Biology 30: Reproductive System
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Male Reproductive System
Overall function is production of offspring. Testes produce sperm and male sex hormone, and male ducts and glands aid in the delivery of sperm to the female reproductive tract.
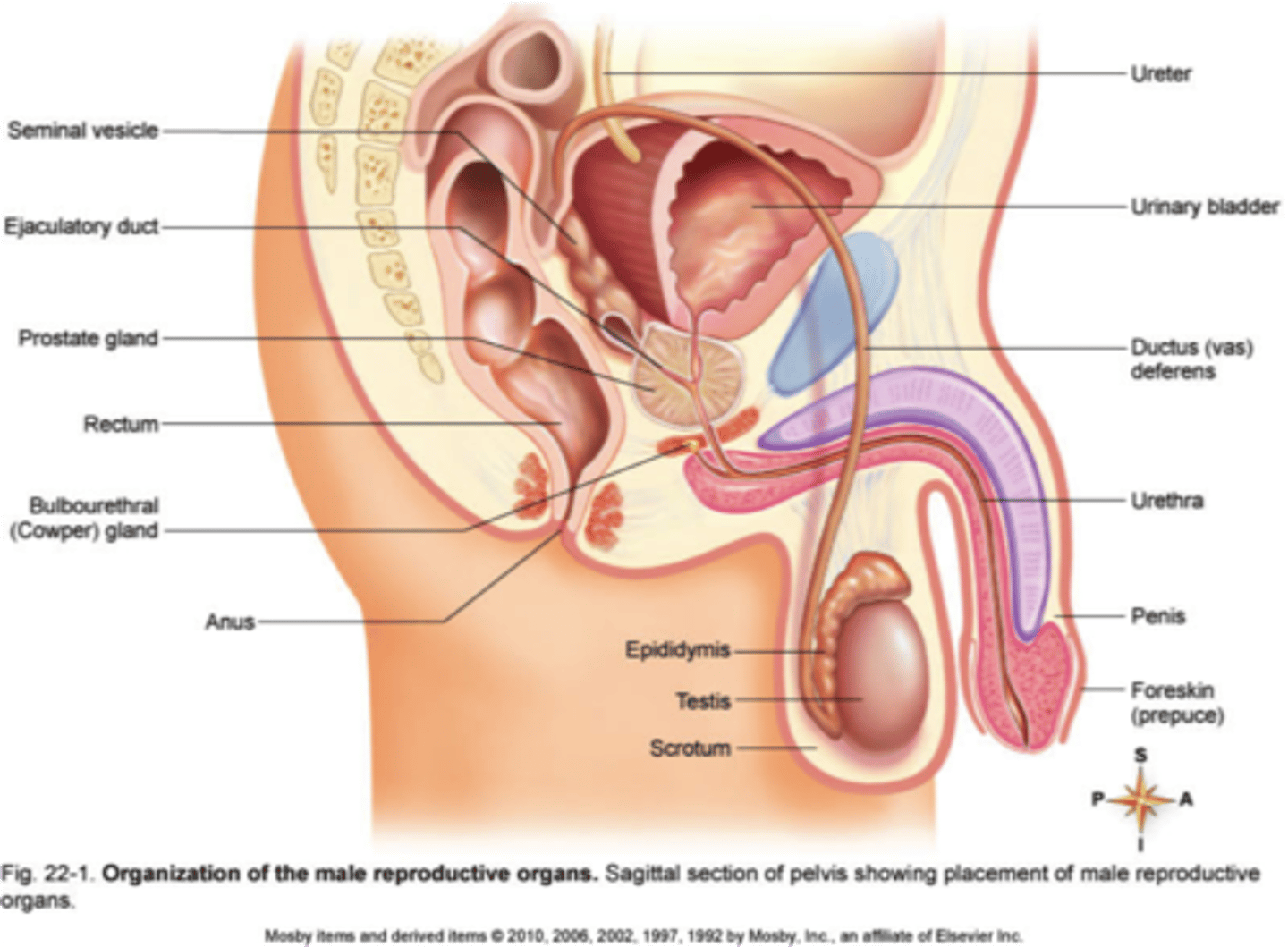
Scrotum
External pouch of skin that encloses the testicles and provides a decrease in temperature for sperm development.
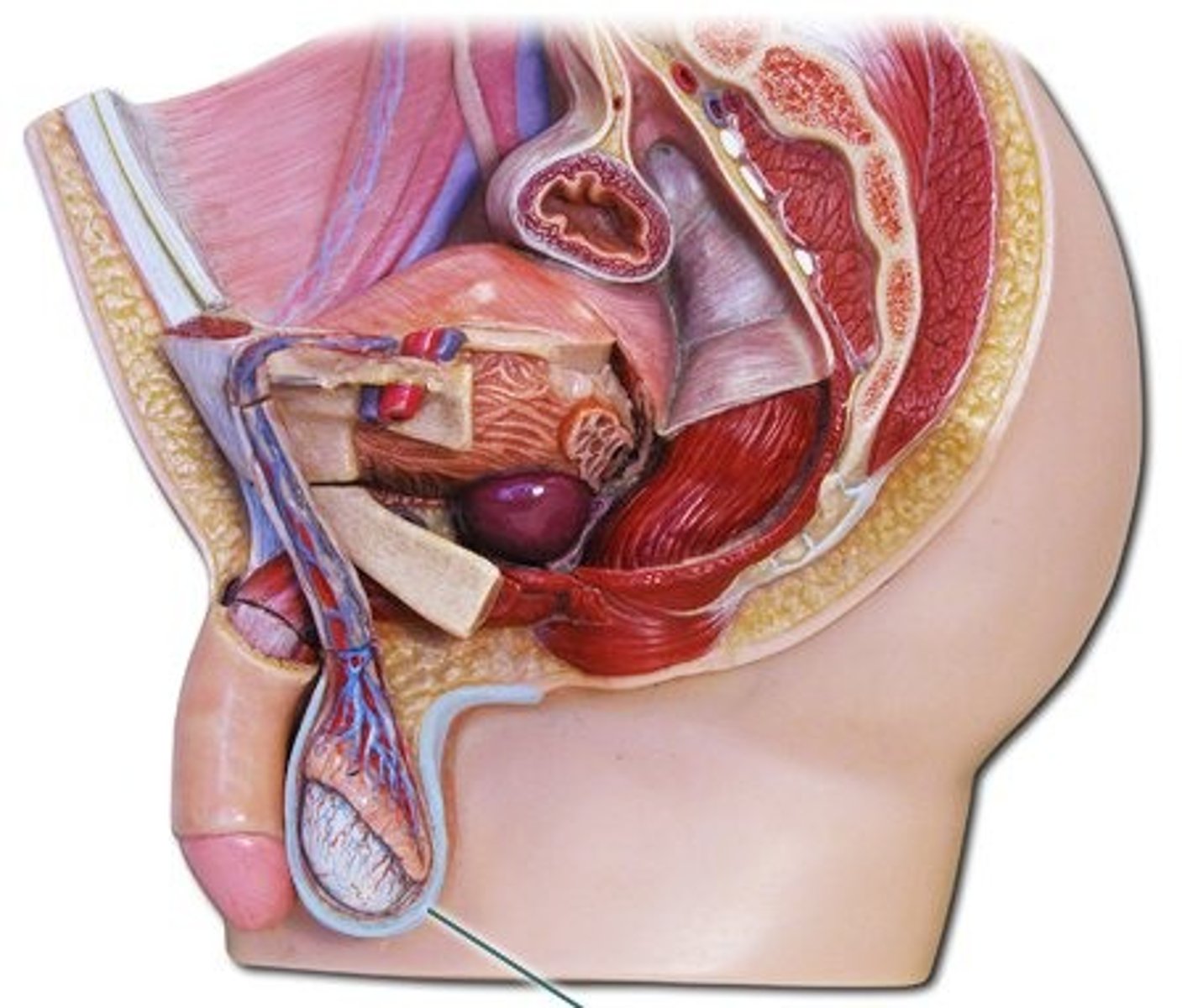
Testicles (testes)
Oval organs that lie in the scrotum, responsible for making testosterone and generating sperm
- Full of interstitial cells that make testosterone
- Full of seminiferous tubules where sperm are made and "nursed" by sertoli cells
Interstitial Cells
In the testes, these cells lie between the seminiferous tubules and produce the hormone testosterone; stimulated by LH from the pituitary gland
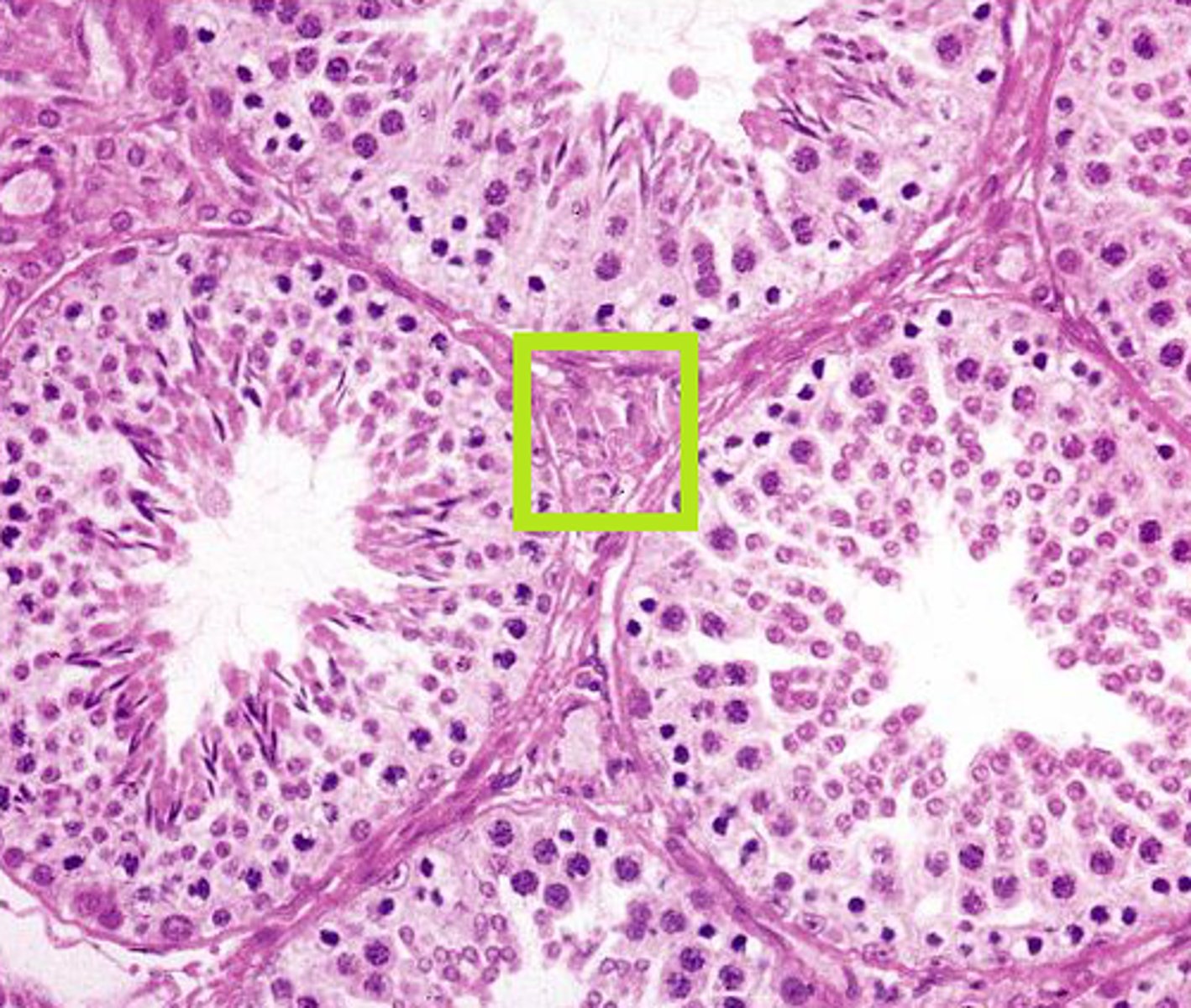
Seminiferous Tubules
Narrow, coiled tubules that produce sperm in the testes.
- Where spermatogenesis occurs
- Also contains sertoli cells that nourish and provide energy for growing sperms
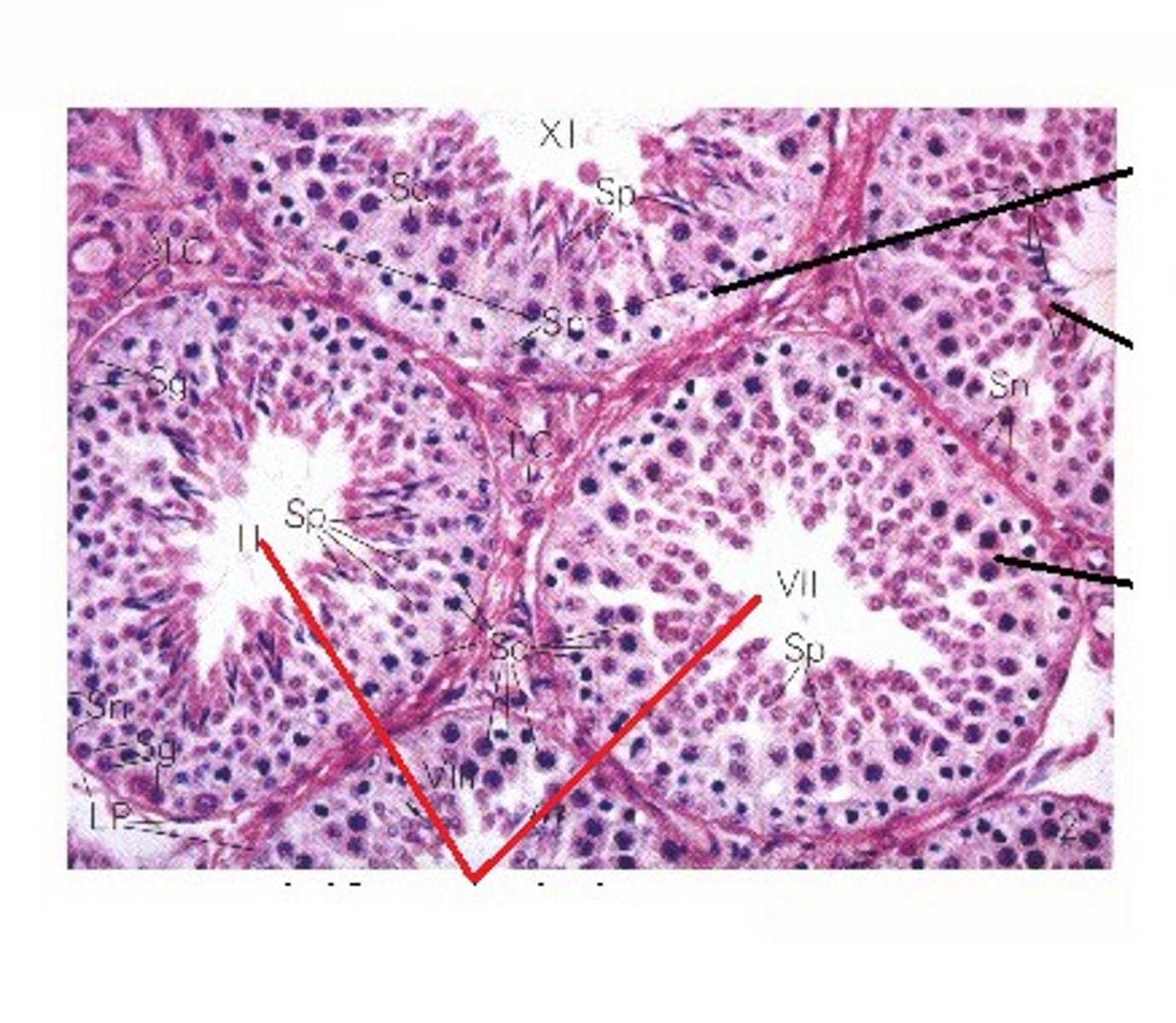
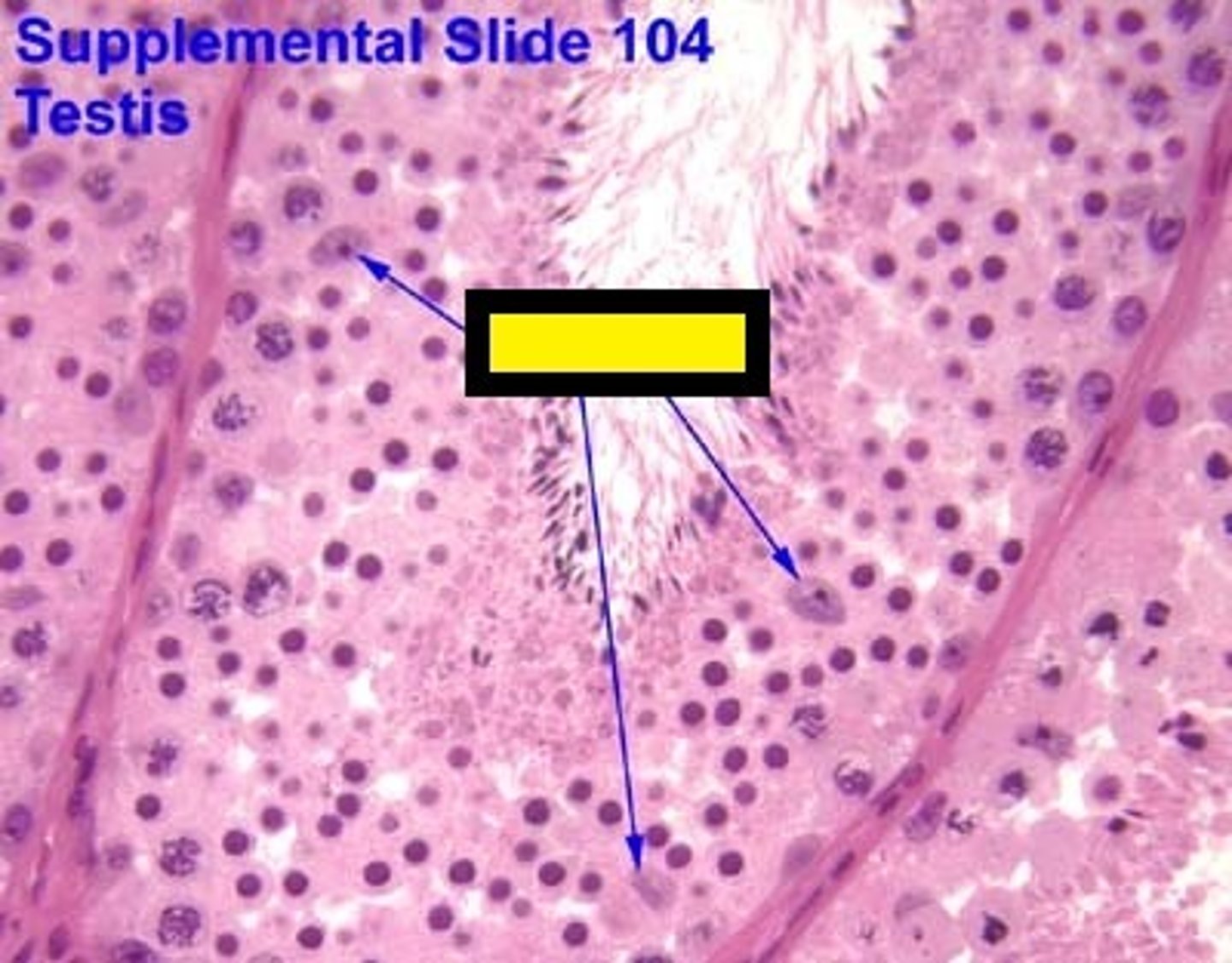
Sertoli Cells
Cells found within the seminiferous tubules that provide metabolic support for the spermatids
- "nurse cells"
Stimulated by FSH from the pituitary gland and sends inhibin back to the pituitary gland for negative feedback.
Epididymis
Structure in the male reproductive system in which sperm are fully matured and are stored
- aka. "testicle hats", aka "sperm high school"
- a compact, coiled tube on the outer edge of each testis
- where sperm are stored and finish maturing, ex. begin swimming motions
- immune system destroys the defective sperm here
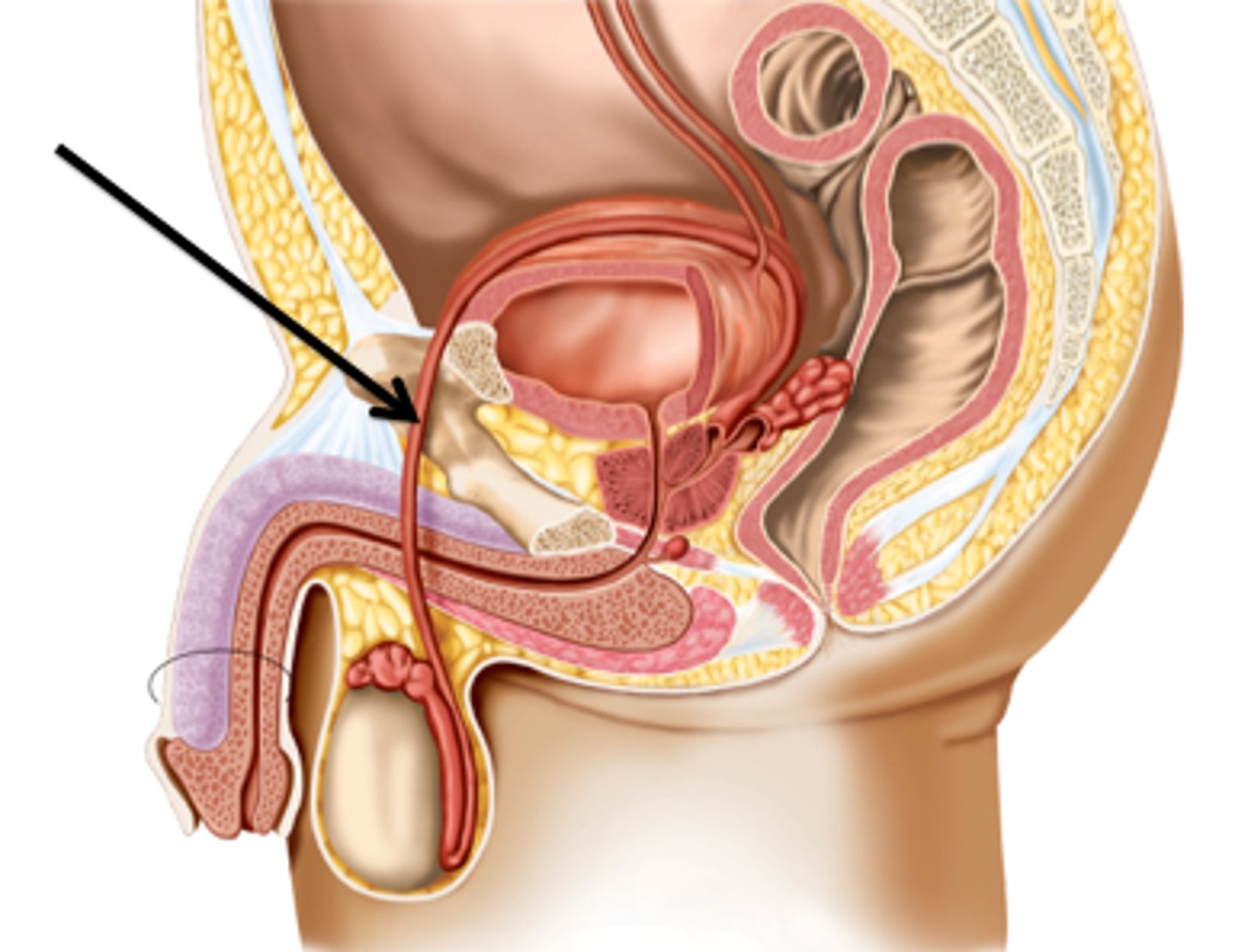
Vas Deferens (ductus deferens)
Excretory duct of testis that joins epididymis with ejaculatory duct
- 2 tubes that carry mature sperm from each epididymis to the ejaculatory duct
- The ejaculatory duct then becomes the urethra
- A vasectomy is when you cut or clamp this duct
Why? Because its PERMANENT BIRTH CONTROL
Seminal Fluid
The substance in which sperm are suspended is produced by three glands in the abdominal cavity
- Secretions made by 3 exocrine glands; seminal vesicles, prostate gland and Cowper's gland (bulbourethral gland)
- Added to the ejaculatory duct
- Required by sperm for their journey
Sperm + ________ ______ = semen
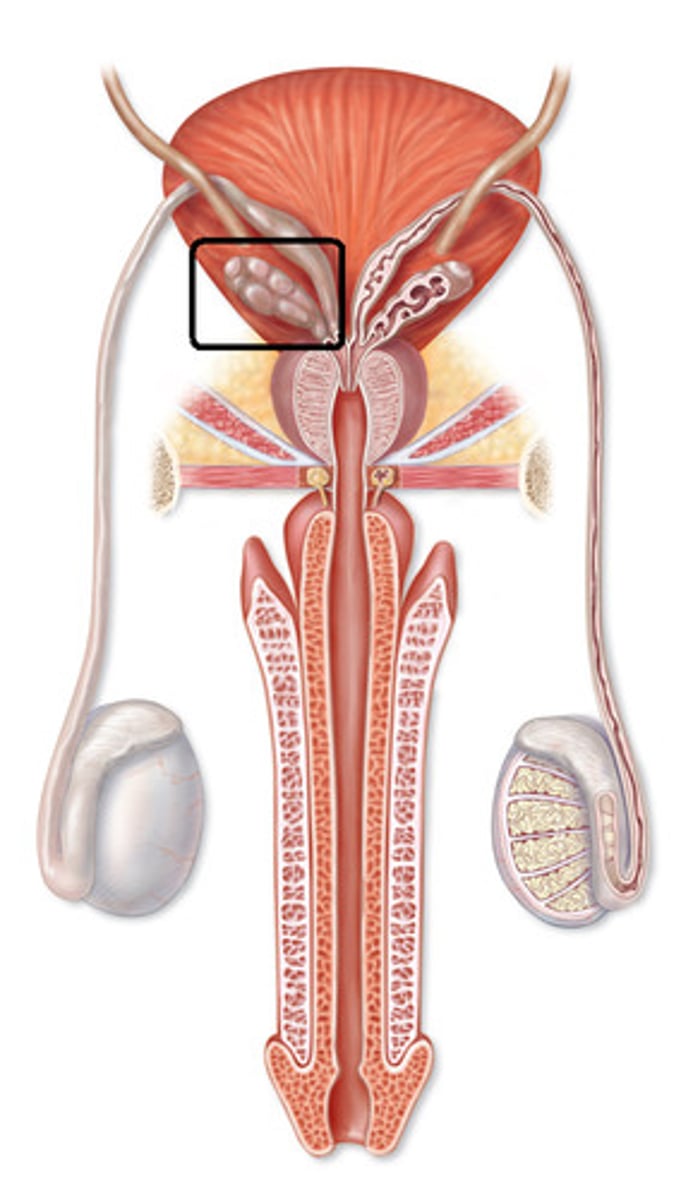
Seminal Vesicles
Two small glands aka. BUNNY EARS
- Produce fructose to provide energy for mature sperm
- Produce prostaglandins: hormones that have local effects; they initiate smooth muscle contractions (even in the female reproductive system) and help sperm move towards the egg
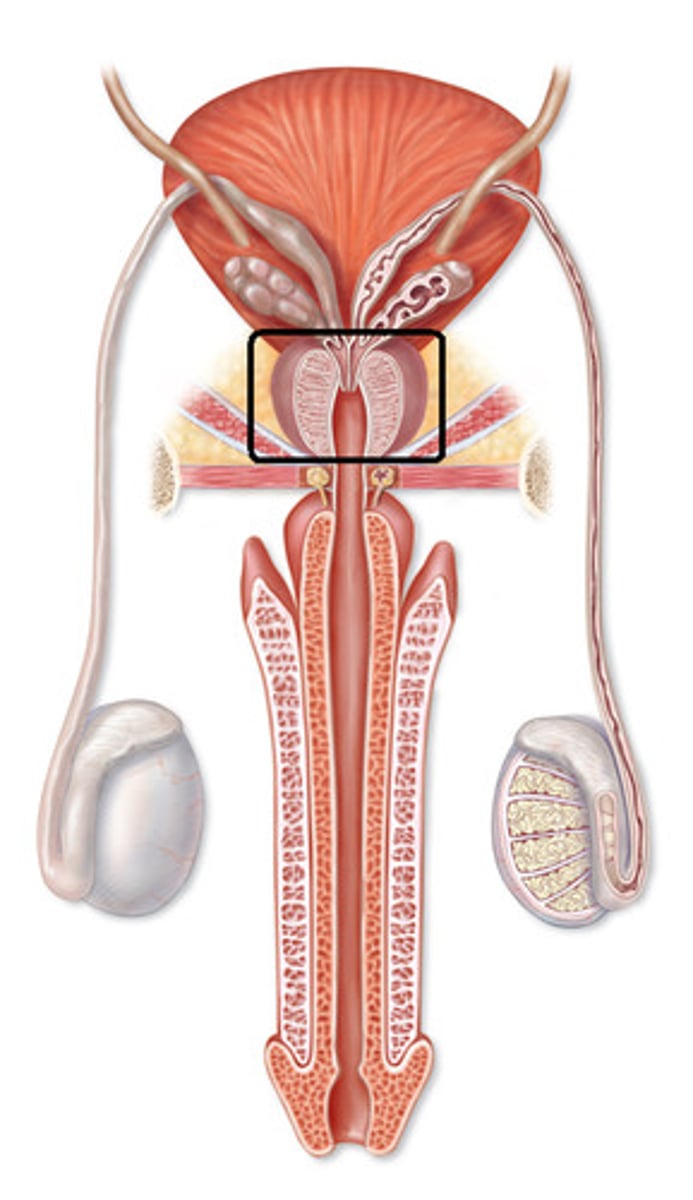
Prostate Gland
A walnut-sized gland that produces part of the semen.
- Produces an ALKALINE BUFFER to help protect against the acidity of the vagina
Also makes some mucus
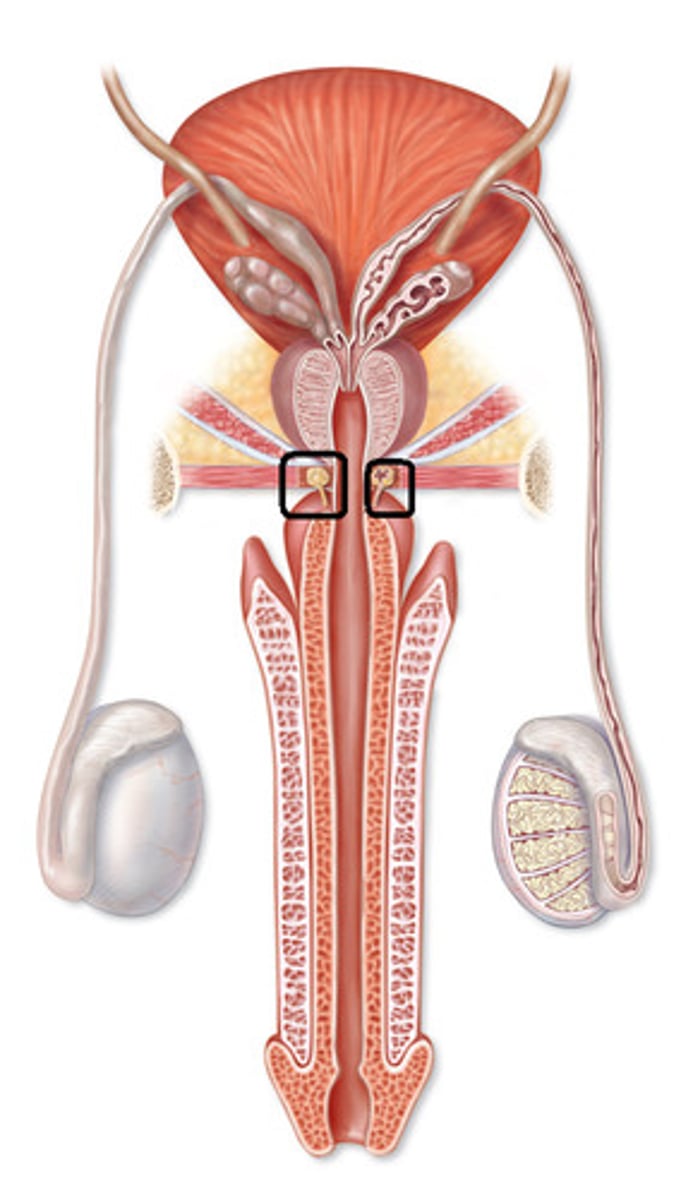
Cowper's/ Bulbourethral Gland
Located below the prostate gland and produces pre-ejaculate; mucus- rich fluid that coats the urethra to protect sperm from acidity.
Penis
- Made of erectile tissue which fills with blood upon sexual arousal; when erect the arteries to the penis dilate and the veins constrict, when flaccid the arteries constrict and the veins dilate
- Parasympathetic nervous system permits an erection and the sympathetic nervous system causes muscles to contract (orgasm) sending about 5mL of semen out of the urethra
SPERM ONLY LIVES 3 DAYS AT BODY TEMP. AND FOR YEARS AT -100
Urethra
A tube running down the middle of the penis that carries urine or semen but never both at the same time
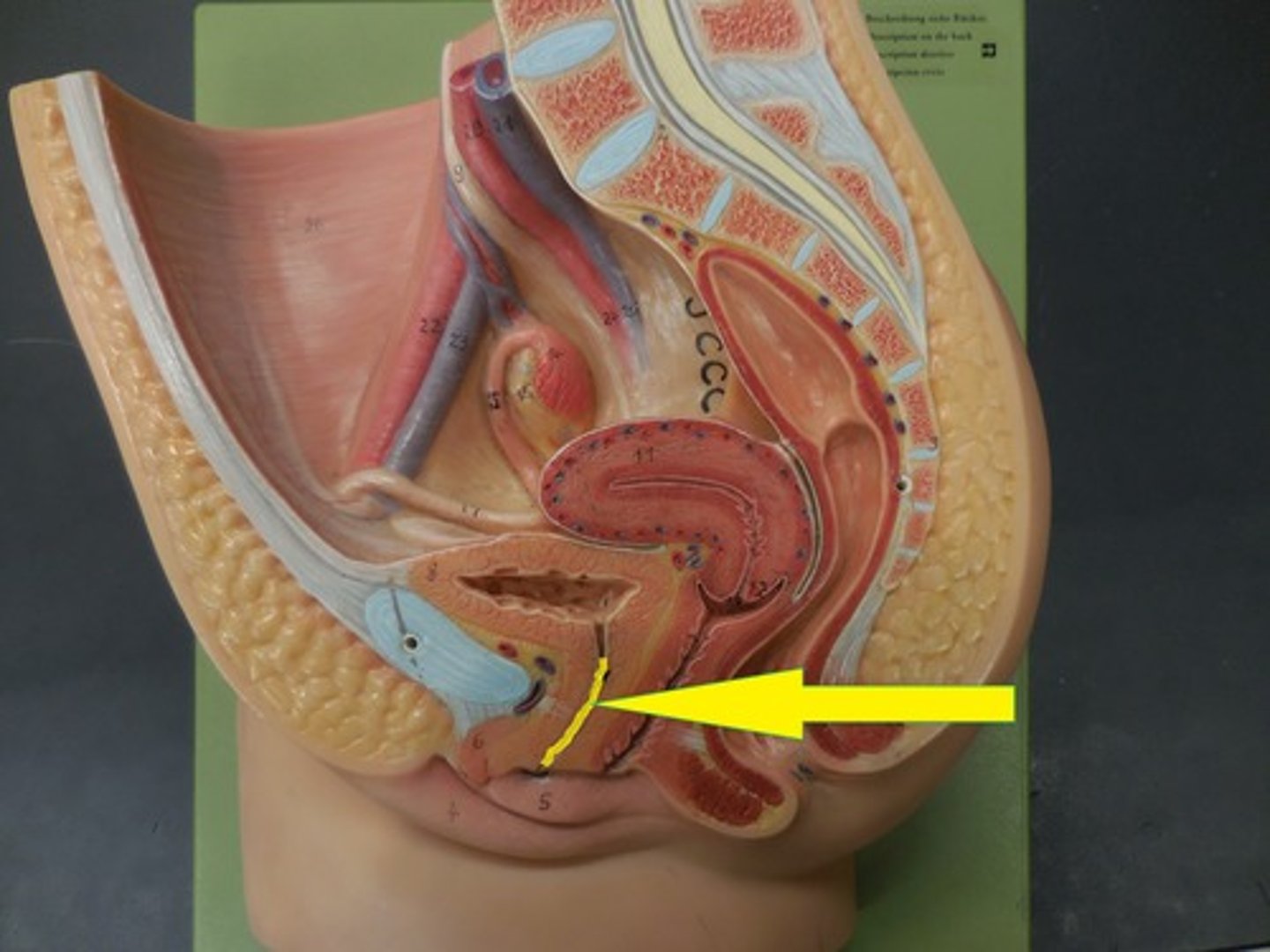
Glans Penis
The enlarged tip with many sensory nerve endings
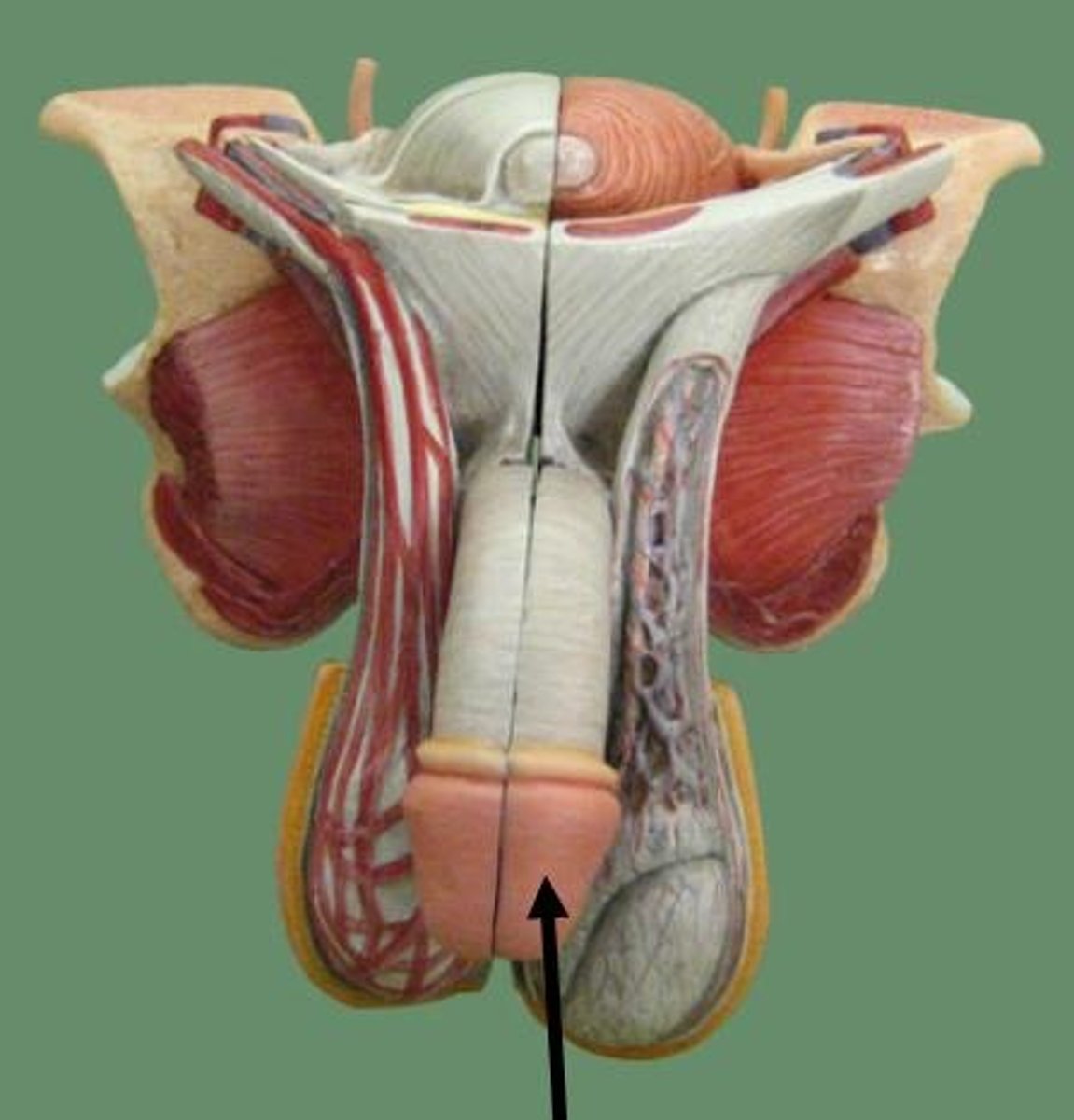
Ejaculatory Duct
Duct formed by the union of the vas deferens with the duct of the seminal vesicle; its fluid is carried into the urethra
- semen collects there seconds before ejaculation
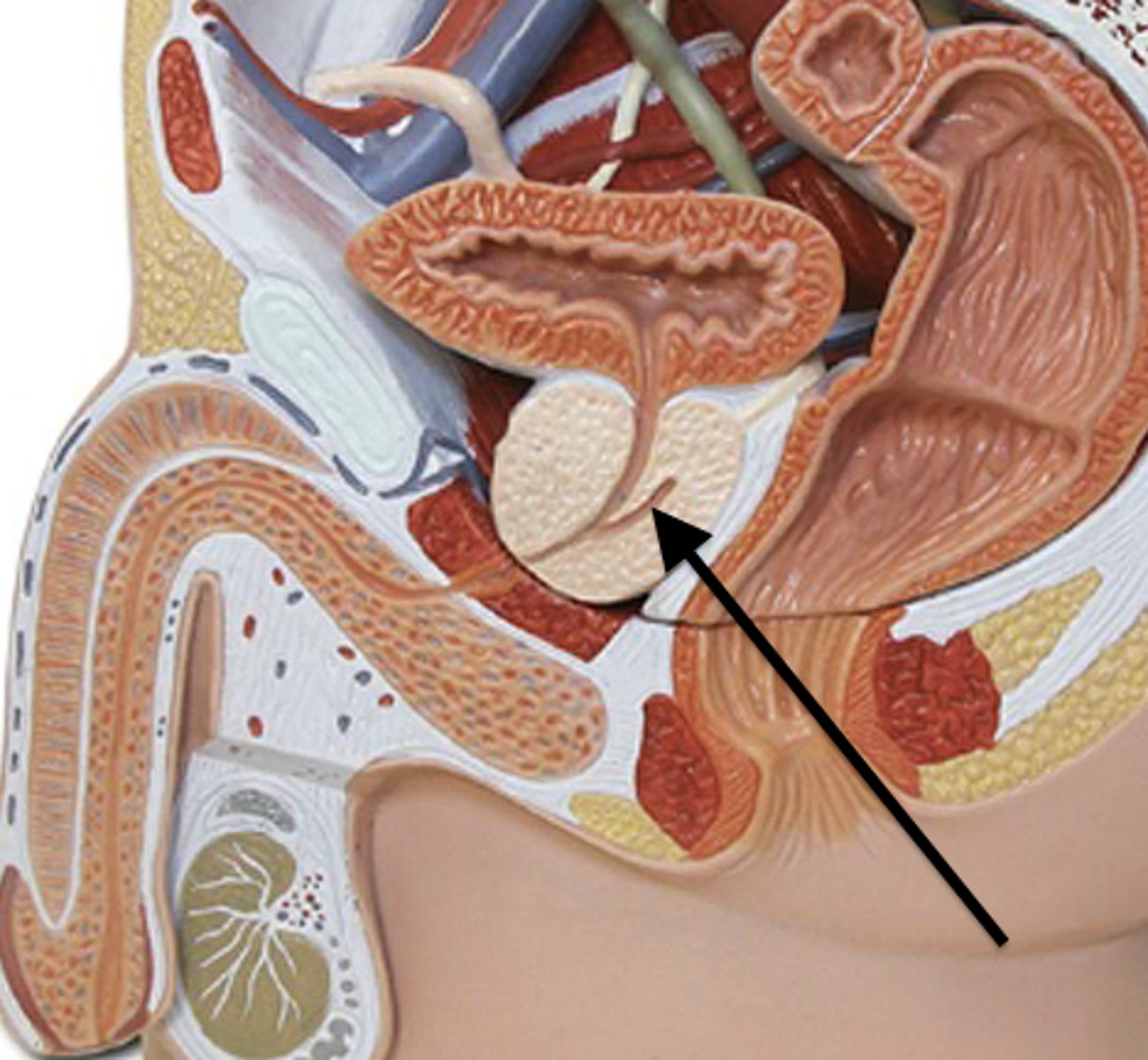
Semen
A thick fluid containing sperm and other secretions from the male reproductive system
- contains sperm and secretions from the seminal vesicles (fructose and prostaglandins), prostate (alkaline buffer), and Cowper's (bulbourethral) gland (mucus).
Male Sex Characteristics
two types, primary and secondary
Male Primary Sex Characteristics
Reproductive structures that develop in utero and are present at birth
- Due to the presence of a Y chromosome
Male Secondary Sex Characteristics
- Begin development at puberty (not born with)
- Influenced by hormones like testosterone
- Maturation related: sperm production (FSH), facial/axillary/pubic hair, increase in muscle mass, aggression, maturation of penis, deeper voice (thickening of larynx), fat deposits on abdomen, coarse skin, increase in metabolism, sex drive, etc...
Causes of male infertility
1. Hormonal: incorrect levels of FSH (for example) due to a malfunctioning endocrine gland, tumors, compounds in the environment etc...
2. Other Causes:
- blocked vas deferens (sperm can't get from epididymis to ejaculatory duct) ex. congenital or scarring from an STI
- injury/ inflammation
- extreme heat (undescended testes, fever)
- drugs/ medications (ex. chemotherapy)
- impotence (inability to get an erection); due to parasympathetic nerve damage, blood flow issues, alcohol, drugs, stress
- reduced sperm mobility
Sperm
Male gamete
- hormone for development = FSH
Carries limited energy reserves
- energy source during development = sertoli cells
- energy source during journey = fructose from seminal vesicles
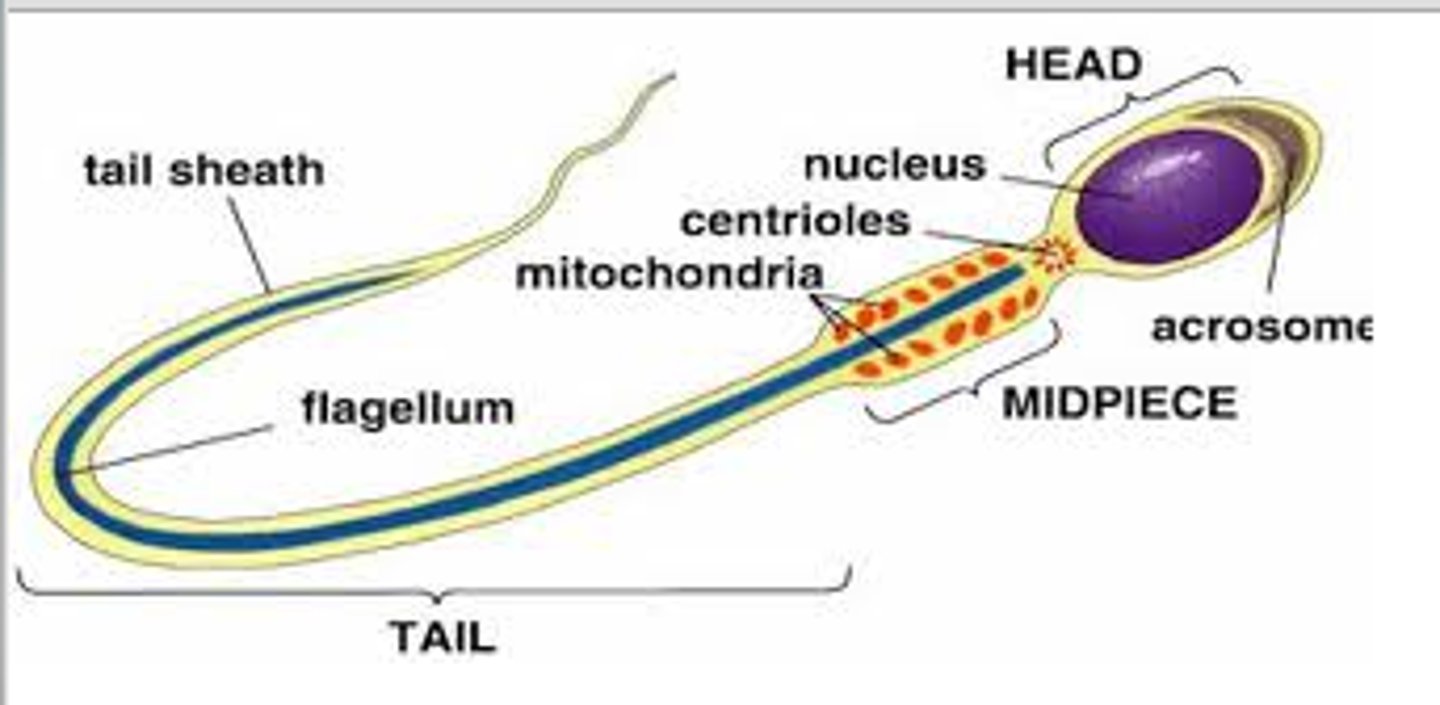
Sperm Structure
head, midpiece, flagellum
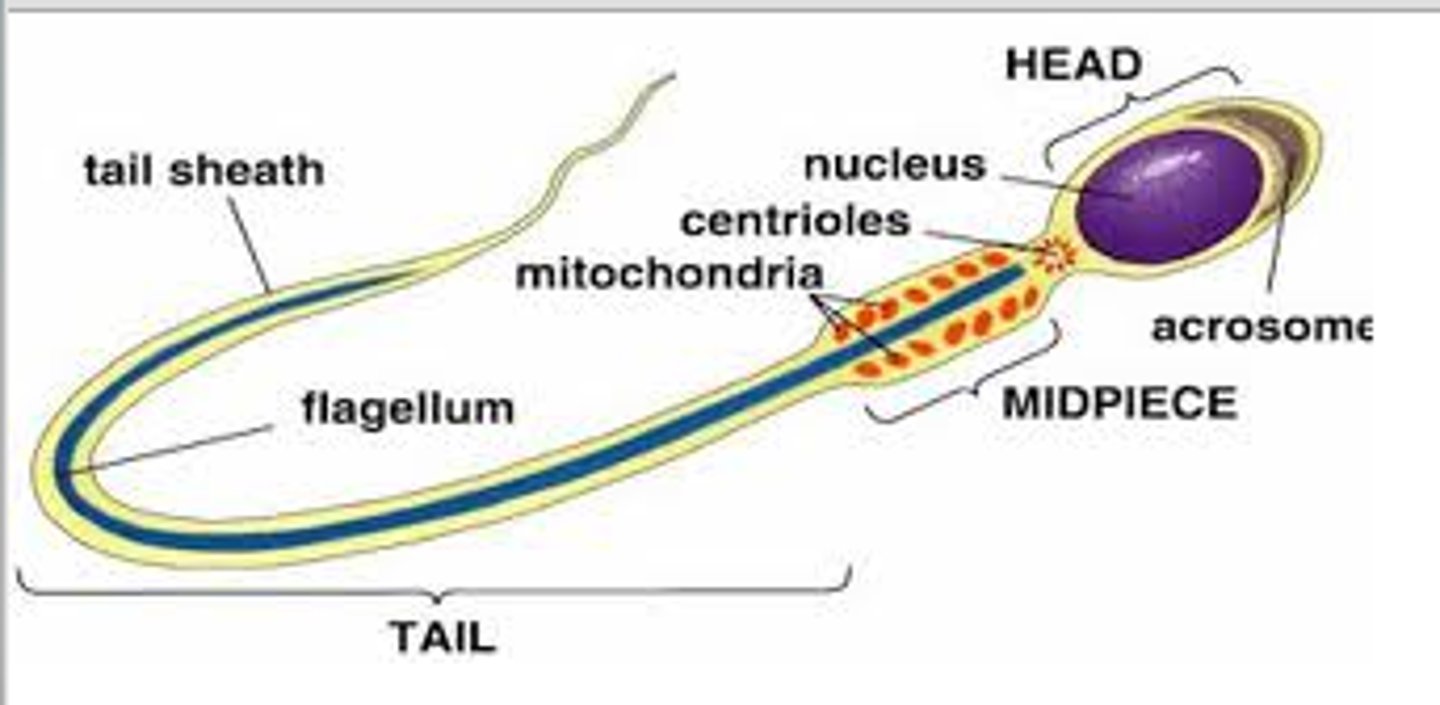
Head
- contains the nucleus (DNA)
- cap on top contains the acrosome which is full of digestive enzymes that dissolve the eggs outer shell
- only one sperm gets in per one egg
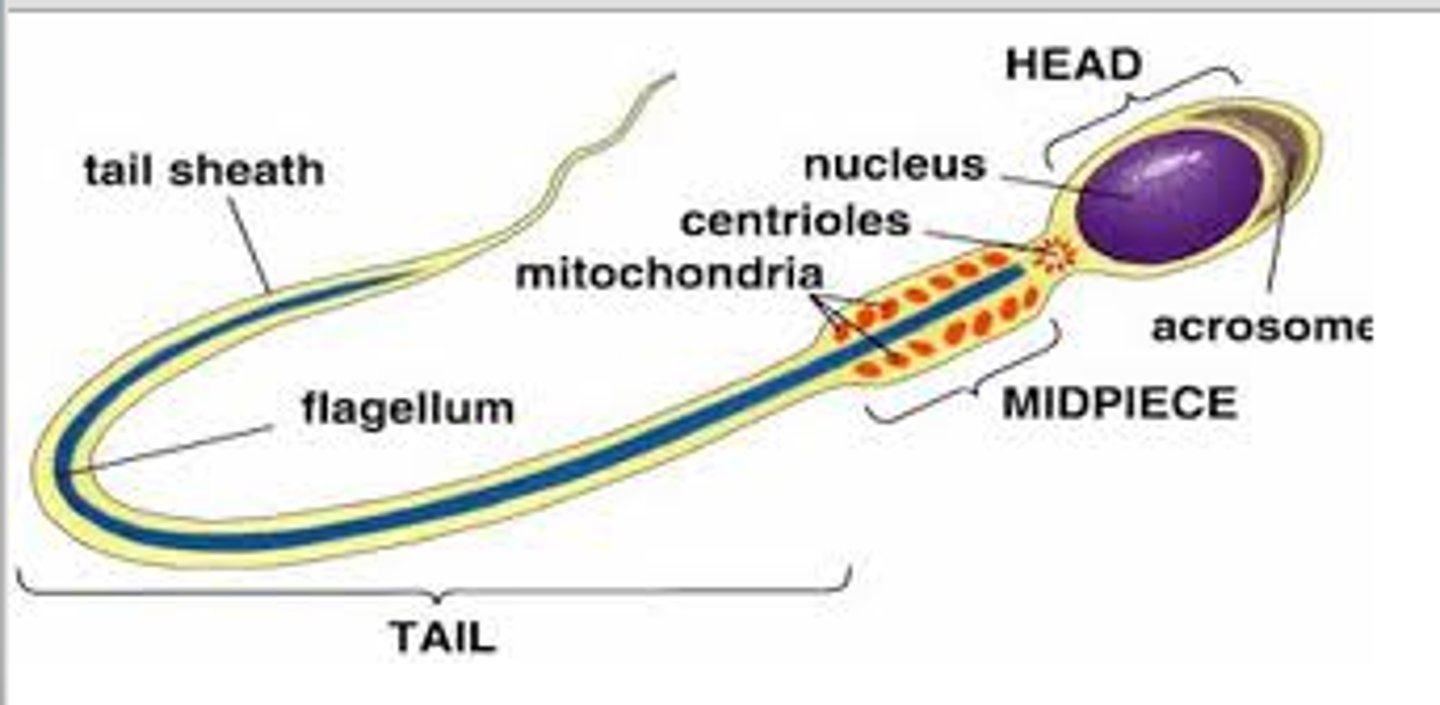
Acrosome
A region at the head of a sperm cell that contains digestive enzymes which, when released during the acrosome reaction, can facilitate penetration of the outer shell of the egg, and subsequently, fertilization
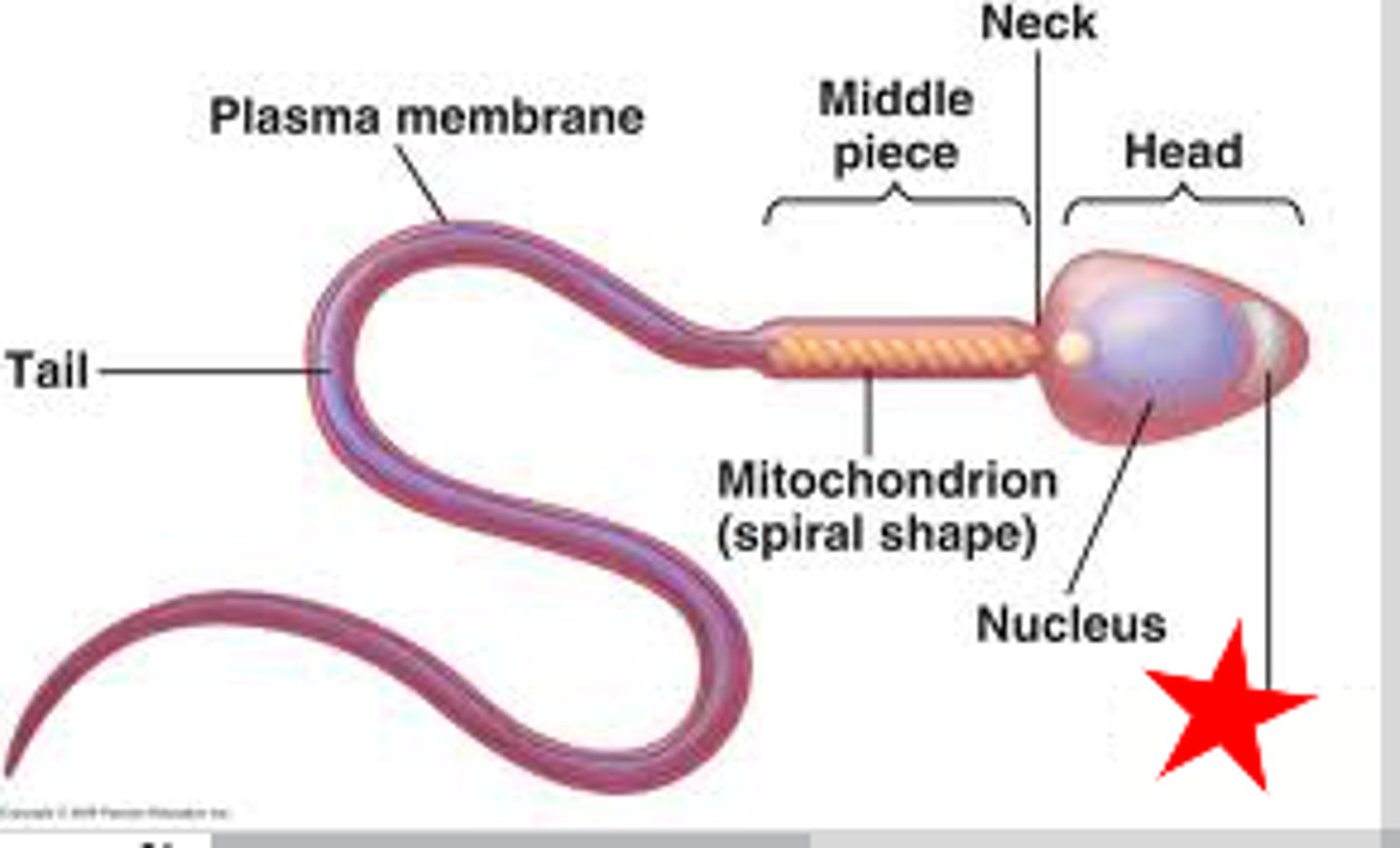
Midpiece
The portion of the tail of a sperm closest to the head, containing mitochondria that make ATP for the tail
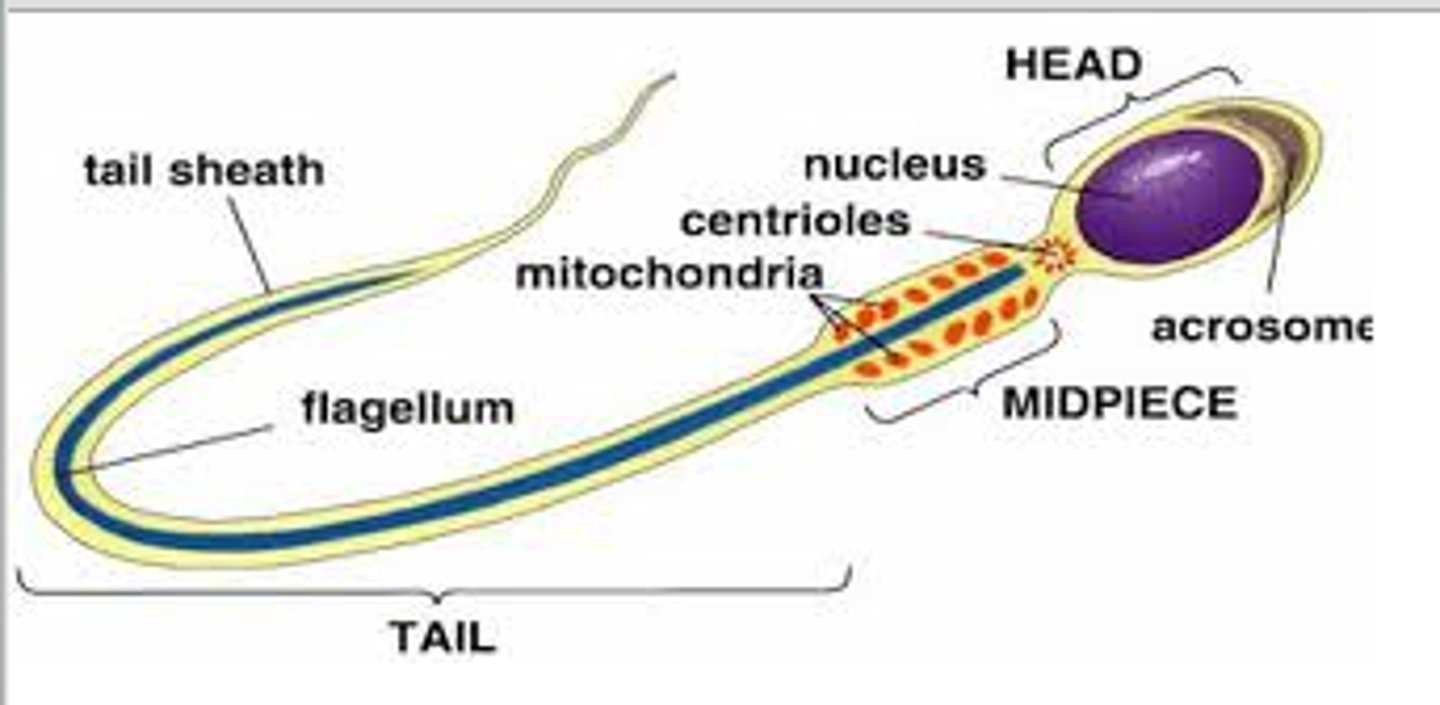
Tail
whip-like flagellum
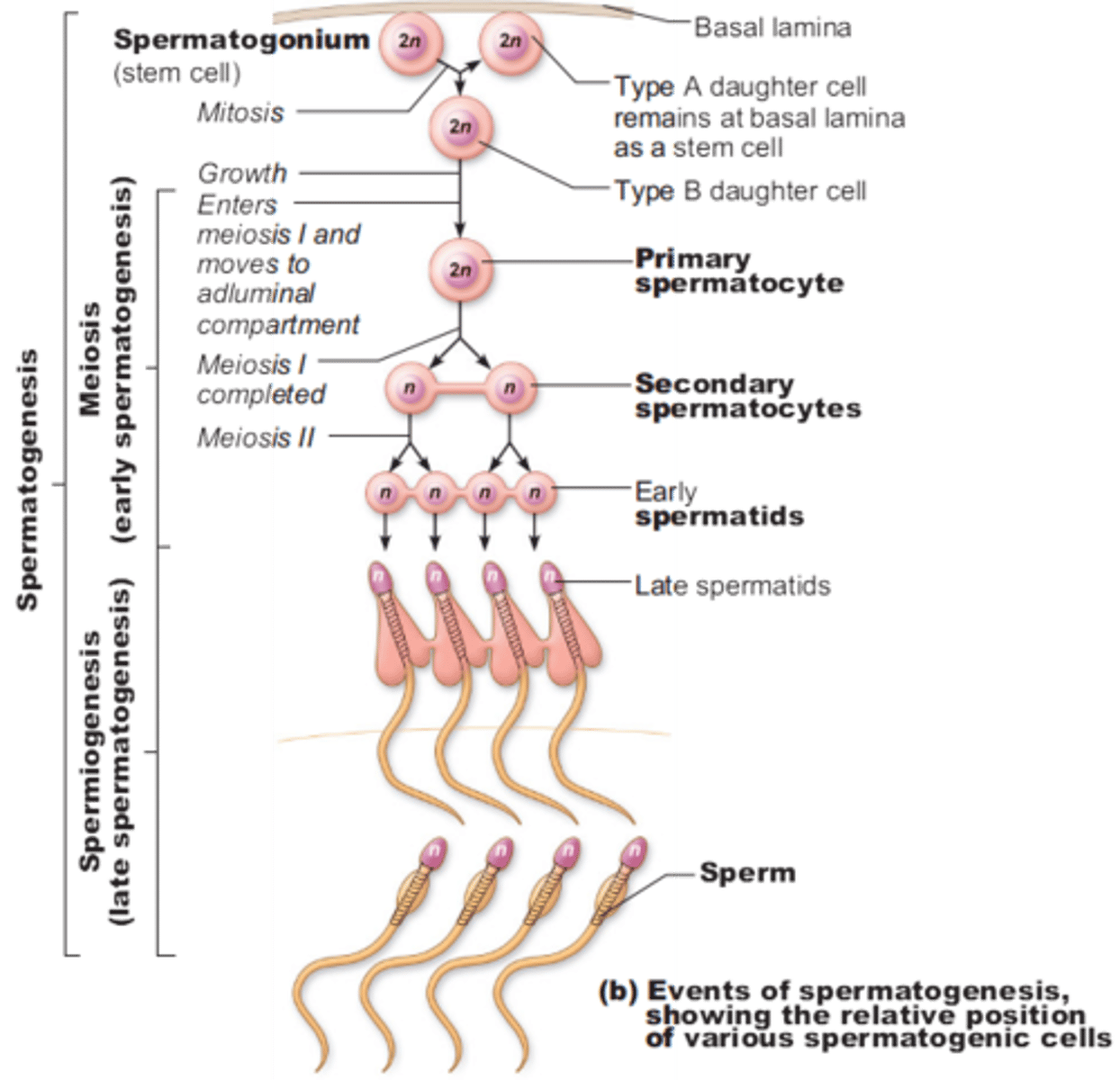
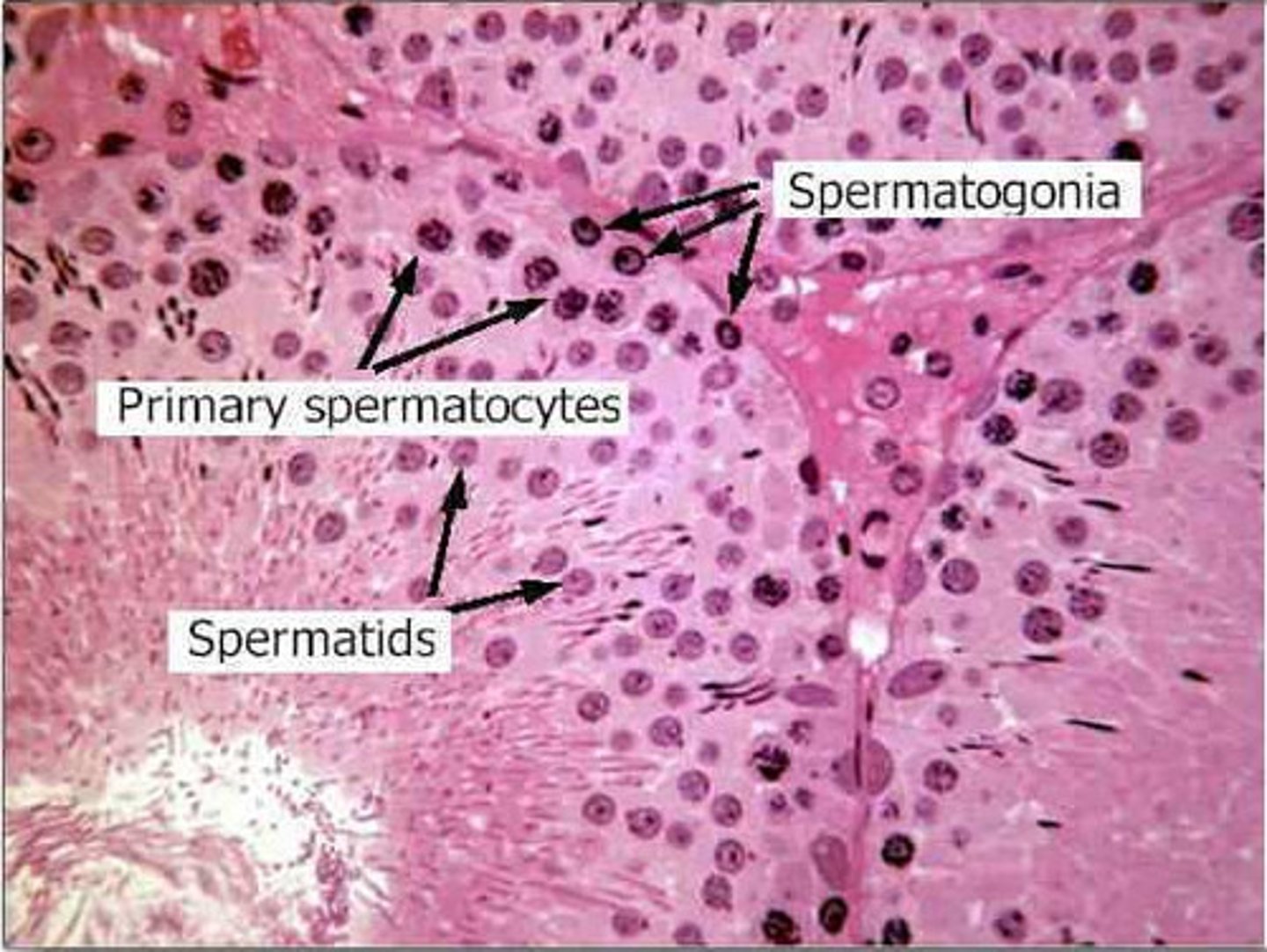
Spermatogenesis Stages
1. Spermatogonia
(i wanna become a sperm today)
2. Primary spermatocyte
(meiotic division 1)
3. Two Secondary spermatocyte
(meiotic division 2)
4. Four Spermatid
(doing some rearranging)
5. Four Spermatozoa
Spermatogenesis
The production of sperm cells
- Spermatogonia surround the edges of each seminiferous tubule note: males always make more and more identical spermatogonia through mitosis
- As spermatogonia develop into sperm they move towards the middle of the tubule
- Development of sperm = process of meiosis
- The chromosome number is halved when the primary spermatocytes become secondary spermatocytes
note: 1 primary spermatocyte (46 chromosomes) creates 4 GENETICALLY DIVERSE sperm (23 chromosomes)
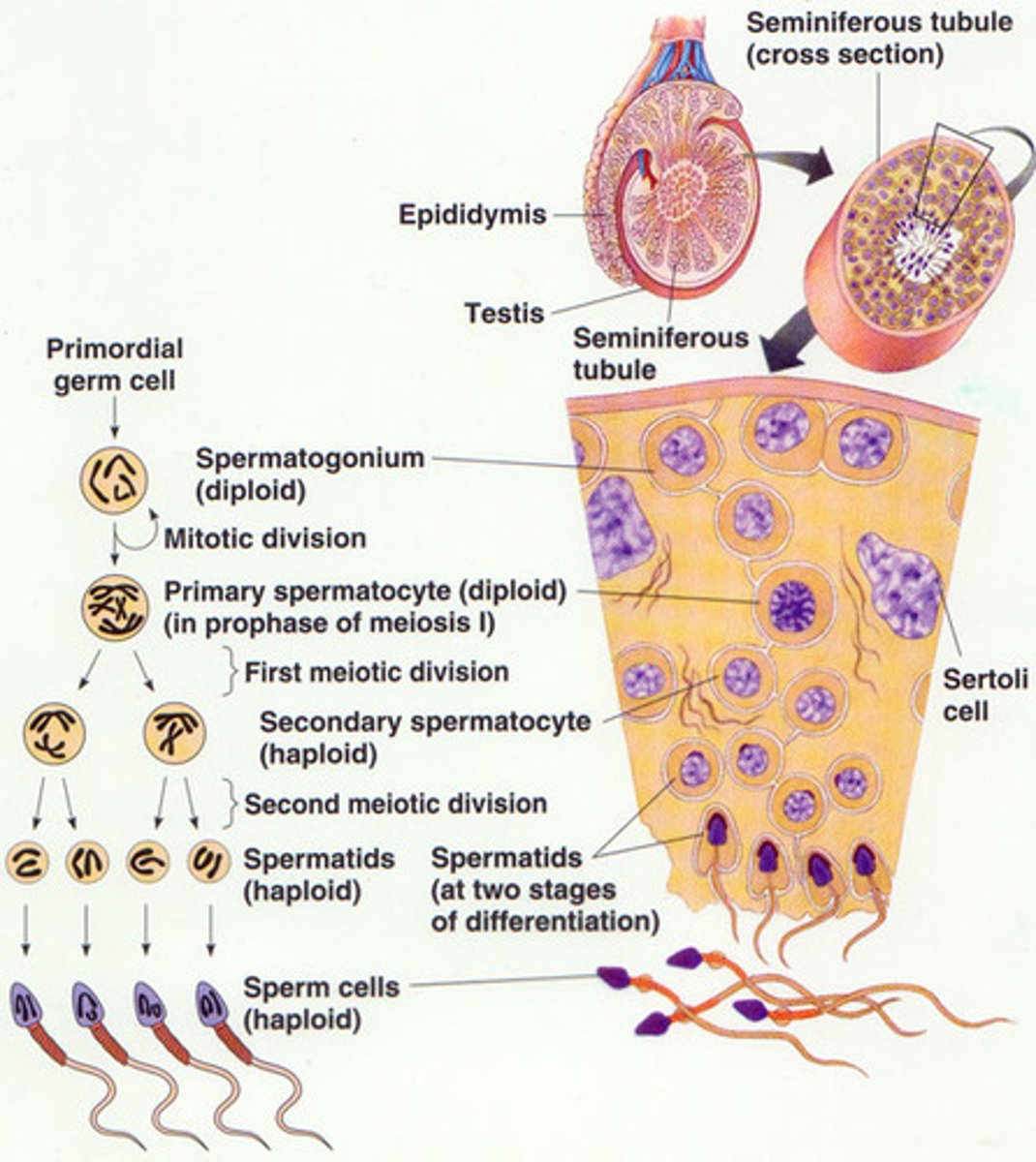
Inside the seminiferous tubules
.
Gamete
= sex cell = sperm (male) = egg (female)
Meiosis
= making gametes = gametogenesis = spermatogenesis (male) = oogenesis (female)
Diploid Cell
A cell containing two sets of chromosomes (2n), one set inherited from each parent.
= 2n cell = full chromosome number
ex. 46 chromosomes for humans
ALL SOMATIC CELLS ARE "2n" ONLY GAMETES ARE "n"
Haploid Cells
A cell containing only one set of chromosomes - gametes
= n cell = half chromosome number
ex. 23 chromosomes for humans
ONLY GAMETES
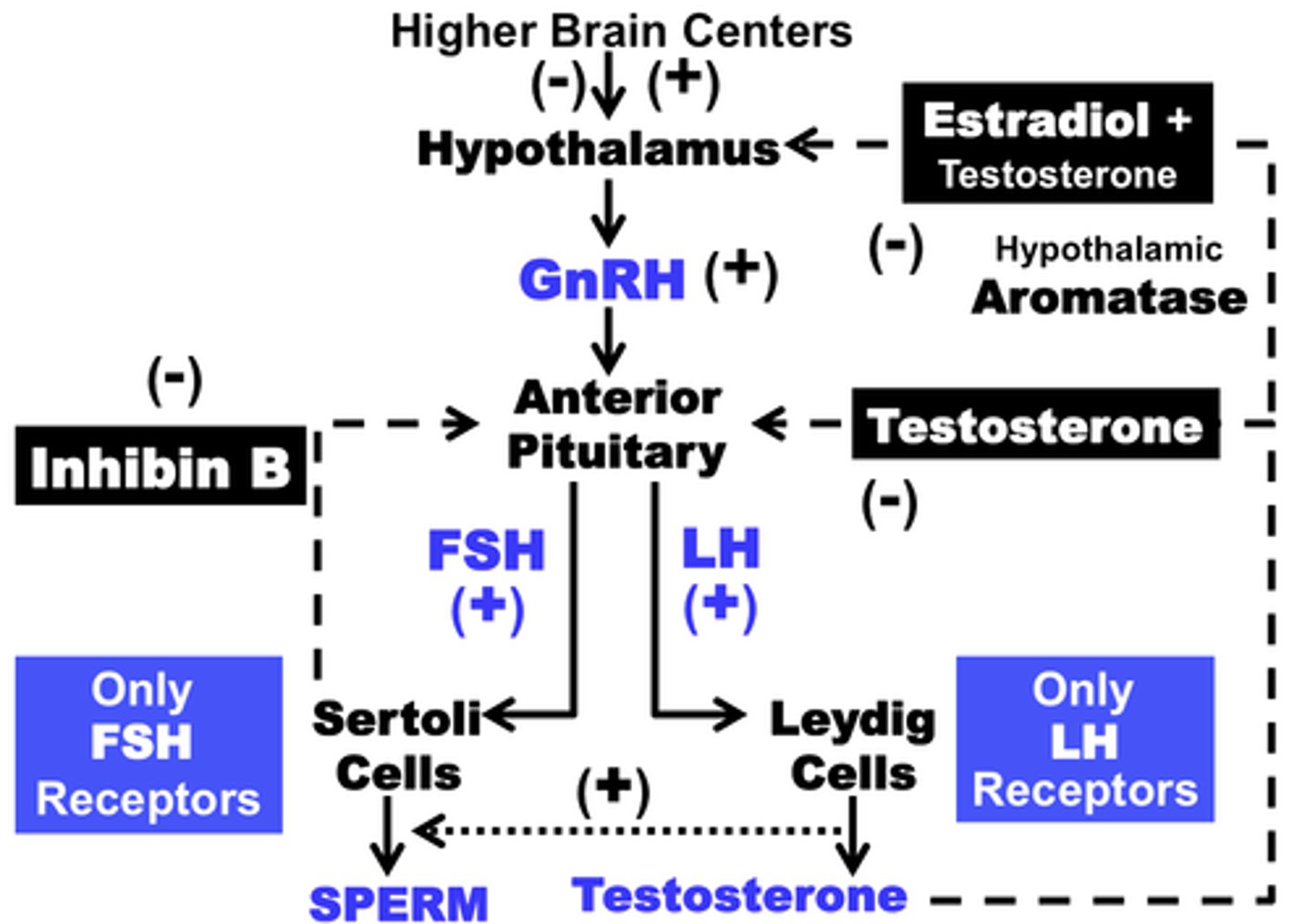
Male Negative Feedback Loop
stimulus: puberty
hypothalamus releases GnRH
pituitary releases FSH and LH
FSH stimulates sertoli cells to aid in spermatogenesis and LH stimulates interstitial cells to release testosterone
result: spermatogenesis and testosterone to give an extra kick
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK ARROWS GO FROM TESTOSTERONE TO PITUITARY AND HYPOTHALAMUS AND INHIBIN IS SENT FROM SERTOLI CELLS TO PITUITARY
GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone)
A hormone secreted by the hypothalamus that regulates the pituitary's secretion of gonad-stimulating hormones; LH and FSH
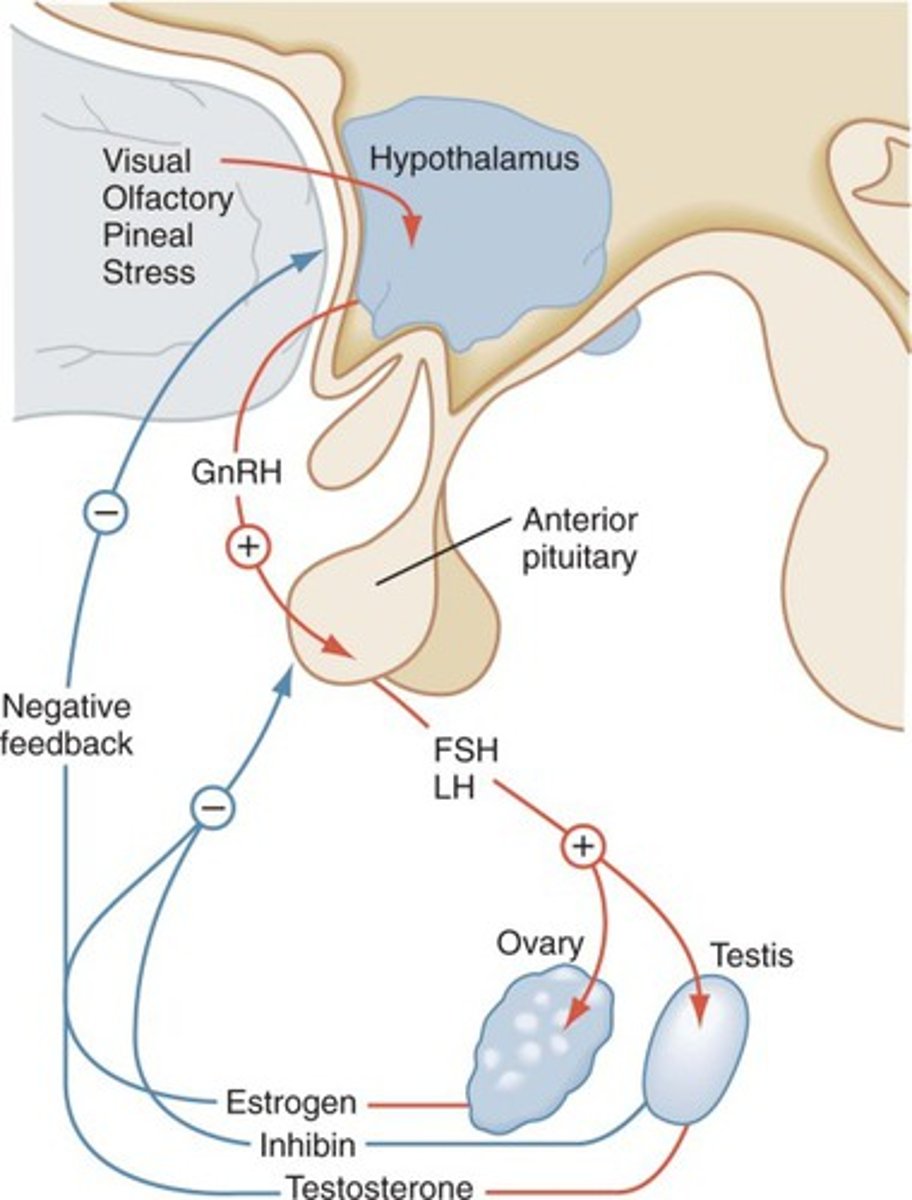
LH (luteinizing hormone)
A hormone located in the pituitary that is released and stimulates interstitial cells to produce and release testosterone
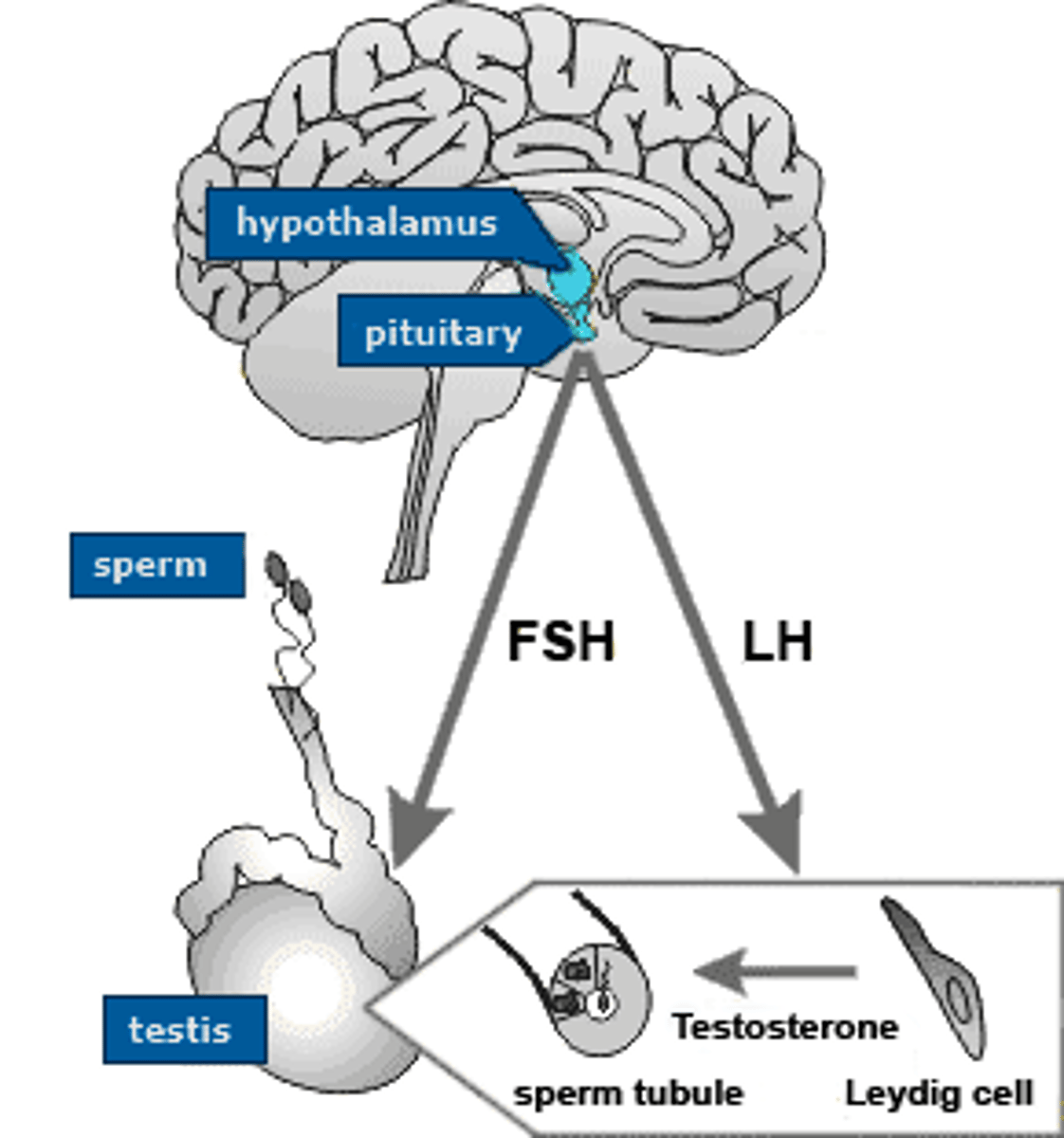
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
Located in the pituitary and is released to stimulate sertoli cells to aid in the production of sperm aka. spermatogenesis
Testosterone
Produced by interstitial cells and stimulates spermatogenesis, promotes and regulates the development of secondary sex characteristics and is associated with sex drive levels
Inhibin
Acts directly on the pituitary to selectively suppress the secretion of FSH, released by sertoli cells
Female Reproductive System
Organs that produce and transport egg cells and secrete female hormones, as well as, provides a place for a baby to grow
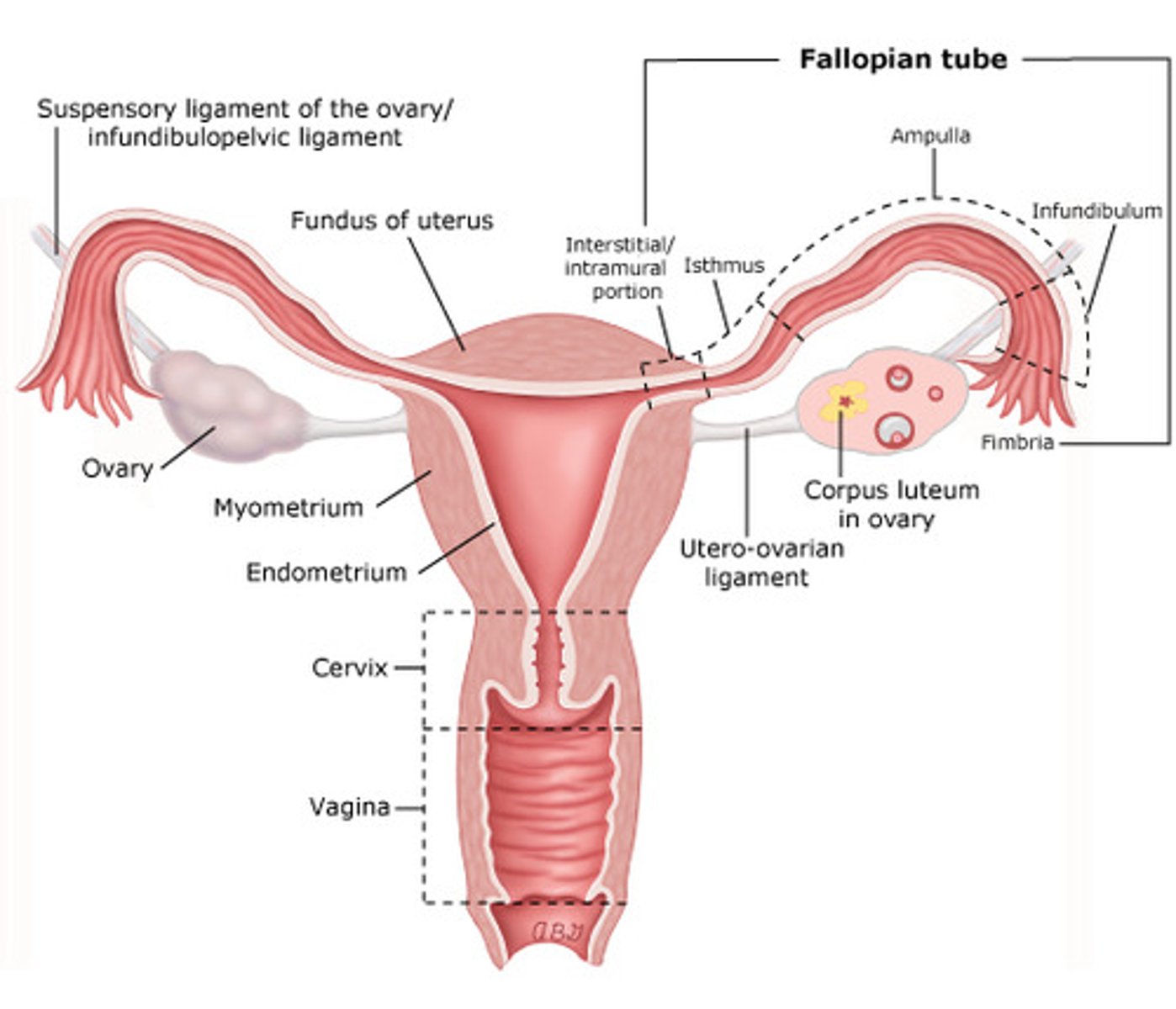
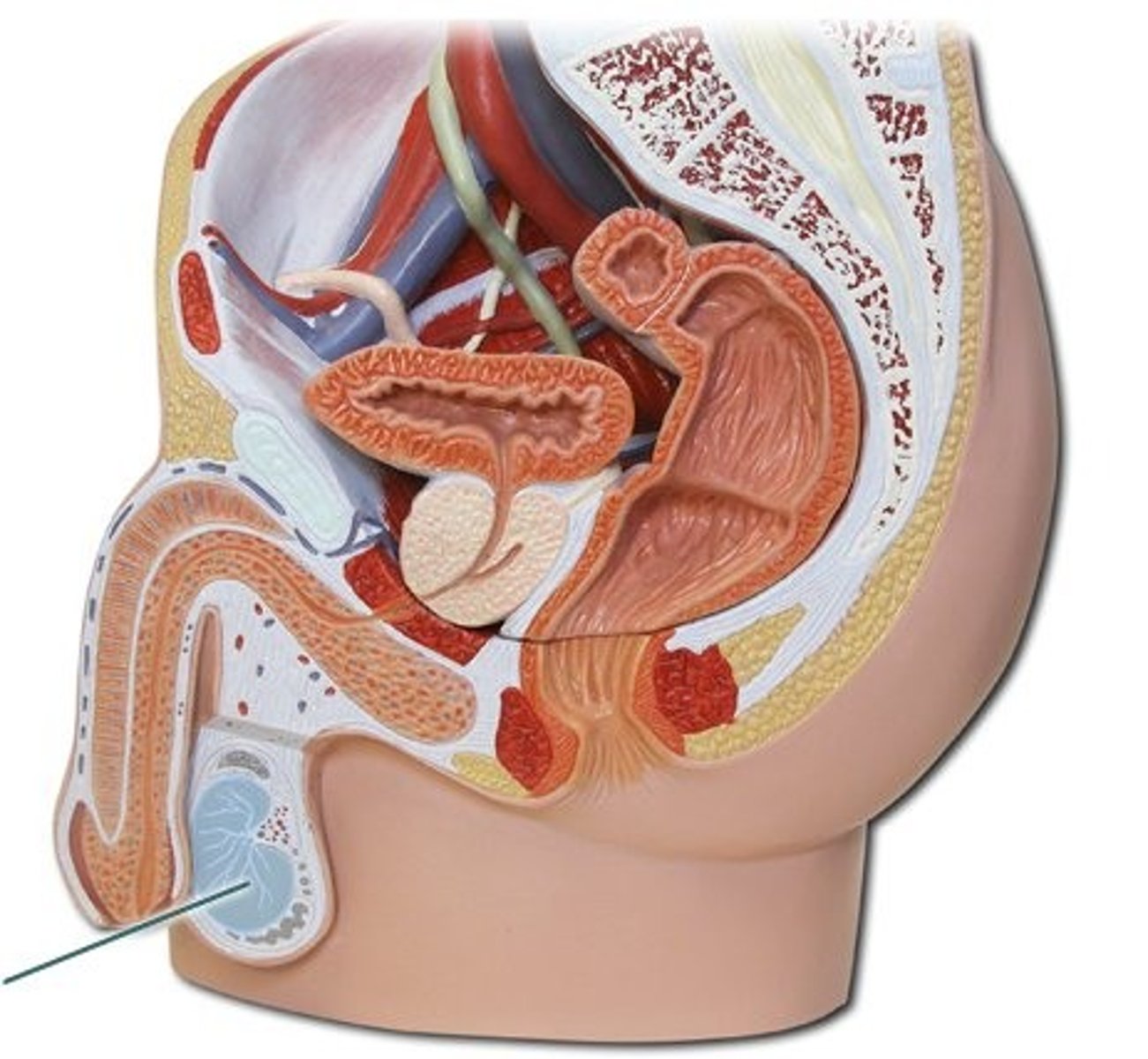
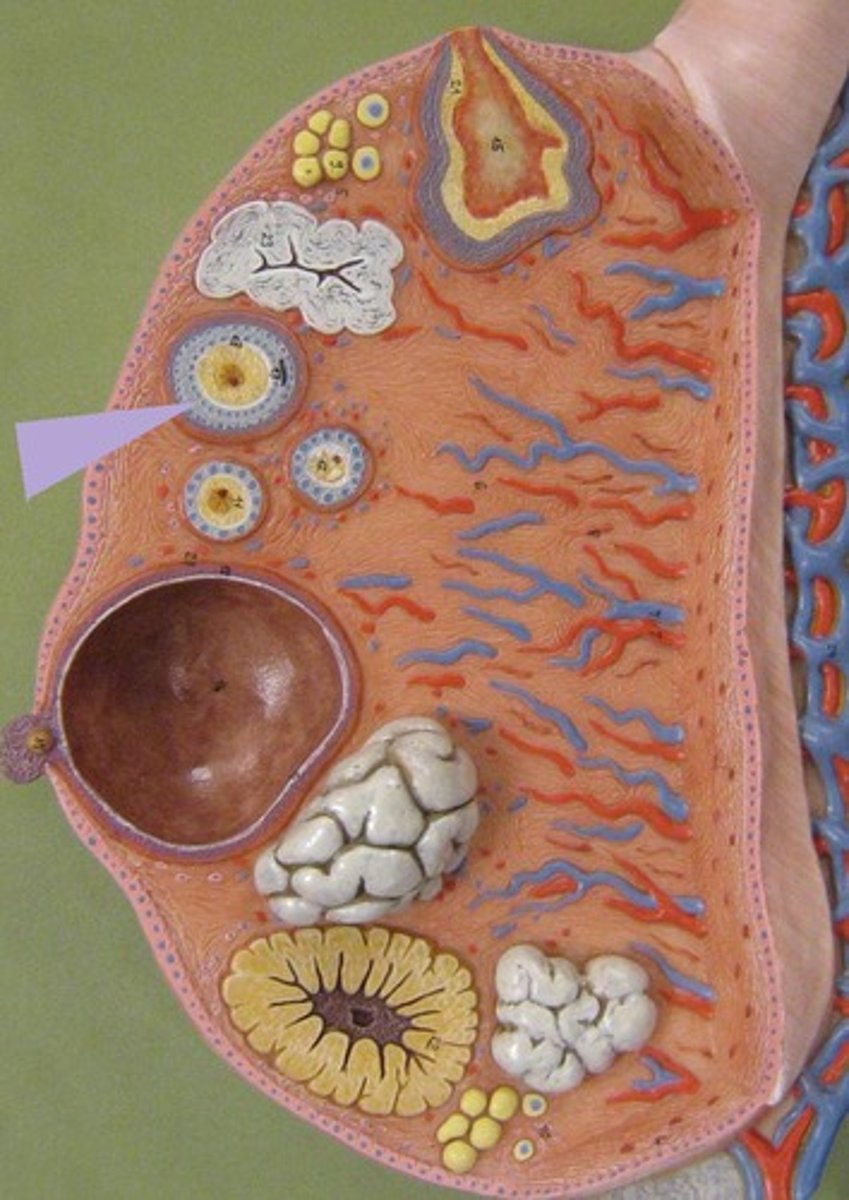
Ovaries
Glands that produce the egg cells and hormones
- Full of groups of cells called follicles ("flowers")
- Inside of the follicle = egg cell (oogonium, oocyte, ovum)
- 1 mature egg is ovulated every 28 days from puberty up until menopause
- Outer follicle cells make 2 female sex hormones: estrogen and progesterone
Follicles
Clusters of cells surrounding a single egg. Its function is to help an egg mature for release into the reproductive tract, where it can be fertilized
- 3 functions: produce the egg, estrogen and progesterone
Estrogen
The female sex hormone that signals certain physical changes at puberty and controls the maturation of eggs; produced in the outer follicle cells
Progesterone
A hormone produced by the ovaries which acts with estrogen to bring about the menstrual cycle.
- hormone produced by the corpus luteum in the ovary and the placenta of pregnant women
- prevents uterine contractions
think "pro-gestation" and/or "pro-pregnancy"
Fallopian Tube
- Transports the egg from the ovary to the uterus
- Fimbria sweep in the egg after its been ovulated
- Fertilization occurs here
- Egg must be fertilized within 24 (or it dies)
- Tubal ligation aka. "tubes tied" = permanent birth control
Causes of Female Infertility
-reduced sperm transport
-antibodies to sperm
-tubal blockage
-failure to ovulate
-poor quality eggs
-failure to implant
-pregnancy loss (miscarriage)
1. hormonal deficiencies
2. block/scarred fallopian tubes from STIs
Uterus
- Where the fertilized ovum (zygote) will implant and develop
zygote to embryo to fetus to baby
- 2 Parts to this organ:
a. myometrium: outer, muscular layer (contractions!), contains lots of progesterone and oxytocin receptors
b. endometrium: inner, nutrient-rich lining (blood!), nourishes the embryo or is shed every 28 days = menstruation
Cervix
- Strong muscular band at the lower end of the uterus
- Prevents the fetus from entering the birth canal prematurely
- Plugged with mucus to reduce uterine infections
- Thins and dilates 10cm when giving birth
- PAP Test: gentle sample of cervical cells to check for abnormalities (precancerous cells)- early detection has high cure rates and HPV is a virus that causes 70% cervical cancers, among many others.
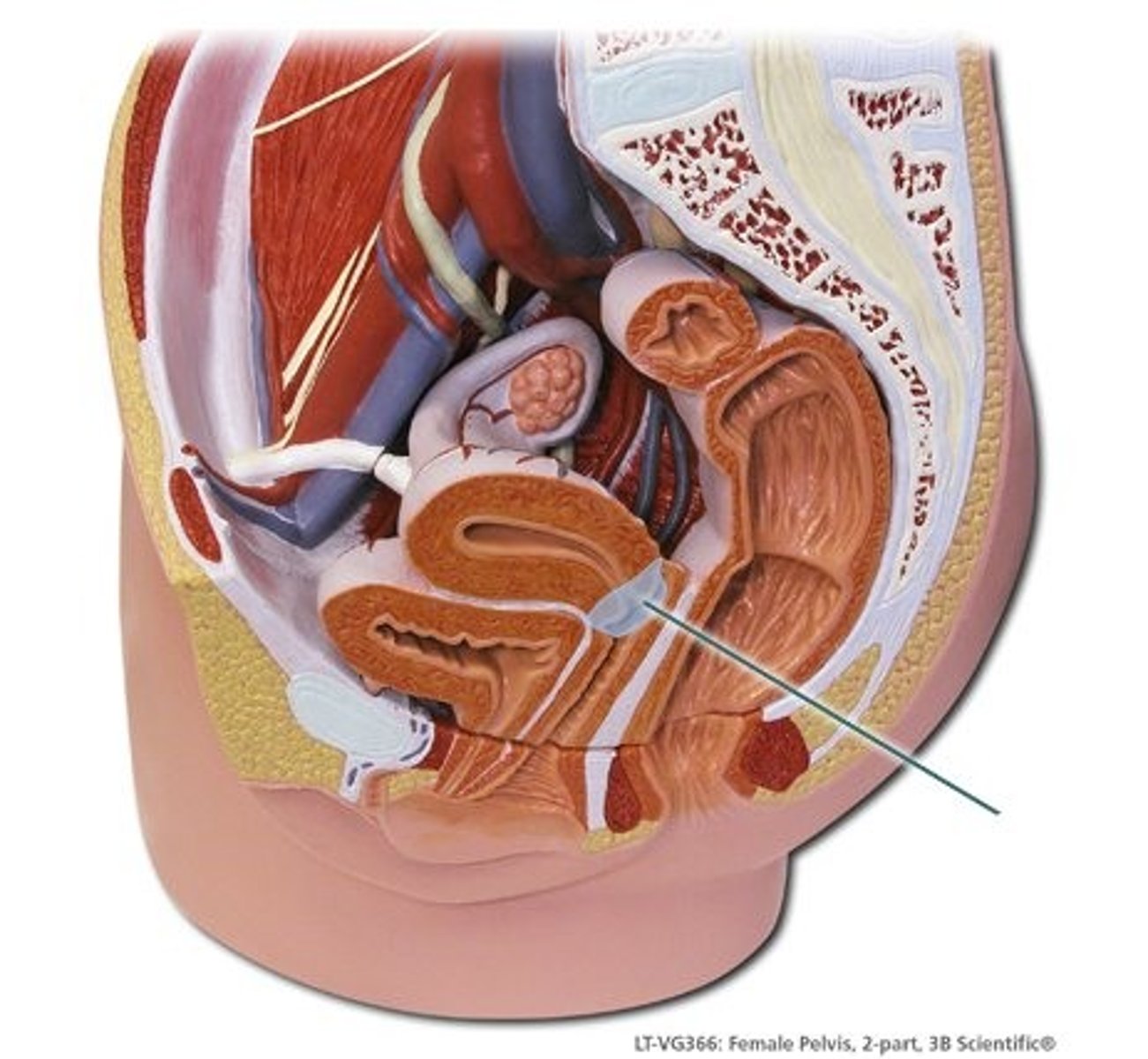
Vagina
A muscular, elastic passageway that extends from the uterus to the outside of the body.
aka. birth canal
- Muscular canal (tube) that connects the uterus to the external environment
- Sexual intercourse occurs only within this canal
- Acidic; "hostile environment" to invading microbes
- Also has its own useful microbes for defence against infections
Female Sex Characteristics
Two types: primary and secondary (relies on estrogen)
Female Primary Sex Characteristics
ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina
- Reproductive structures that develop in utero and are present at birth
- Due to a LACK of Y chromosome
Female Secondary Sex Characteristics
- Begin development at puberty
- Influenced by hormones, especially estrogen
- Development/ thickening of ENDOMETRIUM (right after menstruation is done)
- Growth of mammary tissue
- Fat deposits on hips, thighs, breasts, etc...
- Maturation of vagina, etc...
- Pubic and axillary hair (actually due to androgens- estrogen blocks facial hair!)
follicle development
Oocytes exist inside the follicle
Develop in stages when stimulated by FSH
Only 1 Follicle per cycle reaches Mature Follicle Stage
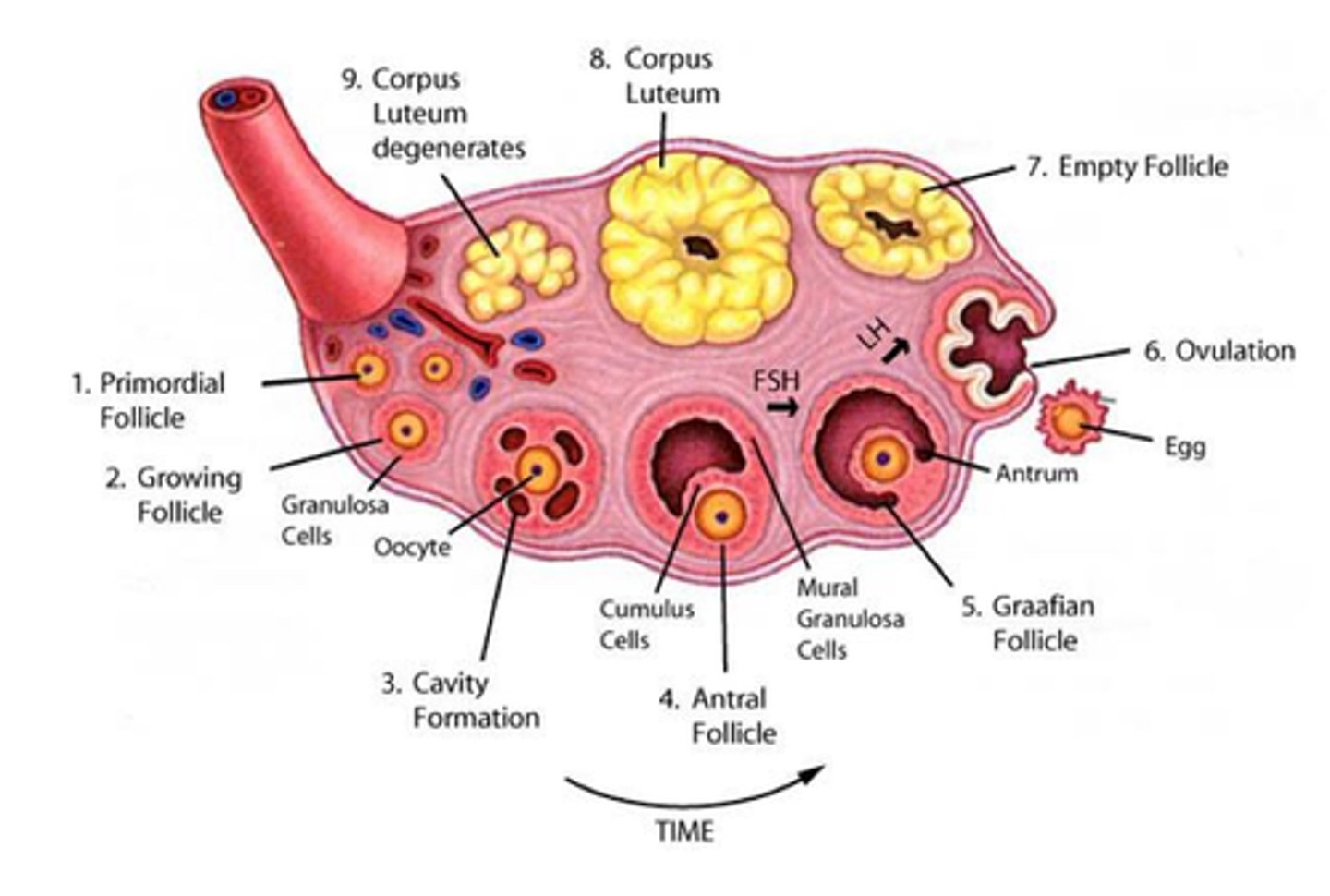
Functions of Follicle
1. Produce the Egg (ovum): by the process of oogenesis (aka. meiosis and gametogenesis), 1 egg bursts out on day 14 (when the female is most fertile); called ovulation
2. Produce Estrogen: responsible for secondary sex characteristics like developing/ "restoring/ thickening" the endometrium etc...
3. Produce Progesterone ("pro-pregnancy"): Produced only AFTER ovulation occurs and maintains the endometrium- prevents uterine contractions.
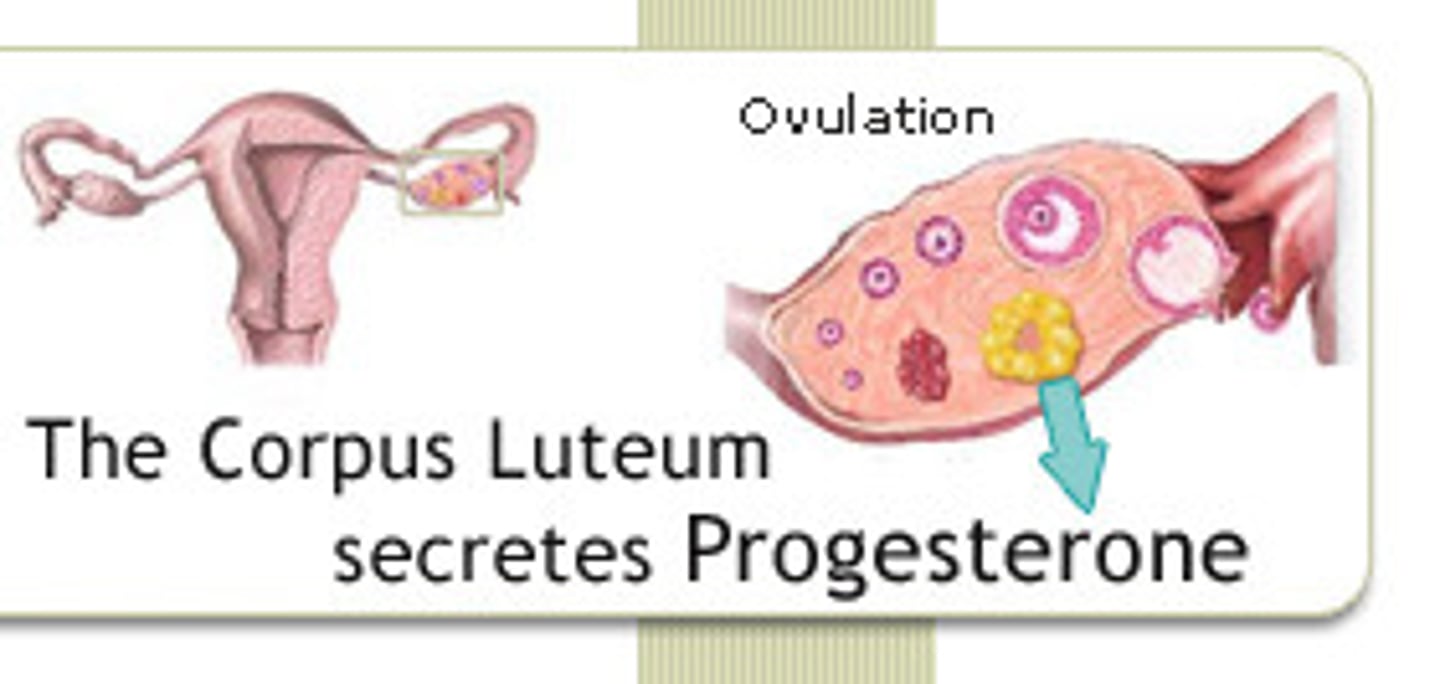
NOTE: after ovulation the eggless follicle = corpus luteum
Corpus Luteum
Endocrine tissue which produces hormones, estrogen, and progesterone which prepares the uterine lining for receiving an embryo
- EGGLESS FOLLICLE BLOB AFTER OVULATION
- ruptured follicle = corpus luteum
Ovary and Follicle Development
.
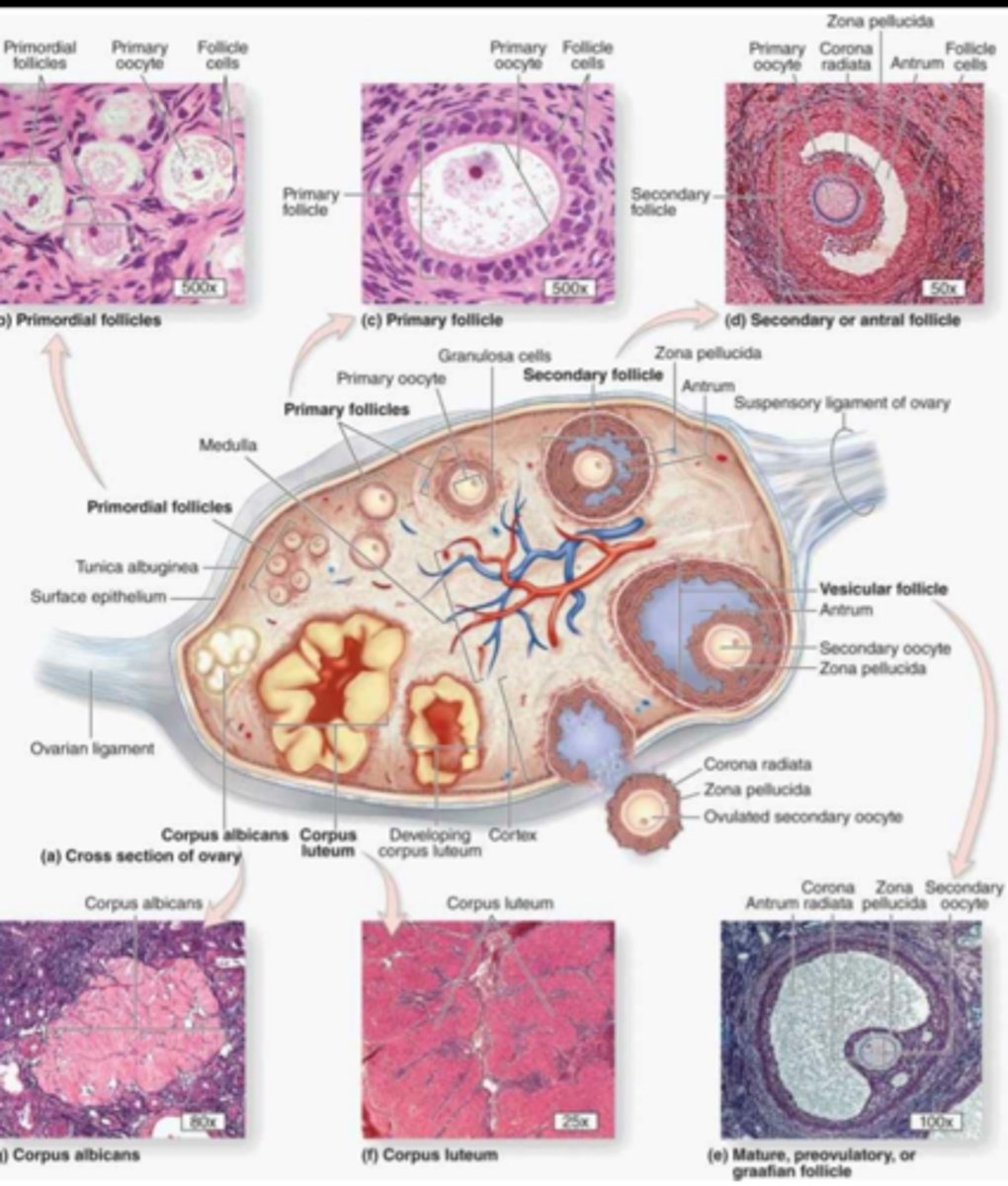
Female Hormone Negative Feedback Loop
stimulus: puberty
hypothalamus releases GnRH
pituitary release FSH FIRST and the follicle releases estrogen, then this release of estrogen sends negative feedback and positive feedback to the pituitary to stop secreting FSH and start secreting LH.
pituitary starts releasing LH which triggers ovulation and the formation of the corpus luteum which releases estrogen and progesterone which send negative feedback to the hypothalamus and pituitary and the cycle starts over again.
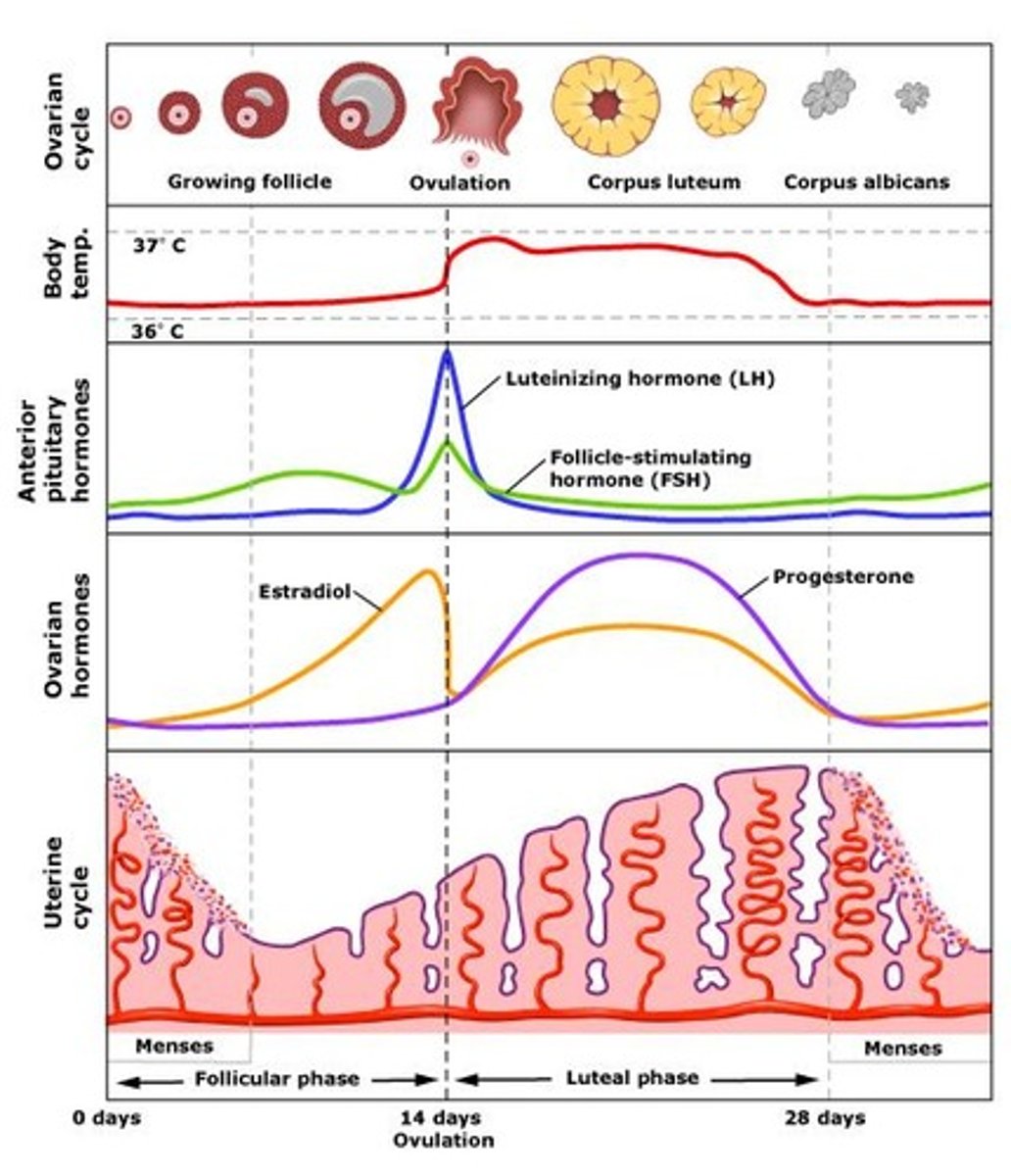
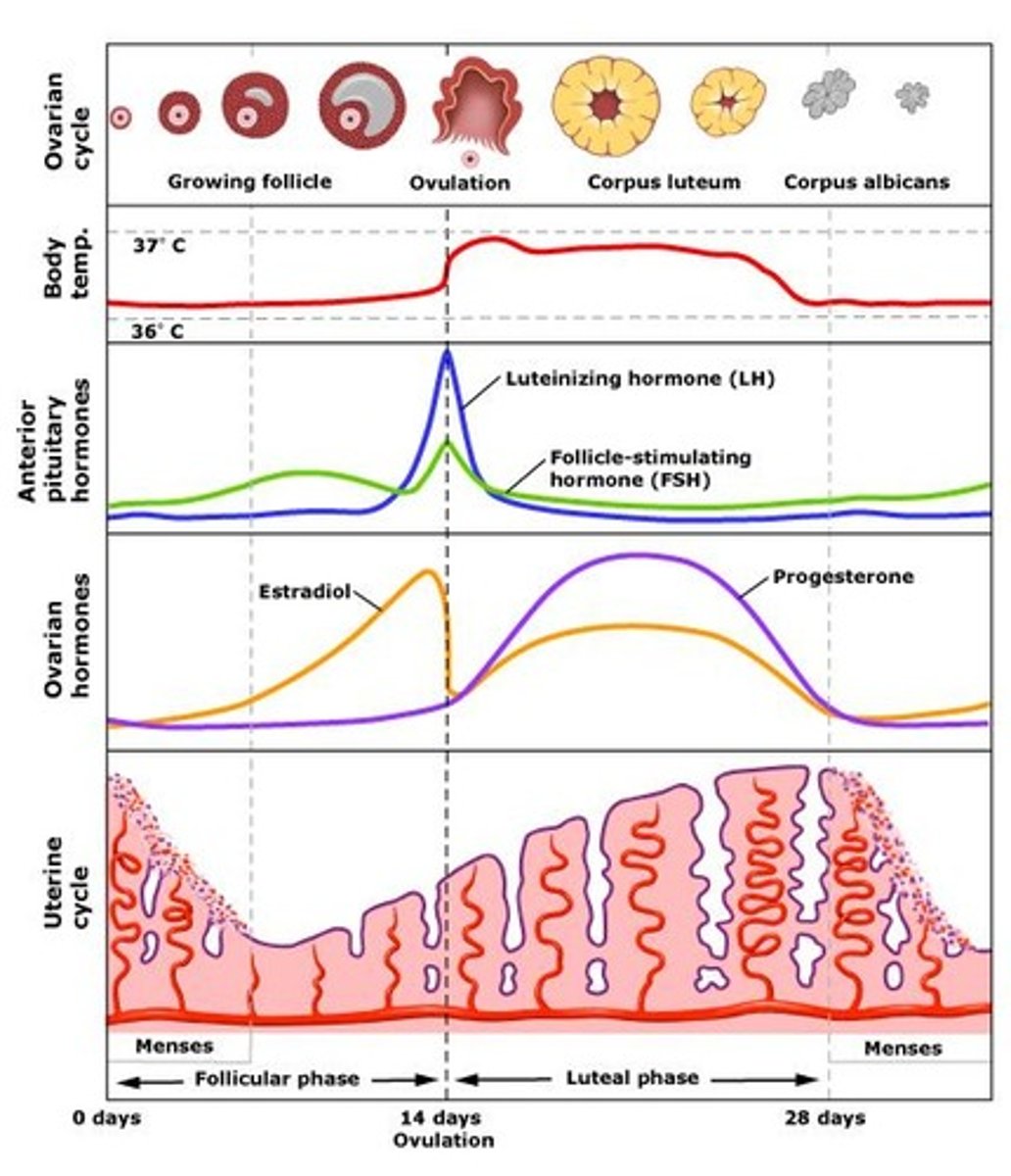
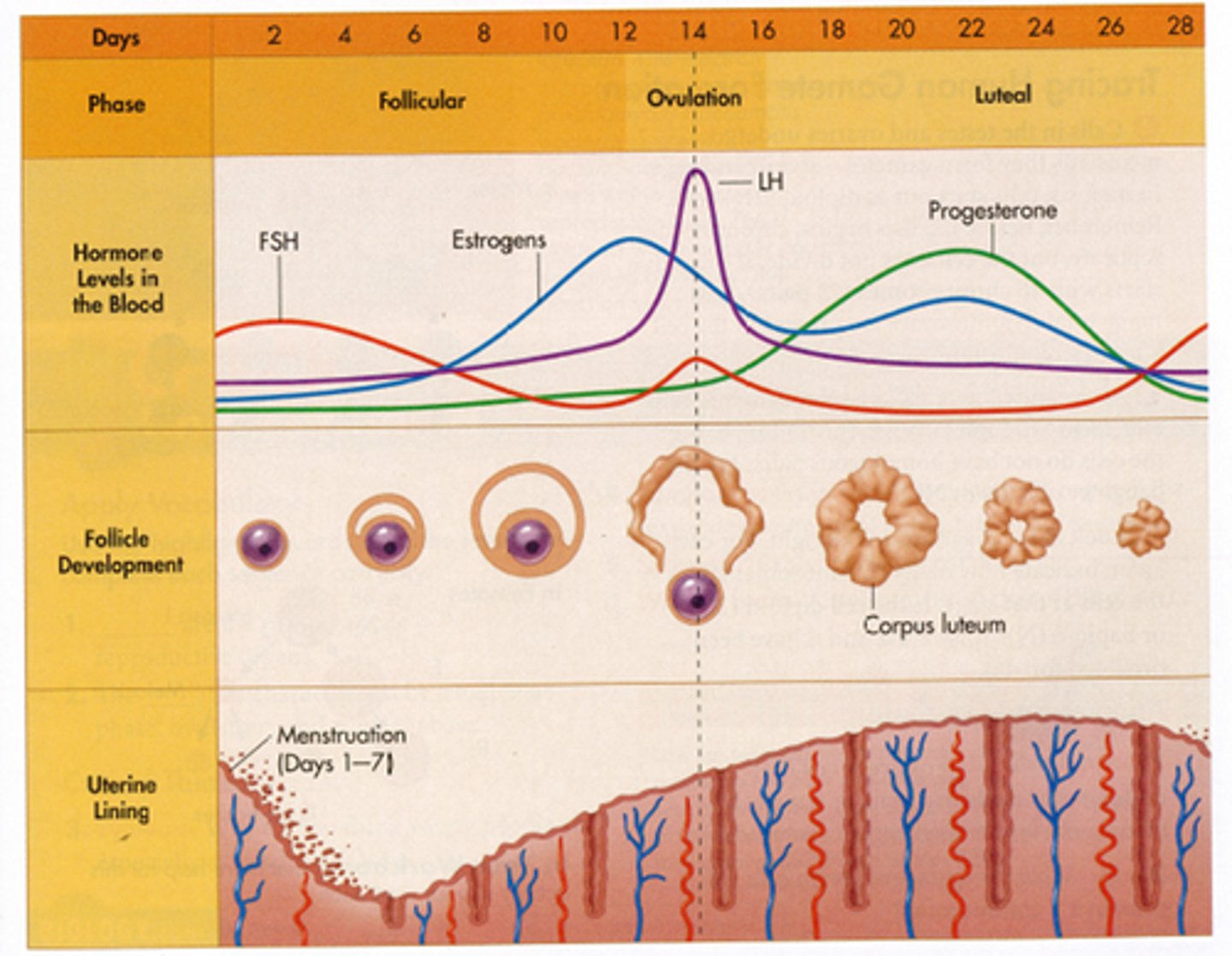
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
flow (days 1 to 5) ---> follicular phase (days 6 to 13) ---> ovulatory phase (day 14) ---> luteal phase (days 16-28)

Flow Phase (days 1 to 5)
- Estrogen and progesterone levels have crashed because there was no fertilized egg
- Menstruation (shedding of the endometrium) occurs
- Weak uterine contractions
Follicular Phase (days 6 to 13)
- Follicle matures under the influence of FSH (stimulated by GnRH)
- Primary oocyte undergoes meiosis 1 and becomes the secondary oocyte and 1st polar body
ESTROGEN IS HIGHEST NEAR THE ND OF THE FOLLICULAR PHASE
- estrogen is secreted: 1. endometrium is restored, 2. negative feedback to FSH cells of the pituitary, 3. positive feedback is sent to LH cells of pituitary
Ovulatory Phase (day 14)
LH spikes and ovulation occurs: secondary oocyte (egg) bursts and is swept into the fallopian tube by the fimbria
Luteal Phase (days 16-28)
- "eggless" follicle is renamed the corpus luteum
- estrogen is still secreted; now only has negative feedback
- most important secretion at this time is PROGESTERONE- think "pro-pregnancy"- maintains endometrium to prepare the uterus for an embryo and prevents uterine contractions and gives negative feedback on menstrual cycle (decrease GnRH, FSH and LH)
- Days 26-28, if there is no fertilized egg, the progesterone and estrogen levels will fall and the entire cycle begins again ("reset" button)
- birth control pills contain synthetic progesterone = negative feedback effect on the menstrual cycle = no egg production = no ovulation
Hormones during menstrual cycle
Low estrogen at the beginning, LH and FSH increases, follicle maturation secretes estrogen, FSH continues to increase, midcycle LH surge, ovulation, corpus luteum secretes progesterone and estrogen (inhibiting FSH and LH), corpus luteum expires in 14 days, menses
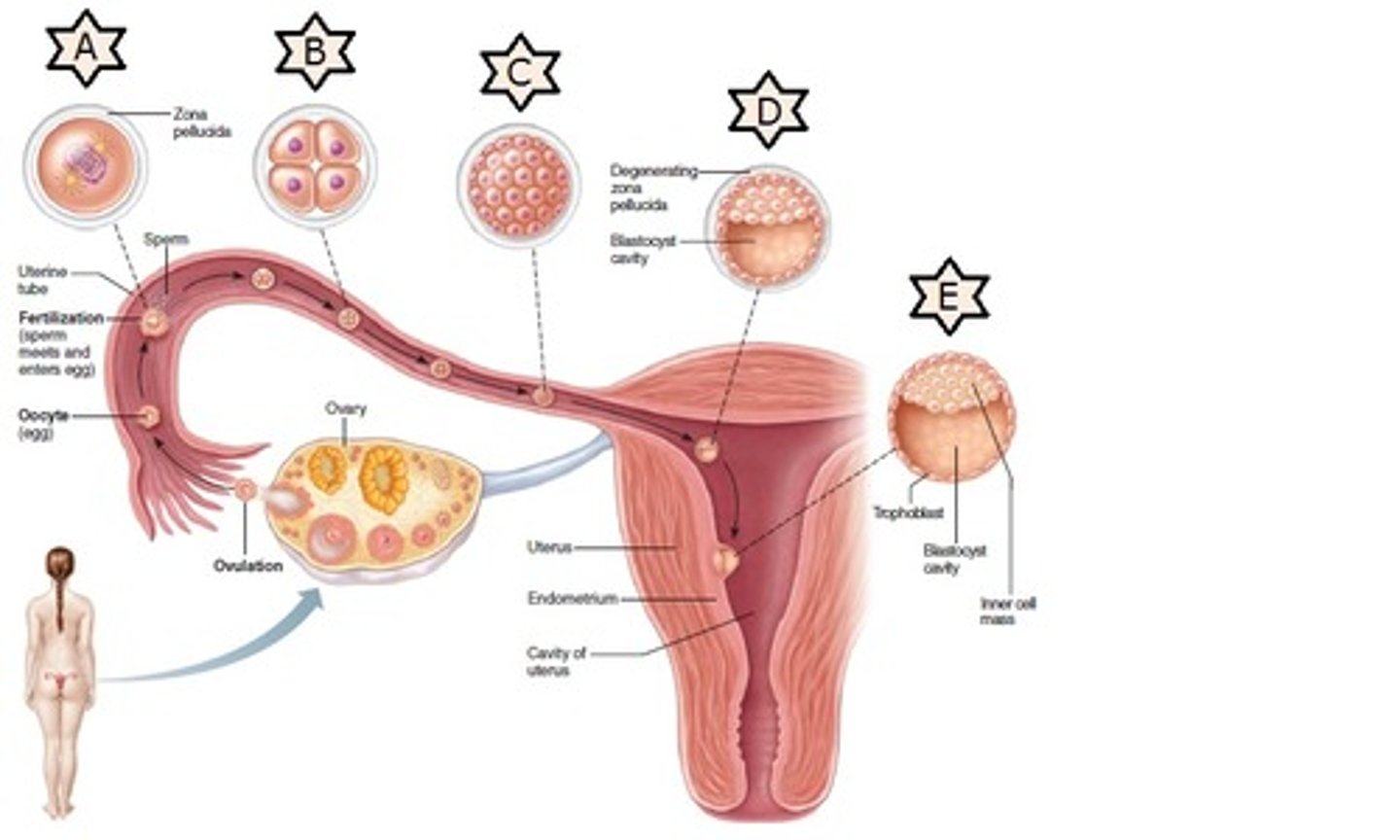
Making Babies
1. fertilization
2. implantation of blastocyst
3. formation of extra-embryonic membranes
4. gastrulation then differentiation and morphological development of the embryo
5. placental development and fetal morphogenesis\
6. parturition
7. lactation
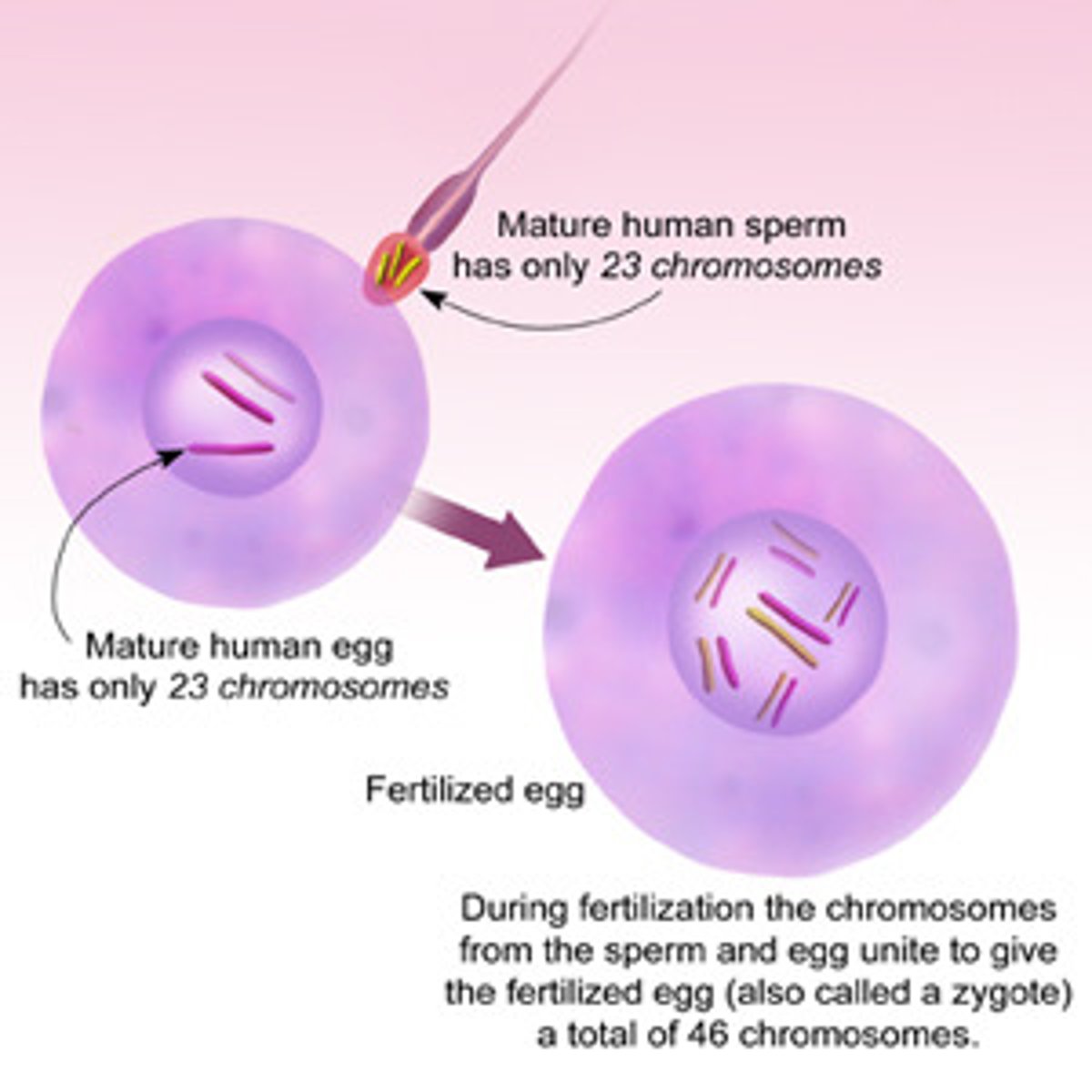
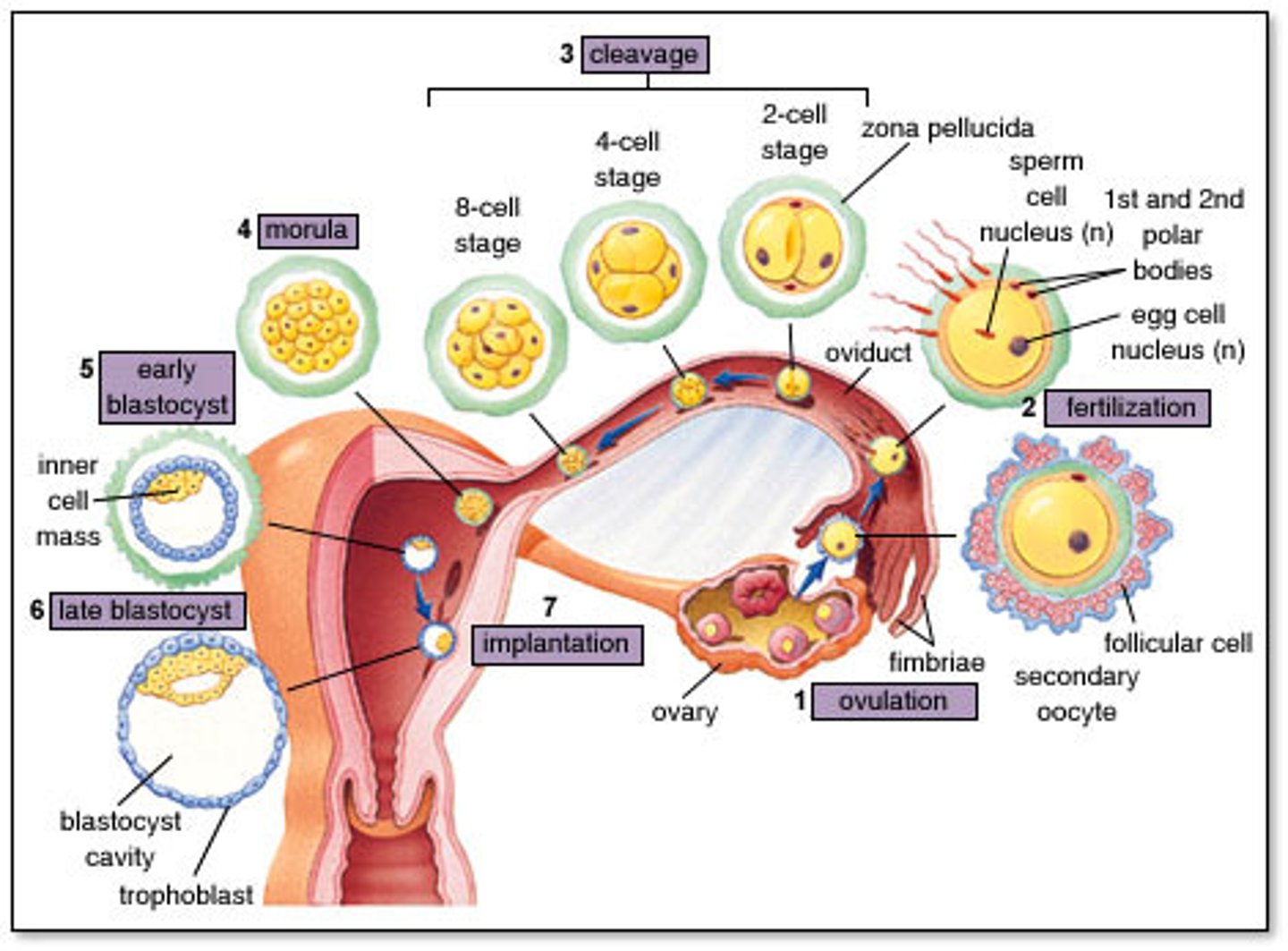
Fertilization (day 0)
- occurs in the fallopian tube
- only a few hundred sperm reach the egg, all releasing acrosomal enzymes to break through the zona of the egg
- only one sperm will inject only its haploid nucleus (23 chromosomes) into the haploid nucleus of the egg
- a diploid cell (46 chromosomes) is now created: a zygote
- within 24 hours the zygote undergoes cleavage (mitosis)
- creates a small cluster of cells now called the morula
- the morula then becomes a hollow ball of cells called a blastocyst
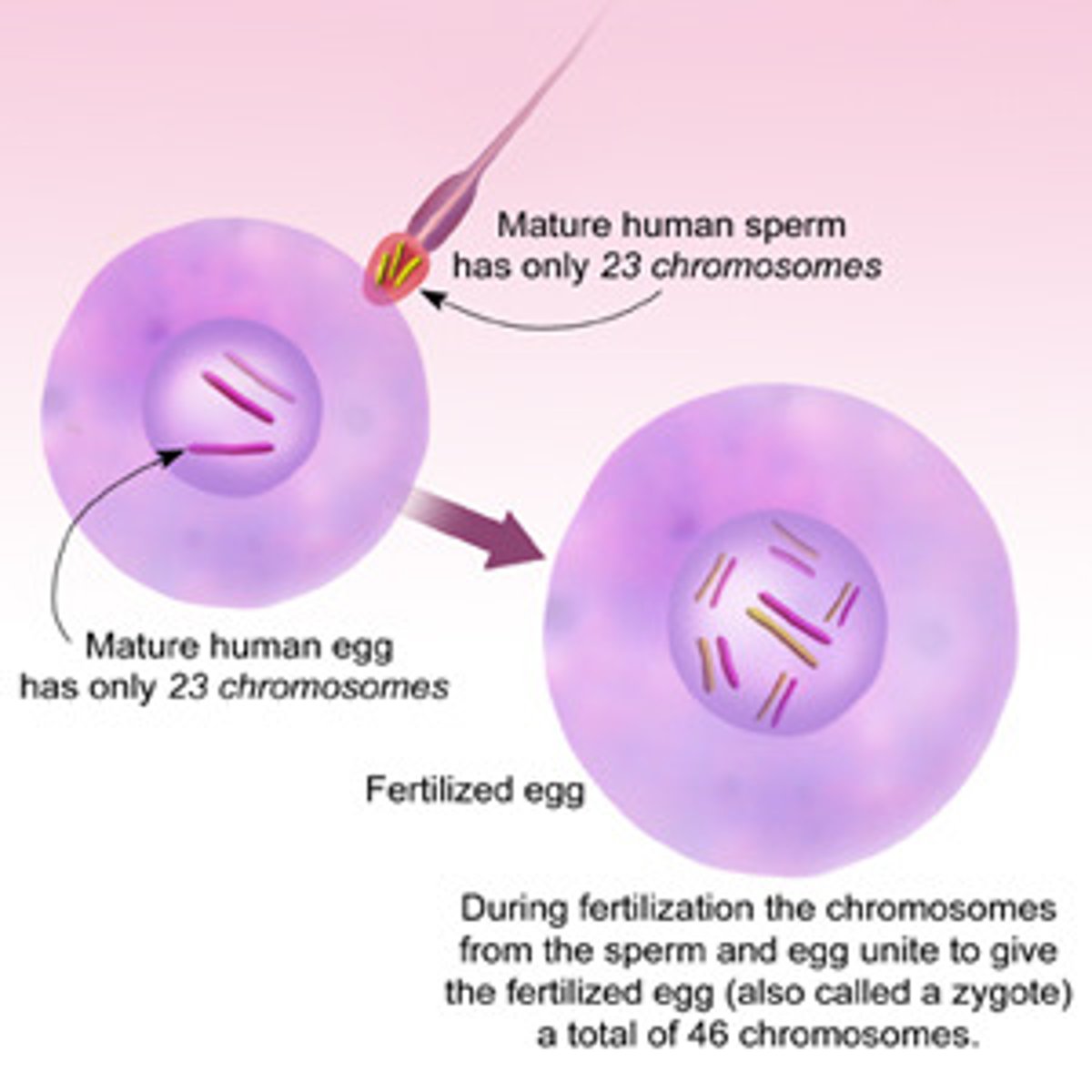
the mom (egg)
Who are ALL your mitochondria from?
the dad (sperm) (because there's "boy" sperm w/ a Y chromosome and "girl" sperm with an X chromosome)
Who determines the biological sex of the baby?
Development of the cellular structure after fertilization
zygote ---> morula ---> blastula ---> embryo
Zygote
a diploid cell resulting from the fusion of two haploid gametes; a fertilized ovum.
Morula
a solid ball of cells resulting from the division (mitosis) of a fertilized ovum, and from which a blastula is formed.
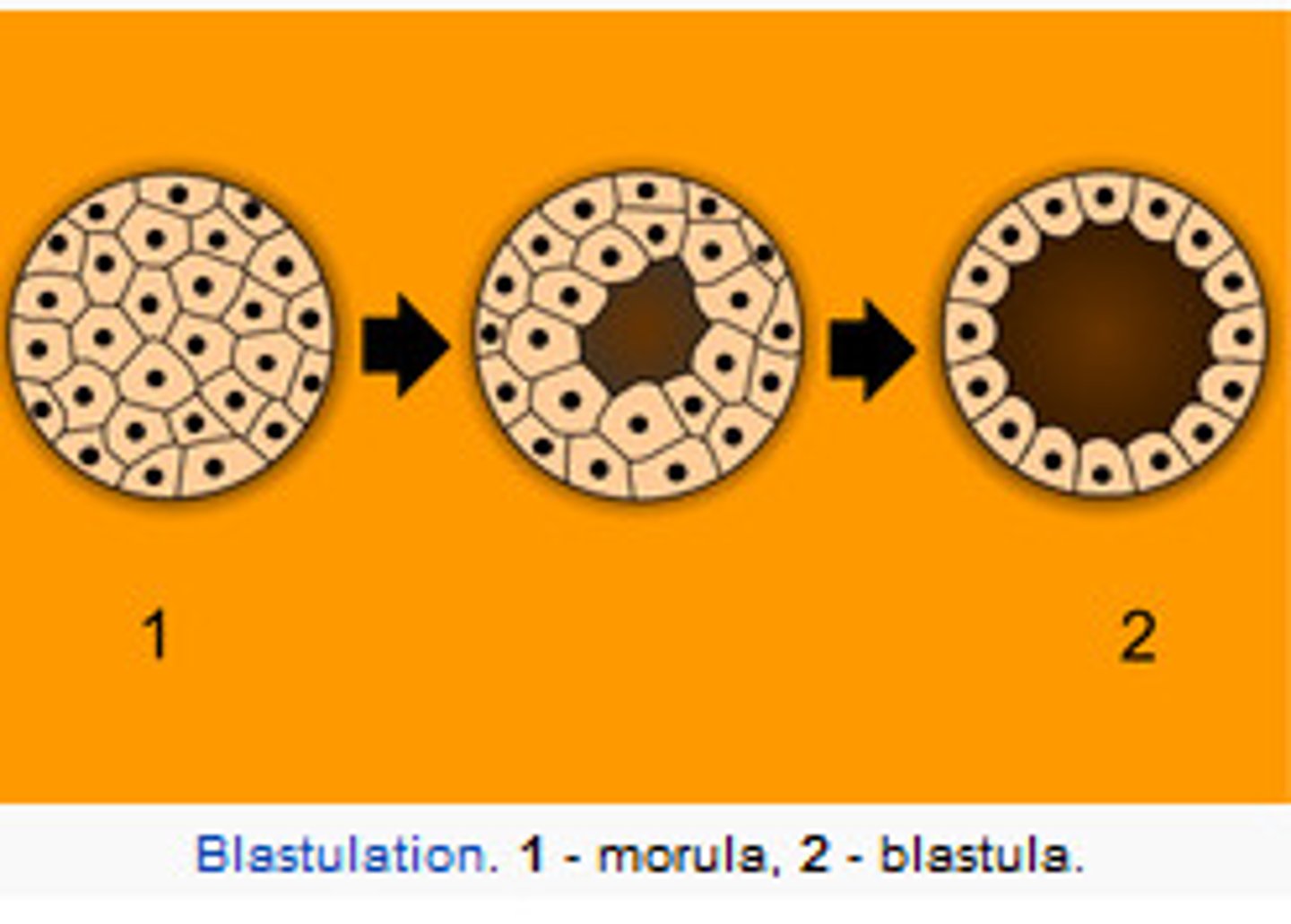
Blastocyst (blastula)
A fluid-filled sphere formed about 5 days after fertilization of an ovum that is made up of an outer ring of cells and inner cell mass (embryo). This is the structure that implants in the endometrium of the uterus.
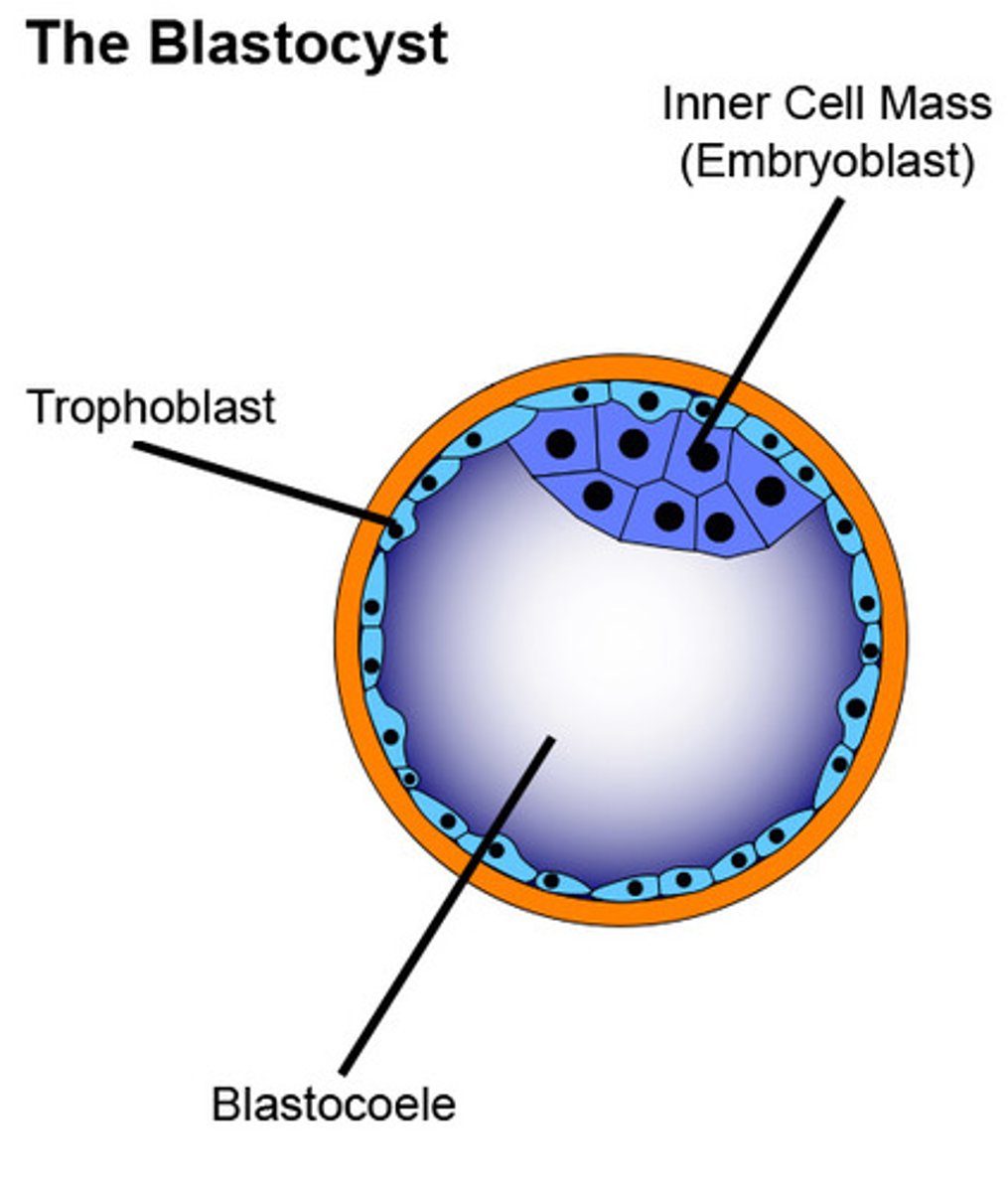
Implantation of Blastocyst
- The inner cell mass = embryo = you!
- The outer layer of cells are called the chorion cells the secrete 2 important products: enzymes to digest the wall of the endometrium allowing implantation and hCG hormone that maintains the corpus luteum thereby maintain high estrogen and progesterone levels (screams "i'm in here!" to the body)
NOTE: the zygote/blastula was surviving off the nutrients in the egg cytoplasm until implantation
Twins
3 types:
1. fraternal
2. identical
3. conjoined
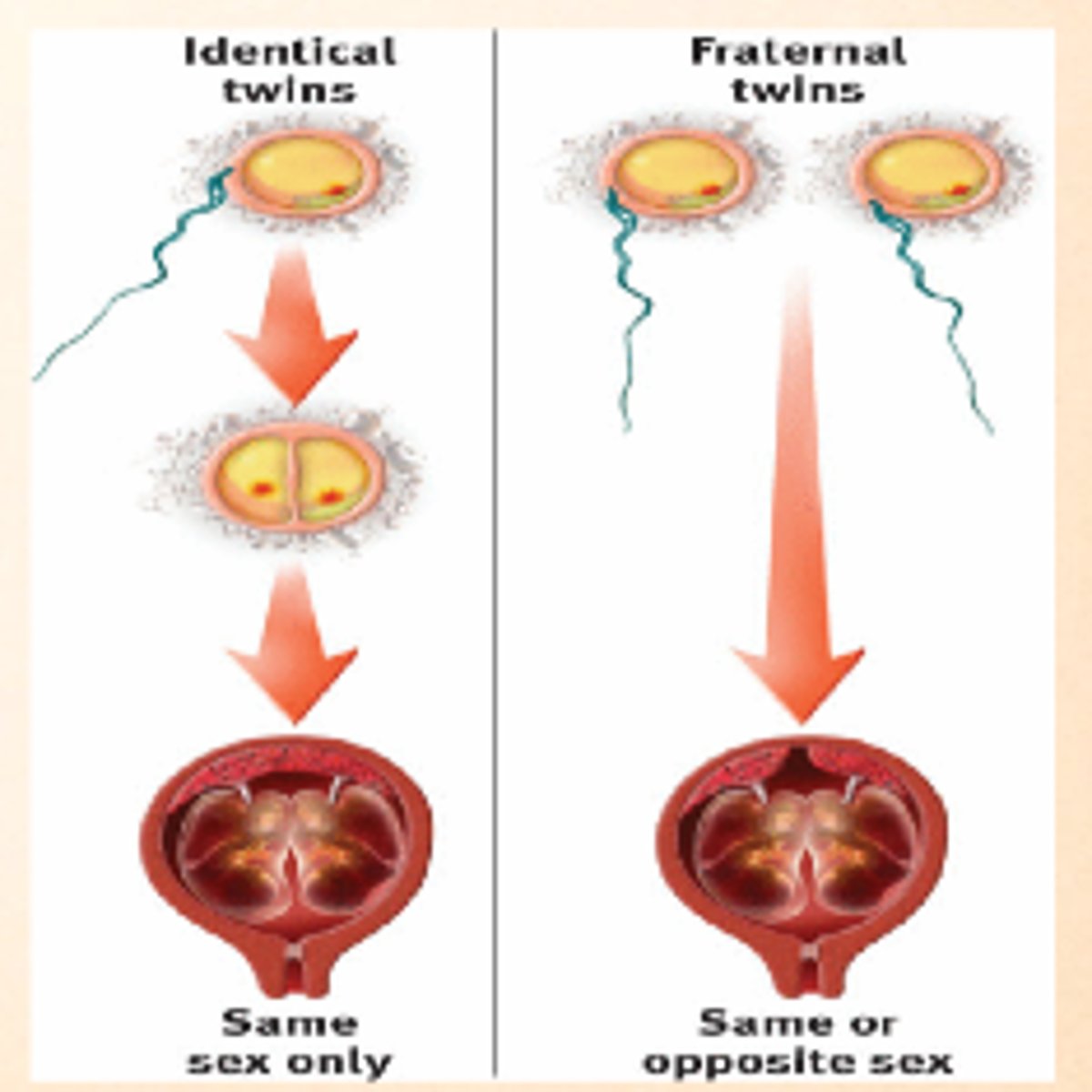
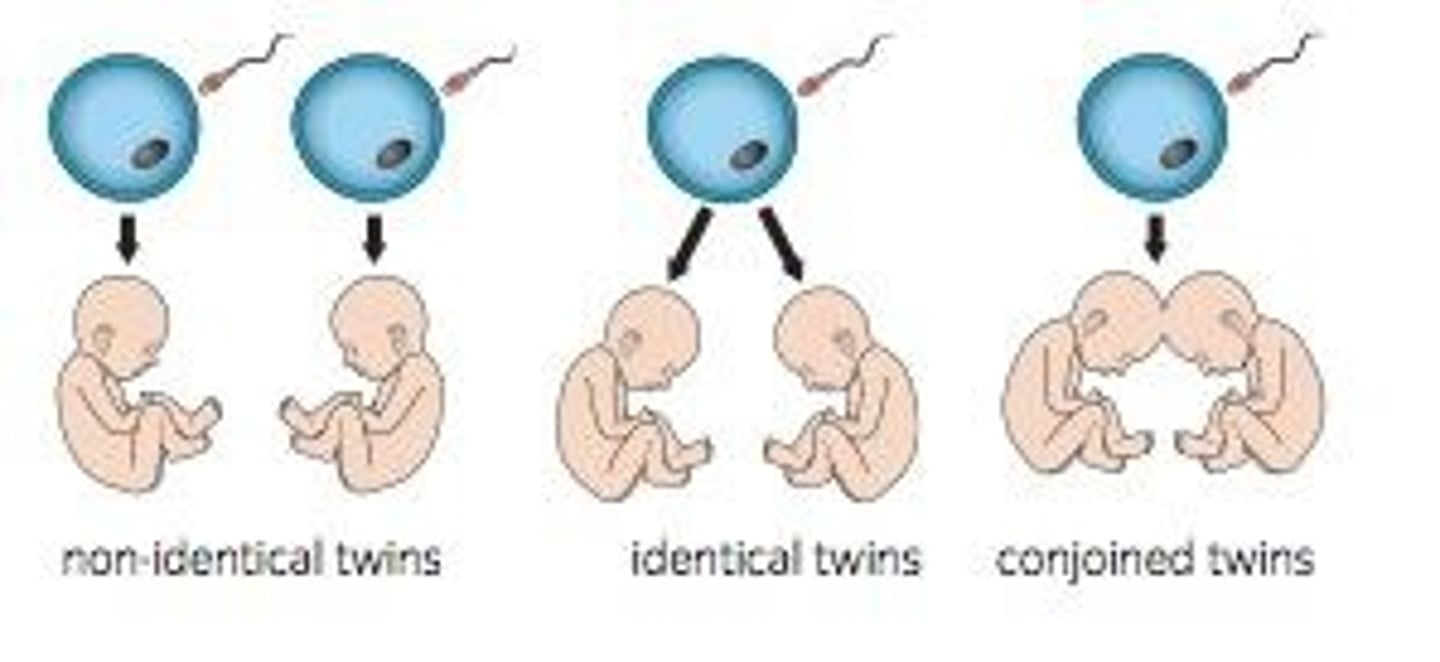
fraternal twins (dizygotic twins)
Twins who develop from separate fertilized eggs. They are genetically no closer than brothers and sisters, but they share a fetal environment.
- aka. dizygotic twins
- 2 different eggs fertilized by 2 different sperms resulting in 2 different zygotes with different DNA
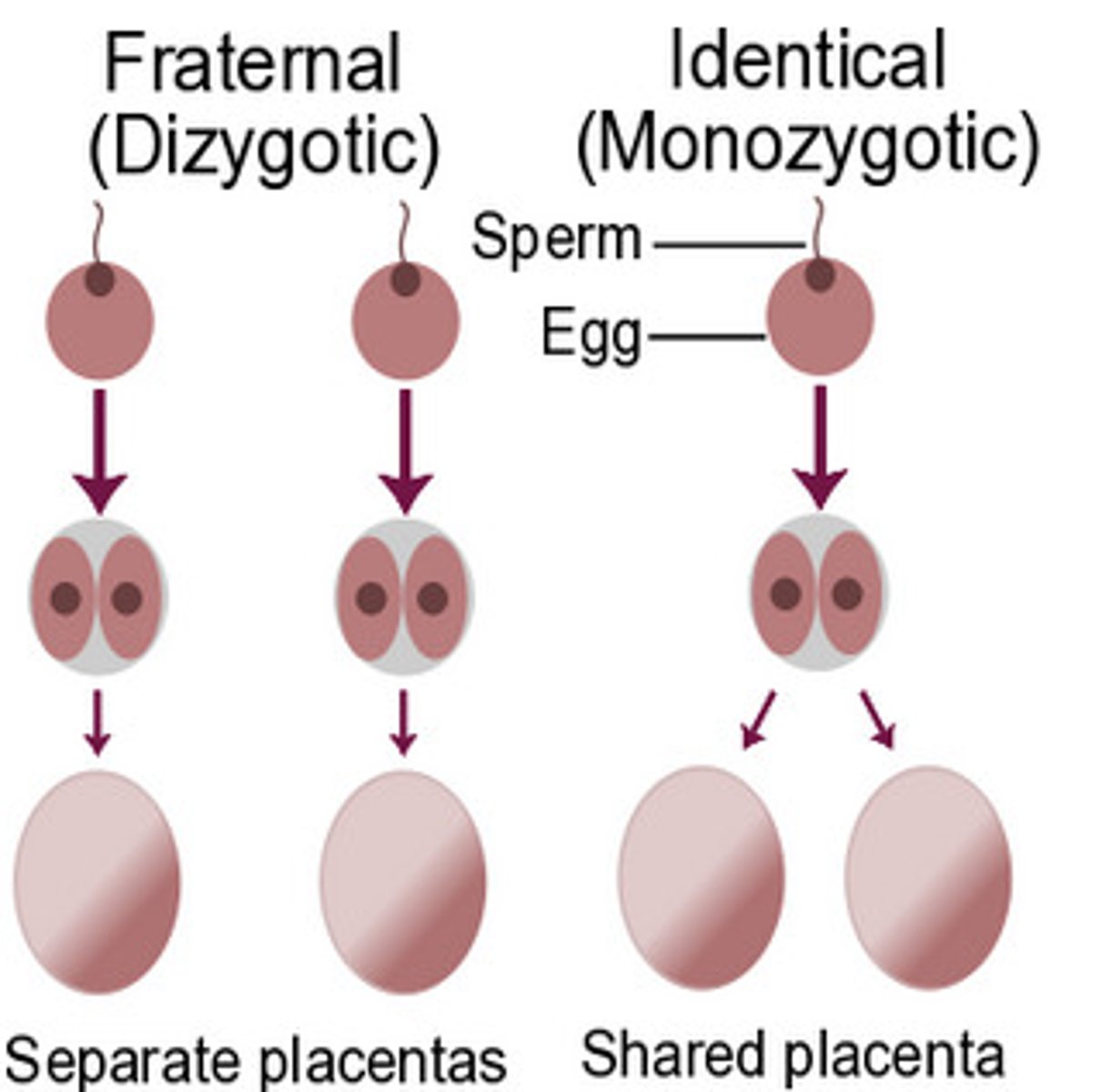
identical twins (monozygotic twins)
Twins that develop from a single fertilized egg that splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms
- aka. monozygotic twins
- 1 egg fertilized by one sperm, is one zygote but splits into 2 separate morulas with identical DNA
conjoined twins
Monozygotic twins who are born physically joined to one another.
- identical twins that failed to completely separate
Formation of extra-embryonic membranes
"CAAY"
1. chorionic membrane
2. amniotic membrane
3. allantois
4. yolk-sac
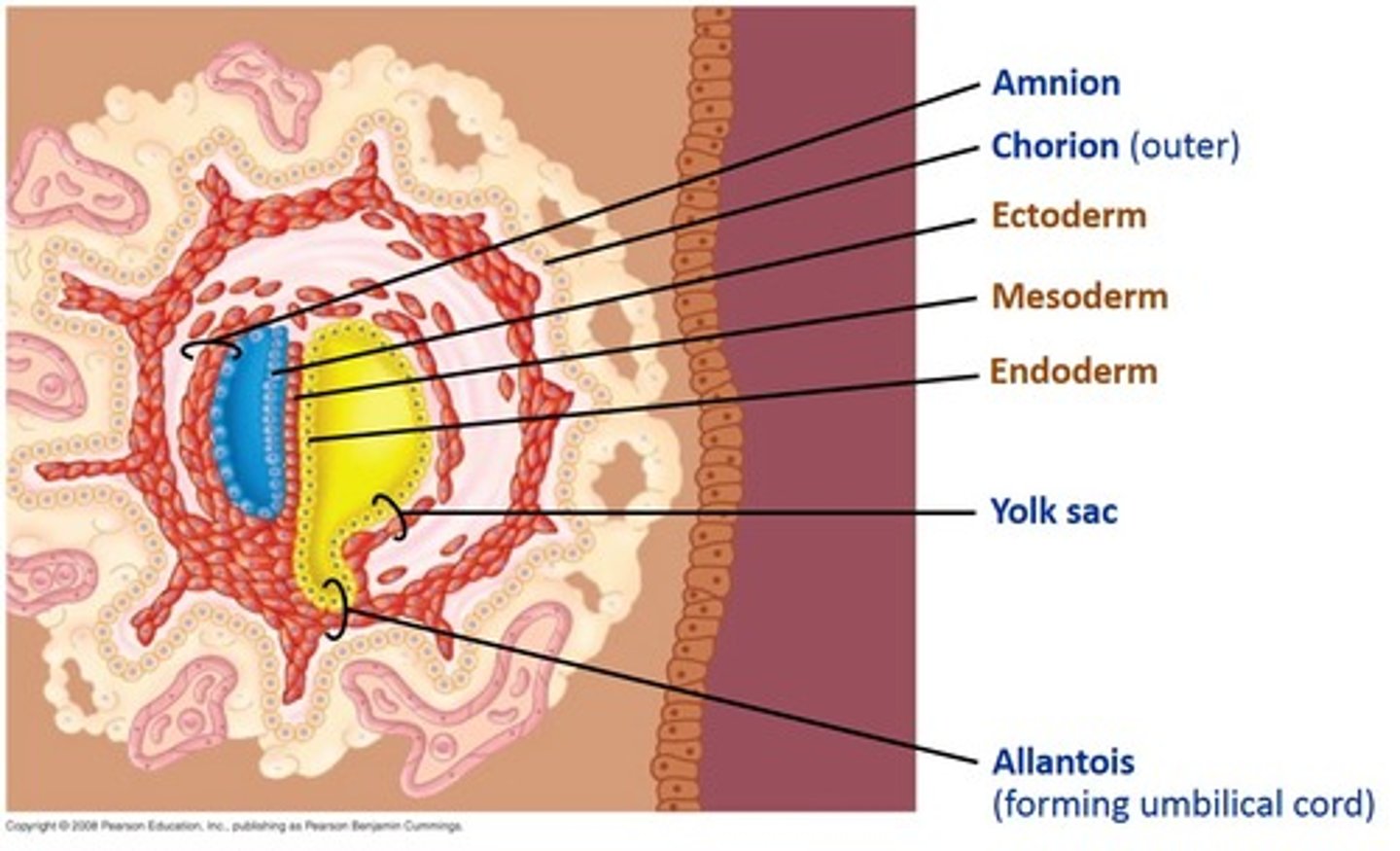
Chorionic Membrane
The outer membrane that has villi that project into the endometrium; where the villi connect to the endometrium is where the placenta forms
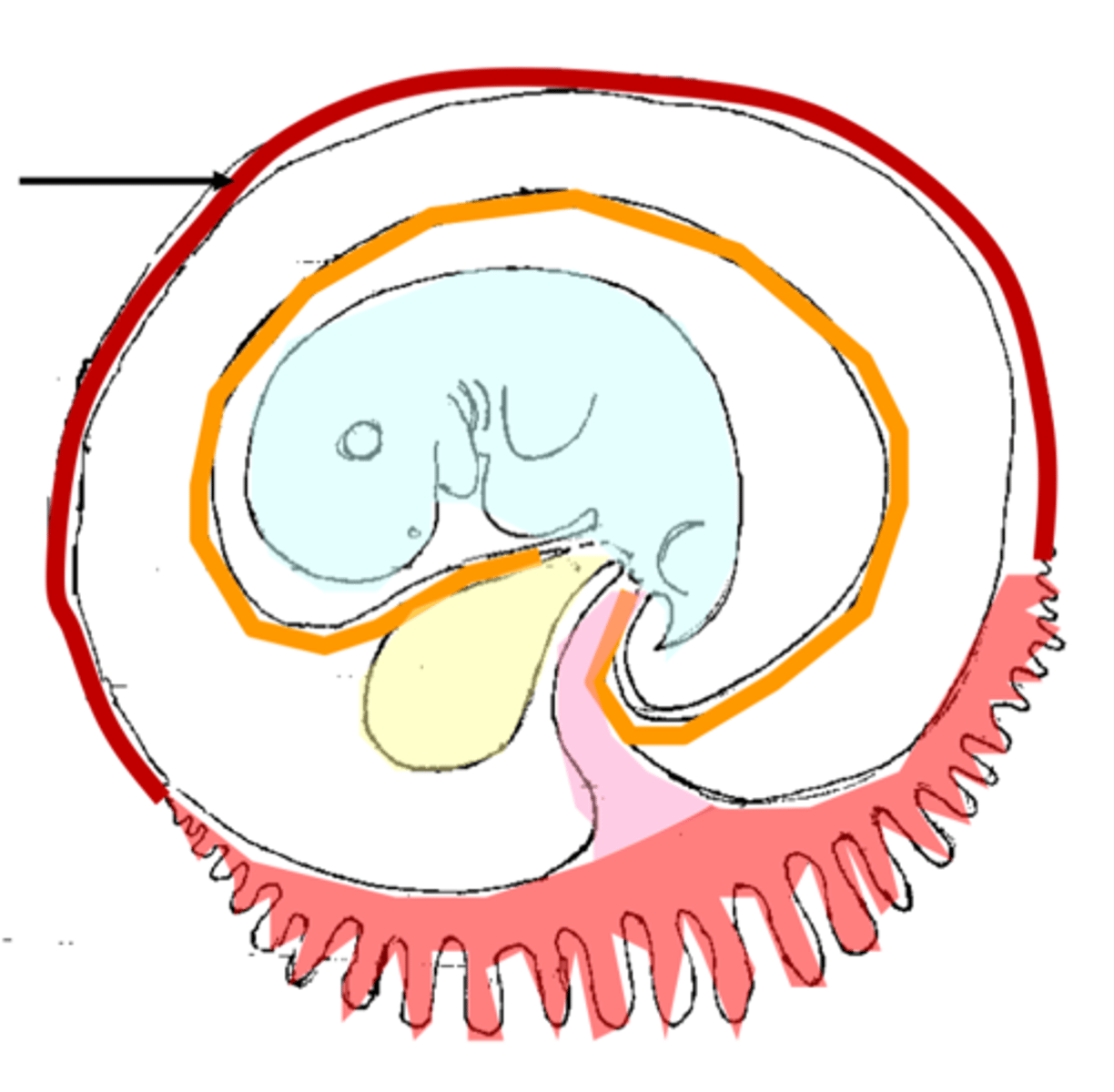
Amniotic Membrane (amnion)
Inner membrane that surrounds the embryo and contains amniotic fluid to protect and insulate the fetus from impact, temperature changes, dehydration and infection
Allantois
one of the four extra-embryonic membranes that creates the umbilical cord blood vessels that reach into the chorionic villi/placenta
Yolk Sac
The yolk sac is an extra-embryonic membrane that provides food for the embryo in chickens and produces blood for humans before they have bones and bone marrow
Gastrulation then differentiation and morphological development of the embryo
"phase four" of fetal development
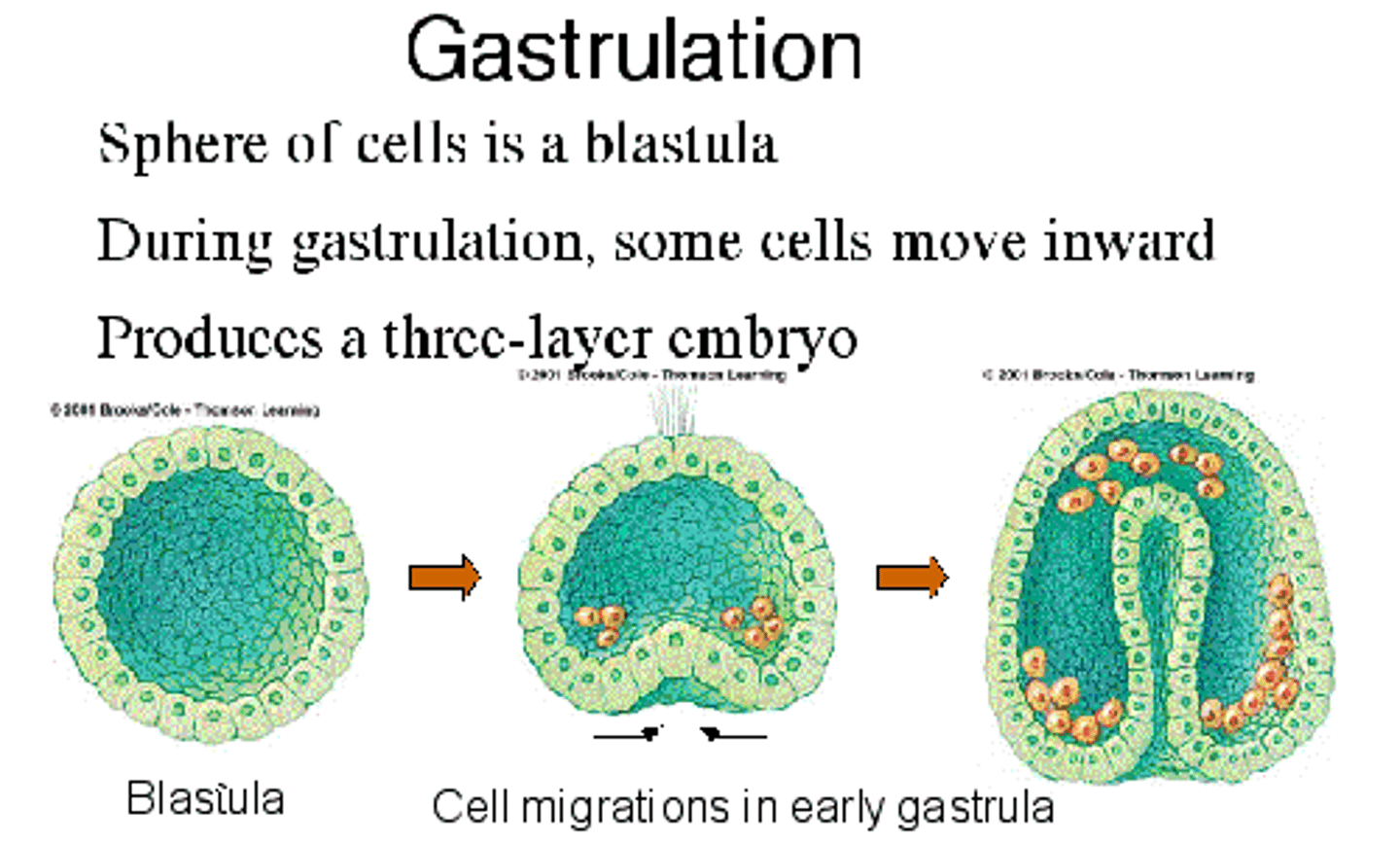
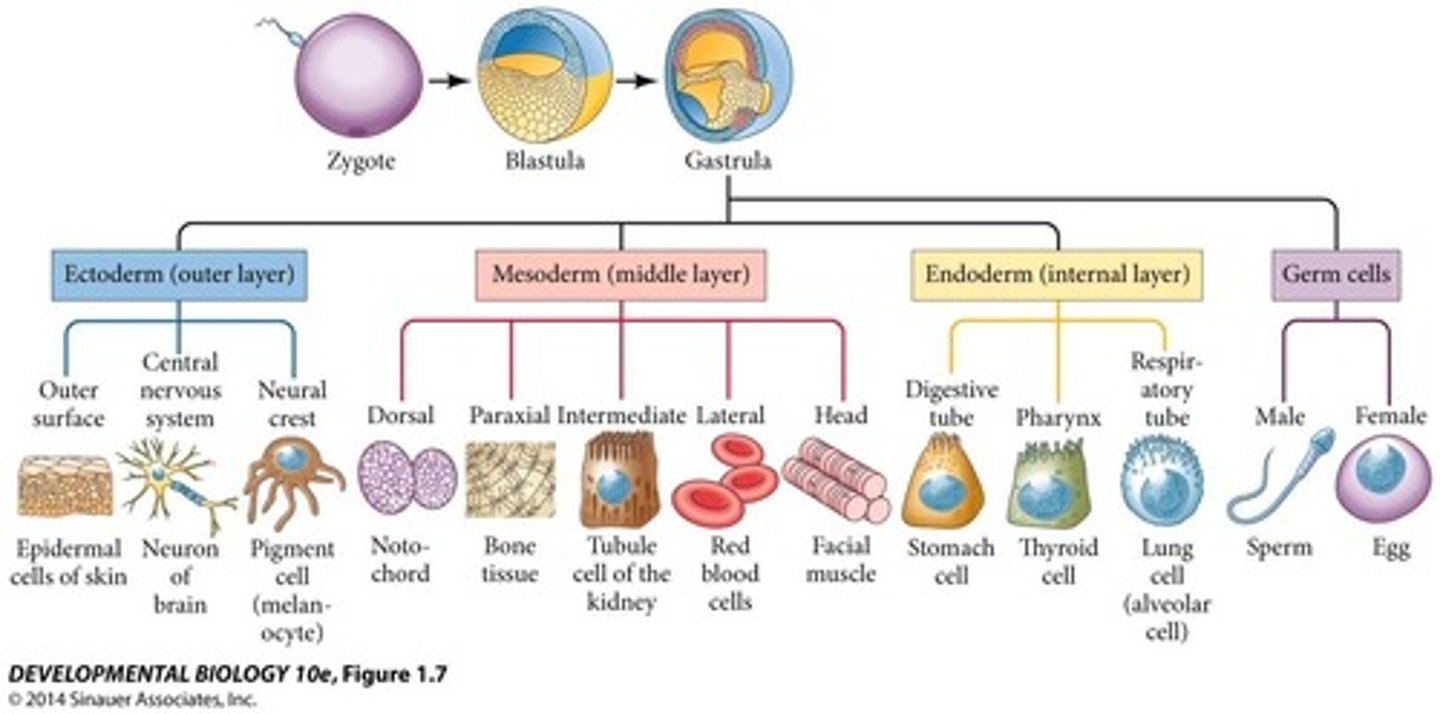
Gastrulation
The process by which a blastula develops into a gastrula with the formation of three embryonic layers
- when the 2-layered embryo folds in on itself to create 3 germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm
- each layer will differentiate and create specialized cells due to different genes in the DNA being turned "on and off"
Differentiation
A process in which cells become specialized in structure and function
- creates specialized cells due to different genes in the DNA being turned "on" and "off"
Ectoderm
outermost germ layer; produces sense organs, nerves, and outer layer of skin
- aka. "nervous epidermis"
- creates the CNS, PNS, eyes, ears, hair, skin, nails
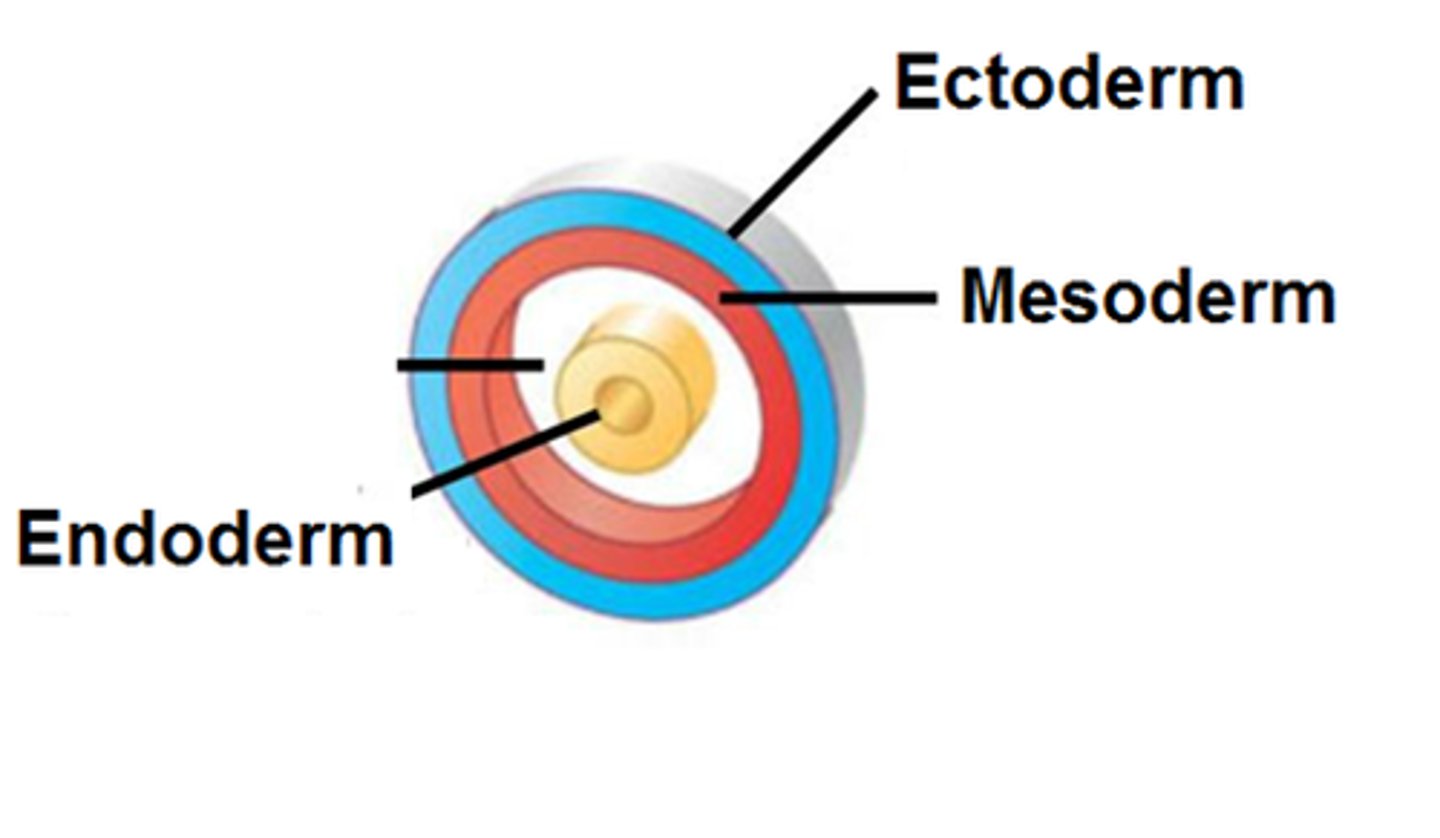
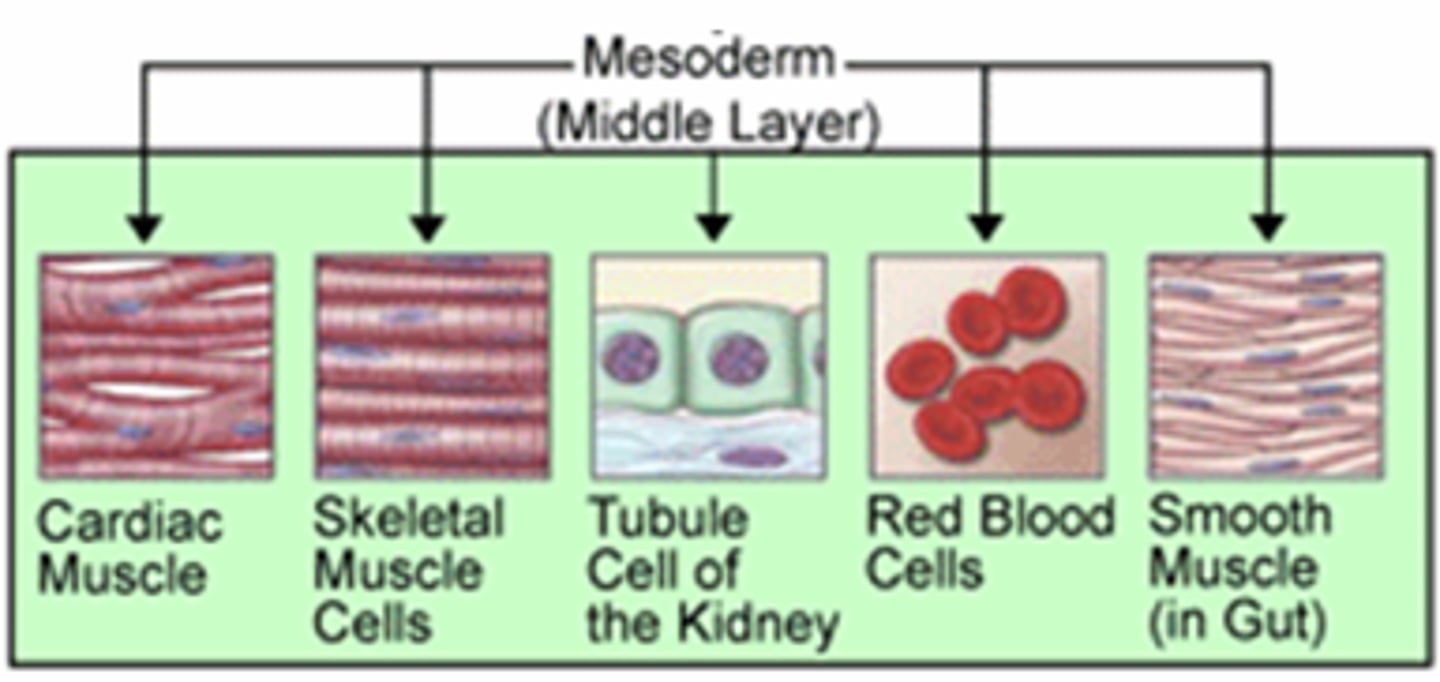
Mesoderm
middle germ layer between the ectoderm and the endoderm; develops into muscles, and much of the circulatory, reproductive systems and excretory systems
- middle layer that produces bones, muscles, reproductive and circulatory systems
Endoderm
The inner germ layer that develops into the lining of the endocrine glands, as well as, the digestive and respiratory linings
- inner layer that produces the respiratory and digestive linings and the endocrine glands
Importance of Y Chromosome
in approximately the 7th week of pregnancy the SRY gene on the Y chromosome tells the gonads to become testes and the secretion of testosterone begins; the male primary sex characteristics from (penis, etc..)
Placental Development and Fetal Morphogenesis
"phase 5" of gestation
sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Infections that can be, but are not always, transmitted from one person to the next through sexual contact.
- STIs (viruses, bacteria, etc...) have negative effects on the reproductive system
ex. can cause inflammation/ scarring or blockage of vas deferens or cervix = infertility (hopefully temporary)
- some have cures like bacterial infections have antibiotics and there are preventative cures like vaccines for HPV, and some only have treatments for symptoms but no actual cures for viruses like herpes
the only protection we have is avoiding skin to skin contact through abstinence and condoms)
Birth Control (contraception)
Two main classifications:
a. hormonal: contain synthetic progesterone and estrogen to provide negative feedback on FSH and LH throughout the entire month so no eggs are produced and ovulated (no oogenesis)
ex. female birth control pill
b. not hormonal: involve devices/behaviours
- usually creates a barrier so that sperm will never reach the egg
ex. male/female condom
ex. IUD (intrauterine device)
ex. VASECTOMY and TUBAL LITIGATION = permanent birth control
Placenta
A structure that allows an embryo to be nourished with the mother's blood supply.
- fully functioning by the 3rd month
- made of 2 parts: endometrium (maternal part) and chorionic villi (fetal part)
- 2 functions: secretion of estrogen and progesterone (no longer needs the corpus luteum so it dies), as well as the diffusion of nutrients, hormones, antibodies, gases, viruses, etc... between the fetal and mother circulatory system (not blood cells)
- has an umbilical cord that transports fetal blood to and from the organ
Functions of Placenta
- production and secretion of estrogen and progesterone (corpus luteum dies because its no longer needed)
- diffusion/ exchange of nutrients, hormones, antibodies, gases, viruses, teratogens, wastes, etc... between the fetal and maternal circulatory systems (but NOT blood cells!)
- the umbilical cord transports fetal blood to and from this organ
Umbilical Cord
A flexible cordlike structure containing blood vessels and attaching a human or other mammalian fetus to the placenta during gestation.
- the tube that transports fetal blood to and from the placenta that contains blood vessels formed by the allantois.
Fetal Development
day 1 gametes fuse to form one cell with 46 chromosomes
days 3-4 egg travels down fallopian tube to the uterus
days 5-9 egg implanted in the wall of the uterus; starts to get outside nourishment and gets bigger
days 10-14 embryo starts producing its own hormones that also affect the mom
day 20 foundations of brain, spinal cord, nervous system are established(gastrula)
day 21 heartbeat begins
day 35 can see beginnings of fingers, eyes, hands, etc.; things become distinct^; about the size of a grain of rice
day 40 functioning nervous system; brainwaves can be detected
week 6 brain begins to control movements
week 7 teeth, eyelids develop
week 8 about an inch long; starts being called a fetus; looks like a tiny baby; everything it needs it pretty-much has; responds to touch; coordinated muscular/nervous system
week 9 fingers can grasp
week 11 about 2 inches long
week 12 start to have sleeping/breathing
week 13 starts to grow hair; gender can be determined
month 4 about 8-10 inches long; ears functioning
month 5 about a foot long; starts to be startled by things
month 6 has a good chance of surviving if it is born premature
month 7 starts recognizing the mothers voice
months 8-9 just more growth
first trimester
- 0-12 weeks, aka. the first 3 months
- MOST IMPORTANT for the fetus
- all the major organs and systems form during this time
- note: this is when the effects of poor nutrition and teratogens are most damaging because these teratogens cross the placenta and mutate the DNA of the developing embryo
Teratogens
Agents that damage the process of development, such as drugs and viruses
- substances that can cause birth defects by crossing the placenta and mutating the DNA of the developing embryo
ex. alcohol, medications, drugs, viruses, etc..
ex. thalidomide and the "flipper babies"
second trimester
- months 4-6
- organs continue to grow and develop
ex. growth of eyelids, nasal septum, body hair, etc...
- embryo is now called a fetus
third trimester
- months 6-9
- growth of fetus! and putting on fat (like myelin!)
- still called a fetus