Introduction to Classical Studies: Key Concepts and Themes
1/493
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
494 Terms
Classical Studies
Study of ancient Mediterranean cultures, primarily Greece and Rome.
Ancient Mediterranean World
Region encompassing diverse cultures from 1600 BCE to 476 CE.
c. (circa)
Latin term meaning 'around' or 'approximately'.
BCE
Before Common Era, counting down to year 0.
CE
Common Era, counting up from year 0.
5th c. BCE
Period from 499 to 400 BCE.
5th c. CE
Period from 400 to 499 CE.
Late Bronze Age
Period from c. 1600 to 1100 BCE in Greece.
Dark Ages
Period from c. 1100 to 750 BCE with limited records.
Archaic Period
Period from c. 750 to 480 BCE characterized by cultural development.
Classical Period
Period from 480 to 323 BCE known for art and philosophy.
Hellenistic Period
Period from 323 to 31 BCE marked by Greek cultural influence.
Roman Kings
Period from 753 to 509 BCE before the Republic.
Roman Republic
Period from 509 to 31 BCE with elected officials.
Roman Empire
Period from 31 BCE to 476 CE with imperial rule.
Classis
Latin noun meaning 'fleet' or 'army', indicating a group.
Classicus
Latin adjective meaning 'belonging to the best group'.
Evidence Problem
Limited ancient texts survive, less than 1% original.
Ancient Papyri
Fragile manuscripts from ancient times, few in number.
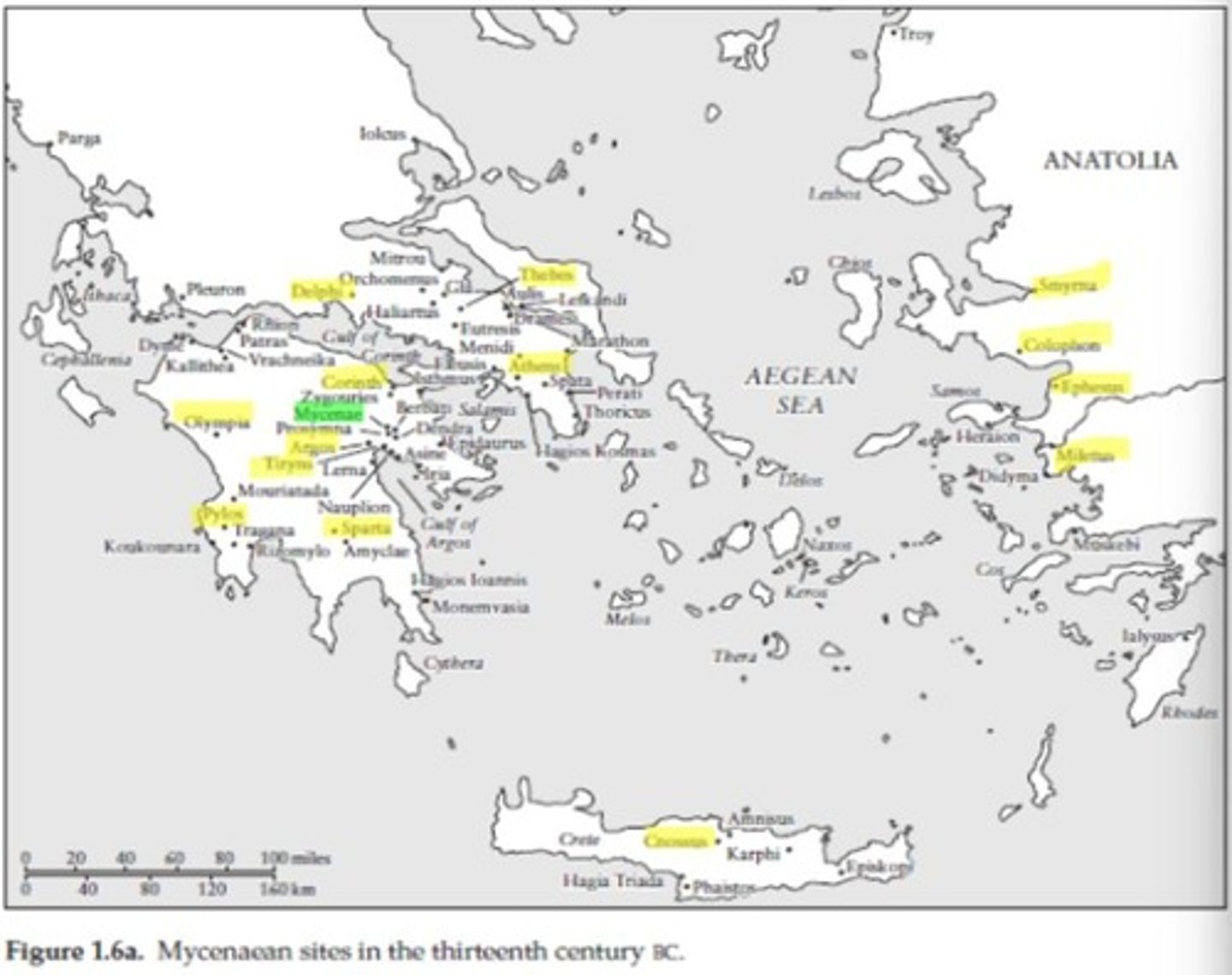
Mycenaean Greece
Dominant culture in Greece from c. 1600 to 1200 BCE.
Ahhiyawa
Hittite name for Mycenaeans, resembling later Greeks' Achaeans.
Peloponnese
Mainland Greece, literally 'island of Pelops'.
Cyclades
Aegean islands, literally 'encircling ones'.
Chariot Technology
Advanced warfare technology used by Mycenaean warriors.

Tholos Tombs
Grand burial structures reflecting Mycenaean wealth.
Literate Archivists
Mycenaeans used written language for record-keeping.
Linear B
Early Greek script translated by WWII analysts.
Tukate
Early Greek word for 'daughter'.
Kowo
Early Greek term for 'boy'.
Lawagetas
Term for 'populace' in Linear B.
Wanak(a)
Linear B term for 'lord' or main ruler.
Qasireu
Term for 'king' or chief in Linear B.
Megaron
Massive palace center overseen by wanax.
Place economies
Economic systems in 14th-13th centuries.
Redistributive economy
Economic model redistributing resources among populace.
The Dark Ages
Period of cultural decline post-Mycenaean collapse.
Iron Ages
Another name for the Dark Ages.
Mass depopulations
Widespread population decline during the Dark Ages.
Subsistence model
Economy focused on basic survival needs.
Basileis
Local chiefs overseeing small communities.
Nomoi
Traditional customs governing local societies.
Thetes
Paid serfs without land in society.
Epic poetry
Oral tradition preserving memories of the past.
Hesiod and Homer
Key figures in early Greek epic poetry.
Agonistic context
Competitive environment for oral storytelling.
Aoidoi
Professional bards performing epic poetry.
Opis(s)o
Greek term meaning 'backwards' or 'afterwards'.
Cultural idealization
Exaggeration of past glories in literature.
Lefkandi
Site with significant archaeological findings from the era.

Nichoria
Community with notable mud huts and chief's house.
Rhapsodes
Improvisational performers of epic poetry.
Cithara
A type of lyre used in epic performances.

Rhabdos
Time-keeping stick for rhythm in poetry.
Dactylic Hexameter
Poetic meter of long-short-short syllables.
Spondee
Two long syllables at the line's end.
Enjambment
Continuation of a sentence without pause.
Epic Similes
Extended comparisons in epic poetry.
Programmatic Proems
Introductory passages invoking the Muses.
Catalogues
Lists showcasing memory and knowledge.
Didactic Poetry
Poetry intended to teach moral lessons.
Hesiod
Ancient Greek poet from Boeotia, 8th c. BCE.

Theogony
Hesiod's poem on the origins of the universe.
Works and Days
Hesiod's practical guide to living well.
Eris
Concept of discord in Hesiod's works.
Productive Discord
Strife leading to action and justice.
Destructive Discord
Strife causing resentment and passivity.
Prometheus
Titan who stole fire for humanity.
Pandora
First woman, bringing evils to humanity.
Aetiological Myth
Myth explaining the origin of a phenomenon.
Kleros
Inherited land in ancient Greek society.
Lofty Diction
Elevated language used in epic poetry.
Mythological Narratives
Stories based on traditional myths.
Proto-Capitalist Ethos
Early ideas promoting competition and striving.
Pandora
Embodiment of all gods' gifts.
Hephaestus
God who shapes earth and water.
Athena
Goddess of wisdom and cunning.
Aphrodite
Goddess of love and beauty.
Hermes
God of deceit and trickery.
Epimetheus
Prometheus' brother, symbolizes afterthought.
Elpis
Personification of hope and expectation.
Golden Age
Era of peace, abundance, and no labor.
Silver Age
Short-lived, foolish generation destroyed by Zeus.
Bronze Age
Warrior society with no agriculture.
Heroic Age
Era of demi-gods and great wars.
Iron Age
Time of trouble, pain, and moral decay.
Zelos
Personification of jealousy and envy.
Aidos
Social force regulating normative behaviors.
Nemesis
Divine retribution for hubris.
The Hawk and the Nightingale
Fable illustrating justice and power dynamics.
Daimones
Spirits of the Golden Age.
Makares
Blessed beings of the Silver Age.
Hemitheoi
Demi-gods of the Heroic Age.
Pantheon
Collective of all Greek gods.
Olympians
Twelve principal gods of Greek mythology.
Hesiod
Poet who described the ages of man.
Polytheism
Belief in many gods coexisting.
Henotheism
Worship of one god among many.
Panhellenism
Cultural unity among Greek city-states.
Anthropomorphic
Gods depicted with human traits.
Hybris
Excessive pride leading to downfall.