Bio Chapter 8 Photosynthesis (Part 1)
5.0(6)
Card Sorting
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:46 PM on 11/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1
New cards
What forms does energy come in?
Light, heat, and electricity.
2
New cards
Where can energy be stored in?
Chemical compounds.
3
New cards
Where do living things get their energy to survive from?
They get that energy from food.
4
New cards
What do plants use to produce their food?
Plants use light energy from the sun to produce food.
5
New cards
What are autotrophs?
- Organisms that make their own food via photosynthesis.
- Example: Plants
- Example: Plants
6
New cards
What are heterotrophs?
- Organisms that consume other organisms for food (cellular respiration).
- Example: Animals
- Example: Animals
7
New cards
Define ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
Compound that cells use to store and release energy. All cells use it as their basic source of energy.
8
New cards
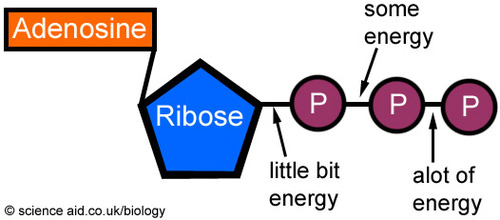
What does ATP consist of?
Because it is a nucleic acid, it is composed of:
- Adenine (the nitrogenous base).
- Ribose (5-sugar component).
- 3 phosphate groups (key to storing/releasing energy).
- Adenine (the nitrogenous base).
- Ribose (5-sugar component).
- 3 phosphate groups (key to storing/releasing energy).
9
New cards
How many phosphate groups does ADP have?
Instead of 3, ADP has 2 phosphate groups.
10
New cards
What does a cell add to ADP if it has energy available?
If a cell has energy available, it stores small amounts of energy by adding a phosphate group to ADP.
11
New cards
How is energy stored in ATP released?
Energy stored in ATP is released by breaking the chemical bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphates.
12
New cards
How is energy in ATP stored?
ATP stores energy by re-forming its phosphate groups/bonds.
13
New cards
Why is ATP like a rechargeable battery?
It can re-attach phosphates; cell organelles use the energy and turn ATP to ADP. Mitochondria gives energy and turns ADP to ATP.
14
New cards
How is the process of ADP transforming into ATP like the process of charging up a battery?
ADP is like a partially charged battery and by adding a phosphate group to it (energy), it becomes the fully charged battery that is ATP.
15
New cards
What is the energy in ATP used for?
Cellular activities such as active transport, protein synthesis, and muscle contraction.
16
New cards
Why do cells regenerate ATP from ADP as needed by using the energy in food?
Cells regenerate ATP from ADP as needed because ATP is not good at storing energy for long. So, most cells only have a small amount of ATP.
17
New cards
What does all energy on Earth come from?
All energy on Earth comes from the Sun.
18
New cards
What do we depend on to provide energy for our cells?
To provide energy for our cells, we depend on plants, algae (underwater plants), and cyanobacteria (photosynthetic bacteria).
19
New cards
Define photosynthesis.
Using sunlight energy to transform CO2 and water into oxygen and carbohydrates (glucose, C6 H12 O6).
20
New cards
What is the photosynthesis equation?
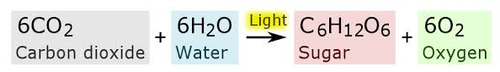
21
New cards
In what form does energy travel to Earth?
Energy travels to Earth in the form of light.
22
New cards
How do we see colors?
- We perceive different wavelengths of light as colors.
- Objects absorb every wavelength except one.
- The wavelength that is not absorbed is reflected (the color we see).
- Objects absorb every wavelength except one.
- The wavelength that is not absorbed is reflected (the color we see).
23
New cards
Why are dark objects dark?
Dark objects absorb all wavelengths of light equally and do not reflect any light back.
24
New cards
Why are white objects white?
White objects reflect all wavelengths of light equally.
25
New cards
How do photosynthetic organisms capture energy?
They capture energy from sunlight with pigments (light-absorbing molecules).
26
New cards
What are the two types of plant pigments?
Chlorophyll A and Chlorophyll B.
27
New cards
Why do plants look green?
Its pigments absorb well in red and blue but poorly in green. Therefore plants reflect green, hence why they look green as well.
28
New cards
Define cartenoids.
They absorb light in other regions of the spectrum, reflecting orange and red wavelengths.
29
New cards
Where is the energy transferred to when a pigment absorbs sunlight?
Energy is transferred to electrons in pigments when they absorb sunlight. High energy electrons are needed to start light-independent reactions (LIR).
30
New cards
Where does photosynthesis take place?
In chloroplasts.
31
New cards
Diagram of a chloroplast
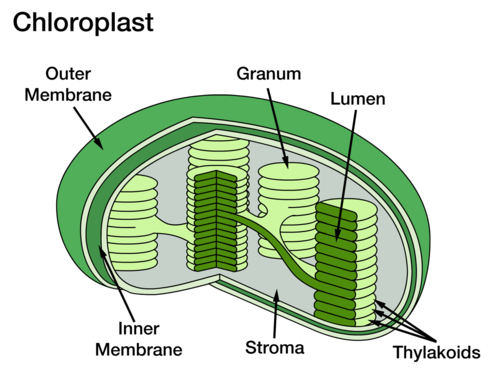
32
New cards
Define thylakoid.
Saclike membranes found in chloroplasts (location of LDR) that contain chlorophyll pigments.
33
New cards
Define grana.
Stacks of thylakoids.
34
New cards
Define stroma.
Cytoplasm of chloroplasts.
35
New cards
Define chloroplast membrane.
Bilayer surrounding the chloroplast (monitors what enters and exits).
36
New cards
Define thylakoid membrane.
The barrier surrounding thylakoids; pigments such as chlorophyll are found there, which act like "light antenna".