Quiz 3 Appendicular Skeletal System
1/82
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
What are the 4 parts of the pectoral girdle
2 scapulas and 2 clavicles
What is the shape of the pectoral girdle
- incomplete ring
- open in the back between scapulae
- bones in front are separated by sternum
What is another name for clavicles
collarbones
Where is the clavicle located
- base of neck
- run horizontally between the manubrium and scapulae
What is the function of the clavicles
- to hold the shoulders in place
- provide attachments for the muscles of the upper limbs, chest, and back
What is the common name for scapulae
shoulder blades
What shape are the scapulae
somewhat triangular
What divides the scapula
- the spine that leads to an acromion process
- the spine divides the posterior surface of each scapula into unequal portions
What is the acromion process?
- the tip of the shoulder
- articulates with the clavicle and provides muscle attachments for upper limbs and chest
What shape is the clavicle
S-shaped
What is the coracoid process?
- A coracoid process curves anteriorly and inferiorly to the clavicle.
- provides attachment points for upper limb and chest muscles.
What bones does the appendicular system consist of?
1) Pectoral Girdle
2) Upper Limbs
3) Pelvic Girdle
4) Lower Limbs
What is the glenoid cavity?
- located on the lateral surface of the scapula
- found between the acromion and coracoid processes
- depression
- articulates with the head of the arm bone (humerus)
The bones of the upper body form framework of ___________________________________
arm, forearm, and hand
What are the bones of the upper limbs?
a humerus, a radius, an ulna, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges
What is the humerus?
- long bone
- extends from the scapula to the elbow
- the upper end is a smooth, round head that fits into the glenoid cavity of the scapula
What is just below the head of the humerus?
- 2 processes
- a greater tubercle on the lateral side
- a lesser tubercle on the anterior side
What is the function of the greater tubercle and lesser tubercle?
Provide attachments for muscles that move the upper limb at the shoulder
What is between the greater tubercle and lesser tubercle?
A narrow furrow called the intertubercular sulcus (intertubercular groove)
What is the anatomical neck?
- narrow depression along the lower margin of the humerus head that separates it from the tubercles
What is the surgical neck?
- just below the head and the tubercles
- tapering region
- named because fractures commonly occur there
What is the deltoid tuberosity?
- near the middle of the bony shaft on the lateral side
- rough, v-shaped
- provides attachment for the muscle (deltoid) that raises the upper limb horizontally to the side.
What are condyles?
- 2 smooth condyles
- lateral capitulum
- medial trochlea
- articulate with the radius on the lateral side and ulna on the medial side
- articulate with the tibia of the leg
what are epicondyles?
- above the condyles on either side
- provide attachments for muscles and ligaments of the elbow
What is the coronoid fossa?
- depression between the epicondyles anteriorly
- receives a process of the ulna (coronoid process) when the elbow bends
What is the olecranon fossa?
- depression on the posterior surface
- receives ulnar process from the olecranon process
- when the elbow straightens
What is the radius?
- located on the thumb side of the forearm
- extends from the elbow to the wrist
- crosses over the ulna when the hand is turned so that the palm faces backward
What allows the radius to rotate?
- thick, disklike head at the upper end of the radius that articulates with the humerus and a notch of the ulna (radial notch)
What is the radial tuberosity?
-process on the radial shaft just below the head
- attachment for a muscle (biceps brachii) that bends the upper limb at the elbow
What is the lateral styloid process?
- at the distal end of the radius
- provides attachments for the ligaments of the wrist
What is the ulna?
- longer than the radius and overlaps the end of the humerus posteriorly
What is the trochlear notch?
- at the proximal end of the ulna
- wrenchlike opening
- articulates with the humerus
- The olecranon process and coronoid process are above and below this notch and provide attachments for muscles
What is at the distal end of the ulna?
Knoblike head that articulates laterally with a notch of the of radius (ulnar notch) and with a disc of fibrocartilage inferiorly.
What does the disc of fibrocartilage in the ulna join?
The triquetrum (wrist bone)
What is the term for wrist bone?
Triquetrum
What provides attachments for wrist ligaments in the ulna?
A medial styloid process at the distal end of the ulna provides attachments for wrist ligaments.
What does the hand consist of?
wrist, palm, and fingers
What forms the carpus?
- eight small carpal bones firmly bound in two rows of four bones each
- carpus articulates with the radius and with the fibrocartilaginous disc on the ulnar side
- distal surface articulates with the metacarpal bones
What bones form the framework of the palm (metacarpus)?
-five metacarpal bones in line with each finger
- the metacarpal bones are cylindrical, with rounded distal ends that for the knuckles of a clenched fist
How are the metacarpals numbered?
- numbered 1-5
- begins with the metacarpal of the thumb
What do the metacarpals articulate with?
- articulate proximally with the carpals and distally with the phalanges
What are the phalanges?
- finger bones
- each finger has three phalanges (proximal, middle, and distal phalanx) except the thumb which lacks a middle phalanx
What does the pelvic girdle consist of?
- 2 hip bones: coxal bones and pelvic bones (or innominate bones)
- both hip bones articulate with each other anteriorly and with the sacrum posteriorly.
What is the pelvis?
- bowl-shaped
- sacrum, coccyx, and pelvic girdle
What is the function of the pelvic girdle?
- supports the trunk of the body
- provides attachments for the lower limbs
- protects the urinary bladder, the distal end of the large intestine, and reproductive organs
What 3 parts does the hip bone develop into?
- an ilium
- an ischium
- a pubis
What is the acetabulum?
- the 3 parts of the hip bone fuse in the region of a cup-shaped cavity called the acetabulum.
-depression on the lateral surface of the hip bone
- receives the rounded head of the femur (thigh bone)
What is the ischium?
- forms the lowest portion of the hip bone
- L shaped
What is the ischial tuberosity?
This is the angle of the ischium, pointing downward. It is the bone we sit on. The lowest bump on the pelvic girdle
What is the ilium
- largest and uppermost portion of the hip bones
- flares outward, forming the prominence of the hip
- The margin of this prominence is called the iliac crest
What is the iliac crest?
- The part of the pelvis that forms the "wings".
- upper most part
- prominence of the hips
What is the sacroiliac joint?
the joint between the sacrum and the ilium
what is the anterior superior iliac spine?
-bony projection of iliac bone- can feel it on your hip
- can be felt lateral to the groin
- provides attachments for ligaments and muscles
What are the functions of the ischial tuberosity?
- a rough surface that provides attachments for ligaments and lower limb muscles
- supports the weight of the body during sitting
What is the ischial spine?
- Above the ischial tuberosity
- near the junction of the ilium and ischium
- sharp projection
- the distance between the ischial spines is the shortest diameter of the pelvic outlet
What is the pubis?
- anterior portion of the hip bone
What is the pubic symphysis?
joint between the two pubic bones that come together at the midline
What is the pubic arch?
-inferior to the pubic symphysis; angle helps distinguish male from female pelvis
- angle formed below the symphysis
What is the obturator foramen?
- largest foramen in the skeleton
- large opening between the joinings of the pubis and ischium
What is the pelvic brim?
a line from the sacral promontory to the upper part of the pubic symphysis
What is the difference between male and female pelves?
The male pubic arch is more narrow than the female pubic arch.
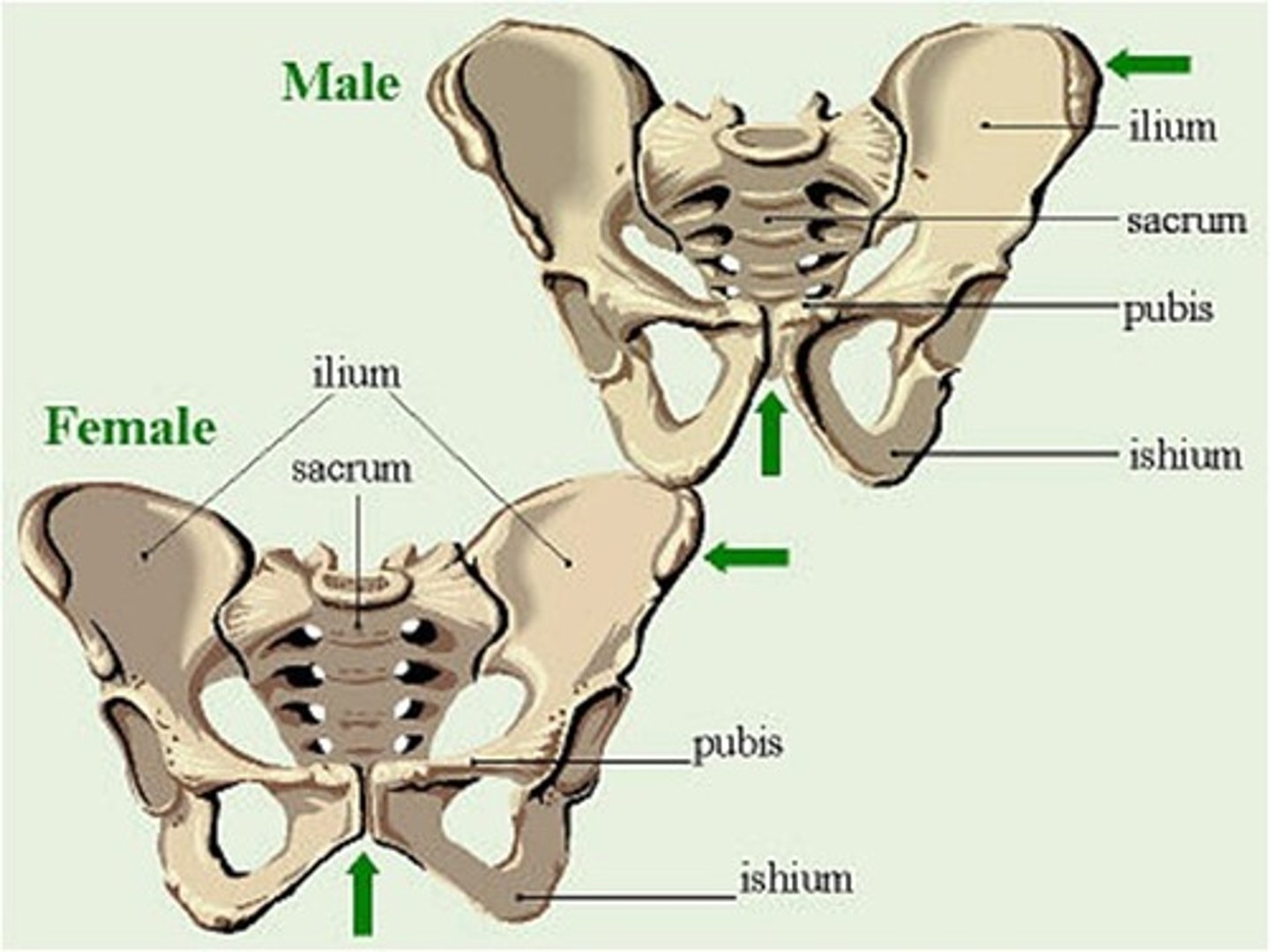
What does the lower limb consist of?
- framework of thigh, leg, and foot
- bones include a femur, a tibia, a fibula, tarsals, metatarsals, and phalanges.
What is the femur?
- thigh bone, the longest bone in the body
- extends from the hip to the knee
A large, rounded head at its proximal end projects medially into the acetabulum of the hip bone.
What is the fovea capitis?
- pit in the head of a femur
- marks the attachments of a ligament
What is below the head of the femur?
- just below the head are a constriction, or neck, and two large processes - a superior lateral greater trochanter and an inferior medial lesser trochanter
What is the patella?
- kneecap
- articulates with the femur on its distal anterior surface
- the patella is located in a tendon that passes anteriorly over the knee
What is the tibia?
- the shin bone
- larger of the two leg bones and is located on the medial side
What are the condyles of the tibia?
- its proximal end is expanded into medial and lateral condyles: has concave surfaces and articulates with the condyles of the femur
What is the process located below the condyles of the tibia?
- tibial tuberosity
- below the condyles, on the anterior surface
- provides an attachment for the patellar ligament
What is the patellar ligament?
A continuation of the patella-bearing tendon
What is the medial malleolus?
- attachment for ligaments
- at its distal end, the tibia expands to form a prominence on the inner ankle called the medial malleolus
What articulates with the talus?
- inferior surface of the tibia's distal end articulates with a large bone (talus) in the ankle
What is the fibula?
- The fibula is a long, slender bone on the tibia's lateral side
- Its ends are slightly enlarged into a proximal head and a distal lateral malleolus.
- the head articulates with the tibia just below the lateral condyle; however, it does not enter into the knee joint and does not bear any body weight.
- The lateral malleolus articulates with the ankle and protrudes on the lateral side.
What is the foot made of?
ankle, instep, and toes
What is ankle and what is it composed of?
- ankle is known as tarsus
- composed of seven tarsal bones
How are the bones of the ankle composed?
- bones are arranged so that one of them, the talus, can move freely where it joins the tibia and fibula,
- the remaining tarsal bones are bound firmly together, forming a mass supporting the talus
What is the largest tarsal?
calcaneus (heel bone)
What are the functions of the calcaneus
- helps support the body weight
- provides an attachment for muscles that move the foot
What is the metatarsus?
- instep
- consists of 5 elongated metatarsal bones that articulate with the tarsus
They are numbered 1-5, beginning on the medial side
- heads at the distal ends of these bones form the ball of the foot
What is a longitudinal arch?
- extends from the heel to the toe
what is a transverse arch
- stretches across the foot
What are the functions of the arches of the foot?
- provide a stable, springy base for the body
- tissues that bind the metatarsals may weaken, producing fallen arches or flat feet.
What are the phalanges of the toe?
- align and articulate with the metatarsals
- each toe has three phalanges (proximal, middle, and distal phalanx except great toe)