BIO transport in plants
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Transport in plants
The process in which substances which are absorbed or synthesised in a particular of the plant are moved to other parts of the plants
Which system carries transport in plants
Vascular system or conducting system (Xylem and Phloem)
Which tissue carries water in plants
Xylem
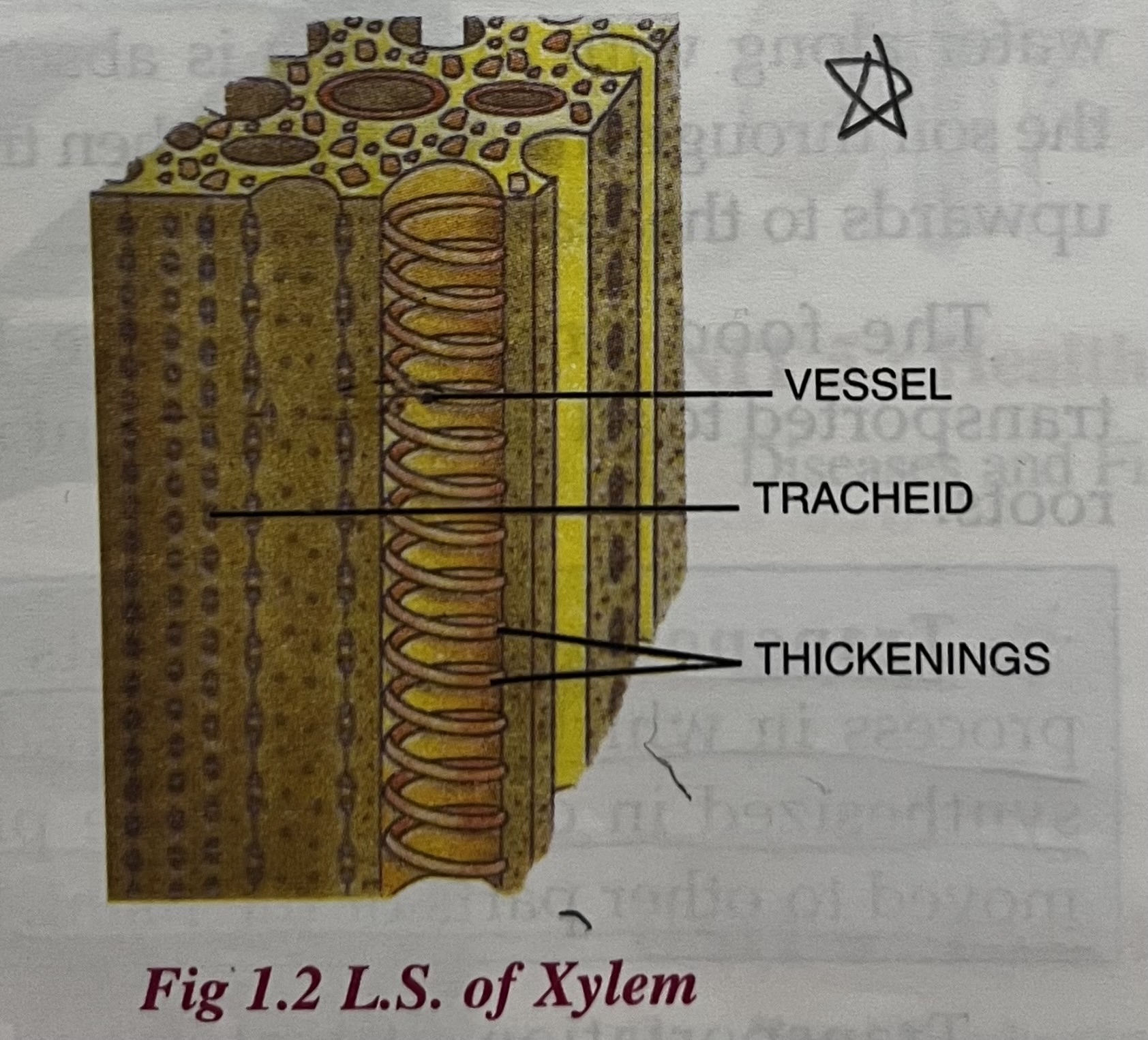
what does xylem consist of
Trachieds
Vessels
Xylem parenchyma
Xylem fibres
Trachieds
Are elongated dead cells with tapering ends. These cells have thickenings with lateral pores. These cells provide mechanical strength and support in addition to conducting water and minerals upwards
Vessels
These are tube like structures open at both ends. These cells are placed end to end to form long channels. Just like trachieds provide mechanical strength and support along with conducting water and minerals
Xylem parenchyma
Are small thick walled living cells which store food and help conduct water and minerals
Xylem fibres
Thick walled long narrow cells with tapering ends. They provide only mechanical support to the plant
Lower segment of xylem
LEARN
Function of xylem
To transport water and minerals from the roots to the aerial parts of the plant
Which parts of xylem provide mechanical support to the plant
Trachieds
Vessels
Xylem fibres
Xylem rings
The rings seen in the trunk of a tree cut transversly. The age of the tree is determined by these
What tissue transports food in plants
Phloem
What does phloem consist of
Sieve tubes
Companion cells
Phloem parenchyma
Phloem fibres
Sieve tubes
Are formed of cylindrical cells that are devoid of any nucleus. They are seen arranged in vertical rows and placed end to end. The ends of these cells are perfortrated and called sieve plates. Through these cells food materials pass through
Companion cells
Are thin walled living cells that are seen attached to the sieve tubes. They help in transportation
Phloem parenchyma
Are thin walled parenchymatous cells which store food
Phloem fibres
Dead sclerenchyma fibres formed of elongated cells which provide mechanical strength and support to the plant
Function of phloem
To transport food manufactured in the leaves to other parts of the plant
What do phloem parenchyma and phloem sclerenchyma do
Phloem parenchyma stores food
Phloem fibres provides mechanical support
Differences between xylem and phloem
LEARN

Translocation of solutes
The process in which glucose is converted into starch and then to sucrose solution for transportation
Property of cappilary
The attraction of water molecules towards narrow spaces
What do roots consist of
Main root
Lateral root (Branch)
Root hair
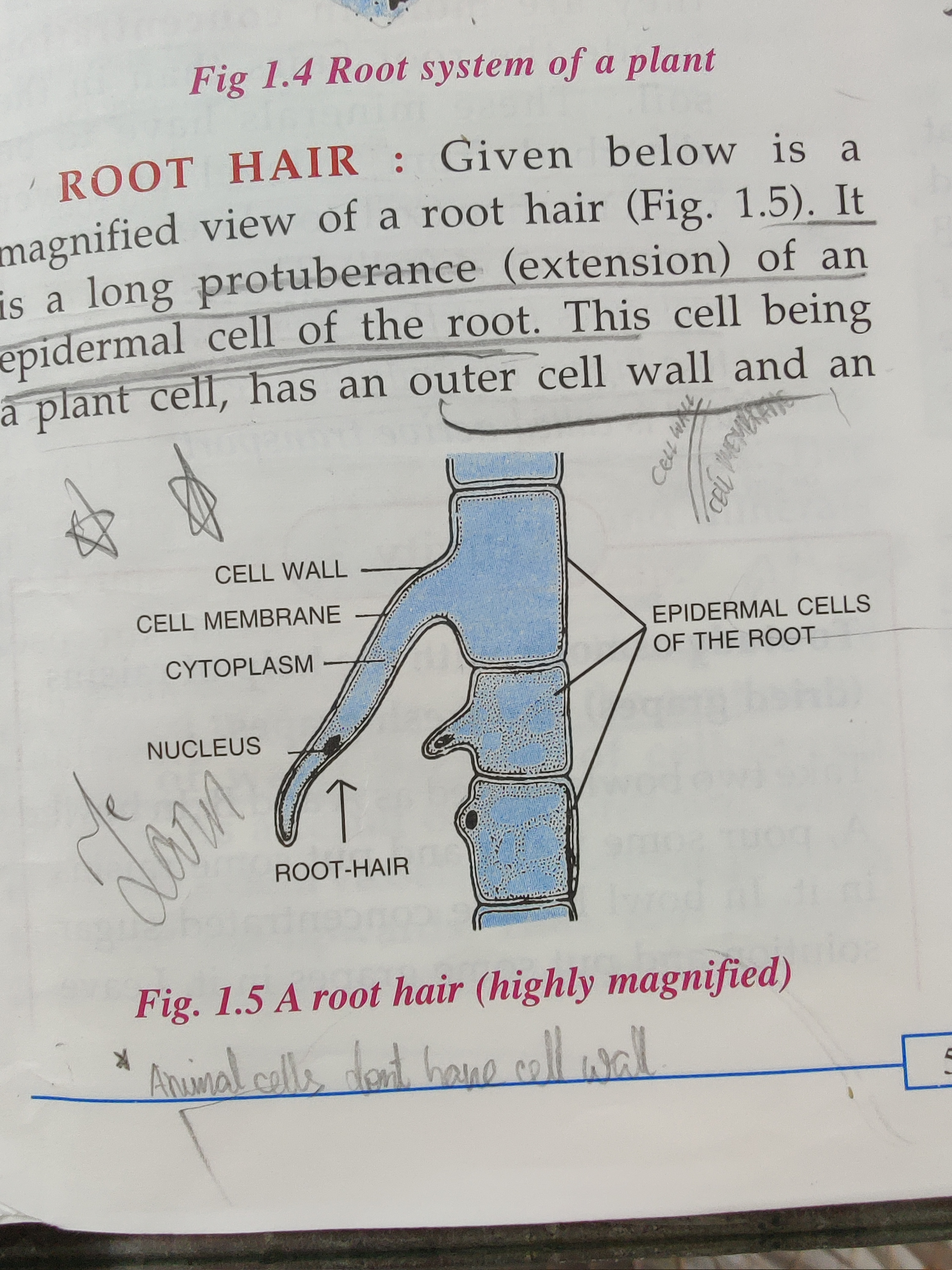
Root hair
The long (protuberance) extention of the epidermal cell of a root hair
Why does a root hair have a cell wall
Because all plant cells have a cell wall
Parts of a root hair
Main root
Lateral root (branch)
Root hair
Freely permeable
Allows all substances to pass through (cell wall)
Semi permeable
Allows only certain substances to pass through (cell membrane)
What promotes water absorption in roots
The cell sap in the root hair cell is at a higher concentration as it contains more solutes compared to the surrounding soil water this promotes water absorption
Speciality of root hair
-The numerous root hair provide a large surface area. More the area more is the absorption
-Root hair has cell sap at a higher concentration than the surrounding soil water
-The cell wall is freely permeable whilst the cell membrane is semi permeable
Osmosis
The movement of water molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semi permeable
Three types of movements of molecules in plants
Diffusion
Osmosis
Active transport
Diffusion
The movement of molecules (gas liquid or solid ) from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
Active transport
The movement of molecules from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration through a semi permeable membrane which requires energy
Ascent of sap
The upward movement of water and minerals (sap) by cell to cell osmosis is called assent of sap
Root pressure
The pressure developed in the roots due to continuous inflow of water by cell to cell osmosis
Transpiration
The loss of water in the form of water vapour from the aerial part parts of the plant
Transpirational force
The force that causes the water to be pulled up from the xylem in the roots to the stem and into the leaves. This pulling force is called transpirational force
What are the factors affecting the rate of evaporation
-Sunlight- because the stomata is open in the morning and closed at night
-Temperature
-Wind
-Humidity - the air can’t hold water water of it is laden with moisture
Importance of evaporation
Evaporation is important as
It produces a cooling effect
Transpiration helps in maintaining the concentration of the sap inside the plant body
Uses of water in the plant
Water is used for :
Transportation
Food production
Cooling
Why do you feel cold when you stand under a tree
You feel cool when you stand under a tree because the water transpires (evaporates) and producing a cooling effect
What are nutrient elements divided into
These are divided into
Macro nutrients
Micro nutrients
Macro and micro nutrients of plants
LEARN

Remember you have to prove yourself