Spinal cord and segments
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is the main sensory function of the spinal cord?
pass signals along from the sensory receptors (found all over the body) to the brain
What is the main motor function fo the spinal cord?
pas signals along from the brain to different part of the body (usually muscle groups)
What does the spinal cord help to coordinate?
reflexes (quick responses to outside stimuli)
Describe the general structure of the whole spinal cord.
- long flattened cylinder of nervous tissue
- starts off at the medulla oblongata and tapers off, finishes before the vertebra do
- has inconsistent diameter due tot the number of cell bodies in each area
- each segment gives off a pair of spinal nerves
What is the foramen magnum?
- the hole in the base of the skull through which the spinal cord passes.
- position varies between species depending on the head to neck angle
What are the main protective structures of the spinal cord?
1. Vertebral column
2. Meninges
3. Connective tissue
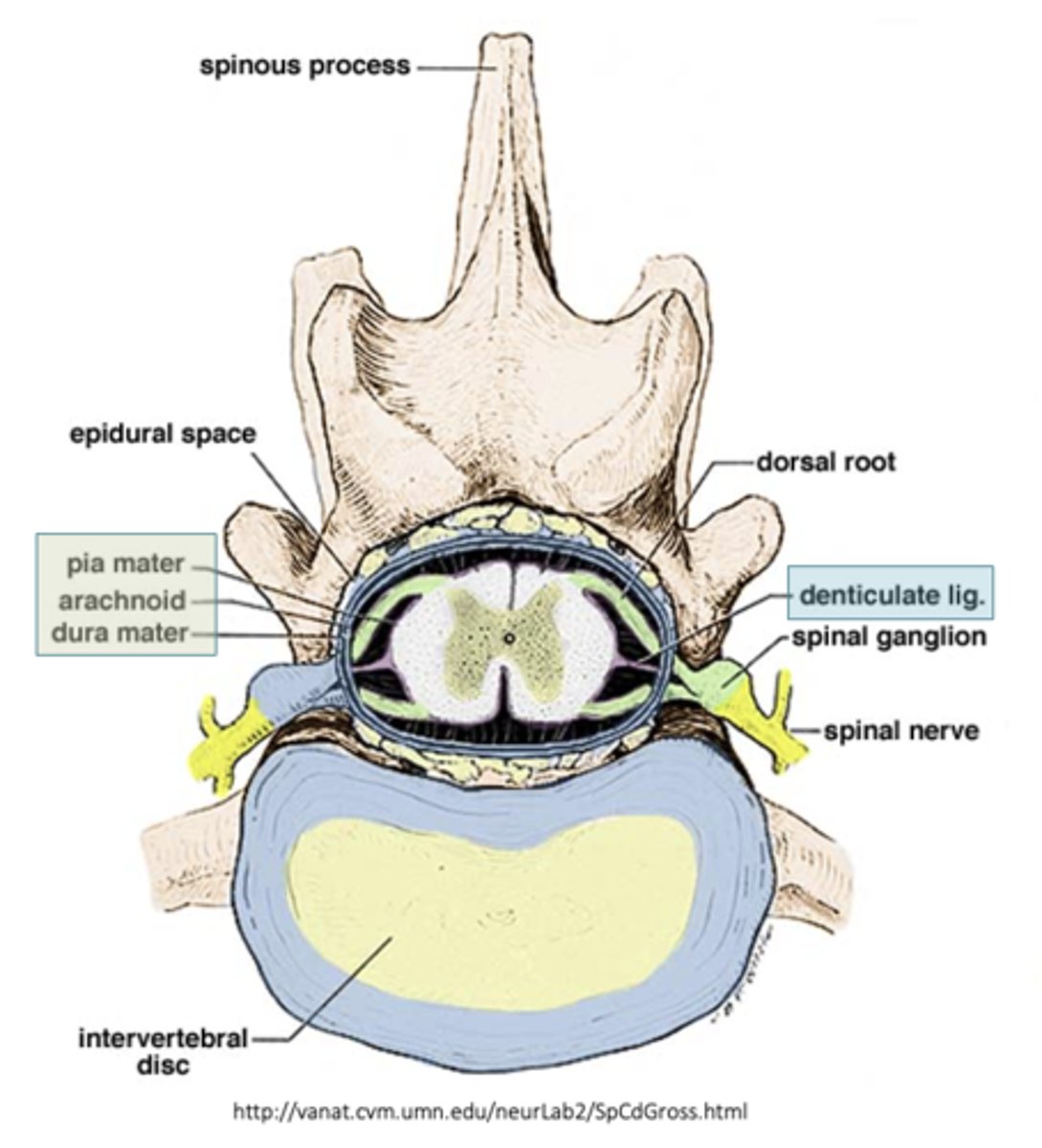
What is the denticulate ligament?
where the Pia mater communicates with the dura mater to suspend the spinal cord within the meninges
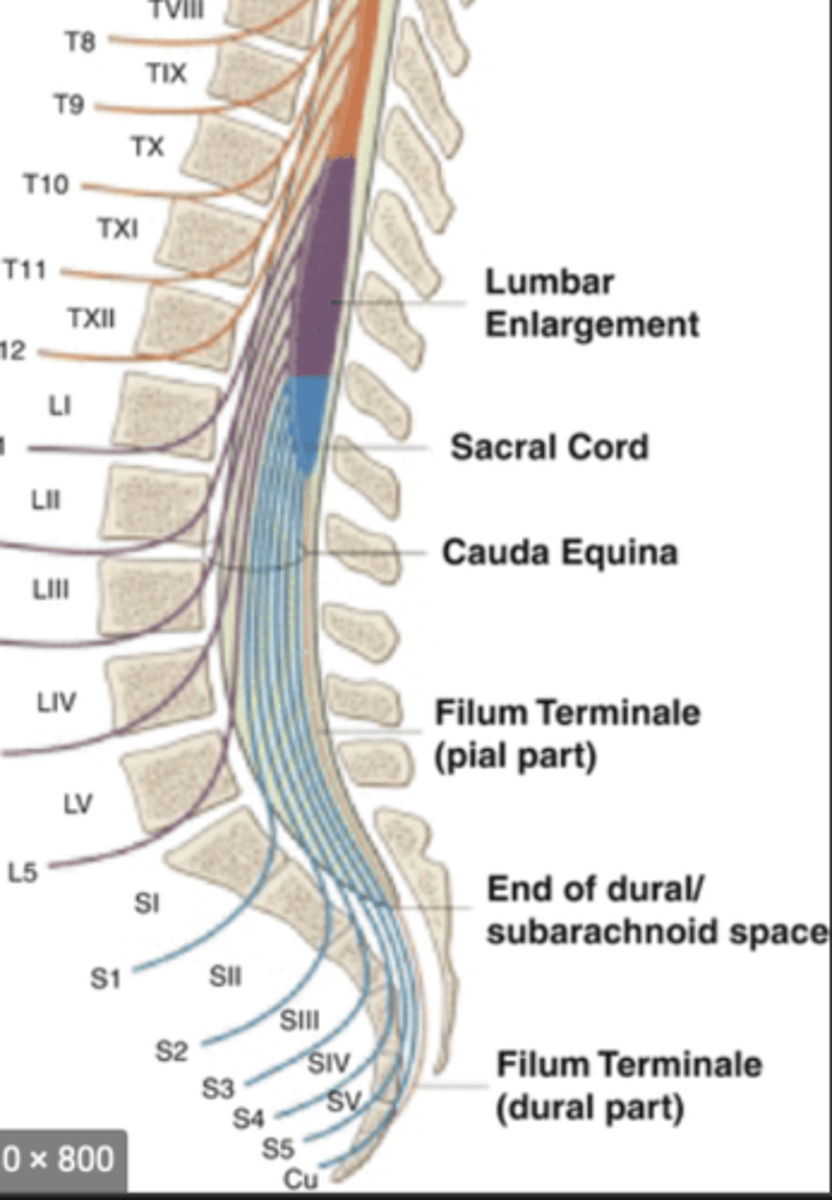
What is the name given to the enlargements of the spinal cord and what are the two main ones?
- intumescences
- cervical (containing nuclei suppling forelimb)
- Lumbar (containing nuclei supplying the hindlimb)
What is the conus medullaris?
- cone shaped ending of the spinal cord caudal to the lumbosacral intumescence
What is the cauda equina?
- collection of spinal nerve roots distal to the conus medullaris
- named for its resemblance to a horses tail
What is the tissue of the spinal cord dived into?
- grey matter 'horns'
- white matter funiculi and fascicles
- central canal containing CSF
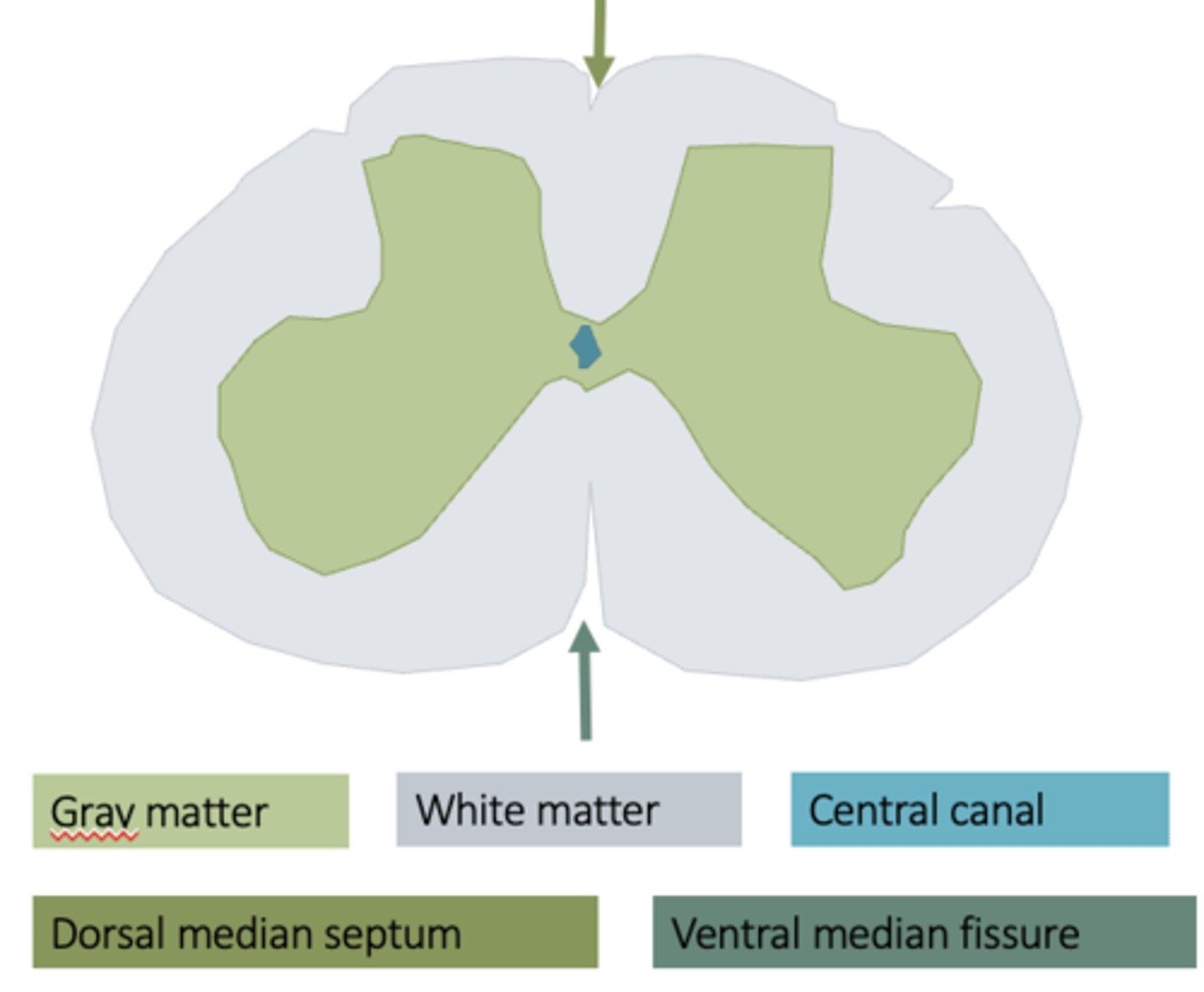
How is the grey matter further divided?
- Dorsal horn
- Lateral horn (only in thoracolumbar segments)
- Ventral horn
What sort of information feeds into the dorsal horn?
sensory input
What sort of information originates in the ventral horn?
motor output
What does the lateral horn contain?
cell bodies of sympathetic nervous system and interneurones
How is the spinal cord divided?
- into segments
- each with a pair of spinal nerves communicating with the spinal cord via dorsal and ventral roots
What sort of information travels in the dorsal root?
sensory/ afferent information obtained from the body travels through eh dorsal root to the spinal cord
What sort of information travels in the ventral room?
motor/ efferent information travels from the spinal cord to the rest of the body via the ventral root
Where do the dorsal and ventral roots combine?
before leaving the vertebral canal and form the final nerve (mixture of sensory and motor fibres)
Where is the spinal ganglion located?
in the distal aspect of the dorsal root (cell body of the sensory neurone)
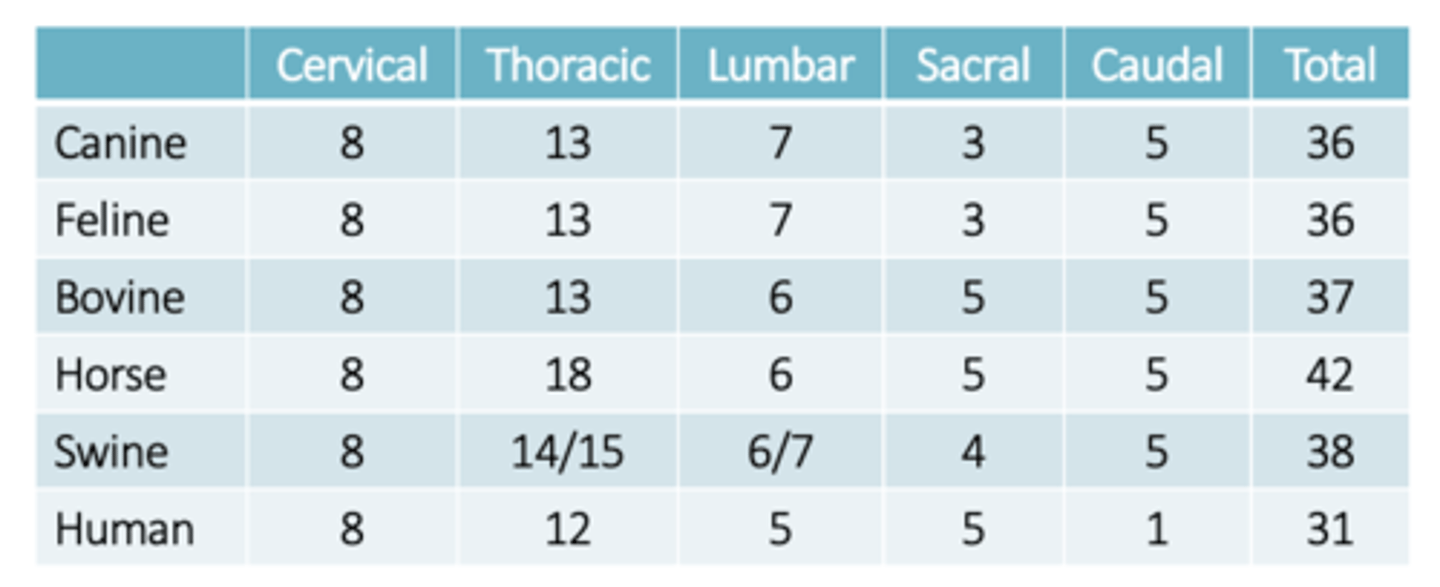
Does the number of spinal segments directly correspond to the number of vertebrae in each section of the spinal column?
- no, there are 7 cervical vertebra and 8 cervical spinal segments
- important to remember when interpreting spinal cord injury
Where does the spinal cord terminate in the different species?
- Canine = L6/7
- Feline = L7
- Bovine = S1
- Horse = S2
What is the film terminale?
fine terminal filament of neural tissue at the end of the spinal cord
List the anatomical regions of the spinal cord
Cervical = C1-8
Thoracic = T1-T13
Lumbar = L1-L7
Sacral = S1-S3
Caudal = Cd1- Cd5
List the functional regions of the spinal cord
- Cervical: Neck = C1-C5
- Cervical intumescence : forelimb = C6-T2
- Thoracolumbar: thorax and abdomen = T3-L3
- Lumbosacral intumescence: pelvic cavity, hindlimb and perineum = L4- S3
- Caudal: tail = Cd1-Cd5
What are dermatomes?
skin zone (extending in a belt-like fashion around the body longitudinally in the extremities) supplies by the sensory nerve fibres from each spinal segment
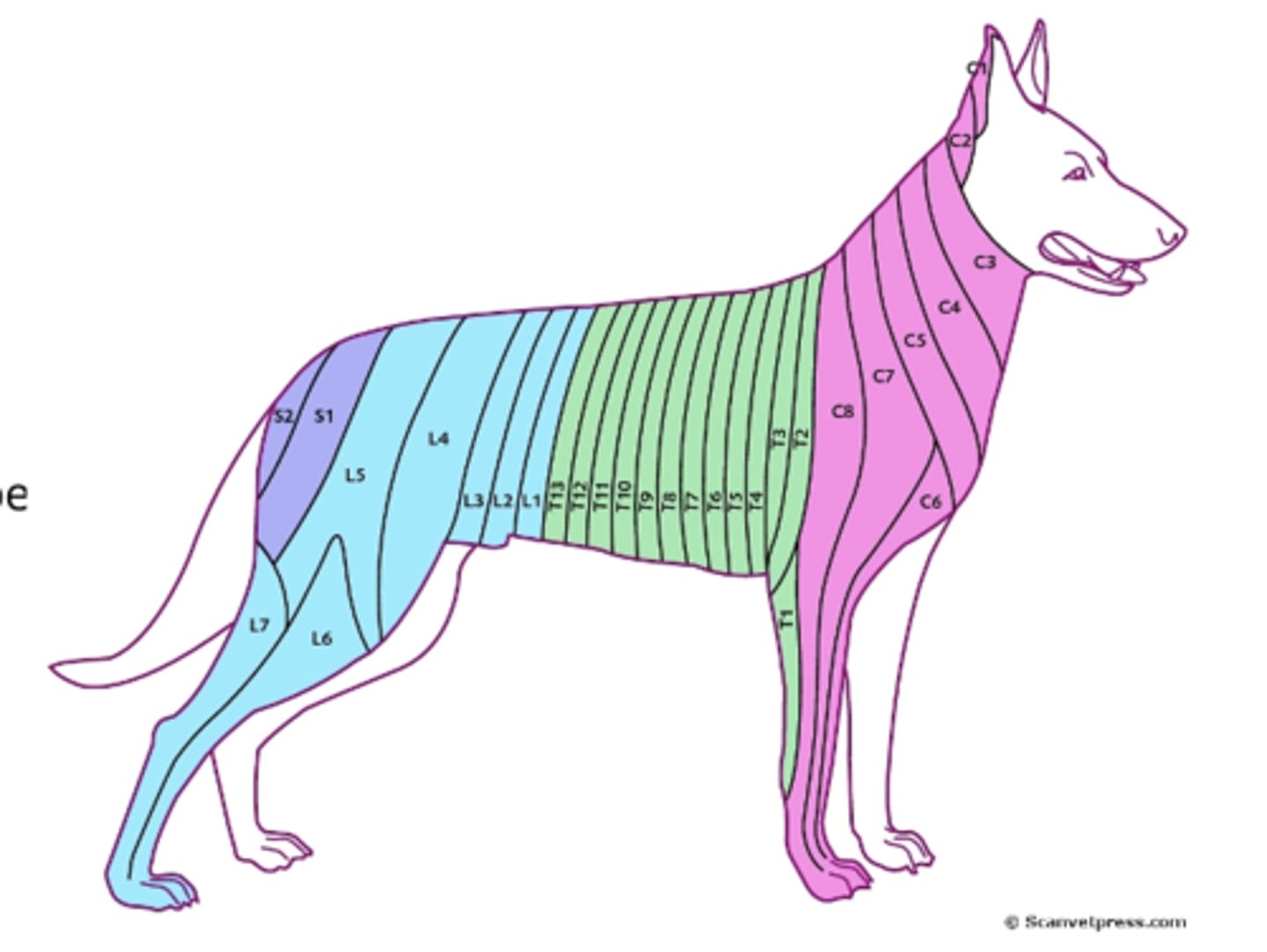
What is the clinical importance of the dermatomes?
injury to a spinal nerve will be associated with a characteristic pattern of numbing of the skin within the relevant zone
What are plexi?
- where the dorsal and ventral branches of spinal nerves connect with neighbours to form continuous dorsal and ventral networks
- C6-T2 = brachial plexus
- L4-S3 = lumbosacral plexus
What does white matter consist of?
-'highway' of central nervous system
- contains mixture of glial cells and myelinated axons
(myelin gives the white colour)
How is the white matter divided?
- into funiculi
- dorsal, lateral and ventral
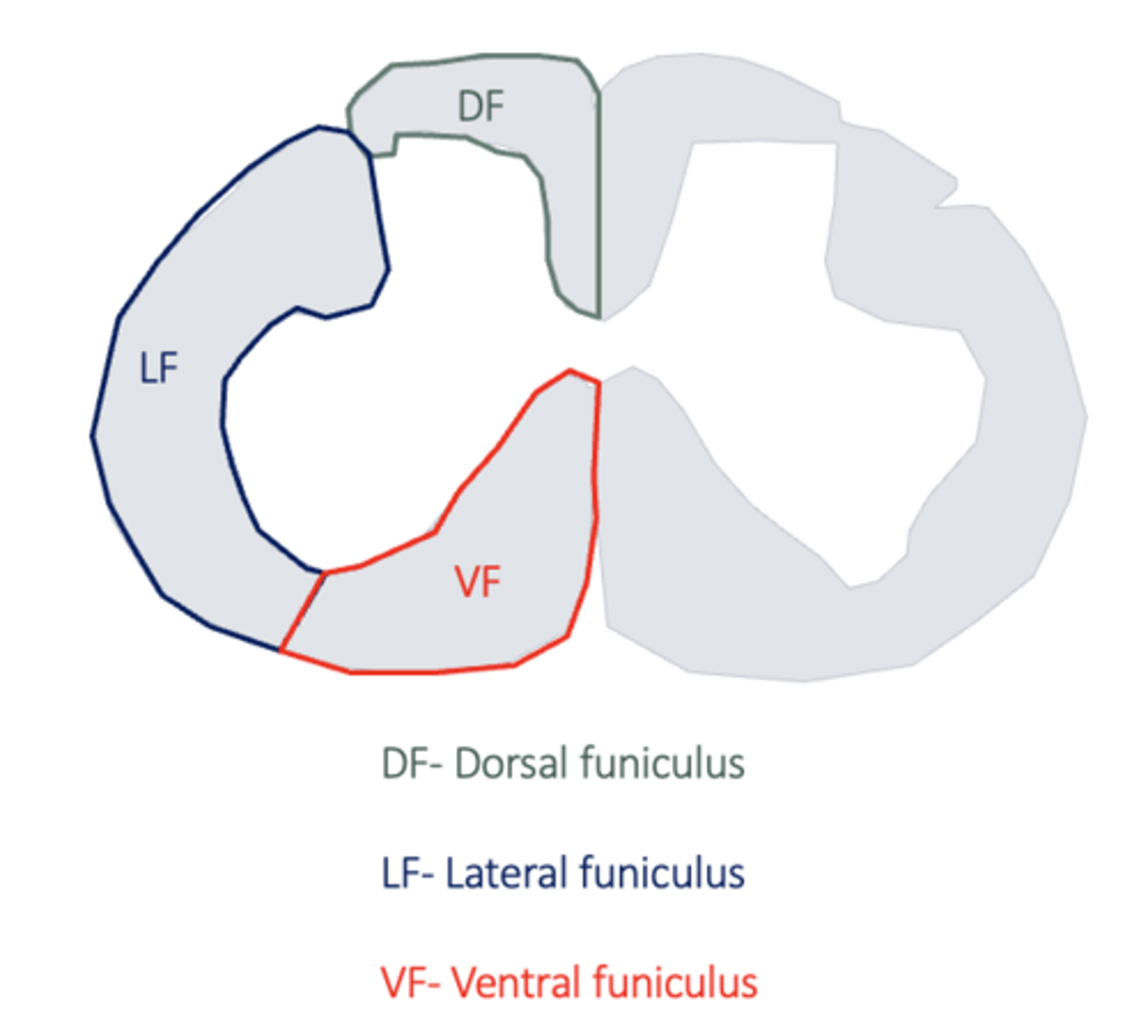
What tracts does the dorsal funiculus contain?
sensory
What tracts does the lateral funiculus contain?
- lateral part = sensory
- rest = mixed sensory and Motor
What tracts does the ventral funiculus contain?
mixe sensory and motor
What is a fasciculus?
- groups of short fibres, ascending and descending, and crossed and uncrossed, within the spinal cord
- divisions of the funiculi