Histology ( Epithelial tissue )
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
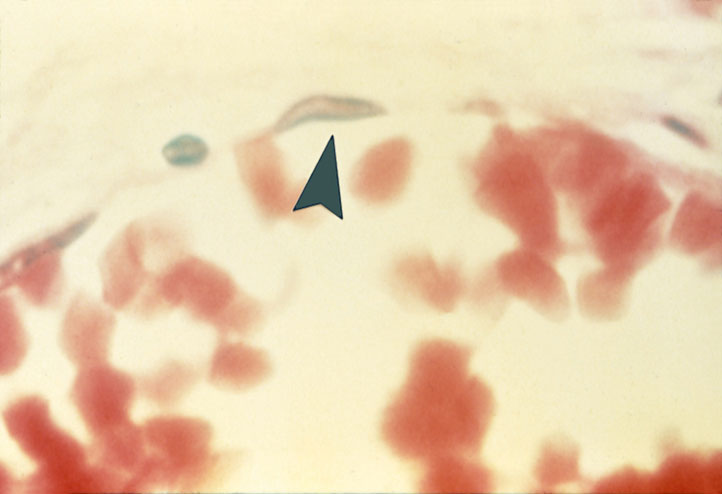
“Simple Squamous Epithelium (ET)(Endothelium)“
tissue found lining a blood vessel. bright red cells in lower half are RBC's.
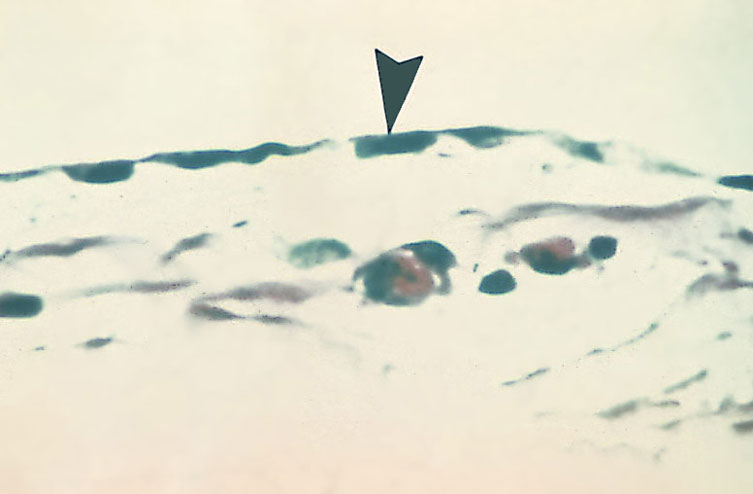
“Simple Squamous Epithelium (ET)(Mesothelium)“
note the absense of RBC on the aplical side of the tissue.
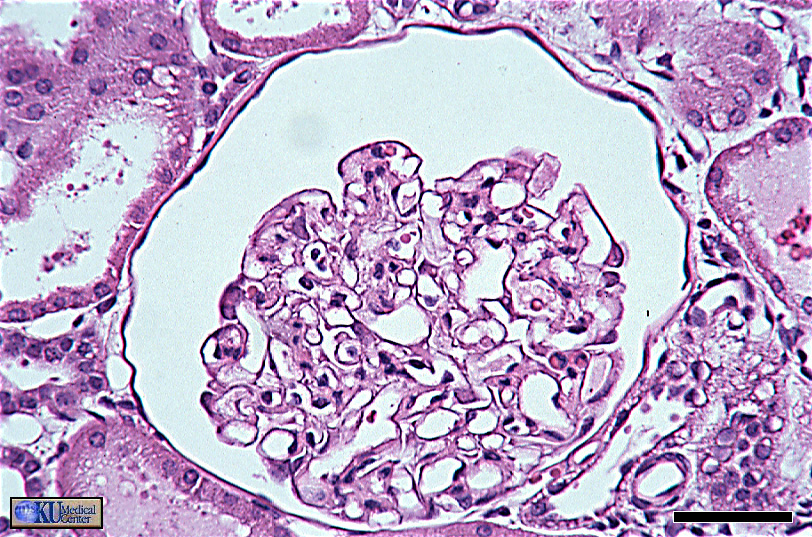
“Simple Squamous Epithelium (ET)”
the tissue of interest is the dark line of cells around the periphery of the large space.
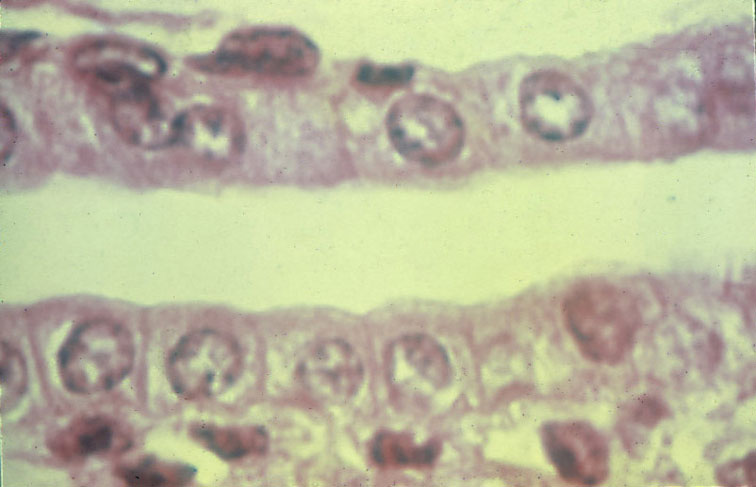
.
“Simple Cuboidal Epithelium (ET)”
longitudinal section of a kidney tubule. Cross section of a kidney tubule, cell shapes are "pinched" at the apical ends due to the curvature of the tube wall.
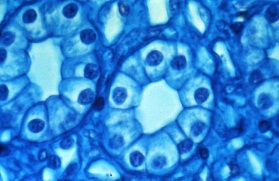
“Simple Cuboidal Epithelium (ET)”
Cross section of a kidney tubule, cell shapes are "pinched" at the apical ends due to the curvature of the tube wall.
.
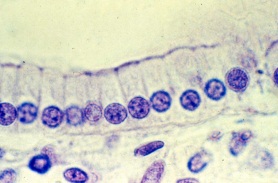
“Non-Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium (ET)“
the microvilli on the apical surface & width of cells relative to their height
.
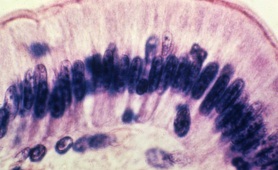
“Non-Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium (ET)”
the nuclei are more enlongated in this image. this oval shape is more typical of this type of tissue.
.
“Non-Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium (ET)”
.
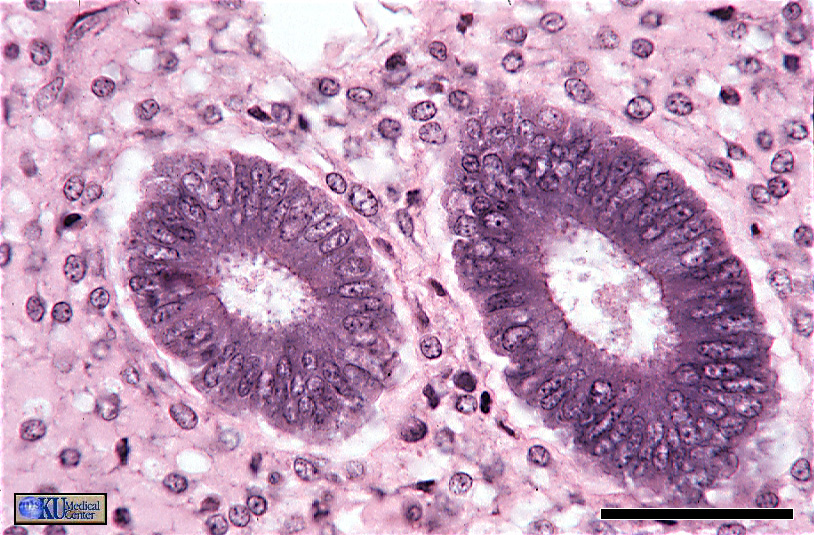
“Non-Ciliated Simple Columnar Epithelium (ET)”
cross section through uterine glands, shows some bunching/pinching due to curvature.
.
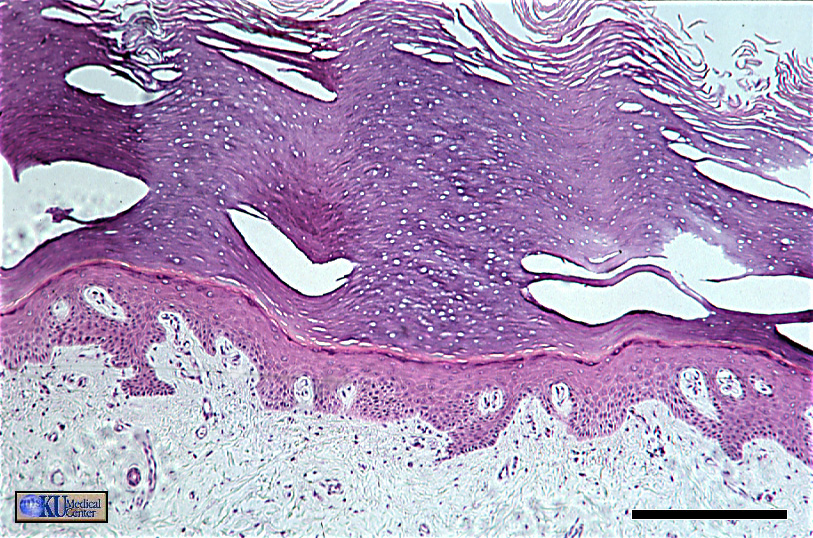
“Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium (ET)”
note the convoluted edge of the basal surface and the fraying of the kertinized apical portion of the tissue.
.
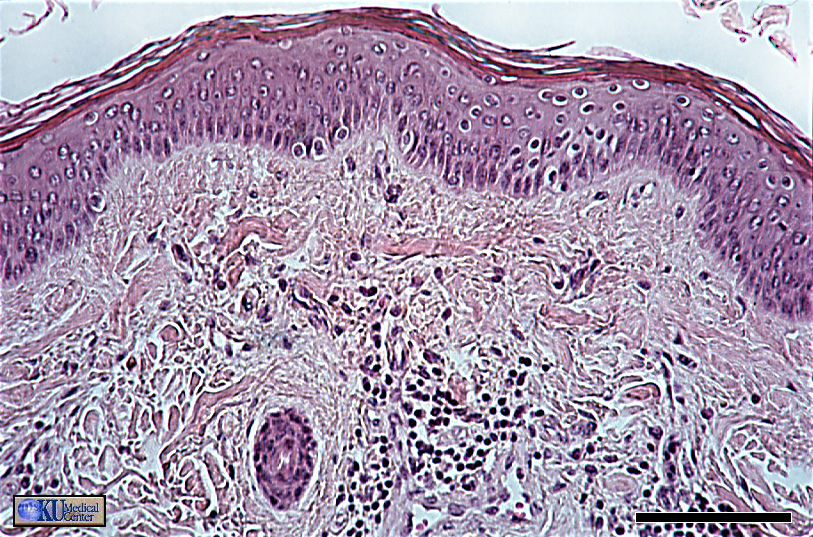
“Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium (ET)”
Easier to see the nuclei of the living cells in basal portion of the tissue. Note the fraying and slight color difference in the apical portion indicating keratization.
.
“Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium (ET)”
Greater thickness, particularly of the apical keratinized portion.
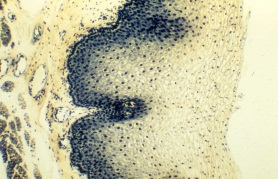
.
“Non-keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium (ET)”
Overall similar to keratinized version, but note the presence of live nuclei on the apical portion.
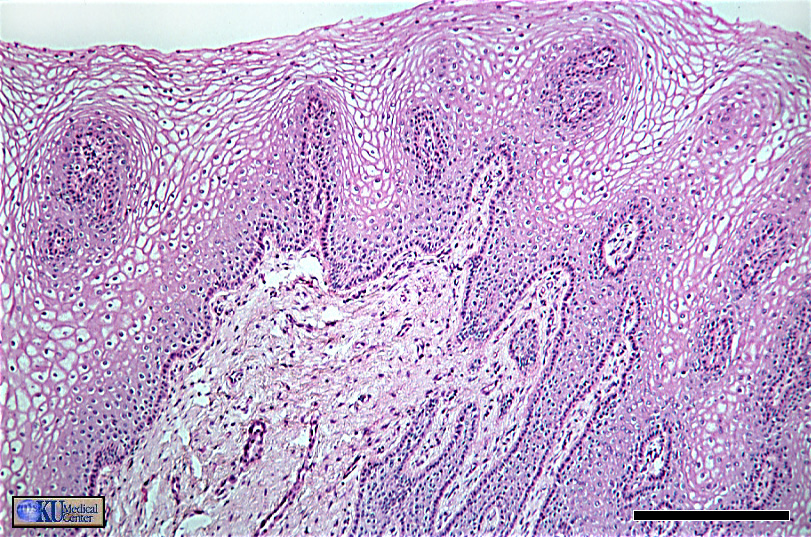
“Non-keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium (ET)”
more presence of nuclei in the apical portion.
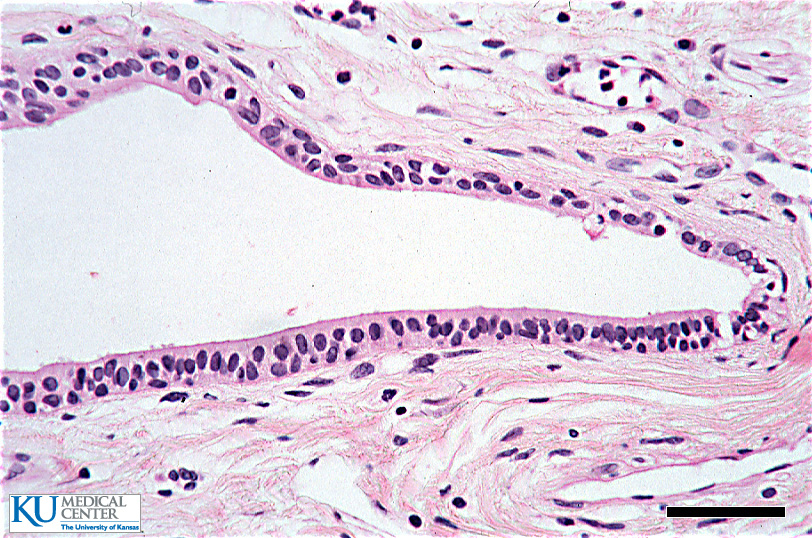
.
“Stratified Cuboidal/Columnar Epithelium (ET)”
A section from the wall of a sweet gland duct. The shape of the apical layer is more columnar in some areas.
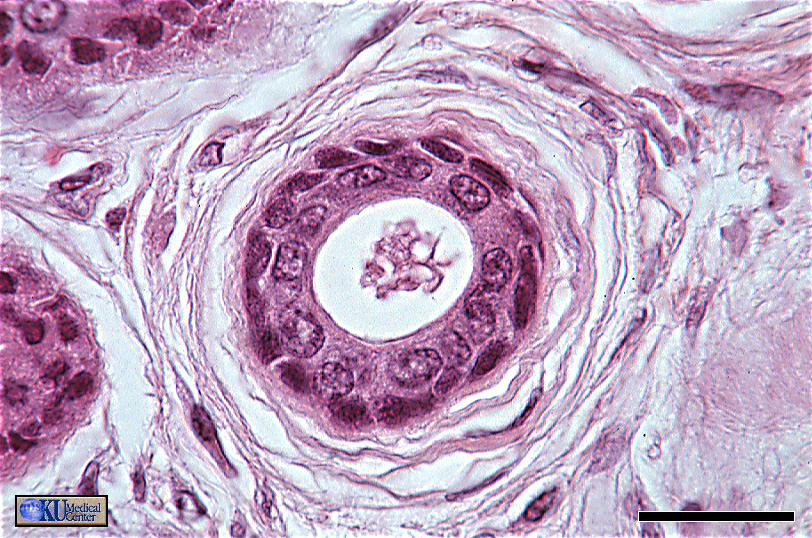
.
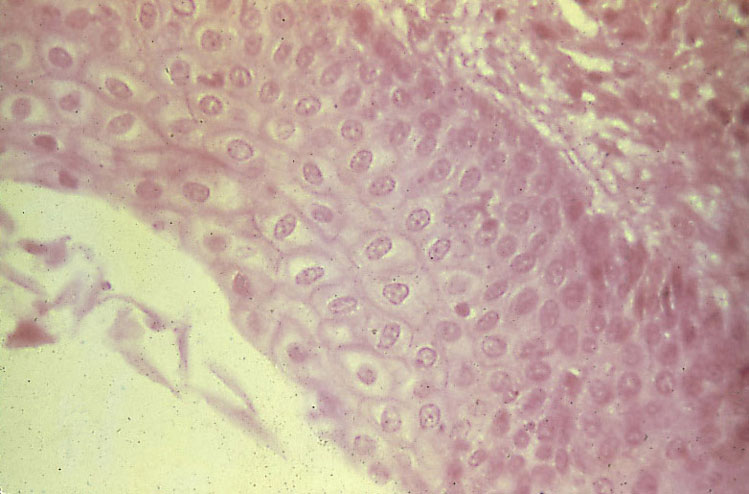
“Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium (ET)”
Cross section through the duct of a sweat gland. Note the difference in shape and color of the basal ans apical layers of cells; the basal layers consist of what are called myoepithelial cells.
.
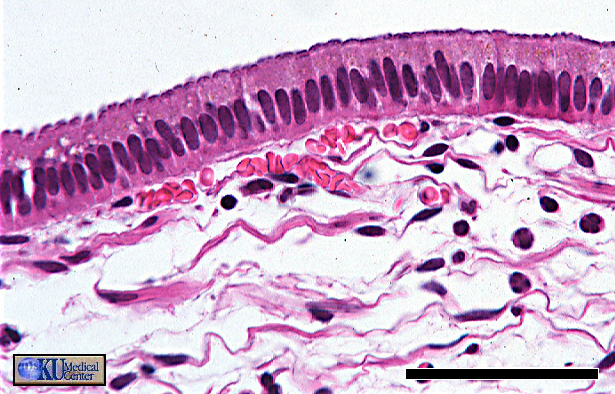
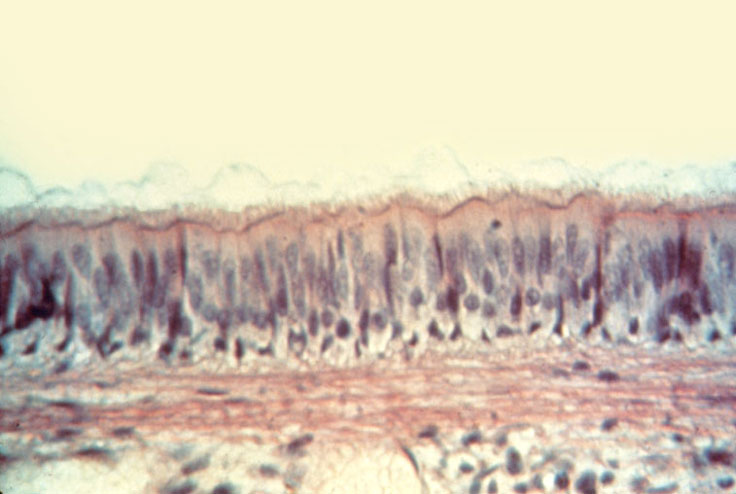
“Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium (ET)”
Note the seemingly multilayered arrangement of the nuclei, this is the result of cells of different heights. All cells in this tissue are attached to the basement membrane. Also note the long cilia on the apical surface extending into a layer of mucus.
.
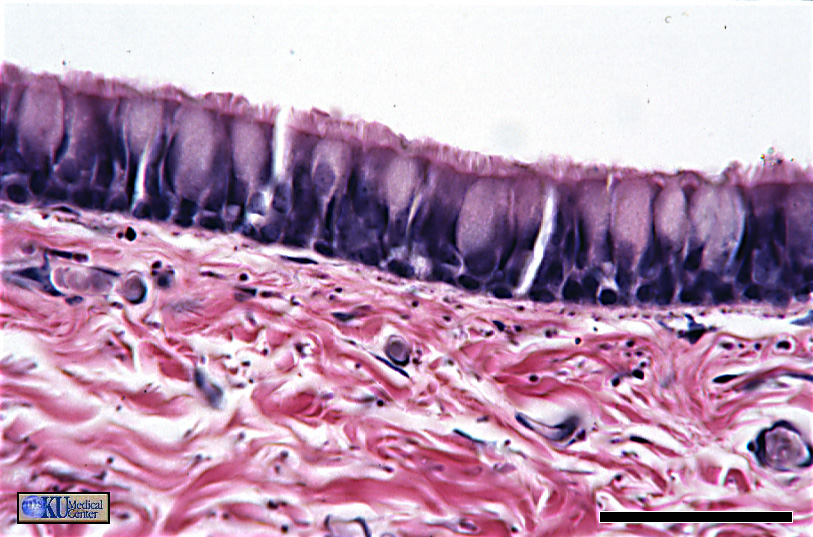
“Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium (ET)”
The cilia in this image are easier to see.
.
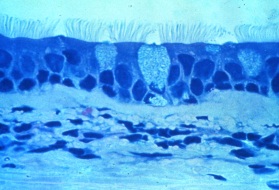
“Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium (ET)”
The pseudo-layering of the nuclei is really obvious in this image, as are the cilia and the presence of goblet cells.
.
“Transitional Epithelium (ET) (partially relaxed)”
In this state, the cells in the apical portion are allowed to relax into a cuboidal-to-spherical shape.
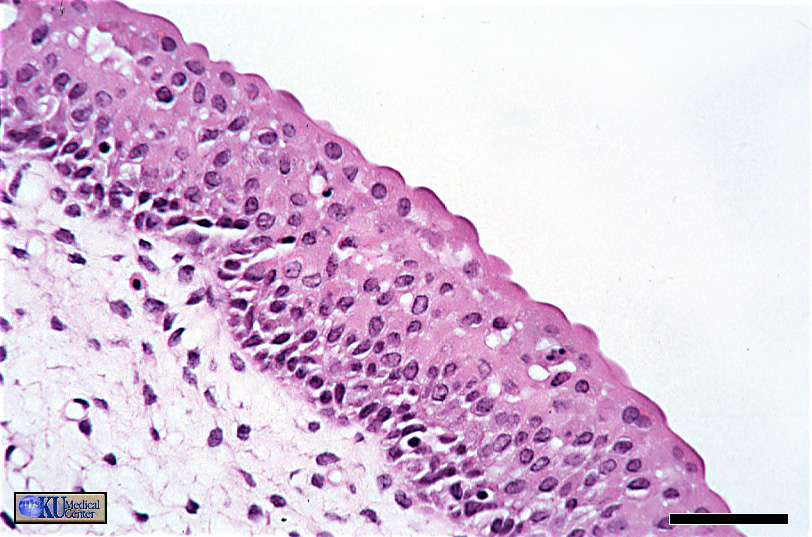
.
“Transitional Epithelium (ET) (relaxed)”
Note the shape of the cells in the apical portion and that the relaxation gives the apical surface a “fluffy” edge.