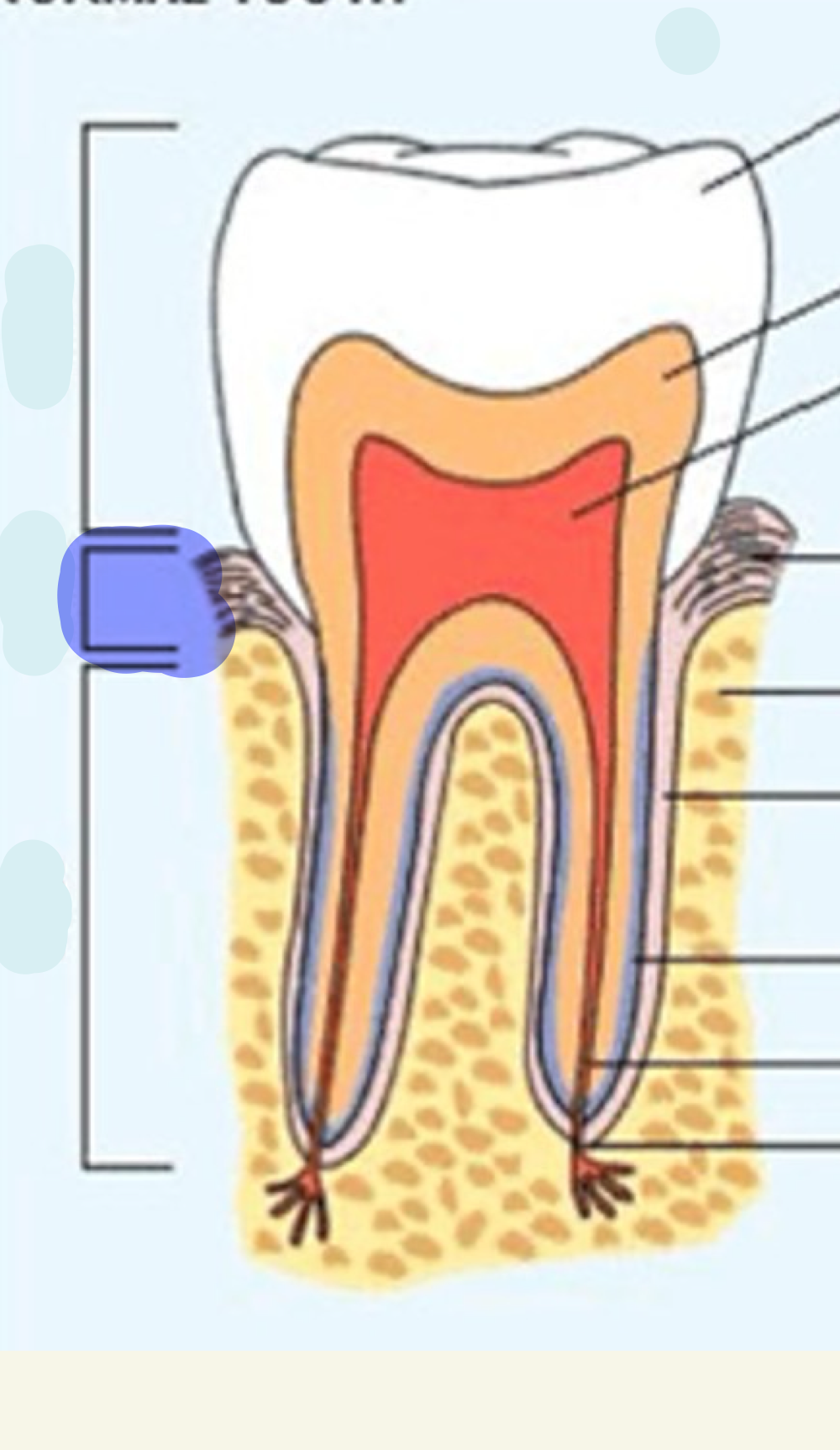
crown
what is this
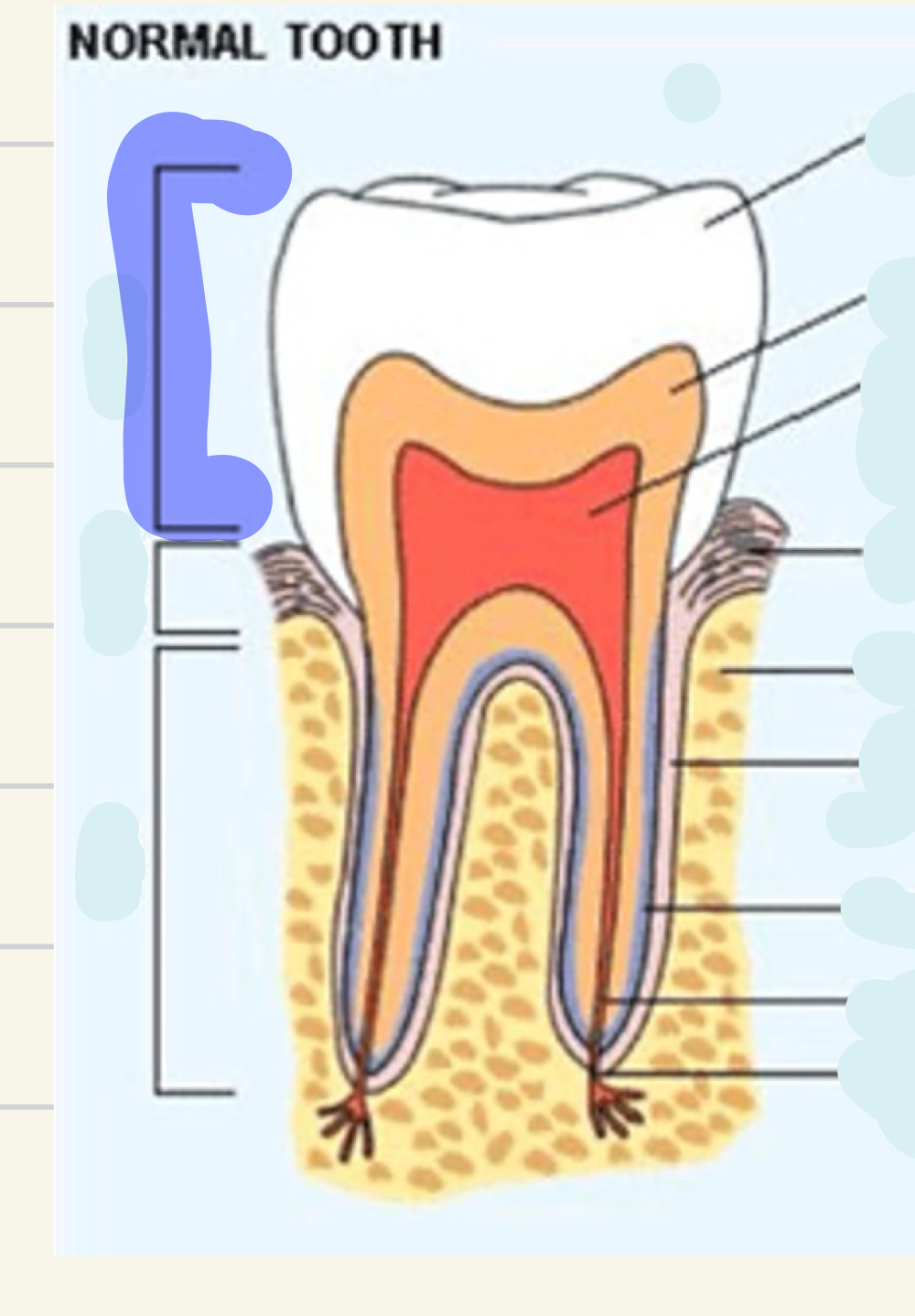
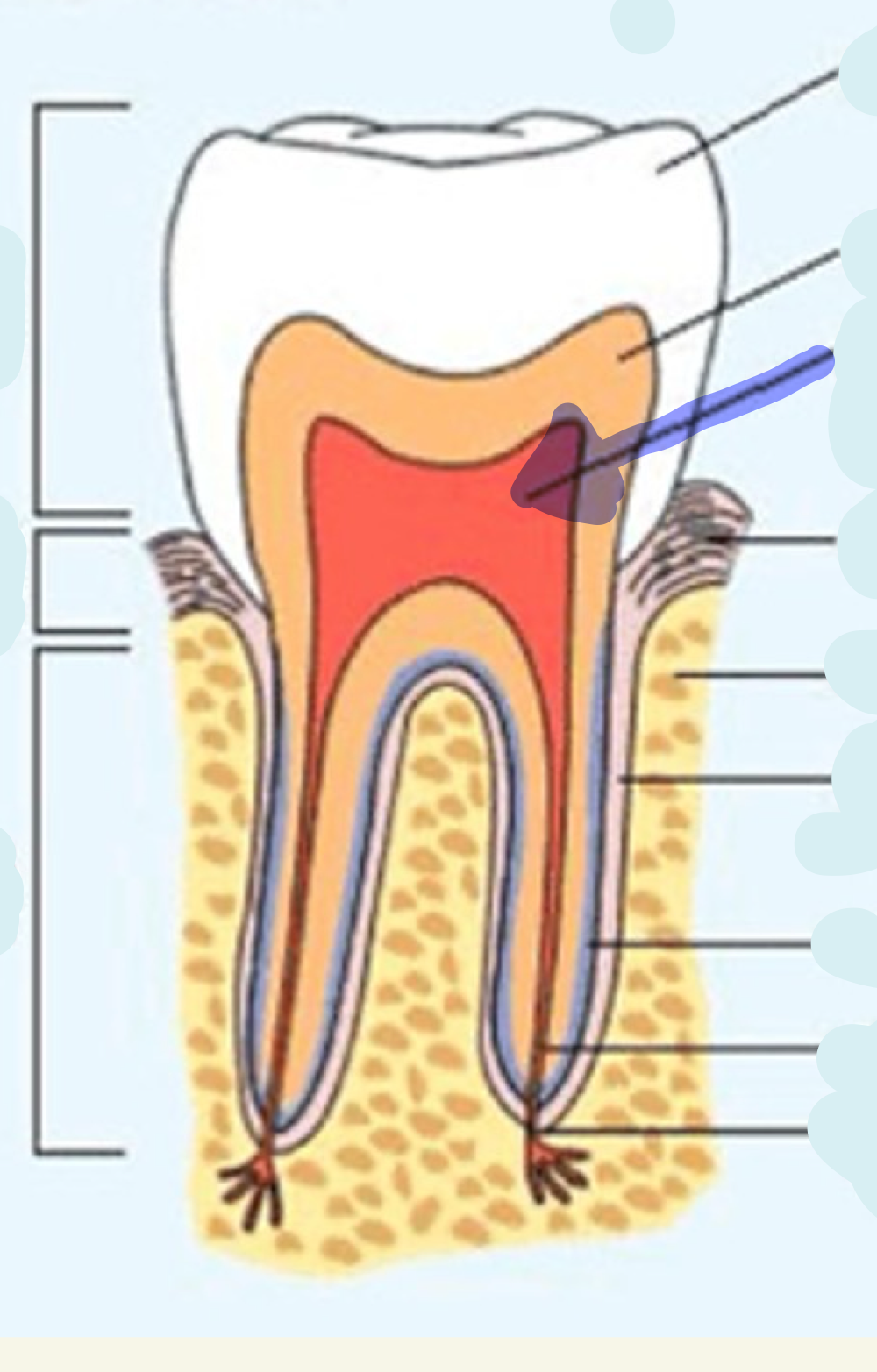
cementum
what is this
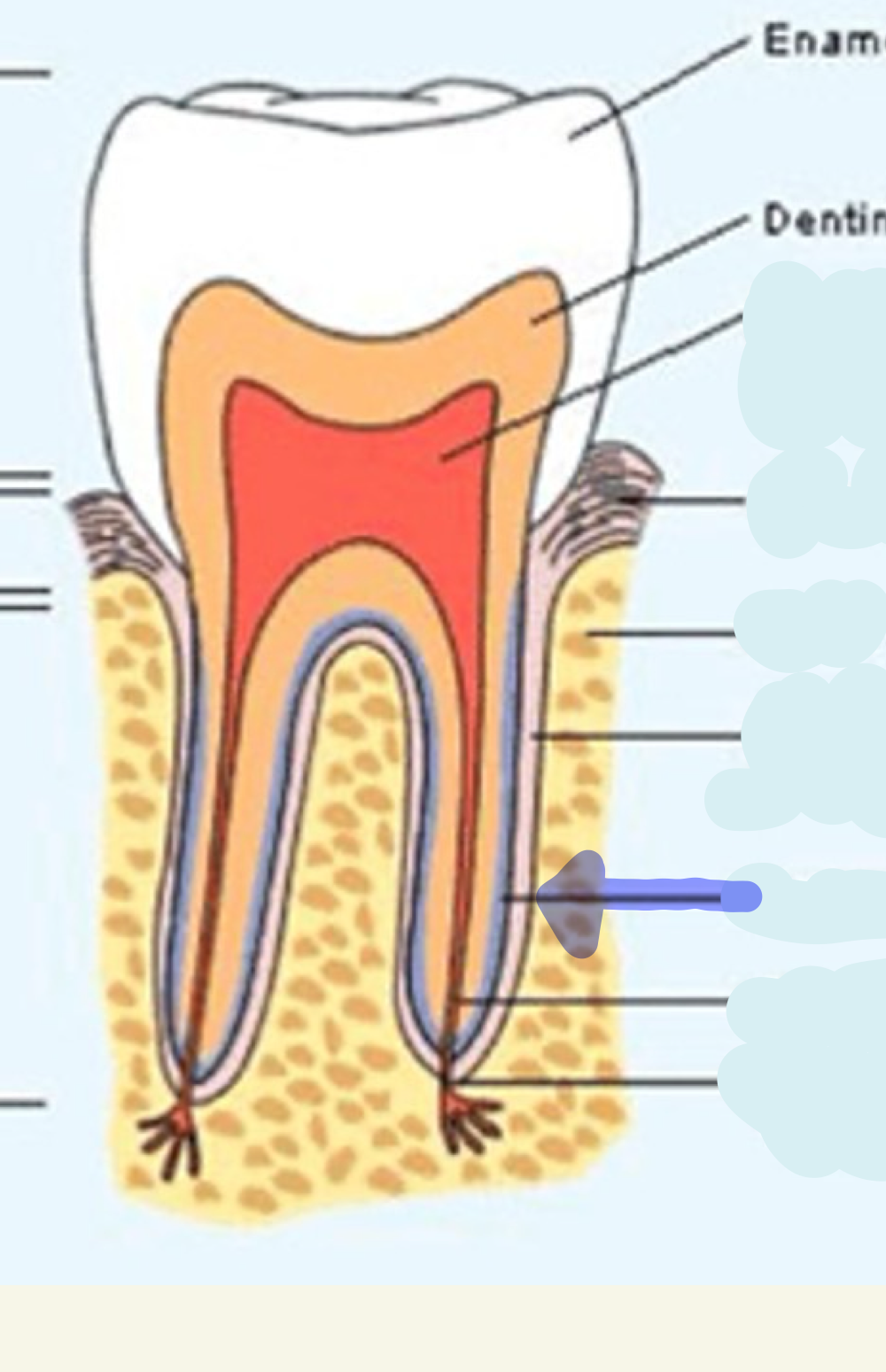
enamel
what is this
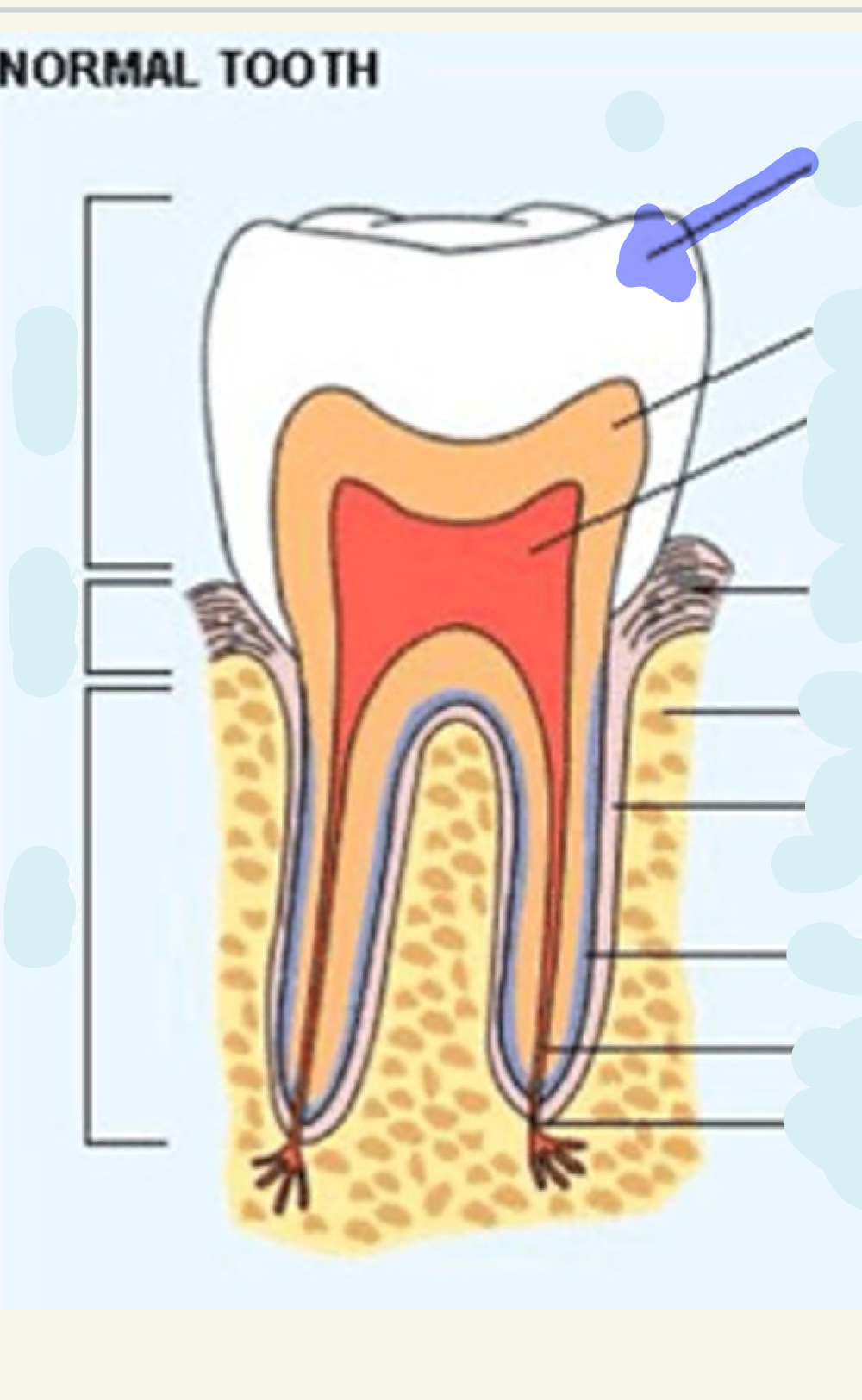
dentine
what is this
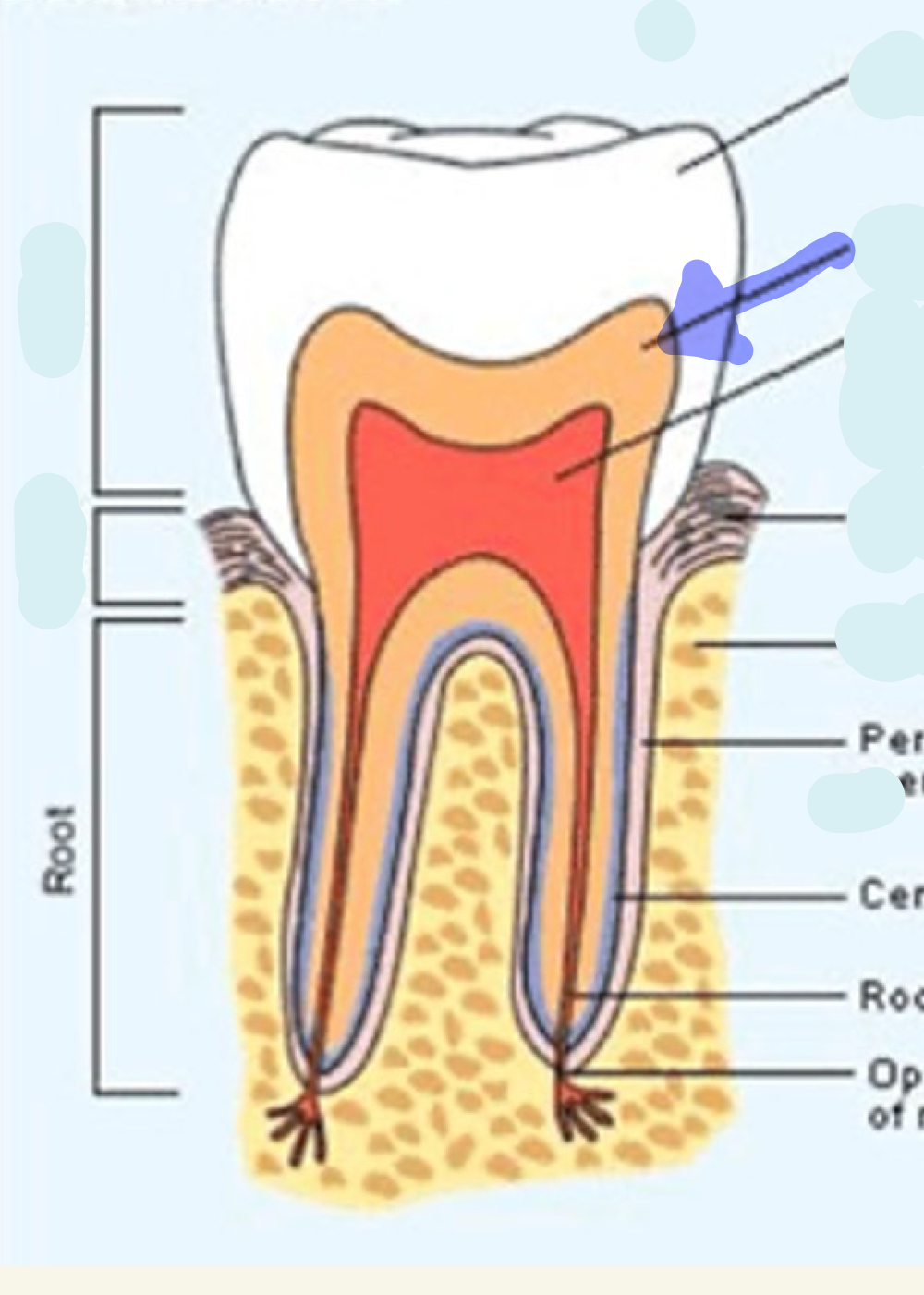
pulp
what is this
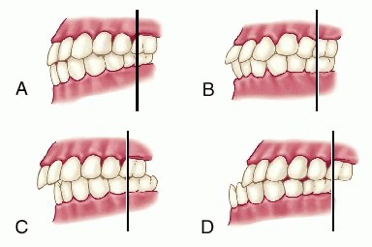
class I occlusion
what is a
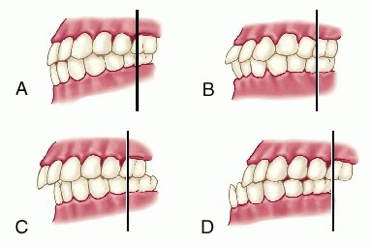
class I malocclusion
what is b
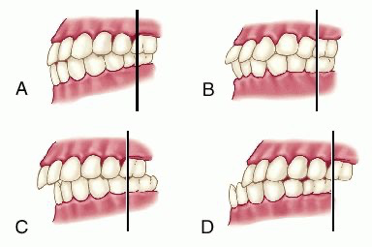
class II malocclusion
what is c
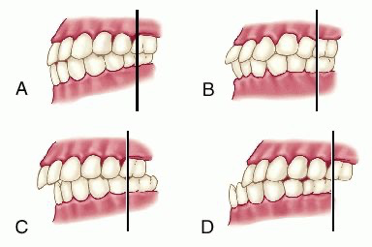
class III malocclusion
wha is d
orbicularis oris
lip muscle
Serves as a point of insertion for other muscles
Completely encases mouth opening
Runs in a circle around the mouth
Superior and inferior portion
Contraction: closes oral opening
Sounds: m, p, b, (w)