Psych Exam 2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What is Erikson known for?
His influential theory of psychosocial development. Erik Erikson is known for proposing eight stages of human development, each characterized by a specific conflict that individuals must resolve to progress successfully.
ego psychology
a branch of psychology that emphasizes the role of the ego in human behavior and development, focusing on how it mediates between instinctual drives and external reality.
What does Freud say about the ego?
The ego is weak in comparison to the powerful id. It mediates between the id and reality.
What does Erikson say about the ego?
The ego is a powerful agency that helps people to resolve inner conflicts and environmental challenges, ultimately promoting health.It plays a crucial role in achieving ego identity during each stage of development.
What is the main focus of ego psychology?
The development of a strong ego identity as individuals resolve the crises inherent in the developmental process.The emphasis on the ego's role in adapting to social and personal challenges throughout life.
What does Erikson maintain about personality development?
Personality develops in a predetermined order through eight stages of psychosocial development, from infancy to adulthood.Each stage involves a conflict that must be resolved for healthy personality development.
What is the epigenetic principle?
A genetically determined sequence of human development that occurs in a series of stages, universal to humankind, and unfolds in a predetermined sequence.It posits that each stage builds on the outcomes of previous stages, influencing an individual's development.
What are crises according to Erikson?
Critical points in the maturation process.These crises involve conflict between two opposing forces, which must be resolved for healthy personality development.
What is the result of positive resolution of each crisis?
Strengthening of the ego.This strengthening leads to greater psychological resilience and adaptive functioning in future stages.
positive resolution in one stage _____ the chances of positive resolution in later stages
increases
Failure to successfully complete a stag can result in a ______ ability to compete further stages, and there, the development of an unhealthy personality and sense of self
Reduced
According to Erikson, does psychosocial development occur throughout the lifetime?
Psychosocial development occurs across all stages of life. Yes.
What results from the successful completion of each stage?
A healthy personality and the acquisition of basic virtues.This process contributes to overall development and resilience throughout life.
What happens if there is failure to complete a stage?
There may be a reduced ability to complete further stages, leading to an unhealthy personality and sense of self.This can result in difficulties with relationships and a lack of basic virtues.
Can stages be resolved successfully at a later time?
Yes. Individuals can re-address earlier stages and resolve them effectively later in life.
What does Ego Strength equal?
Virtue.It refers to the individual's ability to successfully cope with life's challenges, reflecting overall psychological resilience.
What are virtues according to Erikson?
Human qualities or strengths that emerge from successful resolution of the crisis associated with various developmental stages.They contribute to a healthy personality and sense of self.
What is the ego strength in the oral-sensory stage?
Hope.
Basic trust vs mistrust , 1st stage -The oral-sensory stage, occurring from birth till 1st year of life, is a crucial developmental phase where an infant develops trust based on the consistency of care they receive from caregivers.
What is the ego strength in the muscular-anal stage?
Will.
Autonomy vs shame/doubt - 2nd stage ; The muscular-anal stage occurs between the ages of 2 and 3 years, where children learn to exert control over their bodily functions, engage in toilet training, and develop a sense of independence through autonomy.
What is the ego strength in the locomotor-genital stage?
Purpose.
3rd stage, initiative vs guilt : The locomotor-genital stage occurs between the ages of 4-5 years, where children begin to assert their power and control over their environment. They learn to initiate activities, engage in imaginative play, and develop a sense of purpose through exploration and social interaction.
What is the ego strength in the latency stage?
Competence.
industry vs inferiority - 4th stage - The latency stage occurs from around 6 years to 12. During this stage, children focus on developing skills and engaging in activities with peers. They learn to work collaboratively, build friendships, and develop a sense of competence in various tasks without the direct involvement of sexual feelings.
What is the important event in latency stage according to Erikson?
Attendance at school. This period marks a time when children learn to form relationships and develop competencies in various skills through interactions with peers, teachers, and engaging in learning activities.
adolescence
identity vs role confusion, 5th stage , age 13-19 - During adolescence, individuals explore different identities and social roles, leading to personal growth or confusion about their place in society.
What is the ego strength for the adolescence stage?
Fidelity. This stage occurs from puberty to young adulthood, where individuals develop a sense of identity and personal values. They learn to form deeper relationships and commitments, exploring their beliefs and self-concept in relation to society.
identity
multifaced concept that involves knowing who you are and where you are going, as well as what you are not and do not want to be, the unified sense of self as uniquely different from others.
What are the two identities involved during adolescence according to Erikson?
Sexual (understanding one’s sexual orientation) and Occupational (identity that involves exploring different career paths).
What time is the identity crisis normal during?
Adolescence. it is a moratorium:a period of exploration and experimentation in forming personal identity.
role confusion
concerning one's identity and social roles, often resulting in uncertainty about personal values and direction in life. concern for who they are and what they will become.
identity crisis
a developmental stage where individuals explore various roles and beliefs, often leading to confusion and uncertainty about their personal identity.
What does an unresolved crisis result in according to Erikson?
An unresolved crisis can lead to the development of a negative identity. This occurs when individuals struggle to navigate the key conflicts of a particular psychosocial stage, resulting in the formation of an identity that is based on social rejection or maladaptive behaviors. Instead of establishing a positive sense of self and direction, individuals may adopt roles or characteristics that are antithetical to societal norms or expectations, often as a reaction to the perceived failures or conflicts they face. This negative identity can hinder personal growth, lead to further social isolation, and impact future relationships and opportunities.
Erikson believes that pressuring someone into an identity can result in rebellion in the form of establishing a negative identity, and in addition to this feeling of unhappiness.
Erikson
What is the focus of the young adulthood stage according to Erikson?
Intimacy vs. isolation, 6th stage, 20-24. The focus of the young adulthood stage is on the conflict of Intimacy versus Isolation. where individuals strive to form deep, meaningful relationships with others. Intimacy refers to the ability to connect with others on a personal level, sharing thoughts, emotions, and commitments without fear of losing one's own identity. Success in this stage leads to strong interpersonal relationships, including romantic partnerships, friendships, and a supportive social network. Failure to establish intimacy can result in feelings of isolation, loneliness, and a sense of disconnection from others, which can contribute to emotional distress and hinder personal development in other areas of life.
intimacy
the ability to form close, personal relationships with others, sharing thoughts and emotions. And to abide by commitments with significant compromises and sacrifices necessary.
What is the ego strength for young adulthood?
The ego strength for young adulthood is Love. This stage focuses on forming deep, meaningful relationships characterized by trust, empathy, and mutual respect. Successfully achieving Love enables individuals to share their lives with others and fosters emotional health. Conversely, difficulties in cultivating love can lead to isolation and hinder personal growth.
What is the focus of the middle adulthood stage?
Generatvity vs stagnation. 7th stage, 25-64. The focus of the middle adulthood stage, is on Generativity versus Stagnation. Generativity involves creating or nurturing things that outlast the individual, such as parenting, mentorship, or community contributions, reflecting productivity and a desire to impact future generations. Stagnation, on the other hand, signifies a lack of growth and fulfillment, leading to self-absorption and feelings of purposelessness. Successfully navigating this stage fosters a sense of accomplishment and the ability to care for others.
generativity
the concern for establishing and guiding the next generation through parenting, mentoring, and community engagement. It encompasses a broader desire to create and contribute to society, ensuring a meaningful legacy.
stagnation
the state of feeling unproductive or disengaged, characterized by self-absorption and a lack of personal growth or fulfillment.
What is the ego strength for middle adulthood?
The ego strength for middle adulthood is Care. This stage, typically between ages 40 and 65, emphasizes the desire to nurture and guide the next generation through parenting, mentorship, or community involvement. Developing Care fosters a sense of purpose and fulfillment by creating meaningful connections and promoting the wellbeing of others. Conversely, a failure to cultivate this strength may lead to stagnation, self-absorption, and emotional disconnection from society.
What is the focus of the late adulthood stage?
Ego integrity vs despair, 8th final stage. 65 to death. The focus of the late adulthood stage, typically from age 65 onward, is the conflict of Ego Integrity versus Despair. Individuals reflect on their lives, seeking a sense of fulfillment and acceptance of their choices. Achieving Ego Integrity leads to feelings of wisdom and peace about one’s legacy, while despair stems from regrets and a sense of wasted opportunities, resulting in bitterness and fear of death. Successfully navigating this stage allows individuals to embrace the end of life with dignity.
ego integrity
the state of feeling fulfilled and at peace with one’s life choices in late adulthood.
despair
a feeling of regret and dissatisfaction with life choices, often leading to bitterness and fear of death.
What is the ego strength for late adulthood?
Wisdomis the ego strength for late adulthood. It reflects the culmination of life experiences and the ability to find meaning in one’s journey, promoting acceptance and peace in the face of life’s end.
What is wisdom according to Erikson?
Detached concern with life itself in the face of death.Wisdom, according to Erikson, involves a deep understanding and acceptance of life experiences, allowing individuals to maintain a sense of perspective and meaning as they approach death.
strength in Eriksons theory
its ability to tie together important psychosocial development across the entire lifespan.
Erikson Positive evaluation
Erikson’s theory says personality keeps developing throughout life, not just in childhood. Because of him, psychologists now see middle and late adulthood as important times for personal growth, rather than irrelevant. Many people connect with his ideas because they match their own life experiences.
Erikson Negative Evaluation
Erikson’s theory doesn’t clearly explain what experiences help people grow through different life stages, and it lacks a universal way to resolve crises. It also focuses mainly on social and personal attitudes, ignoring things like cognitive and emotional development. His ideas were influenced by his own life rather than scientific data. Critics say his theory uses unclear terms, doesn’t fully describe each stage, and makes weak claims about personality differences between men and women.
James Marcia
Refined and extended Erikson’s work
Developed 4 identity statuses of psyochological identity of development, focusing mostly on adolescent development
the main idea is that one’s sense of identity is determined largely by the choices and commitments made regarding certain personal and social traits.
What does Marcia's theory of identity achievement argue?
That two distinct parts form an adolescent's identity: crisis and commitment. Marcia's theory of identity achievement argues that individuals undergo a process of exploration (crisis) and make commitments to various life choices, shaping their identity through these experiences.
differences between erikson and marcia
Erikson's theory emphasizes psychosocial development across the entire lifespan with eight stages, while Marcia focuses specifically on adolescence and the processes of identity formation through the states of crisis and commitment.
What are Marcia's four identity statuses?
Identity diffusion; 2. Foreclosure; 3. Moratorium; 4. Identity achievement.
What model did Jean Phinney develop?
Model of ethnic identity based on Erikson's and following Marcia's work.Phinney's model describes how individuals develop a sense of ethnic identity through stages of exploration, commitment, and integration of their cultural heritage.
ethnic identity
A person's sense of belonging to a specific ethnic group, shaped through exploration and commitment to cultural values.
What is bicultural identity?
Positive attitudes toward one's own ethnic group and toward the majority group.Bicultural identity refers to the ability to integrate aspects of both one's own ethnic culture and the dominant culture, fostering positive interactions and a sense of belonging within both.
Jacop Orlofsky 3 major criteria
1.Does the person have close relationships with male and female friends?
2.Does he or she have an enduring heterosexual relationship?
3.Are the person's close relationships deep or superficial? (Depth includes openness, affection, respect, loyalty, a capacity to accept and resolve differences, and mutuality.)
Jacob Orloksy 6 intimacy statues
1.Intimate individuals: deep relationships with male and female friends and involved in enduring, committed heterosexual relationships.
2.Preintimate individuals: close emotional ties but ambivalent about committing to enduring love relationships.
3. Stereotyped individuals: have many relationships, but superficial, lack closeness and commitment.
4. Pseudointimate individuals: like above, relationships lack depth yet still in enduring heterosexual commitments.
5. Isolated individuals: withdrawn from social situations and relationships with peers.
6. Merger individuals: committed themselves to enduring relationships but become absorbed in their relationships at the expense of their own autonomy and sense of self. Enmeshment.
Assessment tecniques
Egalitarian and personal with patients
Disciplined subjectivity
Transference, free association, and dream analysis, though interpreted them in psychosocial terms, not sexual.
Play-therapy techniques
Disciplined Subjectivity
sought to analyze and understand the patient's problems through empathy as well as by examining the historical events that affected the patient's life.
Psychohistorical analysis
technique for analyzing the lives of historical figures on the basis of Erikson's theory of ego development.
Who was a pioneer in psychohistorical analysis?
Erikson. Erik Erikson was a pioneer in psychohistorical analysis, known for his theories on psychosocial development and identity formation.
theory of self actualization
a psychological framework proposed by Abraham Maslow, suggesting that individuals strive to realize their full potential and achieve personal growth.
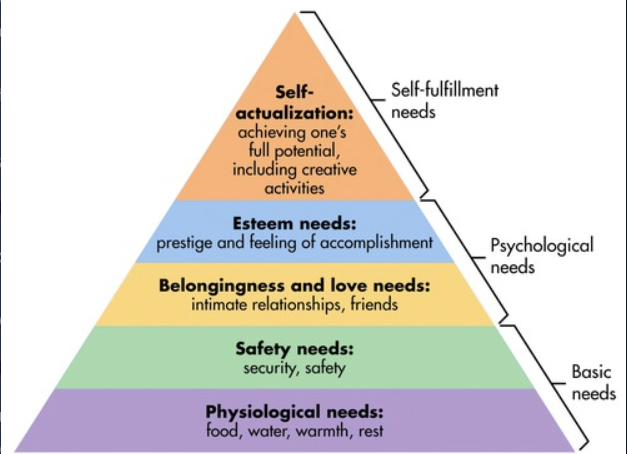
What are Maslow's hierarchy of human needs?
Self-Actualization, Esteem Needs, Belongingness and Love Needs, Safety Needs, Physiological Needs.
Maslow's hierarchy of human needs is a motivational theory that categorizes human needs into a five-tier model, with basic physiological needs at the bottom and self-actualization at the top, suggesting individuals must fulfill lower-level needs before addressing higher-level psychological needs.
What is the Jonah complex?
Fear of fully utilizing one’s intellectual abilities due to potential responsibilities.The Jonah complex refers to a psychological phenomenon where individuals experience anxiety or fear about achieving their full potential, stemming from concerns about the expectations and responsibilities that might accompany success.
What does rogers believe is the ideal condition for the development of a healthy self-concept?
Unconditional positive regard.According to Carl Rogers, unconditional positive regard is the ideal condition for the development of a healthy self-concept, emphasizing acceptance and support regardless of an individual's circumstances.
What does self-actualization refer to?
Reaching one's fullest potential and highest level of functioning.Self-actualization refers to the process of realizing and fulfilling one's talents and potential, often considered the pinnacle of Maslow's hierarchy of needs.
What are the three essential ingredients therapists need to provide according to Rogers?
Genuine; 2. Empathetic; 3. Unconditional positive regard for the client. For a therapist to be genuine, they must be authentic, transparent, and true to their feelings and experiences. This means showing their real self to the client, fostering trust and openness in the therapeutic relationship.
What are the three parts of active listening?
Paraphrase; 2. Invite clarification; 3. Reflect feelings.Active listening involves fully concentrating on, understanding, responding to, and remembering what the other person is saying. This process includes paraphrasing what the speaker has said, inviting them to clarify their points, and reflecting back their feelings to ensure understanding.
What characteristics does Rogers say a fully functioning person has?
Openness to experience, existential living, trust in their organisms, creativity, and a richer life.A fully functioning person, according to Rogers, possesses characteristics such as being open to experiences, living authentically, trusting their own instincts, exhibiting creativity, and enjoying a more fulfilling life.
What is Identity Diffusion?
Identity Diffusion refers to a status where individuals lack a clear sense of identity and direction. They have not made commitments to values, beliefs, or goals and may feel confused about their role in society.
What is Foreclosure?
Foreclosure is the status where individuals make commitments to goals and values without experiencing a crisis or exploration. They adopt the identity prescribed by parents or society, often leading to a lack of personal agency and self-discovery.
What is Moratorium?
Moratorium is a state of active exploration and searching for identity. Individuals in this status are examining various options and beliefs but have yet to make firm commitments, allowing for personal growth and self-discovery.
What is Identity Achievement?
Identity Achievement refers to the status where individuals have explored options, resolved their identity crisis, and made firm commitments to their beliefs and goals. This leads to a strong sense of self and direction.
What are Physiological Needs?
Physiological needs are the basic requirements for human survival, including air, food, water, shelter, sleep, and clothing. These needs must be met for individuals to function properly and ensure physical well-being.
What are Safety Needs?
Safety needs encompass the desire for security, stability, and protection from physical and emotional harm. This includes personal security, financial security, health and well-being, and safety nets against accidents and illness.
What are Belongingness and Love Needs?
Belongingness and Love Needs refer to the human desire for interpersonal relationships, including the need for friends, intimacy, and family. Establishing connections with others is essential for emotional health and feeling accepted.
What are Esteem Needs?
Esteem needs include the desire for self-esteem and the esteem of others. Individuals seek respect, recognition, achievement, and a sense of contribution, which culminate in feelings of self-worth and confidence.
What are Self-Actualization Needs?
Self-Actualization Needs represent the desire to realize one’s potential, pursue personal growth and peak experiences, and fulfill aspirations. This is the highest level in Maslow's hierarchy, focusing on becoming the best version of oneself.