Physics igcse edexcel all
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
D/t graph
gradient = velocity
horizontal line = stationary
distance 0 = back at starting point
curved line = acceleration
v/t graph
area under the line is the distance travelled
Newton's First Law
object has a constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force
newtons second law
f=ma
Newton's Third Law
every force has an equal and opposite reaction force
terminal velocity
no air resistance at first, only weight
as it falls it accelerates and increases in speed
acceleration decreases as drag increases
a = d, no resultant force
no acceleration, terminal velocity reached
thinking distance
distance travelled in the time between realising you need to brake and actually pressing the breaks
factors affecting thinking distance
greater speed
slower reaction time due to alcohol or tiredness
braking distance
time between pressing the brakes and the vehicle coming to a stop
factors affecting braking distance
greater speed or mass
poor road conditions
stopping distance
thinking distance + braking distance
deformation
when an object does not return to its original shape when the load has been removed
hookes law
F = kx
Force is directly proportional to extension until the limit of proportionality
Moments
anticlockwise moment = clockwise moment (equilibrium)
moment = force * perp distance from pivot
momentum
p = mv (kgm/s)
safety features in cars
increases time taken to come to rest
as time increases, force decreases, due to f = change in momentum / time
ie by stretching
conservation of momentum
total momentum before = total momentum after
in a collision
current
measured in Amps
Rate of flow of charge / electrons
measured with an ammeter in series
conserved at a junction
conventional current
rate of flow of positive charge
opposite direction to electron flow as electrons as negative
potential difference
measured in volts
work done per unit charge between 2 points
voltmeter placed in parallel
resistance
measured in ohms
greater the resistance, harder for current to flow
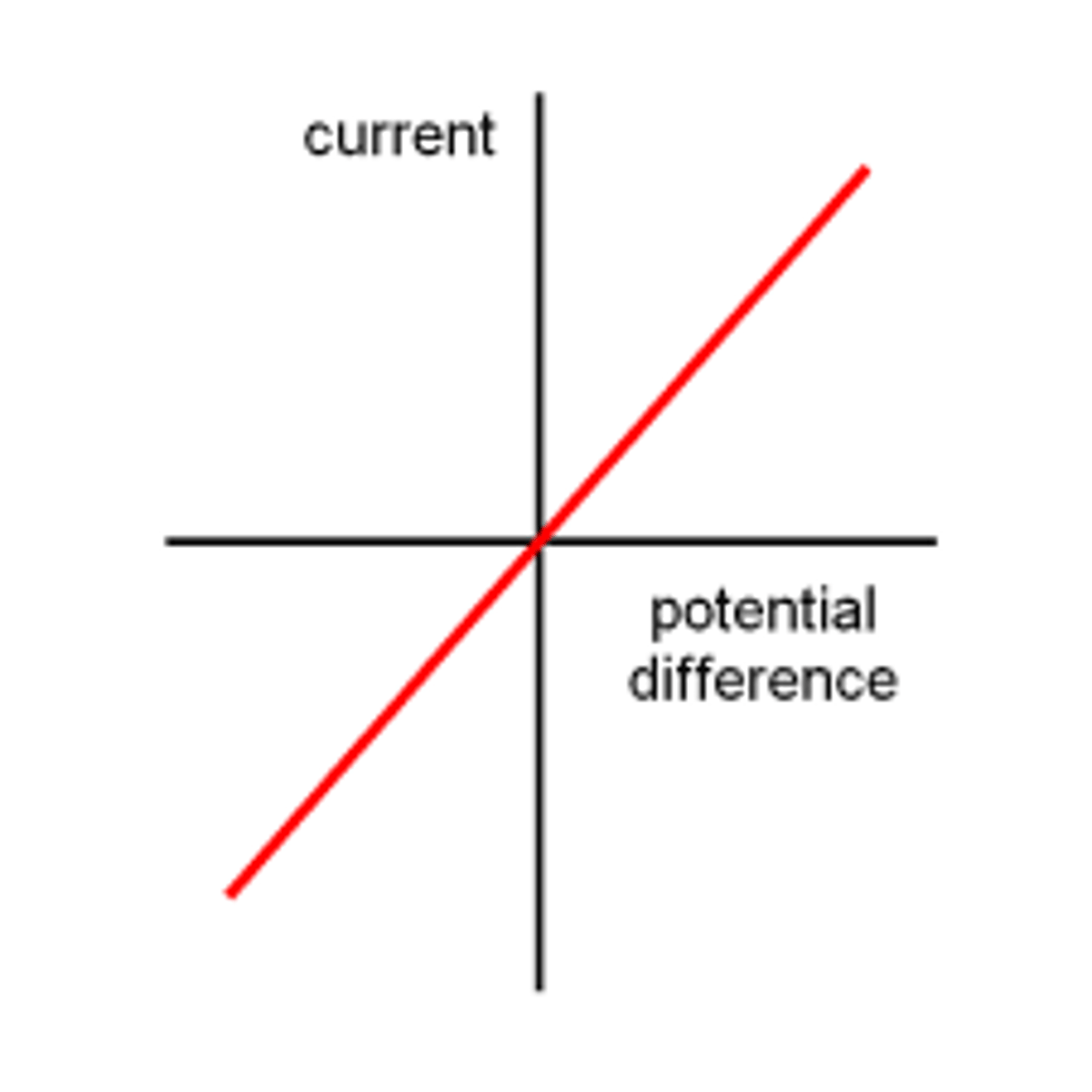
resistor / ohmic conductor
current directly proportional to voltage
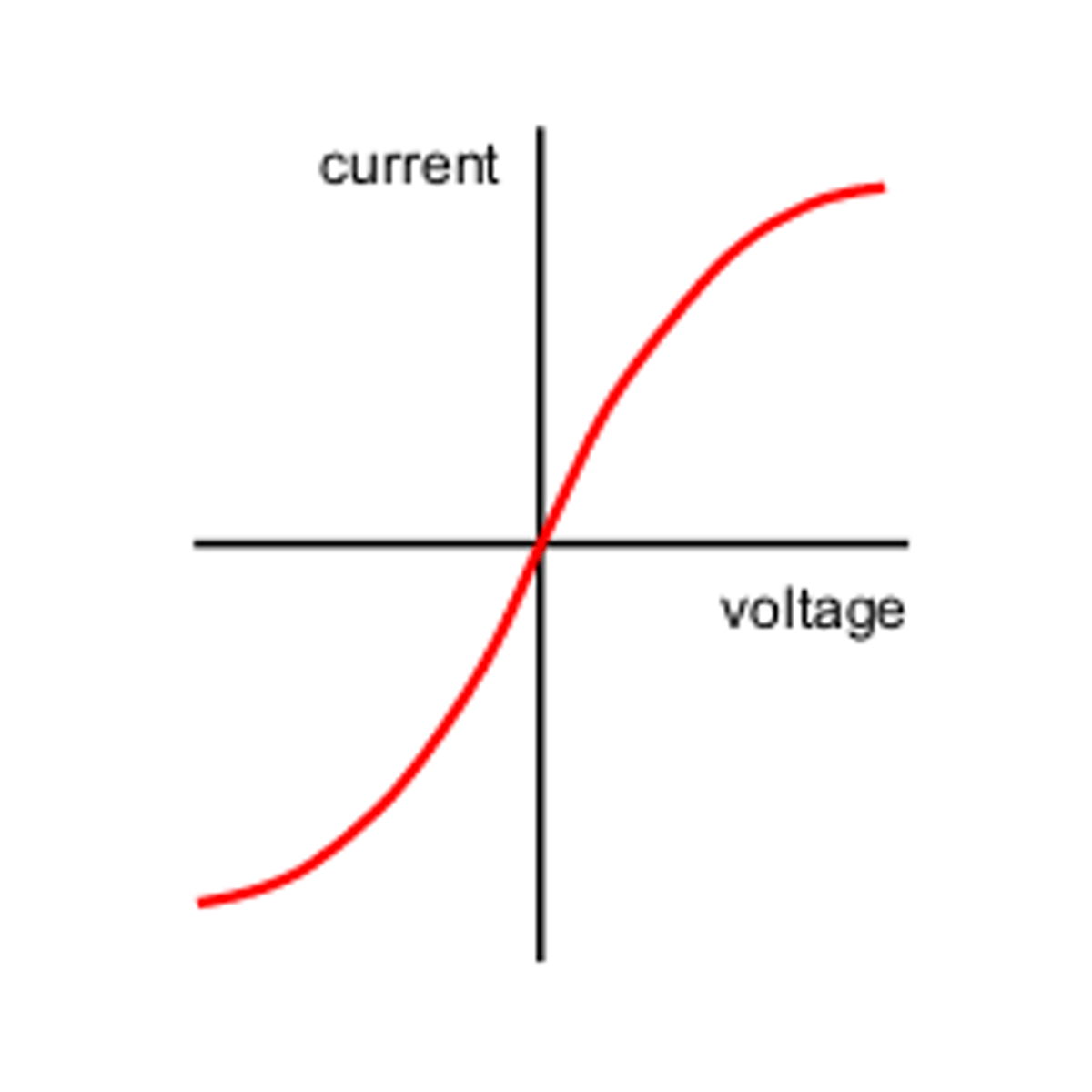
filament lamp
resistance changes as voltage and current change as current increases through filament, so does temperature, increasing collisions and resistance
Thermistor
Resistance decreases as the temperature increases
Used in thermostats
LDR
resistance decreases as light intensity increases
series circuits
same current flows through every component
total resistance = R1 + R2...
voltage is shared
parallel circuits
seperate branches
current is shared between each branch (charge only flows one way)
voltage is same across every branch
dangers of electricity
damaged insulation - fire hazard
overheating of cables - melts insulation
damp conditions - electric shock (water conducts)
fuse
thin piece of wire that overheats and melts if current too high, protecting the circuit. current rating is higher than current in circuit.
circuit breakers
automatic electromagnet switch which breaks the circuit if current rises over a certain value, can be reset and operate faster than fuses
earthing
creates a safe route for current to flow through in case of a short circuit, low resistance so a strong current surges through and breaks fuse to disconnect appliance
double insulation
plastic casings covering electrical components
direct current
1 direction
alternating current
continuously changes direction
longitudinal waves
waves where oscillations are parallel to direction of energy transfer
cannot move in a vacuum
compressions - close together
rarefractions - spaced apart
transverse waves
waves that vibrate perpendicular to direction of energy transfer
amplitude
distance from undisturbed position to the peak or trough of a wave
wavelength
distance from one point on wave to the same point on the next wave in metres
frequency
number of waves passing a second in hertz
time period
time taken for a single wave to pass a point in seconds
wavefront
space between = wavelength
doppler effect
apparent change in wavelength and frequency of wave emitted by a moving source, speed stays constant so wavelength/frequency must increase/decrease
electromagnetic waves
transverse waves that transfer energy from the source of the waves to an absorber
all can go through vacuum at same speed
EM spectrum
radio
micro
infra
visible light
ultraviolet
xrays
gamma
high frequency = high radiation
can be reflected and refracted
visible light spectrum
red = longest wavelength (lowest frequency)
violet = shortest wavelength (highest frequency)
applications of radiowaves
communication (radio and TV)
can be reflected from atmosphere
applications of microwaves
communication
heating food
can penetrate earth's atmosphere
applications of infrared
thermal imaging
night vision
fibre optic communication
undergo TIR
applications of visible light
fibre optic communication
photos/videos
cameras are setup to detect visible light
applications of ultraviolet
fluorescent lamps
it fluoresces with ultraviolet lighting
applications of xrays
x-ray images
x-rays can penetrate soft tissue but not bone
applications of gamma
sterilising medical instruments
treating cancer
gamma kills bacteria
dangers of microwaves
heat damage to internal organs
microwaves emit very large amounts of energy
dangers of infrared
skin burns
to protect, wear gloves
dangers of visible light
bright light can cause eye damage
dangers of ultraviolet
sunburn
eye damage
ionising - kills cells / causes malfunction - resulting in premature aging - and diseases
sunscreen absorbs UV
dangers of xrays and gamma
kills cells
mutations
cancer
ionising - penetrates body - causes gene mutation
minimise exposure / lead apron
reflection
wave hits boundary between two media and doesnt pass through, instead staying in medium, resulting in a change of direction
law of reflection
angle of incidence (approaching boundary) = angle of reflection
less dense to more dense
light will bend towards the normal
PRAC : investigating refraction
draw around perspex block
direct beam of light at side of block
mark where the ray enters and exits the block, as well as a point on the ray entering and exiting the block (ie next to ray box)
join points
repeat for different angles
PRAC: investigating refraction issues
error with 90 not being correct (use set square)
inaccurately marked (sharp pencil)
PRAC : investigating snell's law
draw around glass block
draw norma;
measure angles of incidence and mark on paper
direct beam of light at side face of block
mark point close to ray box, entering and exit points, and exit light ray 5cm away
join dots
repeat for different angles
TIR occurs when
i > c and incident material is denser than second material
TIR is useful because
reflects light along optical fibres - ie for communications and endoscopes, TIR each time it hits each of fibre
Prisms are useful because
periscopes, binoculars, telescopes, cameras, light is TIR
meaning of critical angle
when angle of refraction = 90, light is reflected along boundary, so angle of incidence = c
conservation of energy
energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be transferred from one store to another
conduction
solids
metals are good conductors
non metals are poor conductors (good insulators)
delocalised electrons can collide with atoms - transferring vibrations and energy
convection
liquids and gases
fluid expands and is less dense
hot fluid rises
hot fluid cools and sinks back down
forming a convection current
thermal radiation
hotter objects emit more infrared radiation
black best at emitting and absorbing IR
white and shiny worst at emitting and absorbing IR
PRAC : conduction
attach ball bearings with wax to ends of 4 different metal strips hanging over a heat source
heat middle of strips
heat will be conducted along to the ball bearing which will drop as wax melts
time each ball dropping for the 4 balls
repeat
PRAC : investigate convection
fill beaker with cold water and place potassium permanganate crystals
heat with BB
repeat with hot water
dissolved purple follows convection current faster in hot water
PRAC : radiation
setup four flasks; black, grey, white, silver
fill with hot water
note starting temp, measure temps every 30s for 10m
reducing conduction
use materials with low thermal conductivity - insulators
use fibreglass - air trapped between fibres - prevents convection, air is a poor conductor
reducing convection
reduce formation convection currents - prevent movement
GPE =
KE
so you can use the KE and GPE formulae to find speed or mass
power
rate of energy transfer / work done
pressure in a fluid (liquid or gas)
force exerted evenly in all directions
pressure creates forces
forces act at right angles to surface
kinetic theory of gases
molecules in a gas are in constant random motion at high speed
no specific path = sudden changes in motion due to collision
BROWNIAN MOTION
gas and pressure contianer
gases fill their container
they collide with containers
producing a net force perpendicular to surface
high pressure = more collisions at greater force
compressed - more frequent collisions - higher net force - higher pressure
absolute zero
-273 C
particles have no net movement - zero kinetic energy
kelvin scale
0K = -273C
proportional to avg kinetic energy
increase in temperature
hotter the gas, faster the movement due to having more KE, so more frequent collisions
law of magnetism
like repel
unlike attract
this is non contact force
magnetic materials
magnetically soft (iron) - easy to magnetise and lose magnetism
magnetically hard (steel) - difficult to magnetise, permanently magnetised
magnetic field :
region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnetic material
magnetic field lines
show strength and direction of a field - spacing (strength - closer the stronger)
magnetic field around bar magnet
strongest at the poles - weaker as distance from magnet increases
ALWAYS from north to south
magnetic material examples
iron, cobalt, nickel
types of magnet
permanent - made from permanent magnetic materials ie steel, producing own magnetic field
induced - temporarily magnetised in magnetic field
PRAC : investigate mag field for permanent bar magnet
draw a dot at one end of magnet and place compass next to dot
draw new dot where compass points
repeat until connecting to other end of magnet
current in conducting wire
produces a magnetic field around the wire
no current = no mag field
more current = stronger mag field
right hand thumb rule
thumb - direction of current
other fingers - direction of field
motor effect
a wire with current flowing through it is placed in a magnetic field and experiences a force
producing two interacting magnetic fields (around wire, one wire is placed into)
wire will experience a force
motor effect - dc motor
coil of wire in uniform magnetic field
current flowing through coil produces magnetic field
force exerted on wire from interaction of two magnetic fields
forces act in opposite directions on each side of coil, rotation
after 90 degrees, split ring no longer in contact with brushes - no current flows through coil - no forces act
motor effect loudspeaker
coil of wire around one pole of perm magnet
AC current through coil - current constantly changing direction = direction of field too
interaction of two mag fields
exerting a force on coil
coil oscillates as force constantly changes direction
coil causes speaker to oscillate - air oscillates - creating sound waves
flemings left hand rule
First - mag Field
seCond - Current
THumb - THrust (force)
how is voltage induced in a conductor
when it moves through a magnetic field or when a magnetic field changes through it
generator effect
factors affecting induced potential difference
speed at wire/coil/magnet moved - increases rate mag field lines cut, increases induced pot diff
number of turns - increase induced pot diff as each coil cuts through mag field lines
size of coils - increase area increases pot diff, more wire to cut through
strength of mag fields - increase pot diff induced