[DCN] Protocols and Models + Physical Layer FC
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
165 Terms
Source
The sender of the communication message.
Destination
The receiver of the communication message.
Channel
The medium for communication transmission.
Protocols
Rules governing communication processes.
Rules Establishment
Agreements that govern communication interactions.
Sender Identification
Recognizing the source in communication protocols.
Receiver Identification
Recognizing the destination in communication protocols.
Common Language
Shared language for effective communication.
Message Encoding
Converting information into a transmittable format.
Message Decoding
Interpreting encoded information back to original form.
Message Formatting
Structuring messages based on type and channel.
Message Size
Size of messages measured in bits.
Flow Control
Manages data transmission rate and volume.
Response Timeout
Duration a device waits for a reply.
Access Method
Determines when a message can be sent.
Collision
When multiple devices send traffic simultaneously.
Unicast
One-to-one communication method.
Multicast
One-to-many communication, not all recipients.
Broadcast
One-to-all communication method.
Network Protocols
Set of rules for network communication.
Protocol
Set of rules for data communication.
Network Communications
Facilitates communication between multiple devices.
Network Security
Protects data through authentication and encryption.
Routing
Enables routers to exchange and select routes.
Service Discovery
Automatically detects devices or services on a network.
Addressing
Identifies sender and receiver in communication.
Reliability
Ensures guaranteed delivery of data packets.
Flow Control
Regulates data transmission rate for efficiency.
Sequencing
Labels data segments for proper order.
Error Detection
Identifies corruption in transmitted data.
Application Interface
Facilitates process-to-process communications.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
Governs web server and client interactions.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
Manages conversations and guarantees data delivery.
Internet Protocol (IP)
Delivers messages globally from sender to receiver.
Ethernet
Transfers messages within a Local Area Network (LAN).
Protocol Suite
Group of protocols for a communication function.
Higher Layers
Focus on application-level data handling.
Lower Layers
Concerned with data movement and services.
TCP/IP
Common protocol suite maintained by IETF.
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI)
Standardized model for network communication protocols.
AppleTalk
Proprietary protocol suite by Apple Inc.
Novell NetWare
Proprietary protocol suite by Novell Inc.
WLAN
Wireless Local Area Network protocol for connectivity.
Internet Society (ISOC)
Promotes open internet development and evolution.
Internet Architecture Board (IAB)
Manages and develops internet standards.
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
Develops and maintains internet and TCP/IP technologies.
Internet Research Task Force (IRTF)
Focuses on long-term internet and TCP/IP research.
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN)
Coordinates IP address allocation and domain name management.
Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA)
Manages IP addresses and protocol identifiers for ICANN.
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
Creates standards in power, telecommunications, and networking.
Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA)
Develops standards for electrical wiring and connectors.
Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA)
Creates communication standards for various telecommunications devices.
International Telecommunications Union-Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T)
Defines standards for video compression and broadband communications.
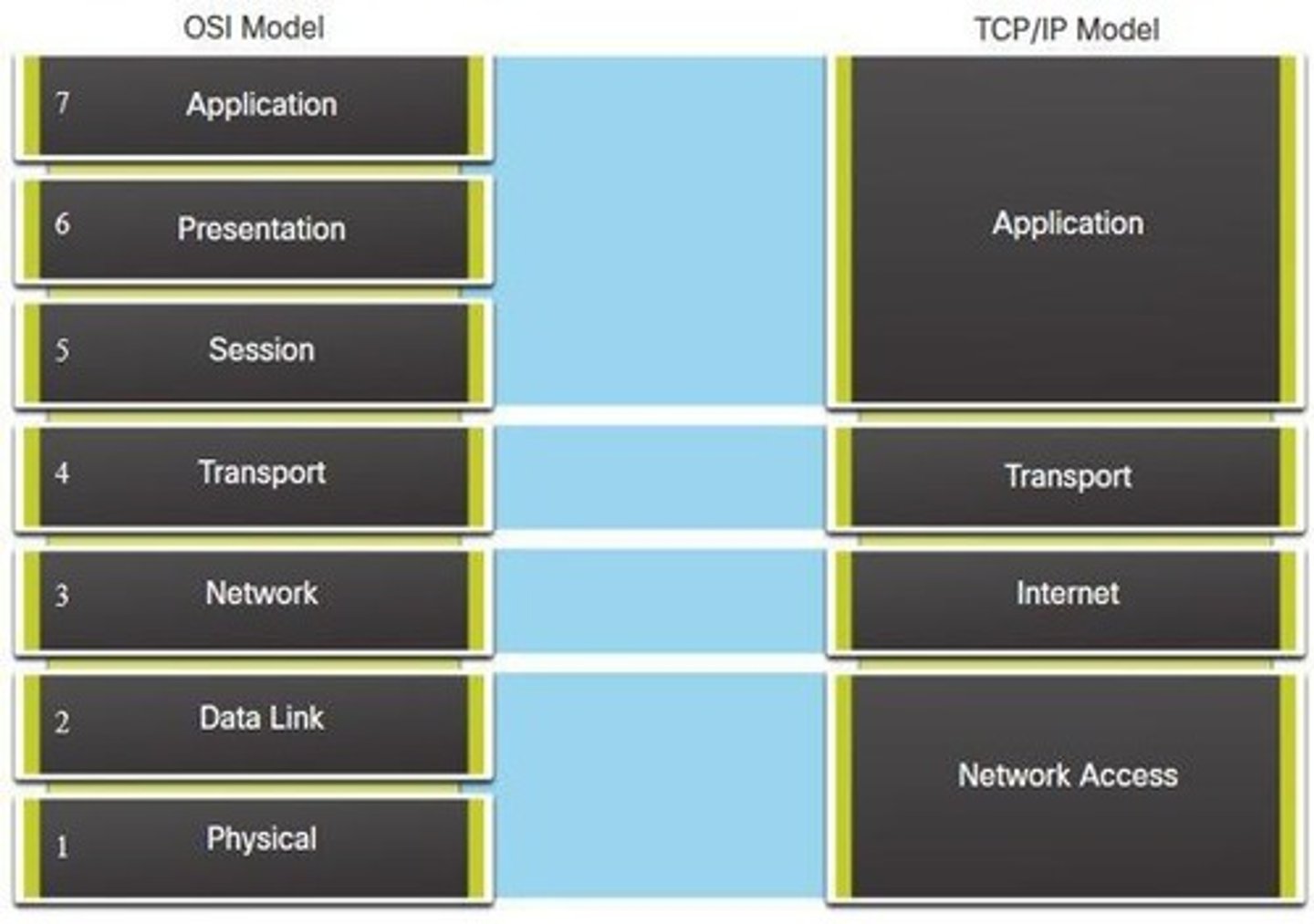
Open System Interconnection (OSI) Model
A conceptual framework for understanding network interactions.
TCP/IP Reference Model
Framework for internet protocol suite and communications.
Layered Model Benefits
Facilitates protocol design and interoperability among vendors.
Application Layer (OSI)
Handles process-to-process communications protocols.
Presentation Layer (OSI)
Ensures common data representation between services.
Session Layer (OSI)
Manages data exchange services for applications.
Transport Layer (OSI)
Segments, transfers, and reassembles data communications.
Network Layer (OSI)
Exchanges individual data pieces over the network.
Data Link Layer (OSI)
Exchanges data frames over shared media.
Physical Layer (OSI)
Activates and maintains physical network connections.
Network Access Layer (TCP/IP)
Controls hardware and media for network communication.
Internet Layer (TCP/IP)
Determines optimal data path through the network.
Transport Layer (TCP/IP)
Facilitates communication across diverse networks.
Segmenting Messages
Breaking messages into smaller units for transmission.
Multiplexing
Interleaving multiple streams of segmented data.
Benefits of Protocols
Enhances speed and efficiency in data transmission.
Sequencing
Numbering segments for proper message reassembly.
TCP
Protocol responsible for segment sequencing.
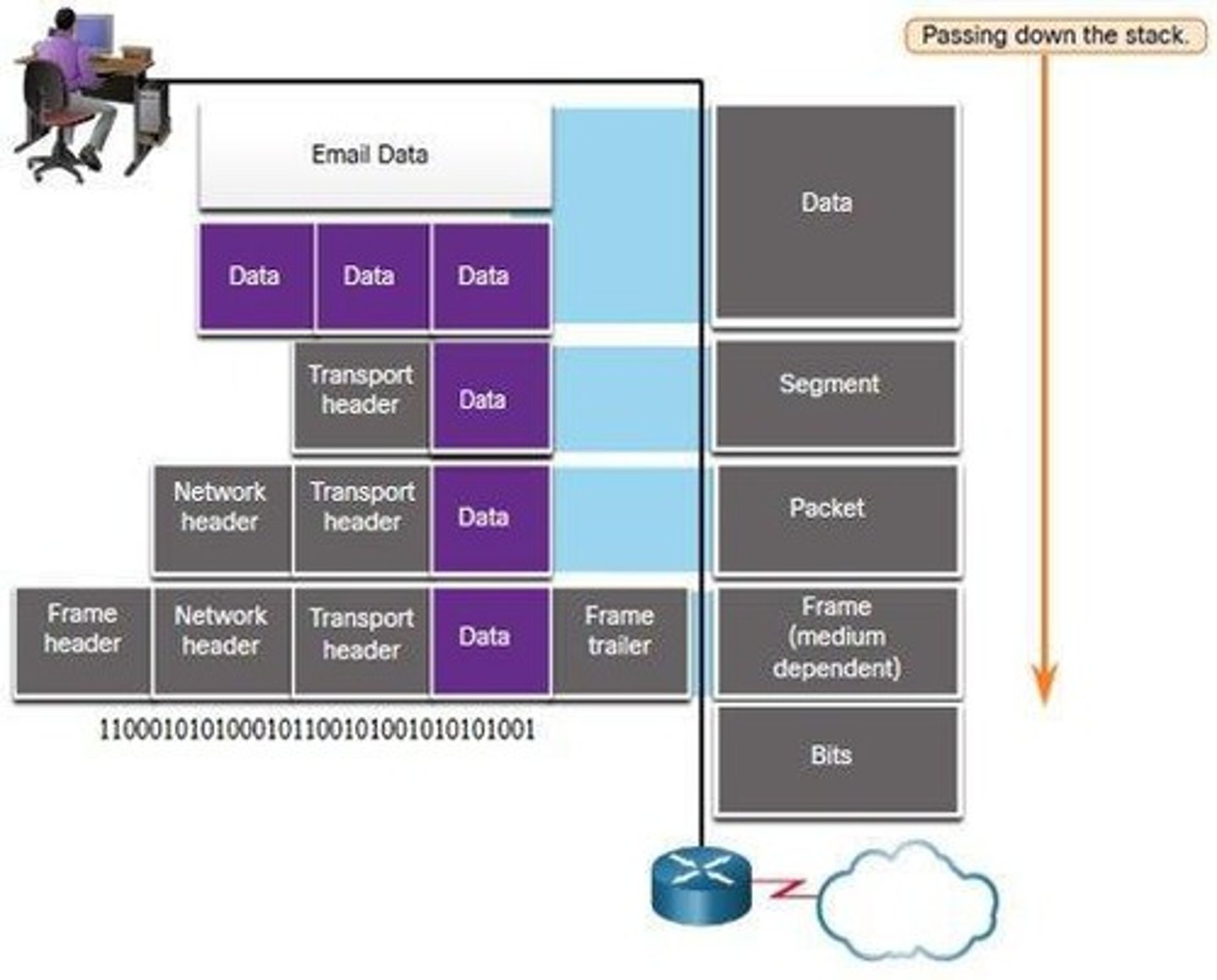
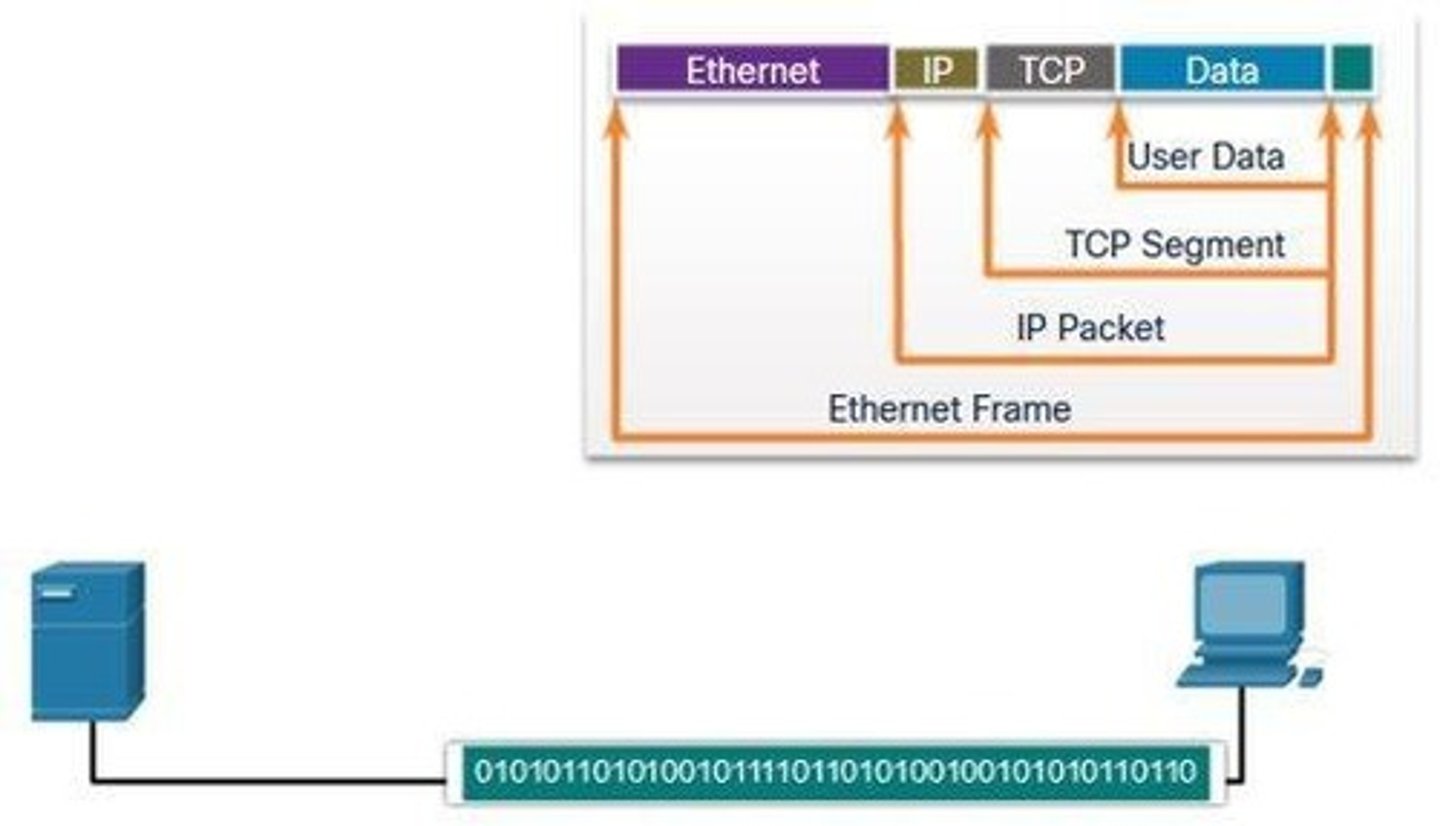
Encapsulation
Adding protocol information to data in layers.
Protocol Data Units (PDU)
Different names for data at each protocol layer.
Data Stream
Original format of data before segmentation.
Segment
PDU at the transport layer of networking.
Packet
PDU at the network layer of networking.
Frame
PDU at the data link layer of networking.
Bits
PDU at the physical layer of networking.
De-Encapsulation
Stripping headers as data moves up layers.
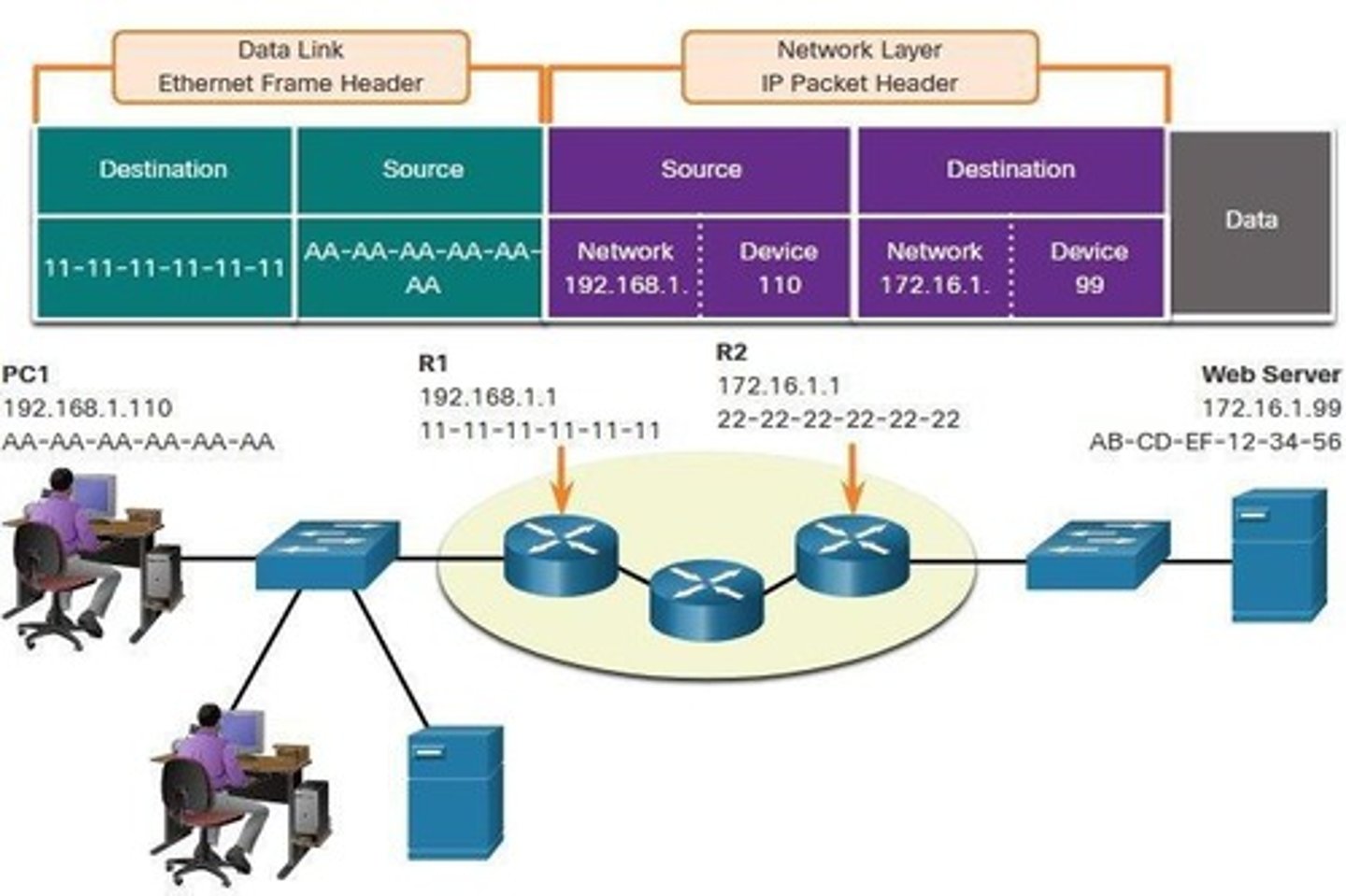
Source IP Address
IP address of the sending device.
Destination IP Address
IP address of the receiving device.
Network Portion
Part of IP address indicating network group.
Host Portion
Part of IP address identifying specific device.
Same Network Devices
Devices share the same network portion in IP.
MAC Address
Physical address used in data link layer.
Data Link Layer Role
Uses MAC addresses for local network communication.
Different Network Devices
Devices have different network portions in IP.
Default Gateway
Router IP address for remote network access.
Routing Process
Forwarding data to reach the actual destination.
Local Addressing
Data link addressing specific to local network.
Data Link Addressing
Local addressing with source and destination for each hop.
MAC Addressing
Unique identifier for network interfaces at Layer 2.
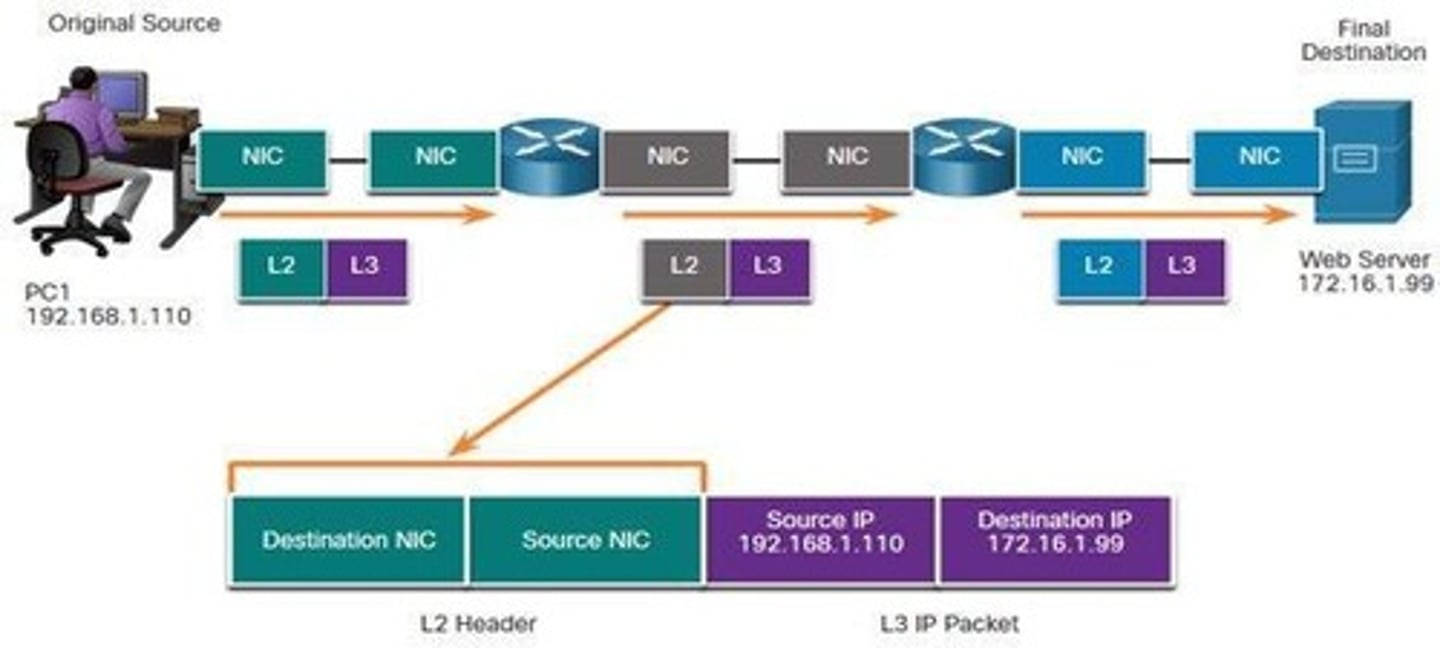
Source MAC Address
Address of the device sending the frame.
Destination MAC Address
Address of the device receiving the frame.
L3 IP Addressing
Global addressing that remains constant across segments.
Physical Layer
Transports bits by converting frames into signals.
Network Interface Card (NIC)
Hardware for connecting devices to a network.
Physical Connection
Wired or wireless link to a local network.
Encoding
Converts bits into recognizable formats for transmission.
Signaling
Represents bit values on the physical medium.