Bacteriology Lecture 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
why is diagnostic workup important?
select treatment
provides specfic pathogen in clinical syndromes
improves clinical care
helps to prevetn transmission, zoonosis, future infection
how are pathogens detected?
detect infecting agent
detect host response to infection
how are antibodies produced in the body?
primary response - small antibody production
secondary response - body produces substantial antibodies and are detectable
what is the path of infection and how are each stage detected?
entry of pathogen (Agent detection) —> dissemination (agent detection) —> colonization disease (Agent and Antibody detection) —> elimination (antibody detection)
what does the selection of type of diagnostic depend on?
nature of infectious agent suspected, host species, and the availability of tests
what are examples of detection methods used for agents or their components?
microscopic examination
bacterial culture
ELISA (direct detection of antigens)
PCR (detection of nucleic acids) MOST COMMON
how is the host immune response used to detect agent?
humoral immune response - antibodies
cell mediated immune response - cellular response - EX skin test
how are samples examined microscopically
examine wet smears or stained smears using light, phase contrast, or darkfield microscope
what are the benefits of microscopic examination?
cost effective
time effective
show number, morphologic characteristics seen
info on likelihood of infection and predominant organism
wh
what are the limitations of microscopy
low sensitivity
low specificity
some bact do not stain
what are gram neg
thin peptidoglycan layer
stains PINK
what is gram positive bacteria
thick peptidoglycan layer
stains PURPLE/BLUE
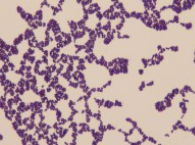
what type of bacteria is this
positive cocci
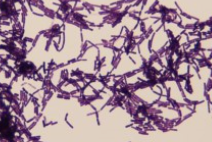
what type of bacteria is this?
gram positive rods
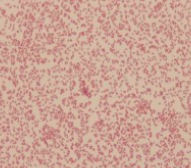
what type of bacteria is this
gram negative coccobaccilus
what does the acid FAST stain test for?
presence of mycolic acid
positive = pink
negative = blue
what are some limitations of culturing?
some bacteria do not provide timely and valuable info; obligate intracellular bacteria can not be cultivated in lab media
what do the culture methods depend on?
bacterial organisms vary in growth, need for oxygen, and nutrients; this changes the growing conditions
how is bacteria identified on the culture?
use of biochemical tests
semiautomated systems
MALDI-TOF - mass spectrometry
what is the main method of molecular detection
PCR - polymerase chain reaction - allows amplification and detection of DNA
what is the steps of PCR
DNA extraction; mix reagents with target DNA
thermocycling - denaturation
agarose gel electrophoresis
visualize under UV light
what is the process of real time PCR
uses labelled probes/fluorescent dyes; able to watch the reaction in real time
mix reagents with target DNA
thermocycling
data analysis
what is the relevance of the CT value in real time PCR
lower the CT value = more DNA present in clinical sample
how are antigen detection tests performed
utilizes specific antibody reagents to detect pathogens in clinical samples
clinical sample + antibody = detectable reaction
serconversion
antibody development after exposure to a pathogen or an antigen; there is a primary response and secondary response
how are antibodies measured?
antibody titer - measure of serum antibody level against an infectious agent
how are titer’s expressed?
expressed as the reciprocal of the highest dilution of serum that positively reacts in a specific test
EX - a titer of 1280 in a test means that the serum sample remains positive when diluted 1:1280
what are paired titers and what is the purpose?
titers determined at 2-4 week intervals during course of infection
2-4 fold increase in paired titer is suggestive of an active infection
How are titer results interpreted?
highest titer number = most diluted sample = highest antibody level
what is the role of a clinician for the diagnostic testing?
develop differential diagnosis absed on hx, symptoms, direct exam of samples
select appropriate samples, tests, collection, transport methods, and a quality lab
provide relevant history, signalment, vaccine and treatment
learn how to interpret results
what should occur if there is a doubt about sample collection and transportation?
call the lab
be aware of transportation safety and packaging regulations for public transport of dx samples and infectious substances
what is biosafety levels?
a risk assessment base on lab practices/techniques, safety equipment, and lab facilities to be used to minimize potential exposure to a biohazard for personnel
what does BSL 4 indicate?
highest level that deals with very infectious pathogens, requires highest level of biosafety