E2 Lec 12 - Reproduction
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Viviparity
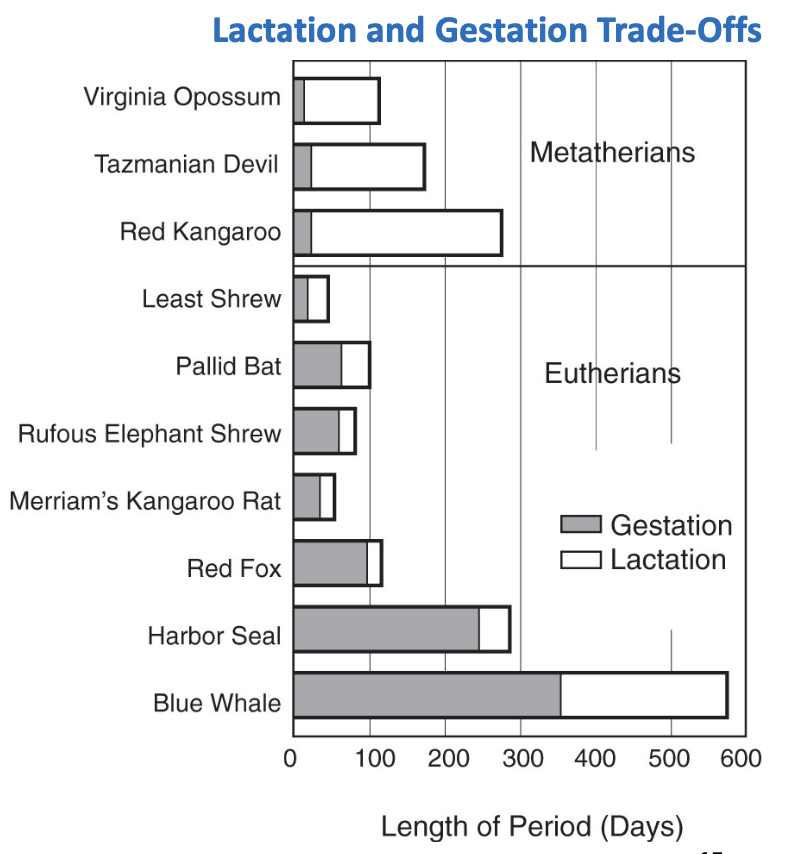
Live-birth, evolved in all vertebrate groups except birds.
Marsupial and Eutherian viviparity differences in:
Estrous cycles
Rates of embryogenesis
Degree of placentation
Hormonal sequences
Environmental and behavioral cues
What are some reproductive characteristics often found in Marsupials?
Pouch
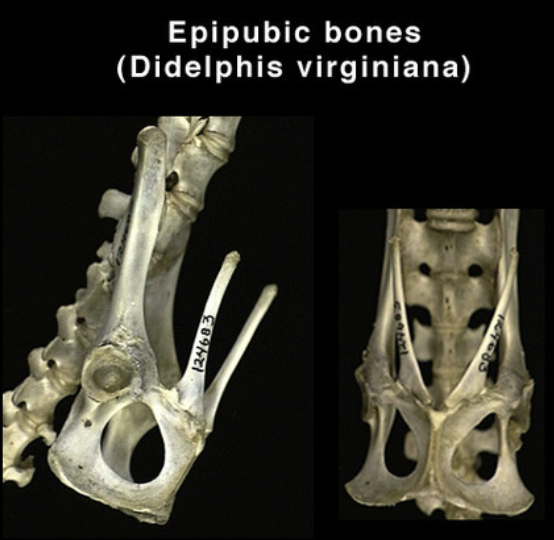
Epipubic Bones
Epipubic bone
Found in all marsupials, monotremes, and reptiles. Function is unclear.
Male Reproductive Anatomy
Testes - produce sperm (gametes)
Testosterone - hormone
Spermatogonia
Undergo cell division from diploid to haploid gametes, spermatozoa, in the testes during breeding season.
Where do gametes form exactly?
Seminiferous tubules
Epididymis
Storage and maturing location for gametes. They are transported from the seminiferous tubules.
Testes can be located abdominal or scrotal (T/F).
True. Descend into scrotum in most mammals, can be seasonal to produce more sperm.
Female Reproductive Anatomy basic characters
Ovaries
Oviduct
Uterus
Cervix
Vagina
Follicles
Ovaries
Primary reproductive organ. Pair of small oval bodies posterior to kidneys. Produce & mature gametes.
Oviduct
Channel from ova (eggs) to uterus.
Uterus
Site of embryonic development
Cervix
Connects the uterus to the vagina.
Vagina
Opening to exterior.
Follicle
Thick layer of spherically grouped cells under the surface of the ovary. Source of steroids, each contains a single egg, present in all eggs in females at birth. Follicles respond to hormones initiated egg maturing.
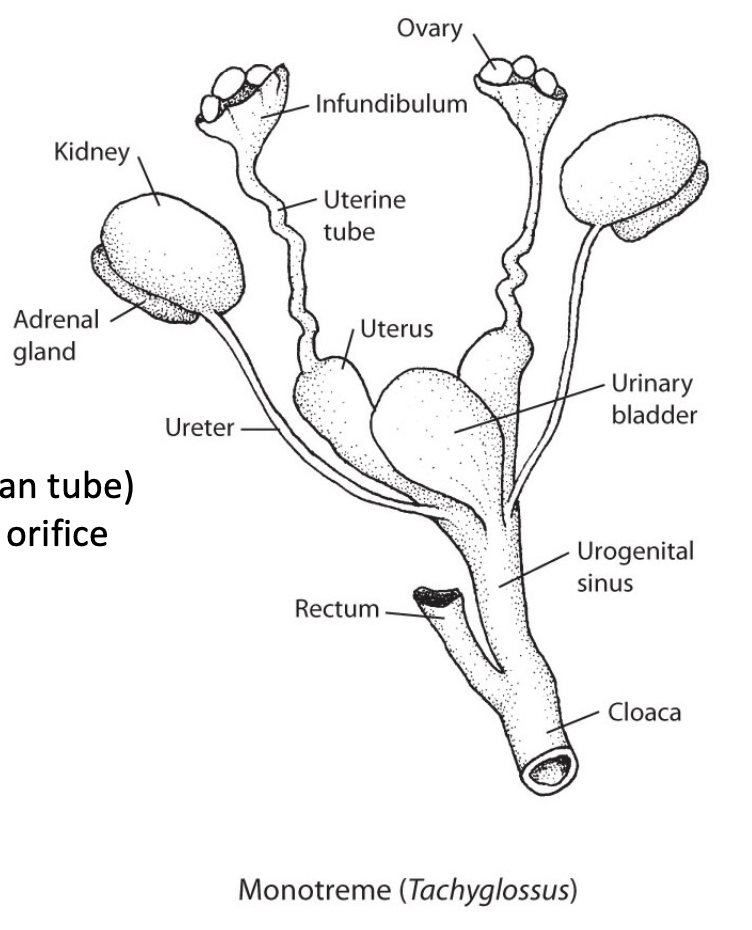
Monotreme reproductive anatomy
Infundibulum - fertilization
Urogential sinus - duct receiving both eggs and waste
Ovaries large with yolk
Cloaca - waste and reproductive hole
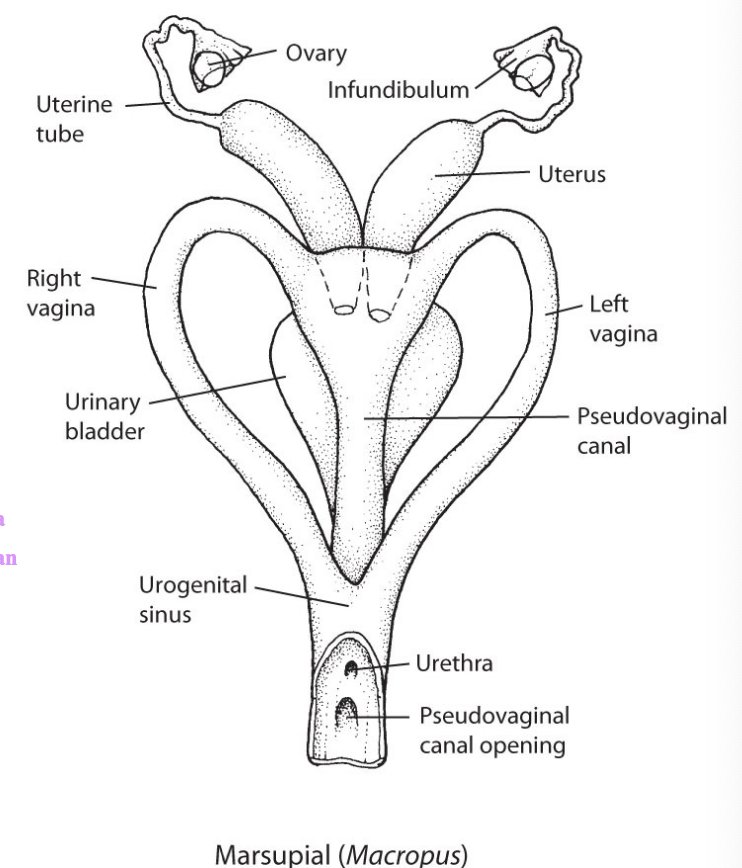
Marsupial reproductive anatomy
Didelphous reproductive tract (uterus, cervix, vagina paired)
Birth through Pseudovaginal canal
Male forked penis
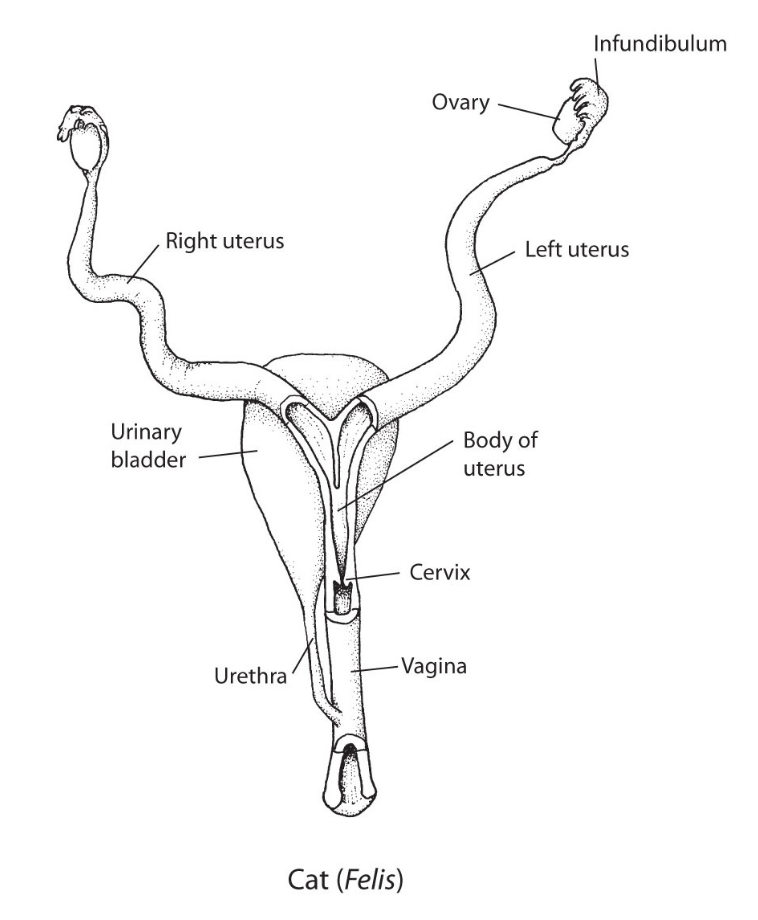
Placental
Pair ovaries
Single vagina
Cervix and uterus may be paired
What are the different types of morphology in female placental reproductive tracts?
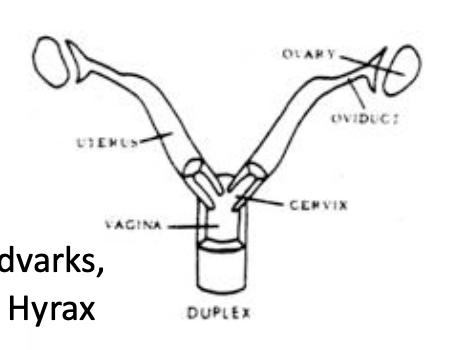
Duplex
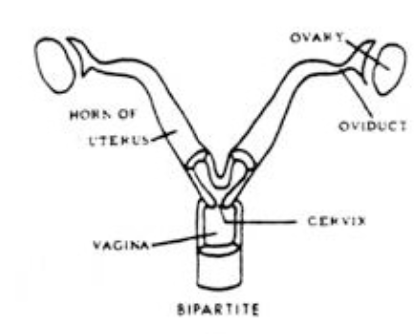
Bipartite
Bicornuate
Simplex
Duplex Placental Uterine
2 uteri
2 cervix
1 vagina
Rodents
Bipartite Placental Uterine
2 uteri
1 cervix
1 vagina
carnivores, whales
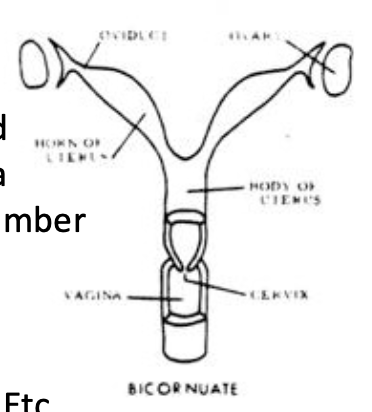
Bicornuate Placental Uterine
2 uteri, fused into common chamber
1 cervix
1 vagina
bats, ungulates
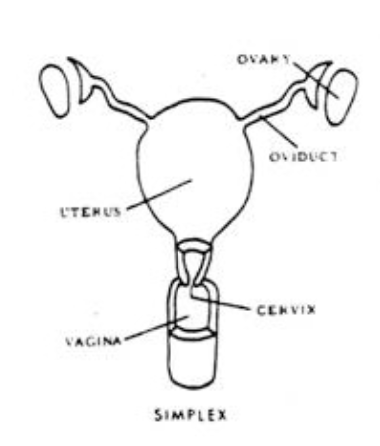
Simplex Placental Uterine
1 uterus
1 cervix
1 vagina
primates
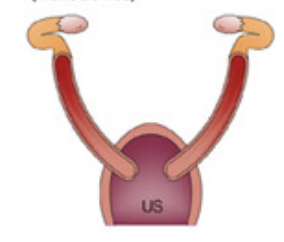
Monotremes (duplex without vagina)
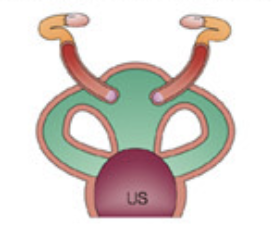
Marsupials (duplex with two lateral vaginae and a median birth canal).
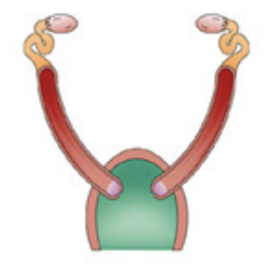
Placental Duplex (with a single vagina, rodents and rabbits).
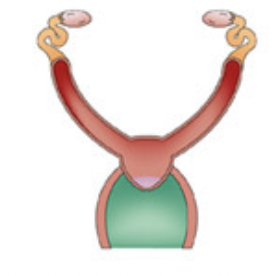
Placental Bipartite (bipartite uterus seen in pigs, marine mammals, mice).
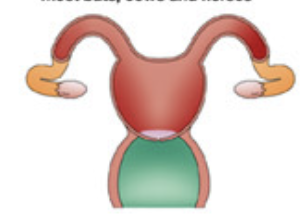
Placental Bicornuate (seen in bats, cows, horses)
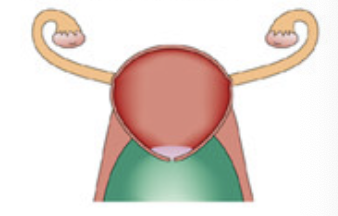
Placental simplex (most higher primates)
Generalized sequence of events in reproduction include which 6 steps?
Gametogenesis
Insemination/ovulation (release of egg) or ovulation/insemination
Fertilization
Implantation (endometrium)
In utero development
Parturition (birth)
What are the two cycles of reproduction?
Ovarian - inside ovary
Uterine - inside uterus
Ovarian cycle
Development of ova in follicle
Follicle bursts
Ova released from ovary
Passage of ova to uterus
Uterine cycle
Series of cyclic changes in the uterus. Changes result in periods of heightened sexual receptivity (estrus or heat).
What are two types of uterine cycles in mammals?
Estrus cycle
Menstrual cycle
Estrous cycle
cyclical pattern of ovarian activity that facilitates female animals to go from a period of reproductive receptivity to non-receptivity ultimately allowing the establishment of pregnancy following mating. Endometrium, uterine lining, is reabsorbed if conception does not occur.
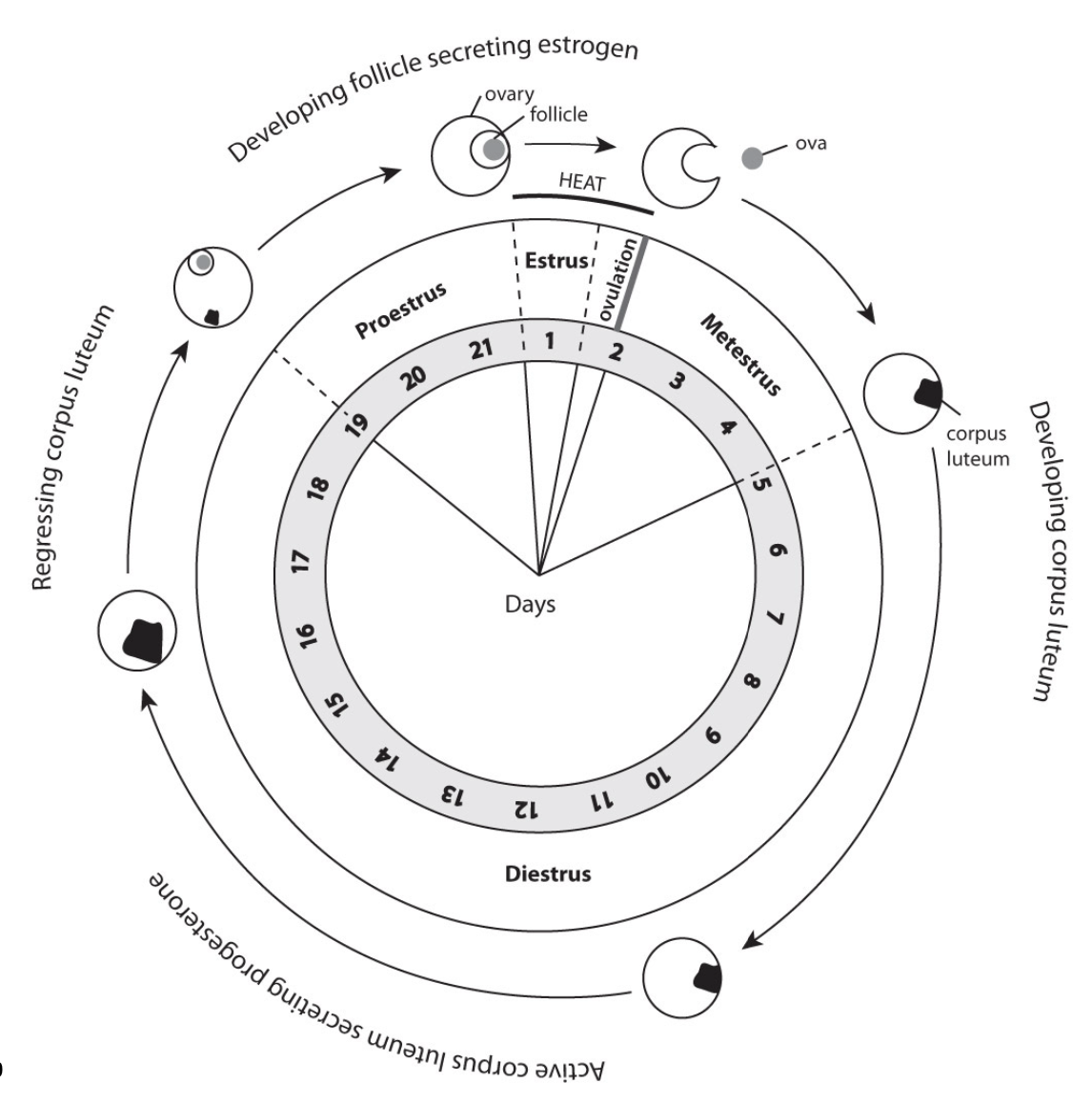
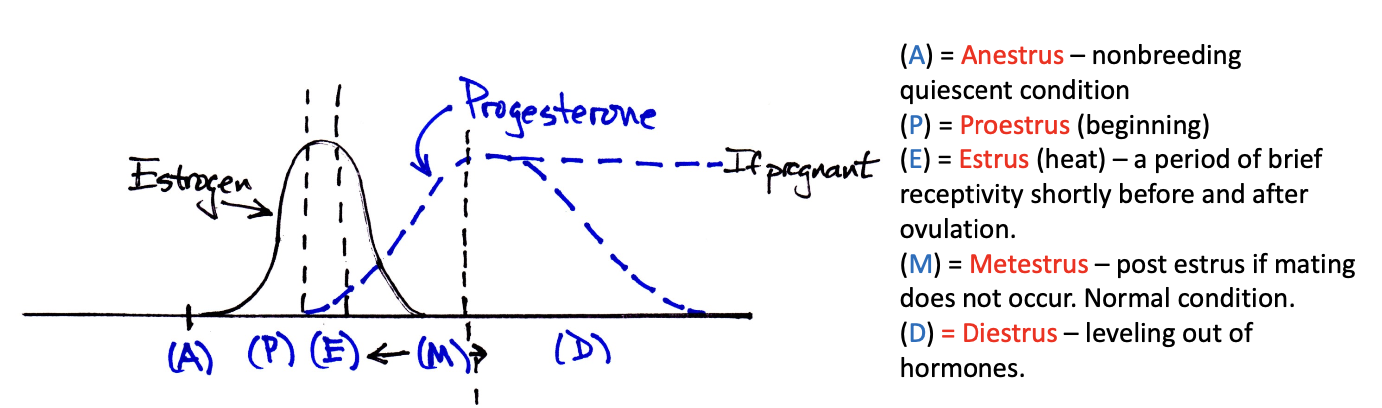
What are four phases of the estrous cycle?
Proestrus
Estrus
Metestrus
Diestrus
(Anestrus)
Menstrual cycle
Endometrium is shed at menstruation instead of being reabsorbed. No discrete phases.
Both the estrous and menstrual cycle of mammals is regulated by …
Hormones
What are major hormones in reproduction?
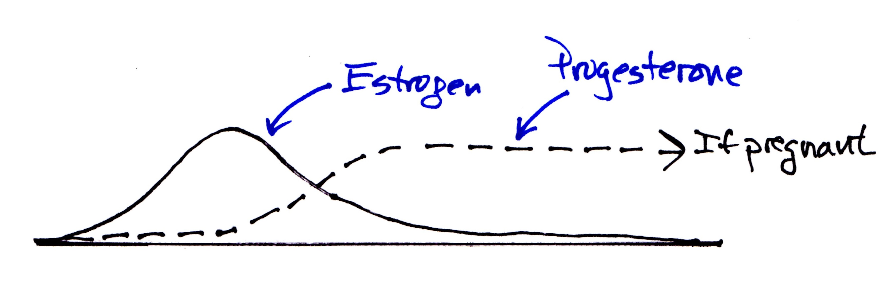
Estrogen - trigger ovulation
Progesterone - hormone of pregnancy
Follicle Stimulation Hormone (FSH) - stimulate testes/ovaries
Luteinizing hormone (LH) - stimulate testes/ovaries
What are organs create hormones important for reproduction?
Anterior Pituitary Gland - FSH & LH
Ovary - estorgen
Corpus luteum - progesterone
Proestrus
Growth of follicle (FSH)
Secretion of estrodial (estrogen)

Estrus
Ovulation (egg release) with high estrogen
Surge of LH
Ruptured follicle develops to corpus luteum
Spontaneous or induced ovulation initiates the process
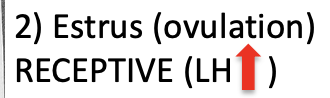
Metestrus
Presence of corpus luteum
LH produced, maintains corpus luteum
Corpus luteum secretes progesterone
Progesterone prepared uterine lining (endometrium) for blastocyst implantation
If fertilization does not occur - corpus luteum regresses
If fertilization and implantation occur, progesterone continues to be secreted.

Diestrus
Leveling out of hormones

What are variation in estrous cycles found in mammals?
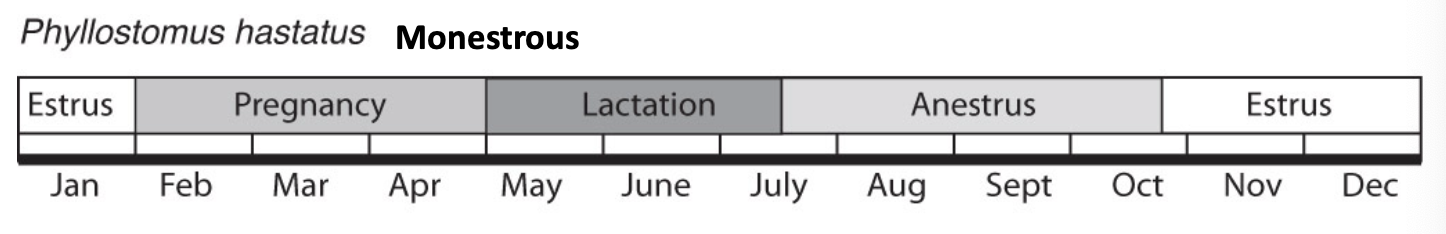
Monstrous (60%)
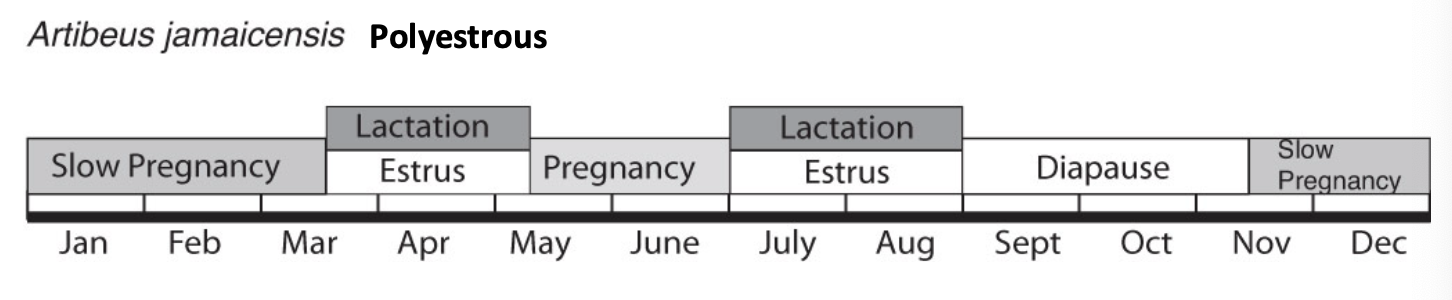
Polyestrous (40%)
Monestrous
Single estrous cycle
Polyestrous
Multiple estrous cycles
Which hormones are important in the Menstrual cycle?
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Estrogen
Progesterone
In what orders is the menstrual cycle seen?
Primates
Some bats
Elephant shrews
One rodent
The menstrual cycle is dependent/independent from the Estrous cycle.
independent
The menstrual cycle has no distinct phases but a cycle of …
hormones
What is the common hormone cycle for menstruation?
Anterior pituitary releases FSH, stimulating follicular growth in ovary and release of estrogen.
High estrogen levels (and FSH, LH) results in ovulation
Uterine lining development (endometrium)
Corpus luteum produces progesterone
How is the estrous cycle monitored be most females?
Restrict copulations for reproduction to specific time. Hormones and nervous system control periods of reproduction which are regulated by environmental cues.
How is the menstrual cycle monitored be most females?
Gradual increase and decrease of hormones, no discrete time or phases.
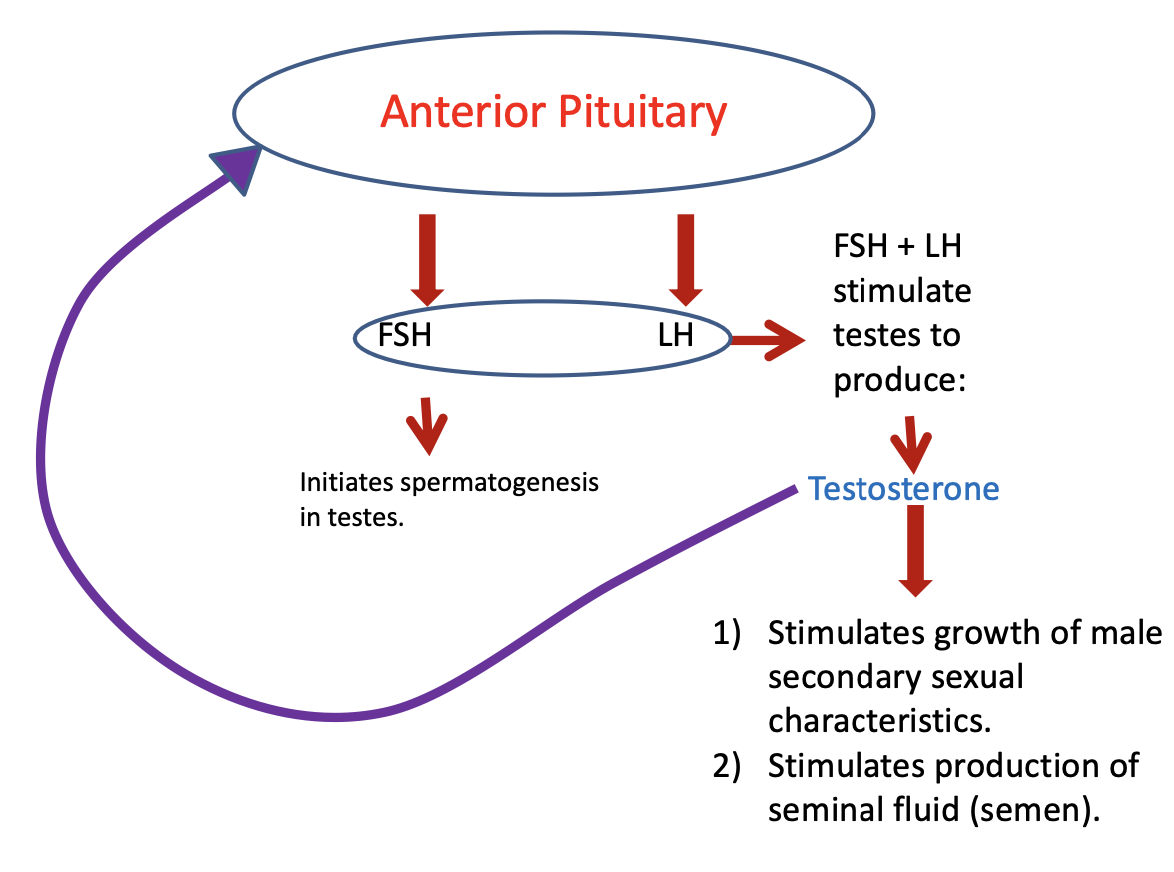
How is the stimulation of spermatogenesis initiated?
Anterior pituitary produces FSH and LH which stimulate the testes to produce testosterone. Testosterone promotes more production of FSH and LH in a negative feedback cycle, and stimulates growth of male secondary sexual characteristics and production of semen.