APAH movements and vocab
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
syncretism
the attempt to reconcile contrary beliefs, often while melding practices of various schools of thought
ex. adding pagan artistic styles/images into early christian art
spolia
“spoils;” reuse of building materials (often from older cultures/civilizations) in new monuments
arcade
series of arches
nave
main aisle of church, intended to accommodate most of congregation
apse
semicircular eastern termination point of many churches, often containing altar
hieratic
formal and stylized (often in byzantine art)
continuous narrative
multiple scenes of narrative in one frame
transept
cross section of a churcha
ambulatory
semicircular aisle winding around the apse; allows crowds without disturbing ceremonies in the apse
radiating chapels
chapels radiating out from the apse/ambulatory, allow more space to stand + often contain reliquaries (holding remains/relics of saints)
barrel vault
half cylinder; series of connected arches
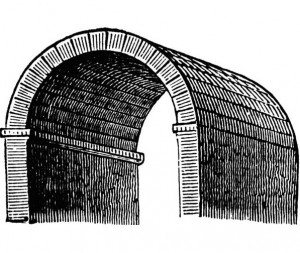
tribune
balcony-like structure opening out to nave from the upper story
tympanum
semi-circular lunette above doorway
jamb
side post of door
hierarchical scale
indicating importance of individuals through relative size
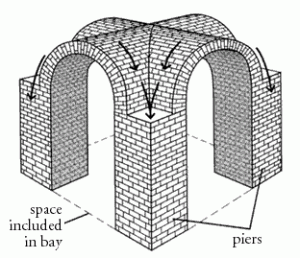
groin vault
two rib vaults intersecting at a right angle
rib vault
groin vault with pointed arches, allow for taller/lighter structures. exclusively gothic
flying buttress
exterior arches/bracing supporting the buildingt
triforium
arcade above church nave/transept
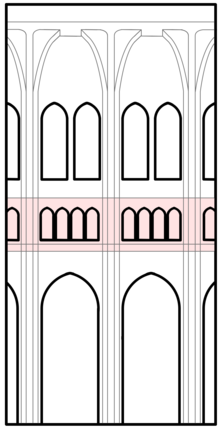

rose window
smaller windows forming an oculus
bay
wall sections of a window, door, etc
clerestory
upper part of nave containing windows
chiaroscuro
single light source
orant figure
figure in prayer posture
cubicula
small underground room in catacomb that serve as mortuary chapels
basilica
(christian) church w nave, side aisles, apse for altar
arabesque
flowing, intricate, infinite symmetrical + floral pattern. symbolize uncentralized creation of god
tessellation
covering a surface with repeated geometric shapes without any gaps or overlaps
contour rivalry
two images share parts/outlines
aniconism
avoiding imagery of divine beings, prophets, other respected religious figures
hypostyle hall
filled with many columns
mihrab
niche in mosque qibla wall (pointing toward kaaba in mecca); must face towards this wall during prayer
minarets
tall towers w internal staircase
iwan
vaulted rectangular recess opening onto a courtyard
humanism
emphasis on man’s abilities
sfumato
smokiness
atmospheric perspective
background fades and cools, becomes blurry
trompe l’oiel
illusion of subject coming out of the surface
poesia
painting operating in a similar manner to poetry (rich colors, beauty, myth, lyrical/sensual); sensuous instead of intellectual
venetian..?
mannerism
pontormo (entombment of christ)
exaggerated/expressive, elegant, elongated/elastic
unusual lighting/coloring, composition, balance
architecture: unorthodox use of classical elements (ex. il gesu except its actually baroque but yeah)
part of late renaissance
pilaster
“fake” column
common hindu beliefs
polytheistic
karma, reincarnation
endless cycle of birth, death, rebirth (samsara)
legalism
people are inherently evil, must control w strict laws and strict punishment
ukiyo-e
japanese printmaking, “floating world”
daguerrotype
shiny surface, clear finish and detail
no negative (not reproducible)
named after Louis Daguerre
calotype
grainy quality
positive and negative image; can be reproduced
ancient near east conventions
art serves religion/state
assyrian: lamassu
persian: audience hall
sumerian: votive figures, white temple, standard of ur
ancient egypt conventions
canon: rectilinear, ideal proportion, twisted perspective
amarna: started by akhenaten; more curvilinear/informal but still used ideal depictions
old kingdom egypt works
seated scribe
great pyramids/sphinx
menkaure and queen
new kingdom egypt works
temple of amun re / hypostyle hall
akhenaten relief
mortuary temple of hatshepsut
tut tomb
judgment of hunefer (book of the dead)
greek periods and conventions
archaic: rigid kore/kouros figures, archaic smile; egyptian influence (rigid stance, ideal proportions)
severe period: transition from archaic to classical (niobedes krater)
classical: heroic, idealized, restrained
architecture: acropolis
sculpture: hegeso, doryphoros
hellenistic: larger variet of works; expressionistic, elicit emotional response, movement
seated boxer, pergamon altar, samothrace
etruscan conventions
temples: mud brick/terracotta, plain pediments, only frontal columns
temple of minerva
sculpture: terracotta, bronze, not nude, dynamic movement
sarcophagus of the spouses
roman conventions
realist, propaganda, convey power/authority
architectural elements: use of concrete, arches (barrel/groin vaults), dome, oculi
roman periods and respective conventions
early empire: follows more greek conventions; idealization, contrapposto
republican roman: head of patrician, alexander mosaic
imperial roman:
colosseum, pantheon, vettii, augustus
late empire: stylistic shift; crowding, squat proportions, etc
ludovisi
islamic conventions
mosques + mihrabs oriented toward mecca
use of arabesques+tesselations (patterns), calligraphy bc can’t depict people/divine figures
medieval art sub-movements in order
late antiquity: priscilla catacombs, santa sabina
early medieval: merovingian, lindisfarne gospels
byzantine: vienna genesis, san vitale, virgin and child
romanesque: st foye, bayeux tapestry,
gothic: chartres, bible moralisees
proto-renaissance: arena chapel
byzantine conventions
flat, frontal, gold, floating
hieratic: formal, stylized style for figures
architecture: domes over squares, squinches support
romanesque conventions
increased emphasis on christian belief; ex. more pilgrimages
churches made to accommodate more people: nave, apse, ambulatory, radiating chapels
gothic conventions
rib vault (pointed arch), flying buttress (outer wall support), rose window (around oculus) all allow bigger stained glass windows and more divine looking light
bays, repeated vertical elements, narrowed vault all emphasize height/verticality
renaissance periods and conventions
proto-renaissance:
beginning of medieval/byzantine tradition rejection
early northern european: campin, van eyck
pioneered oil painting, allows slower painting/build up of color; printmaking
early italian: lippi, botticelli, donatello
balance, symmetry, classical conventions (anatomy, architectural forms), appeal to intellect rather than senses as in gothic
high italian renaissance: michelangelo, da vinci, raphael, titian (venetian)
late renaissance
mannerism: elastic/elongated/elegant figures, unusual lighting/coloring + composition
often associated w protestant reformation; decreased religious influence (durer, cranach)
baroque periods and conventions
italian/spanish/french: religious, dramatic, emotional, grand
tenebrism: dramatic lighting using heavy chiaroscuro
dynamic undulating architecture (il gesu)
borromini, bernini, porta/vignola/gaulli, caravaggio, velasquez, rubens, vau/hardouin-mansart
northern european: more protestant influence = more realistic/naturalistic
rembrandt, vermeer, ruysch
vanitas still lifes: emphasize transience of life
rococo
fragonard (swing), le brun (self-portrait)
continuance of baroque movement/drama but with (french aristocracy) frivolity/indulgence replacing seriousness
colorito (painterly, venetian-influenced lush/sensuous color)
pastel colors rather than deep and rich
enlightenment/neoclassicism
hogarth (tete a tete), wright of derby (orrery); david (horatii), houdon (washington); jefferson (monticello)
return to greek/roman classical art/architectural conventions: symmetry, harmonious proportions, dome, oculus
trend away from rococo frivolity; emphasize knowledge, logic, rationalism, restraint, order, realism
desegno (emphasis on line/form, invisible brushstrokes); dispute w colorito
romanticism
ingres (odalisque), goya (nothing to be done), delacroix (liberty leading people), turner (slave ship), cole (oxbow)
focused on exotic, legends (narratives of heroic struggle), violence, emotion, sublime
diagonal composition, quick brushstrokes
realism
courbet (stone breakers), manet (olympia)
depict mundane daily realities + show discontent w the world, paint real people rather than heroes
positivism (logic, justification, reject theism)
visible/rough brushstrokes, heavy pigment
sometimes odd angles or tilts
photography/photo-secessionism
daguerre (still life), muybridge (horse in motion), stieglitz (steerage)
photo-secession movement: promoted photography as fine art
daguerrotypes and calotypes
impressionism
capture effects of light on surface
fleeting everyday moments (impermanence of images/conditions)
en plein-air: painting outside in natural light
japonisme: influence of jp art (flatness, off centered)
landscape/genre scenes of contemporary life
evident brushstrokes, rough and painterly
post-impressionism
van gogh (starry night), gauguin (who are we?), cezanne (mont sainte-victoire)
thought impressionism was too tied to representation
paint to express emotion/idea rather than mere visual experience
symbolism
munch (scream)
paint expressively and convey emotions/inner world through abstract symbolism/imagery, not realistically
art nouveau
klimt (kiss), sullivan (goth target)
eliminate separations between artistic media
vegetal and floral patterns, complex designs, undulating surfaces
architecture: curvilinear, elaborate wrought-iron structural elements, curtain wall (support skeleton + exterior “curtain), verticality
reaction against industrialization
fauvism
matisse (goldfish)
depict feeling/expression rather than true-to-life depictions, shocking colors, simple design
german expressionism
kirchner (soldier self-portrait), kandinsky (improvisation)
inspired by fauvism
abstraction; depict natural world beyond representation
cubism
brancusi (kiss sculpture), braque (portuguese), picasso (demoiselles)
depict forms/subjects by “shattering” into fragments
challenge view of art: no longer understandable or beautiful
de stijl/neoplasticism
mondrian (composition red/yellow/blue)
abstraction, primary colors, geometry
create universal harmony/pictorial language
line/shape/color symbolizes unity of spiritual/natural forces
dada
duchamp (fountain)
use of readymades and collages
artistic concept over execution
question understanding/value of art, reject conventional representation/exhibition
surrealism
oppenheim (fur cup), lam (jungle)
influenced by dada
create concrete irrationality through juxtaposition of unrelated items, combination of real/unreal
xplore dreams/unconscious
international style
le corbusier (villa savoye)
influenced by bauhaus
clean, spacious, white lines
minimalism, less is more, “house is machine for living in”
organic architecture
frank lloyd wright (falling water)
harmonization with natural site rather than sticking to historic styles
natural materials, ex. rough hewn wood
total design: consider everything in design (including furniture)
modernism
rohe/johnson (seagram)
form follows function, minimalism/simplicity
either organic/sculptural (harmonize with surroundings) or geometric box (stand out from them)
postmodernism
venturi/rauch/brown (new castle county)
playful, accessible, inclusive; combine past/present architecture
reaction against “inaccessible” modernism
less is more!!! excessive (form very much does not follow function)
deconstructivism
gehry (bilbao), hadid (maxxi)
sub-movement of postmodernism
disorient the viewer, challenge architectural conventions/assumptions
disorder, imbalance, unconformity, irregularity, haphazard presentation of volumes and masses
exterior often does not correspond with interior
abstract expressionism
gestural: emphasis on creative action rather than the product
kooning (woman)
chromatic: silence, reflection, created with both chance and control
frankenthaler (bay)
pop art
warhol (marilyn), oldenburg (lipstick)
comments on societal changes: industrialization, consumerism, mass media
alternative to pure abstraction
western art movements in order.. sort of
ancient: egypt, greece, etruscan, rome
medieval: late antiquity, early medieval, byzantine, romanesque, gothic, proto-renaissance
renaissance: early northern, early italian, high italian, late
baroque: italian/spanish, french, northern european
middling.. things: rococo, enlightenment/neoclassicism, romanticism, realism photography, impressionism, post-impressionism
increasing abstraction: fauvism, german expressionism, cubism, de stijl, surrealism/dada, abstract expressionism
modern architecture: international style, organic, modernism, postmodernism, deconstructivism
comments on society: pop art, global contemporary