energetics chemistry edexcel IGCSE
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
what is an exothermic reaction?
a reaction which gives out heat energy to the surroundings
how can you tell an exothermic reaction has occured?
a temperature increase in the surroundings
what is an endothermic reaction?
a reaction which takes in heat energy from the surroundings
how can you tell that an endothermic reaction has occurred?
the temperature of the surroundings decreases
what is the overall change in energy in a reaction called?
the enthalpy change (ΔH)
what are the unites of enthalpy change?
KJ/mol
is the value of the enthalpy change positive or negative if the reaction is exothermic?
negative - giving out energy
is the value of the enthalpy change positive or negative if the reaction is endothermic?
positive - taking in energy
is bond breaking exothermic or endothermic?
endothermic - taking in energy to break bonds
is bond making exothermic or endothermic?
exothermic - giving out energy so bonds are formed
what is the general reason for why an exothermic reaction is exothermic (enthalpy change negative) ?
more energy is given out making bonds than is taken in breaking bonds
what is the general reason for why an endothermic reaction is endothermic (enthalpy change positive)?
more energy is taken in breaking bonds than is given out making bonds
what does a reaction profile diagram show?
they show the relative energies of the reactants and products in a reaction, and how the energy changes
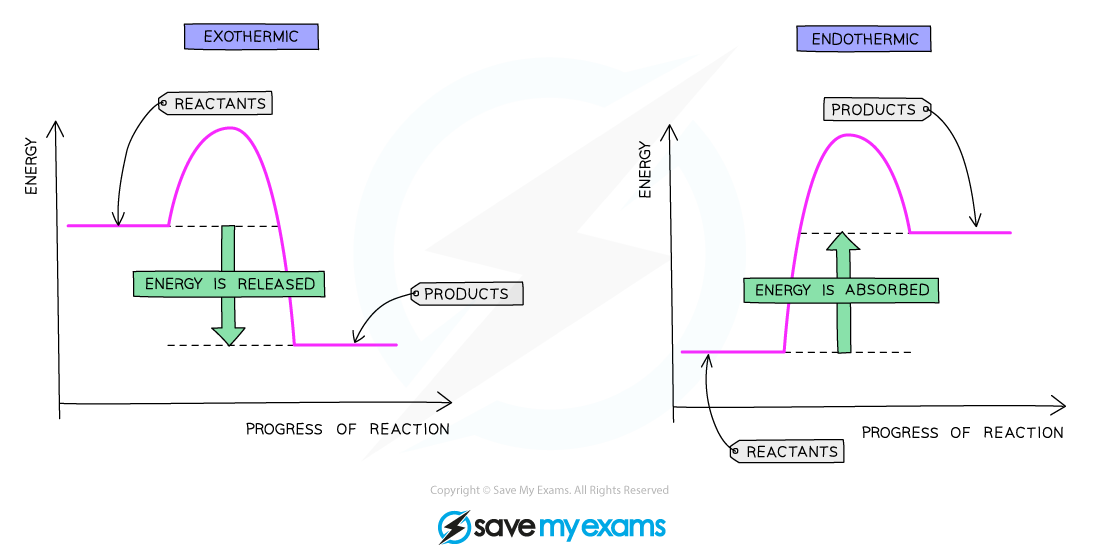
what does a reaction profile diagram for an exothermic reaction look like?
reactants higher than products
curve goes down
what does a reaction profile diagram for an endothermic reaction look like?
products higher than reactants
curve goes up
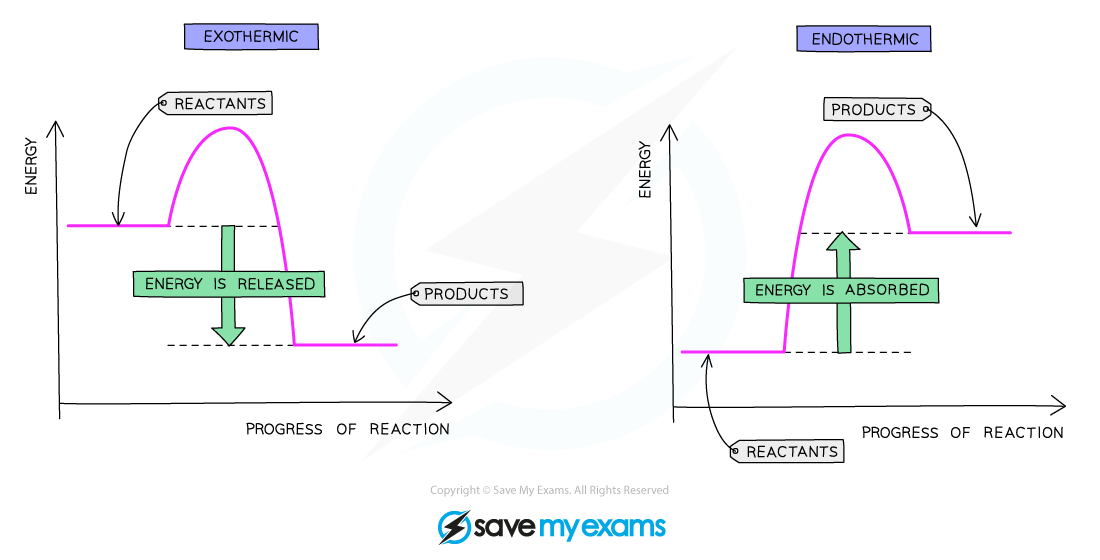
what is the enthalpy change (ΔH) on a reaction profile diagram?
height difference between the reactants and products
what is the activation energy on a reaction profile diagram?
the height difference between the reactants and the top of the curve
what is calorimetry?
a method of experimentation allowing you to find the amount of energy transferred in a chemical reaction
what are the two kinds of calorimetry you can do?
dissolving, displacement and neutralisation reactions
combustion
how would you carry out a calorimetry experiment for dissolving, displacement or neutralisation?
take the temperature of the reactants - make sure they are the same temperature - a water bath may be necessary
mix a set volume of them together in a polystyrene cup
take the temperature of the mixture every 10/20/30 seconds, until the temperature no longer changes/begins to go in the opposite direction
why do you use a polystyrene cup for dissolving, displacement or neutralisation calorimetry experiments?
it is a good insulator
what is the main problem with calorimetry experiments?
energy is lost to the surroundings so the temperature or mass change measurement is inaccurate
how can you reduce energy loss to the surroundings in neutralisation, dissolving or displacement calorimetry experiments?
placing the polystyrene cup in a beaker of cotton wool to give more insulation
putting a lid on the cup to reduce energy loss by evaporation
how would you perform a combustion calorimetry experiment?
put 50g of water in a copper can and record the starting temperature
weigh the spirit burner and lid with fuel
place the spirit burner under the can and light the wick
heat the water, stirring constantly, until the temperature reaches about 50C
put out the flame using the burner lid, and measure the final temperature of the water
weight the spirit burner and lid and calculate mass change
how can you reduce energy loss to the surroundings when performing a combustion calorimetry experiment?
reduce draughts - use a screen to act as a draught excluder
use a metal can as it is a good conductor of heat
what equation can you use for combustion calorimetry experiments?
heat energy transferred
what is the equation for heat energy transferred?
Q = m x c x ΔT where:
Q is heat energy transferred in Joules,
m is mass of liquid being heated in grams,
c is the specific heat capacity in J/g/C,
ΔT is the change in temperature of the liquid in C
what is the specific heat capacity of water?
4.2 J/g/C
what is the equation for molar enthalpy change?
ΔH = -Q/moles where:
-Q is in kilojoules
ΔH is in KJ/mol
what is the equation for normal enthalpy change?
ΔH = total energy absorbed to break bonds (reactants) - total energy released in making bonds (products)
how can you calculate the total energy absorbed to make or break bonds?
add up the individual bond energies of each chemical bond in the compound using displayed formula