Colligative Properties and Raoult's Law
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Colligative Properties
Depend on number of solute particles, not identity.
Vapor Pressure
Pressure exerted by vapor above a liquid.
Raoult's Law
Vapor pressure proportional to solvent's mole fraction.
Mole Fraction
Ratio of moles of component to total moles.
Positive Deviation
Vapor pressure higher than expected from Raoult's Law.
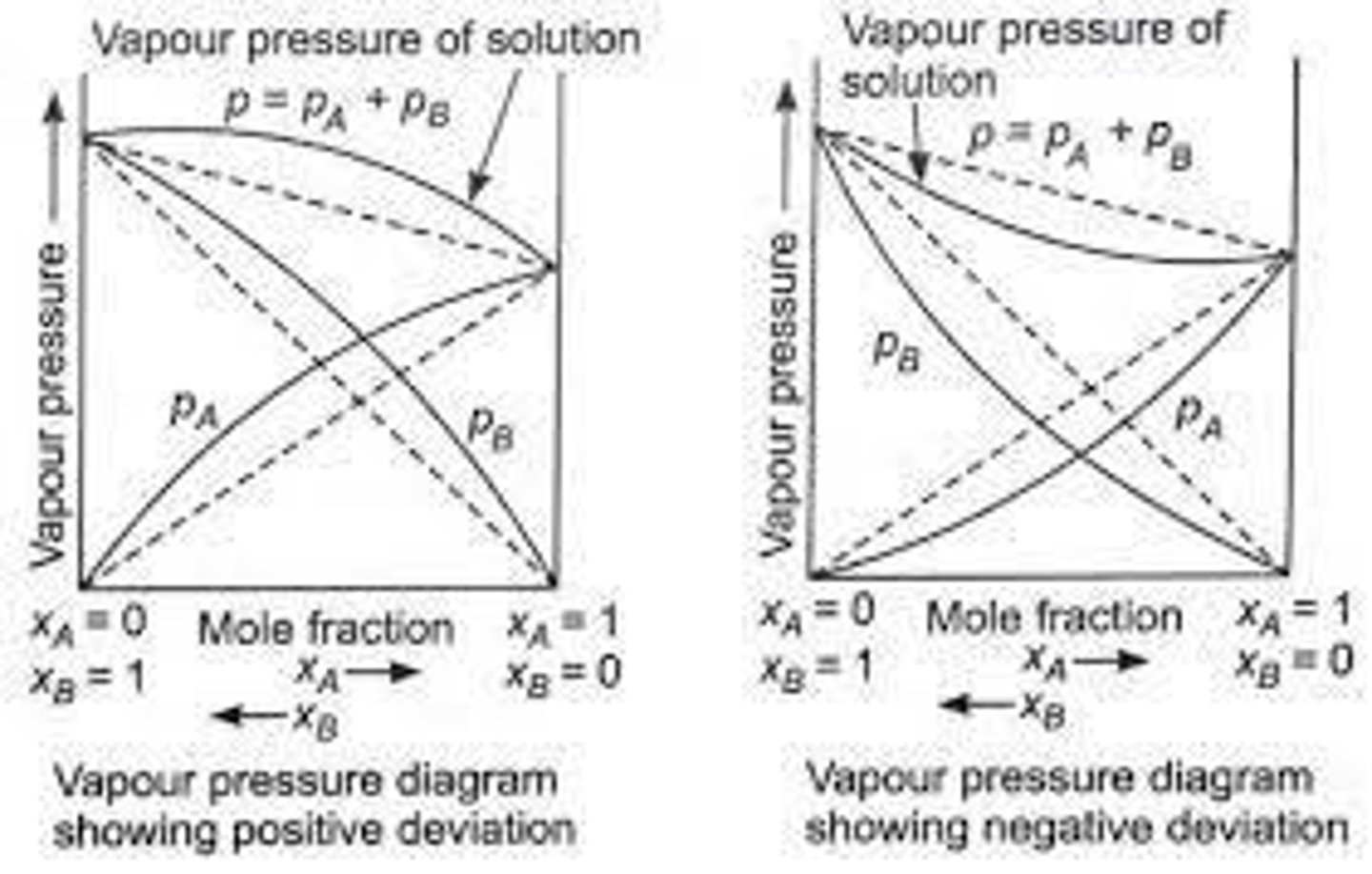
Negative Deviation
Vapor pressure lower than expected from Raoult's Law.
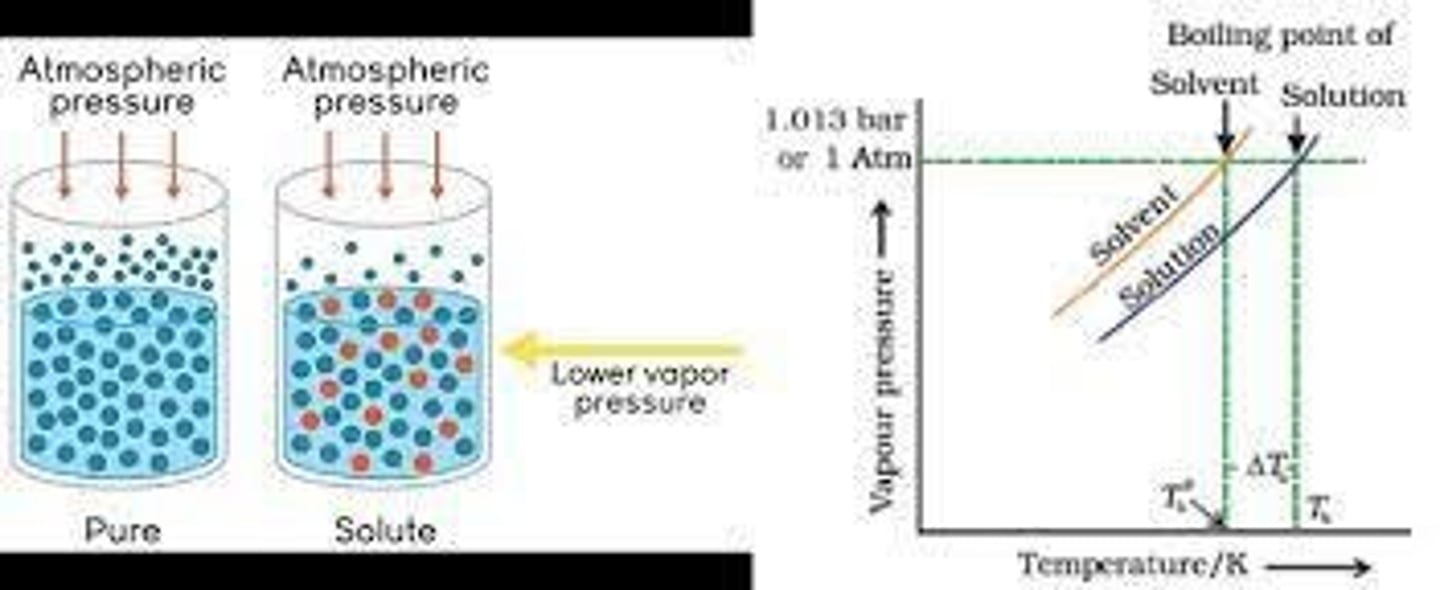
Boiling Point Elevation
Increase in boiling point due to solute presence.
Freezing Point Depression
Decrease in freezing point due to solute presence.
Normal Boiling Point
Temperature where vapor pressure equals atmospheric pressure.
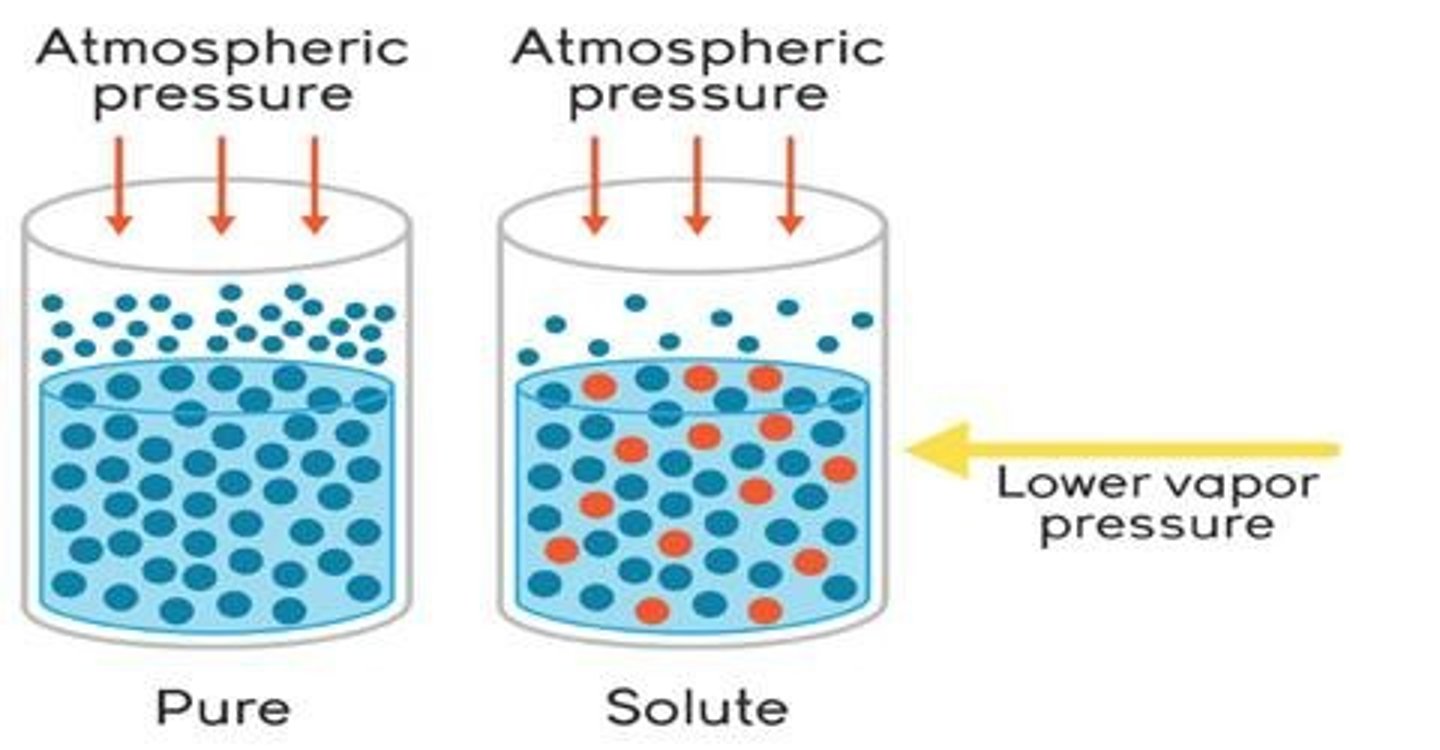
Vapor Pressure Lowering
Reduction in vapor pressure due to solute.
Molality
Moles of solute per kilogram of solvent.
Kb
Molal boiling point elevation constant for solvent.
Kf
Molal freezing point depression constant for solvent.
ΔTb
Change in boiling point due to solute.
ΔTf
Change in freezing point due to solute.
Intermolecular Forces
Attractive forces between molecules affecting properties.
Nonvolatile Solute
Solute that does not vaporize significantly.
Ideal Solution
Solution where solute-solvent interactions are similar.
Non-Ideal Behavior
Deviation from Raoult's Law due to differing interactions.
Osmotic Pressure
Pressure required to stop osmosis in solutions.
Ethanol and Water
Example of positive deviation in vapor pressure.
Trichloromethane and Ethoxyethane
Example of negative deviation in vapor pressure.
Salting Roads
Practical application of freezing point depression.
Ice Cream Making
Uses freezing point depression for texture.