Transport in Animals
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Why do multicellular organisms require transport systems?
Large size (small SA:V), high metabolic rate so demand for oxygen is high
Summarise the different types of circulatory system
Open = blood can diffuse out of vessels (insects)
Closed = blood confined to vessels (mammals)
Single = blood passes through pump once per circuit of body
Double = blood passes through heart twice per circuit of the body
How are arteries adapted to their function?
Thick muscular walls - handles high pressure, elastic tissue - allows recoil to prevent pressure surges, narrow lumen - to maintain pressure
How are veins adapted to their function?
Thin walls - due to low pressure
Valves - ensures blood doesn’t flow backwards
Less muscular and elastic tissue - don’t have to control blood flow
How are capillaries adapted to their function?
Walls are one cell thick - short diffusion pathway, very narrow - can permeate tissues and only one RBC wide so effective oxygen delivery, highly branched - large surface area
What is the role of arterioles and venules in the circulatory system?
branch off arteries and veins in order to feed blood into capillaries
How are arterioles and venules adapted to their function?
Smaller than arteries and veins so that the change in pressure is more gradual as blood passes through increasingly small vessels
What is tissue fluid?
A watery substance containing glucose, amino acids, oxygen and other nutrients
What types of pressure influence formation of tissue fluid?
Hydrostatic pressure - higher at arterial end of capillary than venous
Oncotic pressure - changing water potential of the capillaries as water moves out, induced by proteins in the plasma
What is hydrostatic pressure?
The pressure in a liquid due to the force of gravity
What is oncotic pressure?
The force exerted by proteins in the blood that draws water into the blood vessels
How is tissue fluid formed?
As blood is pumped through increasing small vessels, hydrostatic pressure is greater than oncotic pressure, so fluid moves out of the capillaries
How does tissue fluid differ from blood?
It doesnt contain red blood cells, platelets and other solutes present in blood
How does tissue fluid differ from lymph?
After tissue fluid has bathed cells it loses oxygen and nutrients and contains more waste products, so becomes lymph
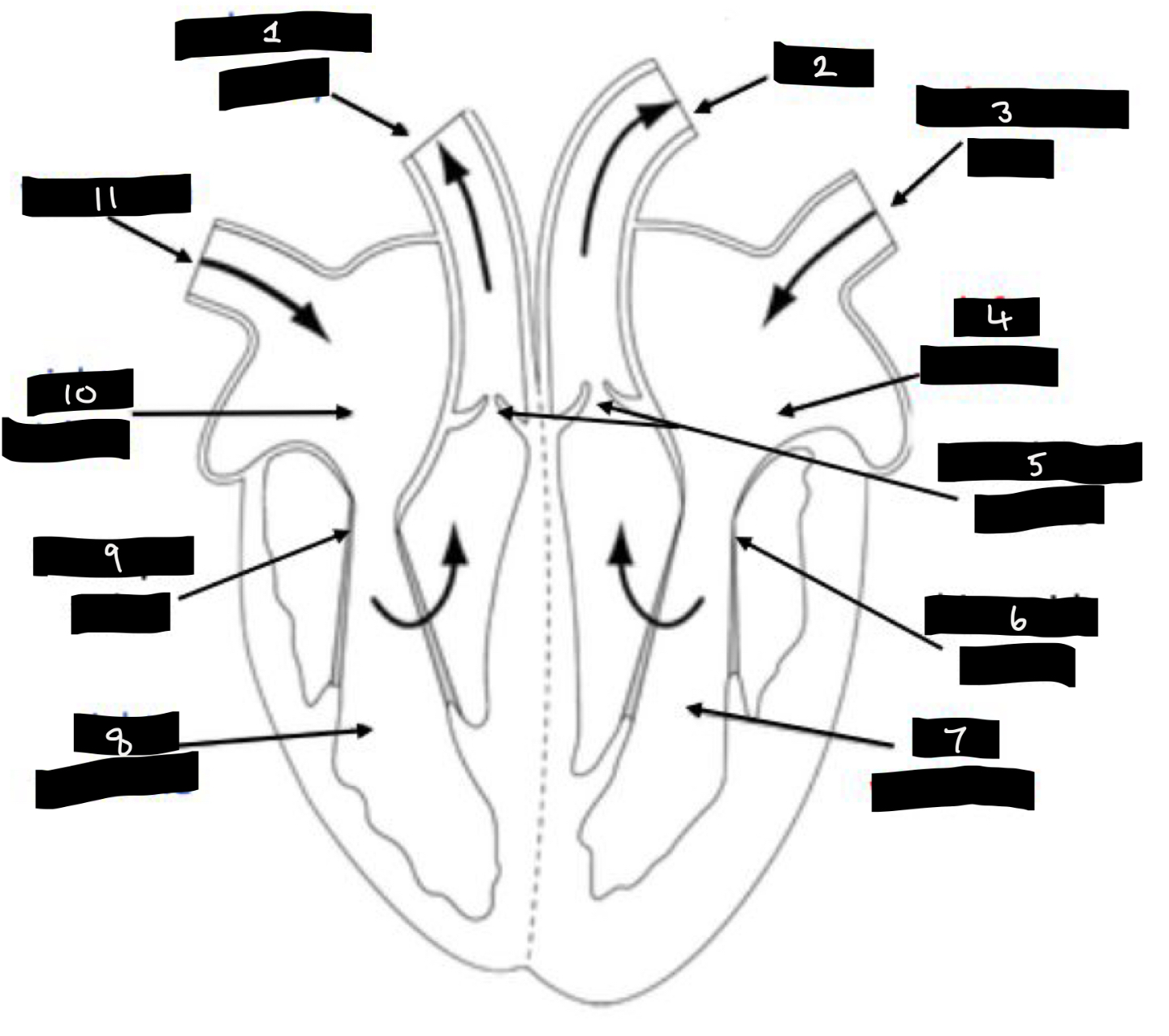
What is 1?
Pulmonary artery
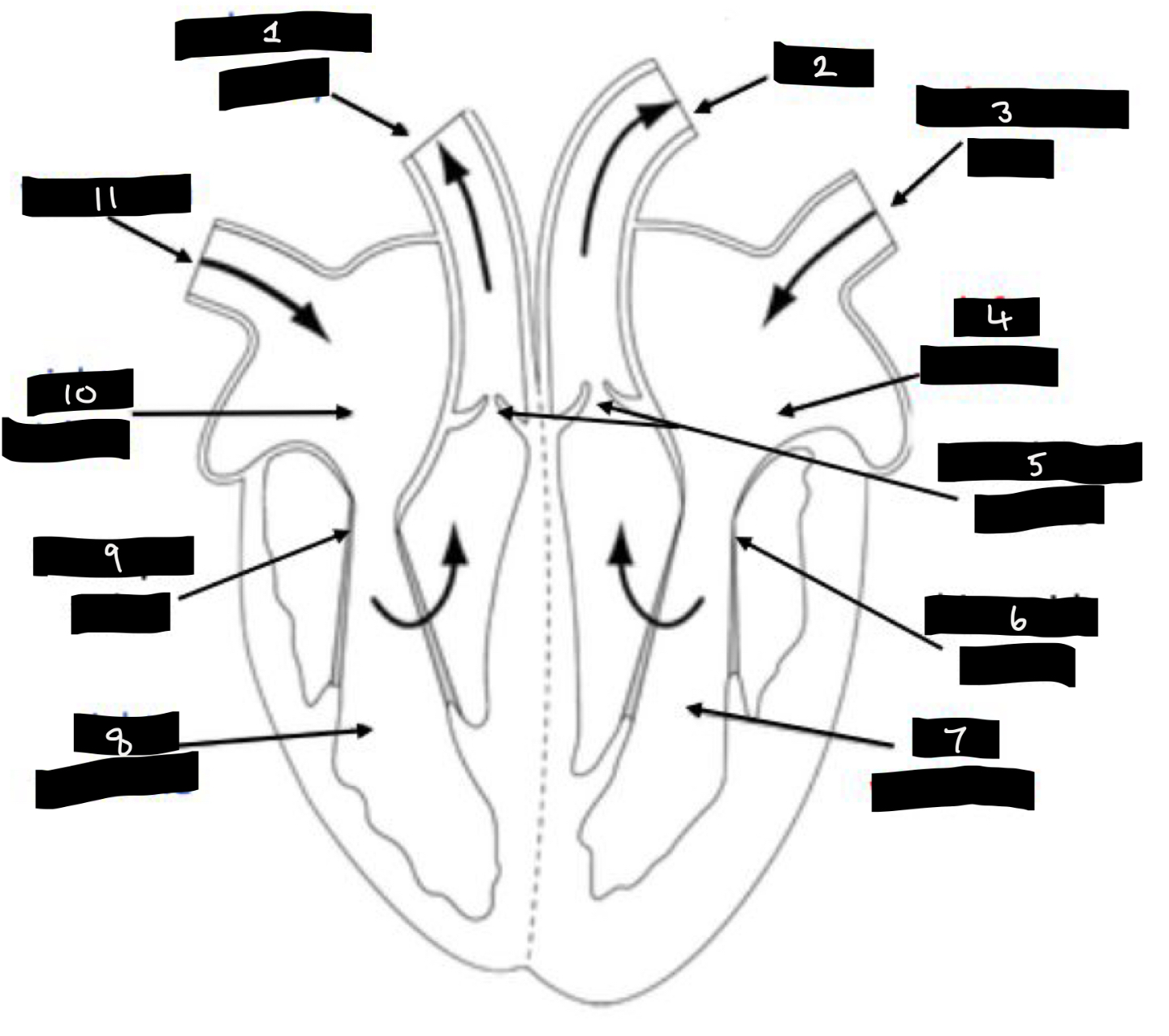
What is 2?
Aorta
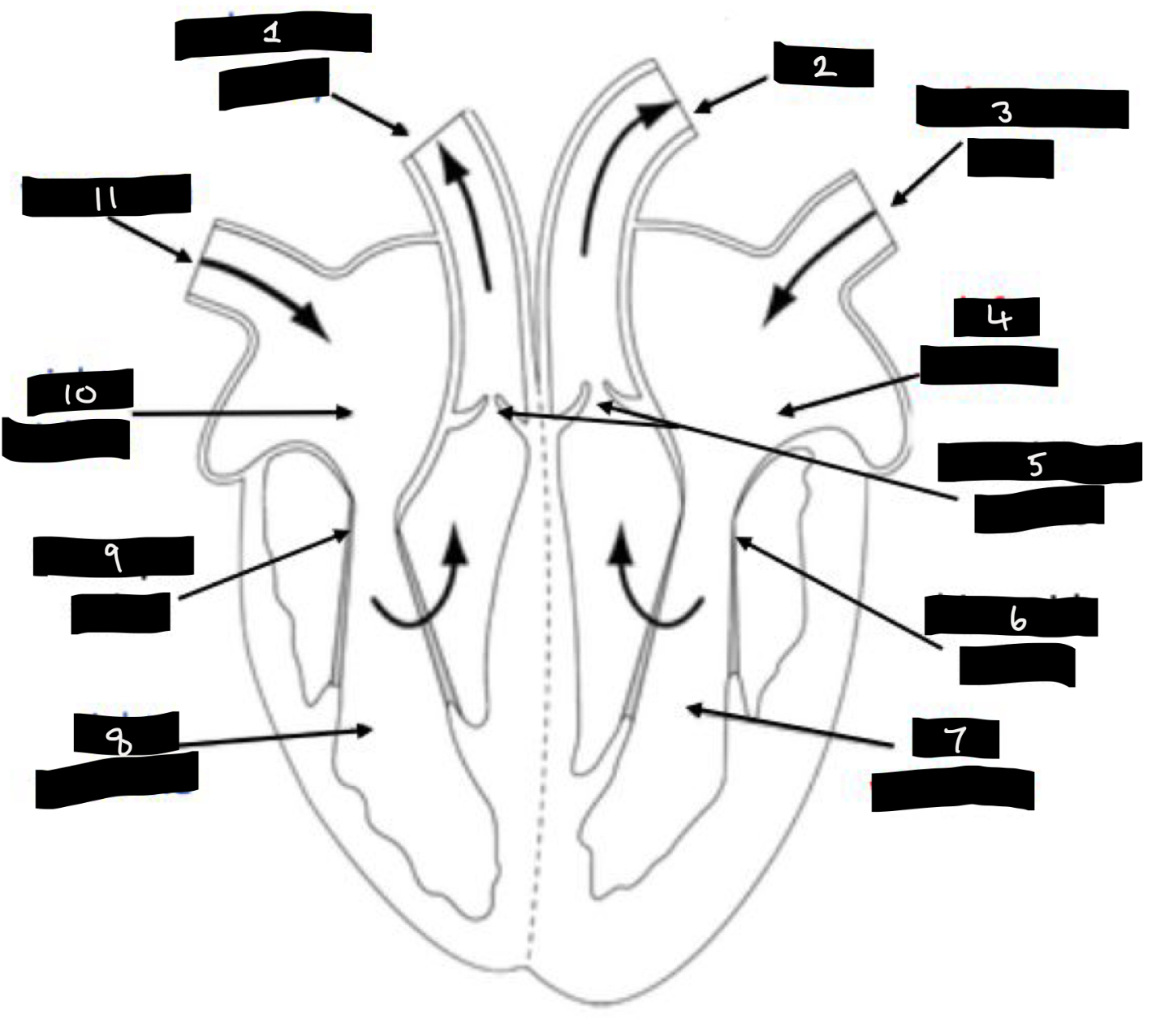
What is 3?
Pulmonary vein
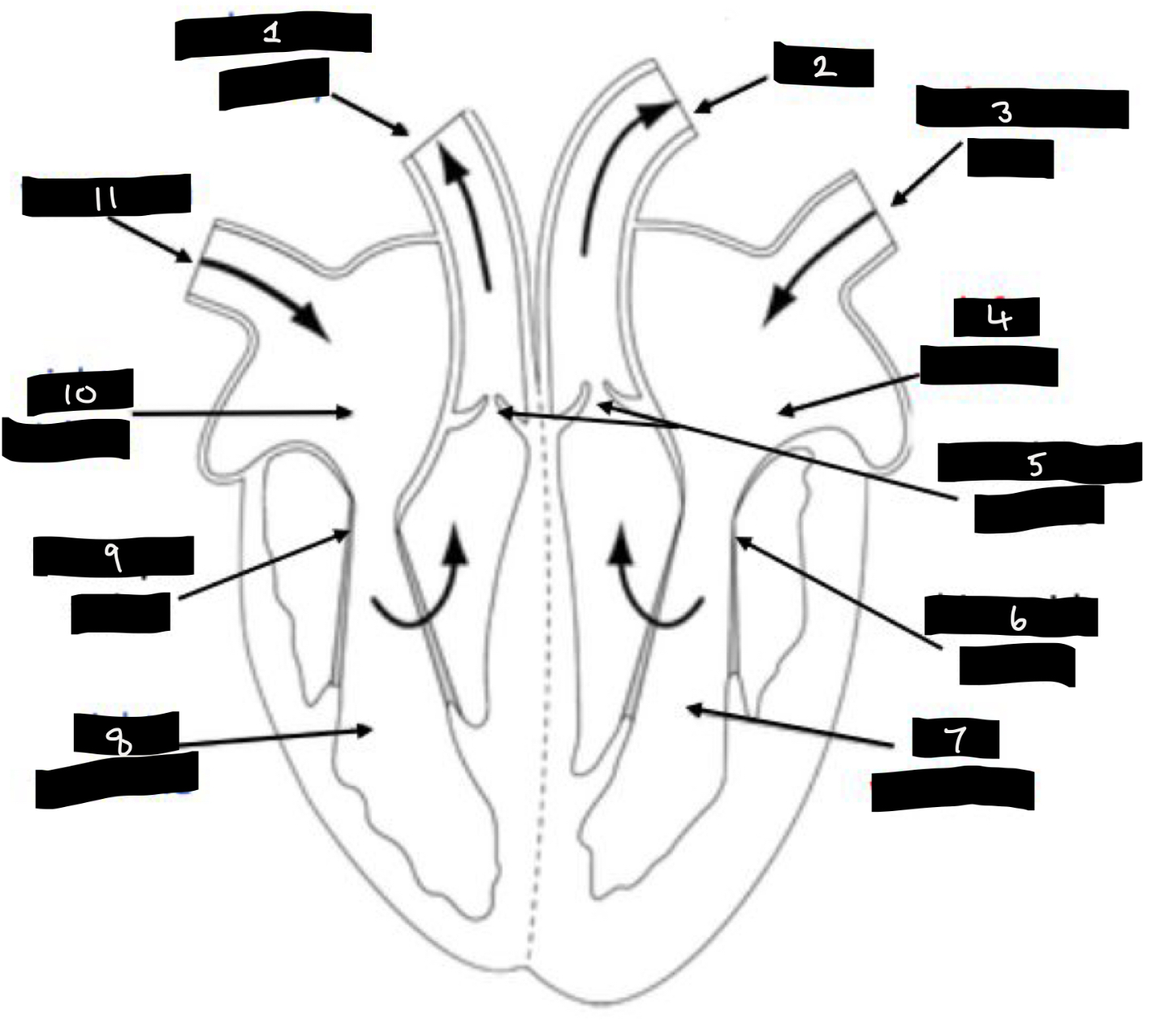
What is 4?
Left atrium
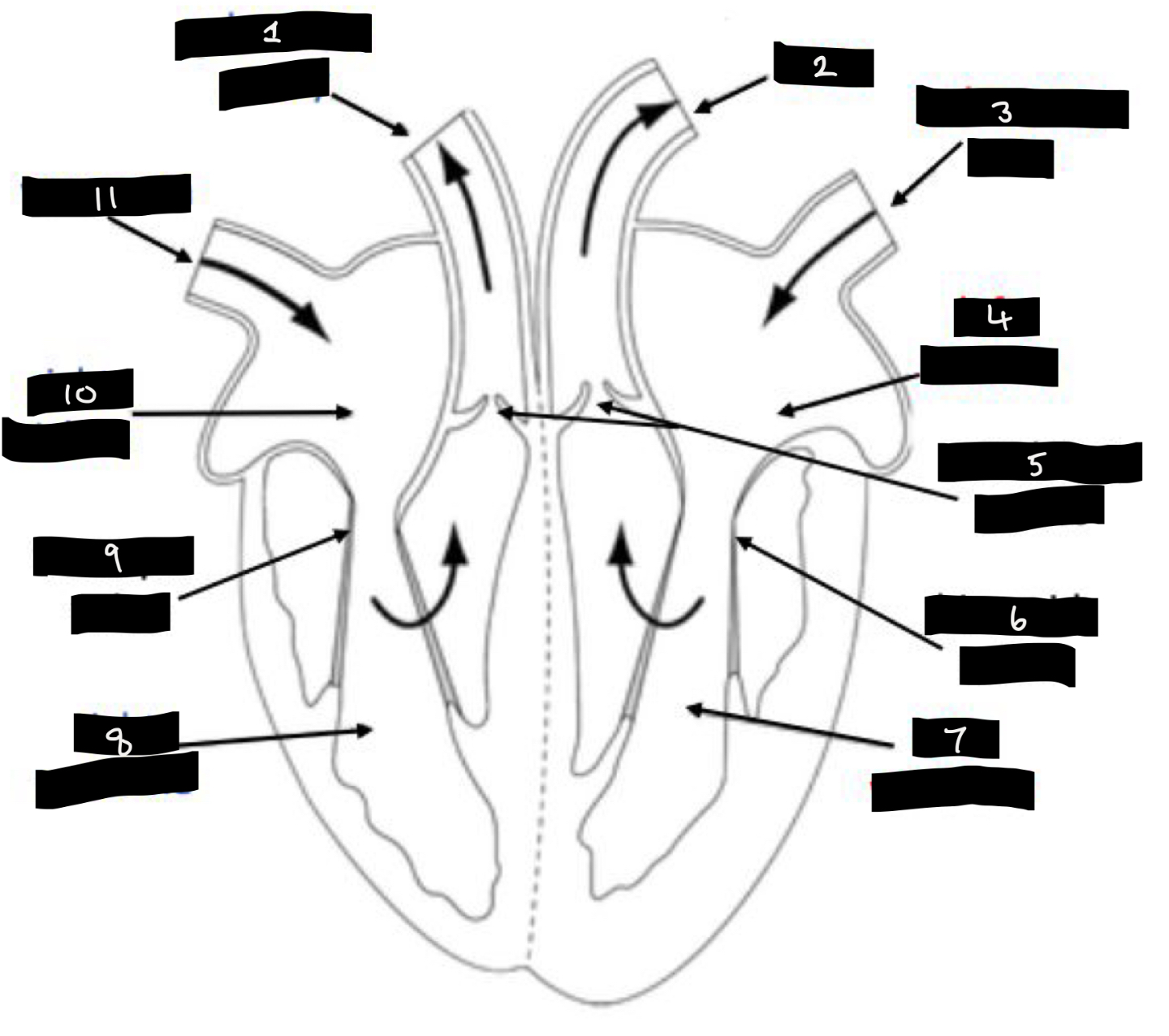
What is 5?
Semilunar valves
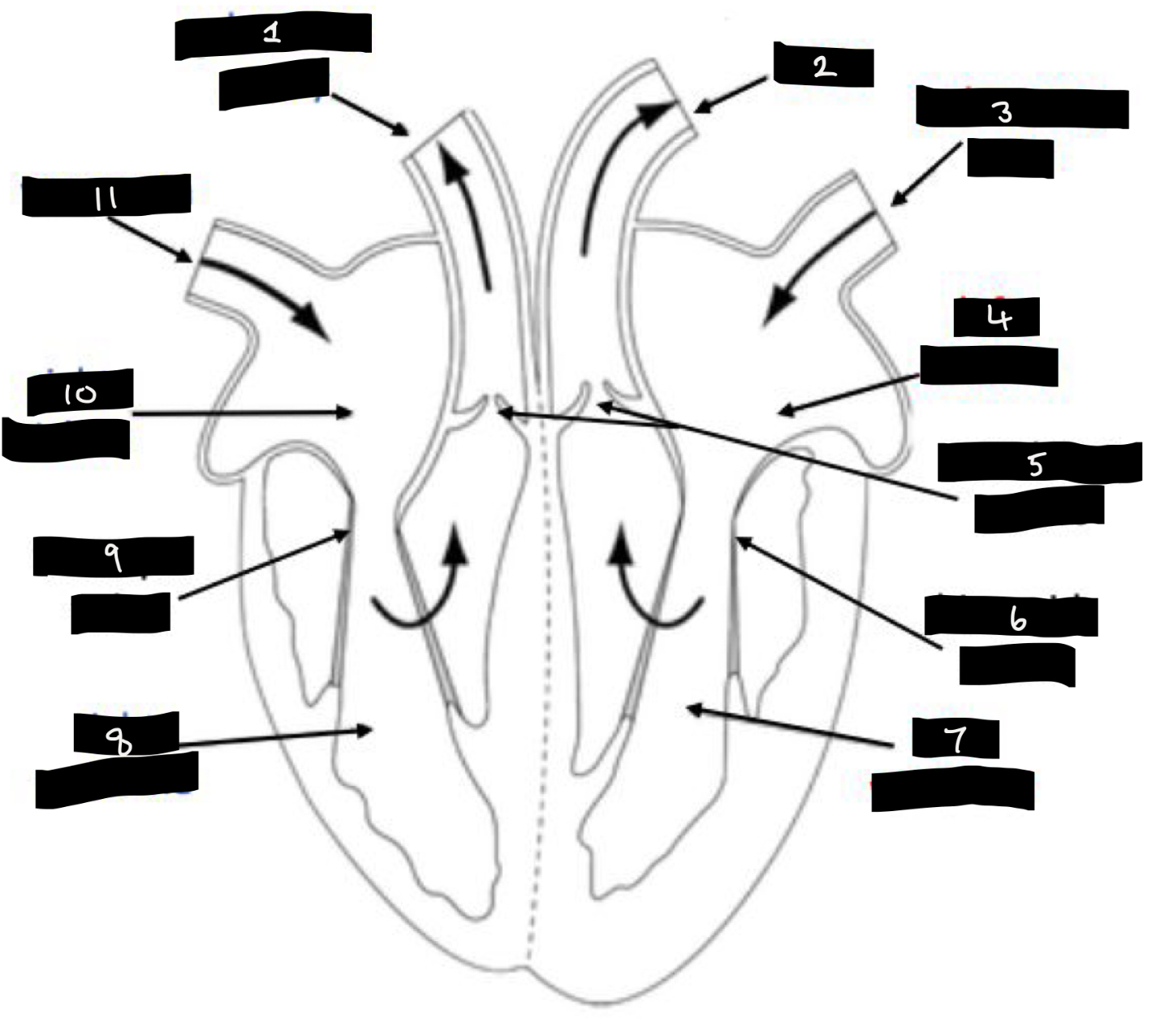
What is 6?
Bicuspid valve
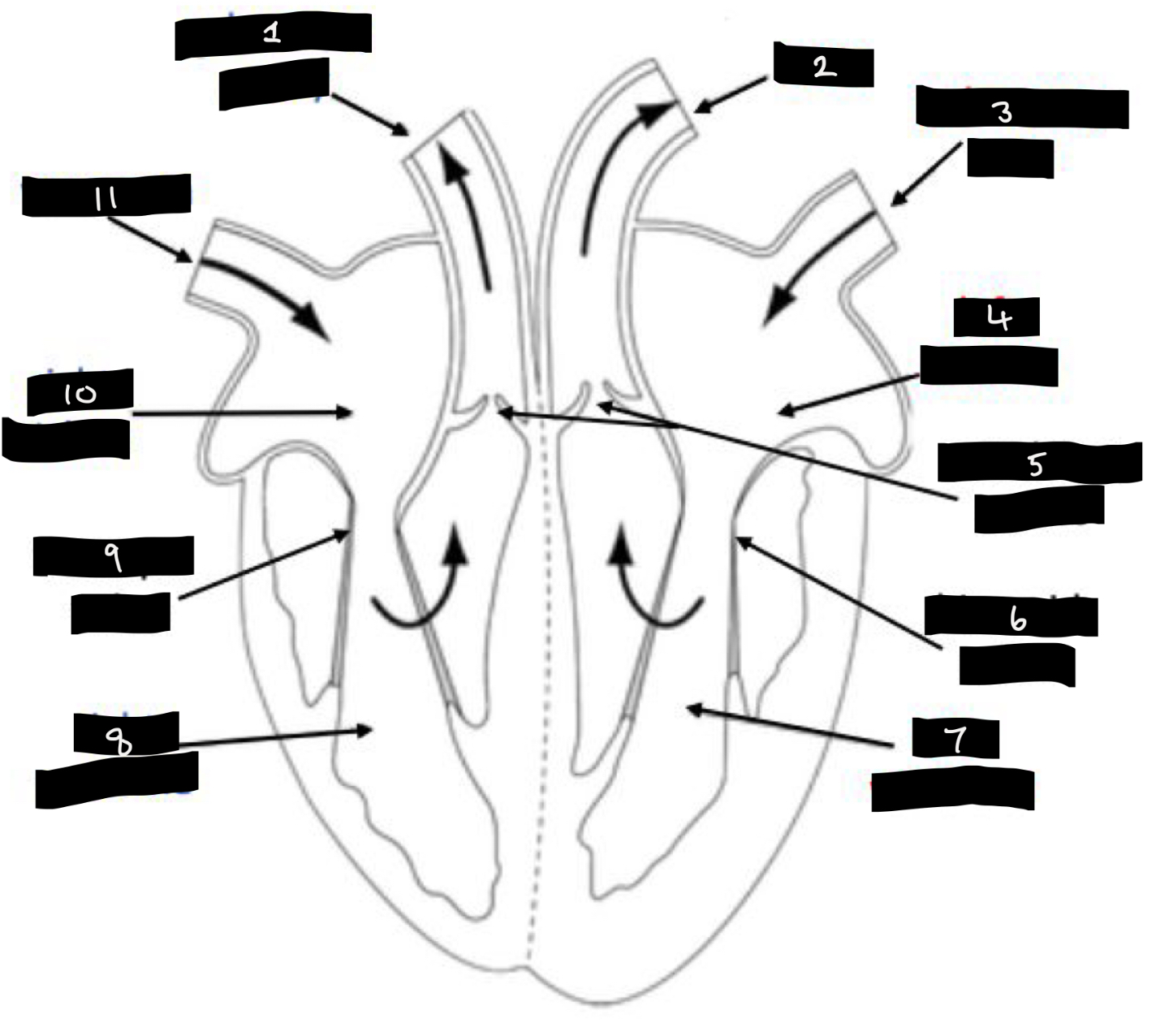
What is 7?
Left ventricle
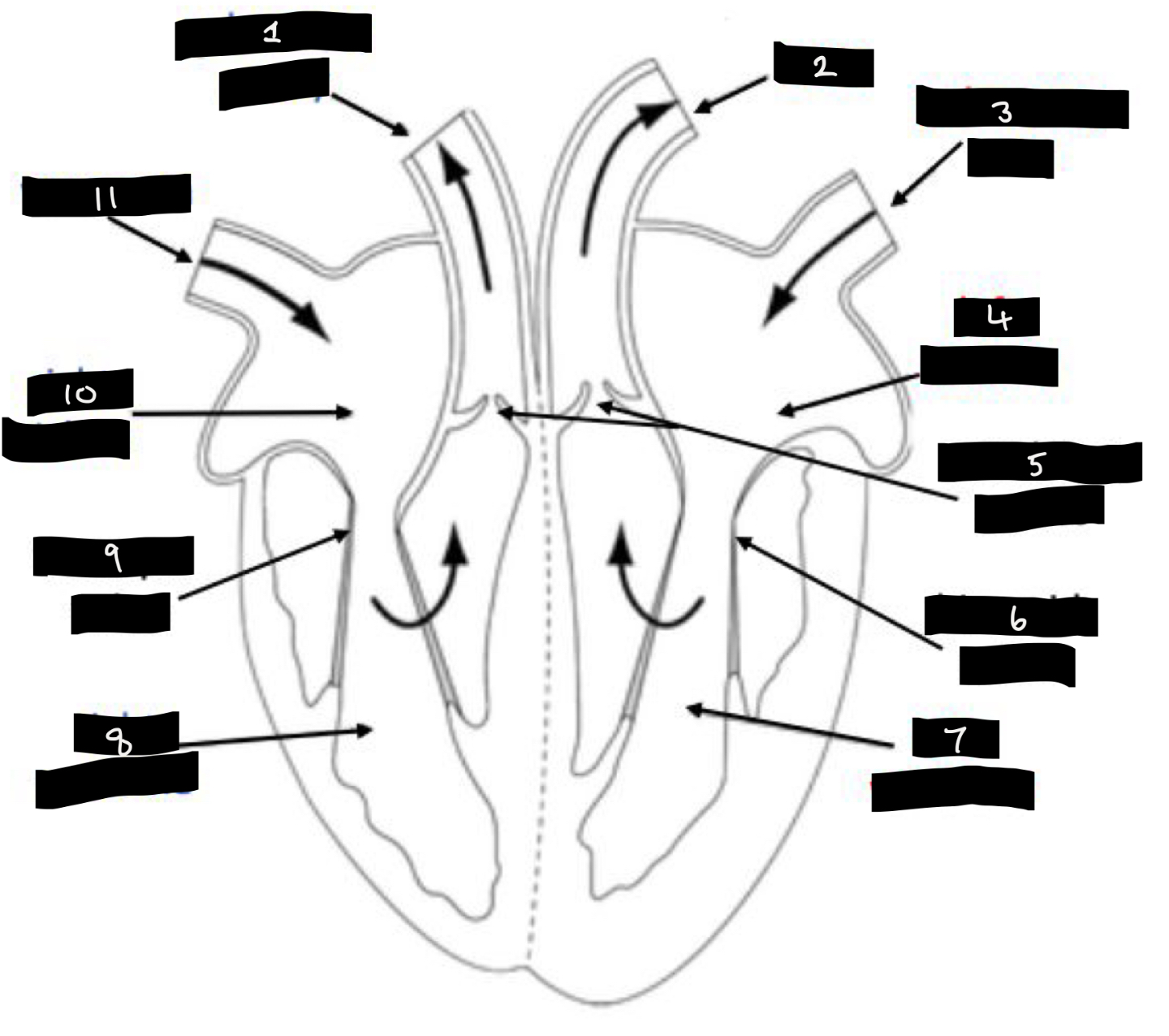
What is 8?
Right ventricle
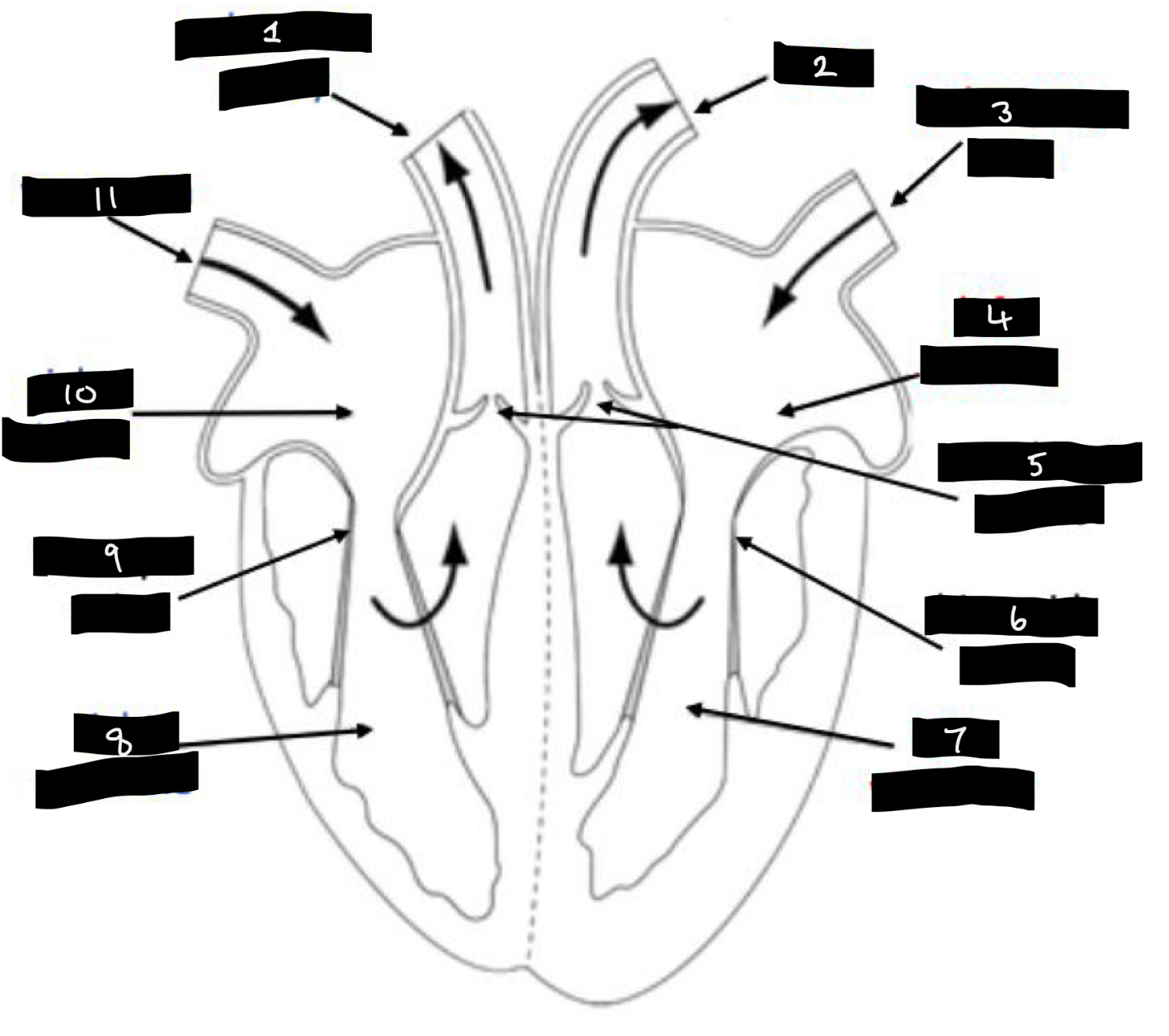
What is 9?
Tricuspid valve
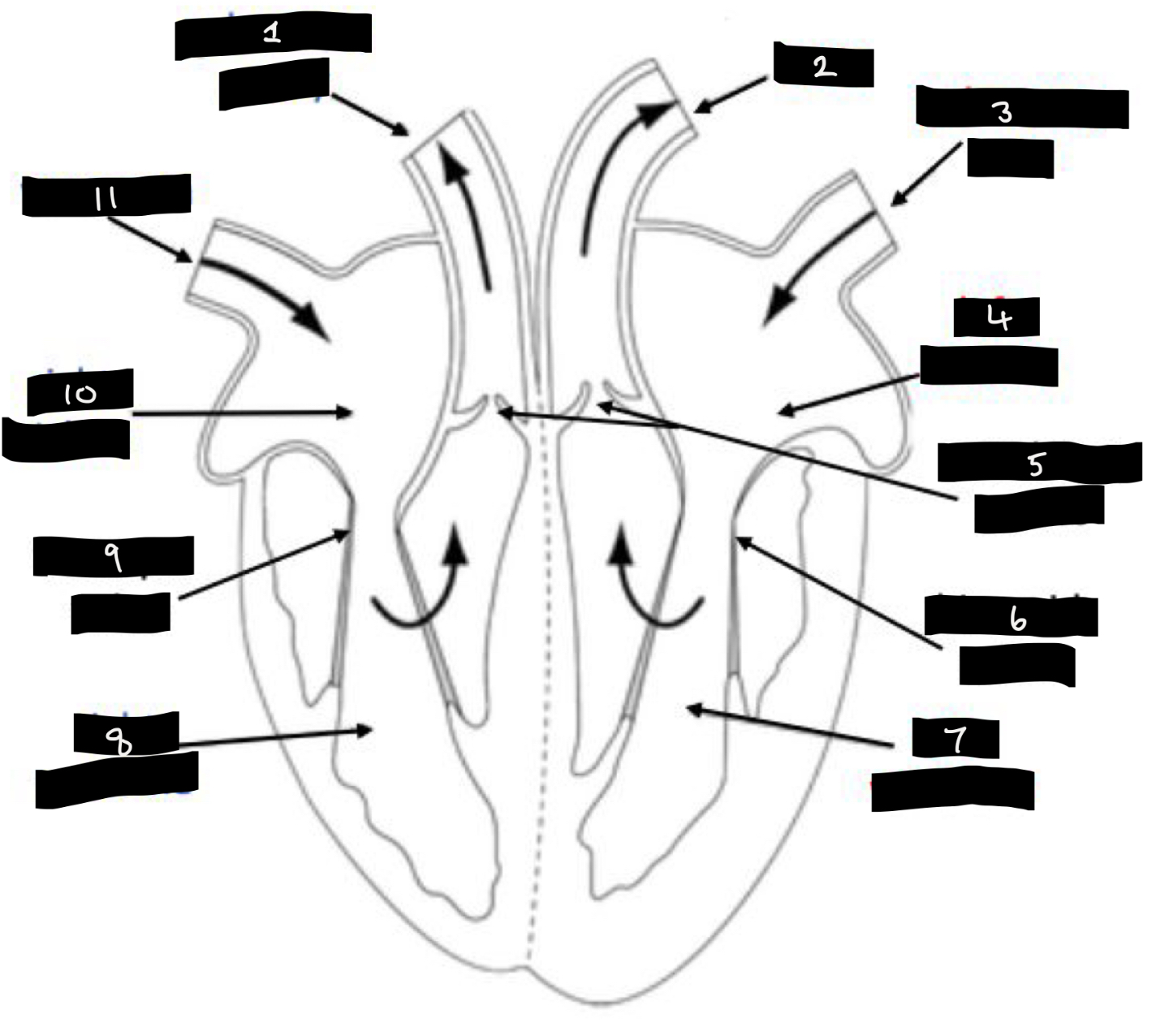
What is 10?
Right atrium
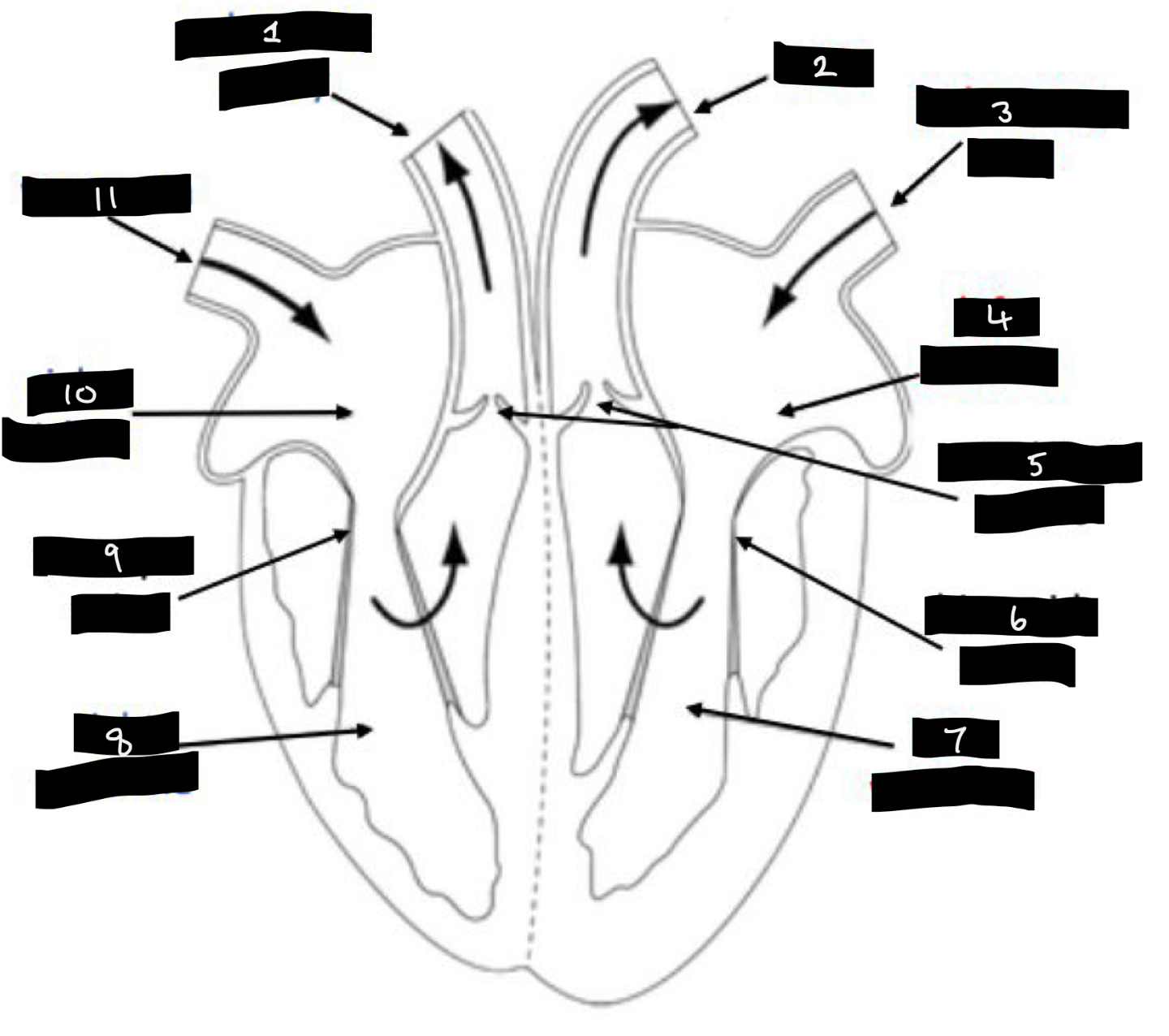
What is 11?
Vena cava
Describe what happens during cardiac diastole
Blood enters atria, atrioventricular valves open, blood flows into ventricles, semilunar valves remain closed
Describe what happens during atrial systole
Atria contracts, pushing any remaining blood into the ventricles
Describe what happens during ventricular systole
Ventricles contract making pressure increase, closing the atrioventricular valves to prevent back flow, and opening the semilunar valves. Blood flows into the arteries
How do you calculate cardiac output?
Heart rate x stroke volume
What does myogenic mean?
The heart’s contraction is initiated from within the muscle itself, rather than by nerve impulses
Explain how the heart contracts
SAN initates and spreads impulse across the atria, so they contract
AVN receives, delays and then conveys the impulse down the bundle of His
Impulse travels into the Purkinje fibres which branch across the ventricles, so they contract from the bottom up
What is an electrocardiogram (ECG)?
A graph showing the amount of electrical activity in the heart during the cardiac cycle
What is tachycardia?
Fast heartbeat (over 100bpm)
What is bradycardia?
Slow heartbeat (under 60bpm)
What is fibrillation?
Irregular, fast heartbeat
What is ectopic (seen on an ECG)?
Early or extra heartbeats
Describe the role of haemoglobin
Present in RBC. Oxygen molecules bind to the haem groups and are carried around the body, then released when they are needed in respiring tissues
How does partial pressure of oxygen affect oxygen-haemoglobin binding?
As partial pressure of oxygen increases the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen also increases, so oxygen binds tightly to haemoglobin. (When partial pressure is low, oxygen is released from haemoglobin)
What is partial pressure?
The pressure an individual gas exerts within a mixture
What is affinity?
The strength of the attraction between two substances
What do oxyhemoglobin dissociation curves show?
Saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen (in %), plotted against partial pressure of oxygen (in kPa)
What do curves further to the left on oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curves show?
The haemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen
Describe the Bohr effect
As partial pressure of CO2 increases, the conditions become acidic causing haemoglobin to change shape. The affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen therefore decreases, so oxygen is released from haemoglobin.
Explain the role of carbonic anhydride in the Bohr effect
carbonic anhydase is present in red blood cells
converts CO2 to carbonic acid, which dissociates to produce H+ ions
these combine with the haemoglobin to form haemoglobinic acid
encourages oxygen to dissociate from haemoglobin
Explain the role of bicarbonate ions (HCO3-)
Produced alongside carbonic acid. 70% of carbon dioxide is carried in this form. In the lungs, bicarbonate ions are converted back into carbon dioxide which we breathe out
Describe the chloride shift
The intake of chloride ions across a red blood cell membrane. This repolarises the cell after bicarbonate ions have diffused out.
How does foetal haemoglobin differ from adult haemoglobin?
The partial pressure of oxygen is low by the time it reaches the foetus, therefore foetal haemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen than adult. Allows both mother’s and child’s oxygen needs to be met