Vaginal/Vulvar Medicine Study Terms & Definitions
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
most acute complaints for patients needing cervical, vaginal, or vulvar care are related to:
- dermatology ("itchy bumps")
- discharge ("smells like fish")
- intercourse ("it hurts")
- position ("something's coming out")
how are our pelvic organs normally supported?
by a network of muscles, fascia, nerves, & ligaments
- damage to any of these can result in weakening of support to pelvic organs
although many are asymptomatic, what may loss of pelvic support cause patient to feel?
uncomfortable:
- pelvic pressure
- bulge
- backache
- dyspareunia
- urinary or bowel changes
cystocele
herniation of bladder wall into anterior vaginal wall
- sx: urinary incontinence, frequency, urgency or retention
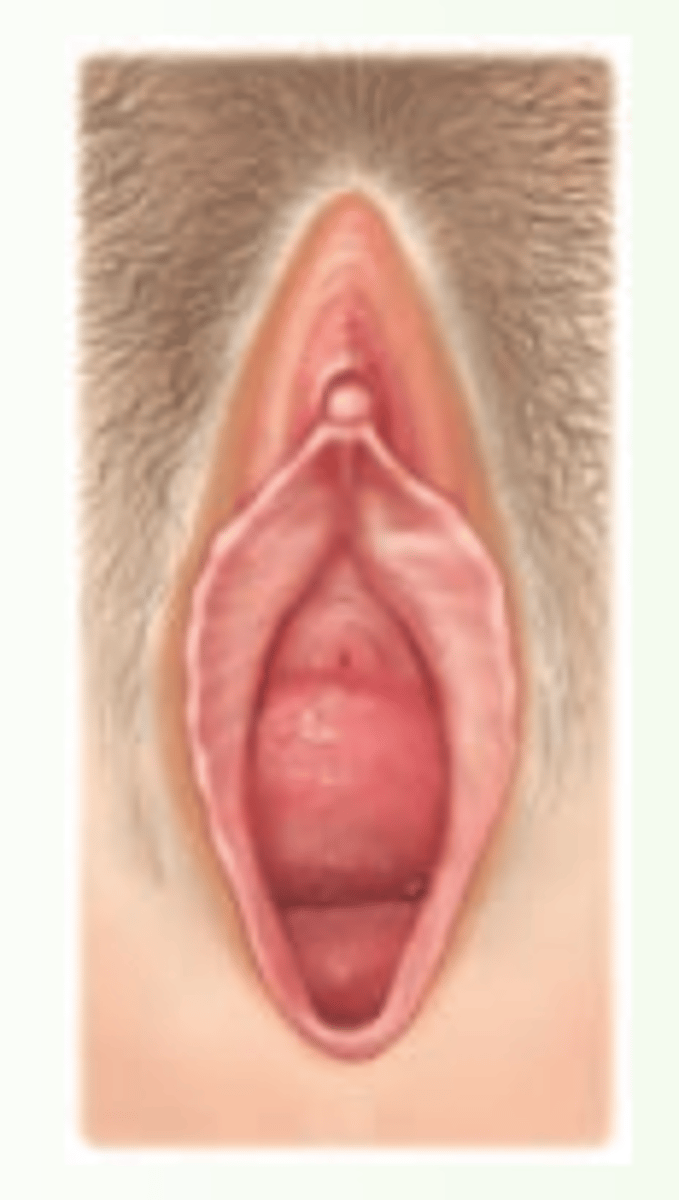
rectocele
herniation of rectum into posterior vagina
- sx: fecal incontinence, constipation, painful or incomplete defecation
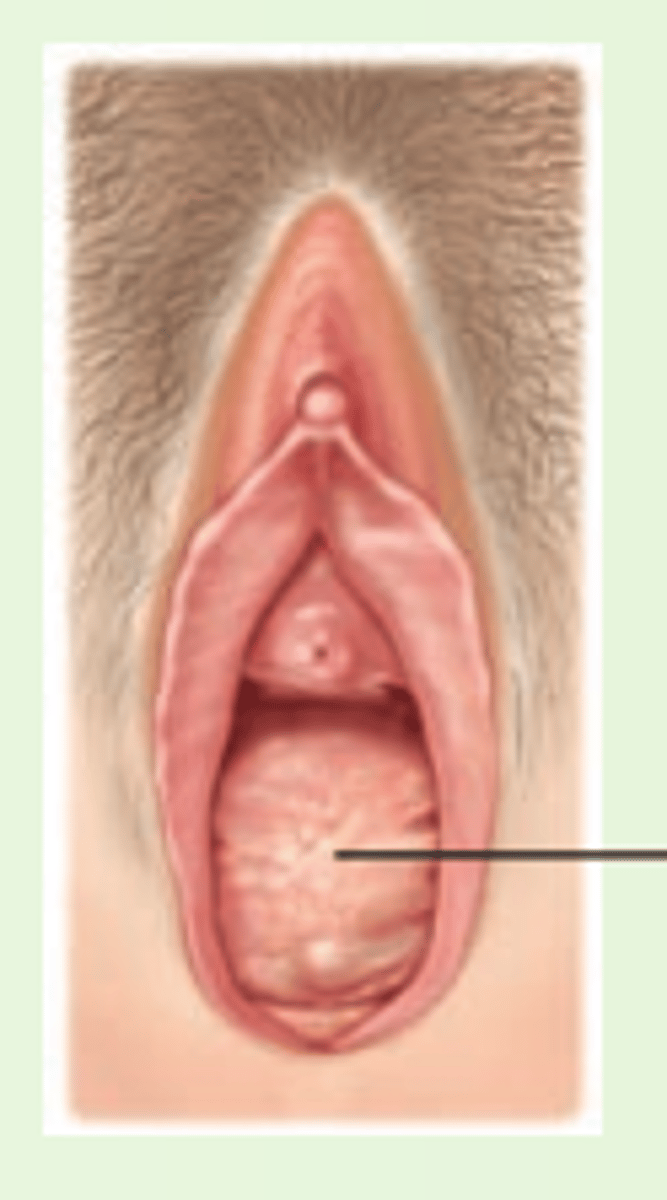
prolapsed uterus
structures holding uterus relax & uterus moves down vaginal vault
urethrocele
sagging of urethra causing bulge in anterior vagina
- rare
enterocele
hernia of small intestine into vaginal vault
- rare
when evaluating disorders related to the loss of support to pelvic organs, view the vagina while the patient ___________________.
strains or coughs
- w/o speculum
stage 0 prolapse =
normal anatomic position
stage 1 prolapse =
halfway to hymen or in upper 2/3 of vagina
stage 2 prolapse =
to the hymen or introitus
stage 3 prolapse =
past the hymen, protrudes outside the vagina
stage 4 prolapse =
entire structure outside the vagina
- maximum descent
how are disorders related to loss of pelvic organ support treated?
depends on extent of prolapse
- weight loss & relief of constipation
- pelvic floor muscle training (kegels, home excerises, PT)
- pessaries (all stages; refer!)
- surgery
do pelvic floor exercises correct the prolapse?
no - only improves sx of incontinence
when may surgery be indicated for a prolapse?
stage 3 or 4 & those w/ incontinence
imperforate hymen
hymen completely encloses the external orifice of the vagina
- may present at puberty w/ lack of menstruation (primary amenorrhea) & cyclic pelvic pain (due to accumulation of menstrual flow behind it)
- tx: surgery
transverse vaginal septum
layer of tissue divides the upper & lower vagina
vaginal atresia
lower vagina does not develop
- vagina appears like a dimple in thick tissue
vaginal (mullerian) agenesis
no development of vagina or uterus in utero
epidermoid cysts
blocked hair follicle or pouch-like cyst in dermis, lined w/ epithelial cells, filled w/ thick, yellow-white keratin
- small, firm, skin colored or whitish nodule w/ punctum (small opening to skin surface)
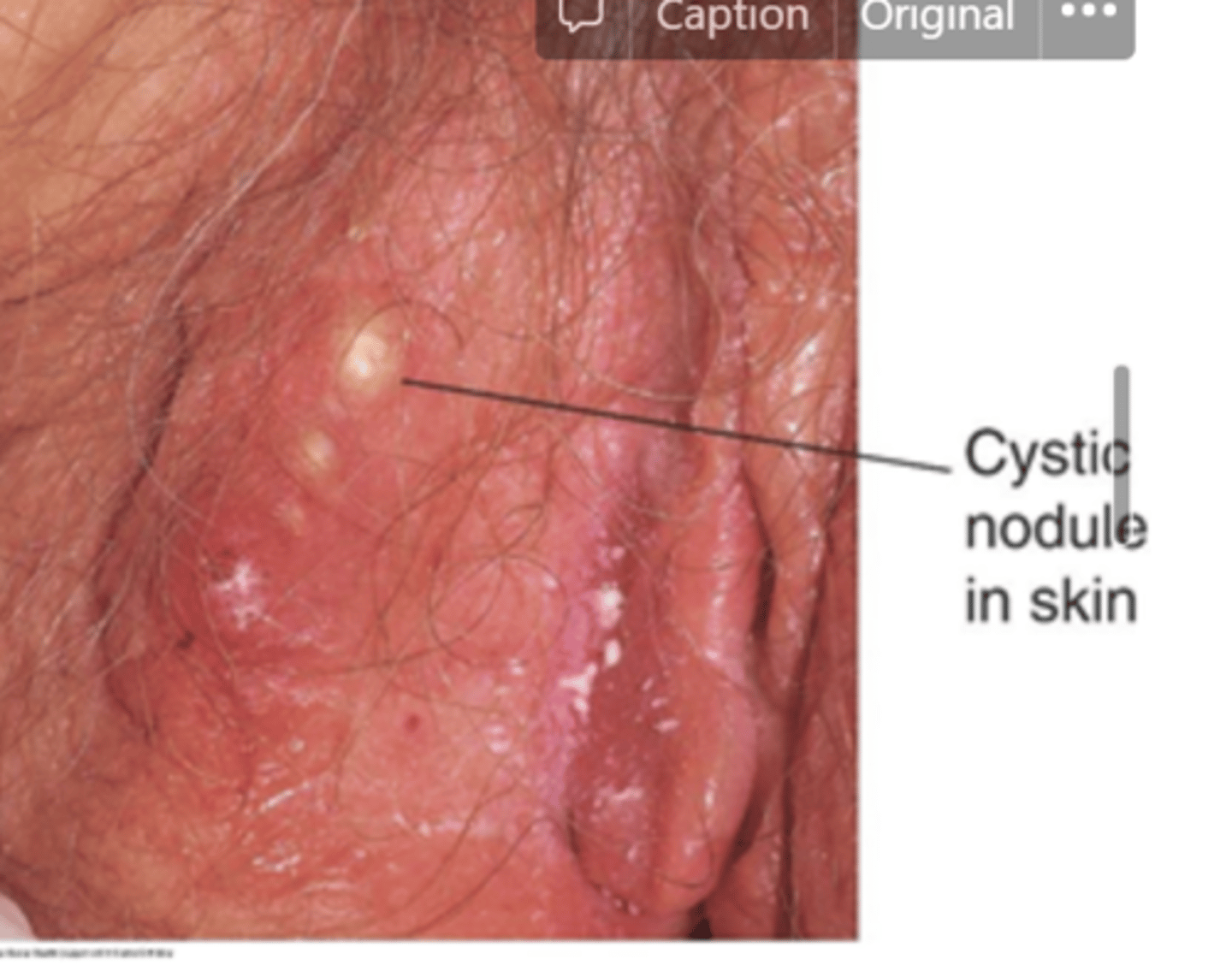
where are epidermoid cysts most commonly found?
labia majora
bartholin's duct cyst/abscess
blockage of bartholin gland
- if infected, abscess forms
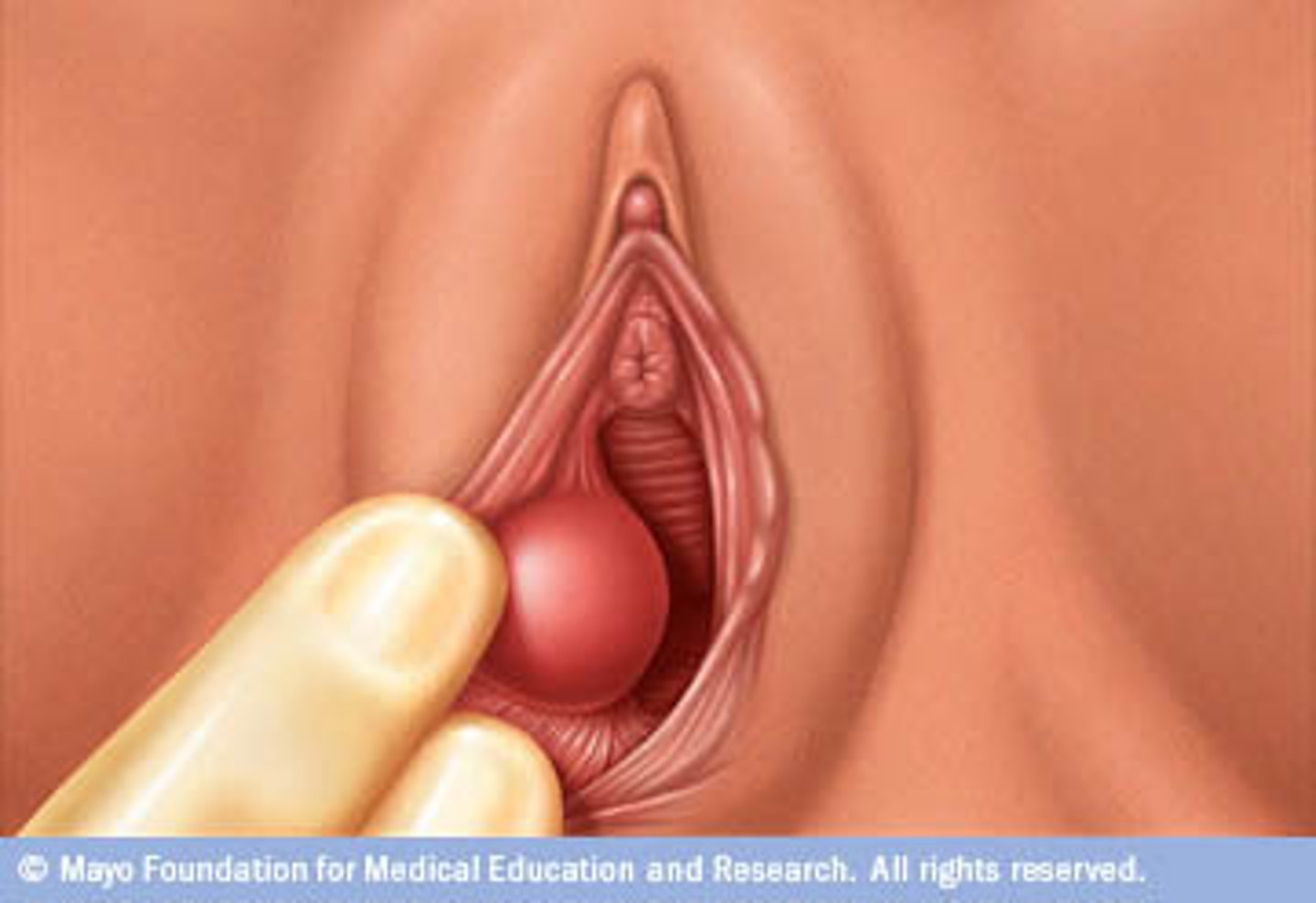
if a bartholin's duct cyst becomes infected & an abscess forms, what are the treatment options?
I & D; however, recurrence is likely
- better option = aspirate, replace void w/ 70% alcohol, wait 5 mins, then aspirate alcohol (sclerotherapy)
if bartholin's cysts/abscesses are recurrent, how should they be treated?
refer for surgical procedure
what should you do if a bartholin's cyst appears for the first time in a woman > 40 y/o?
biopsy to r/o rare bartholin's carcinoma
lichen sclerosus (et atrophicus)
chronic derm disorder of unknown etiology
- considered precancerous lesion to squamous cell carcinoma
- hypopigmented, atrophic, light or shrunken skin w/ pruritic/burning sensation
- tx: topical steroids; refer to dermatologist!
fistula
abnormal passage between 2 organs; may be a hole between:
*bladder & vagina
*urethra & vagina
*rectum & vagina
- results in urine or stool passing through vagina uncontrollably
- rare in US; common in developing countries
apocrine sweat gland cysts
blocked sweat glands
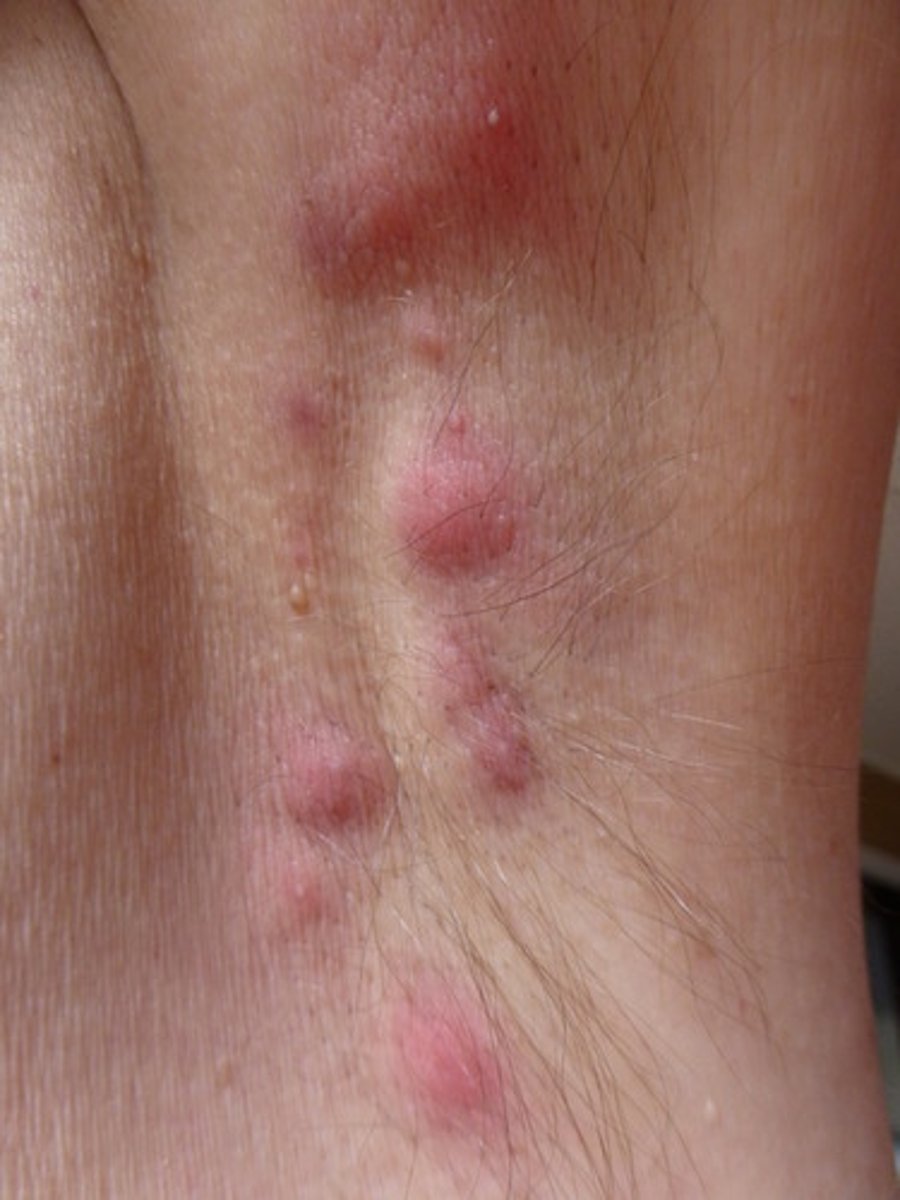
hidradenitis supprativa
multiple blocked sweat glands, resulting in small abscesses
- requires antibiotics
the primary stages of several diseases usually present w/ an ___________________ on the genitalia.
ulcerative lesion
what is the pathogen associated w/ syphilis?
treponema pallidum
what is the primary stage of syphilis?
painless chancre at the site of inoculation
if a pregnant woman becomes infected w/ syphilis, can the fetus become infected?
yes - via the placenta (vertical transmission)
how is syphilis treated?
penicillin
what is chancroid caused by?
haemophilis ducreyi
- uncommon in US
what is lymphogranuloma venereum?
chlamydial infection in the lymph system w/ painful enlargement of lymph nodes
how is lymphogranuloma venereum treated? (chlamydia infection in the lymph)
doxycycline x 21 days
how does genital herpes often present?
w/ painful, burning vesicles that evolve into ulcers (on a red base)
w/ genital herpes, lesions take _____ wks to heal
1-3
w/ genital herpes, lesions take 1-3 wks to heal; however, infection is ________.
lifelong
what causes genital herpes?
herpes simplex
- transmitted through direct contact
w/ genital herpes, the ________ outbreak tends to be more severe & can include constitutional malaise
primary
2 multiple choice options
w/ genital herpes, ________ outbreaks tend to be less severe & are usually limited to skin lesions
recurrent
2 multiple choice options
HSV-1 occurs _____ the waist
above
1 multiple choice option
HSV-2 occurs ______ the waist
below
1 multiple choice option
although HSV-1 typically occurs above the waist, can it be below the waist?
yes, but HSV-2 does NOT seem to go above the waist
3 multiple choice options
what is the gold standard for diagnosis of genital herpes?
PCR swab
- viral swab also possible
both PCR & viral swabs require ______ lesions.
active
2 multiple choice options
in genital herpes, if there are NOT any active lesions, what can be done?
serologic testing
- uncommon
can HSV be cured?
no
1 multiple choice option
what medications are available to speed the healing of lesions & reduce viral shedding for genital herpes?
- acyclovir
- famicyclovir
- valacyclovir
what can be done for patients w/ frequent herpes outbreaks &/or to reduce transmission?
suppressive therapy
- continual daily dosing of one of the aforementioned meds
is HSV contagious when there are no lesions present?
YES! (condoms are 70% effective @ preventing transmission)
1 multiple choice option
what is recommended for a pregnant woman w/ active lesions at the time of delivery?
c-section
3 multiple choice options
HSV-2 increases risk of _____ infection
HIV
genital warts (condyloma acuminata)
flat-surfaced, rough, fleshy lesions (may or may not be pedunculated)
- caused by HPV (which is also associated w/ cervical cancer)
- dx: through PE w/o labs
- tx: excision, cryotherapy, topical trichloroacetic acid, etc w/ weekly f/o; self-tx w/ rx creams (Aldara & Condylox) w/ monthly f/u
are genital warts an indication for cervical HPV testing?
NO
1 multiple choice option
cervical cancers are typically associated w/ HPV serotypes 16 & 18. which serotypes are genital warts associated w/?
6 & 11
does the HPV vaccine (Gardasil 9) protect against the serotypes (6 & 11) associated w/ genital warts?
YES
1 multiple choice option
bacterial vaginosis
overgrowth of normal vaginal bacteria
- polymicrobial
- s/s: grayish, watery, or thin vaginal discharge that is profuse but nonirritating; malodorous
although bacterial vaginosis is polymicrobial, what is the dominant species?
gardnerella vaginalis
is bacterial vaginosis an STD?
no, but incidence does increase w/ multiple sex partners (or a new partner)
1 multiple choice option
other than multiple (or a new) sexual partner. what are other risk factors for bacterial vaginosis?
- douching
- cigarette smoking
- sex between women
- lack of normal vaginal flora
what is normal vaginal flora?
lactobacillus
what tests can be done to diagnose bacterial vaginosis?
- whiff test
- wet mount (microscopic eval)
- pH eval
what is the whiff test?
detection of a fishy odor when a small sample of discharge is placed on a slide w/ potassium hydroxide (KOH)
- odor may be noticeable w/o this as well
what is a wet mount (microscopic eval)? what will it show if bacterial vaginosis present
small sample of discharge is placed on a slide w/ saline solution
- "clue cells" will be visible under microscope
what are "clue cells?"
vaginal epithelial cells covered w/ bacteria
- seen on microscopic eval of discharge associated w/ bacterial vaginosis
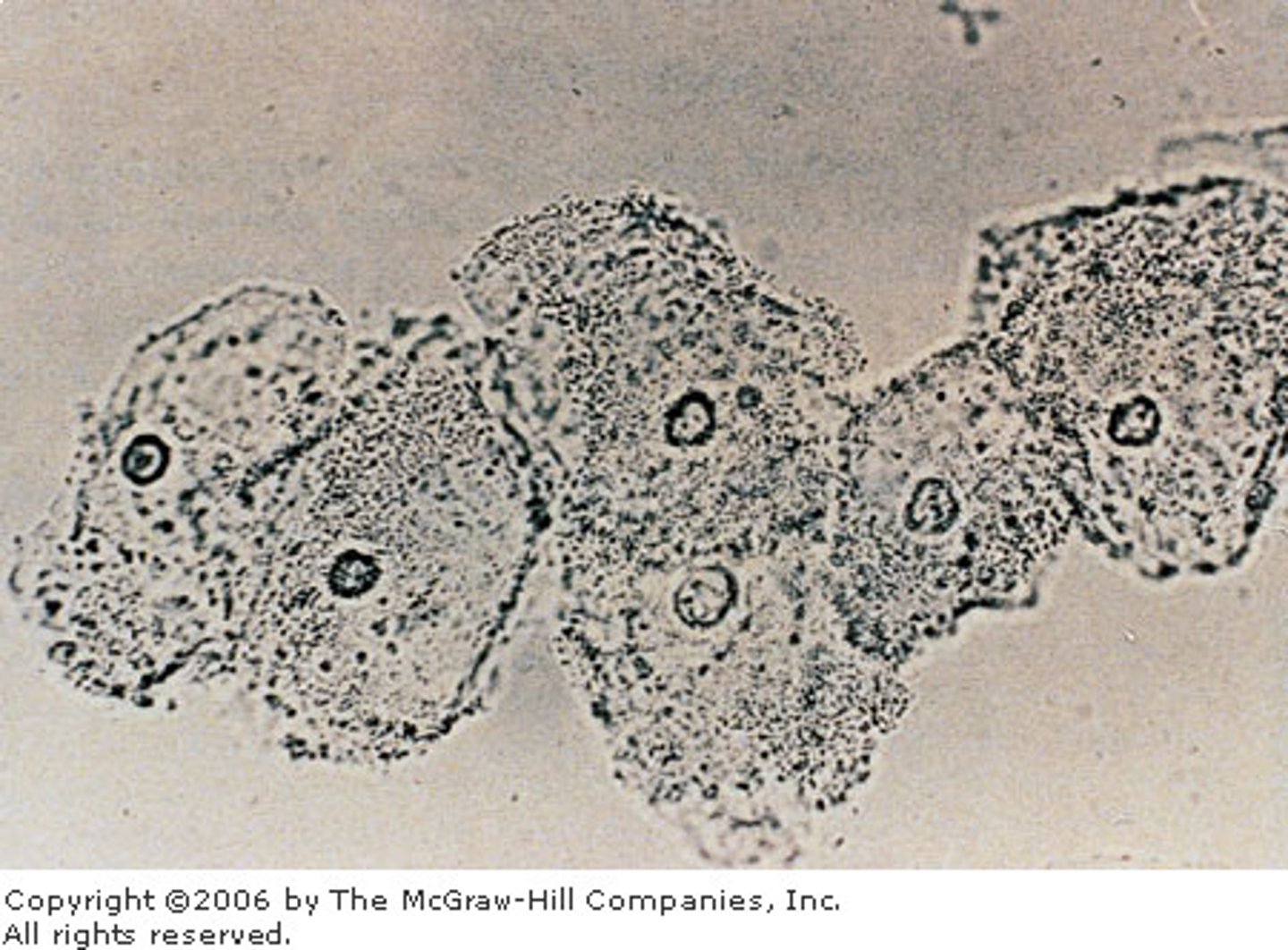
what will the pH of the vaginal discharge associated w/ bacterial vaginosis be?
> 4.5
what is the name of the criteria which can be used for diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis?
Amsel criteria
what is the Amsel criteria?
pt presents w/ 3 out of 4:
- discharge
- + whiff
- increased pH
- + clue cells
how is bacterial vaginosis treated?
metronidazole (500 mg tab po bid x 7 days) or clindamycin (300 mg tab po bid x 7 days)
what are the other options for bacterial vaginosis treatment?
- clindamycin cream 2%
- metronidazole gel 0.75%
how do you treat a patient who has a recurrence of bacterial vaginosis infection w/i 1 yr of being treated for a previous infection?
w/ abx not initially used
- give longer course
what is candidiasis (yeast infection) caused by?
candida albicans
what are possible sx of candidiasis?
- pruritus
- burning
- dysuria
- dyspareunia
- vulvar edema
- erythema
- thick/white/curdlike discharge
if a woman presents w/ dysuria, but her UA is normal, what should you think about?
possibility of yeast infection
what do predisposing factors of a candida infection include?
- recent use of broad spectrum abx
- DM
- decreased immunity
how can candidiasis be diagnosed?
- KOH
- wet mount
when discharge assoc. w/ candidiasis is placed on a slide w/ KOH, what will it reveal?
branching hyphae & spores
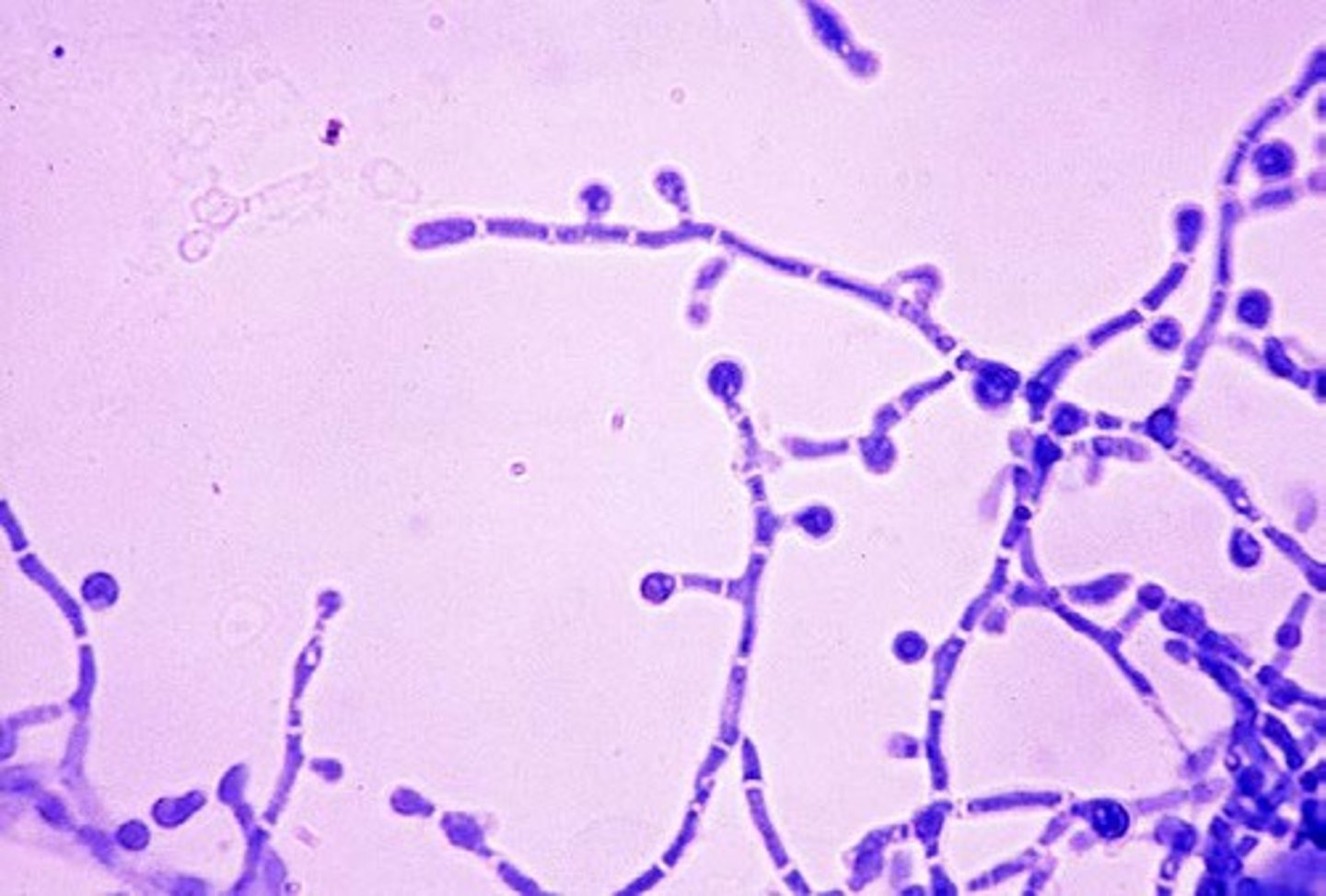
when discharge assoc. w/ candidiasis is placed on a slide w/ saline solution (wet mount), what will it reveal?
hyphae, but you will also see epithelial cells, etc
- this is a way to test for yeast rapidly
how is candidiasis treated?
simply on the basis of s/s
treatment of candidiasis may include:
- OTC topicals (miconazole or clotrimazole)
- RX topicals (Butoconazome 2% cream, Nystatin vaginal tablet)
- fluconazole 150 mg tab, STAT
what can be used to treat candidiasis if pt is allergic to "zoles?"
ibrexafungerp (Bresafemme)
in some patients, chronic or recurrent candidiasis may occur, what should you be sure to do?
- control DM
- review/reduce hormone use
- pt education to wear loose clothing
- various chronic tx regimens
various tx regimens are available for recurrent candidiasis. what is one option?
fluconazole 150 mg tab - 1 po qd x 3 days, then 1 po qwk for 6 months
- monitor LFTs
what causes trichomonas vaginalis?
trichomonas vaginalis
- unicellular flagellate protozoan
is trichomonas vaginalis an STD?
yes
1 multiple choice option
how may a patient w/ trichomonas vaginalis present?
w/ watery or thin, yellow to green to gray, possibly frothy, sometimes malodorous
- vulva may become edematous & tender
- possibly:
*pruritus
*dyspareunia
*dysuria
10% of cases of trichomonas vaginalis have...
a "strawberry cervix" or multiple petechiae on cervix
how is trichomonas vaginalis diagnosed?
wet mount or NAAT
what will the wet mount show w/ trichomonas vaginalis?
the protozoan (trichomonas vaginalis)
if microscopy is not available or is negative, but you still have a high suspicion that this is trichomonas vaginalis, what can be used for diagnosis?
NAAT or rapid antigen test
how is trichomonas vaginalis treated?
metronidazole 2 g po STAT OR tinidazole 2 g po STAT
- treat the partner!
if someone w/ trichomonas vaginalis also has bacterial vaginosis, what can you use to cover both infections?
metronidazole 500 mg bid x 7 days
vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN)
- related to HPV 16 & 18
- pre cancerous
how are VIN lesions more easily seen?
w/ application of acetic acid
paget disease of the vulva/vagina
itchy, velvety, red lesions
- can be assoc. w/ malignant epithelial cell cancer