Biology EOY D
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Plant root/shoot cells
Meristematic cells, protected by root cap, are undifferentiated cells for growth
Yeast mitosis
Asexual reproduction through asymmetric division known as budding.
Unequal cell division causes outgrowth from parent cell, eventual detaching and becoming its own cell.
Animal cell cytokenisis
Contractile ring of actin and myosin proteins tightens around the cell, creating a cleavage furrow at the equator of the cell. Eventually, two daughter cells are formed.
Plant cell cytogenesis
Cell plate forms from vesicles at the equator, starting centrally and building outwards till the cell wall is reached. The first vesicles carry carbohydrates, lipids and proteins fusing together to create two plasma membranes. The final vesicles carry pectin and cellulose and deposit them by exocytosis in the gap forming a cell wall.
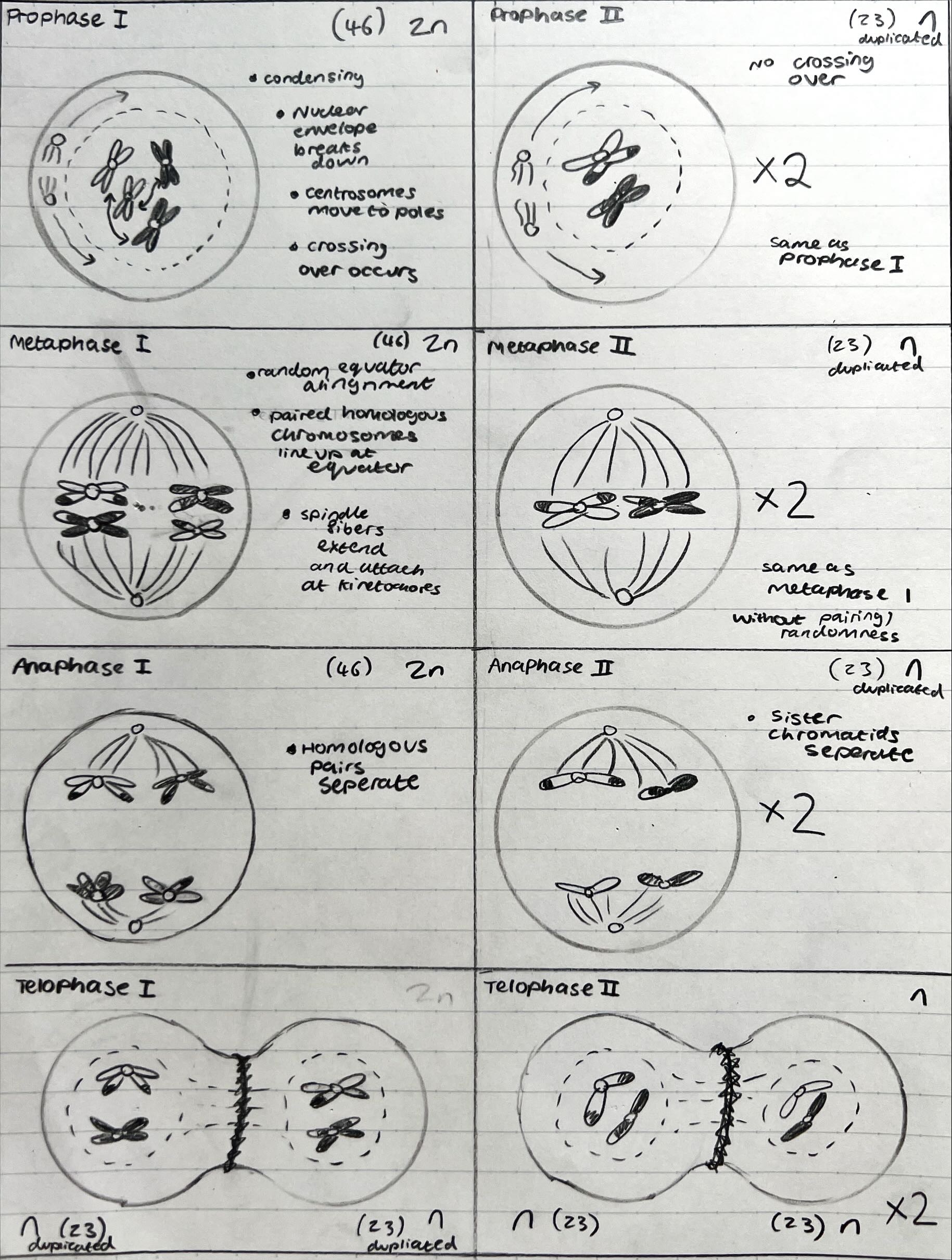
Oogenisis
Primary oocyte formed before birth (2n), separating by Meosis one first into a secondary oocyte (1n) and a polar body (1n) during puberty, then into a full ovum (1n) and a second polar body (1n) when the egg is fertilised.
Protein types and examples
Globular - hemoglobin
Fibrous - collagen
Ribosome sites
A (aminoacyl) site - entrance binding with the incoming tRNA
P (peptide) site - holds the tRNA carrying the growing polypeptide chain
E (exit) site - exit for the deacylated tRNA molecule to exit the ribosome
RNA types
mRNA - messenger RNA, carries genetic information from nucleus to ribosome (codon)
tRNA - transfer RNA, transporting amino acids to ribosome during translation (anticodon)
rRNA - ribosomal RNA, used in ribosome
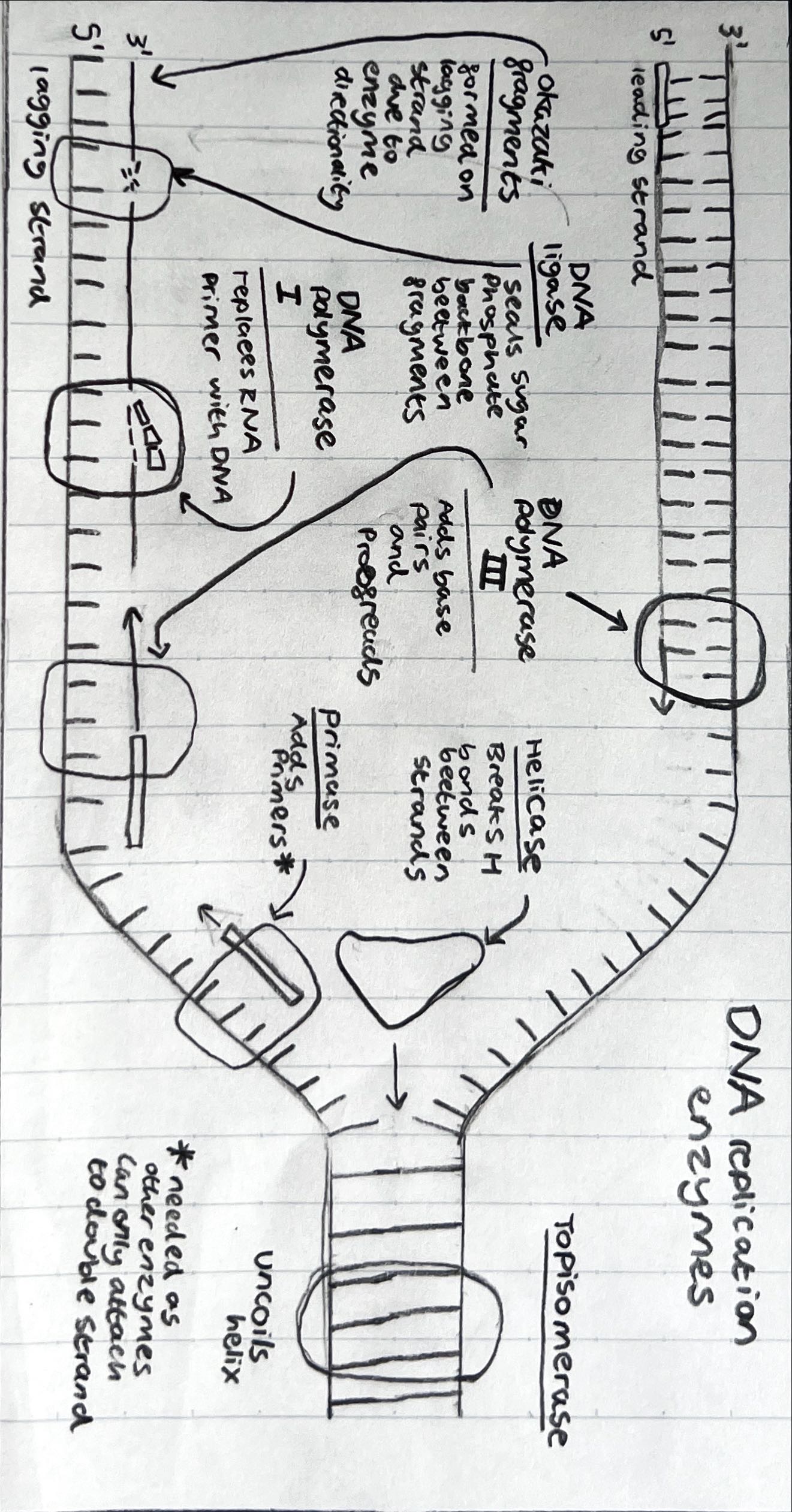
DNA directions
3’ to 5’ direction of enzyme work
5’ to 3’ direction of synthesised daughter strand
RNA direction
5’ to 3’ direction of enzyme work
3’ to 5’ direction of synthesised daughter strand
Types of body cells
Somatic cell - any cell of a living organism other than the reproductive cells.
Germ cell - reproductive cell of an organism
Taq polymerase
Taq polymerase is isolated from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus
As this enzyme’s optimal temperature is ~75ºC, it is able to function at the high temperatures used in PCR without denaturing
PCR process
Denaturation – DNA sample is heated to 90ºC to separate the two strands
Annealing – Sample is cooled to 55ºC to allow primers to anneal
Elongation – Sample is heated to the optimal temperature for a heat-tolerant polymerase (Taq) to function at 75ºC
The cycle repeats (takes about 2 mins each)
30 cycles creates over 1 billion copies (230)
Types of mutation
Substitution - e.g, ATG becomes ACG
Inversion - e.g, ATG becomes AGT
Insertion - e.g, ATG becomes ATCG (changes reading frame)
Deletion - e.g, ATG becomes AG (changes reading frame)
Effects of mutations
Silent - doese’t alter amino acid sequence due to degeneracy of genetic code
Missense - alters a single amino acid (can cause sickle cell anaemia)
Nonsense - causes premature stop codon (can cause cystic fibrosis)
Framshift - change in reading frame effecting entire sequence
Human Genome Project
Sequencing of entire human genome.
Enabled the development of personalized medicine
Improved our understanding of inherited diseases,
Facilitated advancements in cancer research and gene therapy.
Genome definiton
The total genetic information of a cell, organism or organelle
Proteome definition
Entire complement of proteins that is or can be expressed by a cell, tissue, or organism.
Transcriptome definition
The sum total of all the messenger RNA molecules expressed from the genes of an organism.
Methylation types
DNA methylation - decreases gene expression by preventing binding of transcription factors
Histone methylation - affects how tightly DNA is packed around the histone.
DNA transcription factors
Activator proteins bind to enhancer sites increasing transcription rates
Repressor proteins bind to silencer sequences decreasing transcription rates
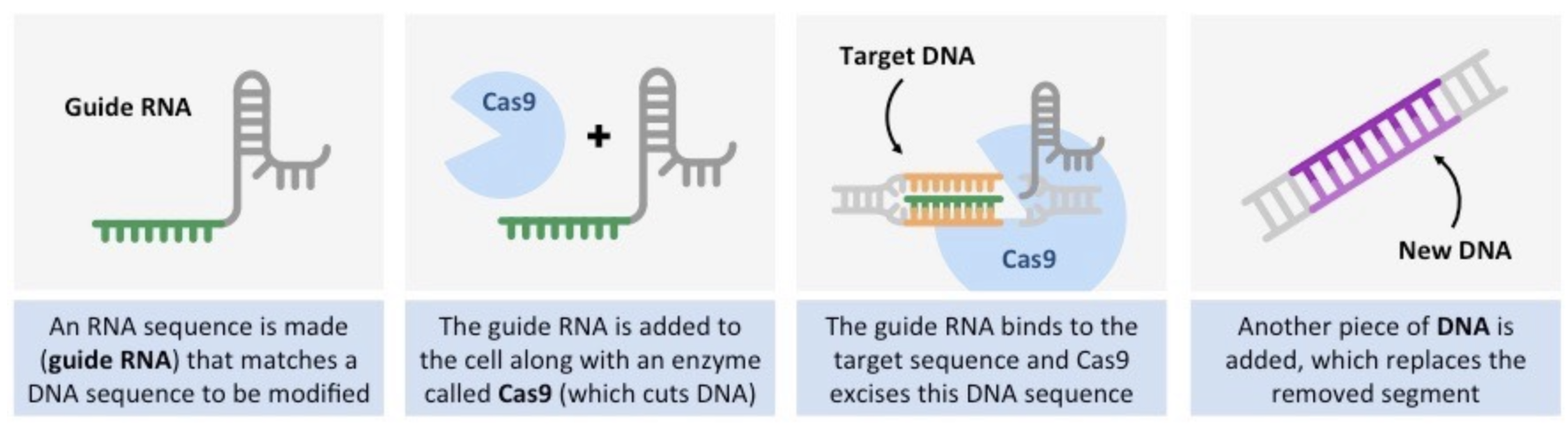
CRISPR
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats.
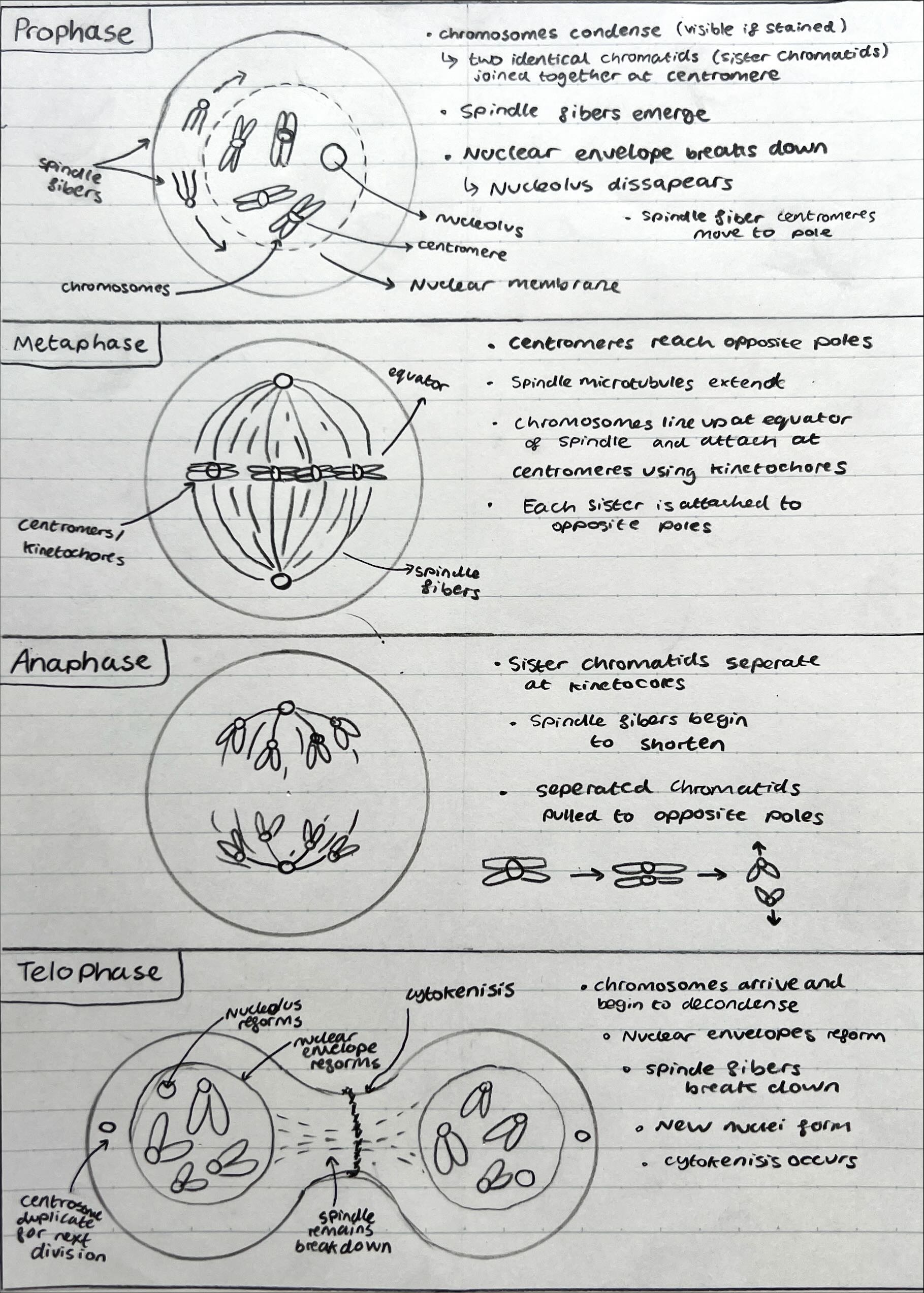
Mitosis
Meosis
Cell cycle and regulation
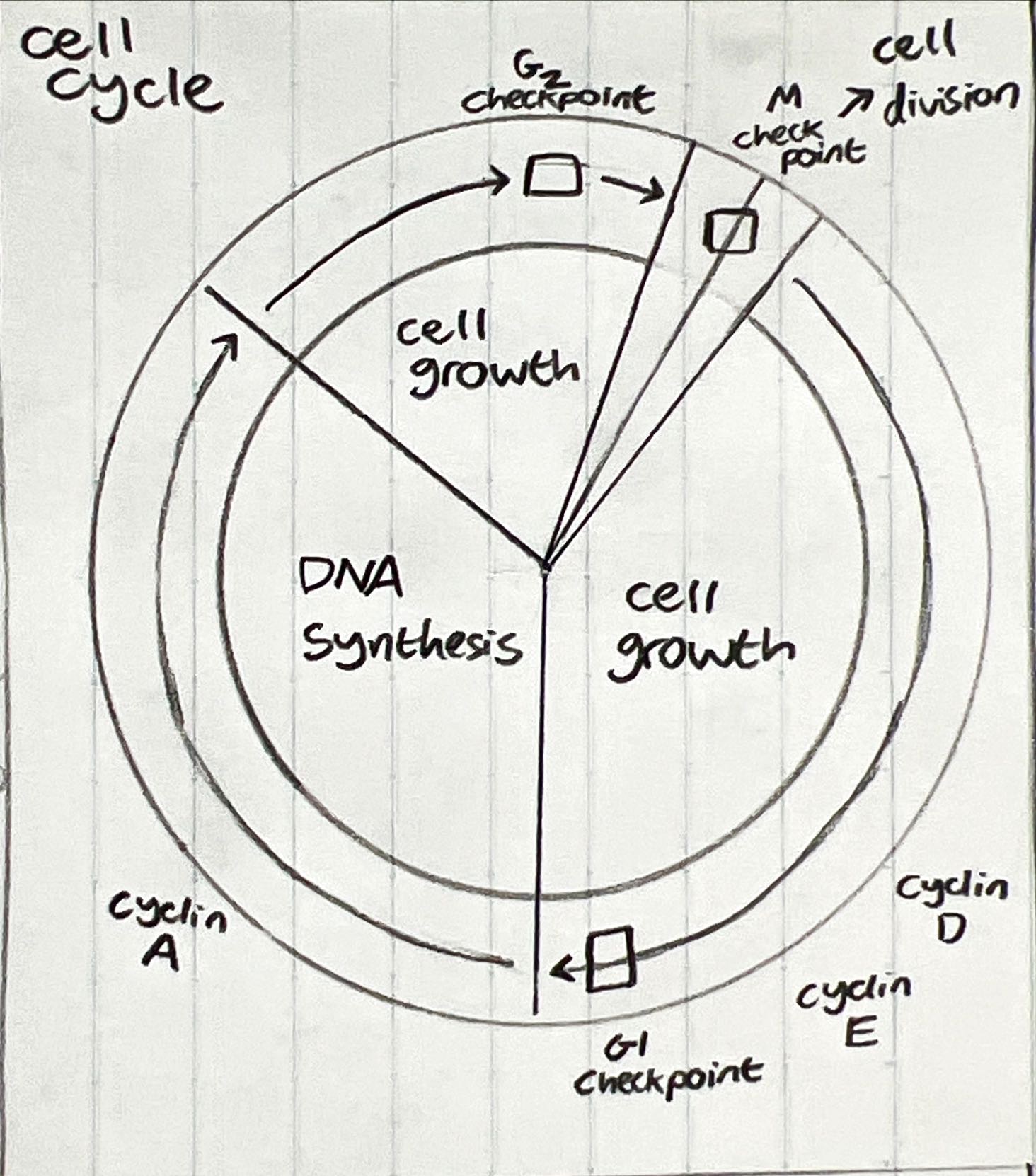
DNA replication