CO220 Final Exam Review
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Plumbum
The Latin word for plumbing
Water
Freezing point 32 degrees "F" & Boiling point 212 degrees "F"
Potable Water
Treated water from local treatment plants. Safe for human consumption.
Non-potable water
Not suitable for drinking and cooking.
Non-potable water usage
Flushing toilets, Washing vehicles, Sprinkler systems for lawns, & Dust control on construction sites.
Surface Water
Rain or snow that runs off the surface of the ground into streams, rivers and lakes.
Ground Water
Rain water that percolates through the soil and is trapped underground in the form of a aquifer or water table.
Impervious Layer
Layer made up of clay, rock and shale. A layer which water can't pass through.
Underground Stream
Horizontal flow of ground water that will follow path of impervious layer.
Percolation Process
Provides natural filtration of surface water to ground water.
Desalination
Process of removing salt contents from water provided by oceans.
Water Analysis
Chemical test and bacteriological testing of potable water.
Building Codes
Established and enforced by local municipality, regional area, national level and state level.
Upfeed System
Water distribution in a building by the use of available pressure from local watermains Booster pumps may be required to increase water pressure to upper floors or remote areas of the facility.
Downfeed System
Water distribution in a building by the use of gravity. Water is pumped and stored in roof top or elevated tanks.
Demand Load
The amount of water required for the operation of all fixtures in a building. (showers, sinks, water closets, hose bibs & washing machines.
Fixture Units
Water demand for each individual plumbing fixture in a building.
Sanitary Sewer Drainage (Waste Disposal)
Disposal of waste matter both fluid and organic. Water and gravity is used to transport waste through sewer pipes.
Domestic Sewage
Sewage from residential and commercial facilities.
Soil Stack
Human waste from water closets that is transported through a stack.
Waste Stack
All waste except for human waste that is transport through a stack.
Vents
Allows gasses in the sewage drainage system to discharge into outside air. Reduces air turbulence in the system.
Traps
Holds a quantity of water to form a water seal or trap seal. Installed at each fixture.
Storm Sewer Lines
Directs surface rain runoff from roofs and paved areas away from building foundations to nearby creeks, streams and lakes.

Storm Drain Pollution
Stormwater washing off pollutants and chemicals from the land, roads, building rooftops, lawns, construction sites, parking areas and driveways
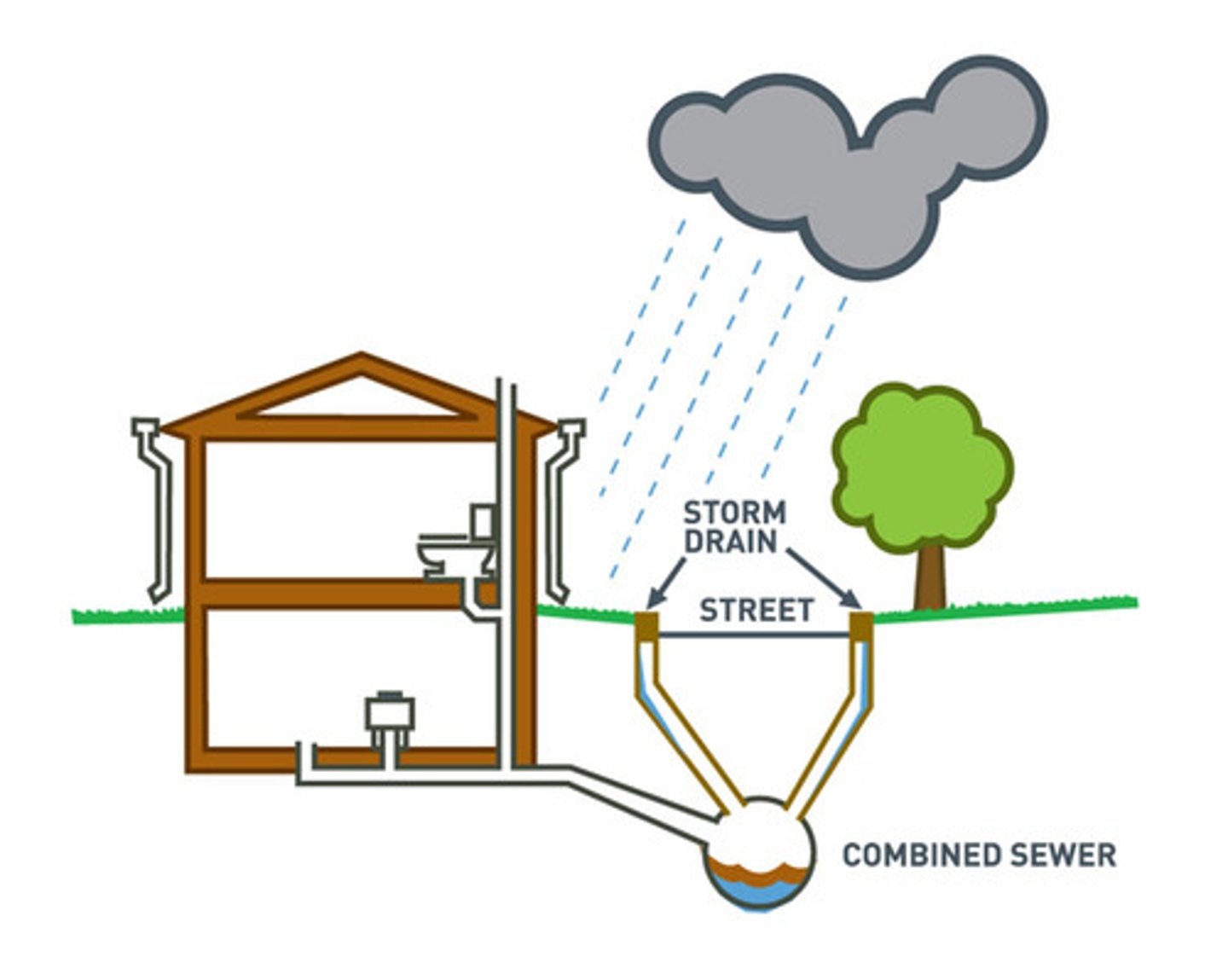
Sanitary Sewers
A sewer that carries raw sewage (liquid or waterborne waste from plumbing fixtures).

Combined Sewer Lines
Combination of Storm and Wastewater. Creates an excess demand load for sewage treatment plants.
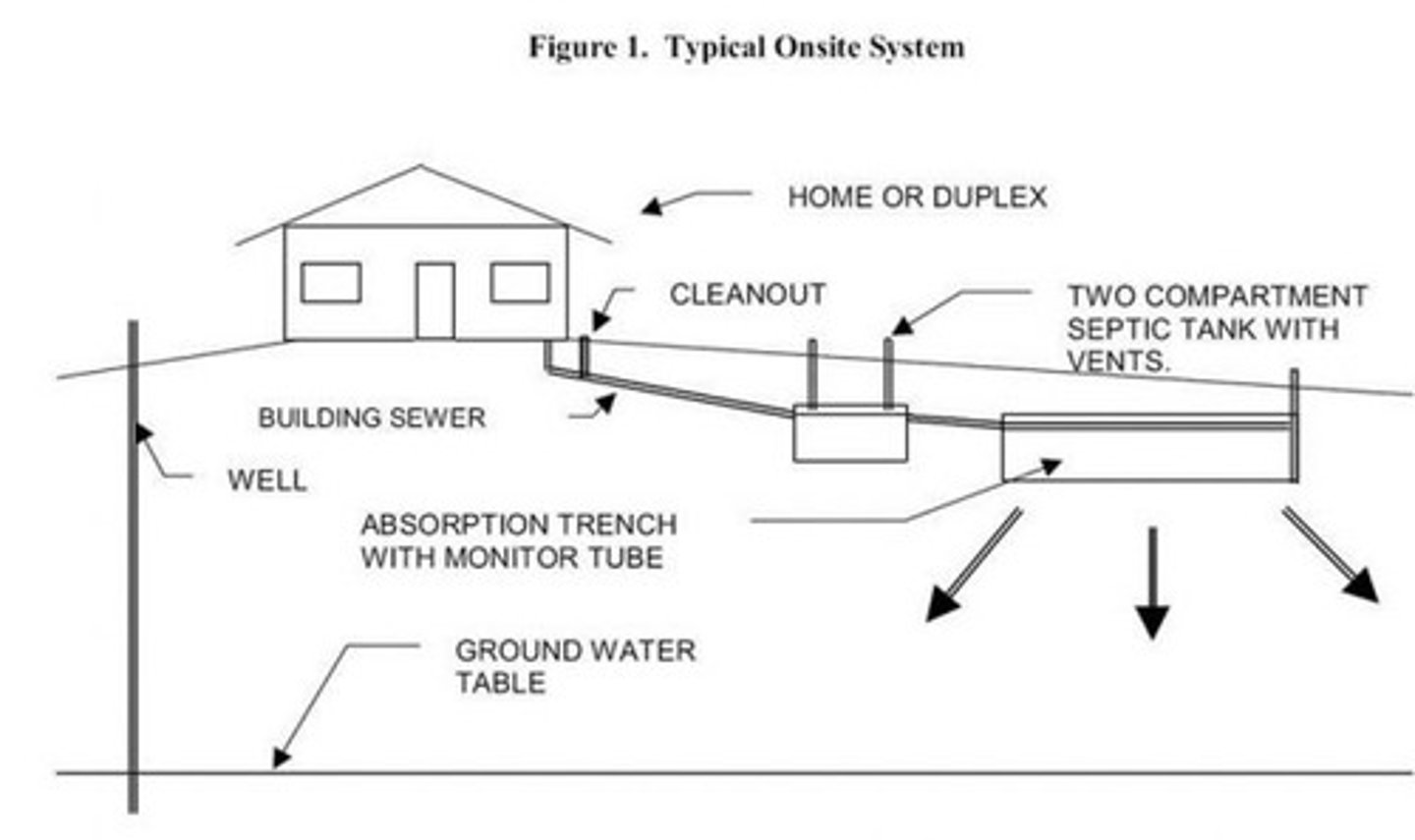
Conventional Septic Components
Septic Tank, Distribution Box, Leach Field & PVC Pipe.
Percolation Test
Analysis of horizontal and vertical movement of water through the pores of the soil.
Percolation Test Procedures
Dig 36" deep hole, add 2" of gravel at bottom, presoak, pour clean water to 6" depth, Observe and record water drop, Repeat test, done
Test Pit
Soil Evaluation of existing soil layers.
Test Pit Evaluation Factors
Soil layer thickness, texture, color, odor, Depth of water, Depth of bedrock,
Water Usage Data
Existing design flow rate information for the design of septic systems.
Performance Tables
Design Criteria for new septic systems.
Domestic Water Composition
Toilet, Laundry, Bathing, Sinks
Electrical Code for New York State
National Electrical Code (NEC)
120/240 VAC, 1 phase - 3W System
Most common residential electrical service.
208Y/120 VAC, 3 phase - 4W System
Small Commercial Buildings
System Voltage
Target voltage entering the service panel.
Utilization of Voltage
Accounts for anticipated voltage drops on branch circuit conductors.
Line Voltage
Measures voltage at an outlet or connection.
Maximum Voltage
Highest voltage to which a wiring device can be exposed.
Series Loop System
System is supplied by a single pipe for both supply and return water. Convector units can't be turned off. Limited control of heat to separate rooms.
One Pipe System
Single pipe established around building perimeter. A percentage of hot water is diverted to each independent convector and then returned to the supply line. Convectors can be controlled separately.
Two Pipe System
Hot water supply is kept separate from returned water passing through convector unit. Separate Supply and Return pipe. Convector units can be controlled separately.
BTU
British Thermal Unit per hour
MBH
Thousand British Thermal Unit per hour.
Forced Air Systems
Use of heated and cooling coils within unit. Circulates outdoor/returned air from a central unit through supply ducts.
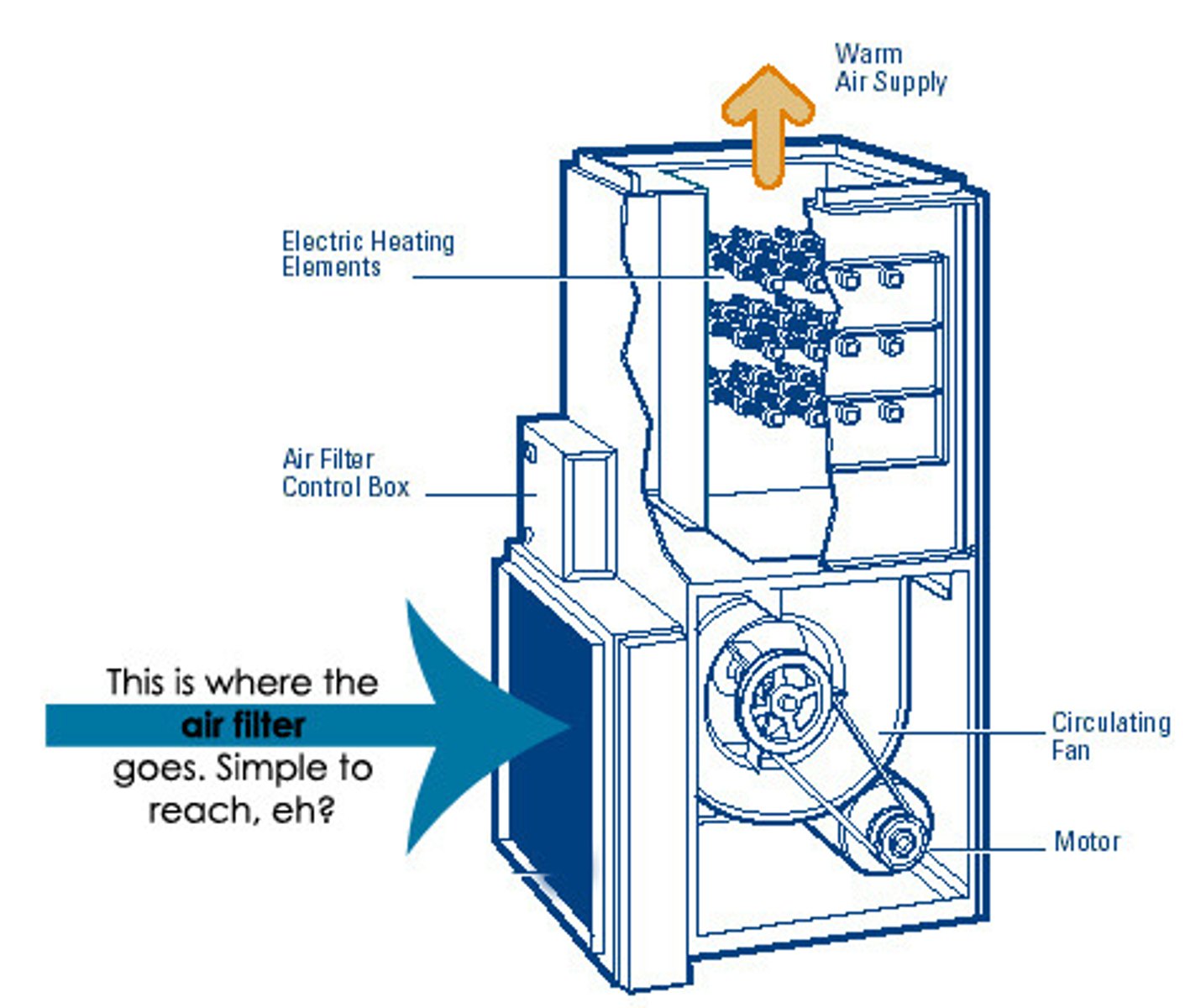
Supply and Return Ductwork
Commonly made from galvanized steel. Ducts located in a heated space do not require insulation. Ducts located in an unheated space require insulation.
Air Plenum
No ductwork required. ceiling area is used as an air return duct. Typically located in corridor areas.
Turning Vanes
Directs air flow smoothly around a corner or bend in ductwork. Reduces vibration noise caused by air turbulence.
C-Value
Measures materials ability to conduct heat.
R-Value
Measures heat flow resistance in relationship to material thickness.
U-Value
Heat flow resistance for entire assembly of walls, floors and ceilings.
Surface Emissivity
Non reflective or reflective value of the materials.
Infiltration
Air leakage between building materials. As wind velocity increases so does the amount or air leakage into the building.
A.S.H.R.A.E.
American Society of Heating, Refrigerating & Air Conditioning Engineers.
H.V.A.C.
Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning
Natural Gas
Heating fuel distributed by cost per cubic foot.

Oil
Heating fuel distributed by various weights and grades per gallon.

Heat Loss
Loss of heat from a building to the surrounding air. Measured in BTU'S.
Transmission
Loss of heat from a conditioned space to an unconditioned space.
Ventilation
Introduction of fresh air into a building envelope. Percentage of air based on activity and occupancy.
Resistance
Flow of heat through building materials.
Heavier/Dense materials (concrete & masonry)
Less resistance and lower "R" values.
Lighter/Less Dense materials (wood & insulation)
More resistance and higher "R" values.
British Thermal Unit (BTU)
Unit of energy. Amount of heat required to raise the temp. of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.

Electricity
Heating fuel distributed by Kilowatts

Heat Transfer
Heat always moves from a warmer place to a cooler place.
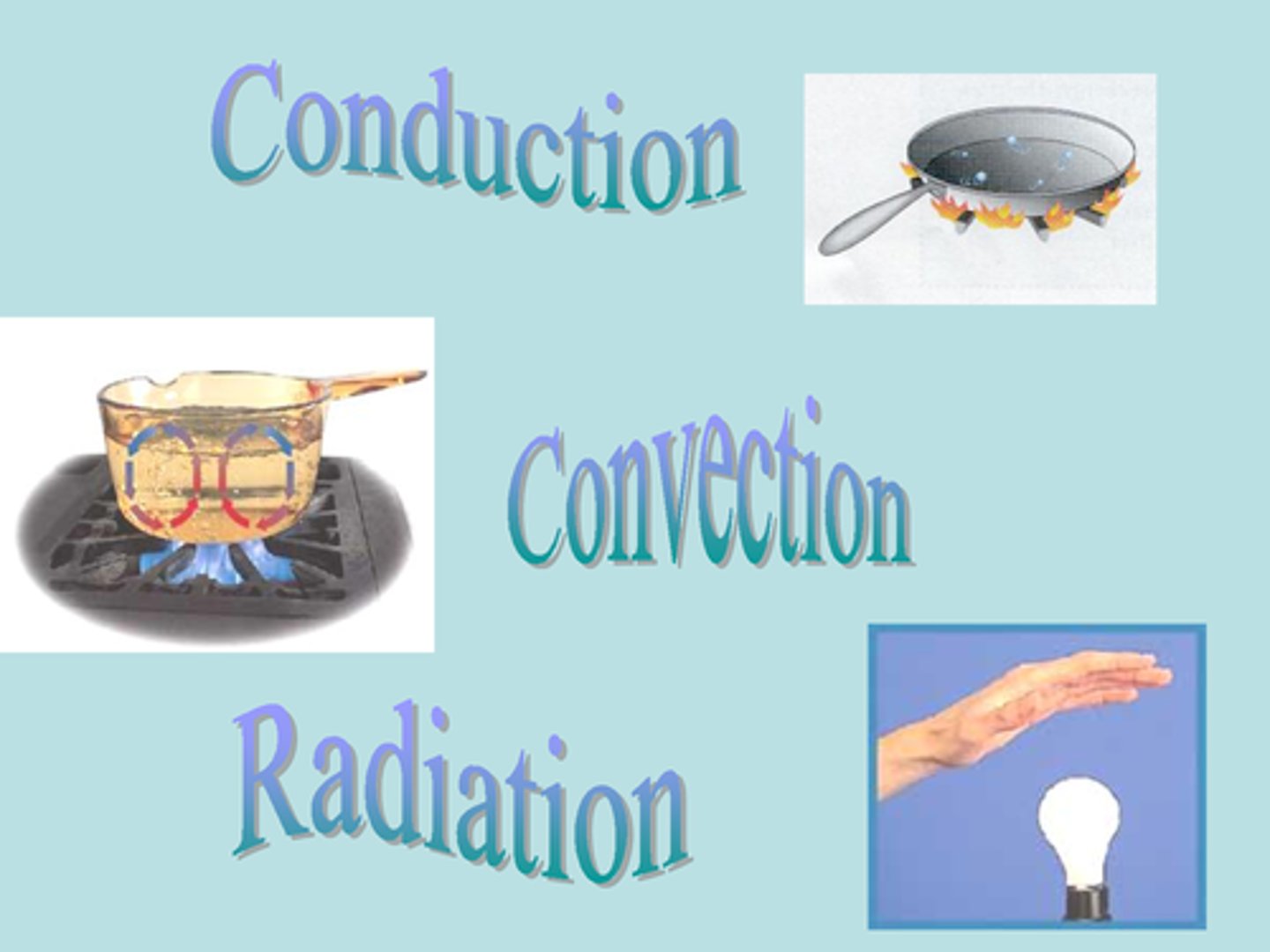
Conduction
As you heat metal, the particles vibrate. The vibrations are passed along the metal and so is the heat.
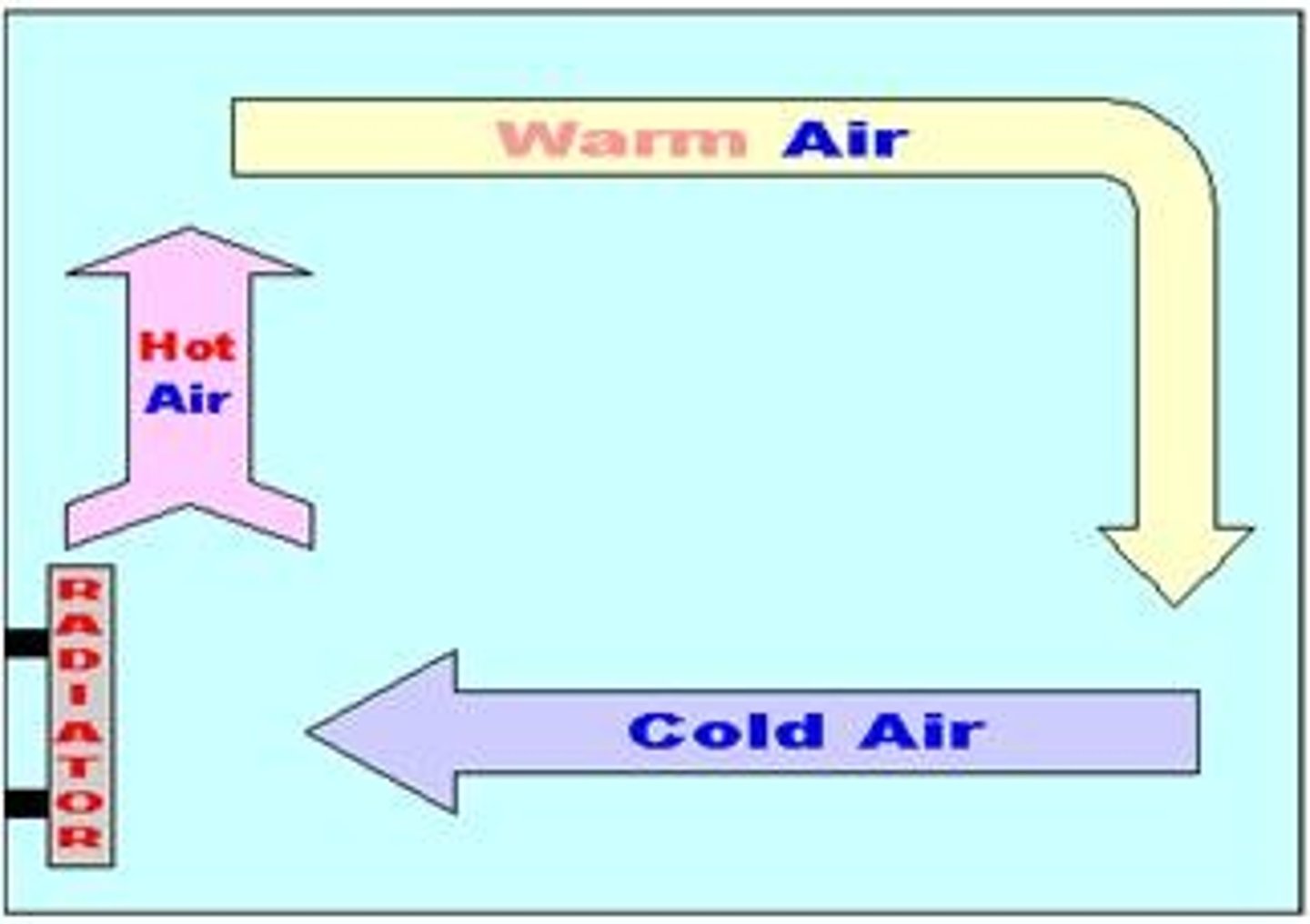
Convection
As the body gives off heat, it flows to the surrounding cooler air. Warm air moves upward and cooler air is pulled behind it.
Radiation
Heat flows from a hot surface to a cold surface. No air movement is required to transfer the heat.
Evaporation
Heat is removed from the surface causing the surface to cool. (Removing heat from the body)
Greatest environmental impact on a building facade
Solar Radiation
Cistern
A collection tank used to hold surface water for water demand loads in facilities.
Natural Filtration
Ground water requires lass treatment than surface water when making water potable due to the percolation process which provide natural filtration.
Static Head
Pressure required to push water vertically.
Booster Pumps
Used in large facilities to increase water pressure losses from the local water mains.
Water Table
The depth of all wells is determined by the depth of the water table or aquifer.
Water Closet
Toilet
Water Hammer
Water shock - noise/vibration caused by water pressure surges in water supply systems.
Department of Health
Requires that all treated water must be tested throughout different intervals in the year to determine is the water meets state requirements.
Btu's
Heat loss and heat gains are measured.
Sanitary Sewers & Septic Systems
Bacteriological water analysis provides a indication of coliform organisms in the quality of water due to contamination from sewage seepage.
Insulation
Ductwork located in a condition space/heated space does not require insulation.
Heating Device Ratings
Amount of heat (BTU's) given off in a 1 hour period.
Resistance Values of wall systems
Surface position and orientation effect heat loss calculation.
Comfort Chart
Designated by A.S.H.R.A.E. that determines temperature design ranges of variable conditions in a space.
Convector Unit
Heat is transferred through convection. Air flow passes by a heat transfer surface. Example: aluminum fins over copper piping.
Three Natural Processes Heat is transferred
Evaporation, Convection & Radiation
Factors used in calculation heat loss
Wall, ceiling & floor assembly types, Geographical area, Wall, ceiling & floor surface area, Amount and size of doors & windows.
Heat Loss control in a building
Type of insulation used, Thickness of insulation used, Building materials with more heat flow resistance, Sealants & Caulks, Doors & windows with more heat flow resistance, Weather stripping, Thermal barriers, Tyvek building wraps, 6 mil polyethylene moisture barriers.
Septic System Layout
Building>Septic Tank>Distribution Box>Leach/Absorption Field