Week 2: Potassium Disorder (Dr. Le)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
what is the level range for potassium
3.5-5.0
what percent of potassium contained with the ICF
98%
•The sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase (Na+K+ATPase) pump located in the cell membrane is responsible what
compartmentalization of potassium
intracellular potassium cncentration is aprox what
130-145
•Both hypo- and hyperkalemia can lead to life-threatening arrhythmias (t/f)
true
defined as serum potassium less than 3.5 is what
hypokalemia
persistent hypokalemia linked to increased mortality to what
HF, CKD, DM
K+ shift for hypokalemia is what
alkalosis, insulin, B2 agonists
K+ deficit in hypokalemia
poor intake, renal/gi issues
renal losses is what
diuretics
gi losses is what
diarrhea
vomiting
in hypokalemia does the EKG changes?
T wave flatten or inversion
U wave elevation
ST depression or flattening
prolonged QT
Often asymptomatic, N/V, muscle weakness is what symptoms
mild hypokalemia
Cramping, weakness, malaise, and myalgias, paralysis, EKG changes, cardiac arrhythmias, death is symptoms of what
moderate/severe hypokalemia
management of hypokalemia depends on what
degree and rapidity of hypokalemia
treat underlying causes for hypokalemia
metabolic alkalosis
magnesium deficiency
medications
clinical syndrome
hydrodialysis
if the K+ <3 mEq what needs to be done
always treat
oral preferred if asymptomatic
IV if severe symptoms or unable to tolerate PO
what are the potassium oral replacement for hypokalemia
potassium chloride
potassium bicarbonate
potassium citrate
potassium glyconate
what is the most common potassium used
potassium chloride
what are the side effects for Potassium replacement oral
Gi side effects: N/v/d, flatulence
if the potassium dose >40mEq, what should be done
divide into smaller doses, split dose twice a day
what are the phosphate oral replacement used for
hypokalemia
how much potassium is contained within ICF
98%
normal range or potassium
3.5-5.0
hypo and hyper kalmia can lead
neuromuslcar and cardiac issues
persistent hypokalemia linked to increase mortality like what
HF
CKD
DM
mechanism of potassium
K+ shift
K+ deficit
alkolosis, insulin, B2 agonists is what mechanism of potassium
K+ shift
poor intake, Renal/GI losses is what mechanism in potassium
K+ deficit
you can stop B2 agonist but cant stop insulin
true
increase the excretion of potassium
diuretics
how to manage hypokalemia
therapy depends on the degree and rapidity of hypokalemia
when the K+ level is 3.5-4 what needs to be done
encourage dietary potassium intake
if K+ is < 3 what needs to be done
oral if asymptomatic
what is the most common of potassium formulations
potassium chloride
what are the 4 type of salt forms for potassium
chloride, bicarbonate, citrate, gluconate
which potassium cause alkalizing effect
potassium bicarbonate
what is the first option for hypokalemia symptomatic
potassium oral replacement
is potassium dose dependent
yes
when not recommend potassium acetate
in alkalosis
usual dose to prevent hypokalemia is what
20 mEq/day
usual dose to treat hypokalemia is what
40-100 mEq/dose
micro encapsulated products have better GI tolerance and no bitter smell or aftertaste
true
if a patients potassium level is 2.9 mEq and you administer him 60 mEq of KCl, what is the expected increase in his K level
3.5
if a patients K level is 2.9 mEq/L how much KCl would you need to administer to raise his K level to 3.7 mEq/L
80
for every ~10 mEq of K+ administer what happens to serum K+
increase by 0.1 mEq/L
•For every ~10 mEq of K+ administered à serum K+will increase by 0.1 mEq/L
true
If a patient's K is 3.3 mEq/L and you give him KCL 40 mEq. What do you expect his K to increase to?
3.7
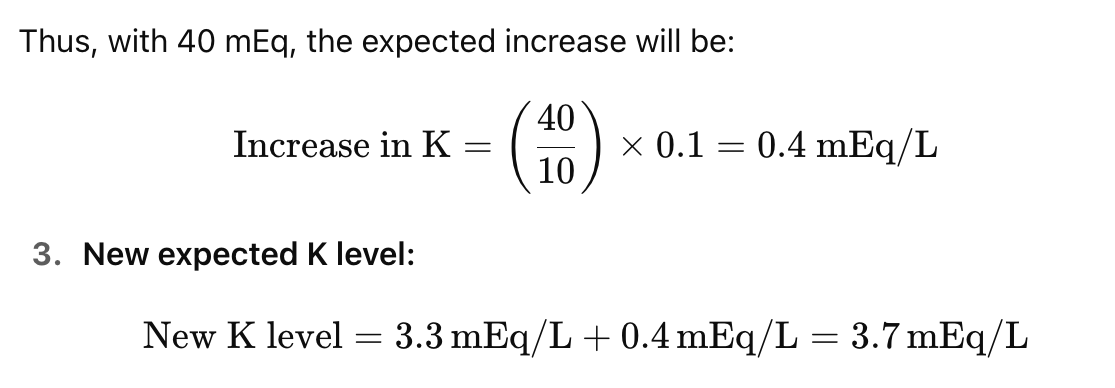
what is peripheral line for IV max rate
10 mEq/hr
what is the central line for IV max rate
20 mEq/hr
If your patient only has a PIV, and the your KCl IVPB is 20 mEq/100mL bag, the nurse ask how fast to program the pump in mL/hr?
50mL/hr
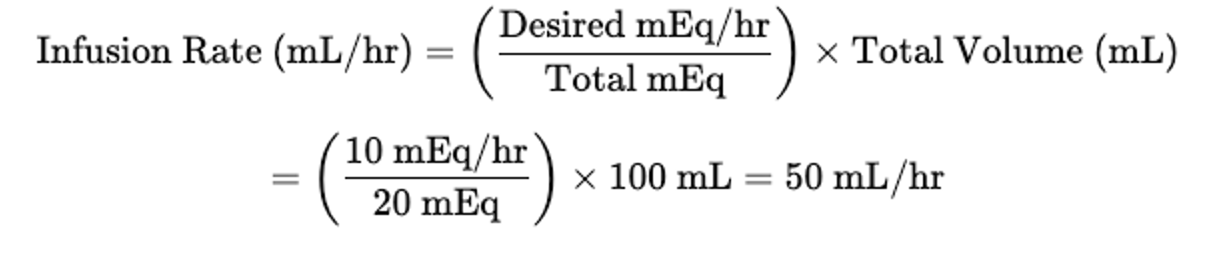
Never give potassium as an IV push, what will happen
cause cardiac arrest
Phlebitis, injection site pain, extravasation are adverse effect
IV potassium
standard infusion for IV potassium
infuse > 10 mEq/hr → EKG monitoring
if cardiac arrest imminent, may give 10 mEq IV over 5 mins
can repeat once if necessary
emergency use of IV potassium
aldosterone antagonists drugs
spironolactone
eplerenone
ENaC inhibitor drugs
Amiloride
Traimterene
caution in patient with renal dysfunction, what should happen to dose
reduce the dose by 50%
What results should you look for in this hypokalemia patients
A. EKG
B. SCr
C. Mg
D. Na+
A, B, C
Dr. Darcie asks for recommendation replace potassium goal to 3.6 mEq/L, patient only has a pIV line in ED. How much potassium should she order, how to administer it
40 mEq PO
if dose is 80 mEq, 10 mEq/hr, how many hours
8 hours
what defines as hyperkalemia
greater than 5.0
Chronic hyperakalemia management are what
dietary
diuretics
cation exchangers
dialysis
symptomatic for hyperkalemia
protect the heart
promote intracellular movement of potassium
enhance excretion from body
remove any offending agents
how to protect the heart in symptomatic hyperkalemia
IV calcium
what is the management for hyperkalemia (C BIG K DROP)
Calcium
Bicarbonate, Beta 2 agonist
insulin
Glucose
Potassium binder
diuretics, dialysis
what are the options for IV calcium
calcium chloride or calcium gluconate
calcium chloride is 3x more calcium than gluconate
true
which calcium is preferred for hyperkalemia
calcium gluconate
what is the adminstration for IV calcium
1g IV bolus over 5-10 mins
what is the first line for intracellular shift of potassium
insulin + dextrose
emergency dialysis can be considered in patient with acute kidney injury with persistent EKG changes or refractory
true
monitoring for hyperkalemia
continuous ECG
Serum K+
blood glucose monitoring
sodium bicarbonate therapy
medication review
•critical electrolyte disorder, often caused by kidney dysfunction. Early recognition and treatment are vital is what
hyperkalemia
mild cases what agent to use in hyperkalemia
resins or diretics
for severe case with EKG changes what do you do in hyperkalemia
give IV calcium