Inflation and the Philips Curve
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
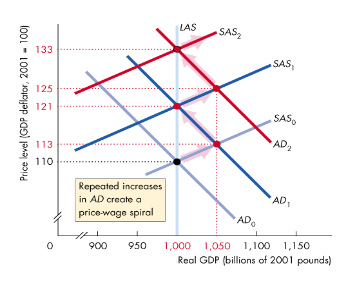
What is inflation and how is it measured?
It’s a continuous rise in the price level, and is measured as the % change in price level per annum.
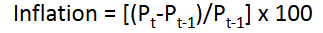
What is the initial cause of cost push inflation?
Caused by an initial increase in costs (i.e. an increase in the AS)
Main sources of costs include:
Increase in the money wage rate
Increase in the money price of a raw material e.g. oil
Explain how cost push inflation persists
An inflationary supply shock shifts the SRAS curve up, increasing the price level. Then to return to equilibrium, monetary accommodation occurs if there’s an increase in the MS when costs rise, but this leads to further shocks and the cycle continues.
How can cost push inflation be stopped?
By not accommodating the price rises with money accommodation, causing GDP to fall as prices rise, returning P and Y to their original levels
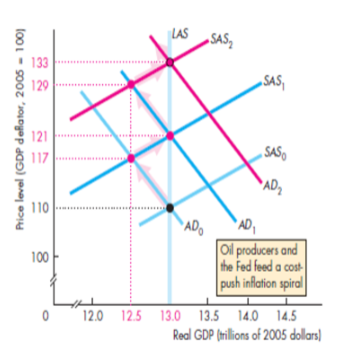
What is the root cause of demand pull inflation?
Caused by a sustained increase in AD due to:
An increase in G
A tax cut
An increase in exports
An increase in the quantity of money
Explain how demand pull inflation persists
Starting from full employment, an increase in AD shifts AD curve right, causing an inflationary gap
This means new equ. is at a higher price level and at a higher GDP
Since there’s an inflationary gap, workers demand a higher wage, meaning the money wage rises, shifting SRAS curve left, meaning real GDP returns to its potential level, but the price level increases
A continued increase in AD leads to the cycle persisting
What is the quantity theory of money? What is it based on?
It’s the proposition that in the long run, an increase in the quantity of money brings an equal percentage increase in the price level
Based on the velocity of circulation
What is the velocity of circulation?
It’s the average number of times a year a unit of currency is used to purchase G+S
What is the equation of exchange, and what are the economic implications of this?
MV=PY or P=(V/Y)M
Where M = quantity of money; V = velocity of circulation; P = Price level; Y = Real GDP
As V/Y is assumed to be constant by classical economists, it means that ΔM→ΔP
Explain how inflation in the long run is correlated to the money growth rate
Inflation can be expressed in terms of growth rates through the equation:
Inflation = Money growth rate + Velocity growth rates - Real GDP growth rate
But as in the LR, neither rate of velocity change nor GDP growth rate are influenced by the growth rate of money, then it can be said that inflation is correlated with the money growth rate
How does the quantity theory of money explain the LR determinants of price level and the inflation rate?
Quant. of money in the economy determines the value of money
Primary cause of inflation is the growth in the quantity of money
If the economy is in equ. and the CB suddenly increased the MS, the MS curve shifts rightwards, the equ. value of money falls and P increases