1. What is business
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Inputs:
Land
People
Finance/ capital
Components/ materials
Natural resources
Outputs:
Services
Goods
Waste
Why do business exist?
Create jobs
Creating wealth for the country
New innovative products for society = enhancing a countries reputation
What is the cycle of business?
Create goods and services
To meet needs of customers
Revenue generated
If higher than costs, profit made
Reinvest for growth or paid to owner as reward
Repeat
What are the three sectors and what do they do?
Primary- extracting raw materials
Secondary- manufacturing
Tertiary- providing a service
What is a mission statement?
A document communicating the purpose of a business and why it exists
Where does a mission statement come from:
Values of the founder
Culture of the business
Society's views
The industry it operates in
What are objectives?
Medium to long term plans to coordinate business functions and act as a target
What are the main objectives of a business?
Profit= sr- tc
Growth
Survival
Cash flow
Social and ethical
Diversification
What are some influences on objectives?
How competitive the market is
Ownership structure
Size of business
Sector
What are corporate objectives based on?
Innovation
Growth
Shareholder value
Social responsibility
What are functional objectives?
Objectives that are made at the department level to help meet the corporate objectives
Why set objectives?
Provide steps to achieve aims
Measure success against targets
To motivate and reward staff
Objectives should be “SMART”. What does this stand for?
Specific- real numbers/ deadlines
Measurable- make the goal trackable
Attainable- challenging but possible
Relevant- be honest with capability
Time based- include a deadline
Business
An organisation that transforms inputs into outputs that are purchased by their customers.
GDP
The value of all the goods and services produced in a country.
Unlimited liability
The owner and the business are the same entity.
Limited liability
The business and owner are separate.
Flotation
The process of converting a private company into a public company by issuing shares available for the public to purchase.
Market capitalisation
The total value of the issued shares of a PLC.
Public sector
Companies owned by the government and funded by them too.
Private sector
Businesses and companies owned by people. Main aim is to make profit.
Third sector
Charities such as Oxfam, not for profit.
Company
An organisation that has its own legal identity (incorporation)
Dividends
Share of profit that are distributed to shareholders.
Social enterprise
Businesses that trade for a social or environmental purpose.
Fairtrade
A social movement that exists to promote improved trading terms and living conditions for producers of products in less developed countries.
Sustainable production
Occurs when the supply of a product doesn't impose costs on future generations by, for example, depleting non-renewable resources.
What is the role of a shareholder?
Own a % stake in a company
Benefit from increases in share price
Benefit from dividend payments every 3-6 months
What factors influence share price?
Speculation
A company announcing it's profit
Announcing job losses
About to be taken over by another business
Economy- recession
What are some demographic factors?
Uk population growing = increased demand
Migration to Uk = increased labour force
Longer life expectancy= changing demand for goods
Increasing amount of working parents= increased demand for childcare services
Diverse communities= demand for non-traditional foods
Market capitalisation calculation
Market capitalisation= number of shares issued x current market price
Flotation- pros
Able to raise finance through stock market flotation |
Limited liability |
Considered more reliable to lenders |
More public awareness |
Flotation- cons
Risk of being taken over |
Financial accounts published |
More public scrutiny |
Shareholders have more influences on how business is run |
What things should a business consider during competition?
The growth rate of their market
The typical profit margins in the industry
Number and size of competitors
Pace of innovation
Bargaining power of suppliers and customers
Internal factors affecting decline
Lower quality
Closing stores
Short term couponing
Product range is too wide
External factors affecting decline
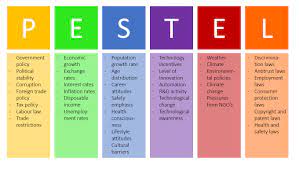
Being a environmentally friendly business- pros
Avoid negative publicity |
Differentiates from others |
Avoid fines and penalties |
Being a environmentally friendly business- cons
Increased cost of raw materials |
Waste disposal costs |
Lower profit margin on fair trade goods |
What are some factors affecting competitiveness of a business?
Number and size of competitors
Bargaining power of suppliers
Extent of which products can be differentiated
Knowledge of buyers and sellers
The amount of regulation
When share prices rise, does demand for shares increase or decrease?
What does this mean for the business?
Positive publicity
Shareholders feel more confident to spend
Managers may receive a bonus
Easier to raise capital
When share price falls, does demand for shares increase or decrease?
What does this mean for the business?
Indicates poor performance
Vulnerable to a takeover
Harder to raise capital
Shareholders less confident to spend
Small businesses in competition, have:
Less competition
Easier for them to build relationships
Less economies of scale
Low barriers to enter the market- more likely for more businesses to enter the market
Large businesses in competition, have:
More potential customers
More regulation
More international competition
Anagram to remember whether the pound is weakening or strengthening
Strong
Pound
Imports
Cheap
Exports
Dear
Positive impacts of competition
Increased innovation |
Pushed to create a wider product range |
Negative impacts of competition
Have to lower prices |
Increase in promotional costs |
May lead to unethical behaviour |