Meteorology 1050 Exam 4 Aldrich
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Weather Forecasting
Predicting how the present state of the atmosphere will change over a period of time
Nowcasting
Present - 6 hours
Short Range Forecasting
1 - 3 Days
Medium Range Forecasting
3 - 5 days
Long Range Forecasting
5 - 10 days
Extended Forecasting
Up to 90 days
Persistence Forecasting Tech.
What happened yesterday will likely happen today
-Accuracy will depend on the weather patterns and your location
Climatology Forecasting Technique
The long term average of weather conditions are used to predict weather for a given day.
While weather does change a lot, climatology can be accurate fairly often.
Trend Method Forecasting Technique
Assumes that the speed and direction of a weather system will not change.
-Based on nearby observations
Analogue Forecasting Technique
Find a date in the past where the weather maps look exactly as it does now
-An okay method as patterns are repeatable, but exact evolution is not always the same
-Works best with severe/winter weather
Numerical Modeling Technique
Numerical equations exist to calculate the future state of certain variables
-Pressure, Temp., Winds, Humidity, Clouds, Precip.
-Predictions come from computer models
Computer Models
Work by dividing the atm. into 3D boxes called grids.
-The point in the middle is called the grid point
-All the mathematical equations are solved at each grid point
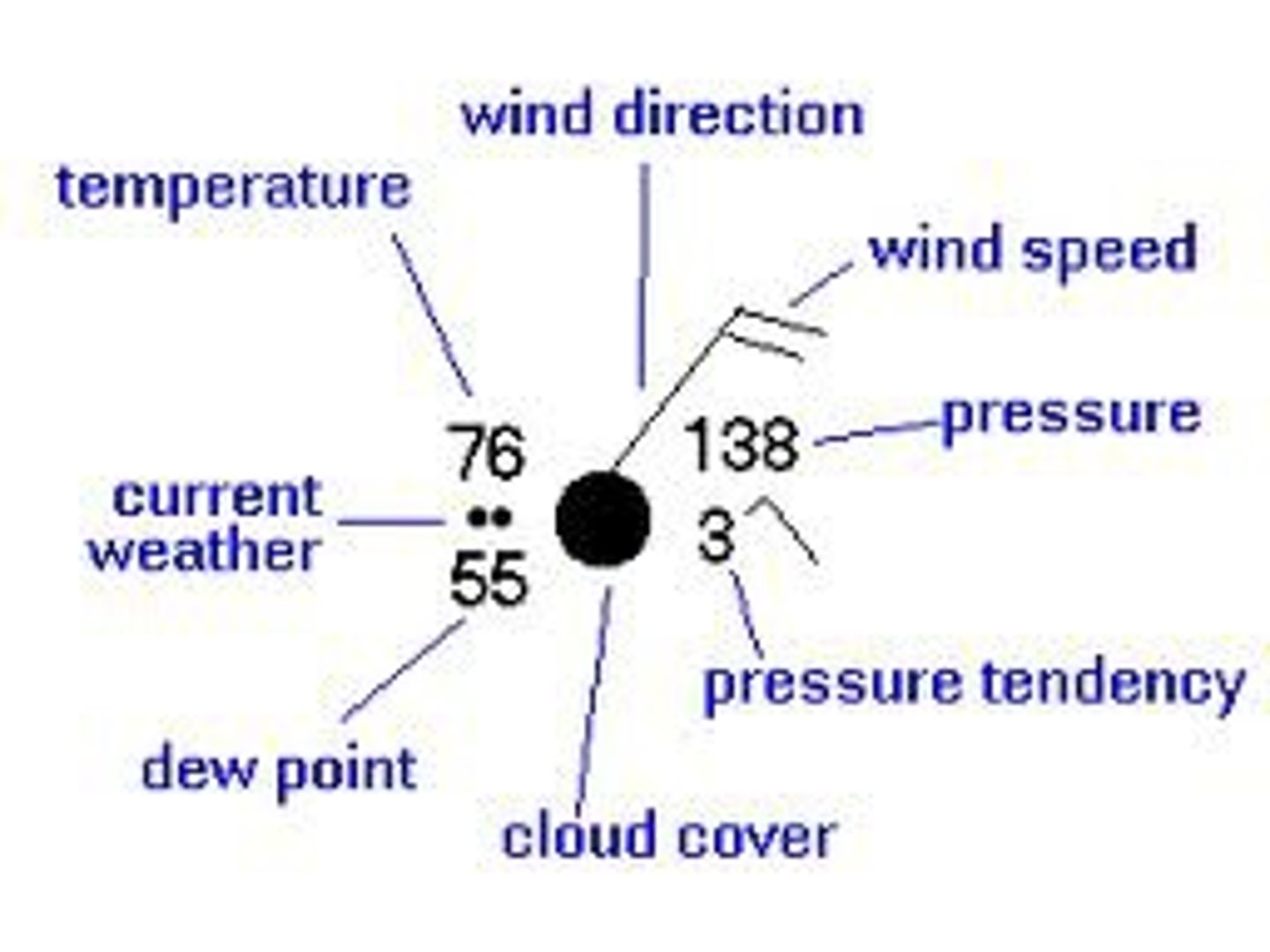
Station Model
A "cluster" of current weather data for one particular weather reporting site.
Thunderstorms
Must contain lightning or thunder
-Strong gusty winds
-Precipitation
-Hail - All sizes
Ordinary (pop-up) Thunderstorm
Most common type of thunderstorm
Form in areas with weak wind shear
Self-Extinguishing
-They actually "kill" themselves with colder, downdraft air
Short lifetime
-Almost always under an hour
Multi-Cell Thunderstorm
Clusters of t-storms that form in different stages in one area
The updrafts are stronger and support more continuous convection than a "pop-up" storm
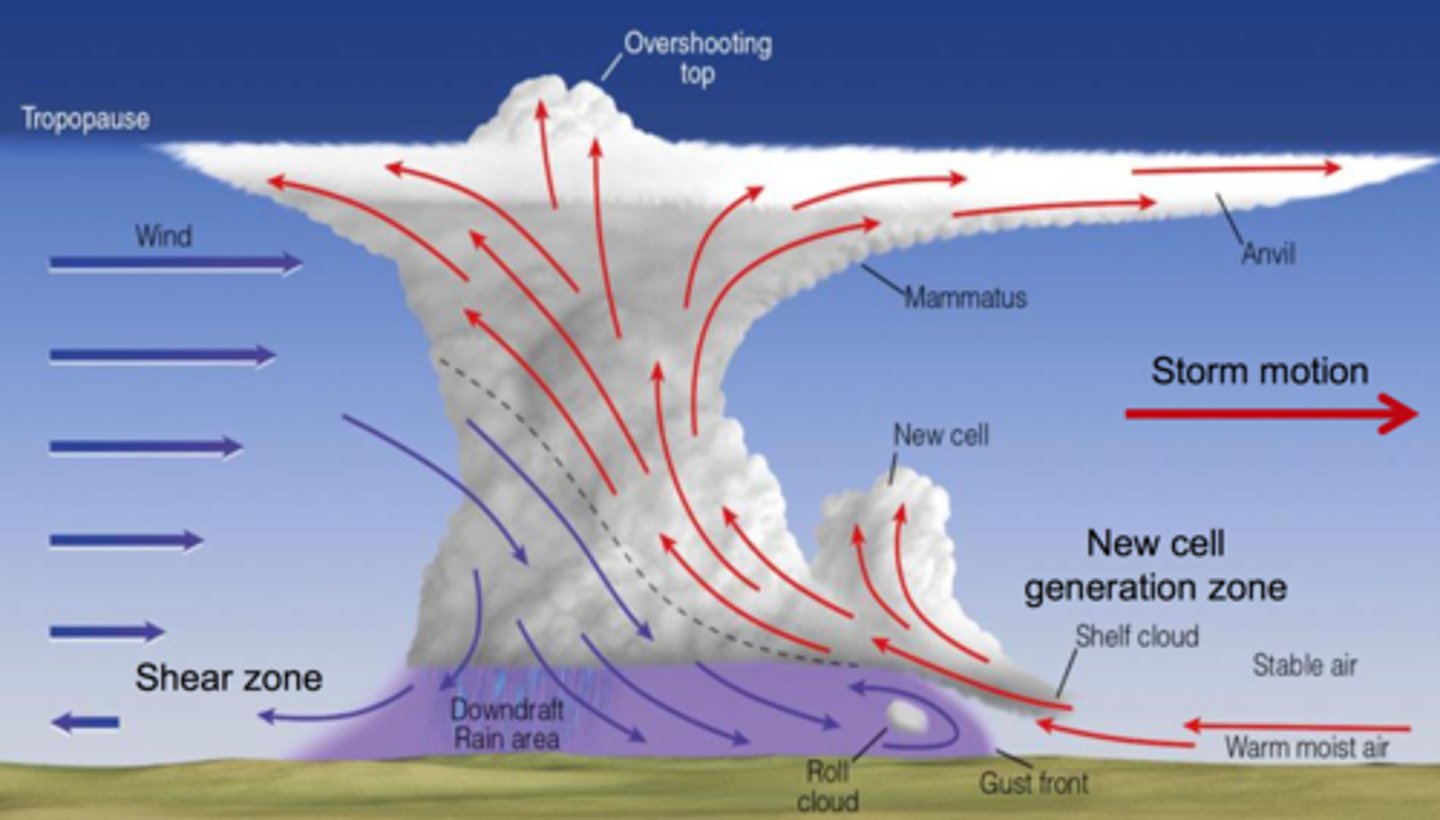
Squall-Line Thunderstorm
Organized line of thunderstorms
-The most intense rainfall is at the leading edge, then tapers off behind the linear
-May form along or ahead of a cold front
-If a portion of the leading edge jumps out ahead of the rest of the line, it's called a bow echo and likely will produce damaging winds
-Gusty winds huge downdrafts
-Heavy rain, winds and hail
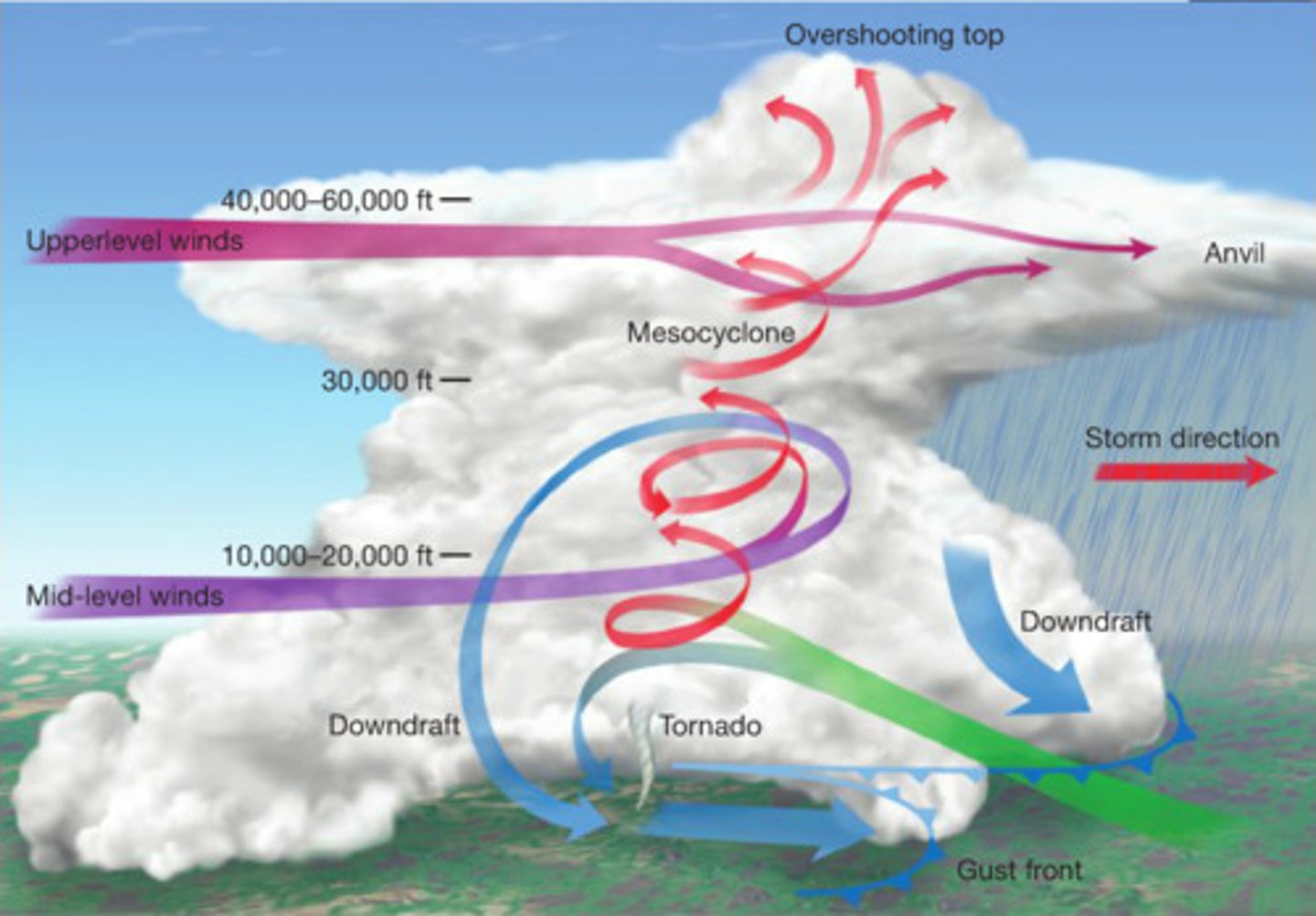
Supercell Thunderstorm
Some of the most dangerous storms
-A t-storm with a rotating updraft
-The rotating updraft is the difference between a multi-cell storm and supercell storm
-The most organized and long-lived type of t-storm
Severe Thunderstorm
Winds greater than 58mph
Hail larger than 1"
Presence of a tornado or possible rotation
Flanking Line (Beaver Tail)
Updraft/food supply for the mesocyclone
Rear-Flank Downdraft
Rear portion of the mesocyclone's downdraft
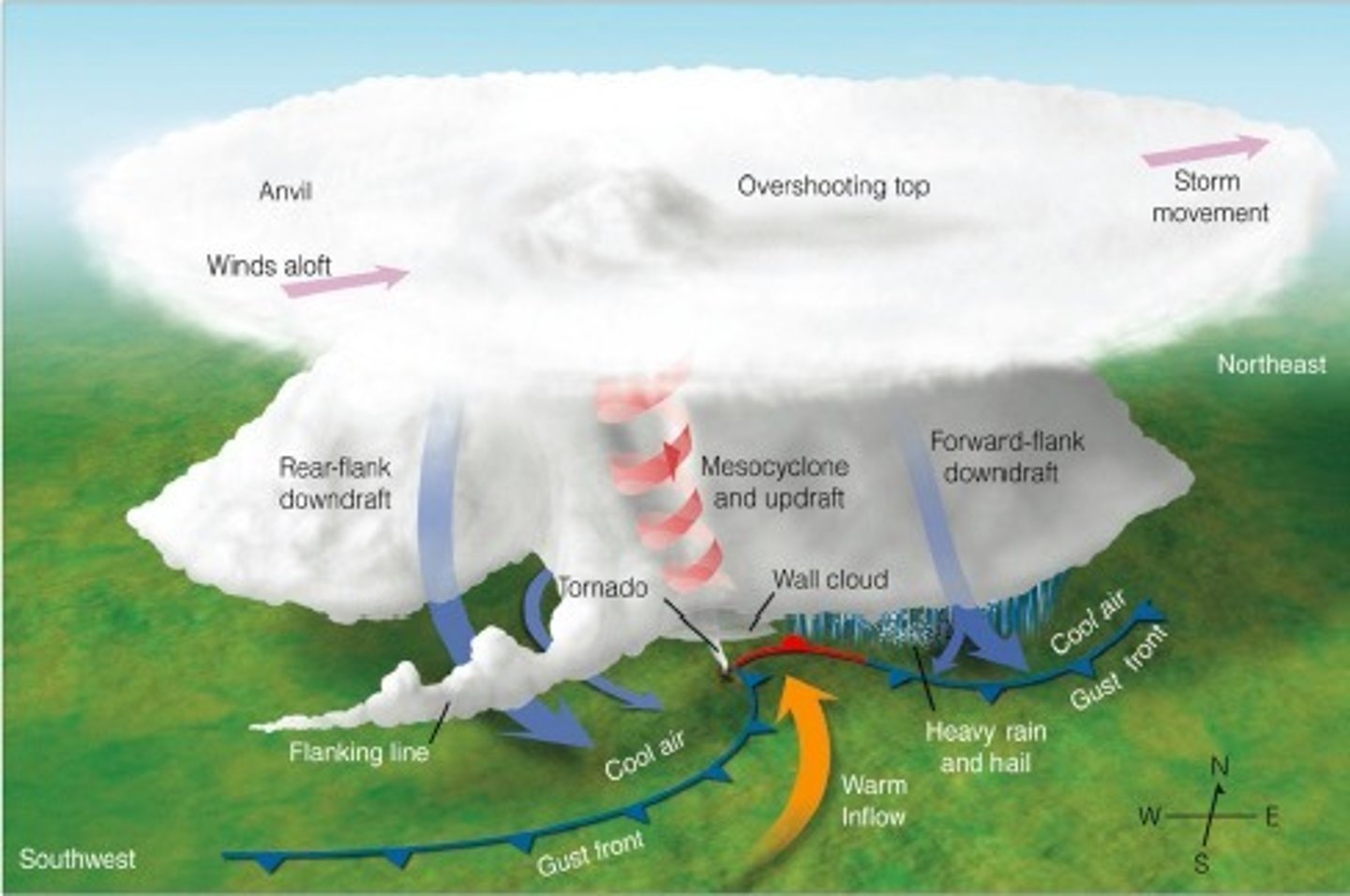
Storm Inflow "Suck Zone"
Influx of moisture rich air into a mesocyclone
Mesoscale Convection Systems
Large grouping of multiple storms that move together and last for hours
-Circular
->Covers many states
->Can produce severe weather
-Linear
->Very strong winds
->isolated, quick tornadoes
Gust Front
Leading edge of cold air coming from a large, severe thunderstorm.
"Shelf Cloud"
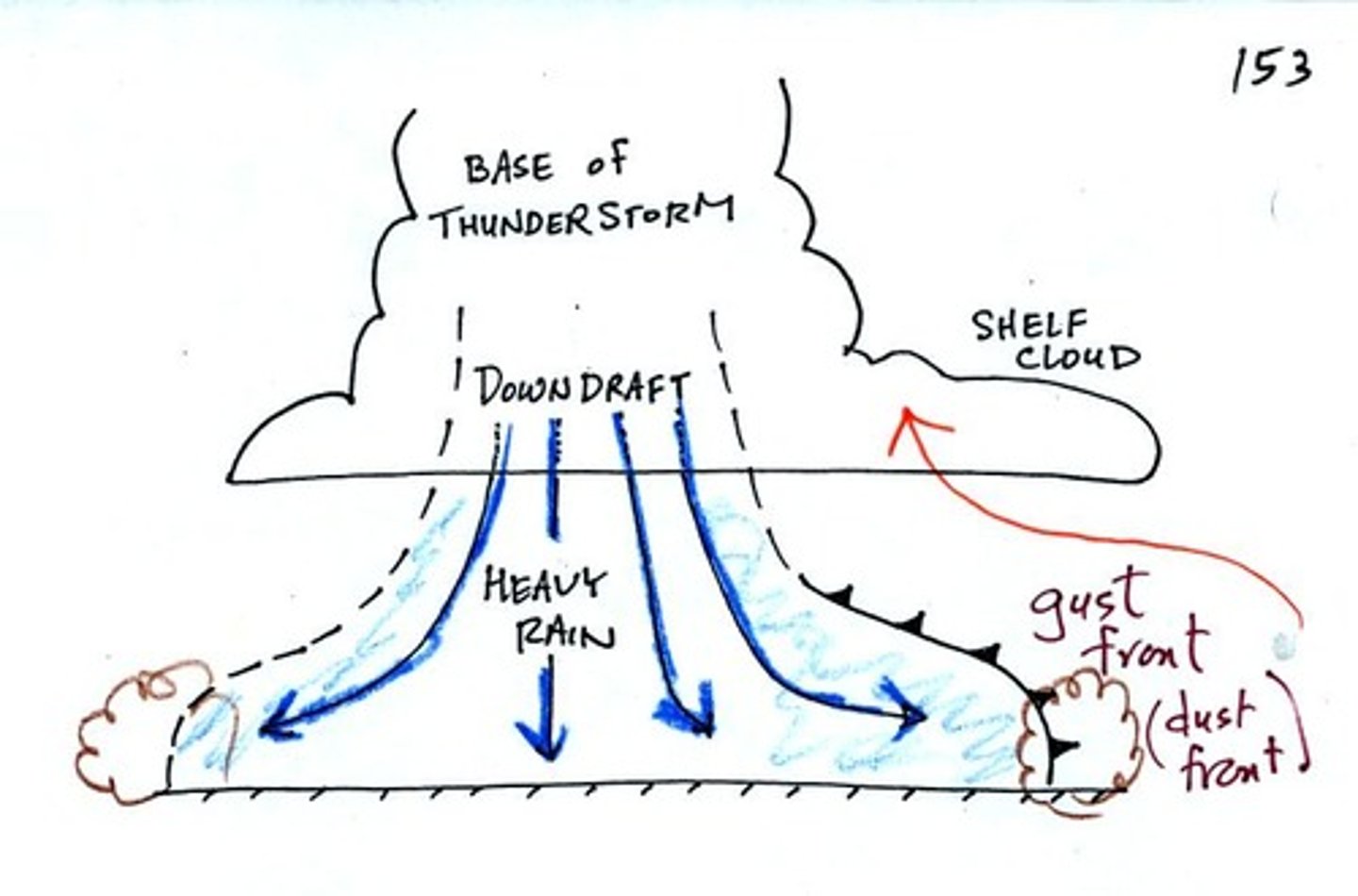
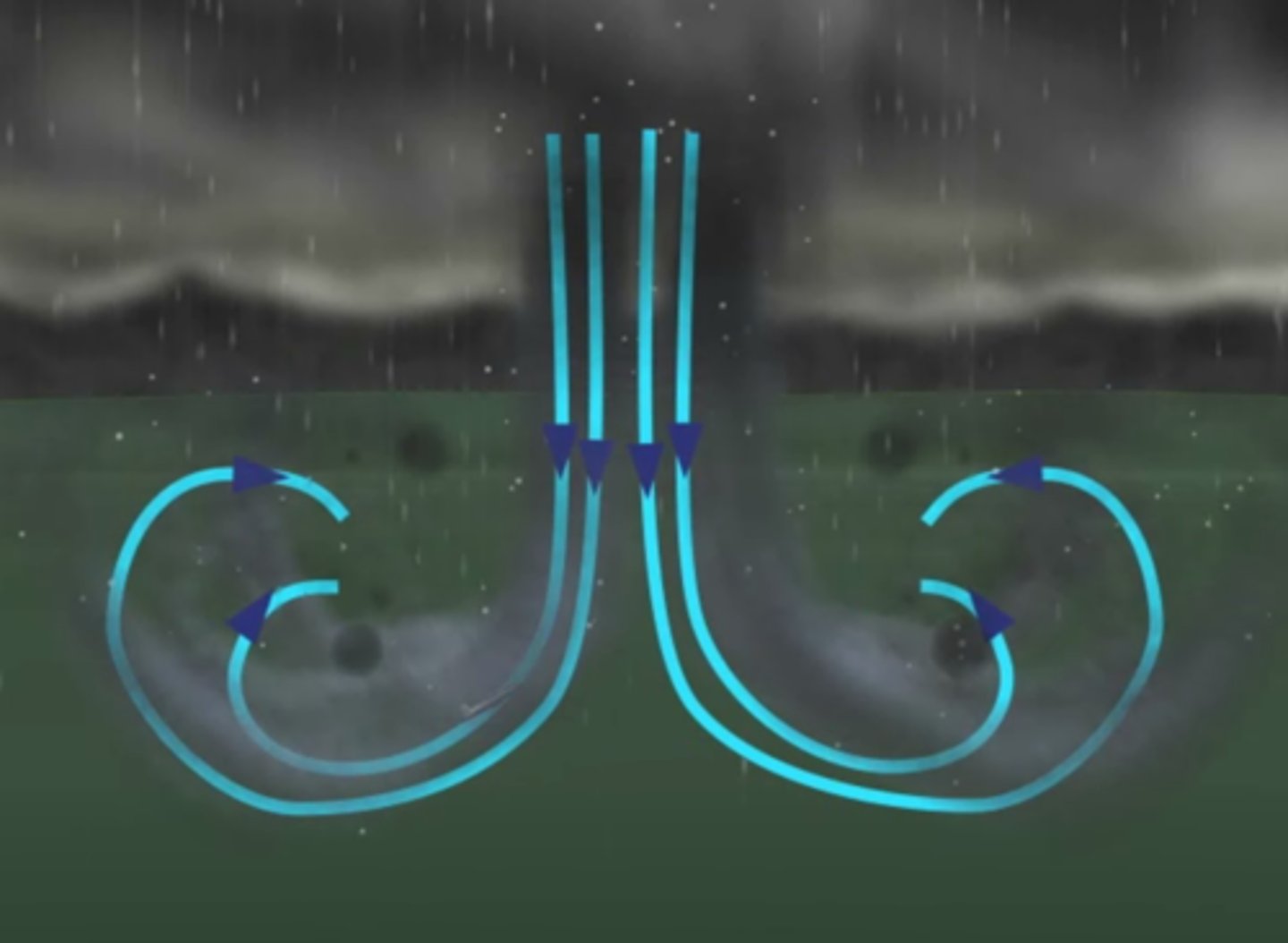
Microburst
A very localized column of sinking air, producing damaging straight line winds at the surface.
Usually located in a strong downdraft area and produces extremely strong straight-line winds.

Derechos
A widespread and long-lived, violent windstorm that is associated with a fast-moving band of severe t-storms usually taking the form of a bow echo.
Usually associated with a very buoyant, warm air mass.
Occur most often in the summer
Lightning
A discharge of electricity in a mature thunderstorm
-Heats the air over 50,000 degrees Fahrenheit
-5 times hotter than the sun
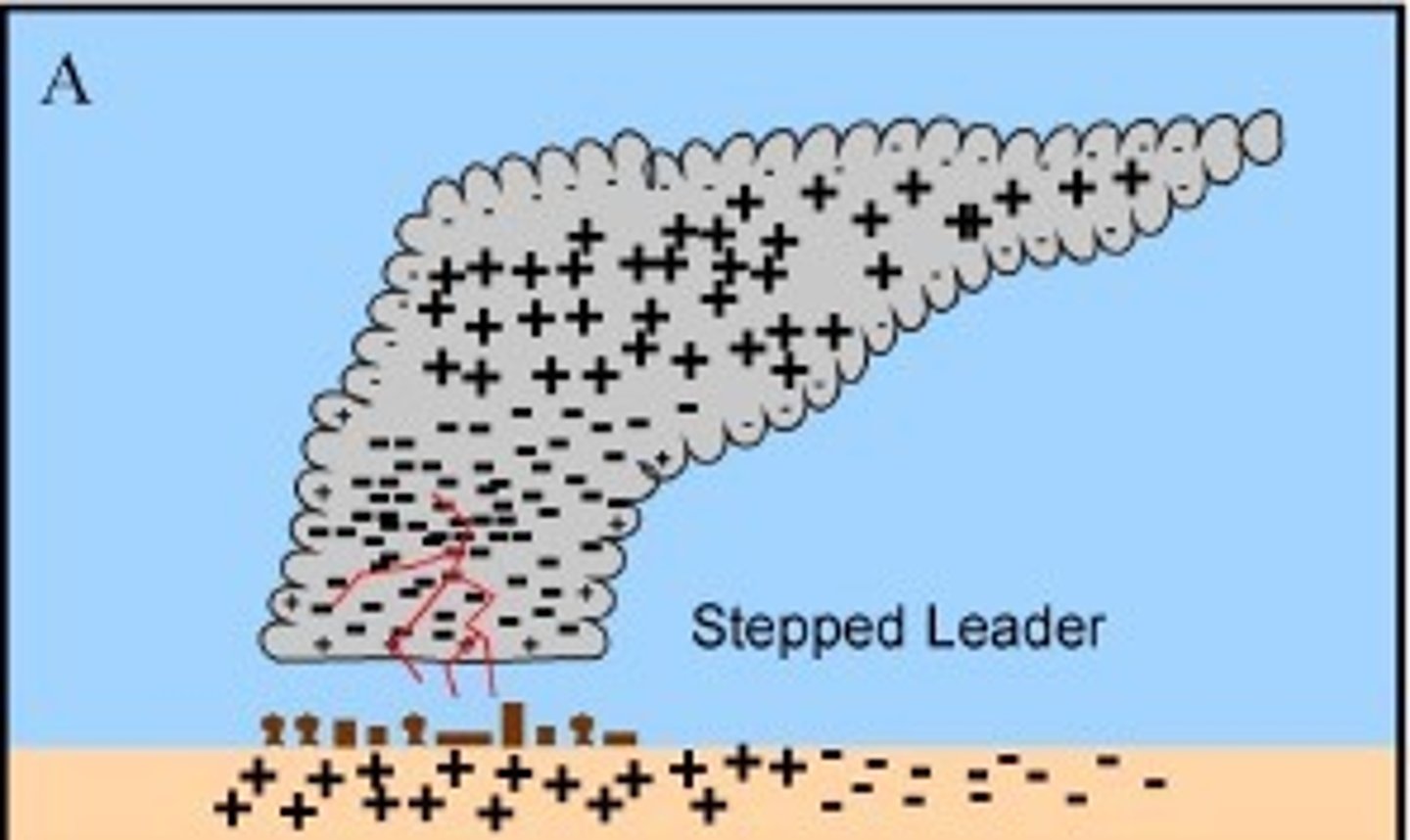
How does lightning work?
Charge separation occurs in the cloud.
Negative charges are found near the cloud base.
Positive charges are higher up in the cloud and at the ground.
The buildup of negative charges at the cloud base will eventually overcome the insulation of the air and "electricity" is created.
Stepped Leader
Initial "spark" of lightning leaves the clouds base.
Very faint and almost invisible
As it approaches the ground, a positive charge starts upward and meets the negative charges
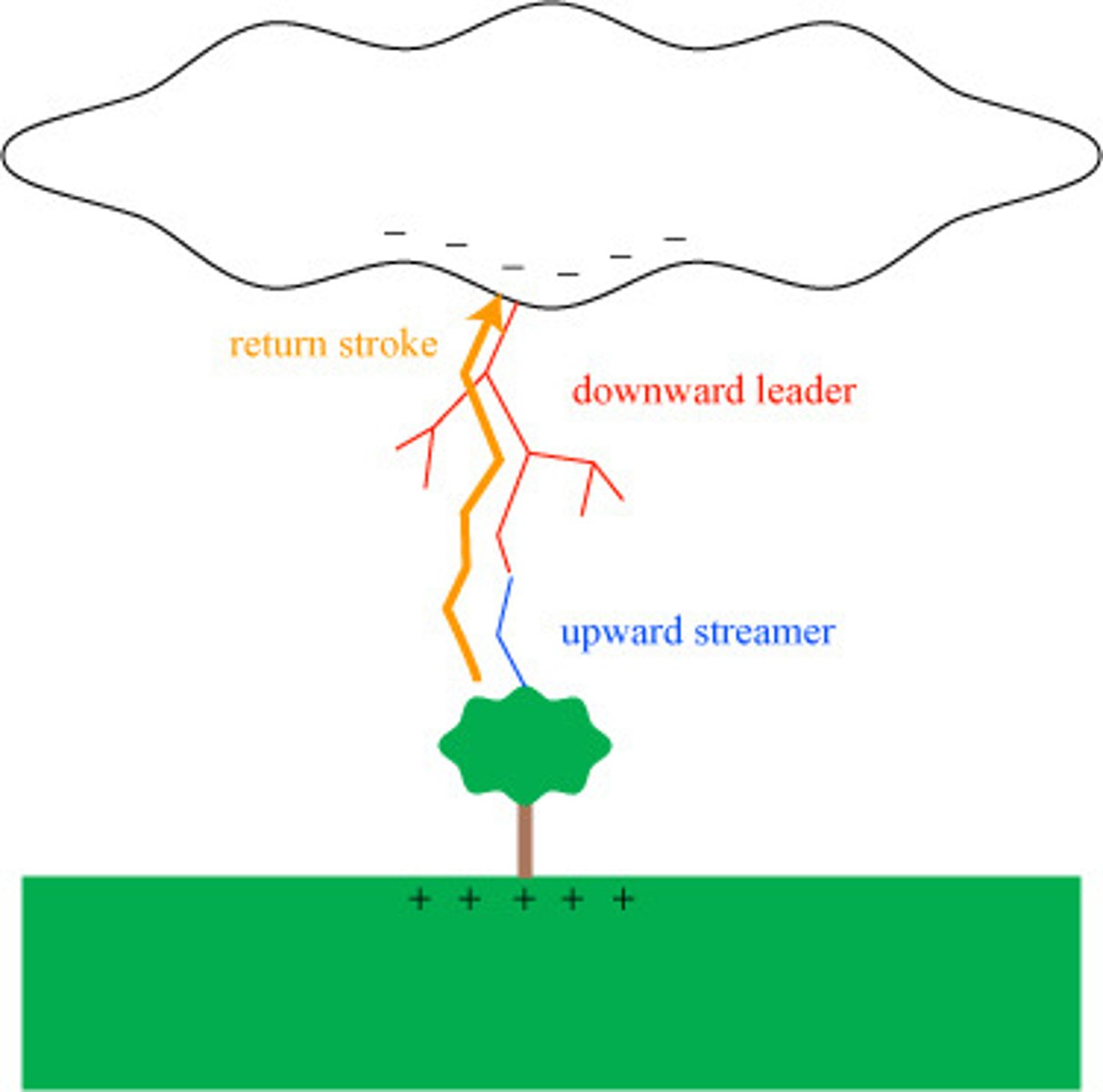
Return Stroke
The upward flow of current that we see as lightning
-This process happens quick. Around 1/10000 of a second
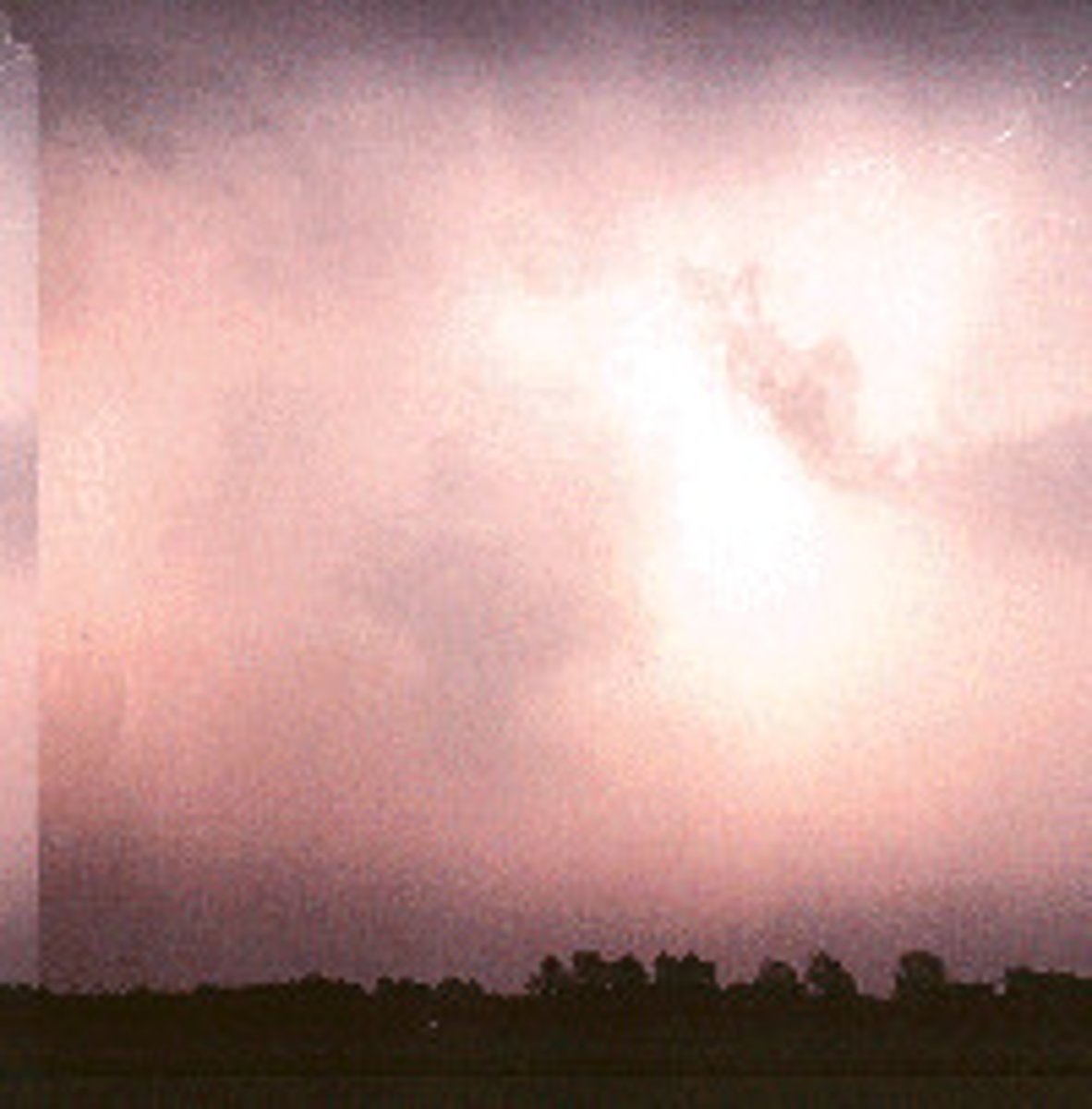
Sheet Lightning
Lightning that occurs within a cloud, and is obscured by other clouds
It appears as a luminous white sheet

Heat Lightning
Distant lightning that illuminates the sky, but is too far away for thunder to be heard.
Has nothing to do with "summer-time heat"
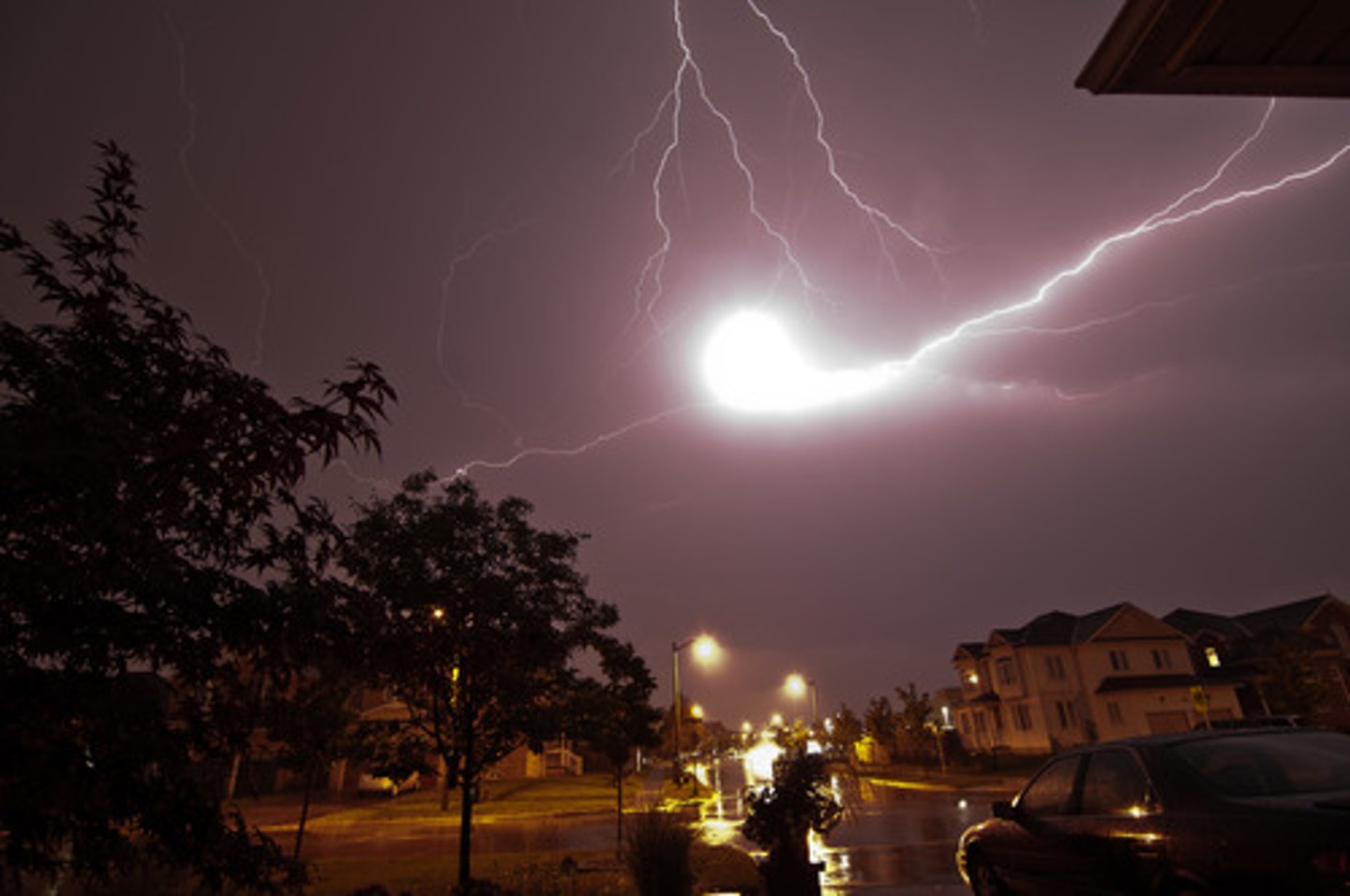
Ball Lightning
A luminous sphere that appears to "float" in the air, or zip around for a few seconds

Ribbon Lightning
When the wind blows a stepped leader horizontally
Thunder
Heating and expansion of the air creates a shock wave.
Sounds like a crack followed by a bang when we're close to the lightning strike.
Rumbles when we're farther away because the sound bounces off various surfaces before reaching the ear
Tornadoes
A rapidly rotating column of air whose rotation reaches the ground.
Characteristics:
Diameter: 100yards
Path length: 2 - 4 miles
Lifespan: 5 to 10 min.
Wind: 80 to 300 mph
Forward Speed 30 mph
Waterspouts
Similar to tornadoes, only over water and with much slower speeds.
Occur in coastal waters and are associated with weal convection t-stroms
Funnel Cloud
A funnel-shaped cloud of condensed water droplets, associated with a rotating column of air.
Extend from the base of a cloud but do not reach the ground
Tornado Dust-Whirl Stage
Dust swirling upward form the grounds and grows towards the funnel cloud in the sky
Tornado Organizing Stage
Downward extend of funnel and "connection" with dust-whirl on the ground
Tornado Mature Stage
Tornado on the ground
Tornado Decaying Stage (Roping Out)
Stretched into a thin funnel shape -rope
Tornado "Time Schedule"
Most occur in the late afternoon due to daytime heating.
Most common month are March, April, May, June and July
Mesocyclone
A large rotating vortex inside a supercell t-storm that will sometimes produce tornadoes
Suction Vortices
Stronger winds than the overall tornado that produces significant damage
-Mini tornadoes inside the main tornado
Doppler Radar
A specialized weather radar that "sees" wind (velocity) and precipitation (reflectivity).
Red: Wind blowing away from the radar
Green: Wind blowing towards the radar
Measuring the Strength of Tornadoes
Meteorologist examine the damage done by tornadoes and the winds are estimated based on damage produced
The Fujita Scale
EF-0 Weak 65-85mph
EF-1 Moderate 86-110 mph
EF-2 Significant 111-135 mph
EF-3 Severe 136-165 mph
EF-4 Devastating 166-199 mph
EF-5 Incredible 200 mph
EF-0 to EF-1 74%
EF-2 to EF-3 25%
EF-4 to EF-5 1%
Tornado Direction and Duration
Most tornadoes travel form southwest to northeast.
Some tornadoes change direction and path
-Some have even traveled backward and made complete circles
Warning Signs
Strong persistent rotation in clouds.
Circulating dust and debris.
Hail and then rapid quietness.
A very loud roar with heavy rain
Tornado Watch
Watch out for t-storms that could produce tornadoes
Thunderstorm Watch
Watch out for severe t-storms
Tornado Warning
A tornado is occurring now - or soon will
Thunderstorm Warning
Severe thunderstorms are occurring now - or soon will.
Thickness charts help forecasters
Predict whether falling precipitation will be rain or snow.
A weather warning indicates that
Hazardous weather is either imminent or occurring within the forecast area.
The ASOS system is designed to provide nearly continuous information about wind, temperature, pressure, cloud-base height, and runway visibility at various airports.
True
False
TRUE
____ tend to steer the movement of surface pressure systems.
Winds aloft
There are many techniques involved in creating a weather forecast. Which of the following do not belong?
Numerical Modeling, Persistence, Farmer's Almanac
According to the National Weather Service, the subjective term "fair" implies a rather pleasant weather situation.
True
False
TRUE
Seasonal forecasts make specific predictions of rain or snow. (In this case, specific refers to exact amounts of rain/snow and on what dates)
True
False
FALSE
An analysis is a
Surface or upper-level chart that interprets the present weather patterns.
A blocking high is a
high pressure system and accompanying ridge that persists in the same location for many days.
For ____ to occur, separate regions containing opposite electrical charges must exist within a cumulonimbus cloud.
Lightning
Squall lines generally do not form
Behind a cold front
The wind shear associated with several major airline crashes is believed to have been caused by
Microburst
An ordinary thunderstorm:
is a scattered/isolated storm and normally not severe.
Large hail is more common in Kansas than in Florida.
True
False
TRUE
Distant lightning that is so far away you cannot hear the thunder is called
heat lightning
The most likely time for an ordinary thunderstorm to form is
Late Afternoon
Thunderstorms are a common phenomenon in areas dominated by subtropical highs.
FALSE
Opening windows during a tornado decreases the pressure on the opposite wall and therefore decreases the chances that the building will collapse.
FALSE
To help distinguish a storm's air motions, a Doppler radar can display ____
wind velocities in color
Tornadoes have occurred in every state, including Alaska and Hawaii.
True
False
TRUE
According to the Enhanced Fujita Scale, an ____ tornado causes only minimal damage, whereas an ____ completely demolishes a house and sweeps it off its foundation.
EF0; EF5
To an observer on the ground, the first sign that a supercell may give birth to a tornado is the sight of ____.
rotating clouds at the base of the storm
Damage from a tornado is normally most severe during the ____ stage.
mature
If a downdraft is too ____, it may inhibit the lifting needed for tornado formation.
cold and strong