Lecture 13: Echinodermata
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Phylum Echinodermata
no brain or head , just oral side & back side
sea stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers, sea lilies, brittle stars
defining characteristics of Echinodermata
endoskeleton made of calcium carbonate
Deuterostomes = first opening in embryo is anus
water vascular system : water filled tube system that control movement, breathing & feeding
Pedicellaria = tiny pincher like structures on skin that help w/ cleaning & defense
Dermal branchiae = tiny skin bump gills that help breathe & rid of waste
Pentaradial symmetry = 5 parts but larvae is bilateral
lives on ocean floor (benthic)
Subphylum Plematozoa ; Class Crinoidea
sea lilies & feather stars
attached sessile animals (motile tho)
epidermis covered in plates
filter feeders
DONT have: spines, pedicellariae, & madreporites
what are madreporites for ?
entry valve for the water vascular system in Echinoderms
Subphylum Eleutherozoa & the classes within it:
Asteroidea
Ophiuroidea
Echinoidea
Holothuroidea
free living
Sea stars
Brittle stars
Sea urchins
Sea cucumbers
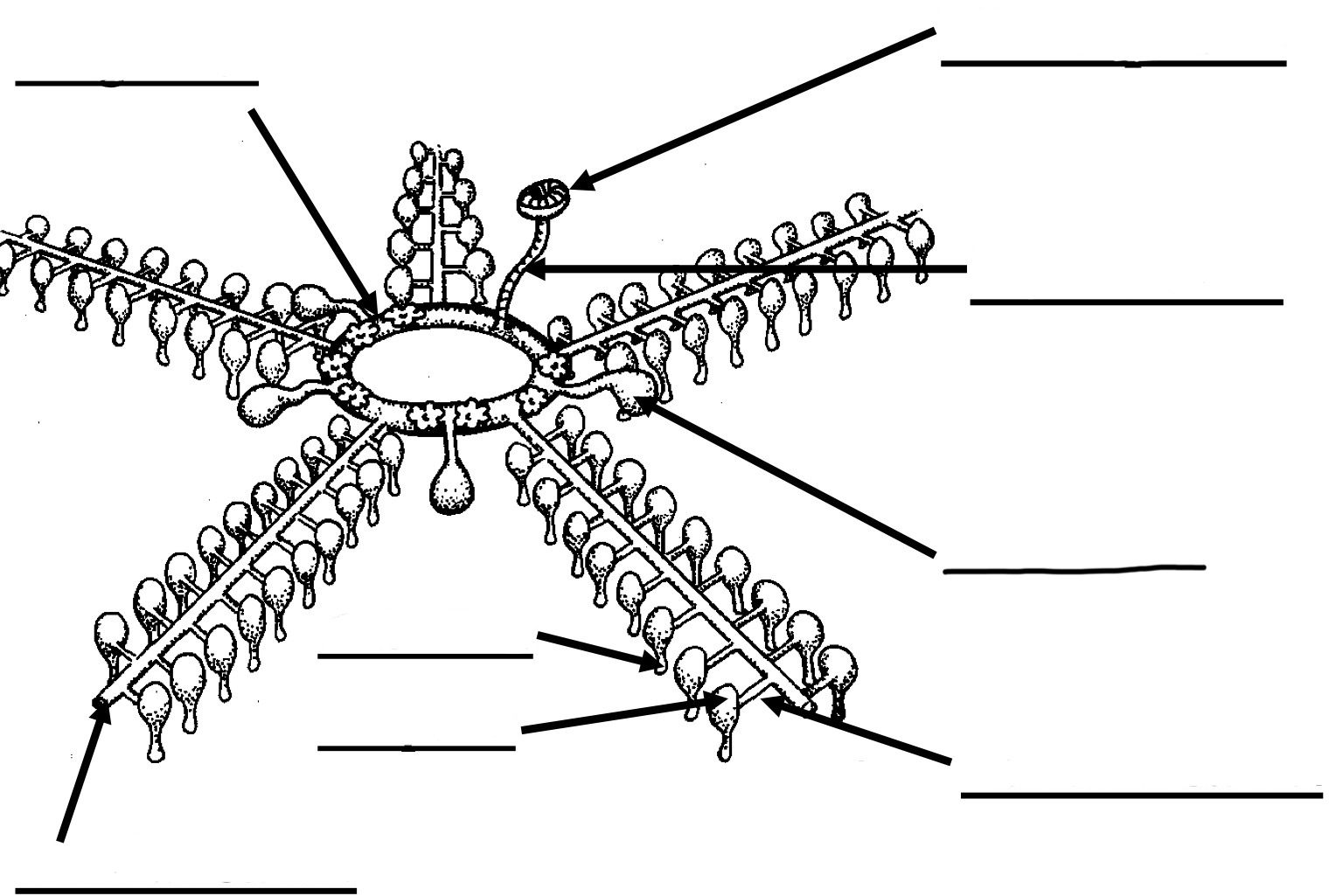
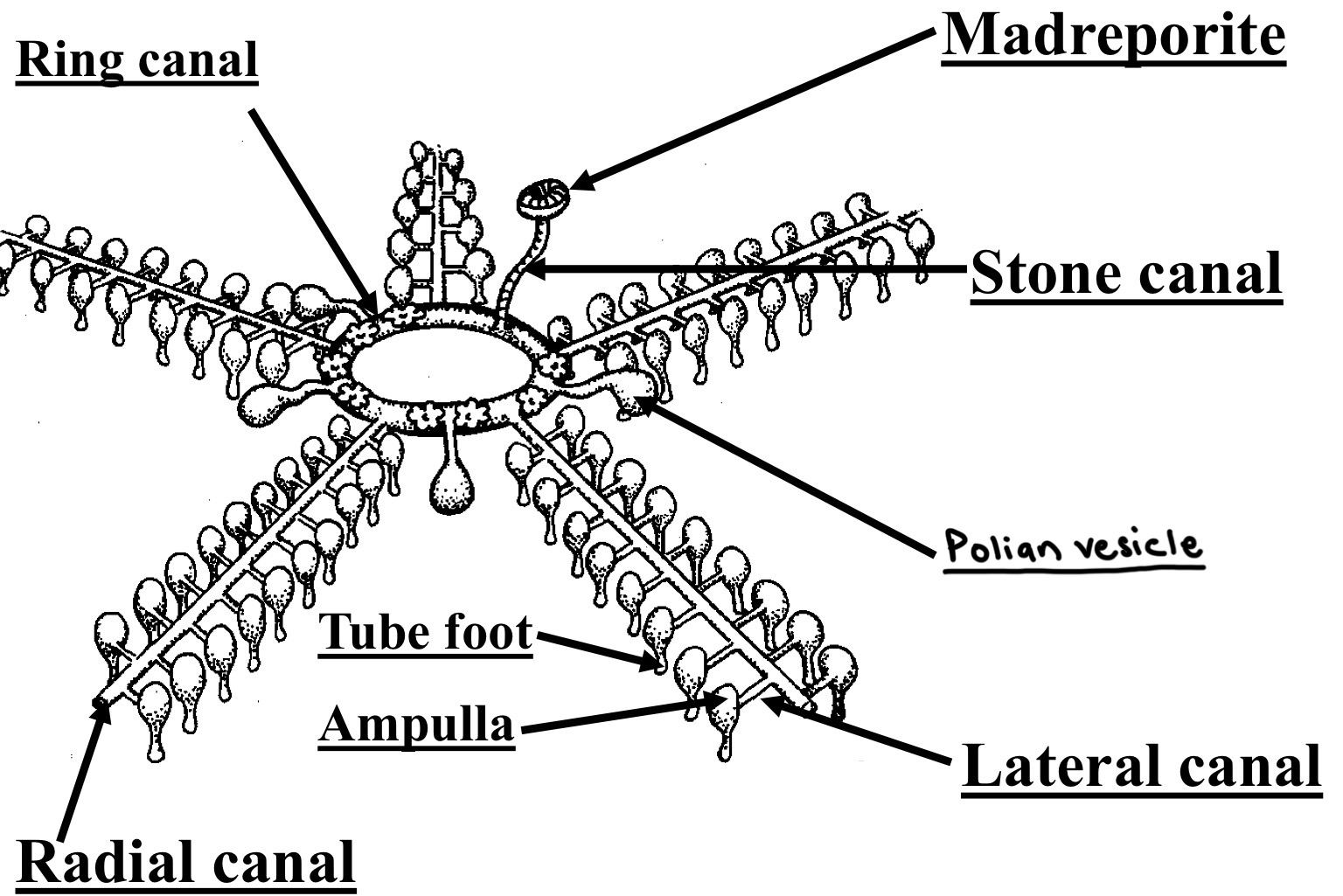
Water vascular system labelling
Madreporite: entrance where water comes in
Stone canal: carries water from madreporite to ring canal
Polian Vesicle: story extra water
Ring canal: circular tube in center of body that distributes water
Radial canals: tubes that go out from ring canal into each arm
Lateral canals: one way valves branching off radial canal to tube foot
Ampulla: a bulb that squeezes water into the tube foot
Tube foot: used for movement and sticking to surface (suction cups)
what muscles does the ampulla use to squeeza water to the podium (tube foot)?
Circumlongitudinal ampullary muscles (CLD)
Pedicellariae
removal of debris & unwanted organisms
protect dermal branchiae
capture live prey
Ophiuroidea characteristics
No ambulacral groove
no pedicellariae
no dermal branchiae
arms bend & move for locomotion
Echinoidea characteristics
Test architecture: 10 rows of plates = 5 zones tube feet + 5 zones of no tube feet
Aristotle’s Lantern
set of 5 sharp teeth in a sea urchin
Holothuroidea
soft leathery body wall
small ossicles
tube feet on ventral side with oral (Trivium)
less tube feet on dorsal side (Divium)
Holothuroidea respiration
breathe through their anus using respiratory tree
cloacal muscles contract to open anus
water enters
anal sphincter closes and water is forced into tree
tree contracts and water is pushed out (gas exchange)
where do pearlfish live ?
live in the respiratory tree of sea cucumbers, enter when it inhales, leaves when it exhales.