Demand
0.0(0)Studied by 3 people
Card Sorting
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:19 PM on 9/20/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
Demand
When you demand something, it means you're willing and able to buy it
2
New cards
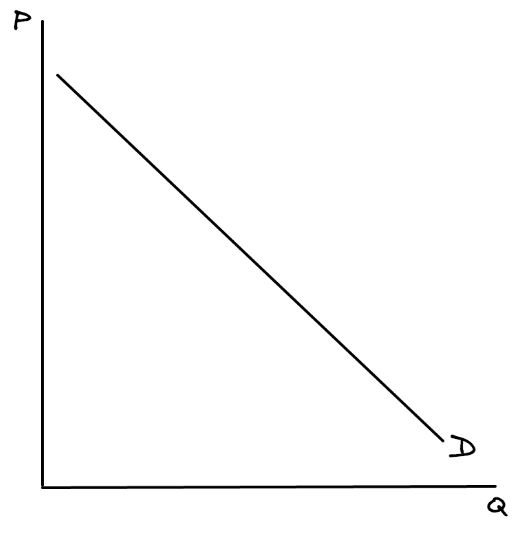
Demand curve
Shows the relationship between the price and quantity demanded of a good or service.
3
New cards
Contraction in demand
When an increase in price leads to a decrease in quantity demanded
4
New cards
Extension in demand
When a decrease in price leads to an increase in quantity demanded
5
New cards
Price elasticity of demand (PED)
PED measures how much quantity demanded changes in response to a change in price PED = %△Qd/ %△P
6
New cards
Elastic demand
When PED is between 1 and ∞. Demand is very responsive to changes in price.
7
New cards
Inelastic demand
When PED is between 1 and 0. Demand is unresponsive to changes in price.
8
New cards
Unitary elastic demand
When PED = 1
9
New cards
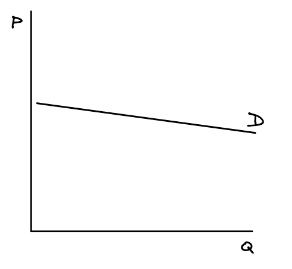
Elastic demand curve
Gentle, flatter slope because a small change along the price axis leads to a larger % change along the quantity axis.
10
New cards
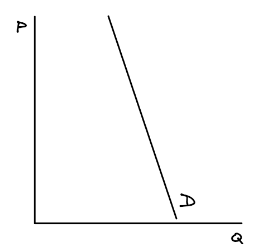
Inelastic demand curve
Steeper slope because a large change along the price axis leads to a smaller % change along the quantity axis.
11
New cards
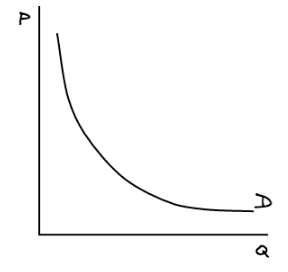
Unitary elastic demand curve
Remember: it looks like the beginning of a "U", for unitary elastic demand.
12
New cards
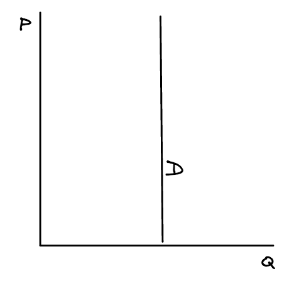
Perfectly inelastic demand curve
Remember: it looks like an "i" for perfectly inelastic demand.
13
New cards
Perfectly elastic demand curve
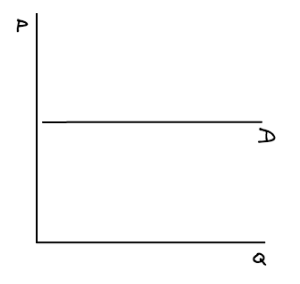
14
New cards
Perfectly inelastic demand
When PED = 0. Demand will not respond at all to a change in price.
\
E.g. life-saving medicine
\
E.g. life-saving medicine
15
New cards
Perfectly elastic demand
When PED = ∞. Demand will be infinitely responsive to a change in price.
16
New cards
The factors which affect PED
**NASBIT**
**N**ecessity or luxury
**A**ddictive or habit-forming
**S**ubstitutes
**B**rand loyalty
Proportion of **I**ncome
**T**ime
**N**ecessity or luxury
**A**ddictive or habit-forming
**S**ubstitutes
**B**rand loyalty
Proportion of **I**ncome
**T**ime
17
New cards
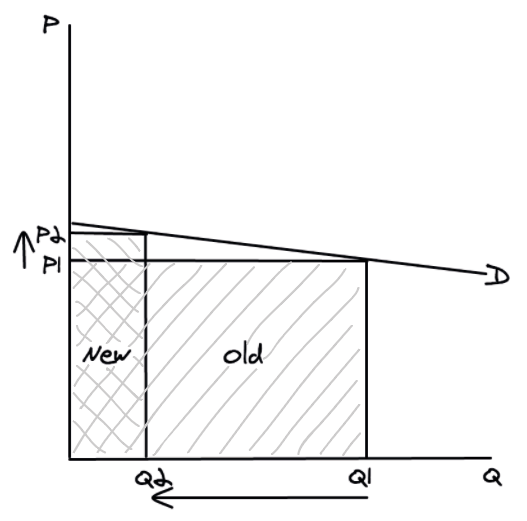
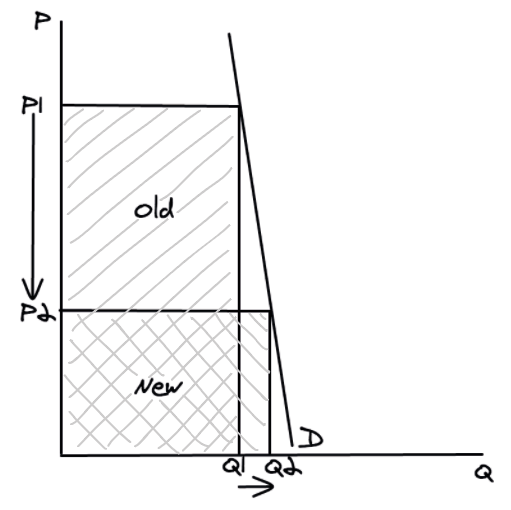
Elastic demand and total revenue
If price **increases**, quantity demanded will **decrease** by a larger %, so overall total revenue will **decrease**.
\
If price **decreases**, quantity demanded will **increase** by a larger %, so overall total revenue will **increase**.
\
If price **decreases**, quantity demanded will **increase** by a larger %, so overall total revenue will **increase**.
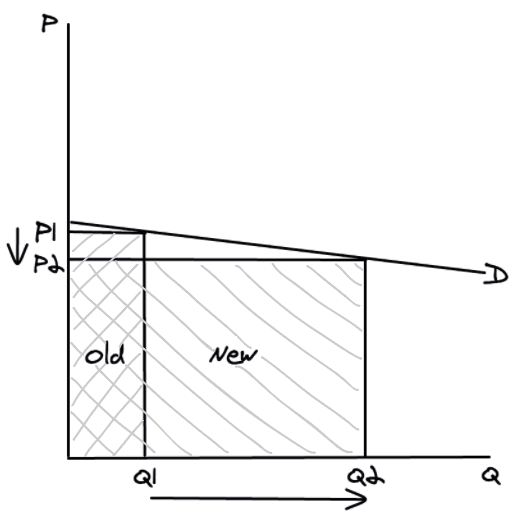
18
New cards
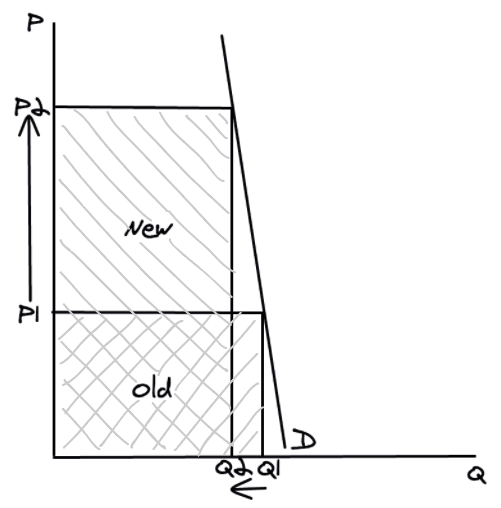
Inelastic demand and total revenue
If price **increases**, quantity demanded will **decrease** but by a smaller %, so overall total revenue will **increase**.
\
If price **decreases**, quantity demanded will **increase** but by a smaller %, so overall total revenue will **decrease**
\
If price **decreases**, quantity demanded will **increase** but by a smaller %, so overall total revenue will **decrease**
19
New cards
Unitary elastic demand and total revenue
Whether price increases **or** decreases, total revenue will **not change** at all
20
New cards
Changes in income (effects on demand)
For **normal** goods (e.g. Ben & Jerry’s ice cream) demand will **increase** when incomes **rise**, and demand will **decrease** when incomes **fall**.
\
For **inferior** goods (e.g. Sainsbury’s Basics ice cream) demand will **increase** when incomes **fall**, and demand will **decrease** when incomes **rise**.
\
For **inferior** goods (e.g. Sainsbury’s Basics ice cream) demand will **increase** when incomes **fall**, and demand will **decrease** when incomes **rise**.
21
New cards
Price of other goods
For substitute goods (e.g. iPhones and Samsungs) demand for the first good (iPhone) will decrease when price of second good (Samsung) falls, and demand for the first good (iPhone) will increase when price of second good (Samsung) rises.
For complementary goods (e.g. iPhones and iPhone apps) demand for the first good (iPhone) will increase when price of second good (iPhone apps) falls, and demand for the first good (iPhone) will decrease when price of second good (iPhone apps) rises.
22
New cards
Income elasticity of demand (YED)
YED measures how much quantity demanded will change in response to a change in income.
YED = %△Qd/%△Y
YED = %△Qd/%△Y
23
New cards
Normal goods
For normal goods (e.g. Ben & Jerry’s ice cream), demand **increases** when income **increases**, which means the YED for normal goods is **positive (0 - 1)**.
24
New cards
Inferior goods
For inferior goods (e.g. Sainsbury’s basics ice cream), demand **increases** when income **decreases**, which means the YED for inferior goods is **negative. 0 to -∞**
25
New cards
Income elastic goods (or luxury goods)
When YED is between **1** and **∞**. Income elastic goods are very responsive to changes in income and are likely to be luxury goods e.g. a rolex
26
New cards
Income inelastic goods (or necessity goods)
When YED is between **-1** and **1**. Income inelastic goods are unresponsive to changes in income, and are likely to be necessity goods e.g. bread
27
New cards
Cross elasticity of demand (XED)
XED measures how much quantity demanded of good A changes in response to a change in price of good B
XED formula = % change in quantity demanded (Qd) of A / the % in price (P) of B
XED formula = % change in quantity demanded (Qd) of A / the % in price (P) of B
28
New cards
Complements (or complementary goods)
Complements are goods which are used and bought together (e.g. iPhones and iPhone apps)
For complements, if the price of good B (iPhone apps) **increases** then demand for good A (iPhones) **decreases**.
XED will be **negative**.
For complements, if the price of good B (iPhone apps) **increases** then demand for good A (iPhones) **decreases**.
XED will be **negative**.
29
New cards
Substitutes (or substitute goods)
Substitutes are goods which can replace one another (e.g. iPhones and Samsungs)
For substitutes, if the price of good B (Samsungs) **increases** then demand for good A (iPhones) **increases**.
XED will be **positive**.
For substitutes, if the price of good B (Samsungs) **increases** then demand for good A (iPhones) **increases**.
XED will be **positive**.
30
New cards
Unrelated goods
Unrelated goods are goods which have nothing to do with each other (e.g. cacti and hover boards) XED = 0 for unrelated goods