Final Exam Study Set
1/337
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is a final exam study set that are completely based on the information in all the slides from the semester.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
338 Terms
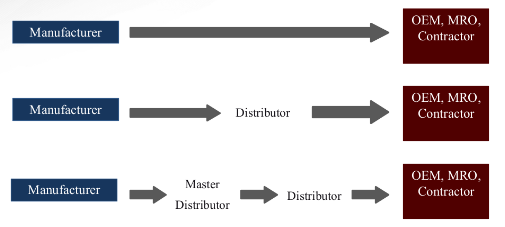
What does are the responsibilities of the manufacturer?
They must determine how best to distribute the product.
With certain products, the distribution functions require minimal resources, and the manufacturer can manage the entire supply chain.
In most supply chains though, the service is better fulfilled by a company focusing on distribution functions.
The distributor fills the role!
Where do you want to be in the business model?
Core customers.
What are cost to serve indicators (CTS)?
Each indicator is weighted according to importance to distributors and suppliers.
What is disintermediation?
Direct to consumer.
What are disadvantages of buying groups?
Less control of product specifications, inflexible shipping schedules, and cost of membership fees.
What does the manufacturer’s agent do?
Usually represent companies whose sales in a territory do not support a full salaried employee
May call on distributors, end users, specifiers, and manufacturers
Complimentary products
Do not typically stock inventory
May also be referred to as a manufacturer rep or manufacturer rep agent (agency)
What skills and expertise does a manufacturer’s agent require?
Product knowledge
Market knowledge
Negotiation skills
Teaching skills
Interpersonal skills
What are some examples of specifiers?
Architects
Engineers
Designers
What are advantages of buying groups?
Lower cost of goods, lower shipping costs, centralized ordering and support.
What do master distributors do?
Common in industries with heavy logistical requirements
Stocks products of represented manufacturers
Only sells to distributors, not to end users
Typically, complimentary products
May also be referred to as a wholesaler
May also function as a manufacturer’s agent
What are some distribution key performance indicators (KPI)?
Order Lead Time
Perfect Order Rate
Back Order rate
Lost Sales
Order Cycle Time
Health and Safety Incident Rate
Employee Turnover
Vendor Performance
Labor and Equipment Utilization
Put Away Cycle Time
What are distribution strategies?
Intensive
Selective
Exclusive
The intensive distribution strategy…
Penetrate the market
As many outlets as possible
No cap on stores or locations
The selective distribution strategy…
Specific locations
Limited number of stores
Target consumer
The exclusive distribution strategy…
High-end and exclusive brands
Limited outlets
Particular locations
What are distribution competitive advantages?
Order Lead Time
Perfect Order Rate
Back Order rate
Lost Sales
Order Cycle Time
Health and Safety Incident Rate
Employee Turnover
Vendor Performance
Labor and Equipment Utilization
Put Away Cycle Time
What is the difference of a manufacturer vs a distributor?
Prefer Stability “Play it Safe”
Research & Development
Salesperson becomes expert
Design, Create and Build
Combination of standardized, catalogued product and custom equipment
Demand Creation at distributor & end user
Sell through multiple channels – direct to end customer, through distribution, or through manufacturer’s rep agency
Responsible for one portion of the project, example for electrical is “the gear”
What is the difference of a distributor vs manufacturer?
Higher Risk, Higher Reward
Hundreds of lines authorized to sell – salesperson knows a little about a lot
Demand Creation with contractors and end users
Transactional & Solution Selling
The “bank” for manufacturers
Must innovate constantly, and find creative approaches
Responsible for all items on the BOM
RELATIONSHIPS are the utmost of importance to succeed (with both vendors & customers)
What are the manufacturer’s expectation of the distributor?
Participate in true partnership
Engage and encourage joint sales calls and social activities
Keep high levels of standard inventory
Be an extension of manufacturer’s sales force
Bridge the gap on end customer credit worthiness, terms and conditions
Provide feedback on pricing, performance, and ways to improve as a vendor
Reach growth goals year over year
Use our e-commerce tools for self sufficiency
What are the distributor’s expectation of the manufacturer?
Participate in a true partnership
Engage and encourage joint sales call and social activities
Provide accurate information for lead times and ship dates
Get their products specified
Support the distributor salespeople and end customers from a technical perspective
Train their salespeople on products and processes
Make it easy for them to do business with – dealing with hundreds of vendors’ e-commerce platforms, billing & invoicing, thousands of shipments a year
What does the industrial supply chain include?
Manufacturers
Master Distributor
Manufacturer’s Agent
Distributor
3PL
Assembler and Processor
End User (Customer)
What does the manufacturers do?
Developing new products
Sourcing components and materials
Manufacturing products
Quality
Efficiencies
Cost Control
Distribution of products
What are the manufacturer’s responsibilities?
Sourcing components and materials
Manufacturing products
Quality
Efficiencies
Cost Control
Distribution of products
What does TQM stand for?
Total
Involving the entire department of the company.
Quality
Achieving customer satisfaction all the time.
Management
Maintaining a high-level quality in every sector.
What are the manufacturer’s priorities?
The primary driver for manufacturing is market share resulting in efficient use of resources.
Due to high fixed costs (facilities, equipment, and labor), higher market share creates higher volume which reduces cost per item to manufacture.
The selected distributors and channel should offer the greatest market access.
The relationship should provide for a solid information exchange and mutually supportive deployment of resources.
What are the roles in the industrial supply chain?
Manufacturer
Master Distributor
Manufacturer’s Agent
Distributor
3PL
Assembler/Processor
End User (Customer)
What is a master distributor?
A master distributor is a wholesale distributor who sells product to resellers (wholesalers). They have direct relationships with brand owners who recognize them as exclusive distributors of their product.
What do manufacturer’s agents do?
Manufacturers' agents or representatives are independent contractors.
They work on commission to sell products for more than one manufacturer.
They are not under the immediate supervision of the manufacturers (principals) for whom they sell.
The relationship generally falls into client-customer patterns.
Manufacturers' agent firms range from businesses operated by a sole entrepreneur to considerably more extensive organizations armed with numerous salespeople covering specific territories.
Key value add is that they are generally paid on commission, thus if there are not sales, there are no costs.
There are no fixed costs to bring them on board.
They generally offer compatible—but not competing—products to the same industry.
What are the risks of a wholesaler?
Competition
Reputation
Property damage
Inability to obtain supply
Legal penalties
Product liability
Theft
Equipment breakdown
Incident tracking
What is a 3PL?
A third-party logistics warehouse, or 3PL for short, is an outsourced business that takes care of a company’s supply chain and logistics operations.
What are 3PLs used for?
Outsourcing third-party warehouse and distribution needs for their customer’s inventory and fulfillment services.
Managing 3PL stock
Holding, and shipping the inventory of multiple businesses or other businesses in addition to their own inventory.
What is a hybrid 3PL?
A 3PL fulfills and stores orders for both their own business as well as their clients.
What does an assembler or processor do?
Every manufacturer assembles goods.
An assembler is determined based on how much of the content of your product is built in-house versus by a supplier.
Are there risks of an assembler or processor?
Risk varies substantially based on whether you are a manufacturer or supplier.
What are the risks of an end user (distributors or retailers)?
Property damage
Inability to obtain supply
Legal penalties
Product liability
Theft
Equipment breakdown
Incident tracking
What is industrial manufacturing?
Fabrication of products from raw materials destined for industrial use
Output from industrial manufacturing keeps other mass manufacturers in business
Produces
Massive industrial machines
Simpler household machines
Other industrial use products
Additionally manufacturer wide range of other industrial use products
Hardware
Paper and packaging materials
Glass
Fixtures
The industrial manufacturing plays?
A crucial role in producing the goods and services vital to the economy in a timely and cost-efficient manner and range of products is vast and shares a common function.
What are the broad classes of industrial equipment?
Standard equipment
Custom built equipment
Standard Equipment are?
Cheaper to build
Used in various industries
Cannot fulfill specific needs of new factories
Custom Built Equipment are?
More expensive
More profitable
Takes longer to build
Can be tailored to incorporate specific attributes, as needed
by the buyer
How many groups can industrial equipment be grouped in?
7 different segments
3 industrial equipment produce special purpose machinery for specific industry segments…
Agricultural, Construction and Mining
Industrial
Commercial and Service
What are the industrial equipment produce special purpose machinery for specific industry segments?
Ventilation equipment
Heating and cooling equipment
Engine and engine related equipment
Other general-purpose machinery
What is the future of manufacturing?
Assembly lines of the future will incorporate robotics, technology, AI, and people to be more consistent, efficient, quick, and more profitable.
As manufacturers innovate and improve how they manufacture products, the distributor must also innovate and improve to remain relevant.
Bullwhip Effect
The bullwhip effect describes the increasing fluctuations in inventory in response to changing consumer demand as one moves up the supply chain.
Observing, analyzing and understanding how the bullwhip effect influences the supply chain can provide us with important insights for improvement.
What causes the bullwhip effect?
Customer orders come in for the retailer, but this information is quickly lost upstream.
This situation is reflective of supply chains with low levels of trust.
Absent customer demand data, forecasts rely on the incoming orders at each successive stage.
The delay or pause in information using traditional forecasting methods and inventory strategies create the bullwhip effect.
What are the benefits of batch ordering?
The discount incentive works!
Typically discounts prompt partners to withhold small orders.
Yet, the tradeoff is that the practice further aggravates the bullwhip effect by:
Causing an added delay in information flow.
Muting the information associated with the order.
Upstream partner can’t be sure whether a bulk order reflects true demand, or a downstream partner’s need for cost savings.
How would we redesign the supply chain?
Implement efficient replenishment practices.
Efficiently manage inventory with Quick Response, Continuous replenishment, Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI).
Efficiently manage logistics through warehousing practices, Direct
Delivery, Cross-Docking.
Other practices such as JIT delivery (auto industry with Kanban system.
What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP) supposed to measure?
Annual spending in the economy by…
Consumer Spending: 67.1%
Government Spending: 16.5%
Business Spending (investment): 16.5%
What actually drives the economy?
Consumer spending does not drive the economy, instead the supply chain does.
Business spending (gross investment): 62%
Consumer spending: 31.5%
Government spending: 6.5%
What should the general model of economics include?
Gross Output (GO) complements Gross Domestic Product (GDP). GO is the missing piece in macroeconomics.
In quarterly financial statements, “Top Line” is?
Revenues or Sales
Total Income
Gross Output (GO) measures revenues at all stages of production
In quarterly financial statements, “Bottom Line” is?
Earnings or Net Income
Profits
GDP means “value added” or final product (similar to “gross profit” in financial statements)
General Model of the Economy
Expand beyond GDP to include GO-the whole production process.
Analyze not just the CPI, but the PPI and Commodity Price Index.
Look beyond "the" interest rate to the yield curve.
Examine more than "the" rate of unemployment, but the structure of employment and unemployment.
Go beyond the broad stock indexes (S&P 500) and look at various industries.
Commercial Firms
Manufacturers, Construction companies, Service firms, transportation companies, select professional groups, distributors, wholesalers, retailers
Institutions
Schools, health care orgs, libraries, foundations, non-profits, etc.
Governments
Federal government (defense & non-defense), state, local, municipalities, counties, townships
A channel is?
Composed of supply tiers
Supply Chain
Any activity needed to transfer goods from raw material extraction through consumption by the final consumer.
Supply Chain Management
Includes both the movement of products as well as critical service operations.
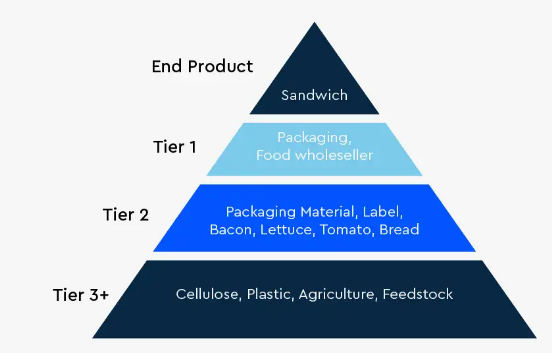
Supply Tiers
Tier 1 suppliers - Companies that provide materials to to a manufacturer
Tier 2 suppliers - Companies that provide products to Tier 1 suppliers
Tier 3 suppliers - Companies that provide products to Tier 2 suppliers
What does Manufacturer’s Agent do?
Usually represent companies whose sales in a territory do not support a full salaried employee
May call on distributors, end users, specifiers, and manufacturers
Complementary products
Do not typically stock inventory
May also be referred to as a manufacturer rep or manufacturer rep agent (agency)
Master Distributor
Common in industries with heavy logistical requirements
Stocks products of represented manufacturers
Only sells to distributors, not to end users
Typically, complementary products
May also be referred to as a wholesaler
May also function as a manufacturer’s agent
Structured Difference of a Manufacturer Compared to a Distributor
High value on brand recognition and perceived product quality
High fixed cost
Significant need for volume
High market share is an extreme predictor of profitability
Structured Difference of a Distributor Compared to a Manufacturer
Less value on brand and quality and more value to customer relationships
High variable cost
Less need for volume
Market share less of a predictor of profitability
What do distributor compensation Includes?
Extended payment terms
Cash discounts
Consignments
Stock rotations and return allowances
Cooperative and market development funds
Special pricing agreements
Volume incentives
Why does pricing matter?
The fastest and most effective way for a company to realize its maximum profit is to get its pricing right.
Getting the price right is one of the most fundamental and important management functions.
“3 C’s” of Pricing
Cost
Competition
Customer
What is the importance of distribution in the economy growth?
Distribution helps to satisfy the needs of consumers by supplying assortment of different products of different producers.
Why is growth important to manufacturers?
Larger market share
Reduce cost per item (recall large fixed costs)
Increased importance to distributor
What is growth to a distributor?
More customers
More sales or profit
More employees
More facility locations
More products and additional inventory
Primary Growth Options
Sell more to existing customers.
Find or build new customers.
Expand or broaden inventory, market, services, and capabilities including eCommerce.
Using business analytics to determine a strategy and implementation plan for growth.
What is an essential step in developing a customer-centric operations strategy?
A classification of customers into groups based on profitability, cost to serve, loyalty, and buying power.
What is the path to growth?
Increase sales to existing customers
New products and services to existing customers
New customers similar to existing customers
New markets
Product innovations
eCommerce
What is a distribution channel?
The paths products and services take on the way from the manufacturer or service provider to the end consumer.
The channel involves a set of interdependent organizations in the process of making a product or service available for use or consumption.
What is a distribution channel strategy?
Distribution strategy is the method used to bring products, goods and services to customers or end-users.
Ensuring an easy and effective way to get your goods and services to people, depending on the item, and its distribution needs.
Organizations consider which distribution strategy is best while being cost-effective and increasing overall profitability.
Can even use multiple or overlapping distribution strategies to reach target audiences and meet company goals or objectives.
Best Practices To Determine Channel Goals
Understand channel context
Set firm-level financial goals
Translate firm goals to channel goals
Identify channel success factors
Why a Better Supply Chain?
Better Supply Chain = Improved Profitability.
Invest in Technology and Talent.
Effective Supply Chain enables a Distributor to compete on Service, Sourcing, and Cost.
Invest in right Processes.
Turn ‘Cost Center’ into ‘Profit Center’.
Avoid Disruptions.
Be aware of ‘Amazonification’
Channel Conflict
Channel conflict can be explained as any dispute, difference, or discord arising between two or more channel partners (e.g. supplier and customer).
The conflict of interest causes channel members to work against each other rather than working together.
One or more members believe they are not being treated fairly.
Industrial Supply Chain
What are the manufacturer’s responsibilities?
Produce quality/competitive products
Create new markets
End-user and specifier calls
Advertising in magazines, trade journals, internet, trade shows, etc.
Provide up-to-date printed or electronic catalogs
Provide technical information and training
Understand value and compensate channel partners
What are manufacturer priorities?
The primary driver for manufacturing is market share resulting in efficient use of resources.
Due to high fixed costs (facilities, equipment, and labor), higher market share creates higher volume which reduces cost per item to manufacture.
The selected distributors and channel should offer the greatest market access.
The relationship should provide for a solid information exchange and mutually supportive deployment of resources.
Factors for Relationships
Trust
Communication
Commitment
How do you earn trust?
Demonstrated and earned over time
Willingness to honor commitments—integrity
Ability to honor commitments—track record, skill sets, authority, and resources
Believe the other person’s best interest is understood and will be pursued
Difficult to build
Easy to destroy
What is the definition of trust?
The firm belief in the reliability, truth, ability, or strength of someone or something
Mutual Trust
Trust is not between firms, but individuals
Trust is earned over time and is for a long-term relationship
Trust is lost very quickly
Trust is about performance, NOT intent
POSIWID
The purpose of a system is what it does.
Communication is…
Open, honest and a two-way street
Ask questions
LISTEN
Provide constructive performance feedback
Discuss opportunities
Develop mutual goals
What are the commitments demonstrated by the manufacturer?
Dedicated personnel and facilities
Efforts to learn about operation
Coordinated reporting systems
Coordinated planning efforts
Coordinated training efforts
Alignment in the mind of the end-user
What are the commitments demonstrated by the distributor?
Dedicated personnel and facilities
Build relationships with manufacturer’s organization
Investment in product training and support
Investment in compatible reporting system
Alignment in the mind of the end-user
Train customer to use manufacturer’s products
Commitment to Relationship
Reputation for treating partners fairly
Demonstration of fair treatment and understanding of supply chain partner
Don’t beat up the manufacturers
A distributor is a partner, not a customer
How you react when conflict exists is critical!
Why is the relationship piece critical?
Provides insight and knowledge into how the manufacturer operates.
Provides information on hot buttons and yields opportunities to secure incentives based on need.
Forms the bonds of trust and mutual understanding.
Builds communication.
Strategic Relationships are
Genuine long-term commitment and trust
Willingness to sacrifice and share
Alignment of goals
Risk of a Strategic Relationship
Becoming dependent on partners
What are the manufacturer’s motivations?
Better coverage at lower cost
Better presentation
Better coordination of marketing efforts
Greater access to information
Pool of potential partners drying up
Loss of distribution
Loss of power
What are manufacturers services?
Choose their customers based on a certain technological offering.
Make a substantial investment in production equipment that is highly inflexible.
Need a distribution channel that can reach and support their customers and help the manufacturer to efficiently control their production investments.
What are the distributor’s motivations?
Assured and dependable supply of desirable products
Enhance marketing efforts
Cut cost
Eliminate redundancy
Differentiate themselves from competition
Discourage competition
What are distribution responsibilities?
Choose a customer market to serve and built the resources needed to serve that market.
Choose a set of suppliers with the products, technology, brand name, and service to set market demand.
Determine and create a network of warehouses, transportation, equipment, and other service capabilities to excel in the chosen market.
Invest in and carry inventories matching the customers’ needs with manufacturers’ capabilities.
How does a distributor’s value add to the manufacturer?
Fabrication
Assembly
Volume Influence
Aftermarket Service
Marketing Support
Product Training
Distributor’s Value Add To the Customer
Customization
Value-added Services
Distributor Branding
Rapid Response Times
Order Tracking
Inventory Management
What do manufacturers bring to the table?
Branding
Expertise
National Accounts
Marketing Support
Minimal Inventory
Variable Delivery Schedule
Manufacturing Technology and Sourcing