Lecture 6: Synovial Joints
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
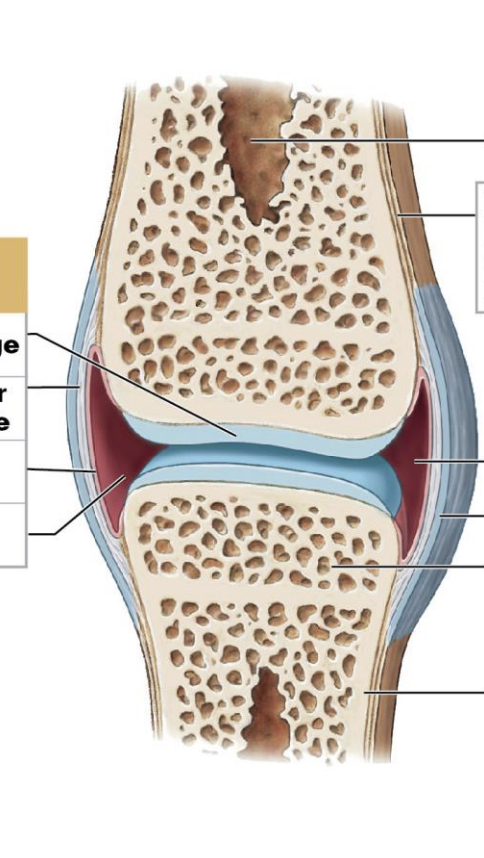
List structures present
Hyaline Cartilage, Joint Capsule, Joint cavity (potential space), Synovial membrane, Ligaments
Function of Hyaline Cartilage in Synovial Joints
Sits on flat ends of bones creating smooth, frictionless movement
Why is smooth, frictionless important in joints?
Reduces damage, reduces energy converted to heat
Joint Capsule
Sheet of DFCT wrapped around joint.
Function of Joint Capsule
Holds the bones together, prevents leakage of synovial fluid.
Joint Cavity
Potential space where needed for bones to move
Synovial Membrane
thin layer of cells that secrete synovial fluid
Function of Synovial Fluid
Fills in inside of joint cavity, contains nutrients for joint loading, reduces friction.
Ligaments
Bands of DFCT inside/outside the joint
Function of Ligaments
Holds bones together, restricts unwanted movement
Types of Ligaments
extracapsular (separate to joint capsule, outside joint), capsular (thickenings of joint capsule), intracapsular (separate to joint capsule, inside joint)
Hinge (example -2)
Ankle, elbow
Pivot (example - 2)
Neck/C1-C2 vertebrae, radioulnar
Condylar (example)
Knee
Ellipsoid (example)
wrist joint (radiocarpal joint)
Saddle (example)
thumb
plane (example - 2)
intercarpal/intertarsal joints
ball & socket (example - 2)
Hip/shoulder
hinge (axis)
uniaxial
pivot (axis)
uniaxial
condylar (axis)
biaxial
ellipsoid (axis)
biaxial
saddle (axis)
biaxial +
plane (axis)
multiaxial
ball & socket (axis)
multiaxial
hinge (movement)
flexion, extension
pivot (movement)
only rotation
condylar (movement)
flexion, extension, rotation (when flexed)
ellipsoid (movement)
flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction
saddle (movement)
flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, opposition (specialised form of rotation)
plane (movement)
sliding and gliding — flat surfaces
ball & socket movement
ALL - flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, rotation
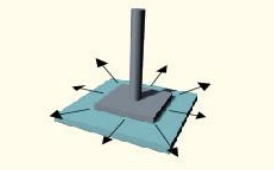
plane
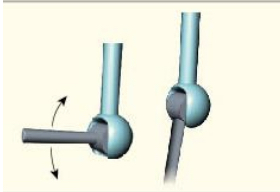
hinge
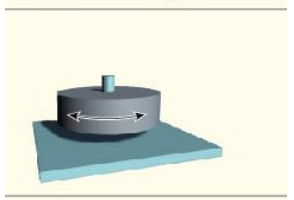
pivot
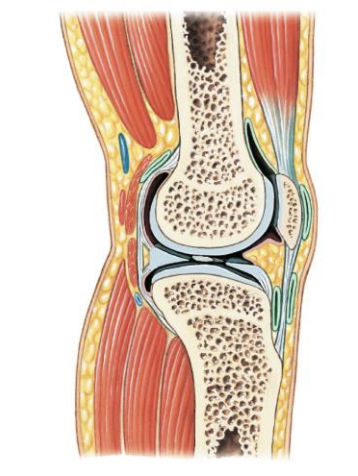
condylar
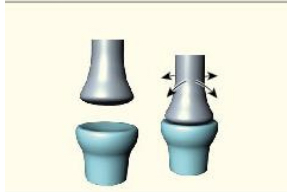
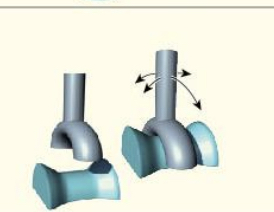
saddle
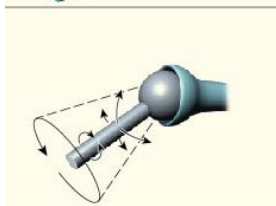
ball & socket
Capsular Ligaments
thickenings of the joint capsule in some joints where more support is needed — restrict movement away from themselves
Extracapsular Ligaments example in the knee (2)
MCL (medial collateral ligament)
LCL (lateral collateral ligament)
Intracapsular Ligaments
separate from joint capsule; additional bands of DFCT inside joint
Intracapsular Ligaments in the knee (2)
ACL (anterior cruciate ligament) and PCL (posterior cruciate ligament)
Fibrocartilaginous pads fucntion
fill in space, absorb shock and deepen articulation
Fibrocartilaginous pads in the knee
menisci are half shaped moon structures that sit between tibia and femur
Function of ACL
stops femur sliding backwards/post. displacement (post. femur → ant. tibia)
Function of PCL
stops femur sliding forwards/ant.displacement (ant. femur → post. tibia)
Function of LCL
restrict adduction
function of MCL
restrict abduction