Engineering Graphics Flashcards
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards for engineering graphics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Tolerance
The allowable amount of variation in a dimension to ensure proper function and interchangeability.
Nominal Size
The general size of a part, usually expressed in fractions.
Basic Size
The theoretical size from which limits are determined.
Actual Size
The measured size of a finished part.
Limits
The maximum and minimum sizes a part can be and still function.
Allowance
The minimum clearance or maximum interference between mating parts.
Maximum Material Condition (MMC)
The state when a part contains the most material-largest shaft or smallest hole.
Least Material Condition (LMC)
The state when a part contains the least material-smallest shaft or largest hole.
Clearance Fit
Always allows clearance between parts; hole is bigger than shaft.
Interference Fit
Always results in interference; shaft is bigger than hole.
Transition Fit
May result in either clearance or interference depending on actual sizes.
Bolt
Used with a nut.
Screw
Used in a threaded hole.
Internal Threads
Inside holes.
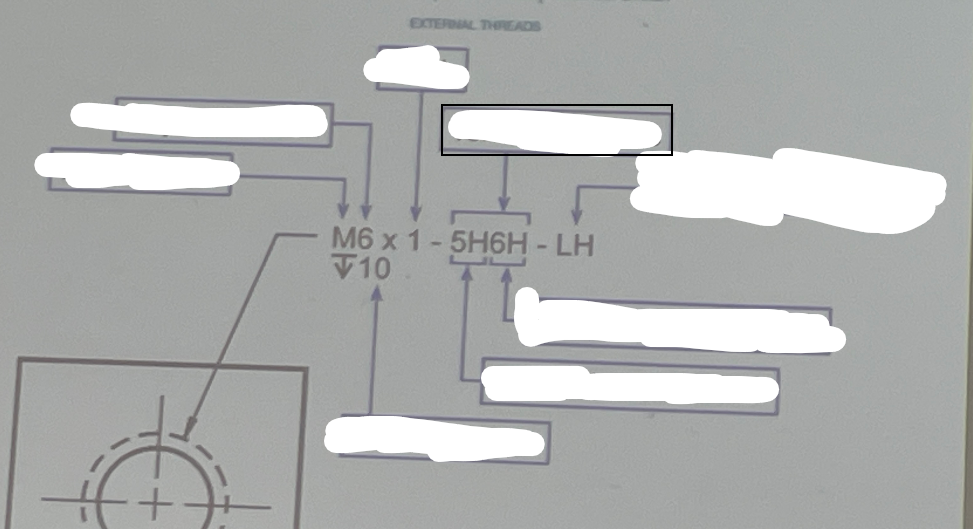
External Threads
On the outside of shafts.
Major Diameter
The largest diameter of a thread.
Minor Diameter
The smallest diameter of a thread.
Thread Pitch
The distance between threads; in English units, expressed as threads per inch
have a longer, gradual taper, making them suitable for starting threads in a new hole.
Taper tap

Cuts full threads to the bottom of blind holes.
Bottoming Tap

$$have a shorter taper and are used for cutting threads after a taper tap has been use
Plug tap

Class 1 Thread Fit
Loose fit for easy assembly.
Class 2 Thread Fit
Standard fit for general use (most common).
Class 3 Thread Fit
Tight fit for high precision and load applications.
Surface Finish
The texture or smoothness of a part's surface.
English Unit System
Inch-Pound-Second (IPS) system.
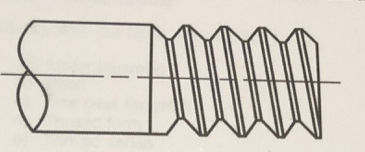
Detailed Representation
Is this a Detailed, Schematic, or Simplified representation of a thread
Simplified Representation
Is this a Detailed, Schematic, or Simplified representation of a thread

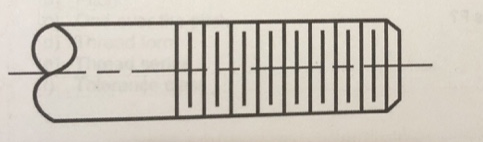
Schematic Representation
Is this a Detailed, Schematic, or Simplified representation of a thread
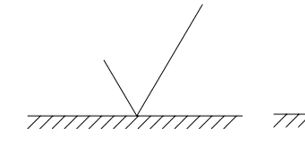
Any Method Surface Finish
What is this Symbol for
Machining Only Surface Finish
What is this Symbol for
Machining Prohibited Surface finish
What is this Symbol for
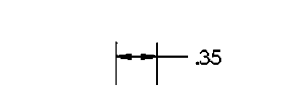
3rd
Where in the order would this dimensioning style fall?
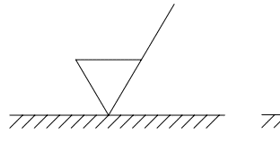
1st
Where in the order would this dimensioning style fall?
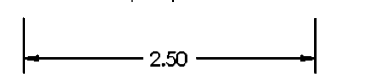
4th
Where in the order would this dimensioning style fall?
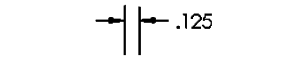
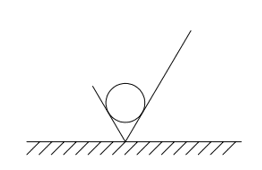
2nd
Where in the order would this dimensioning style fall?
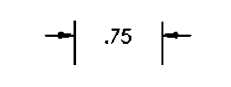
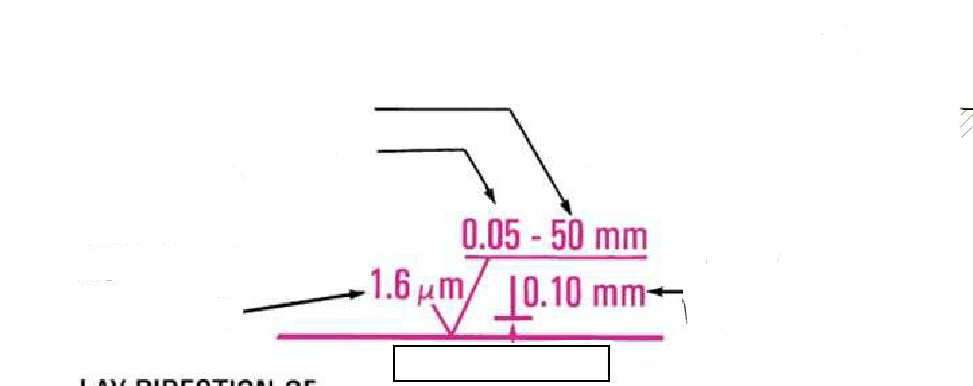
Roughness Width
refers to the width of the surface texture that affects the roughness of a material. It is a critical measurement in engineering graphics for specifying surface finishes.
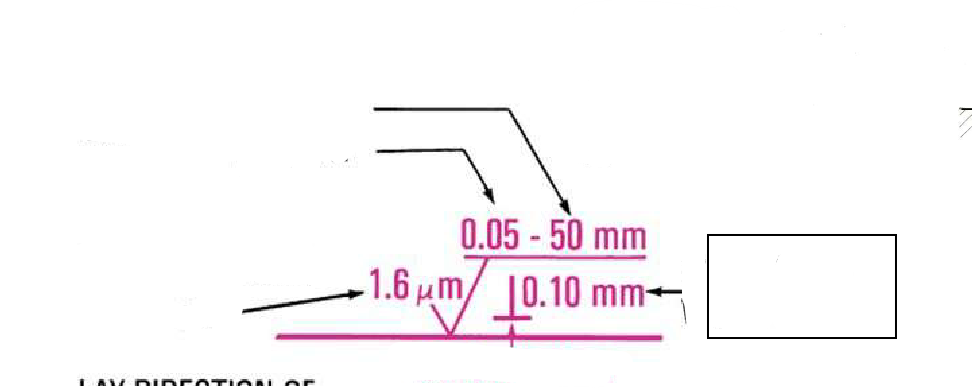
Width
Height (waiveness)
Refers to the amplitude of the surface irregularities, quantifying the peak-to-valley distance of the waviness.
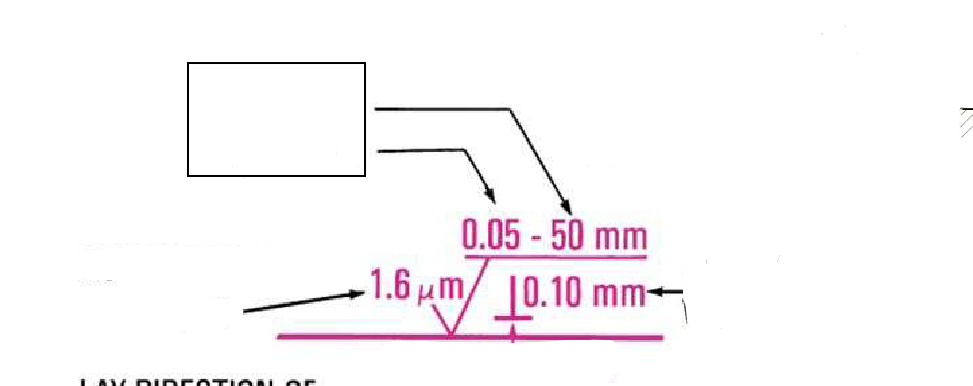
Lay Direction
The orientation of the surface texture relative to a specified reference direction, affecting the functional performance and appearance of a component.
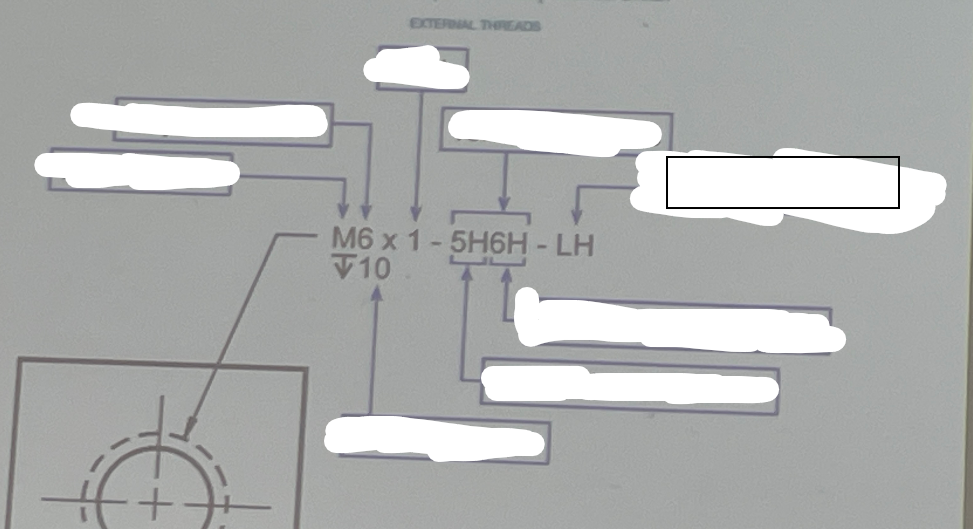
Right/Left Handed
Refers to the orientation in which a part or feature is designed or used, indicating its operational direction based on the user's perspective.
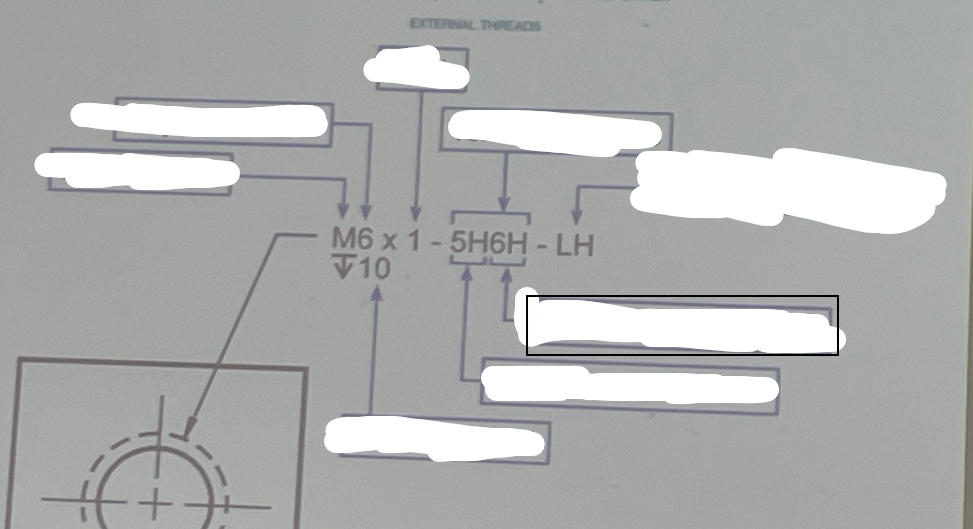
Minor Diameter Tolerance
The permissible variation in the minimum diameter of a cylindrical feature, such as a hole or shaft, ensuring proper fit and function.
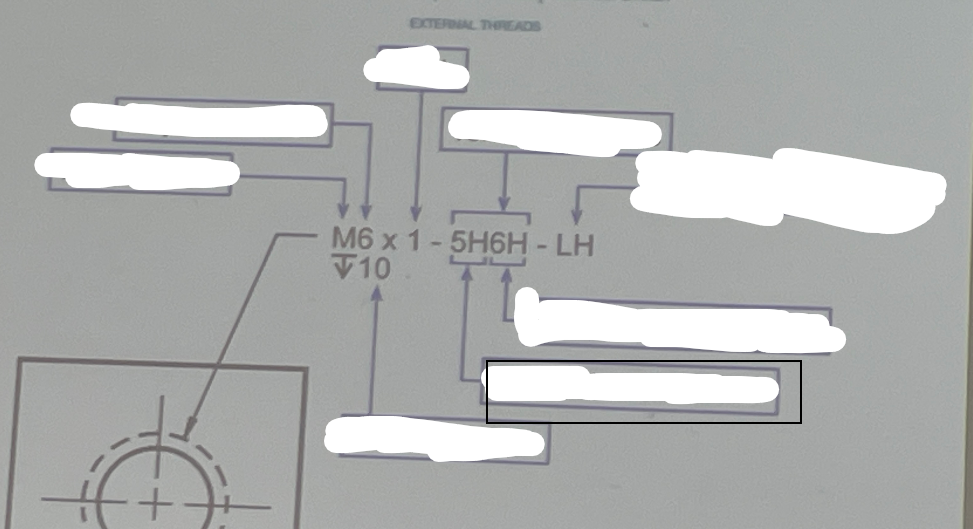
Pitch Diameter Tolerance
Refers to the allowable variance in the pitch diameter measurement of a screw thread. This tolerance ensures that threads will fit together correctly and function as designed.
Thread Depth
The perpendicular distance from the crest to the root of a thread, which determines the thread's height.
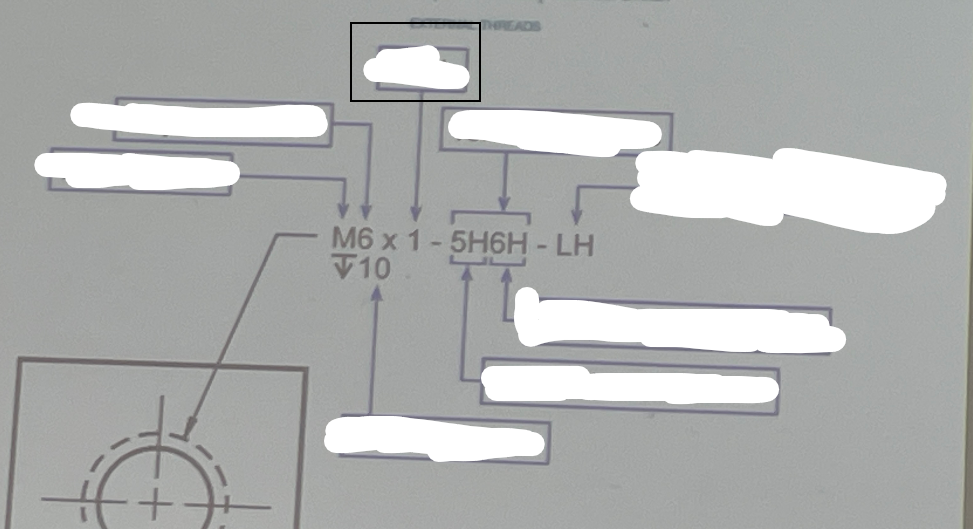
Metric Form
In engineering graphics, metric form refers to a system of measurement where dimensions and tolerances are specified in millimeters and are often applicable to ISO standards, ensuring consistency and precision in technical drawings.
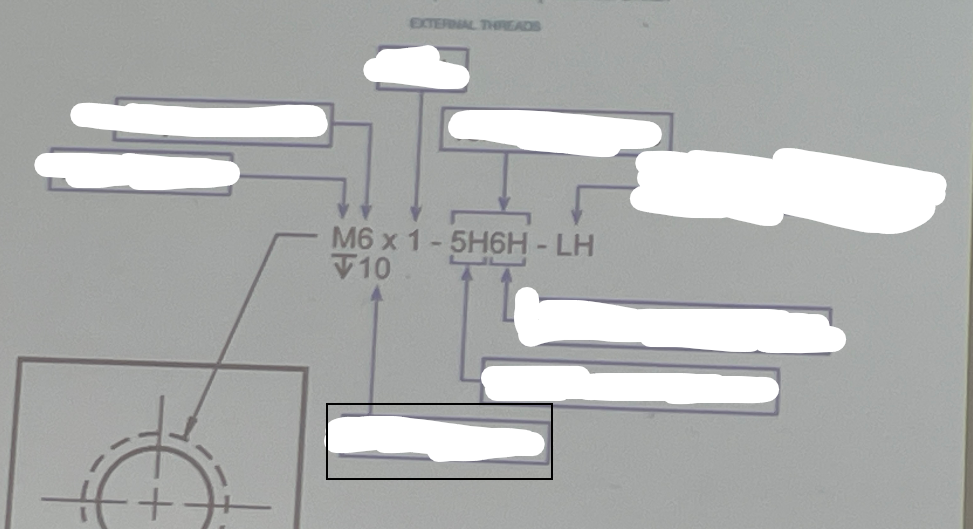
Major Diameter
The largest diameter of a screw thread, measured from crest to crest.
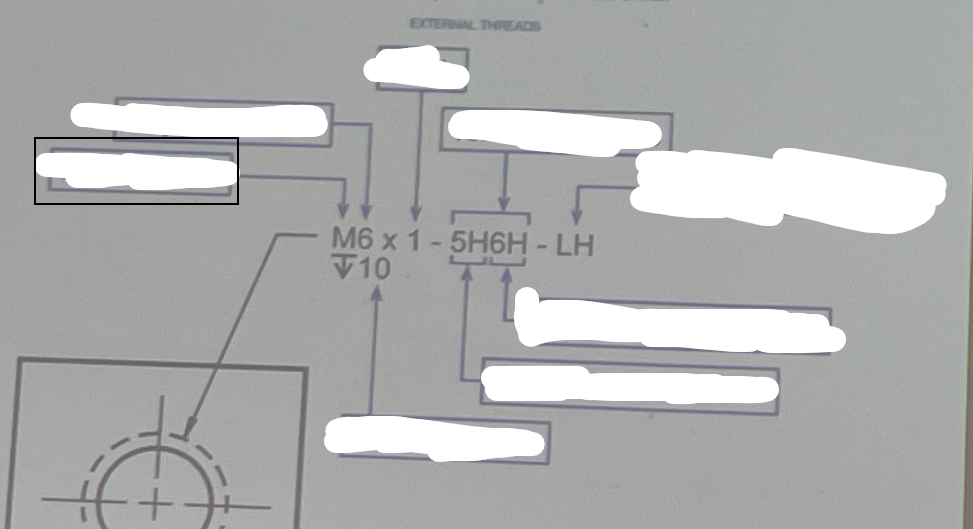
Pitch
The distance between corresponding points on adjacent threads, measured parallel to the axis.
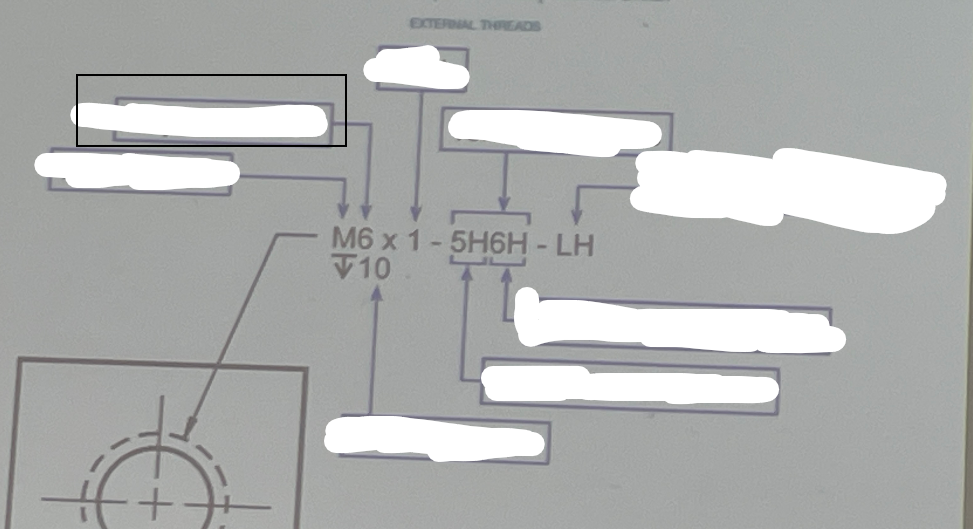
Tolerance Class
A classification that specifies the permissible limits of variation in a dimension or physical property during the manufacturing process.
Major Diameter
The largest diameter of a cylindrical screw or shaft, measured from the outer edges of the threads.
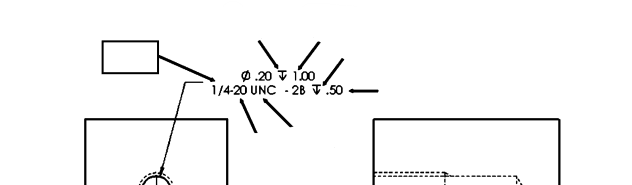
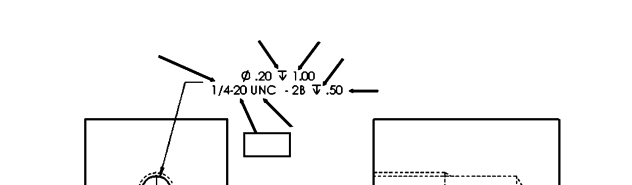
Depth Symbol
A symbol used in engineering drawings to indicate the depth of a hole or feature.
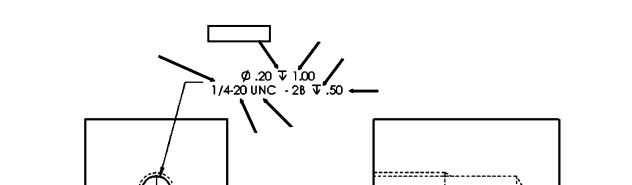
Depth of Hole
The specified measurement from the top of the workpiece to the bottom of a hole, often indicated by the depth symbol on drawings.
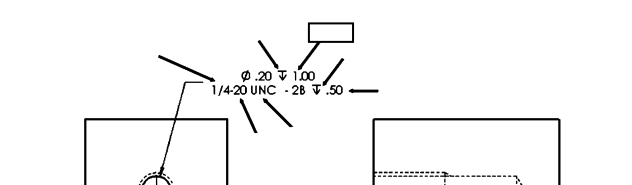
Depth of Thread
The measurement from the crest to the root of a thread, which determines how deep the thread engages with the mating part.
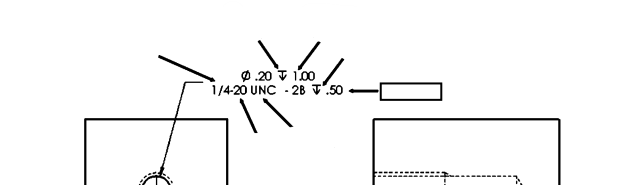
Thread form and series
refers to the specific shape of the thread profile and its corresponding series, such as Unified, Metric, or Acme, which define the thread's size and characteristics.
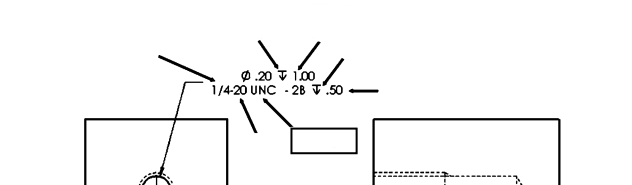
Threads per inch
A measurement indicating the number of threads within one inch of a given length, commonly used for imperial thread specifications.