Analytical Forensic Toxicology Exam 2
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCMS, Derivatization, LLE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
internal standard addition
always after dilution to ensure same amount in each sample
internal standard properties
mirror analyte behavior, not already present in sample, can be separated via chromatogram or mass, does not react with analyte, soluble and stable in diluent, accurately added to samples
how to choose a method
AMR chosen and capability of instrument
AMR
analytical measured range
AMR def
range you can quantitate and report a value based on method validation
internal standard purpose
verification, identification, quantitation
internal standard verification
deemed by successful extraction
internal standard identification
identify compound through retention time comparison
internal standard quantitation
calibration curve
verify before report
calibration % dev, controls in range, negative blanks, no carryover, ion ratios, itsd recover, retention time, rrt, chromatography
internal standard for non specific detector
similar structure, not found in sample, no shared common ion, same extraction, acceptable chromatogram
internal standard for mass spec
isotopically labeled version if analyte or matched
matched isotope
adding deuterium
internal standard accounts for
any loss in sample
standard addition
generate quant results within sample instead of performing external
standard addition common use
no validated method to run sample, difficult matrix like liver tissues
low pka=
stronger acid=donates proton more
pH variable dependent on
matrix and/or extraction solvent
ionization formation ideal
2 pH units away from pKa
amphoteric compounds
has both acidic and basic groups, act as either
zwitterion
has both a pos and neg charge at the same time
direct analysis sample prep types
enzyme immunoassay, headspace
dilute and shoot pros
simple, cheap, easy, reduce viscosity
dilute and shoot cons
potential loss of recovery by diluting analyte, doesn’t remove contaminants,
protein precipitation
dilution and take out matrix components by denaturing proteins
protein precipitation con
doesn’t take out chemical contaminants/interference
partition coefficient
tendency for any species to prefer to be in one chemical phase over another after equilibrium
partition coefficient formula
conc in phase 2/ conc in phase 1
partition coefficient for high recovery
as high and as different as possible
types of extraction
LLE, SPE, SLE, PLD
LLE
liquid liquid extraction
SPE
solid phase extraction
SPE process
sample enters syringe column bed, different liquids are passed through to elute desired target or just the analyte
SPE pros
selectivity, flexibility, high automation potential
SLE
supported liquid extraction
SLE process
one liquid flows through solid support in column trapping some compounds, extracting liquid flows through taking target to collection
PLD
phospholipid depletion
LLE steps
strong base convert analyte, analyte leaves aqueous, mixing and separating layers, isolate layer with compound, run on instrument or dry down
LLE affected by
pH, temperature, affinity for solvent, affinity for matrix, relative volumes, number of extraction steps, immiscibility of phases
LLE three aspects to consider
matrices, the solvents, the analyte
LLE back extraction use
3 layer to increase purity
LLE back extraction layers
add base to neutralize and migrate organic, add acid to attract to aqueous, add base
LLE cons
limited selectivity, difficulty of automation, emulsions
LLE pros
rapid method development, simplicity
emulsions
sample contains high level surfactants that prevent clean separation
fixing emulsions
sample sit, acidify the sample, add table sat, filter sodium sulfate, breakup and centrifuge, ultrasonic bath, change the extraction type
derivatization limitation
can make the molecule too large to volatize
derivatization requirements
heat, time, catalyst, removal of reactant
derivatization goal
chemically react with problematic molecule in native form and convert to gc acceptable form
derivatization outcomes
improve chromatogram, differentiate optical isomers, create charge for LCMS
GC pros
most successful chromatogram, cheap, robust
gc main contaminants
oxygen, moisture, hydrocarbon
GC process
cold sample passes through hot inlet and condenses onto column, oven heats column to provide movement with carrier gas through to detector
septum purge
tiny flow rate to blow away debris
Splitless flow
slow rate, goes through liner, everything onto column
splitless cons
broader bands (higher B), more time for anaytes to breakdown or adsorb
split injection liner
tapered liner
split flow
high rate, takes sample with gas to split vent
split pros
larger quantities, preserve column capacity
split ratio
sample waste: sample to column, high ratio= lower amount of sample enters
split flow peak affect
high flow= sharper peaks
on column use
thermally labile compounds (can’t be heated/explosive)
on column flow and temp
slow flow rate, inlet temp=same as column
on column requirements
specific syringe, wider bore column
Headspace injection types
purge and trap, SPME
SPME
solid phase micro extractions
purge and trap process
push gas into sample, force gas out to be collected in trap, put onto column after a bit
SPME process
sample absorbs into needle/fiber from liquid or gas, fiber introduced to injection port
SPME pros
minimal sample prep, no solvent, different fibers
heated oven purpose
maintain precise control over column temp and changes
Types of oven temp
isothermal, program, zones, ranges, design
oven temperature affects
volatility and flow rate through the column
Chromatography theory
retention dictated by the relative amount of time spent in the stationary phase compared to mobile phase
low affinity to stationary elution effect
short elution, low retention time
system prevention of band broadening
column fittings to inlet and detector reduce dead volume to minimal levels
column efficiency
relative measure of ability to generate clearly resolved peaks
More theoretical plates means
more separation= better resolution
longitudinal diffusion on flow rate
small diffusion= increase flow rate
mass transfer
time analyte equilibrates between two phases before moving to the next plate
GC parameters
temperature, gas flow, carrier gas, injection port liner, injection mode, detector, acquisition
column dimensions
length, diameter, film thickness, temperature, stationary phase
small internal diameter pro
highest efficiency, shorter time, highly complex samples
longer column pro
high resolution
longer column cons
too much time, more expensive
resolution def
ability to distinguish two closely related and/or eluting chromatographic peaks
bigger diameter effects
dec efficiency, inc loadng capacity, inc flow rate, inc analysis time
thicker column effects
longer retention time, lower resolution, broader peak, good capacity
shark fin peak
capacity overloaded, fronting, shape distorted
tailing peak
asymmetrical, from active site at injection or column
gc maintenance
change liner, wool, septum, and column or clip
gcms contamination source
fingerprints, air leak, cleaning solvents, column bleed, dirty materials
Retention time locking
use known molecule with known rt on GC, the instrument will adjust pressure to return molecule to the correct time
isomers differentiation
fragment the same, only differentiate through retention time
fix column bleed
install new column when background noise gets really high
why choose derivatization
Enhance detectability, enhance excitability, stabilize components, increase retention, reduce retention, improve sensitivity, improve gc/ms appearance, bulk weight
which step to derivatize
can be performed at any steps
flash derivatization
occurs very last minute, within injection port
Mass spec instrument components
sample introduction, transfer region, high vacuum, pumps, ionization source, analyzer, detector, data processor
GCMS diagram
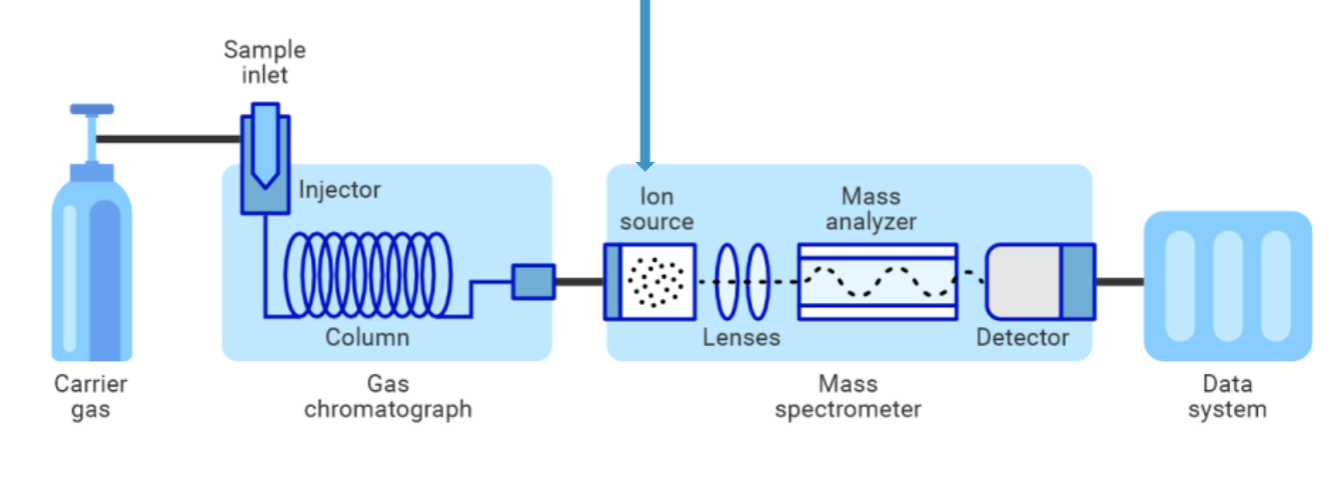
see photo
electron ionization
disrupt electron cloud to cause loss of an electron and create a radical cation