Marketing Exam #2
1/177
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
To create a proper marketing mix, marketers must understand
That consumer preferences are constantly changing
How consumers make purchase decisions
Consumer behavior
processes a consumers uses to make purchase decisions, aw well as to use and dispose of purchased goods or services; also includes factors that influence purchase decisions and product use
Value
a personal assessment of the net worth one obtains from making a purchase , or the enduring belief that a specific mode of conduct is personally or socially preferable to another mode of conduct
Perceived value
the value a consumer expects to obtain from a purchase
Utilitarian value
a value derived from a product or service that helps the consumer solve problems and accomplish task
The consumer decision-making process
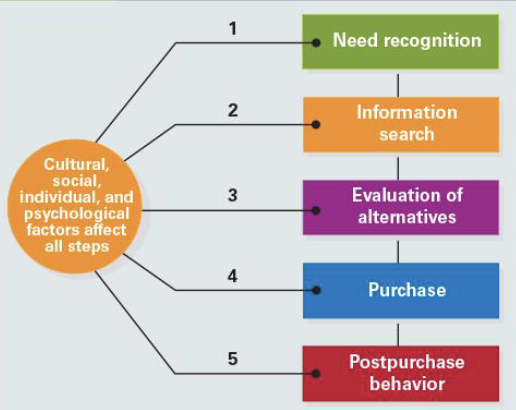
Need Recognition
1st stage in the decision- making process
Need recognition is
the result of an imbalance between actual and desired states
want
recognition of an unfulfilled need and a product that will satisfy it
Stimulus
any unit of input affecting one or more of the five senses: sight, smell, taste, touch, hearing
A marketing manager’s objective is
to get consumers to recognize the “want-got gap”
Information Search
2nd stage in the decision-making process
Internal information search
the process of recalling information stored in the memory (could be from earlier advertising or experiences)
External information search
the process of seeking information in the outside environment
Non-marketing-controlled information source
a product information source that is not associated with advertising or promotion
Marketing-controlled information source
a product information source that originates with marketers promoting the product
The Extent of Information Search: 1
The bigger the risk, the more you search and consider alternatives
The Extent of Information Search
The extent to which an individual conducts an external search depends on his or her…
The Extent of Information Search: 2
Knowledge, less likely to search for additional information
The Extent of Information Search: 3
Prior experience, means everything in our decision to search or not
The Extent of Information Search: 4
Level of interest in the good or service, “do I care”?
evoked set
a group of brands resulting from an information search from which a buyer can choose
Nudge
a small intervention that can change a person’s behavior
Ex: shopping at a convenience store and having to walk to the back for drinks
Evaluation of Alternatives and Purchase
3rd stage in the decision-making process
Evaluation of alternatives and purchase criteria
A consumer will use the information stored in memory and obtained from
outside sources to develop a set of criteria.
The environment, internal information, and external information help consumers
evaluate and compare alternatives.
The process is not always rational
The process is
not always rational
To buy or not to buy
1. Whether to buy
2. When to buy
3. What to buy (product type and brand)
4. Where to buy (type of retailer, specific retailer, online or in store) (Birkenstocks in person)
5. How to pay (and remember, the sale isn’t complete, until it is paid for!)
Three types of purchases: Planned purchase
typically made after the consumer has collected a large amount of information (home, car)
Three types of purchases: Partially planned purchase
typically made when the consumer knows the product category but waits until shopping to choose a specific style or brand (clothing, furniture) (wife at Marshell’s)
Three types of purchases: Impulse or unplanned purchase
often low-priced items or items on sale or purchased with a coupon, sometimes triggered by a nudge (food or snack item)
Brand Loyalty
generally willing to pay more for them
Terms
net 30 - 2%
cash - 5%
n10
n20
Postpurchase Behavior
how will consumer respond to purchase
Cognitive dissonance/Buyers remorse
Regretting a purchase
engage in the 5th P (participation)
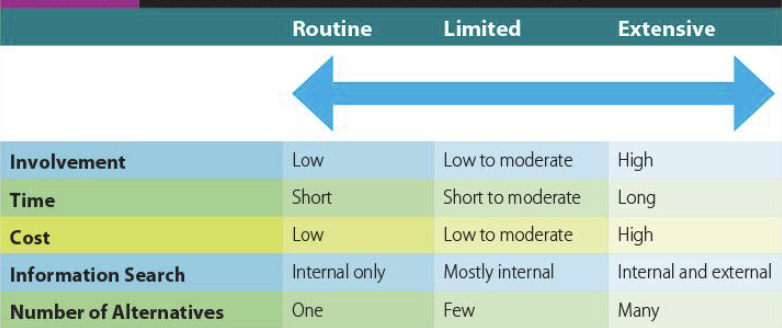
Continuum of Consumer buying Decisions
Profit
Rev. - Ex.
Rev
Sales or quantity x price
When consumers have previous experience with a good or service
the level of involvement typically decreases
Involvement is directly related to
consumer interests and the degree of interest
As the perceived risk (loss of wealth or status, inincreafed anxiety) in purchasing a product increase
so does a consumer’s level of involvement
For high involvement product purchases
marketing managers should engage in extensive and informative promotions
For low involvement product purchases, in-store promotion and targeted mobile ads are important tools
Offering products on a “limited availability” basis is one-way marketers can increase involvement and jump up demand
Ex: airline seats
The consumer decision journey
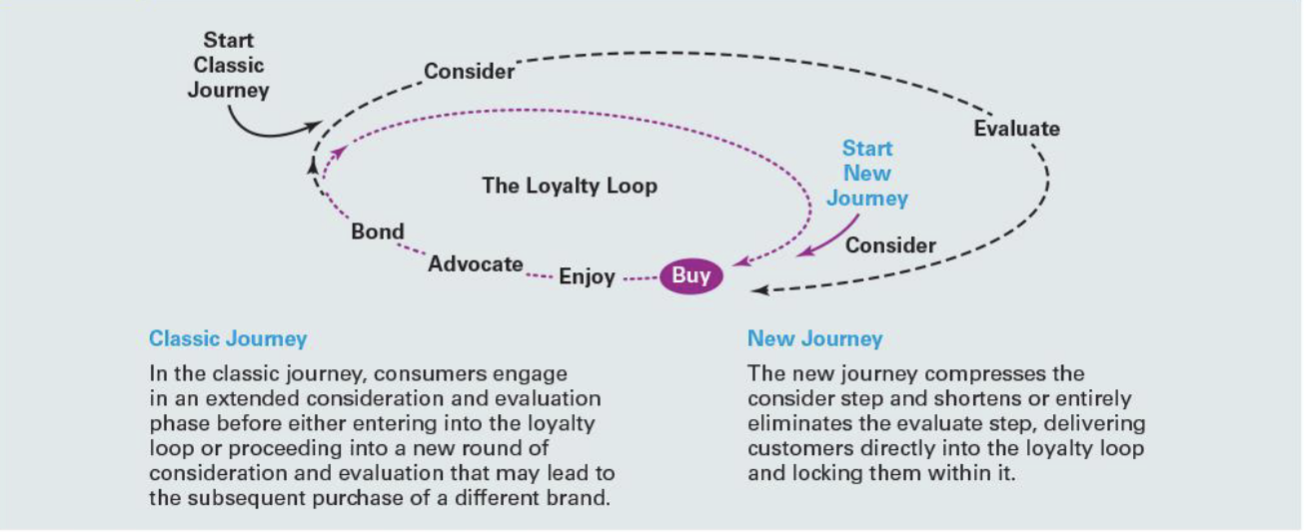
The “satisfied” customer
those who buy regular, often out of habit, because they are satisfied with the brand’s performance over a long period
The “committed” customer
a more intense, involved, emotional relationship with the brand, often becoming brand ambassadors
Culture
the set of values, norms, attitudes, and other meaningful symbols that shape human behavior and the artifacts, or products, of that behavior as they are transmitted from one generation to the next
Underlying elements of culture are
values, language, myths, customs, rituals, and laws that guide consumer behavior
Culture is:
− Pervasive – so ingrained that we are
unaware of it
− Functional – giving order to society
− Learned – handed down through generations
− Dynamic – adaptive and evolving
− Varies by geography
Subculture
a homogeneous group of people who share elements of the overall culture as well as unique elements of their own group (college aged consumers, new graduates, parents, empty nesters, retired people)
By understanding subcultures
marketers can design special marketing strategies to serve the needs of a subculture
Social class
a group of people in a society who are considered nearly equal in status or community esteem, who regularly socialize among themselves both formally and informally, and who share behavioral norms
Social class is measured as
a combination of occupation, income, education, wealth, and other variables
Social class is important to marketers for two main reasons
often indicates which medium to use for promotion
helps determine where to best distribute products
Reference group
all of the formal and informal groups in society that influence an individual’s purchasing behavior
Primary membership group
a reference group with which people interact regularly in an informal, face-to-face manner, such as family, friends, and coworkers
Secondary membership group
a reference group with which people associate less consistently and more formally than a primary membership group, such as a club, professional group/association, or religious group
Opinion leader
an individual who influences the opinions of others -BIG Today
People often rely on each other’s opinions more than marketing messages when making purchase decisions
marketing managers must persuade opinion leaders to purchase their goods or servicesE
Example of culture
pickup in the midwest compared to the coasts
Price today/lose you tomorrow
cheapest now/not cheaper later
We all have opinions and
rely on others in purchasing decisions
Noise/chaos in the marketplace
is an opportunity for you?
Ex: DEF gas - shortage?
as a marketer you need to
provide clarity to the chaos
Family has the strongest influence
children learn by observing parents so they shop like their parents
Socialization process
how cultural values and norms are passed down to children
Social Influences on Consumer Buying Decisions: Initiator
suggests or initiates the purchase process
Social Influences on Consumer Buying Decisions: Influencer
offers valued opinions
Social Influences on Consumer Buying Decisions: Decision maker
the family member who actually makes the decision to buy or not to buy
Social Influences on Consumer Buying Decisions: Purchaser
the one who exchanges money for the product, not always the consumer
Social Influences on Consumer Buying Decisions: Consumer
the end user
Social Influences on Consumer Buying Decisions: Sales
probably the biggest thing looked at for successful sales
Business marketing (industrial, business to business, B-to-B, or B2B marketing)
the marketing of goods and services to individuals and organizations for purposes other than personal consuption
Business product (industrial product)
a product used to manufacture other goods or services, to facilitate an organization’s operations, or to resell to other customers
Consumer product
a product bought to satisfy an individual’s personal wants or needs
The key characteristic distinguishing business products from consumer products is
intending use, not physical form
Content Marketing
a strategic marketing approach that focuses on creating and distributing content that is valuable, relevant, and consistent
Dramatic increase in use of social media, email marketing, search engine optimization, paid search, and display advertising to
increase awareness, build relationships, and pull customers to websites
Increased use of the internet as an effective sales and promotion platform
greater use of applications to provide additional information about customers
Metrics that are useful for increasing the effectiveness of social media: Awareness
the attention that social media attracts, such as the number of followers or fans
Metrics that are useful for increasing the effectiveness of social media: Engagement
the interactions between the brand and the audience, such as comments, retweets, shares, and searches
Metrics that are useful for increasing the effectiveness of social media: Conversions
responsive actions that include everything from downloading a piece of content (like a white paper) to actually making a purchase
Relationship marketing
a strategy for seeking and establishing ongoing partnerships with customer (better margins, longterm sales)
emerged because customers have become more demanding and competition has become more intense-pressuring margins
enables business suppliers to better compete, especially in the digital world. On-line, low cost suppliers targeting your customers
Strategic aliance (strategic partnership)
a cooperative agreement between business firms
(manufactures, manufacturers and customers, manufacturers and suppliers, manufactures and channel intermediaries, and even between competitors)
strategic alliances formed
to strengthen operations and make firms more competitive
strategic alliance forms
licensing or distribution agreements, joint ventures, research and development consortia, and partnerships
A successful alliance is built on: Relationship commitment
a firm’s belief that an ongoing relationship with another firm is so important that the relationship warrants maximum efforts at maintaining it indefinitely
A successful alliance is built on: Trust
the condition that exists when one party has confidence in an exchange partner’s reliability and integrity
Relationships in other cultures
Japan, personal relationships can develop into formal relationship between companies
Ex: Wal-Mart and their grocery business; how did this work?
Keiretsu
a network of interlocking corporate affiliates, based on trust and goodwill
Producers
includes profit-oriented individuals and organizations that use purchased goods and services to product other products, to incorporate into other product, or to facilitate the daily operations of the organization
Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs)
individuals and organizations that buy business goods and incorporate them into the products they produce for eventual sale to other producers or consumer
Ex: Ford, Toyota, John Deere, Boeing
Resellers
includes retail and wholesale businesses that buy finished goods and resell them for a profit
Ex: Walmart, Costco, grocerystores
Governments
includes thousands of federal, state, and local buying units
can be overwhelming and tedious to market to government agencies, but may result in lucrative contracts and lasting, rewarding relatinship
Federal government
buys goods and services valued at more than $875 billion per year, making it the world’s largest customer
can be viewed as marketing to a combination of several large companies with overlapping responsibilities and thousands of small independent units
State, Country, and City Government
generally simpler and less frustration than marketing to the federal government
Institutions (schools, hospitals, colleges and universities, churches, labor unions, fraternal organizations, civic clubs, foundations, and other so-called nonbusiness organizations)
seek to achieve goals other than the standard business goals or profit, market share, and return on investment
Derived Demand
the deman for business products is called derived demand because organizations buy products to be used in producing their customers’ products
Inelastic demand
the demand for many business products is inelastic with regard to price, meaning that an increase or decrease in the price of the product will not simnifically affect demand for the product
Joint Demand
joint demand occurs when two or more items are used together in a final product. Demand for vehicles goes up, demand for tires and still go up
Fluctuating (elastic) demand
The demand for business products tends to be less stable
a small increase or decrease in consumer demand can produce much larger change in demand for the facilities and equipment needed to make the consumer product