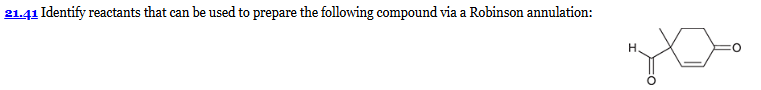chapter 21 : Alpha Carbon Chemistry (enols and enolates)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
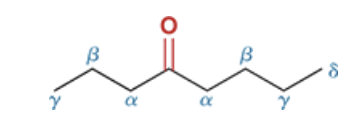
label the carbons of this molecule based on their proximity to the carbonyl group
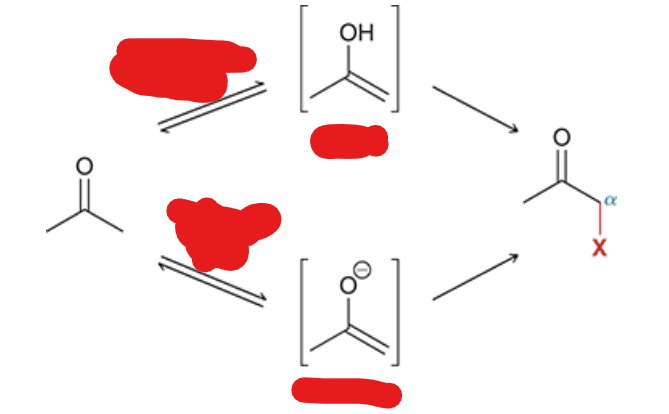
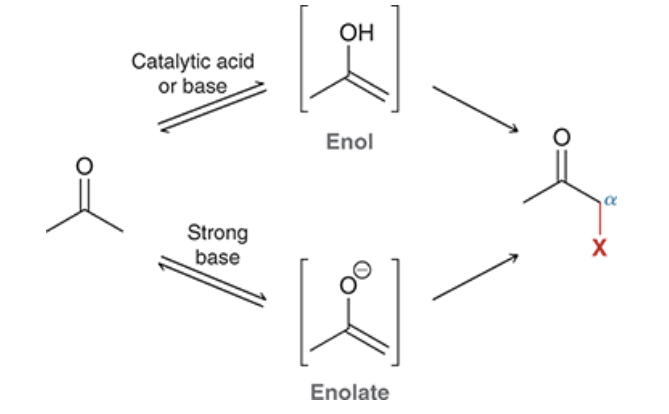
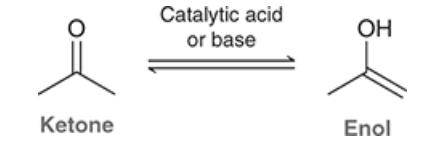
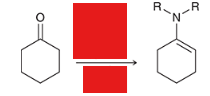
label the reagents and give the general names of each of the intermediates
Draw an enol
Does this molecule exhibit resonance or tautomerization?
tautomerization
draw an enolate
Does this molecule exhibit resonance or tautomerization?
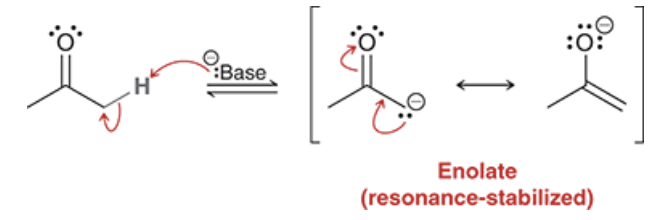
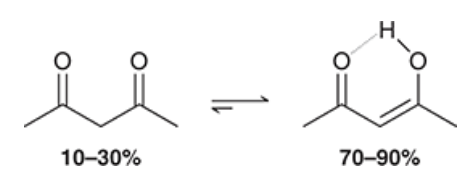
generally the ketone tautomer of an enol is (more or less) favored. what may be the exception to this rule?
generally, ketone is more favored. However enol may be favored in the case of intramolecular H-bonding or a conjugated pi system (as seen in the figure)
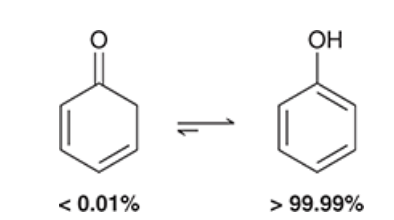
show an extreme example of when the enol tautomer is more favored than the ketone tautomer
phenol, ketone isomer is practically negligible due to aromaticity of the enol isomer
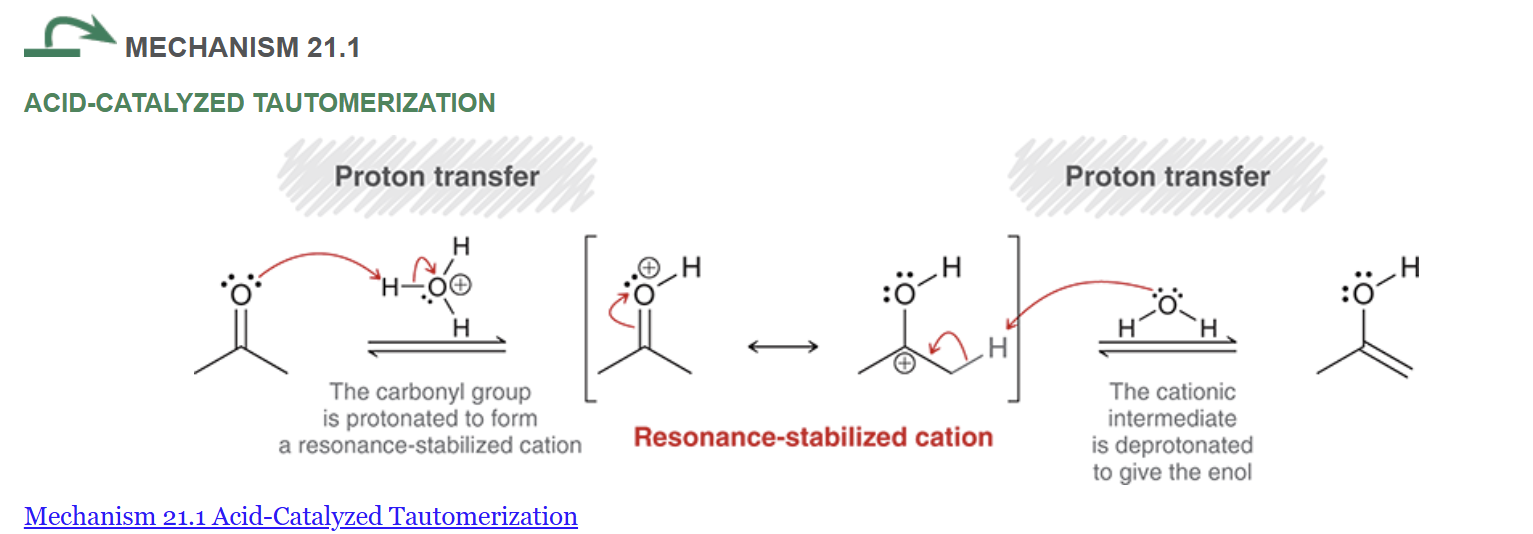
show the mechanism for acid catalyzed enol tautomerization
show the mechanism for base catalyzed enol tautomerization
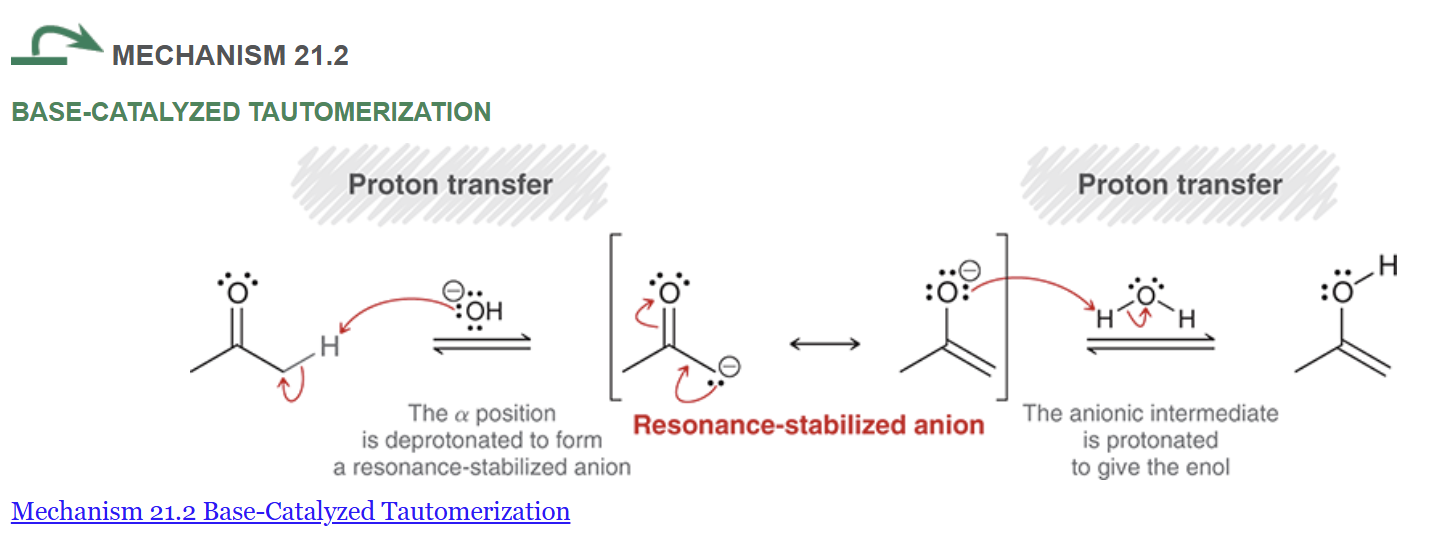
enolates are more (nucleophilic or electrophilic) than enols
nucleophilic
enolates may nucleophile attack via the ______ or the ______. the _______ attack is more common (its the only one of the two attacks we see in this chapter)
Oxygen (O-attack) or the Carbon (C-attack); C-attack
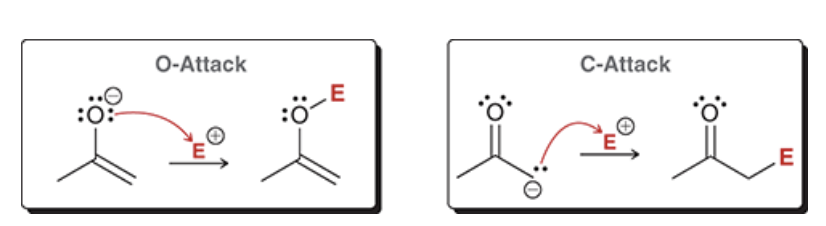
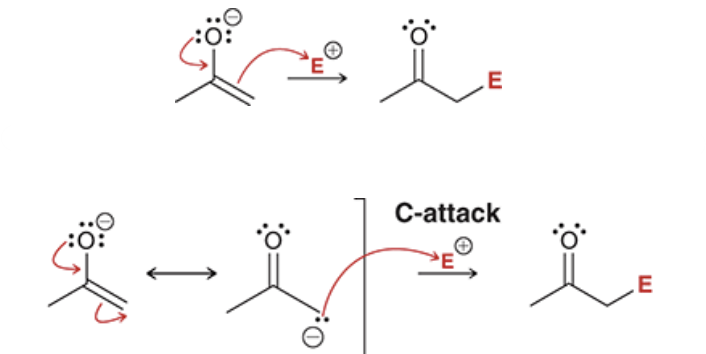
show how an enolate performs a C-attack (use E for an electrophile)
either way works
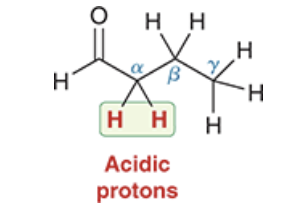
Which protons are acidic protons on an aldehyde or ketone, which may be removed to form an enolate.
T/F generally, NaOH is not strong enough to deprotonate these protons.
T/F Generally, alkoxides (RO-) are not strong enough to deprotonate these protons.
only the alpha protons
True
False
what two strong bases may be used to irreversibly and completely from an enolate? draw both
NaH (H-) or LDA (Lithium diisopropylamide)
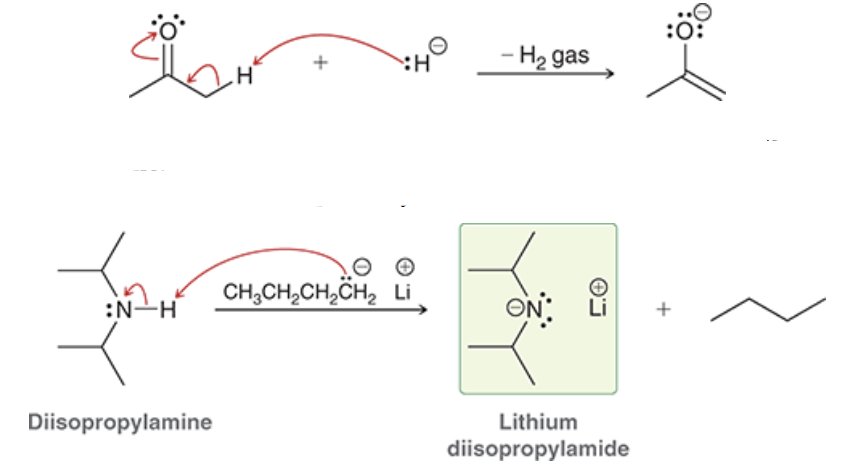
LDA features two bulky _____ groups which allows it to be a strong _____ but not a good _____
isopropyl; base; nucleophile
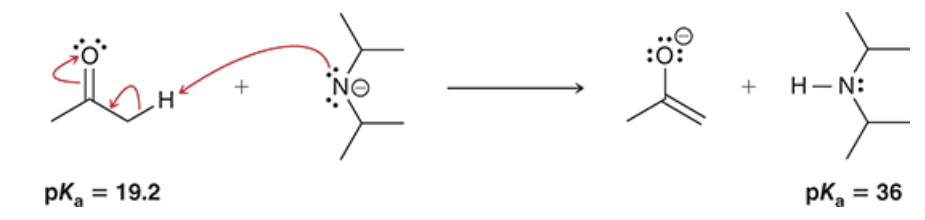
what base may be used to form enolates and ketones in equilibrium? under which conditions may this base have nearly complete enolate formation? what bases always irreversibly form enolates?
alkoxides may be used to enolates and ketone in equilibrium
when protons are alpha to two carbonyl groups, they are much more acidic, making them able to be removed by even water
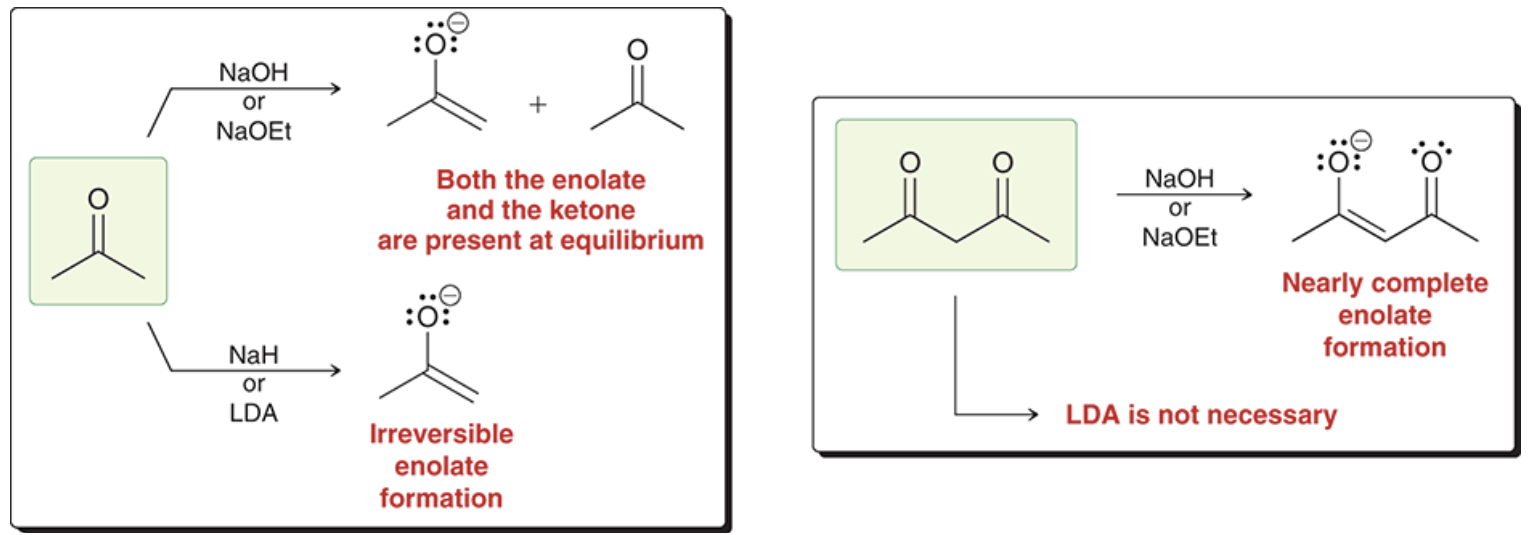
T/F water can remove protons that are alpha to two different carbonyl groups
true
mechanism of acid catalyzed halogenation of ketones
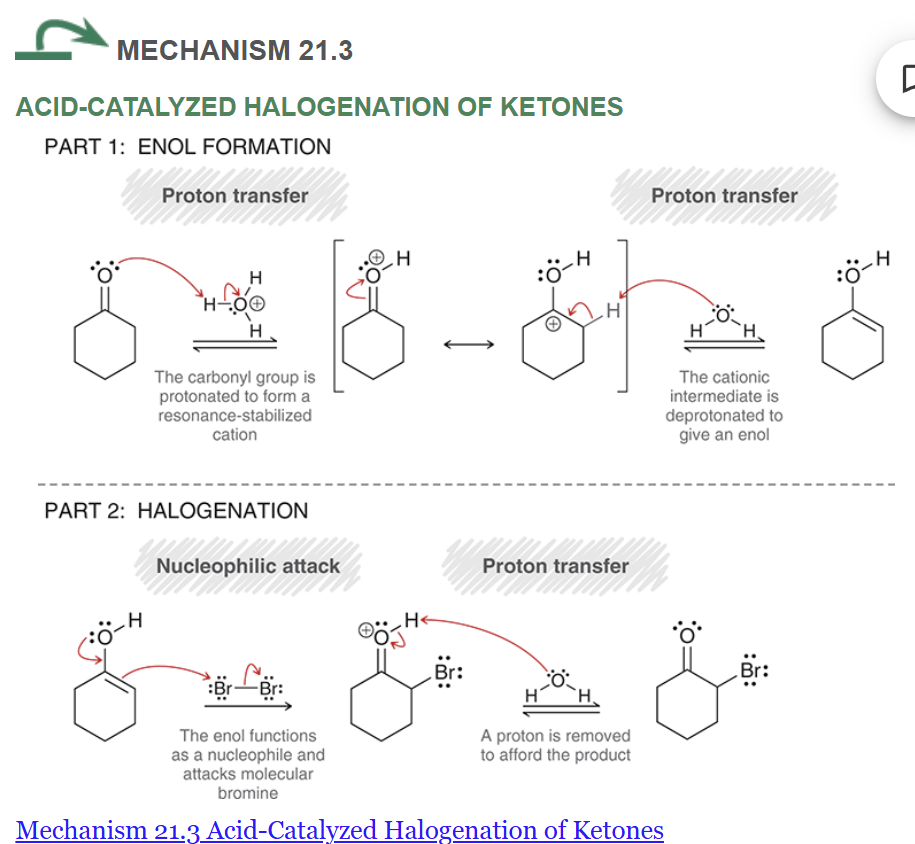
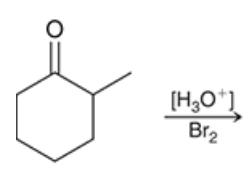
major and minor products?
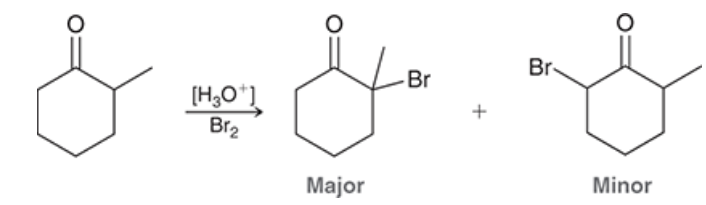

reagents?
note: in step 2, any weaker base would work for the elimination (Li2CO3, NaOEt or pyridine)
If you use T-BuOK, you would get the hofmann product resulting in a different product than shown
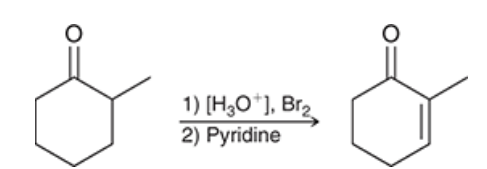
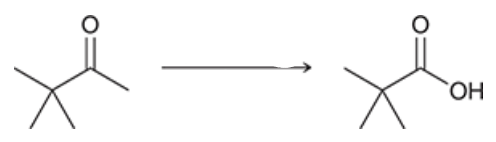
show the general reaction of the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction
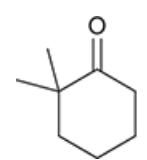
Show how to do the base-catalyzed alpha halogenation with this molecule. Note: What happens when there is more than one alpha proton in this reaction
more than one proton results in further rapid halogenation
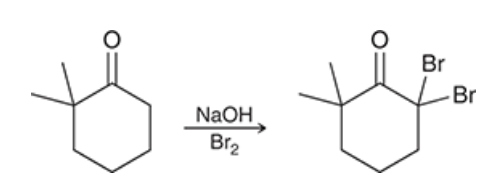
reagents? what is this rxn. called?
Haloform reactions
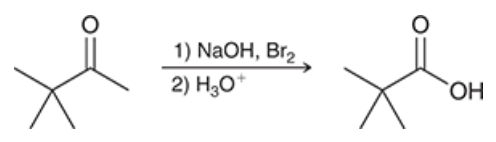

show the mechanism for the haloform rxn. with the starting molecule. What exception is seen in this mechanism??\
unshown first step: base catalyzed alpha halogenation results in 3 brominations at the alpha position
The exception seen is that a carbon is a leaving group in this rxn.
The CBr3- will deprotonate the carboxulic acid to form a carboxylate and bromoform
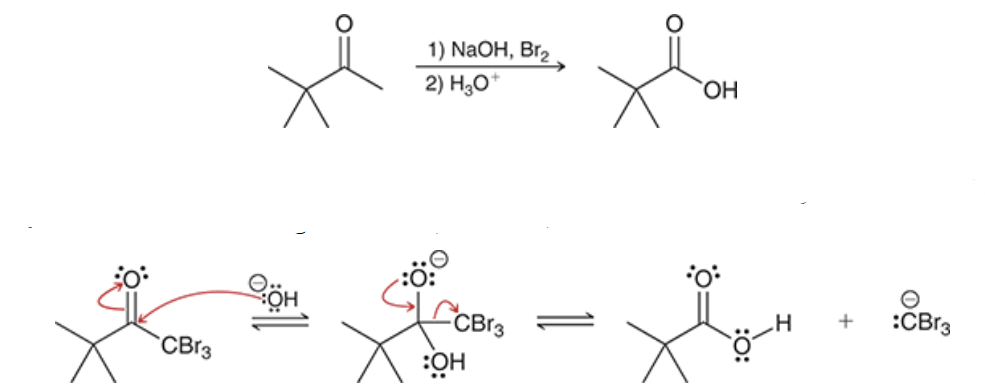
the haloform reaction works best when _________
one side of a ketone has no alpha protons (as seen in this molecule)
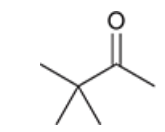
Show the general reaction and mechanism for aldol addition (not crossed). Start with acetaldehyde
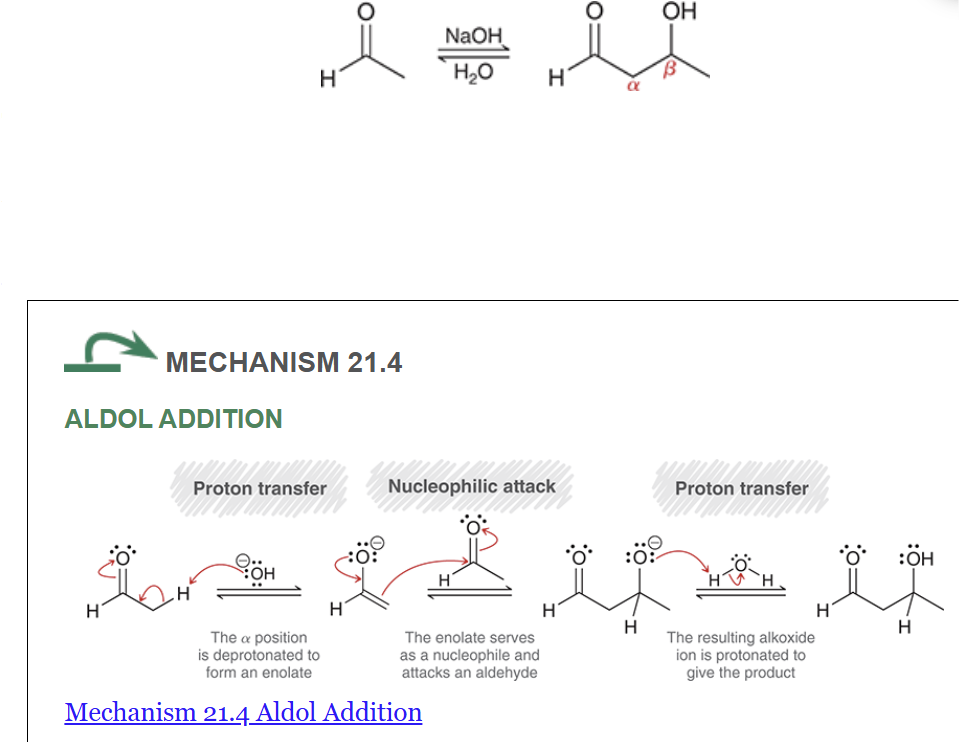
show an aldol. why are they names aldols?
the name “aldol” come from aldehyde and alcohol.
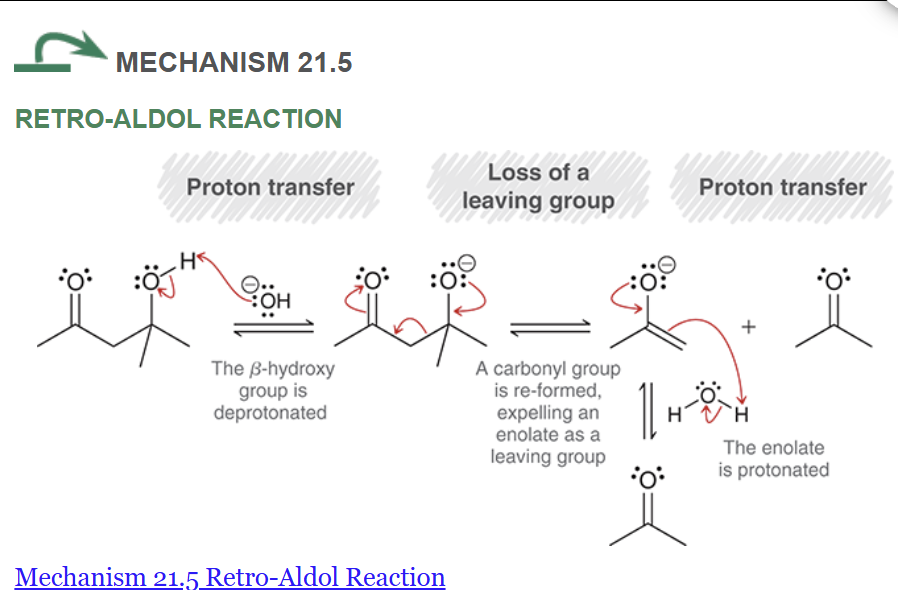
show the mechanism for the retro aldol reaction
For most ______, the aldol product is favored in the aldol addition reaction. The product is not favored for most ______
simple aldehydes;
ketones
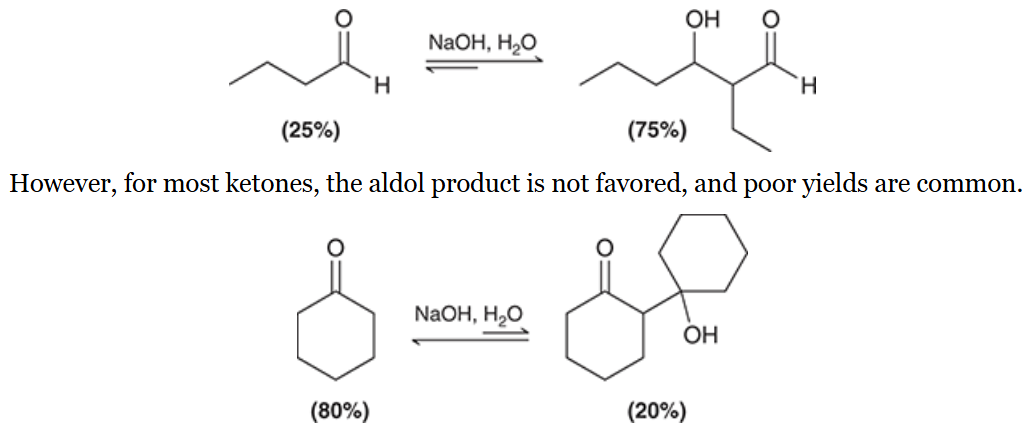
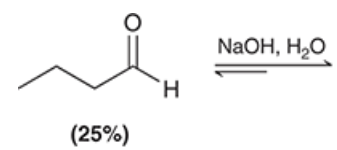
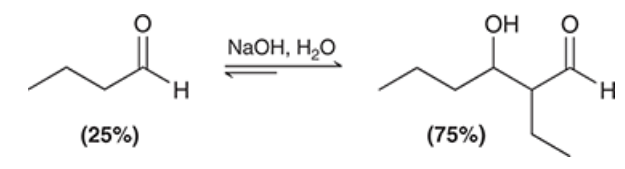
show the product
under what conditions do products of aldol reactions undergo elimination
when heated in acid or base
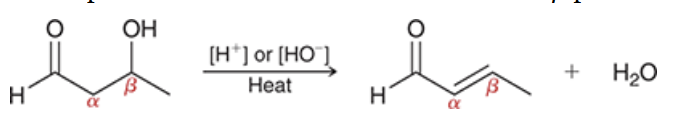
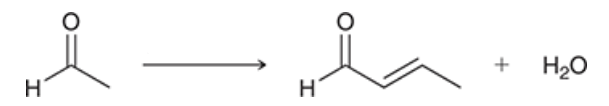
reagents? rxn name?
aldol condensation
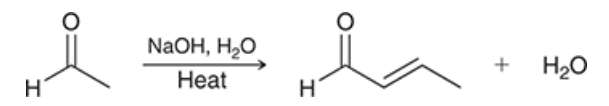
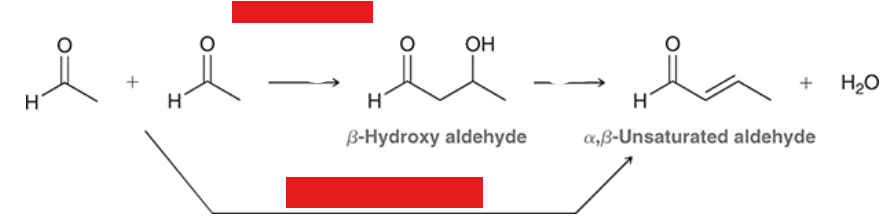
show the name and reagents of each reaction
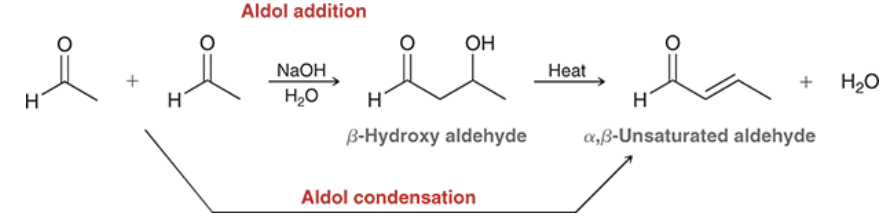
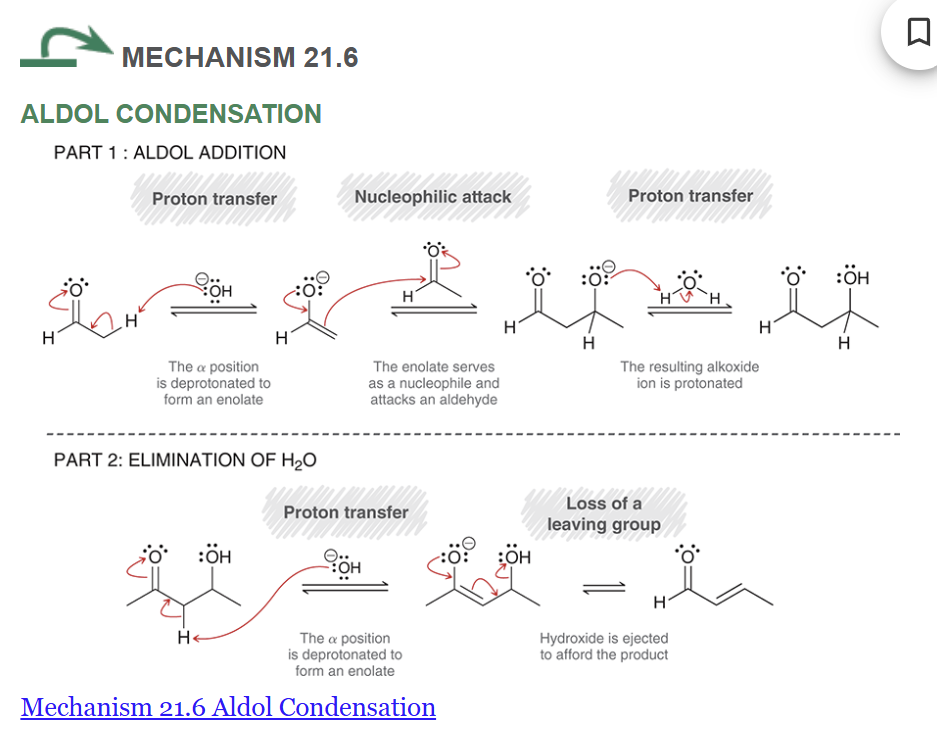
Show the mechanism of aldol condensation starting with acetaldehyde
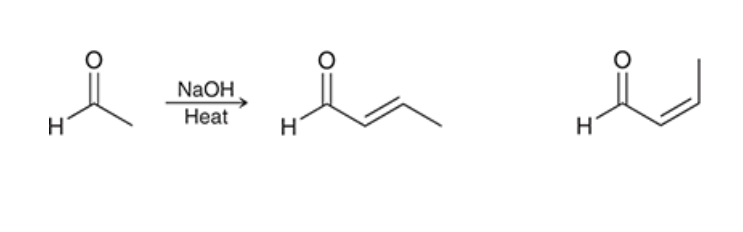
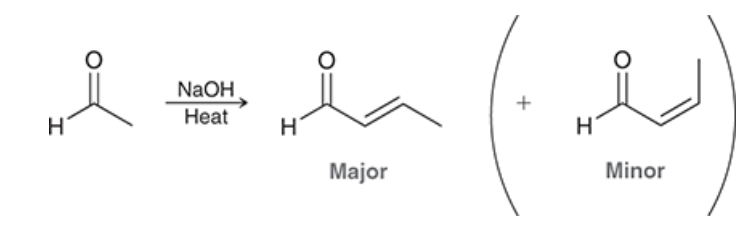
which product is major?
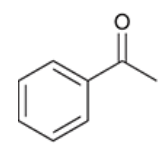
draw the product after this molecule undergoes aldol condensation
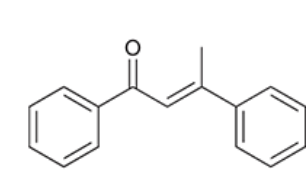
draw each product and indicate whether or not its yield is poor or not
yield is poor on the top equation due to it being a ketone undergoing aldol addition
yield is better on the bottom as the conjugated pie system pushes the reactions towards products
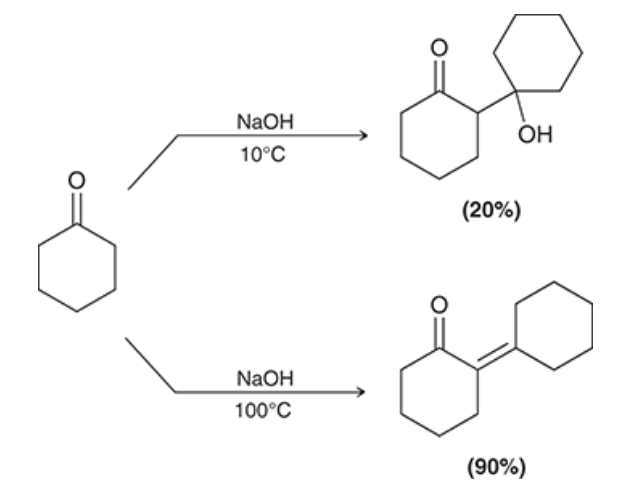
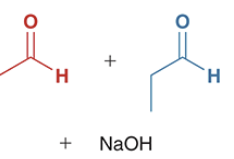
when this crossed aldol reaction occurs, show the possible outcomes of this reaction
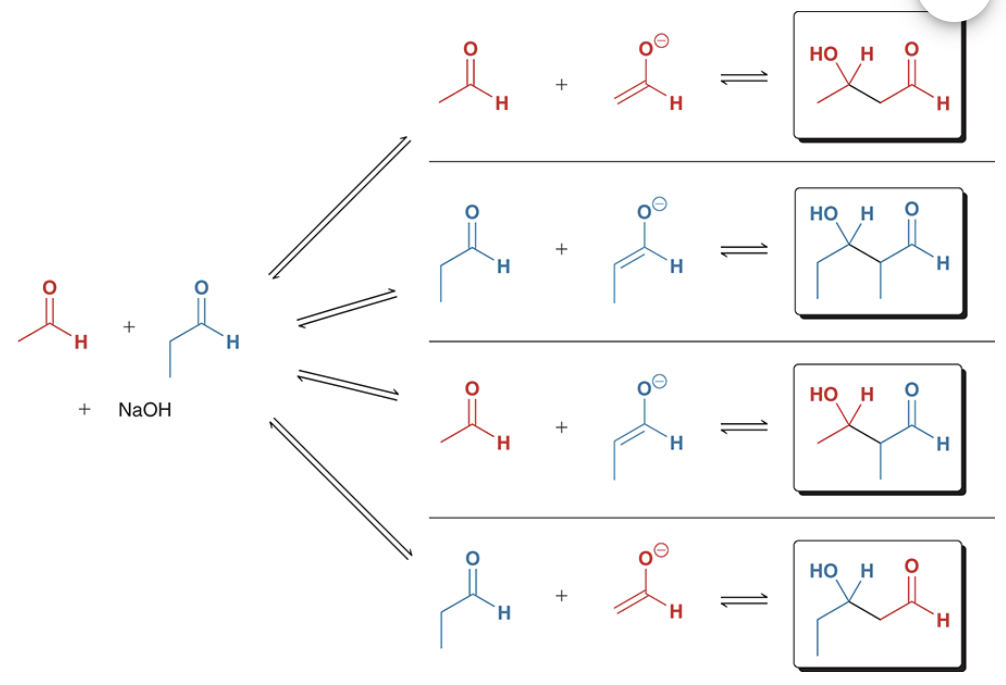
show the crossed aldol reaction between formaldehyde and propanal
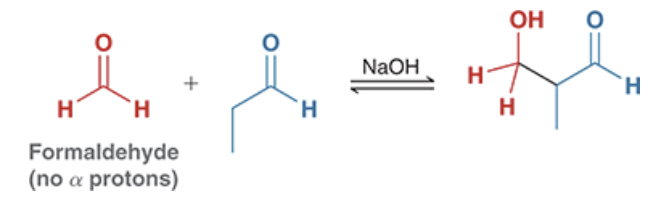
how may you direct a crossed aldol reaction to obtain a certain desired product?
use starting materials where only one alpha position is available for the reaction (ex. formaldehyde or benzaldehyde mixed with another aldehyde molecule)
use LDA to irreversibly from an enolate from one your starting materials, then add the other starting material dropwise (see figure)
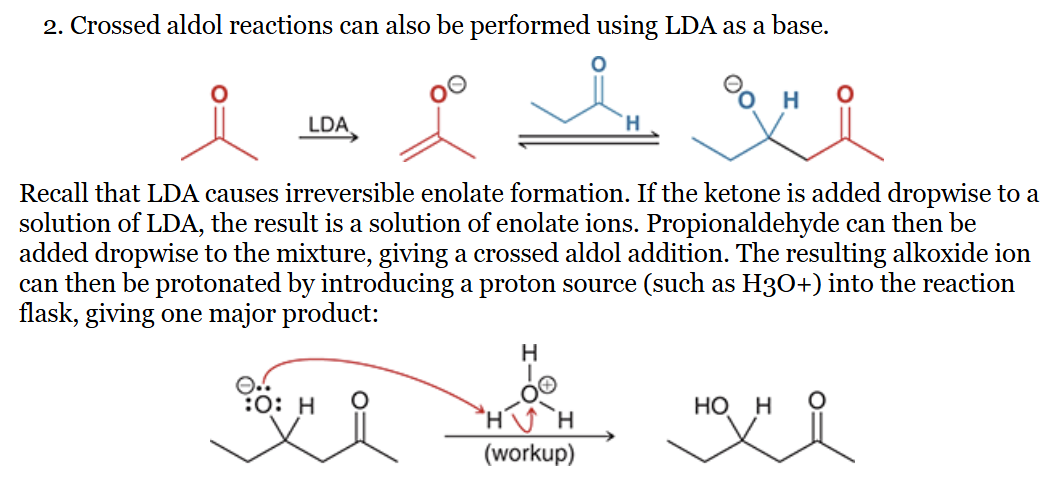
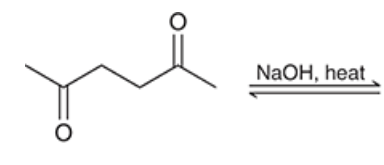
show both the product and mechanism
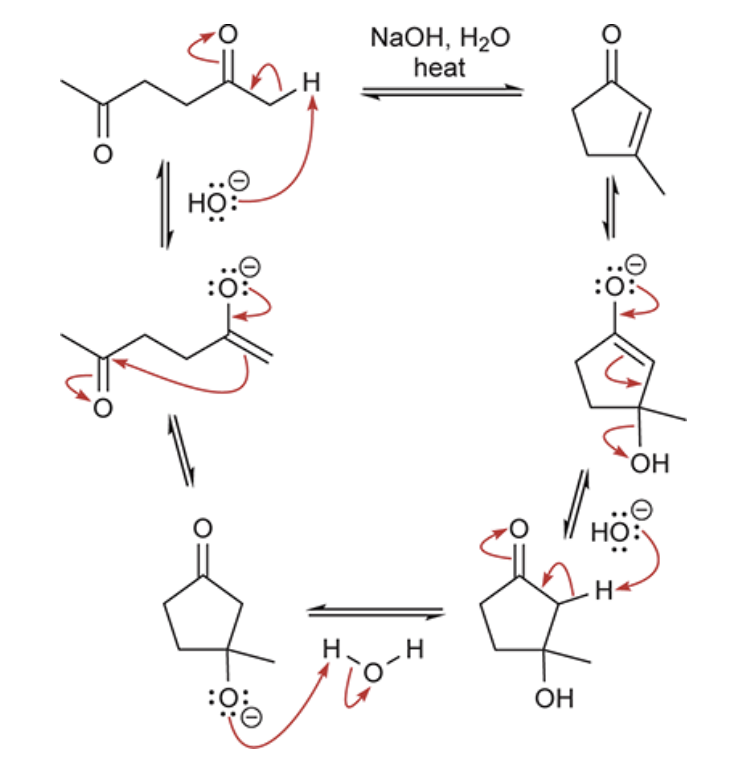
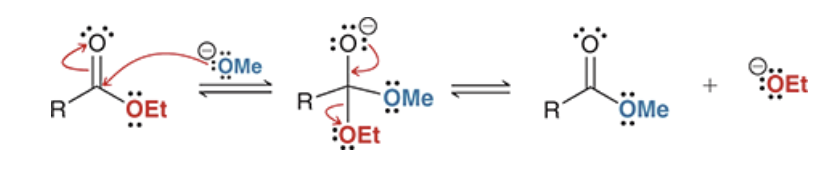
what base must be used in a claisen condensation? why?
the base used must match the group attached to the oxygen of the ester group. this is done to avoid transesterification
show the mechanism of a Claisen condensation
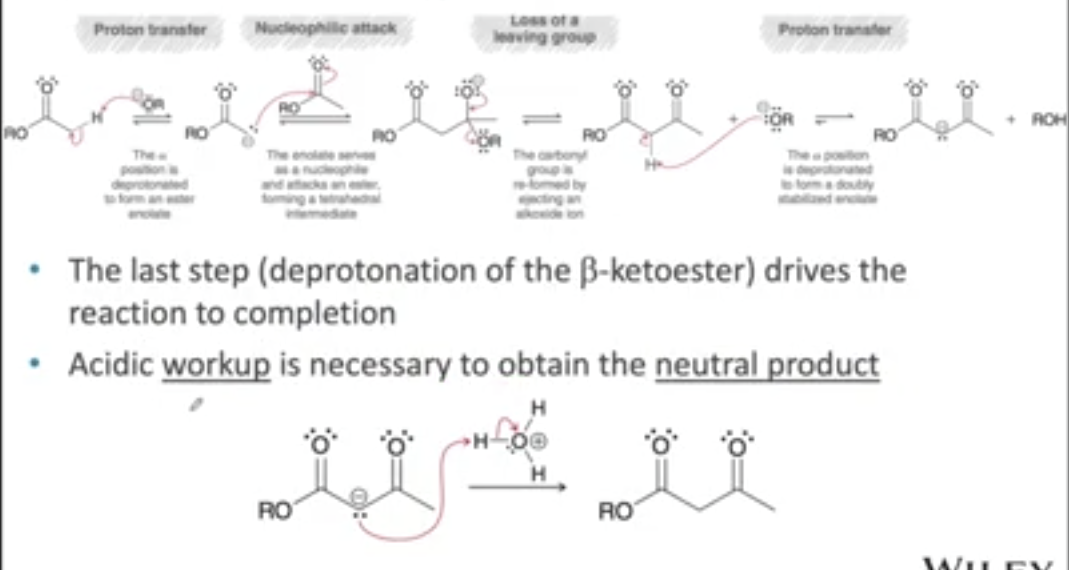
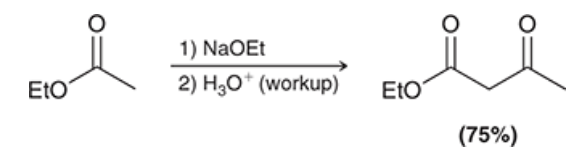
what is the general name of the product of a Claisen condensation?
β-keto ester
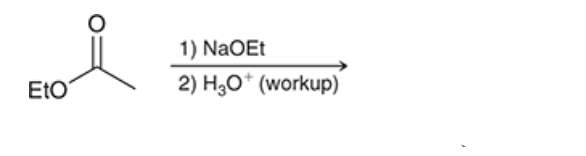
product
limitations of Claisen condensation
starting ester must have 2 alpha protons because removal of second proton by the alkoxide ion drives equilibrium forward
hydroxide may not be used to promote Claisen condensations, otherwise hydrolysis would occur
the alkoxide must match the -OR group of the ester in the rxn
transesterification
the conversion of an ester group into different ester group using an alkoxide ion. This is the result if you try to do a Claisen condensation without matching the alkoxide ion to the -OR group of the ester
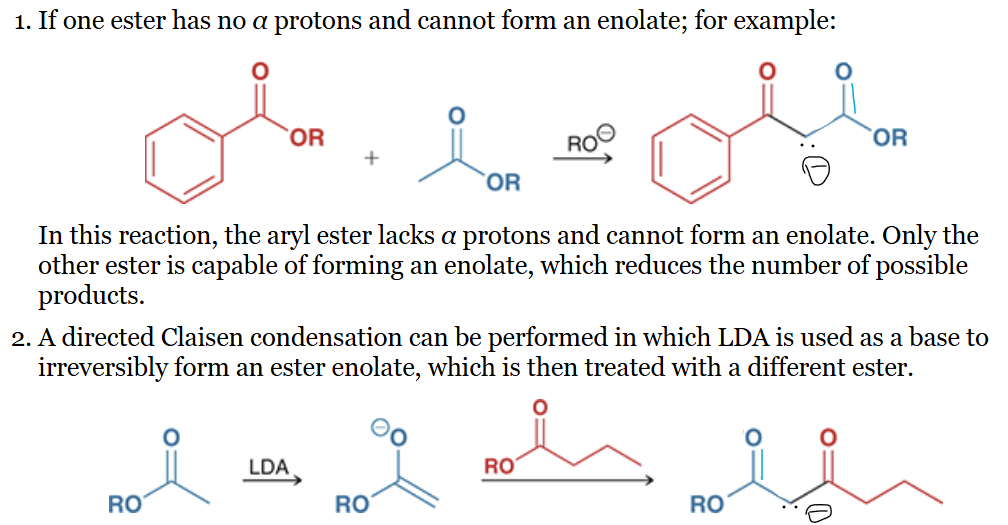
what criteria must be met for a crossed Claisen rxn. to produce only a single product
Note that in both of these reactions the workup step is not shown.
H3O+ would be used to protonate the alpha position
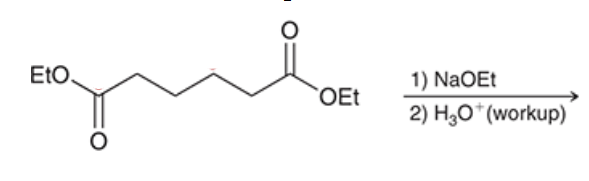
product? name of reaction?
Dieckmann cyclization
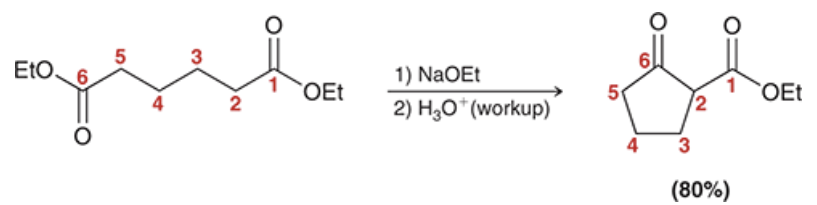
in intramolecular aldol or intramolecular Claisen reactions, what type of rings are preferred to be formed?
5 or 6 member rings
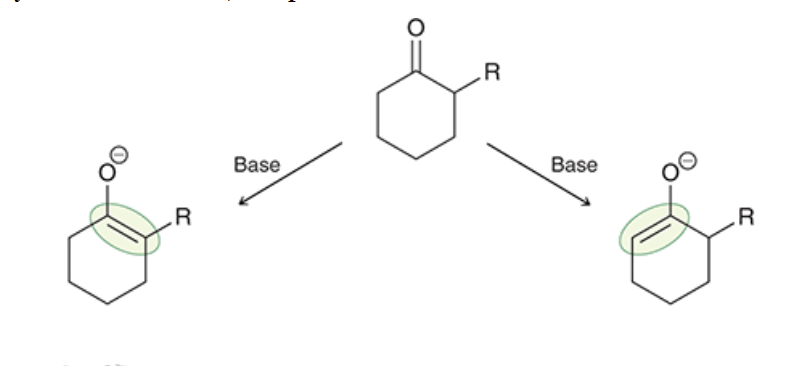
which product is kinetic and which is thermodynamic? which forms faster and which is more stable? lower temperature favor which product? higher temperatures? what type of base favors each product?
kinetic forms faster and is favored at lower temperatures with a bulky base (like LDA)
thermodynamic is more stable and is favored at higher temperatures with a smaller base (like NaH)
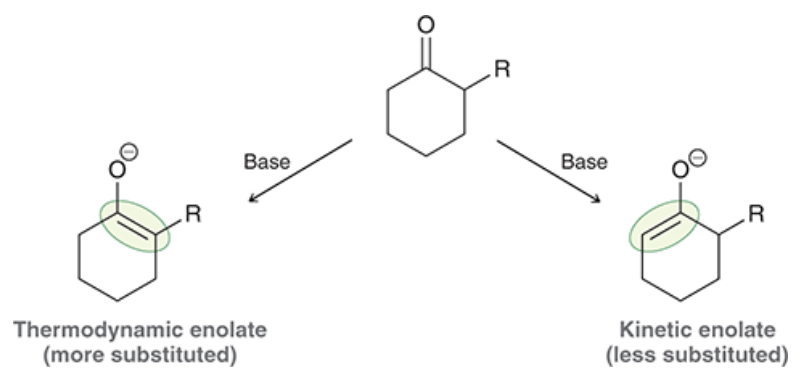
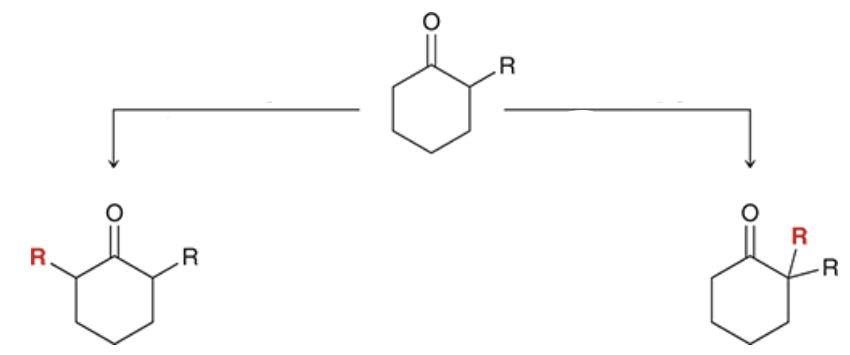
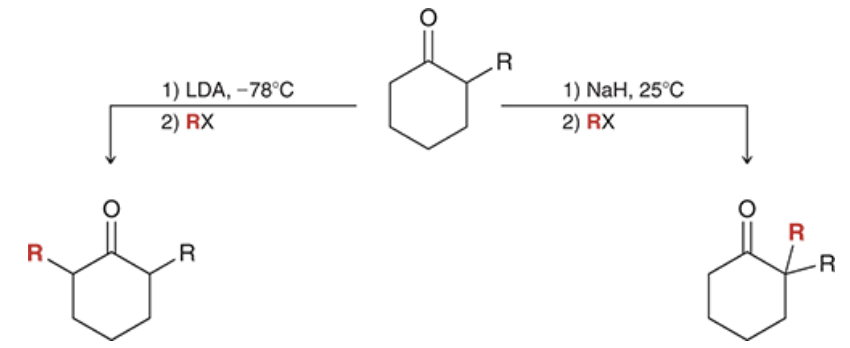
show reagents. Which rxn gives the thermodynamic product? which one gives the kinetic product?
left rxn: kinetic
right rxn: thermodynamic
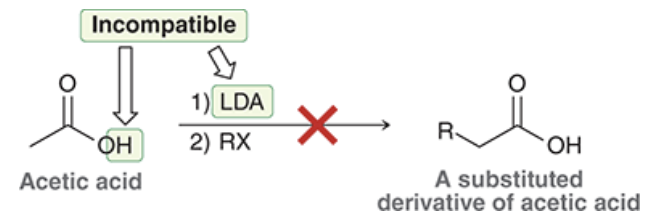
why is this reaction incompatible?
if acetic acid is treated with a strong base, the CA would be deprotonated first. if that happens, then deprotonation of an alpha proton would result in a dianion, which is too high in energy to form.

reagenets? draw out the steps that lead to this product.
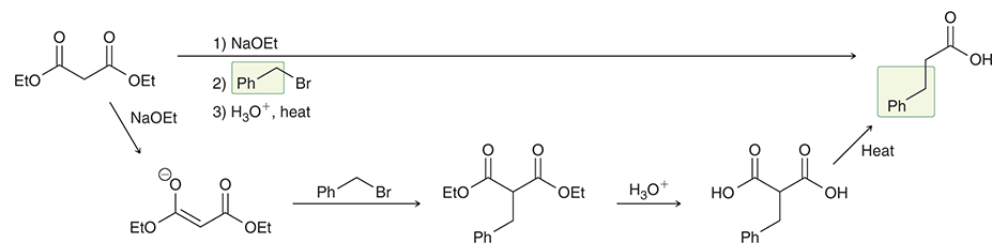

reagents?
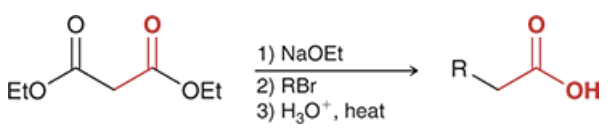
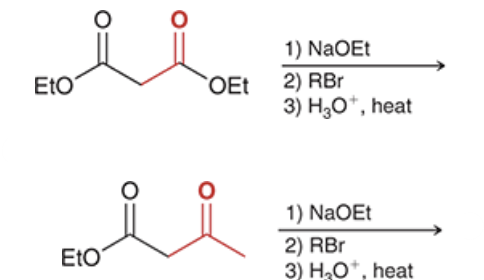
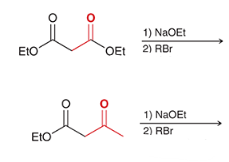
products? name the top and bottom rxn.
top: malonic ester synthesis
bottom: acetoacetic ester synthesis
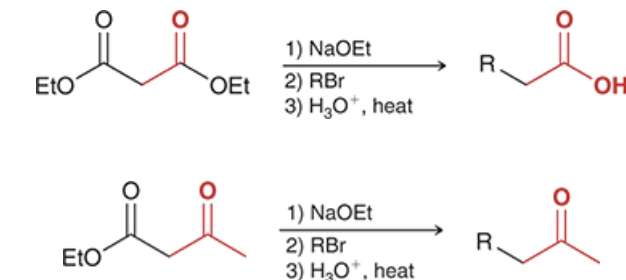

reagents? show the steps that lead to the product.
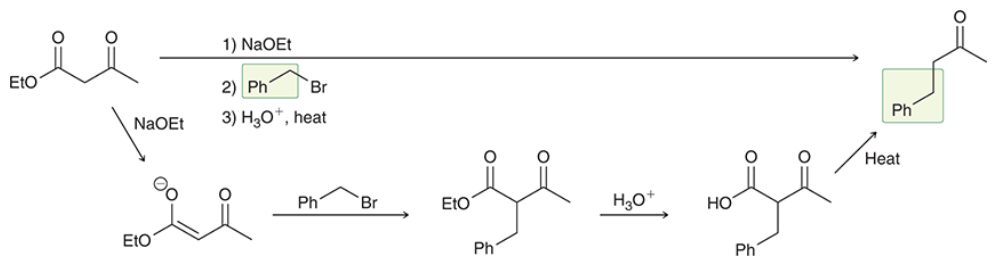
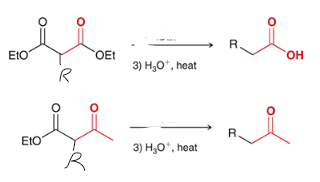
products? what step comes next to complete the acetoacetic ester/ malonic ester synthesis for each reaction?
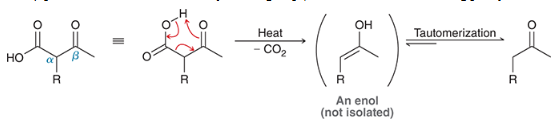
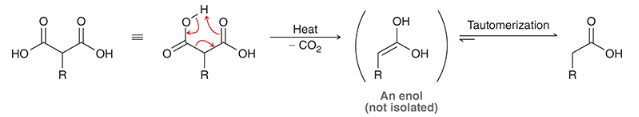
products shown on left. acid hydrolyzes the carbonyl groups to form carboxylic acids on each molecule. when heated, decarboxylation occurs, causing a CA to be ejects as CO2 (gas) is formed.
show the decarboxylation step on the acetoacetic ester synthesis
show the decarboxylation step of the malonic ester synthesis
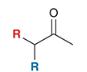
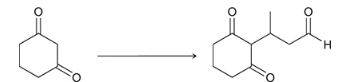
show how to make this molecule
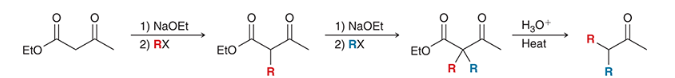
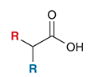
show how to make this molecule
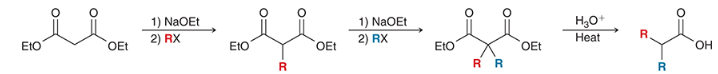
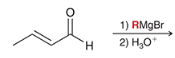
product?
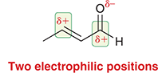
electrophilic positions?
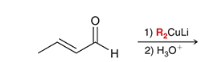
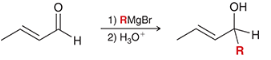
product? what is the general name of the reagent with the red R groups?
Gilman Reagent
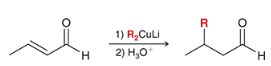

reagents?
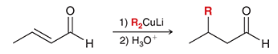
reagents?
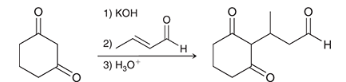
show the general process of a Michael reaction between a Nuc and a α,β-unsaturated carbonyl. this reaction is also called a 1,4 addition, why?
because the Nuc is added to the beta position and the proton is added to the oxygen. the enol rapidly tautomerizes however, so the proton does not remain attached to the oxygen.
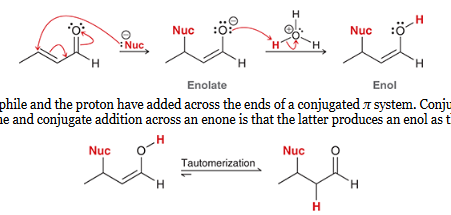
Michael donor
nucleophile which does conjugate addition and attacks the β position of an α,β-unsaturated aldehyde
Michael acceptor
electrophile. an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl who gets attacked by a nucleophile (Michael donor)
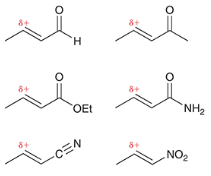
Michael donors are indicated by a _____ charge and ____ groups
negative charge and EWGs
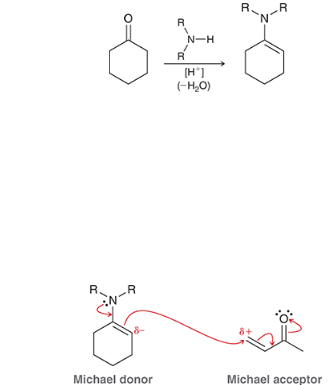
reagents? what is special about the product? what rxn is this product used in?
the enamine may act as a Michael donor in Stork enamine synthesis
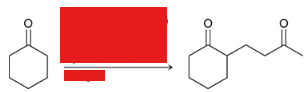
reagents? reaction name? why is it named this?
stork enamine synthesis
it is named this because it uses a enamine int
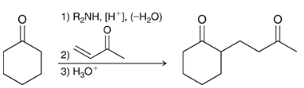
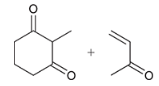
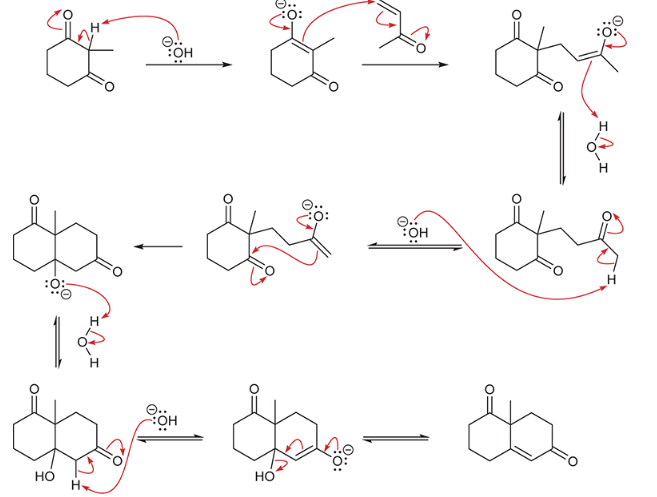
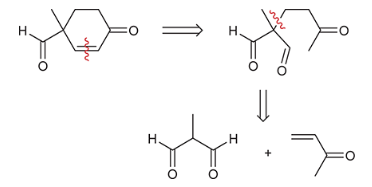
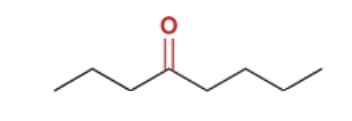
show a Robinson annulation reaction starting with the following molecules show each step and label the reaction names of each step.
general reaction is shown at the bottom
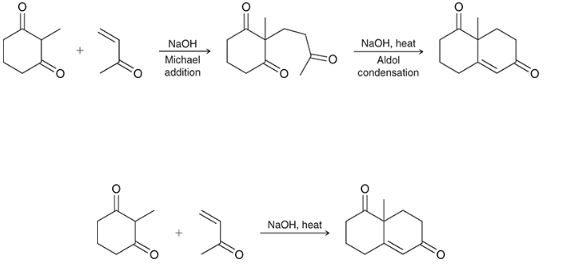

reaction name?
Robinson annulation