Neuroanatomy Lab Midterm 2
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
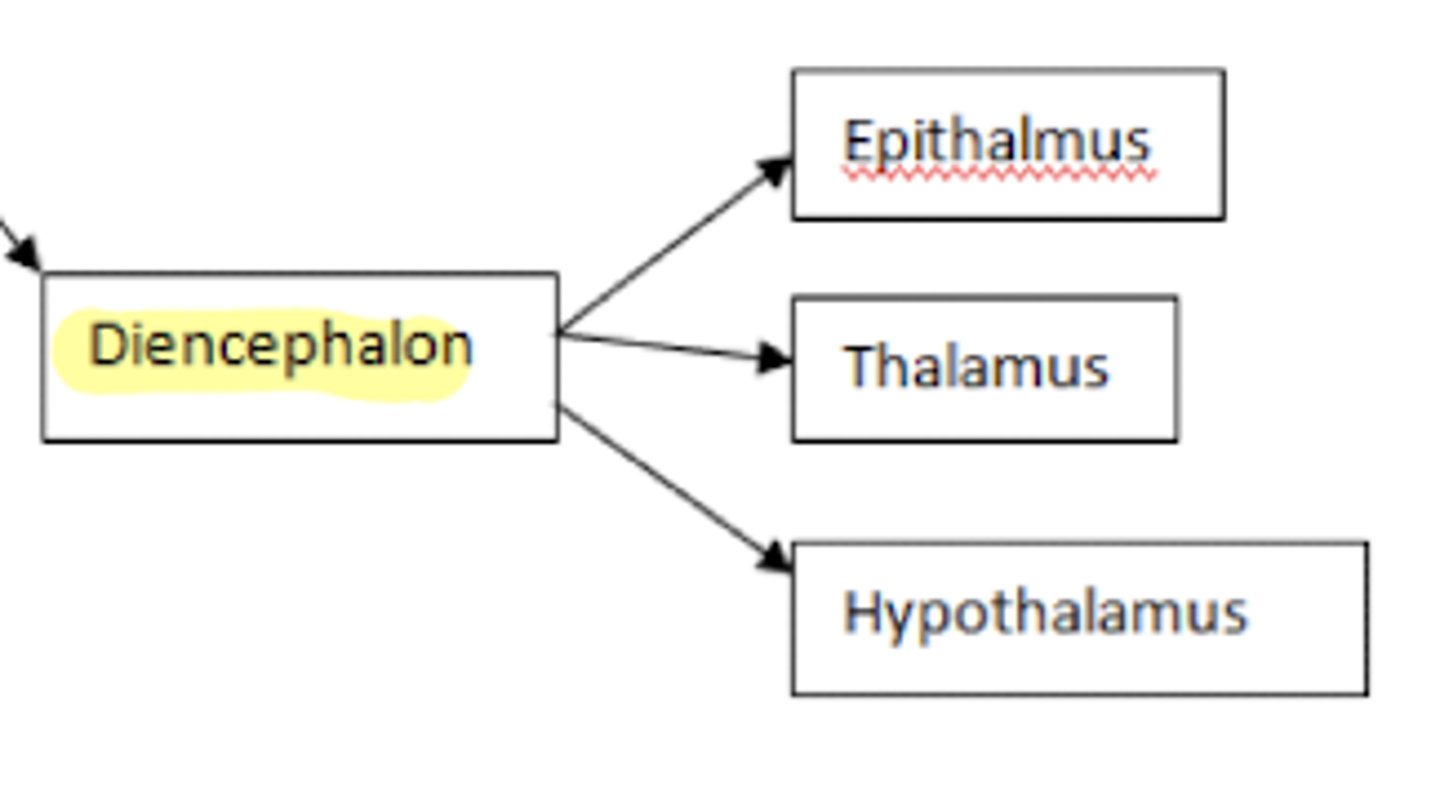
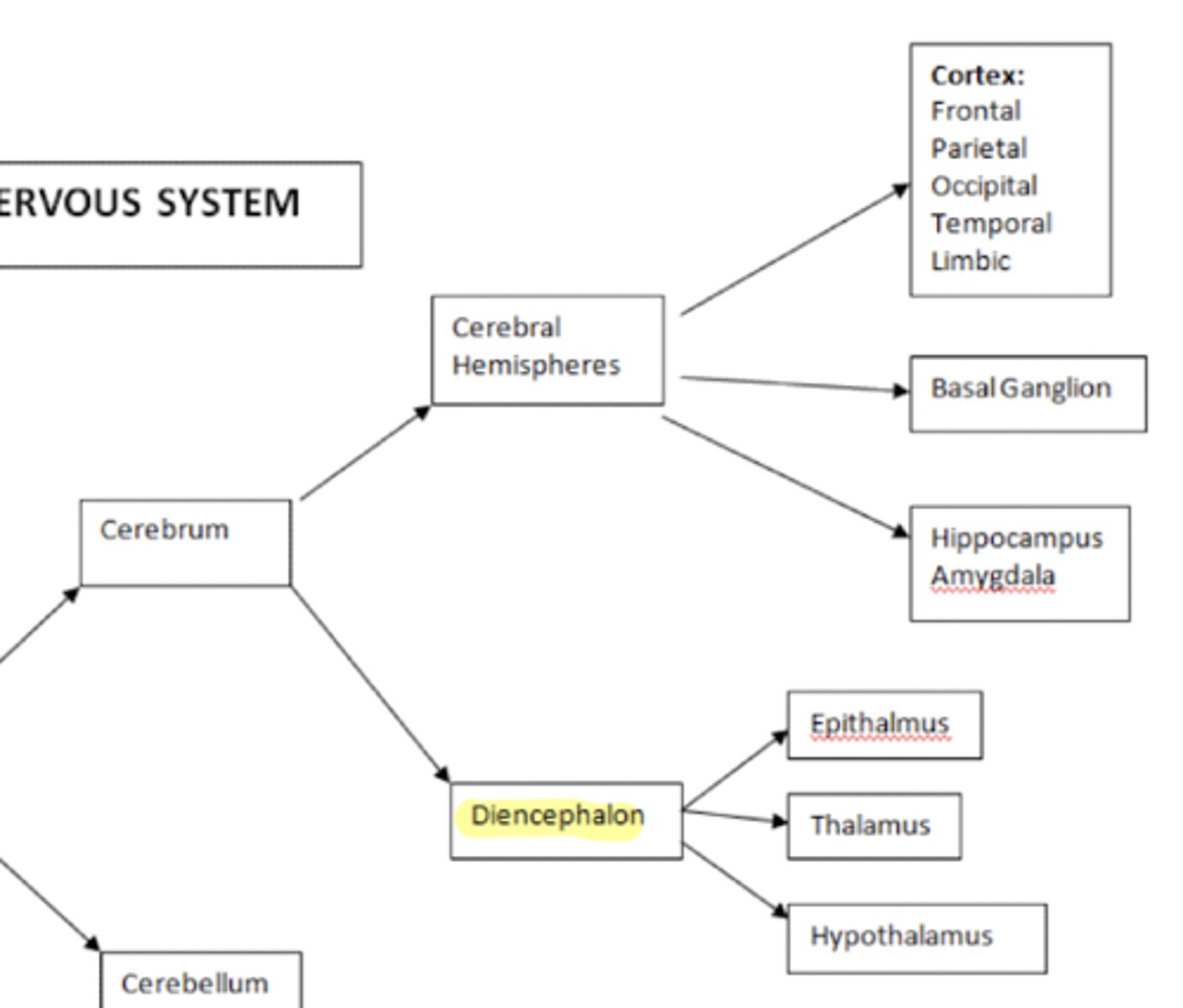
What structures are within the diencephalon?
1. epithalamus
2. thalamus
3. hypothalamus
What structures are within the cerebrum?
1. cerebral hemispheres
2. diencephalon
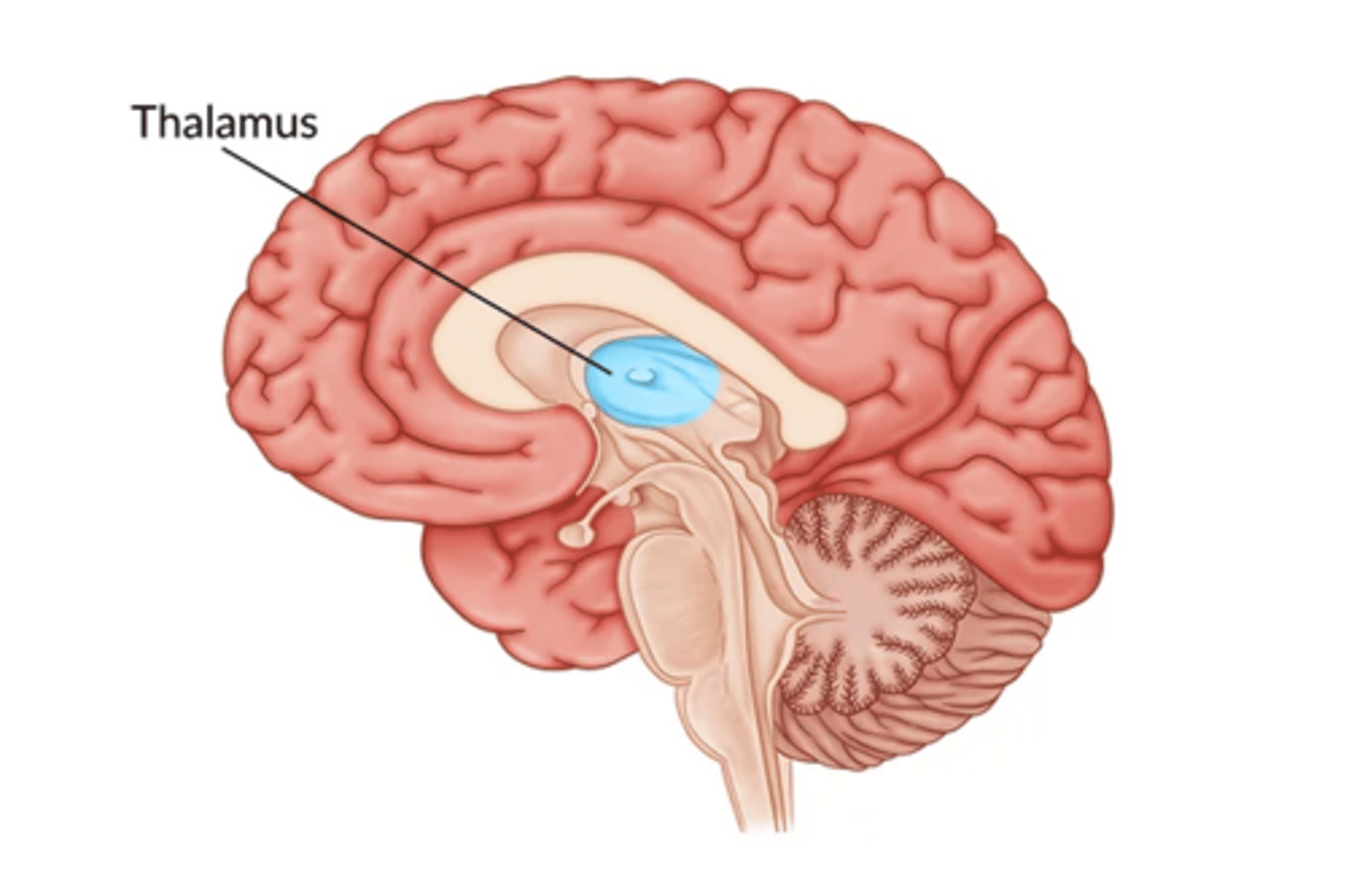
What is the function the thalamus?
sensory relay station
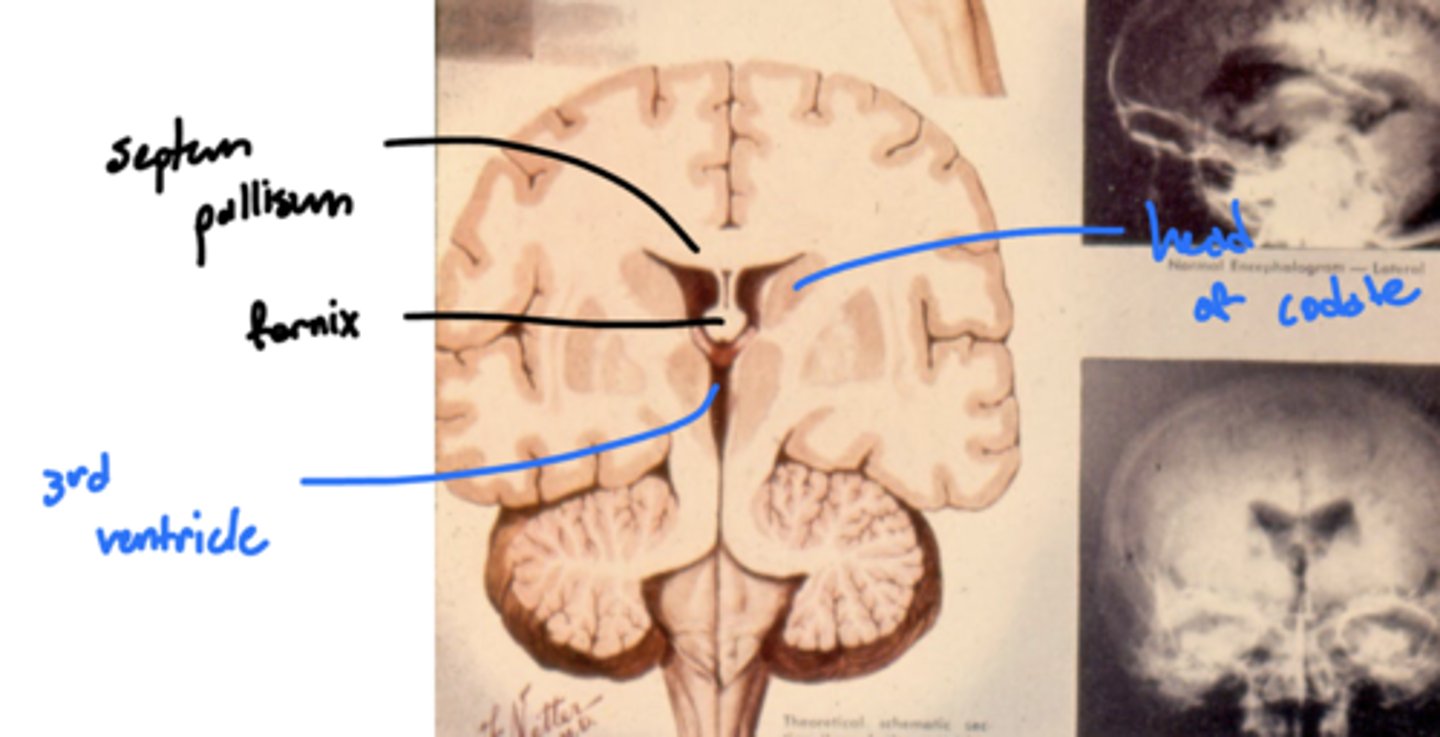
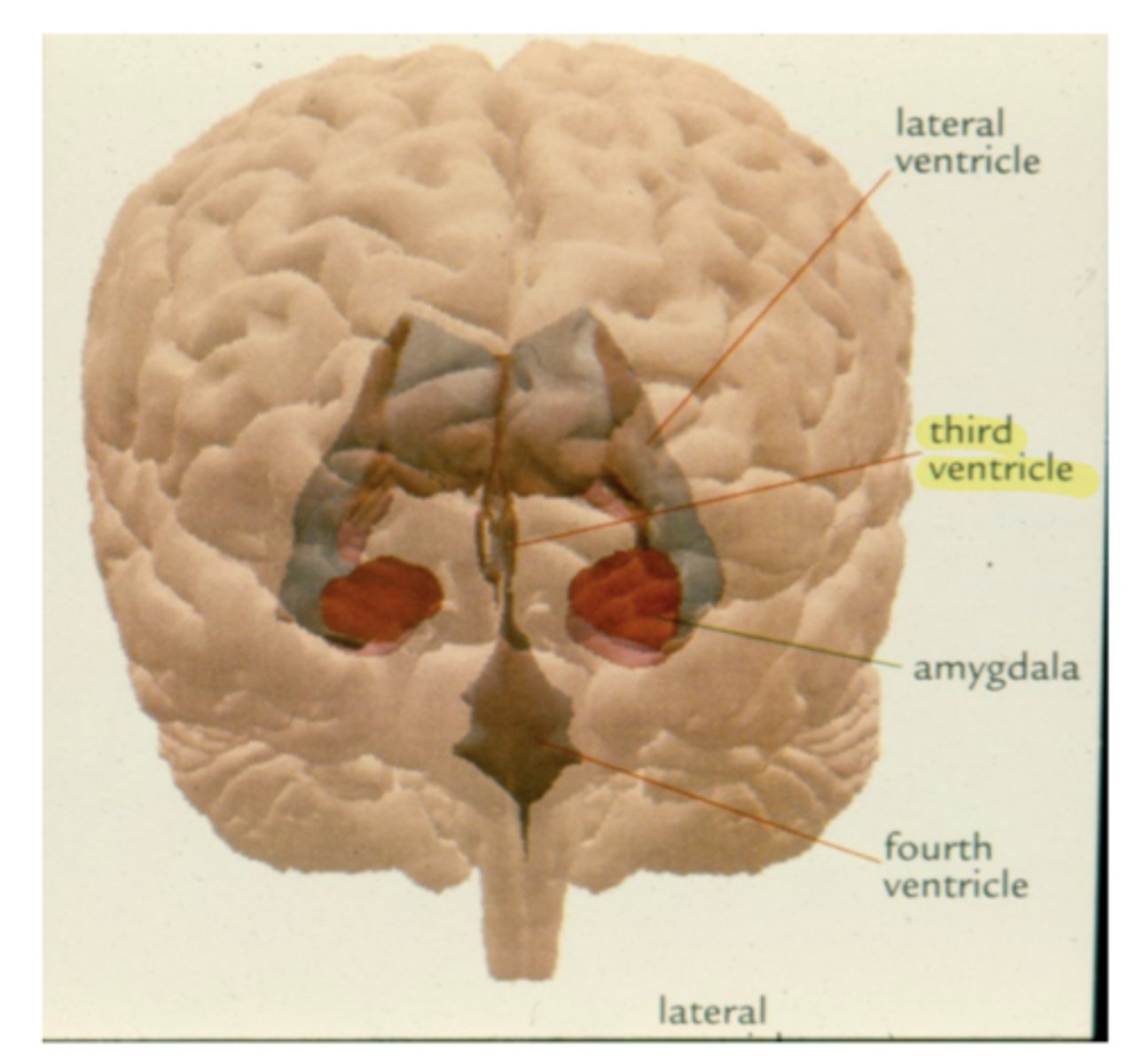
What are the lateral walls of the third ventricle?
thalamus and hypothalamus
What connects the third and fourth ventricles?
cerebral aqueduct
What is lateral to the thalamus?
posterior limb of internal capsule
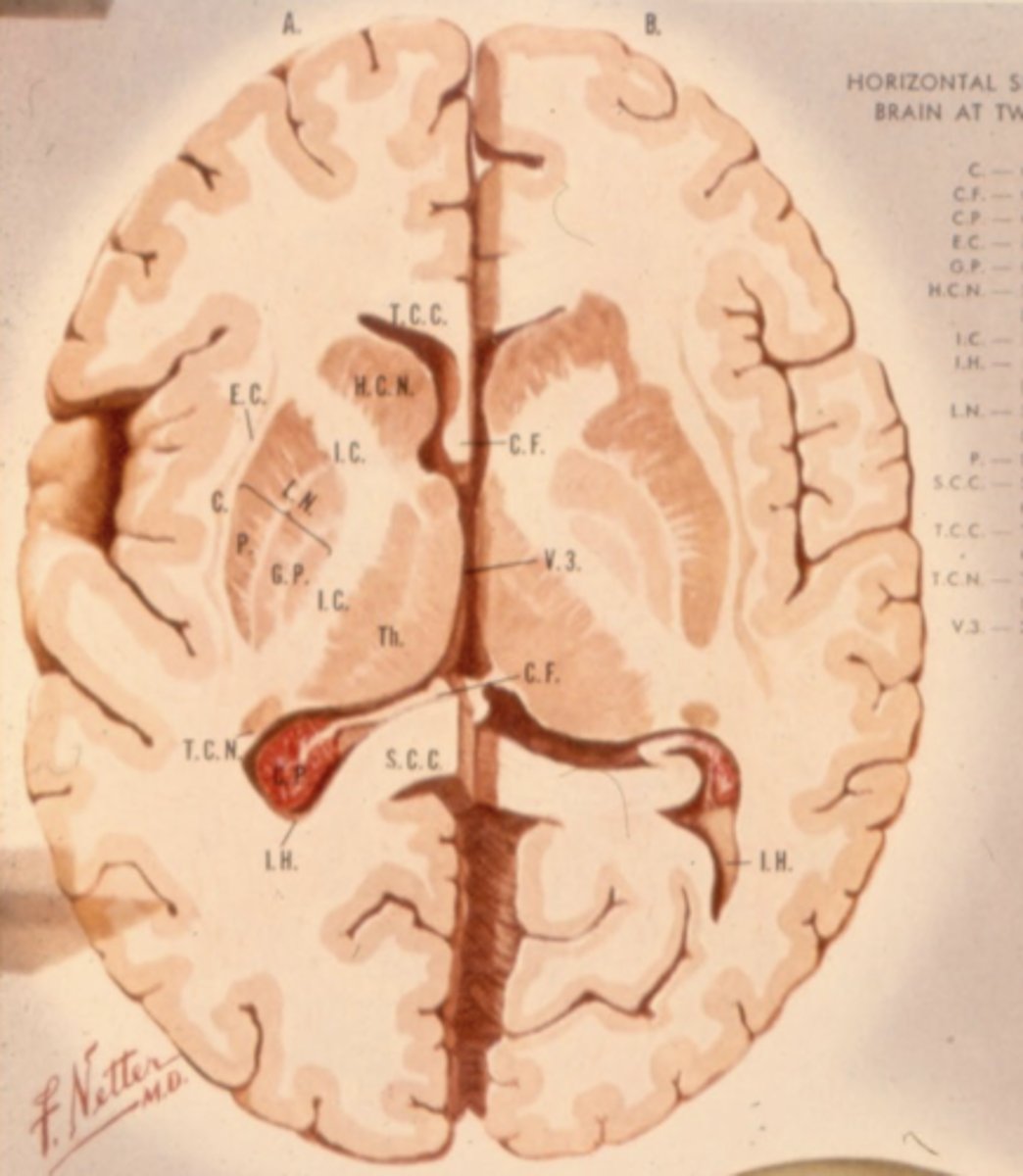
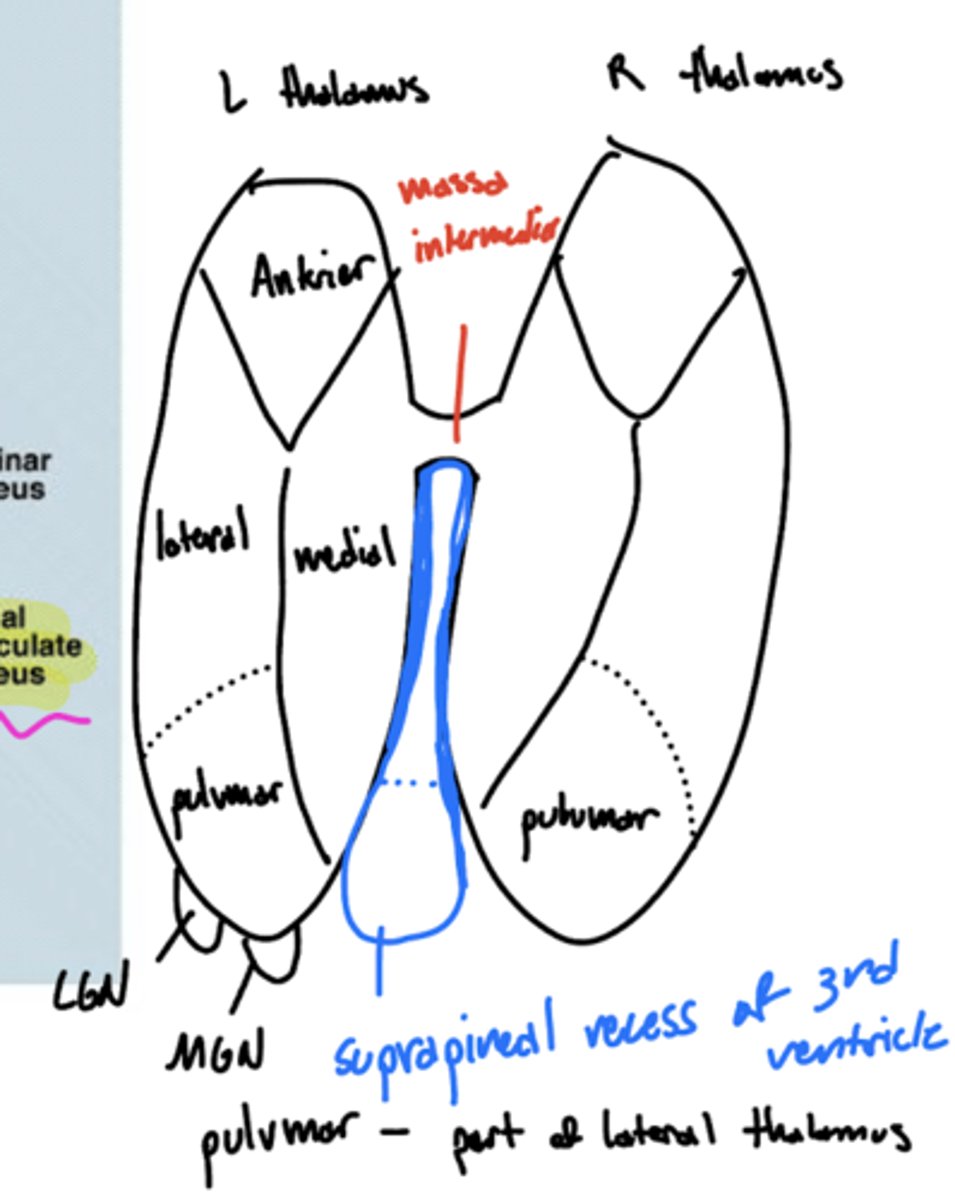
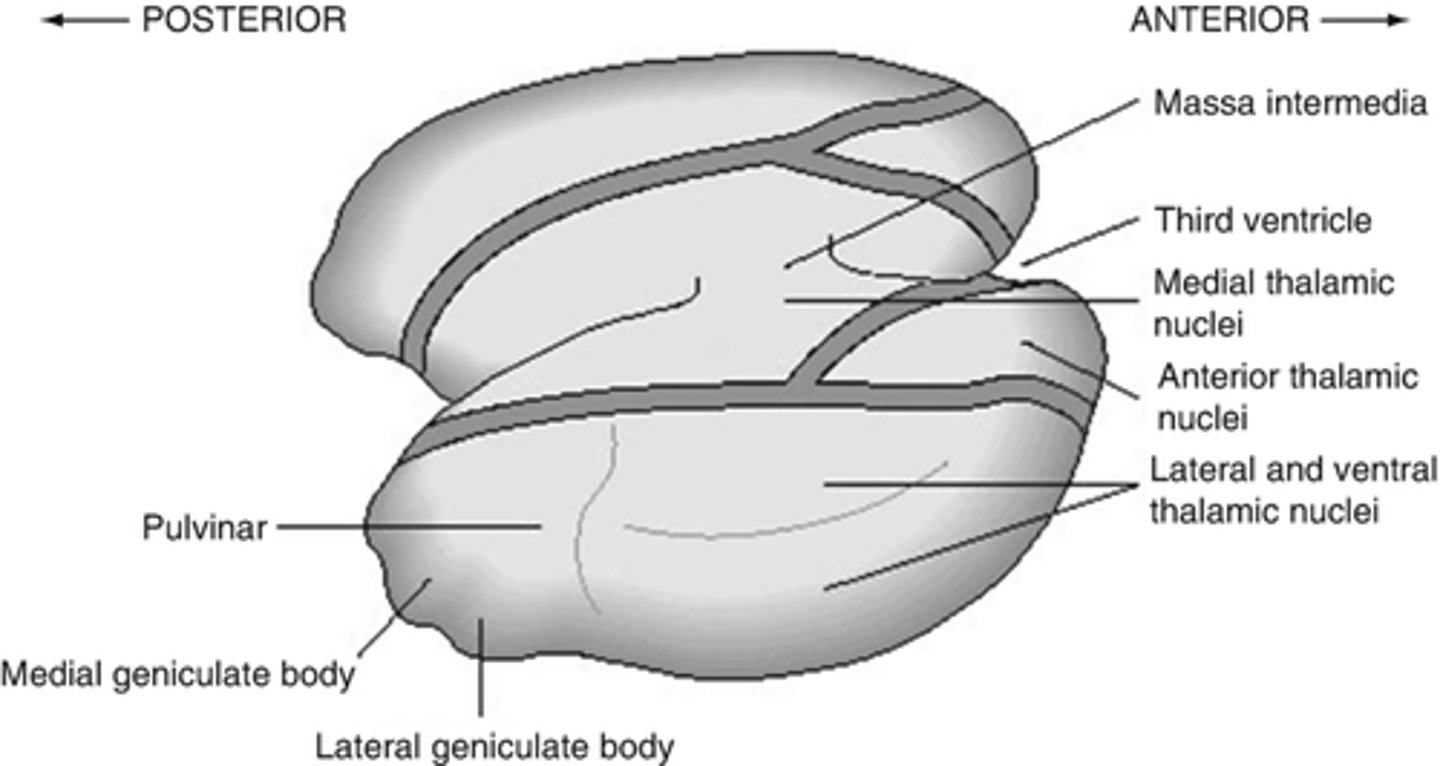
What is the massa intermedia?
the neuronal connection between the two thalami
What does the massa intermedia pass through?
3rd ventricle
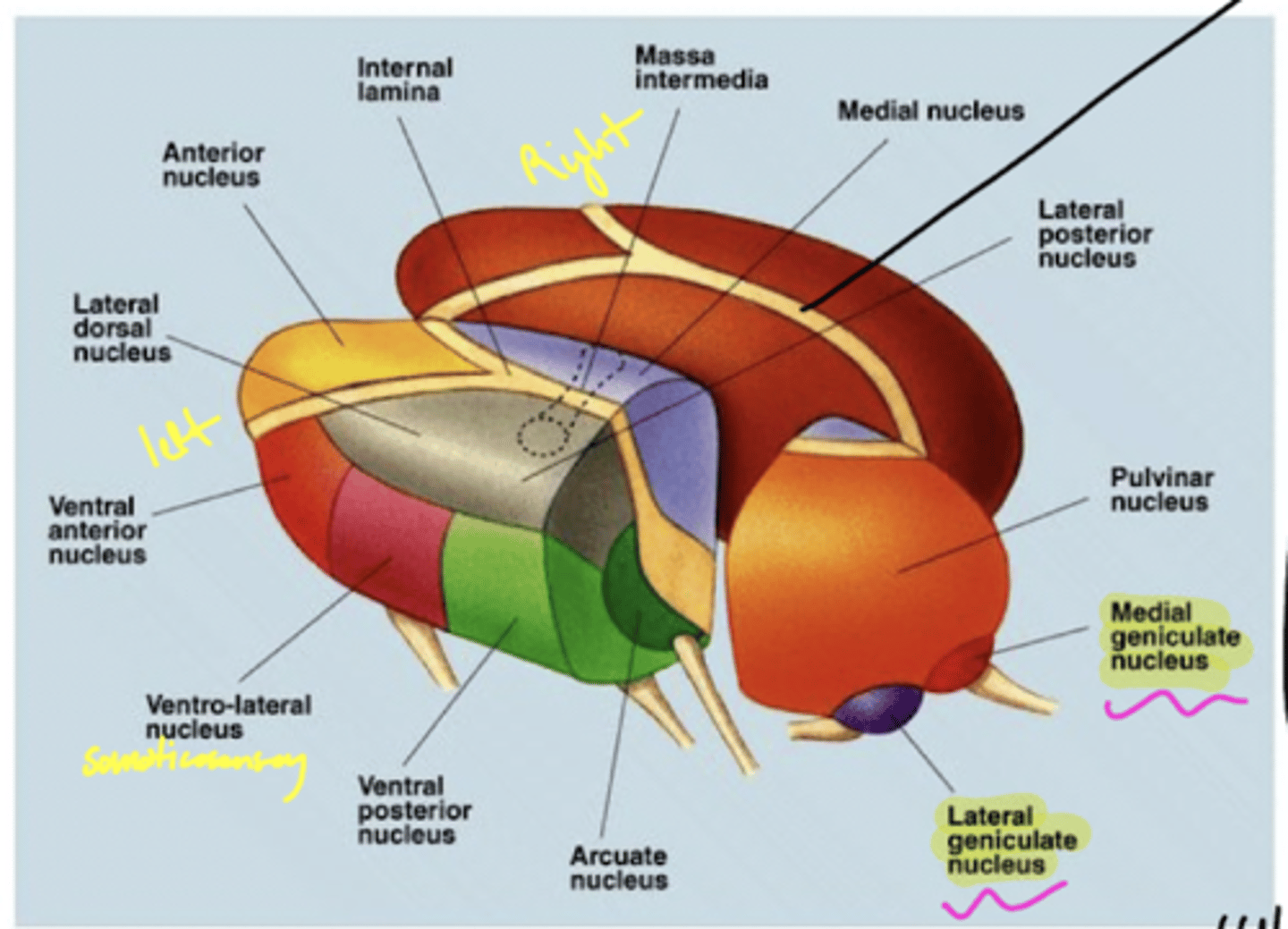
What are the three nuclear complexes of the thalamus?
1. anterior nuclei
2. medial nuclei (connected by massa intermedia)
3. lateral nuclei
What is efferent to the anterior nuclei of the thalamus?
hippocampus via the cingulum
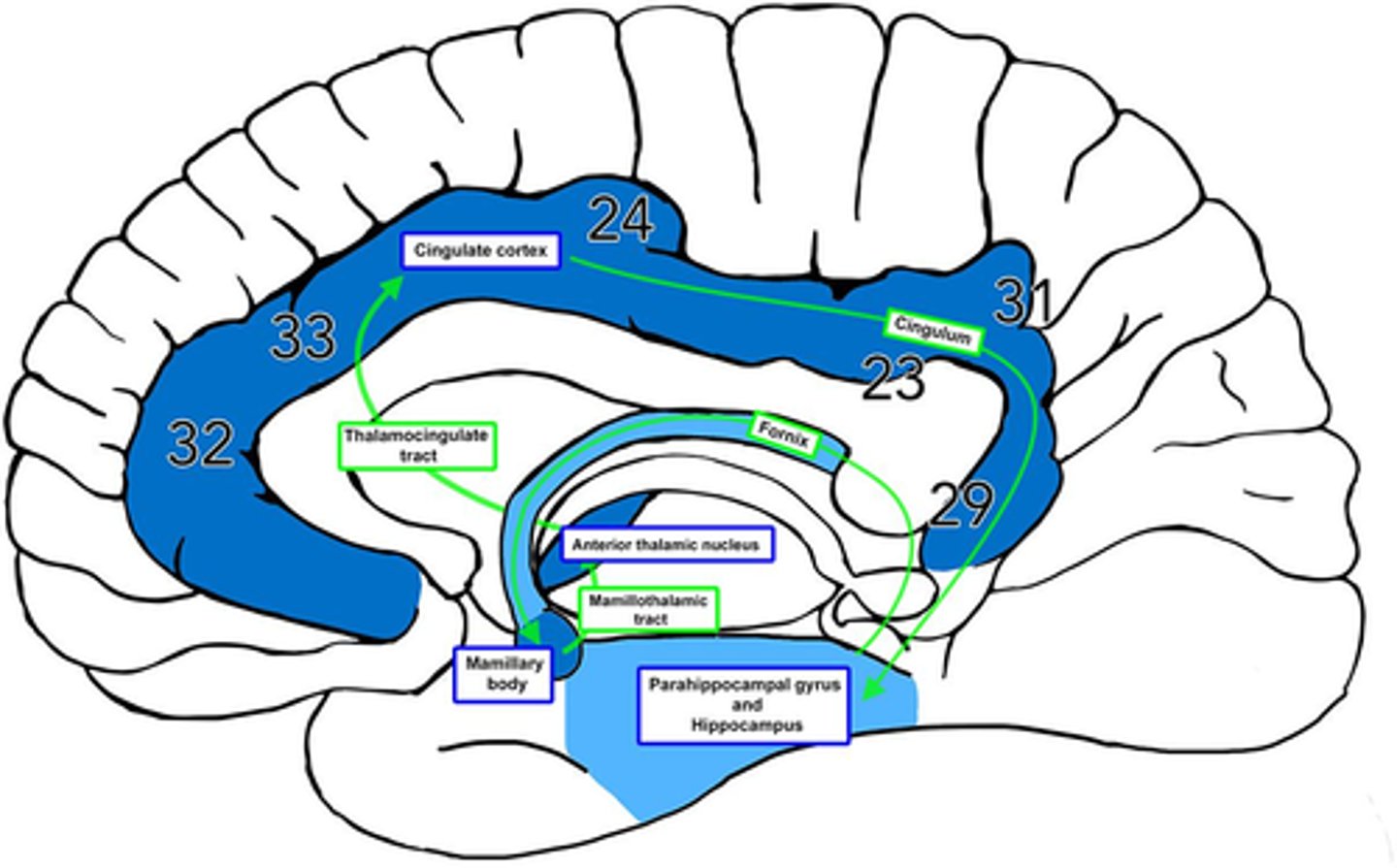
What is afferent to the anterior nuclei of the thalamus?
hippocampus and hypothalamus via mammillothalamic tract
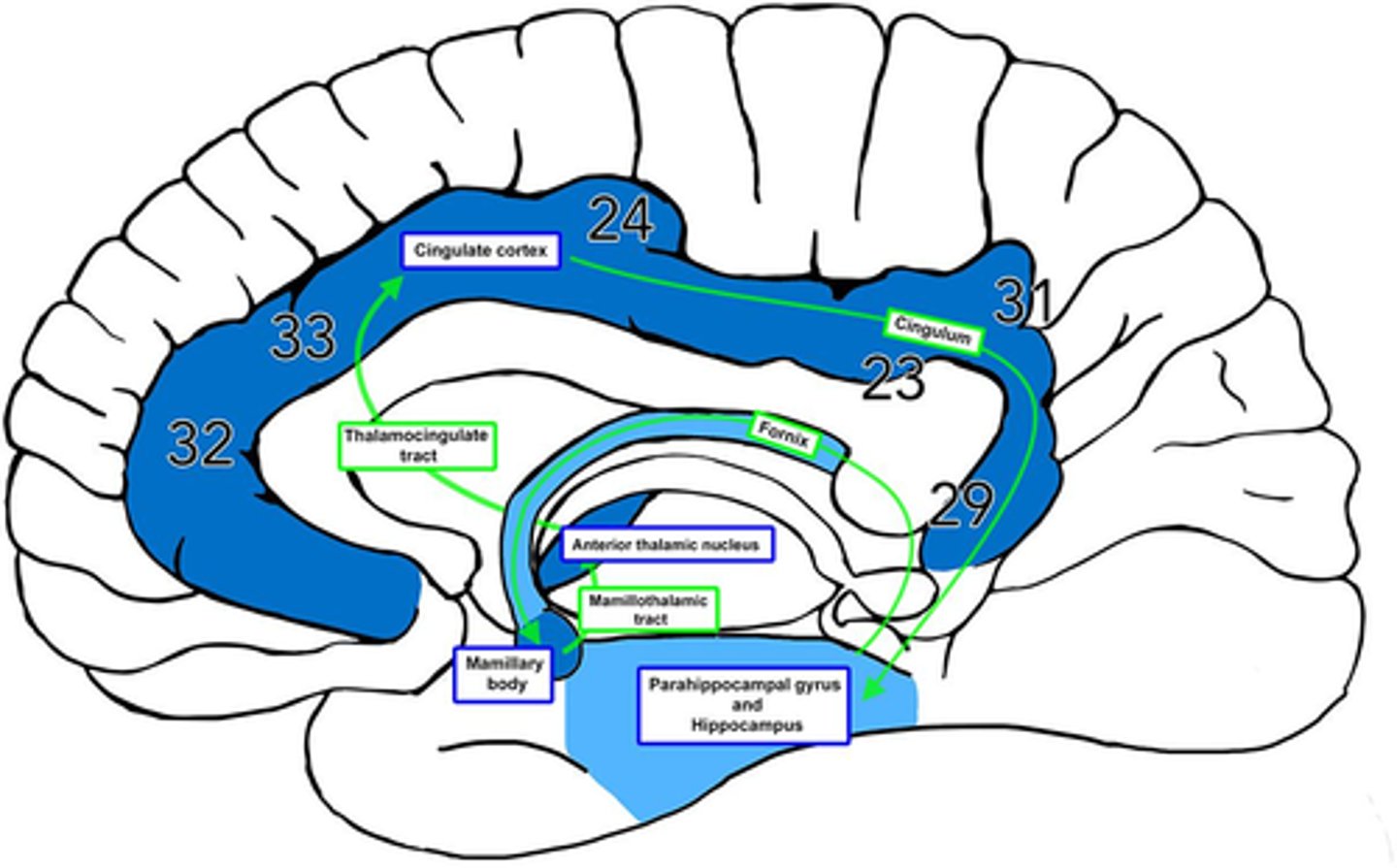
What is the pathway from the hippocampus to the anterior nuclei of the thalamus?
1. hippocampus
2. fornix
3. mammillary nuclei
4. mammillothalamic tract
5. anterior nuclei (thalamus)
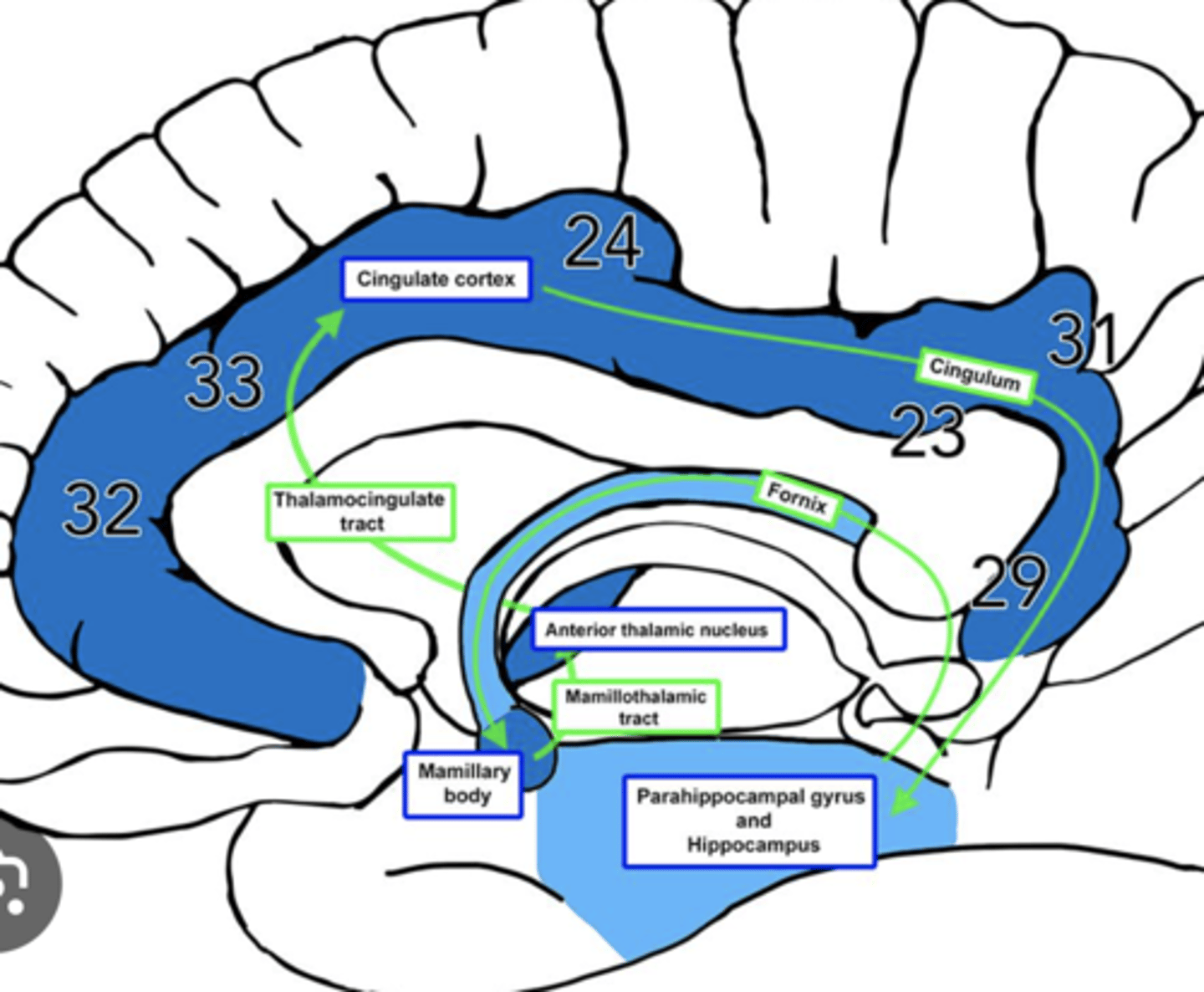
What is the medial nuclei connected to?
1. each other via massa intermedia
2. prefrontal cortex
why prefrontal cortex? -- afferent for medial/lateral portions of the medial nucleus
What are the nuclei (discussed) of the lateral nuclei of the thalamus?
1. LGN
2. MGN
3. pulvinar
4. VPL
5. VPM
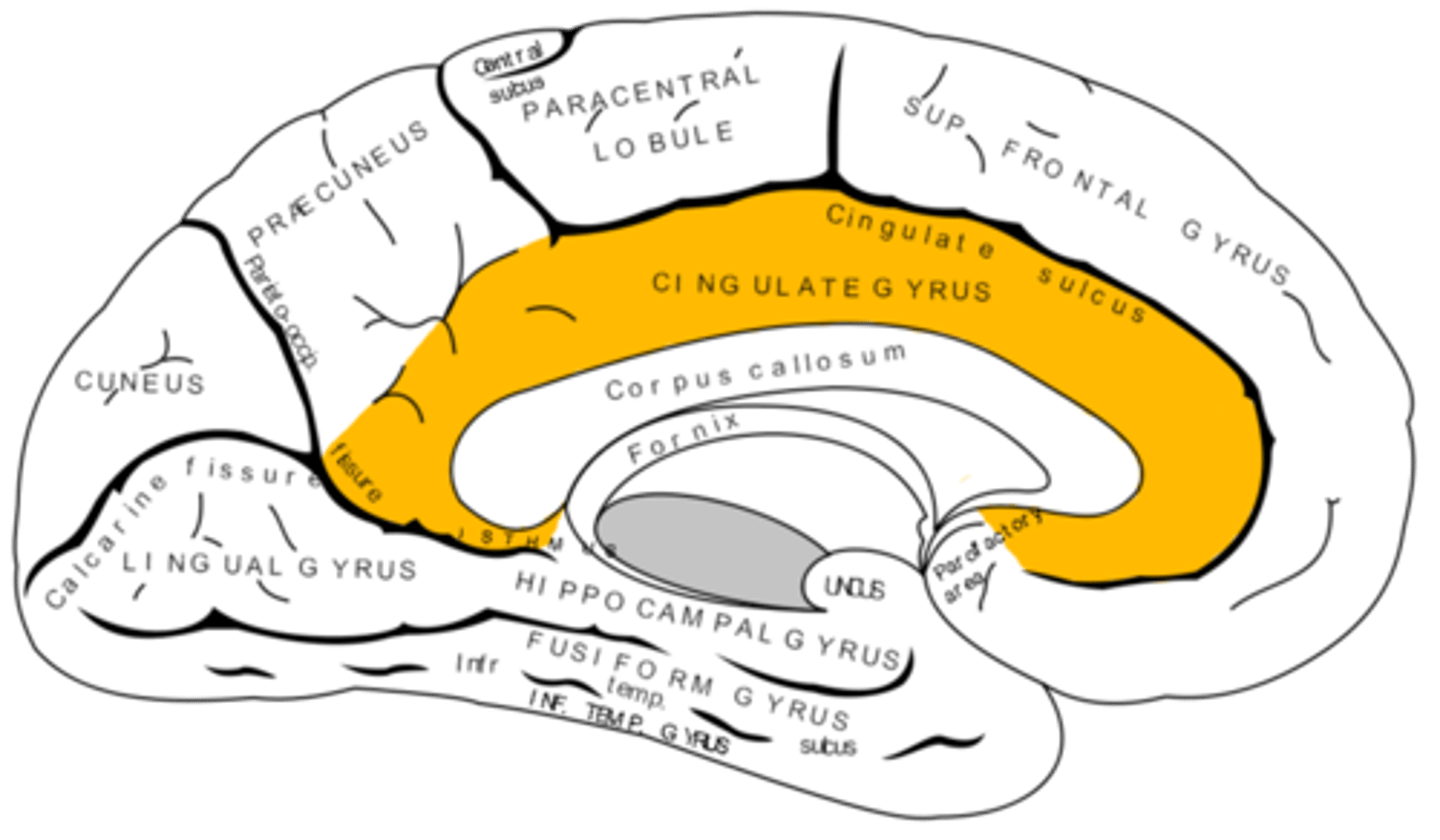
Where does the cingulate gyrus run?
superior to the corpus callosum
What does the lateral portion of the medial nucleus of the thalamus receive projections from?
1. superior colliculus
2. olfactory cortex
3. ventral pallidum
What is the function of the superior colliculi?
coordination of eye movements
What is efferent to the lateral portion of the medial nucleus of the thalamus?
frontal eye fields (anterior cortex of the frontal lobes)
why? -- control eye movements
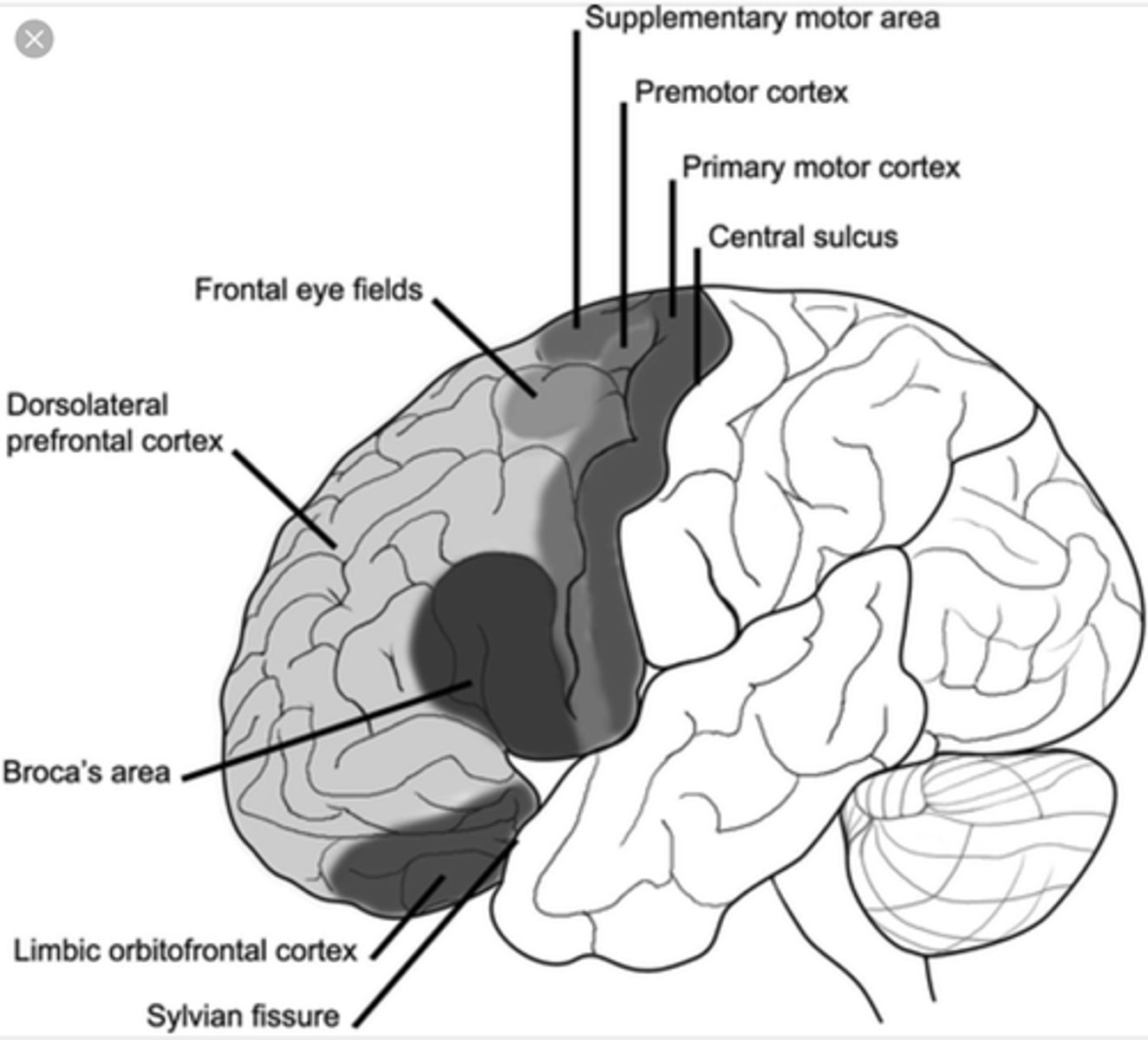
What are the functions of the lateral portion of the medial nucleus of the thalamus?
1. control eye movements and attending to visual stimuli
2. role in emotional "tone"
What is efferent to the medial portion of the medial nucleus of the thalamus?
1. limbic areas (emotion)
2. insular cortex
3. orbital frontal cortex
What are the functions of the medial portion of the medial nucleus of the thalamus?
1. autonomic regulation
2. emotions
why the GI can act up from emotions
What are the nuclei (discussed) of the lateral nucleus of the thalamus?
1. LGN
2. MGN
3. VPL (ventral posterolateral nucleus)
4. VPM (ventral posteromedial nucleus)
5. pulvinar
Where does the LGN project?
17 -- primary visual cortex
Where does the MGN project?
41 -- primary auditory cortex
Where does the VPL project?
3, 1, 2 -- somatosensory cortex (body)
Where does the VPM project?
3, 1, 2 near the lateral fissure -- somatosensory cortex
processing of the face
What is the pulvinar of the thalamus?
largest association nucleus of the thalamus
What is afferent to the pulvinar of the thalamus?
superior colliculus (and its association areas)
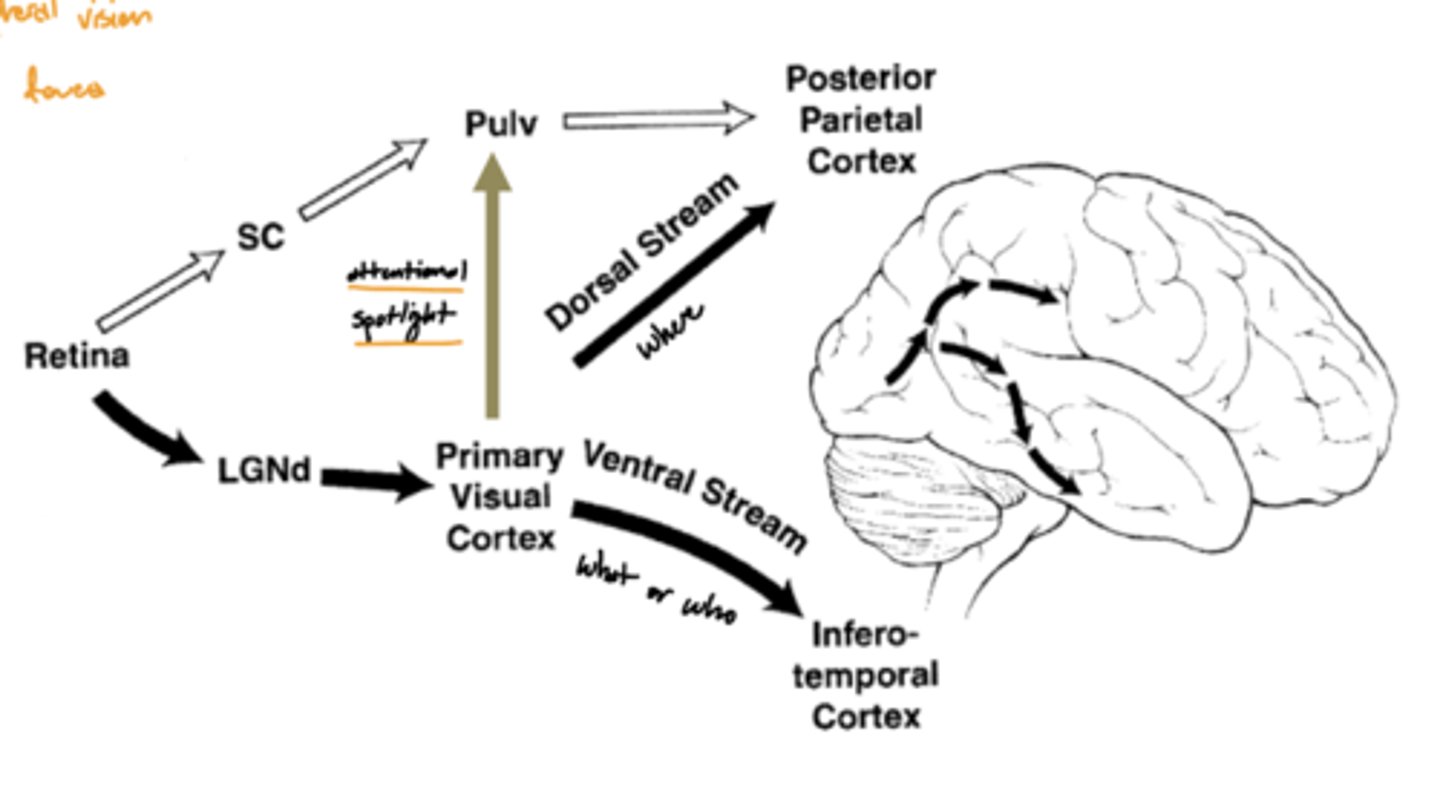
Where does the pulvinar of the thalamus project?
secondary visual areas (and association areas of the parietotemporal region)
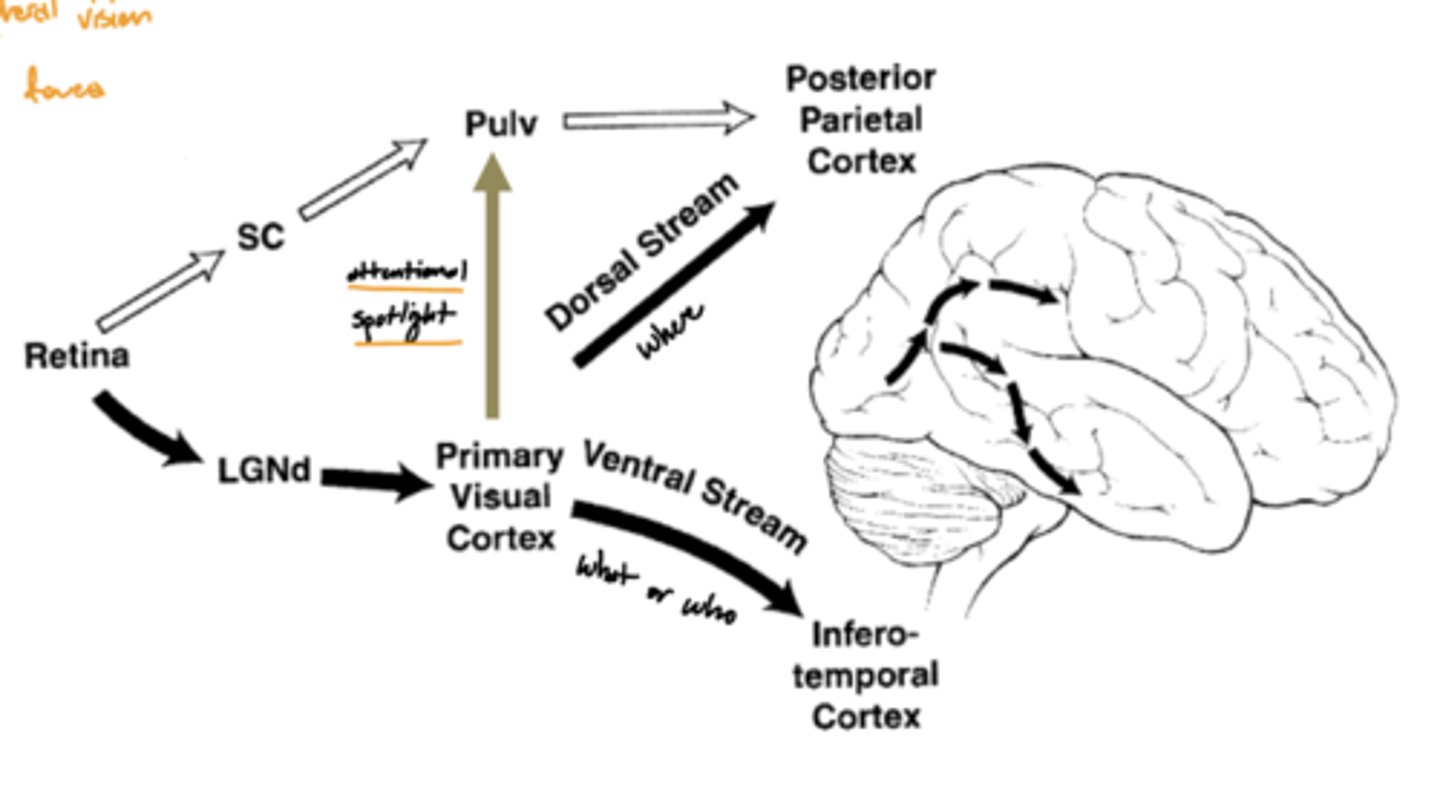
What are the functions of the pulvinar of the thalamus?
1. attention to visual stimuli (even in peripheral vision)
2. eye movements
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
homeostasis
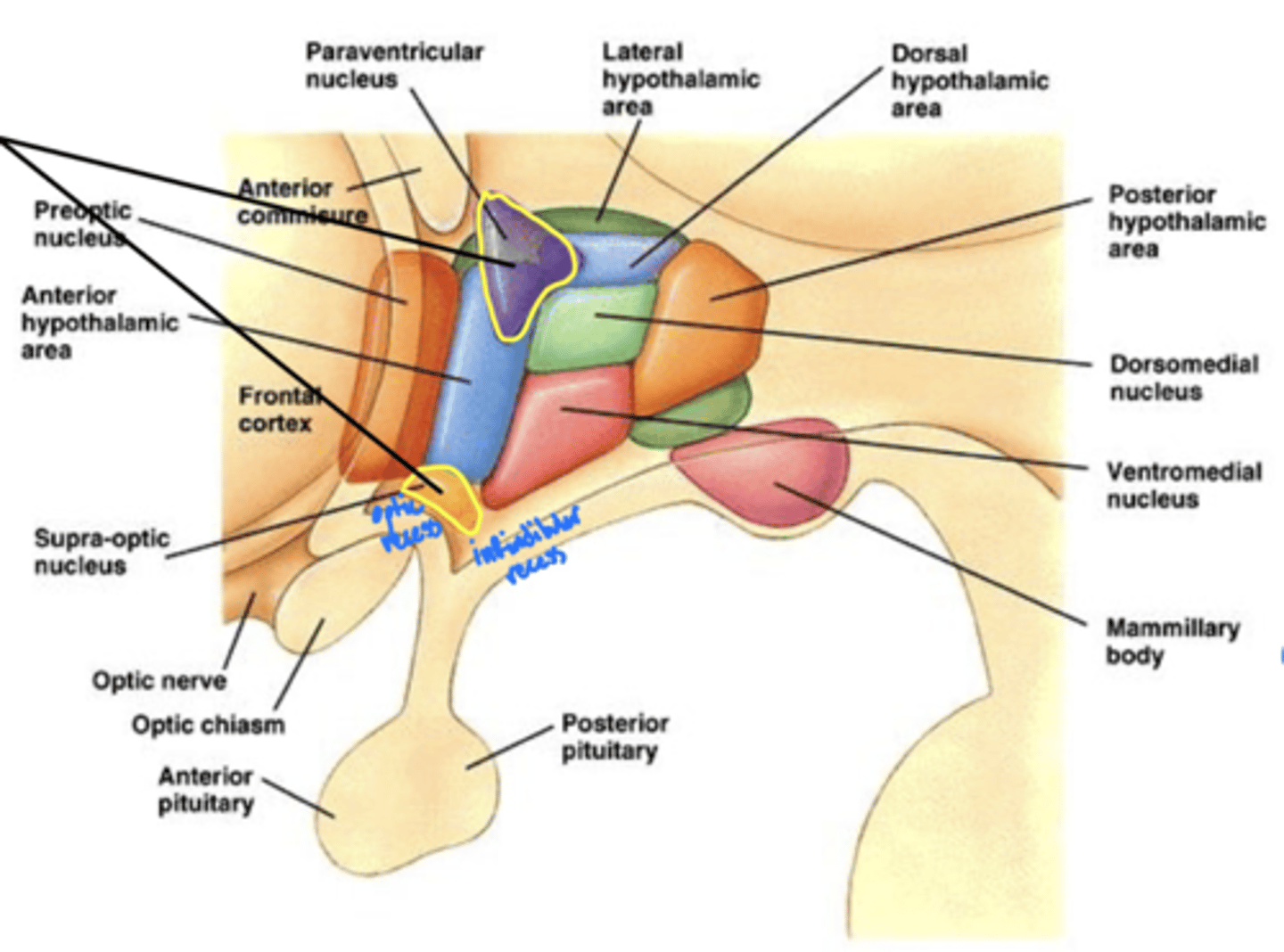
What is the hypothalamus just superior to?
1. optic chiasm
2. pituitary gland
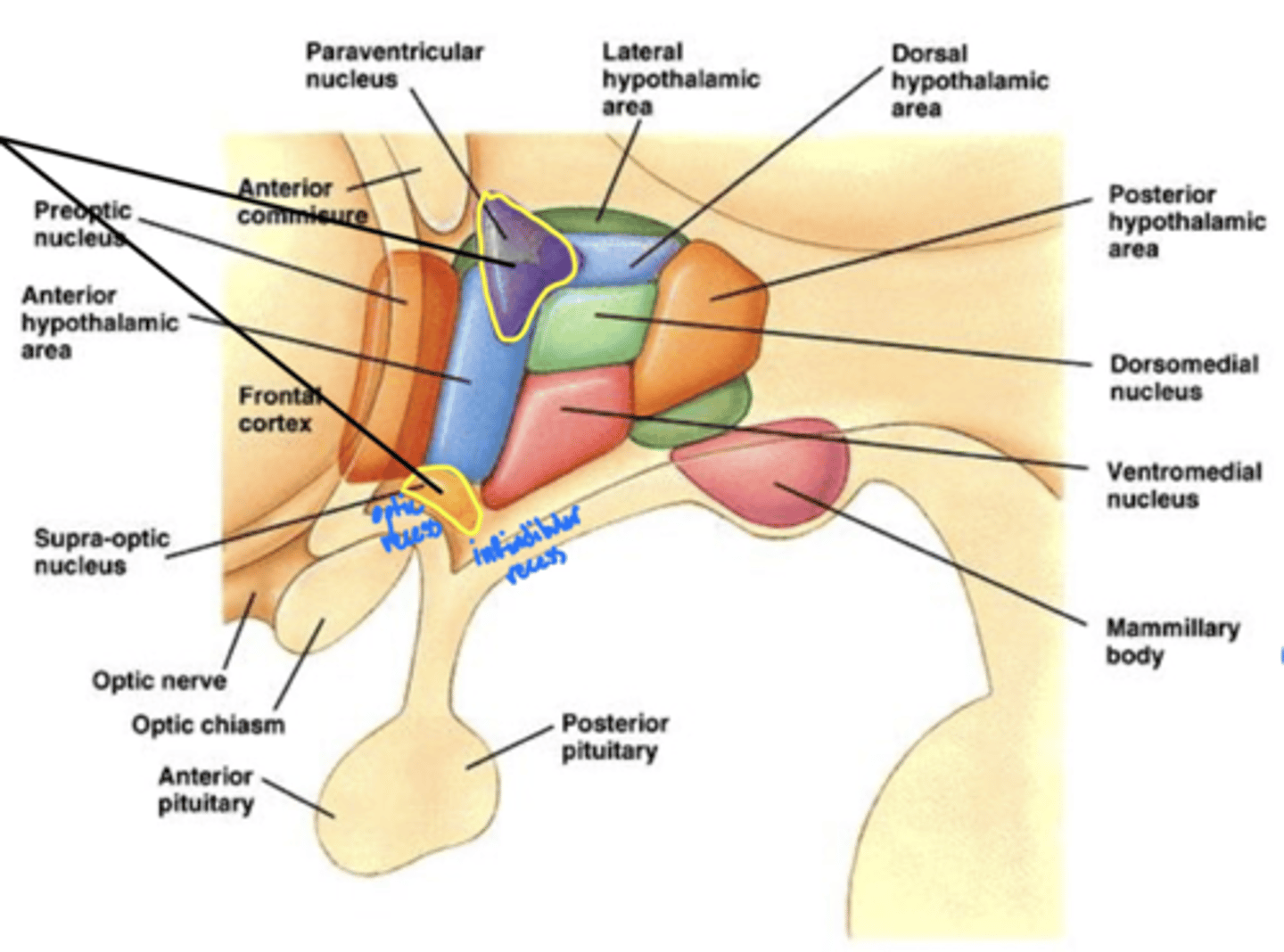
What nuclei of the hypothalamus produce hormones for the pituitary gland?
1. paraventricular nucleus
2. supra-optic nucleus
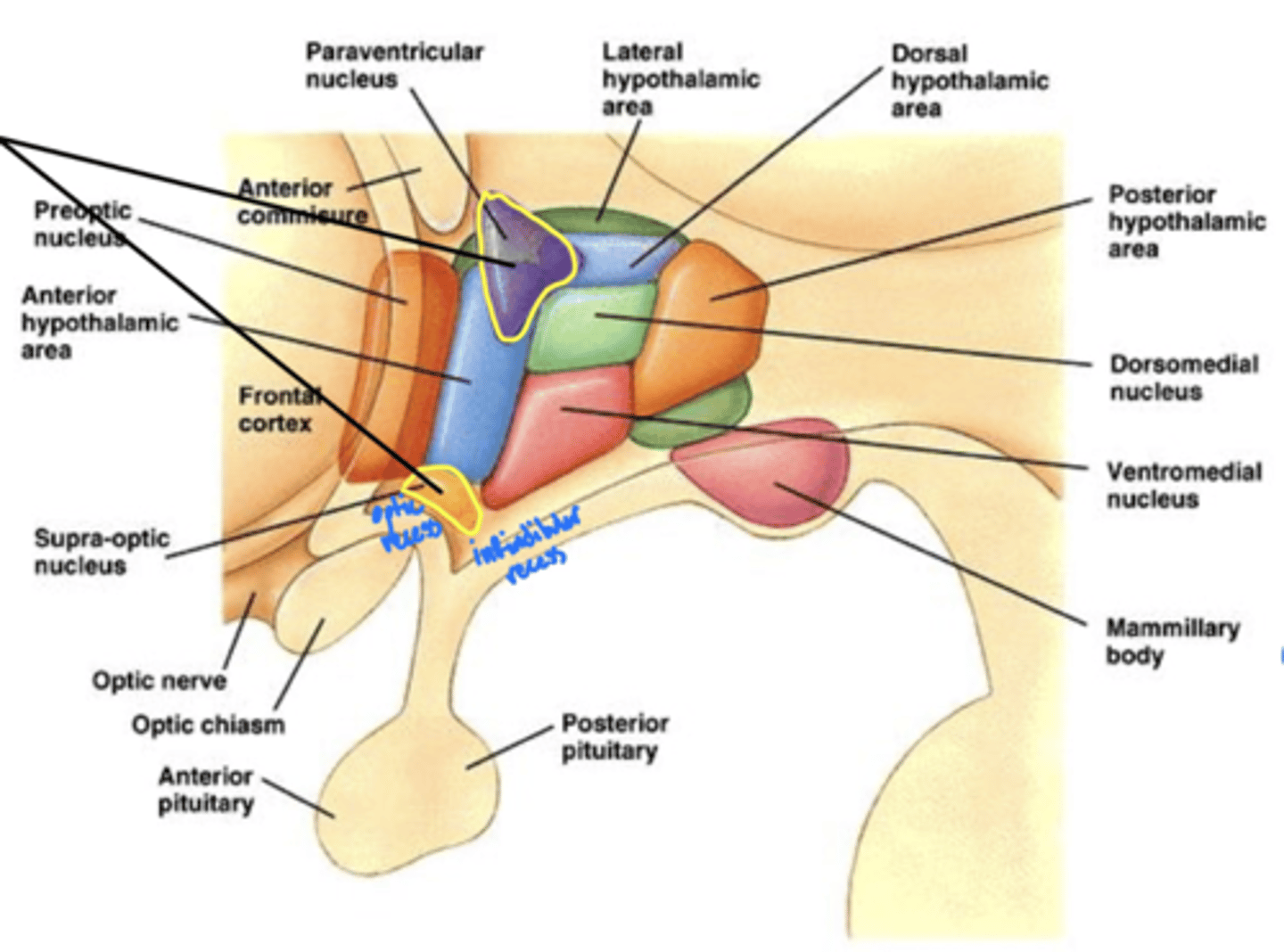
Where is the hypothalamus in relation to the thalamus?
anteroinferior (in front and below)
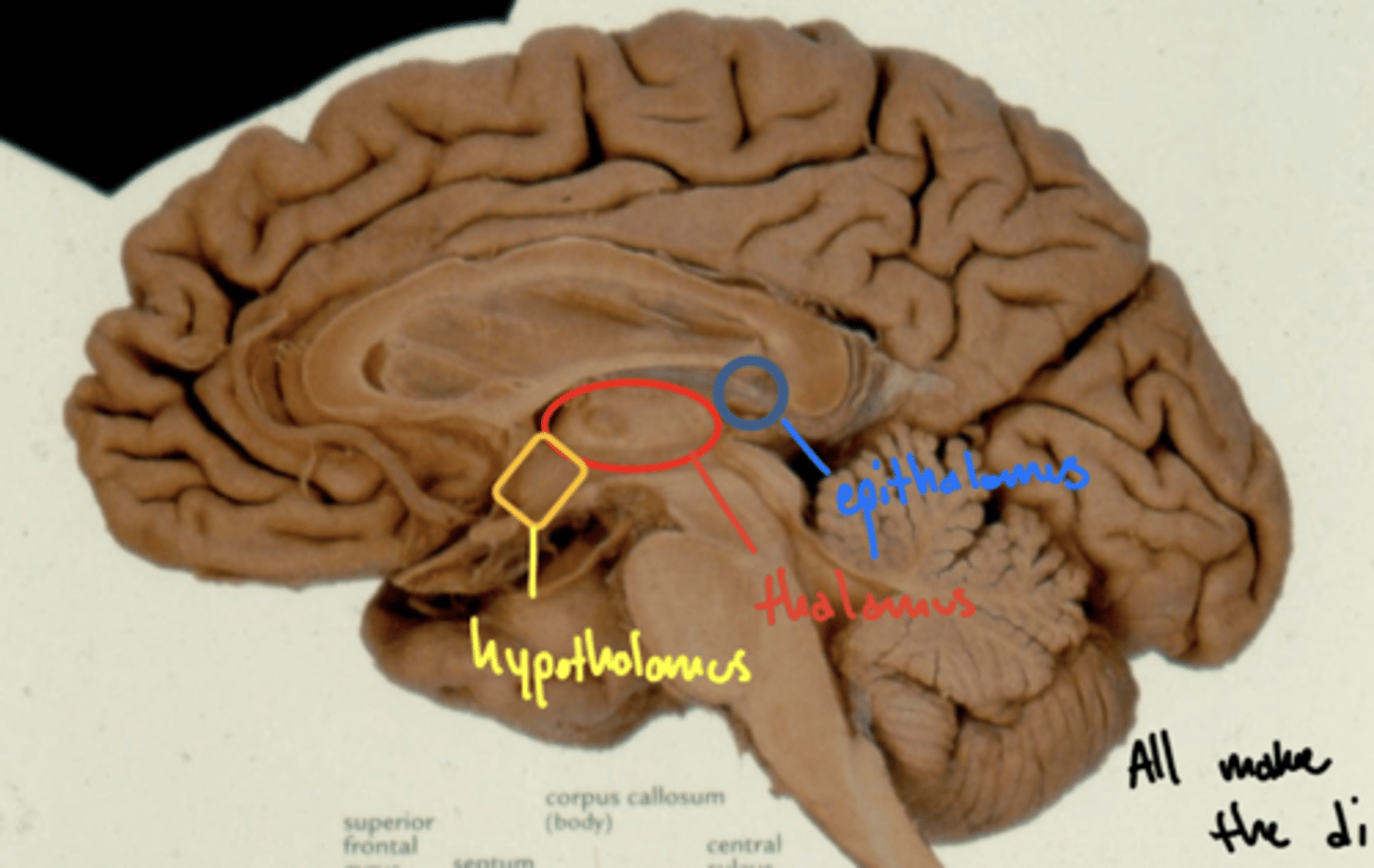
Where is the epithalamus in relation to the thalamus?
posterosuperior (behind and above)
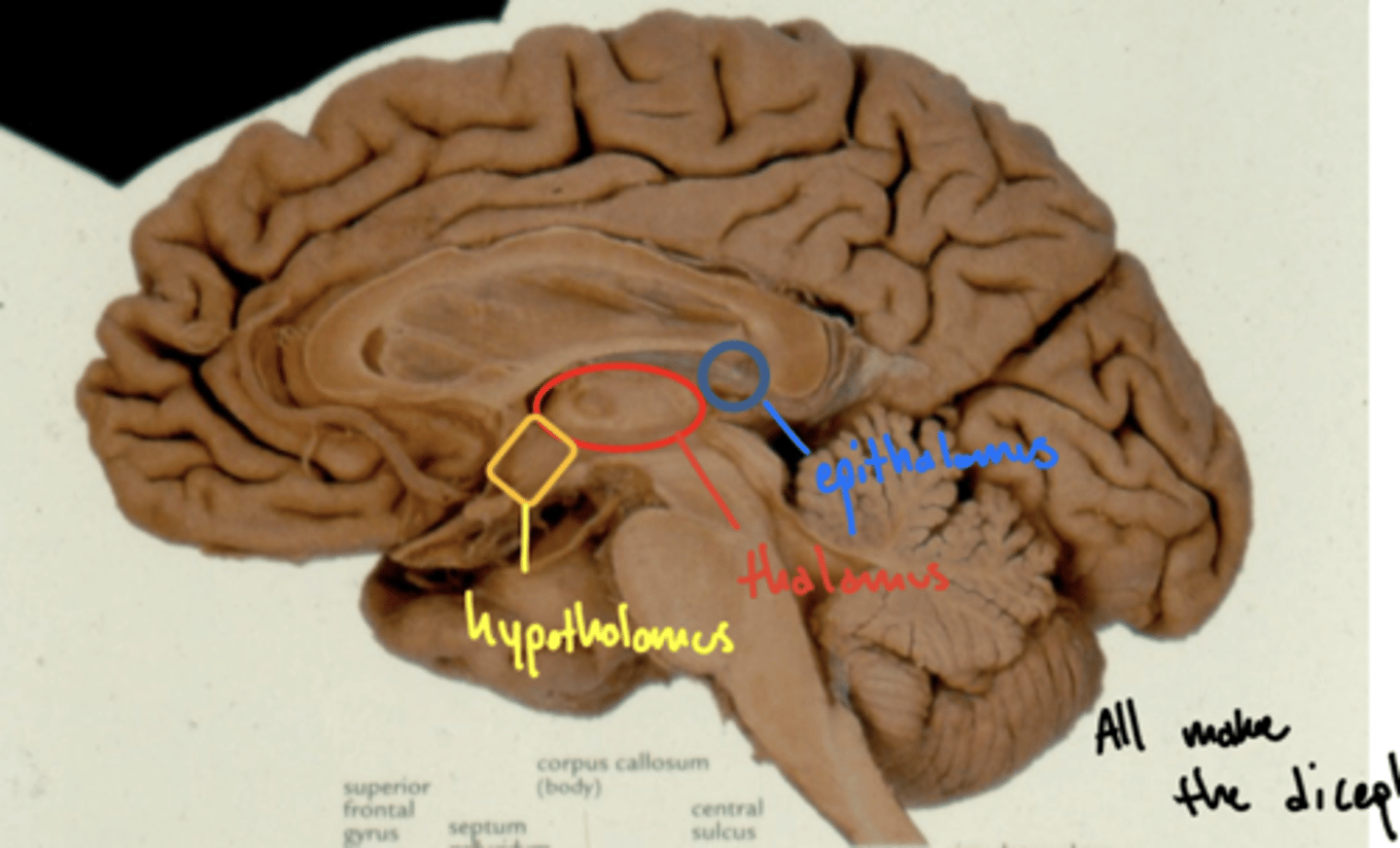
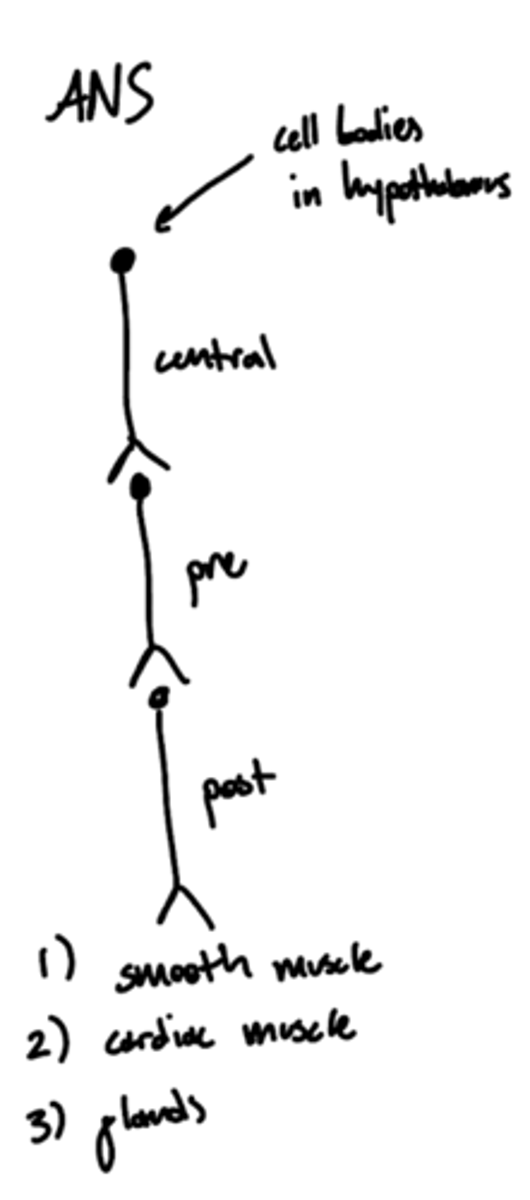
Where are the cell bodies of the central neurons of the autonomic nervous system?
hypothalamus
What is the primary nuclei of the epithalamus?
pineal body/gland
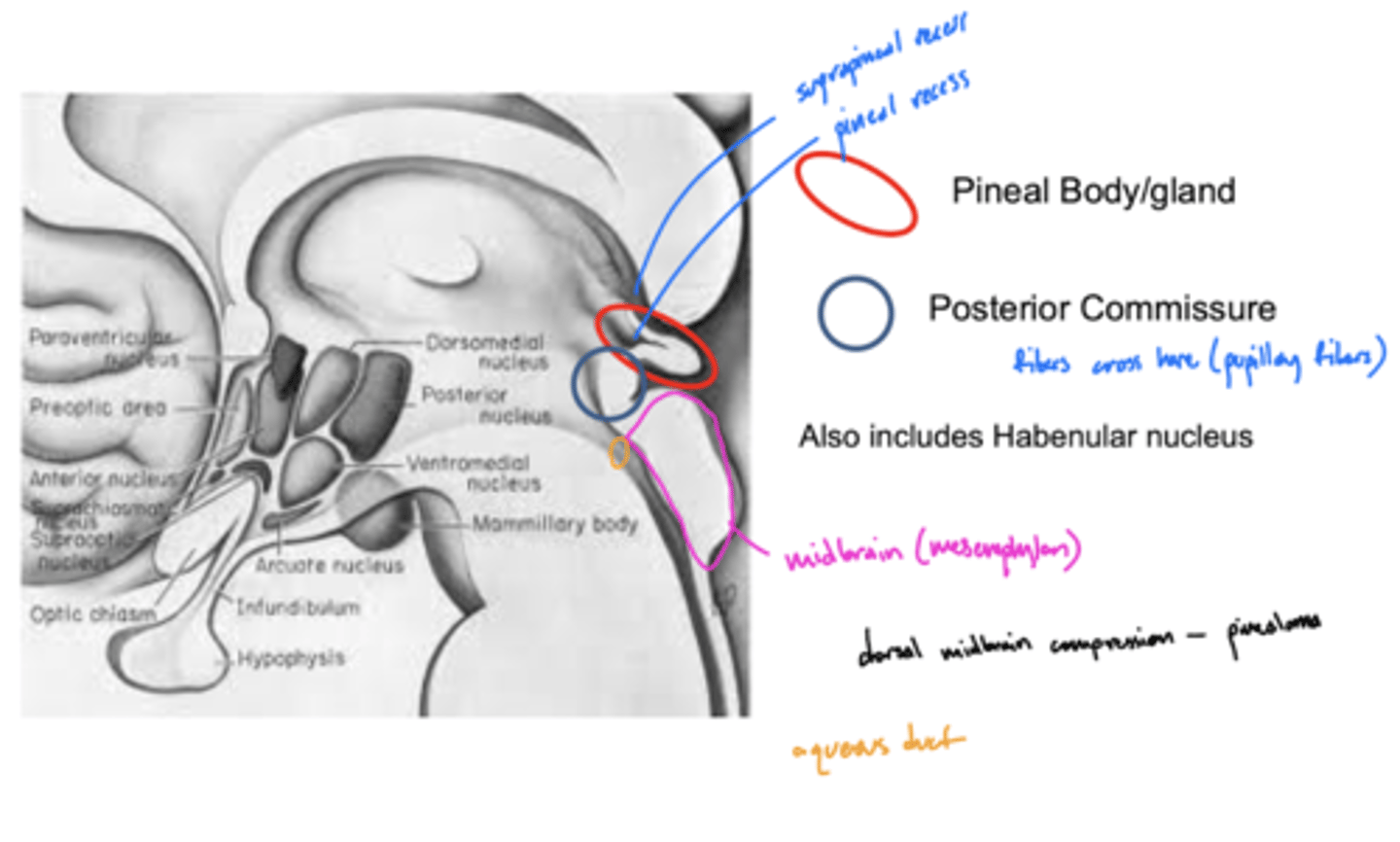
What structure is directly inferior to the pineal body of the epithalamus?
posterior commissure
What is the function of the posterior commissure?
largely unknown -- but... pupillary fibers cross here maybe light pupillary response
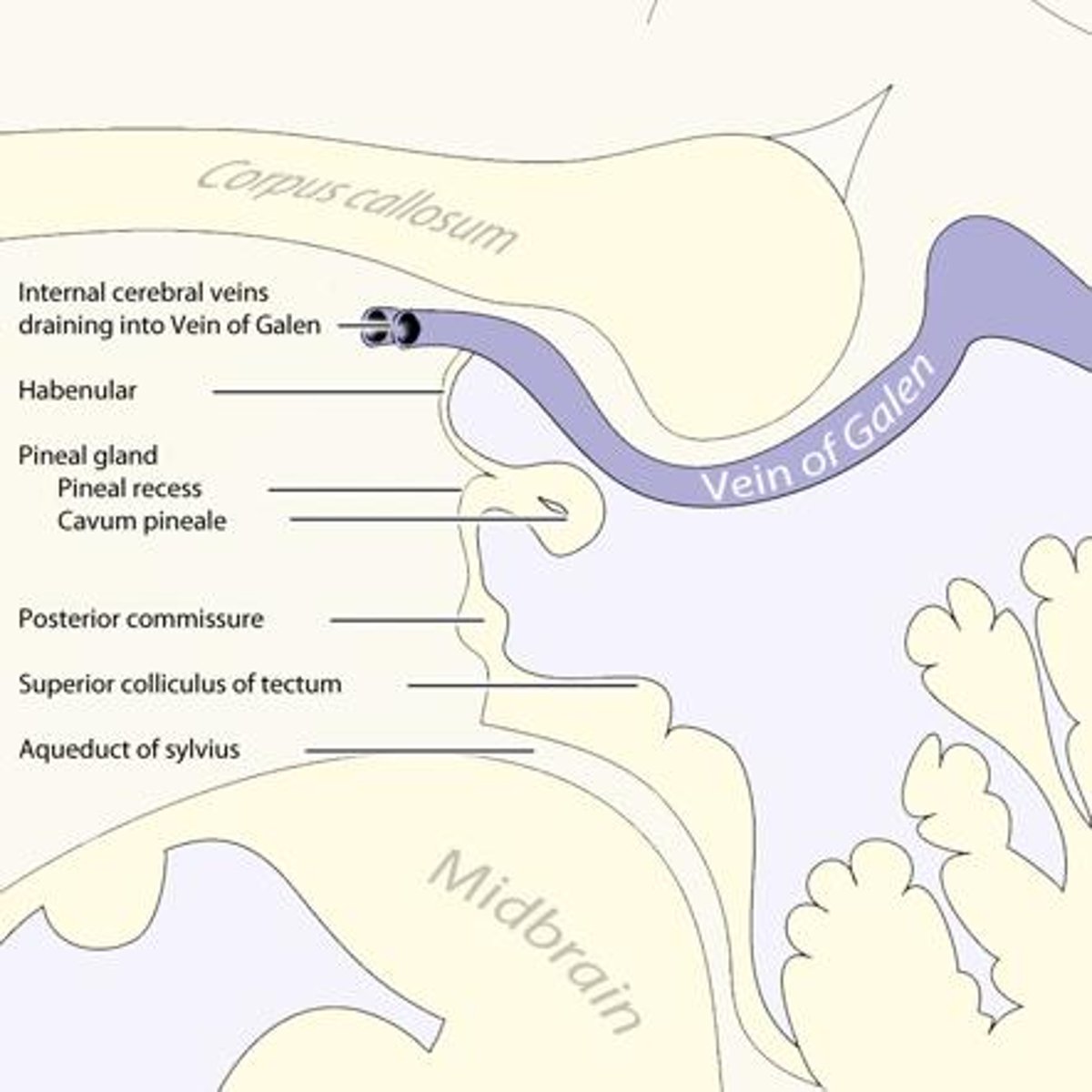
What is the function of the pineal gland of the epithalamus?
produces melatonin (and responsible for circadian rhythms)
What retinal cells project to the pineal gland, and why?
ipRGCs -- peak sensitivity at 480nm (blue), working on screens can interfere with sleep
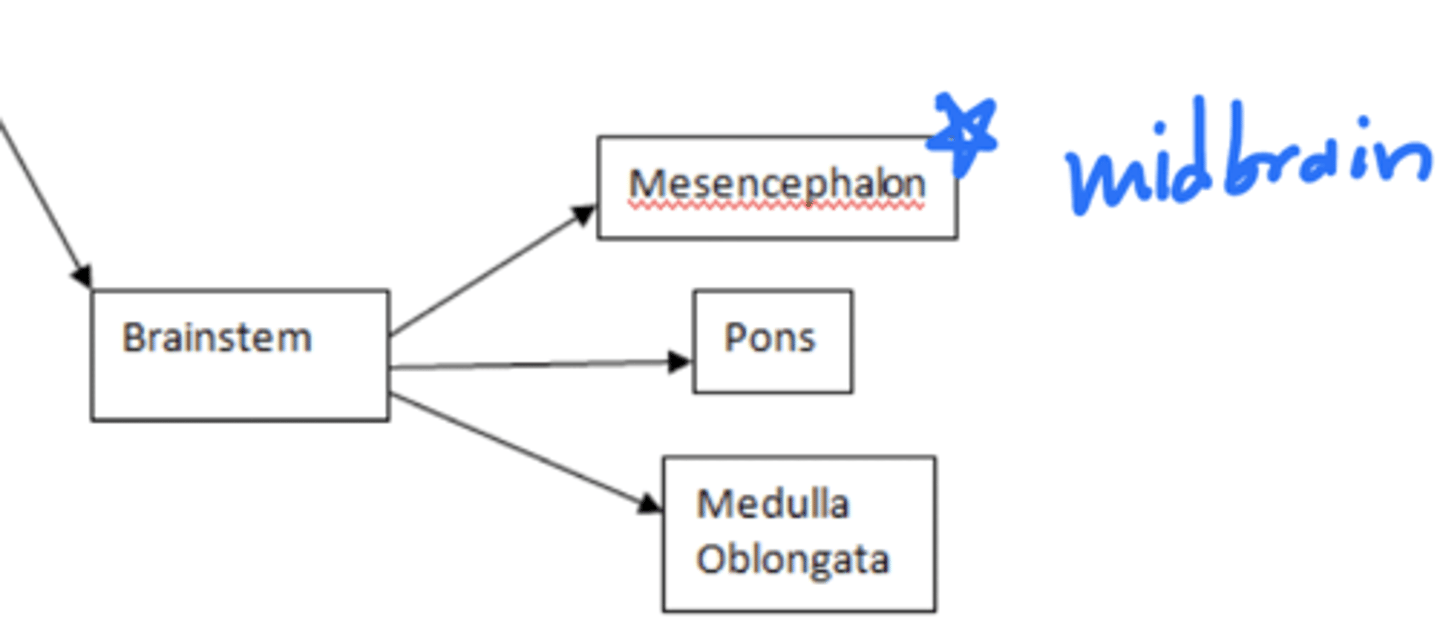
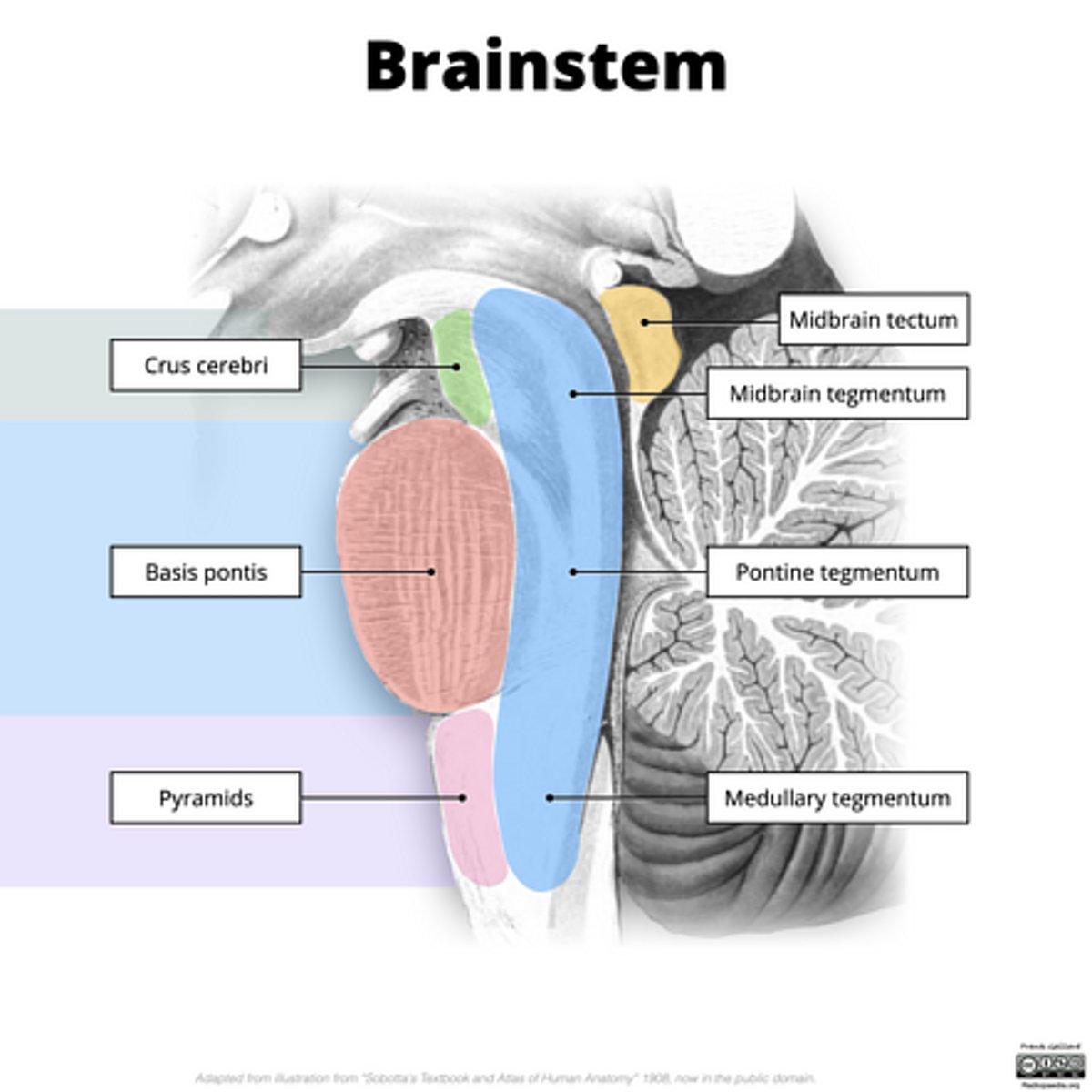
What are the structures of the brainstem?
1. mesencephalon (midbrain)
2. pons
3. medulla oblongata
What is the tectum?
roof of the midbrain
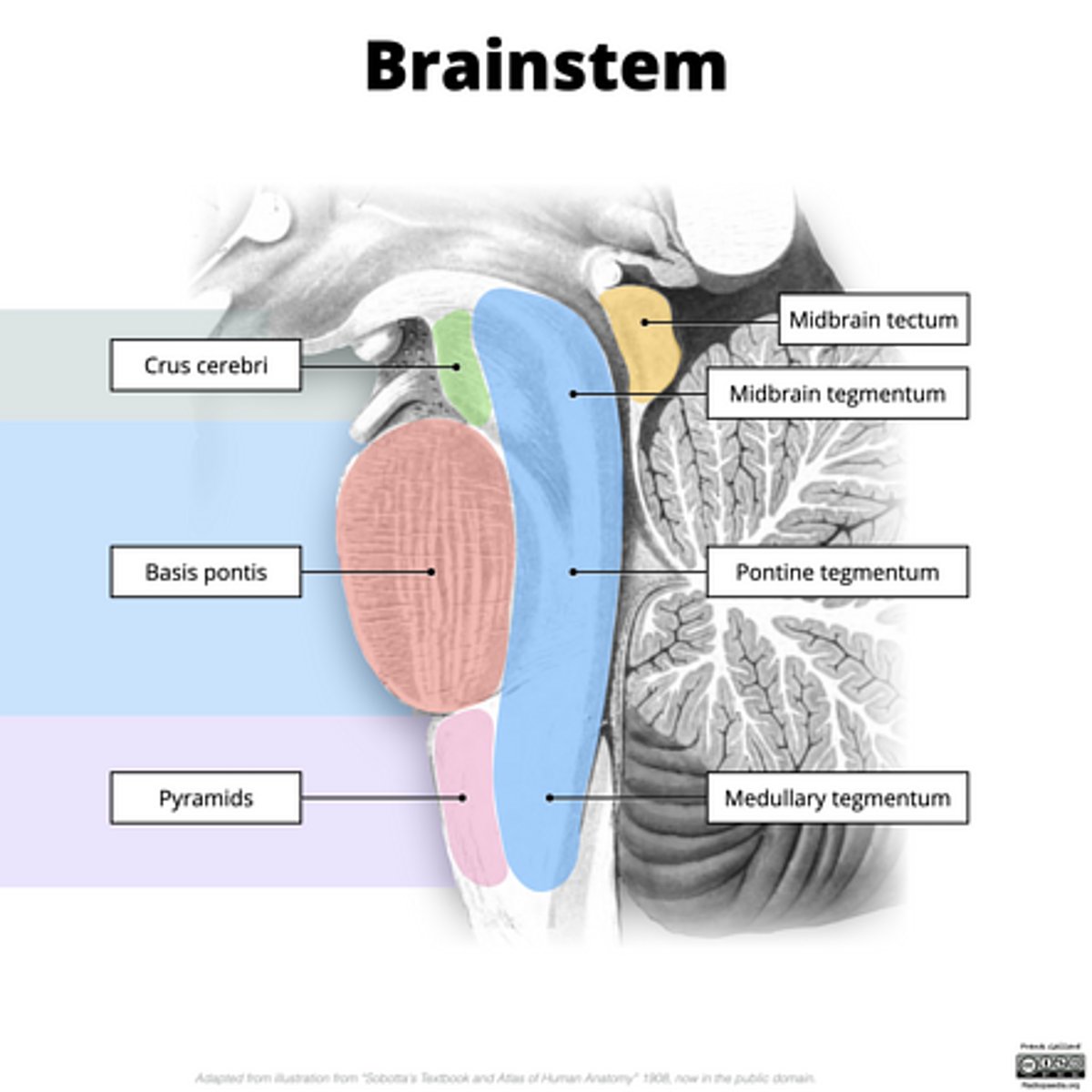
What is the tegmentum?
floor of midbrain
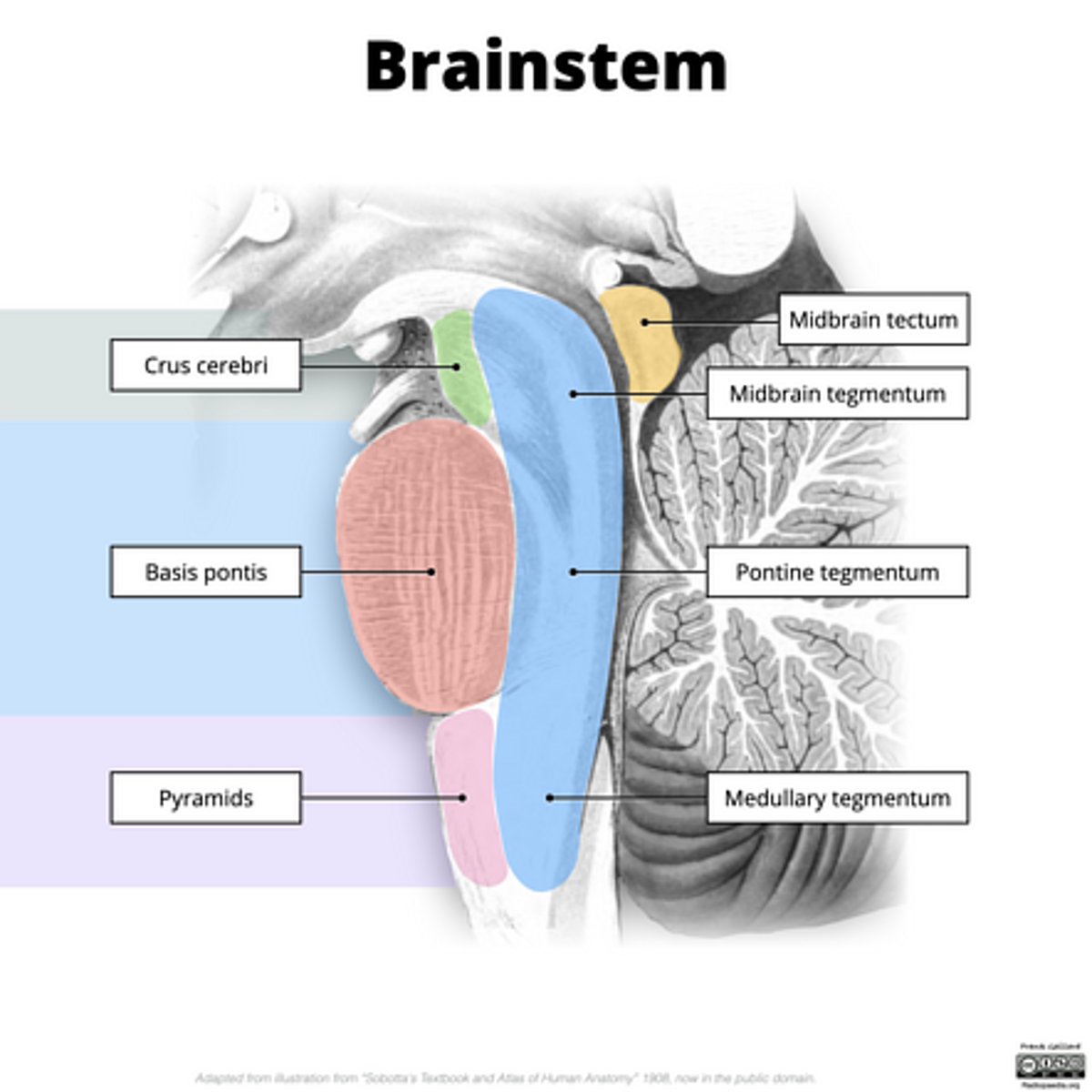
What are the fibers of the tegmentum?
ascending fibers
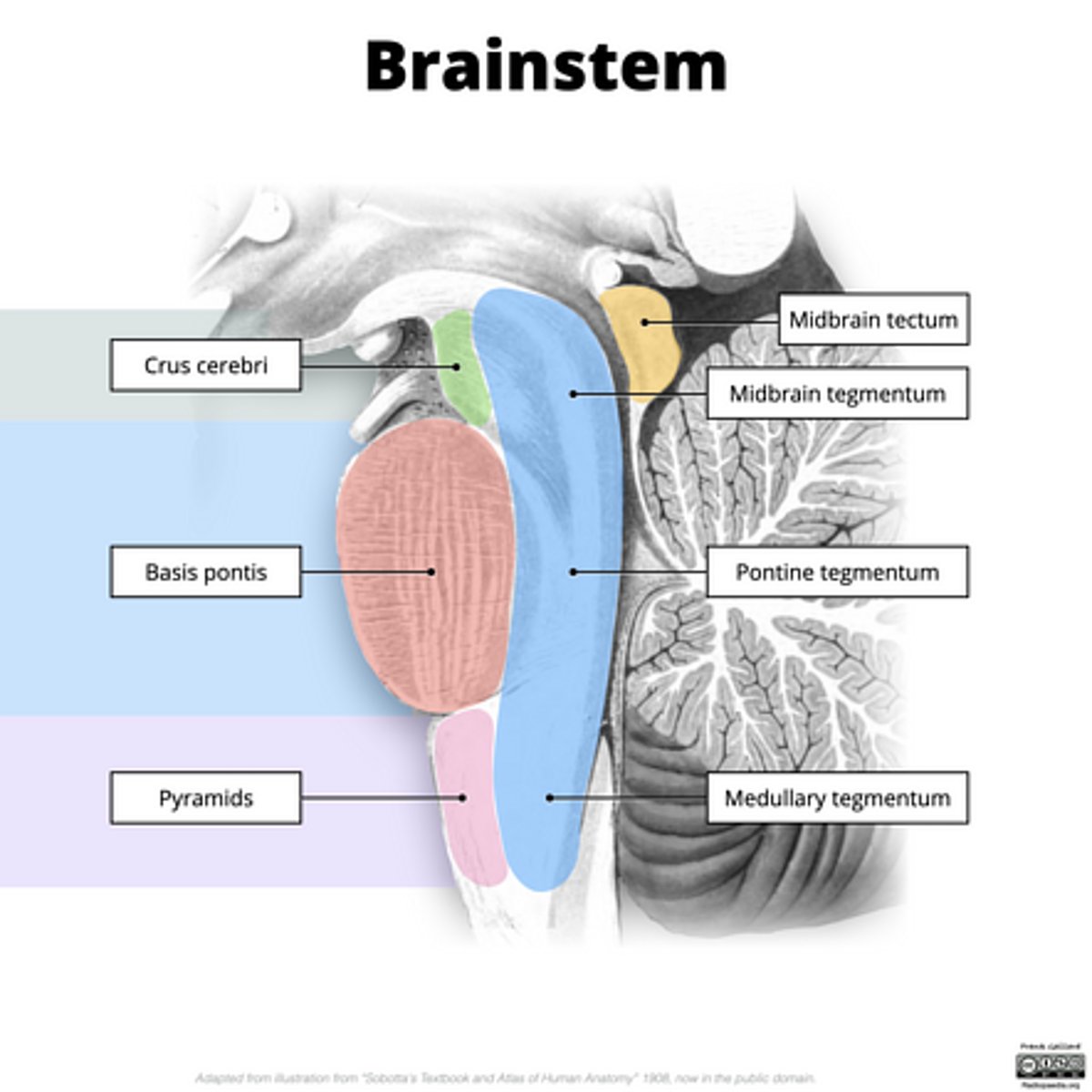
What is the crus cerebri?
part of the cerebral peduncles which contain descending tracts
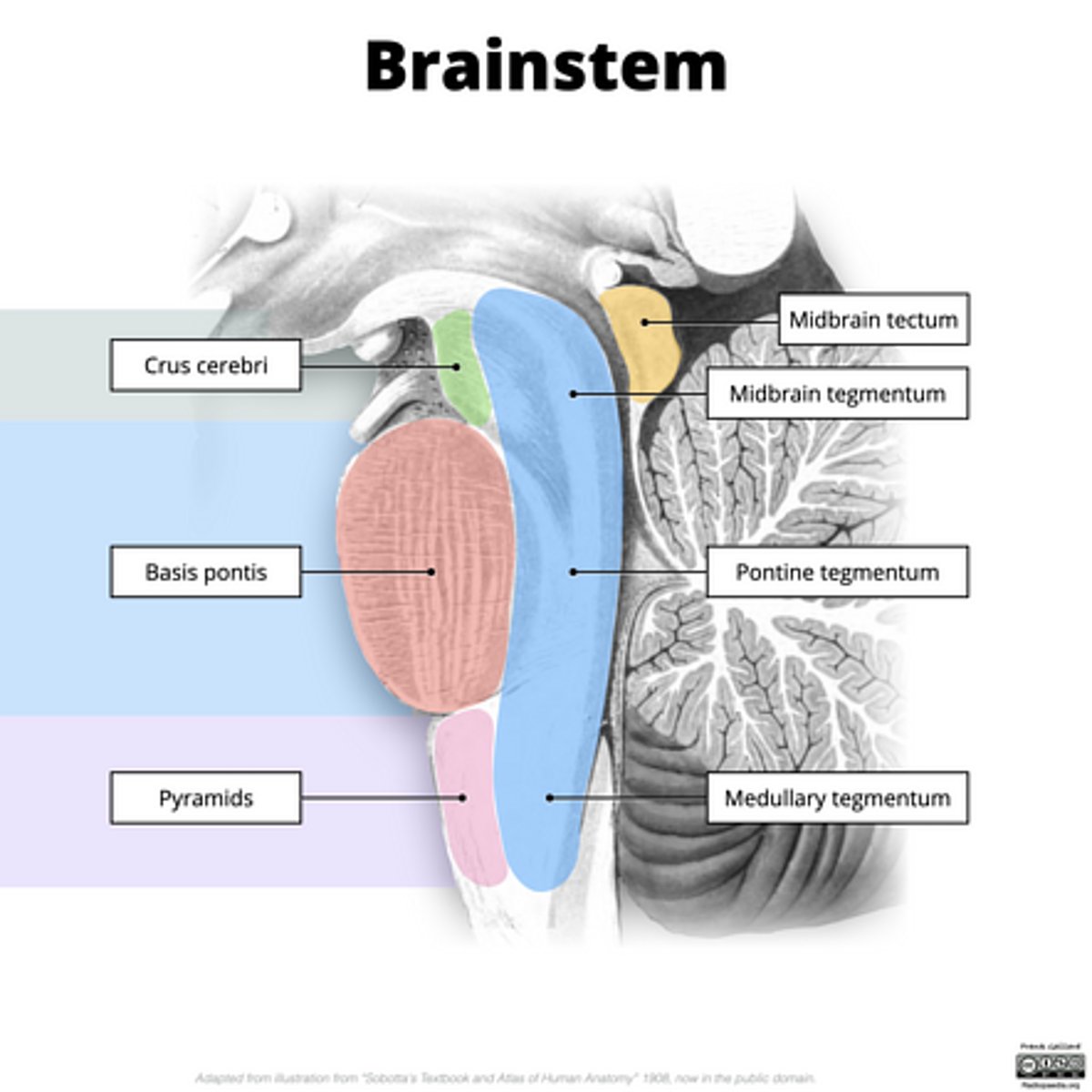
What are the fibers of the crus cerebri?
descending fibers
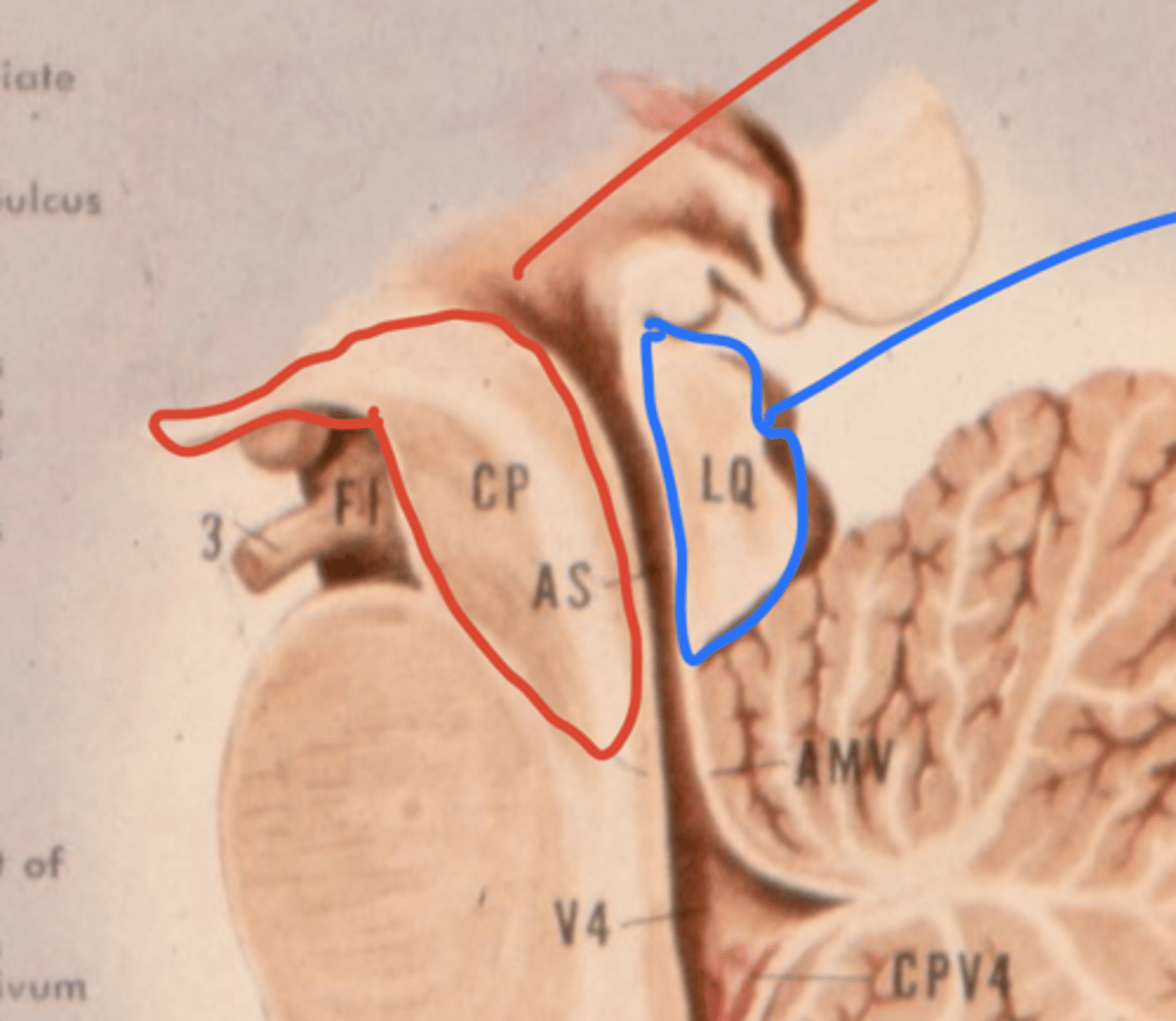
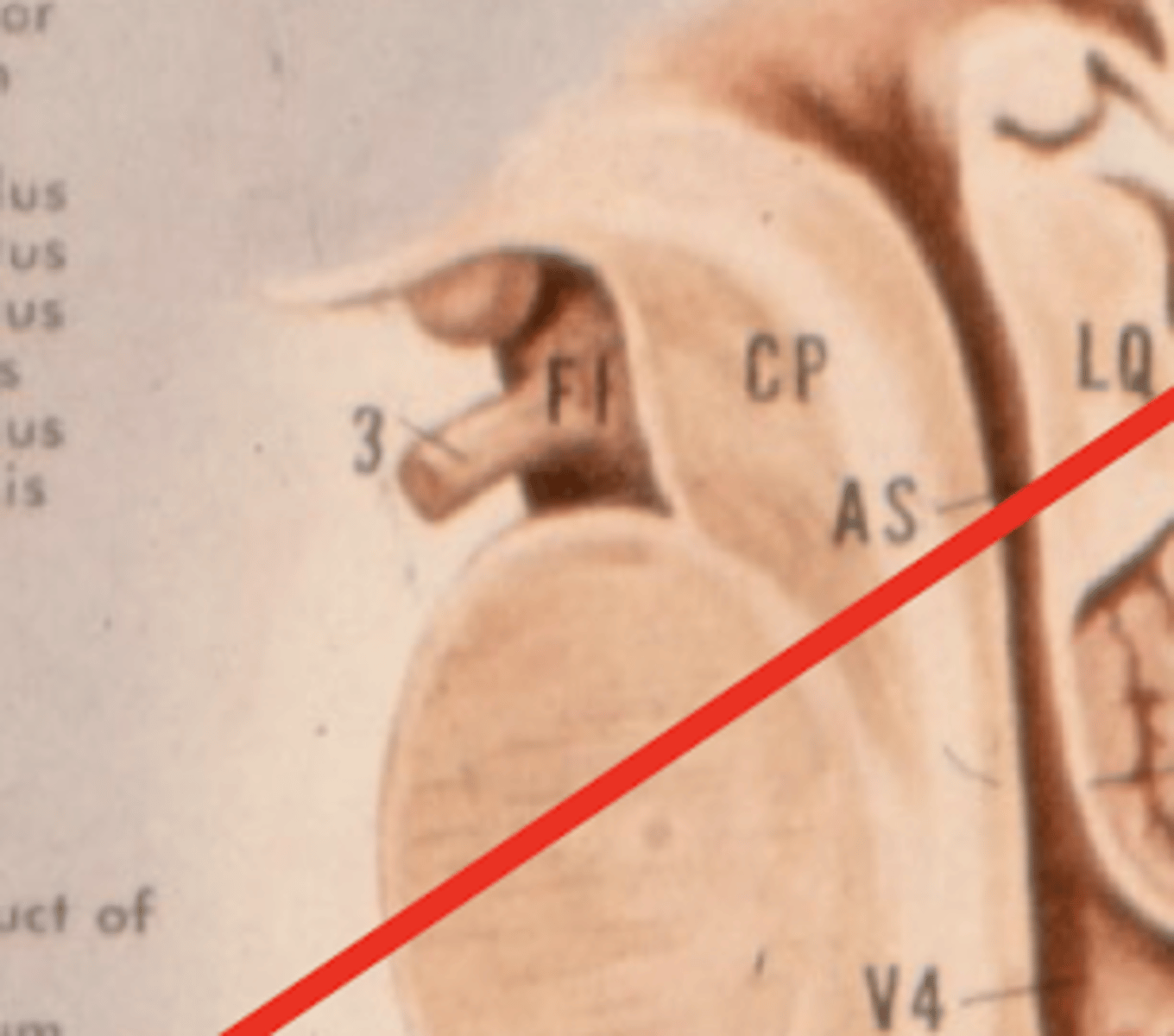
What leaves the interpeduncular fossa?
CN III
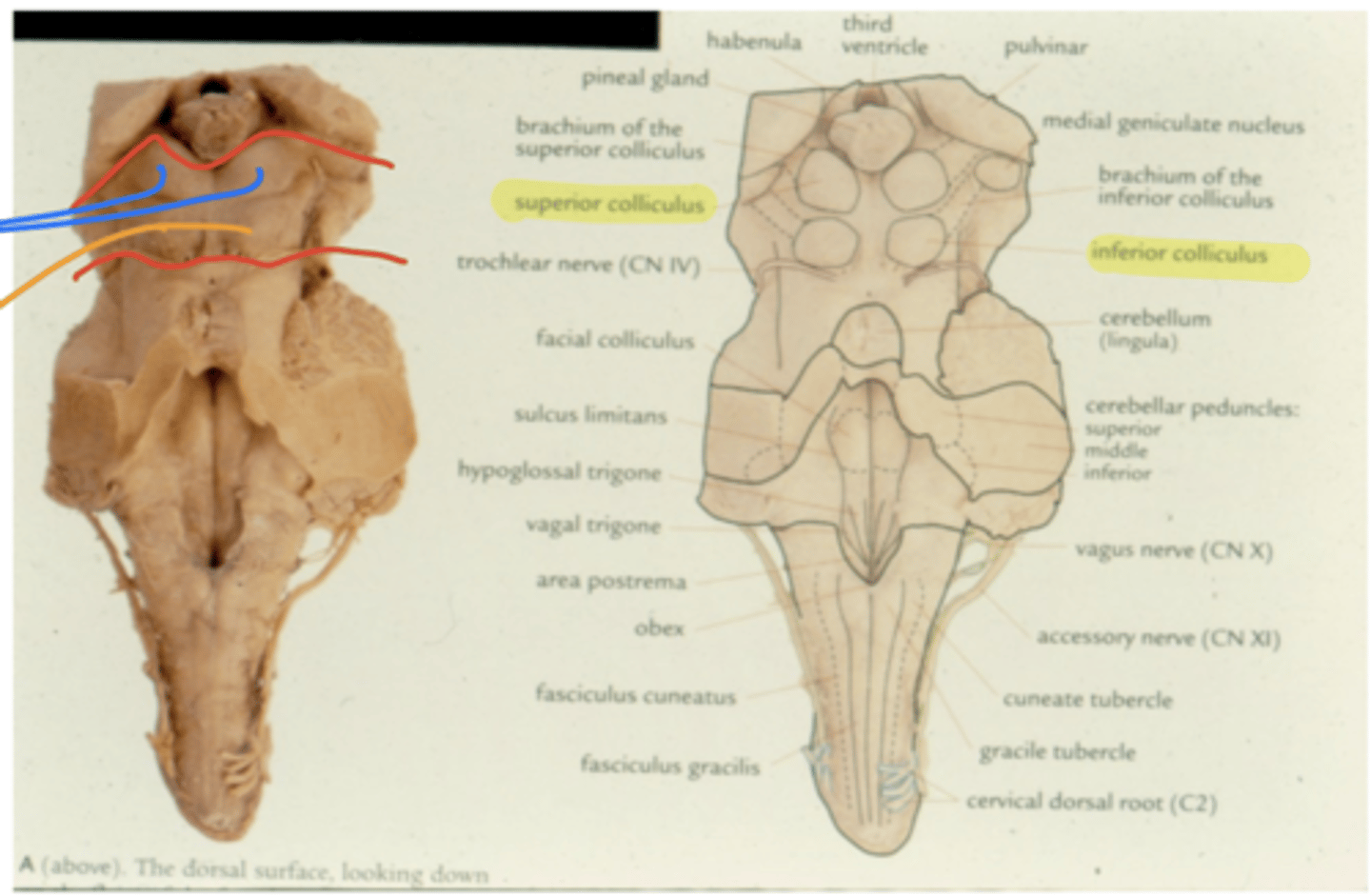
What notable structures are on the dorsal surface of the mesencephalon (tectum)?
1. superior colliculi (right and left)
2. inferior colliculi (right and left)
What are the red nuclei?
projection fibers from the (contralateral) cerebral hemisphere down the spinal cord to limbs
image -- 5
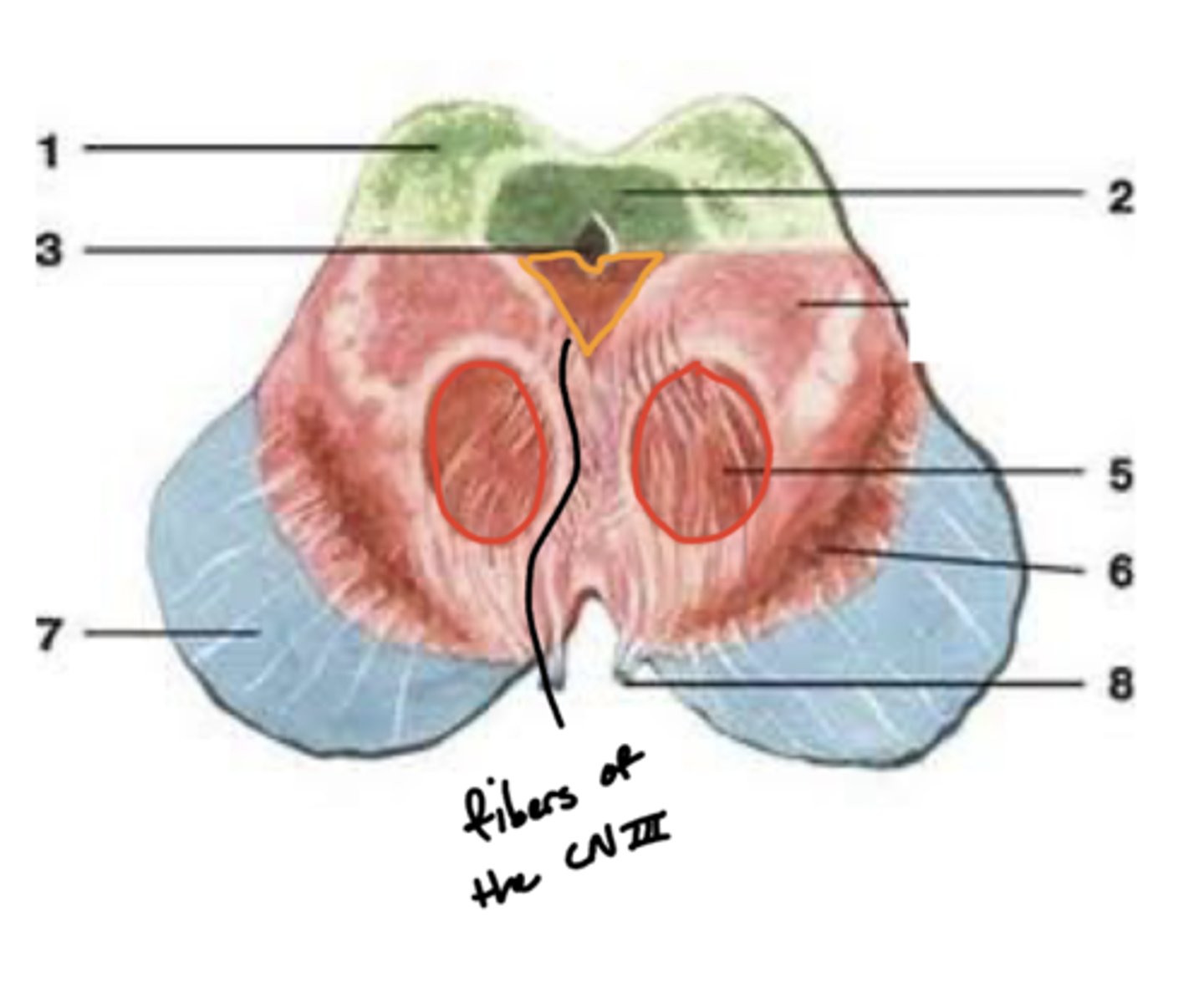
What other notable structure should you see if you see two red nuclei?
"if you see two red nuclei you're at the superior colliculus level"
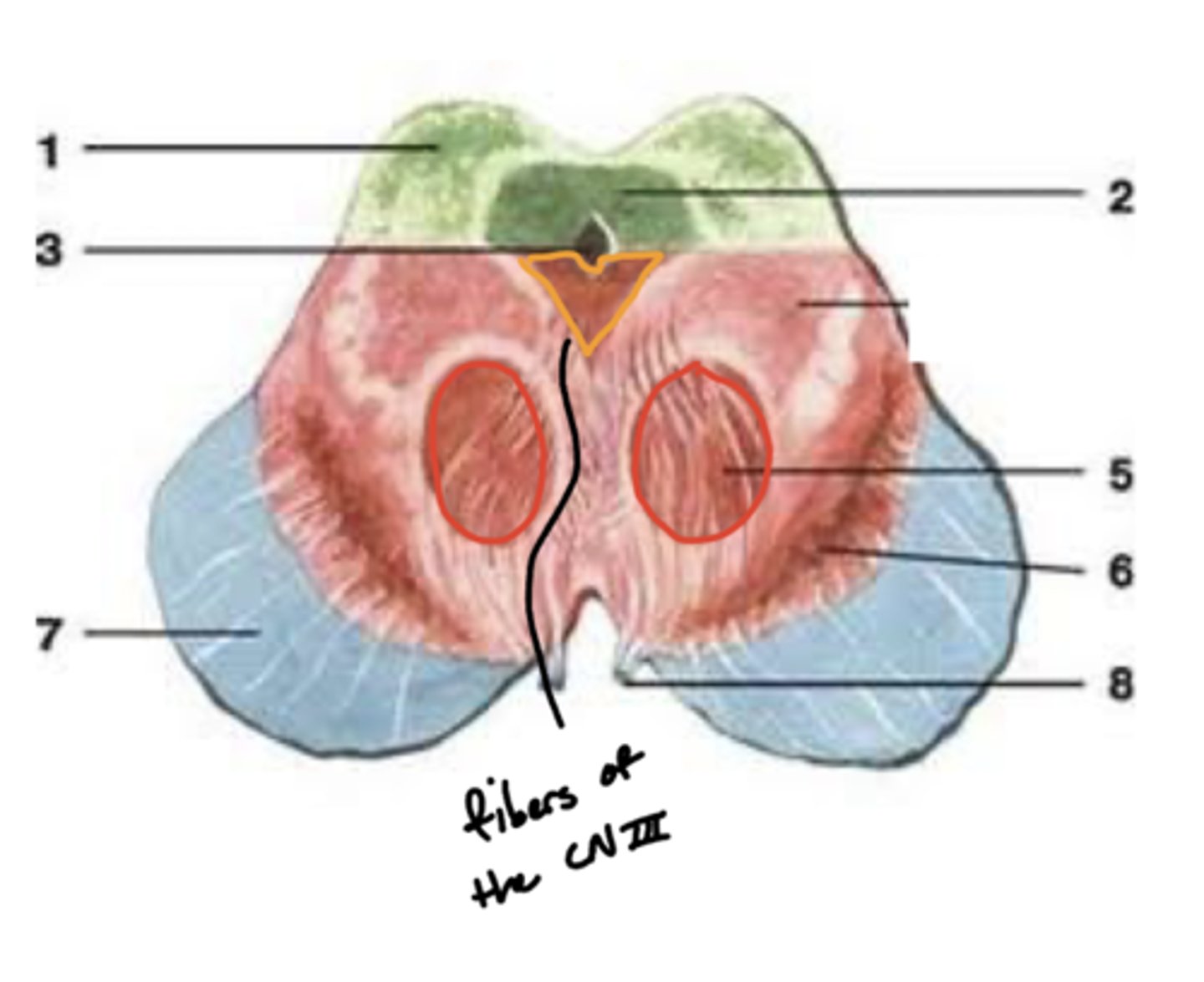
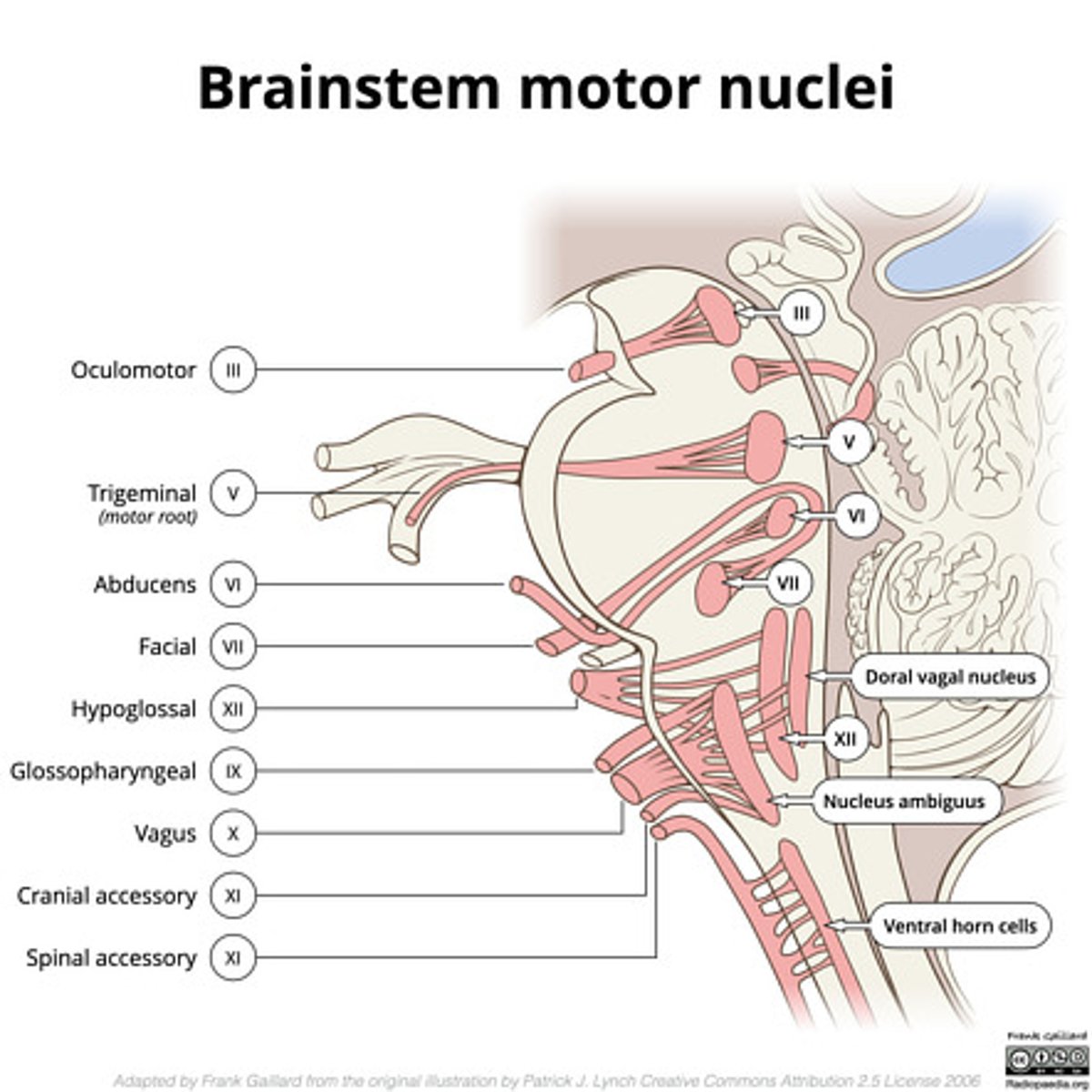
Where does CN III exit the brainstem?
interpeduncular fossa (ventral surface)
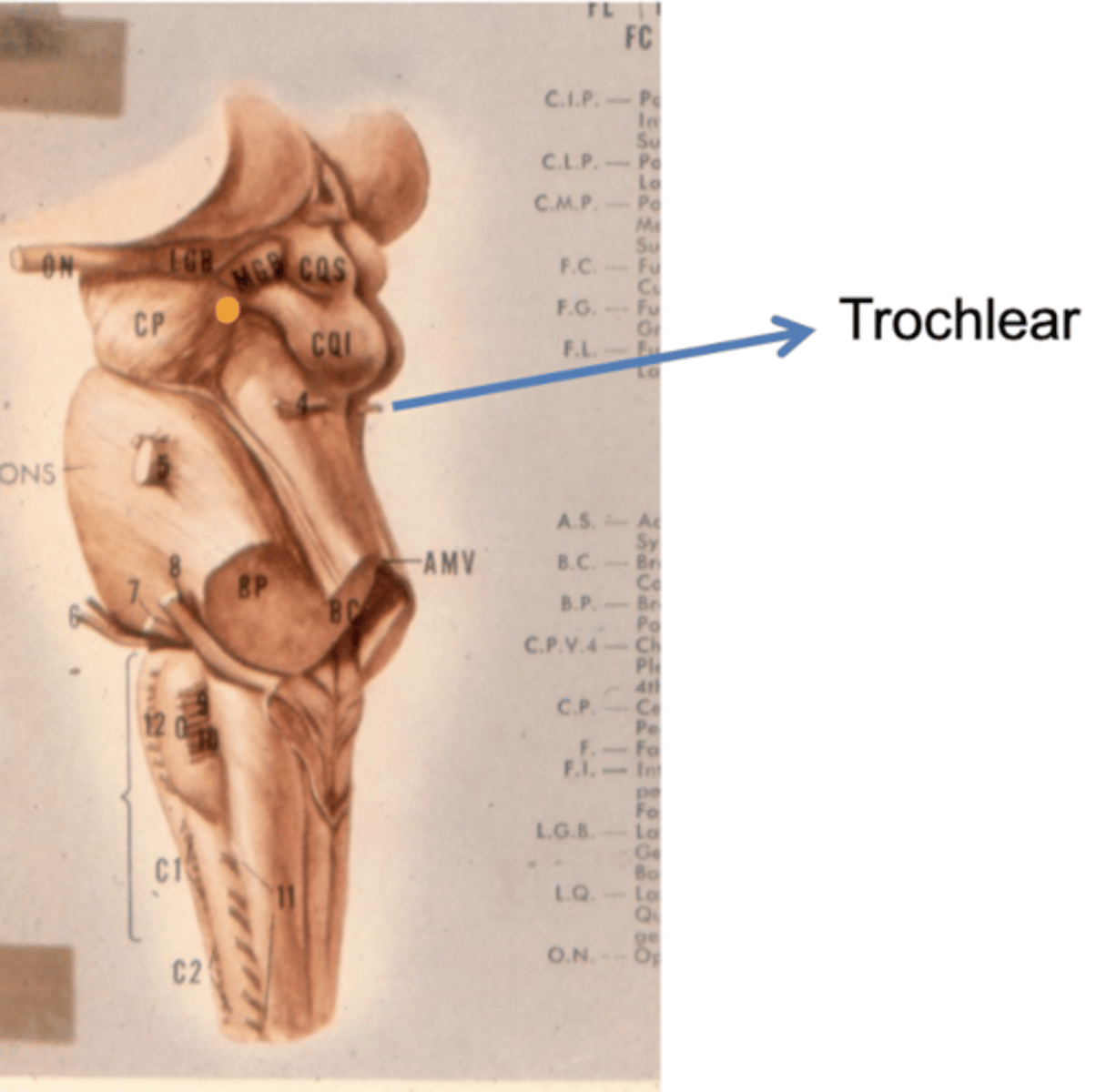
Where does CN IV exit the brainstem?
inferior colliculus (dorsal surface)
exits dorsal + caudal (posteroinferior) to nucleus
Where are the CN III and IV nuclei?
tegmentum mesencephalon
CN III -- anterosuperior
CN IV -- posteroinferior
What injuries usually cause IV nerve palsies?
acceleration/deceleration
why? -- location nerve exits the brain makes it susceptible to being crushed by posterior structure
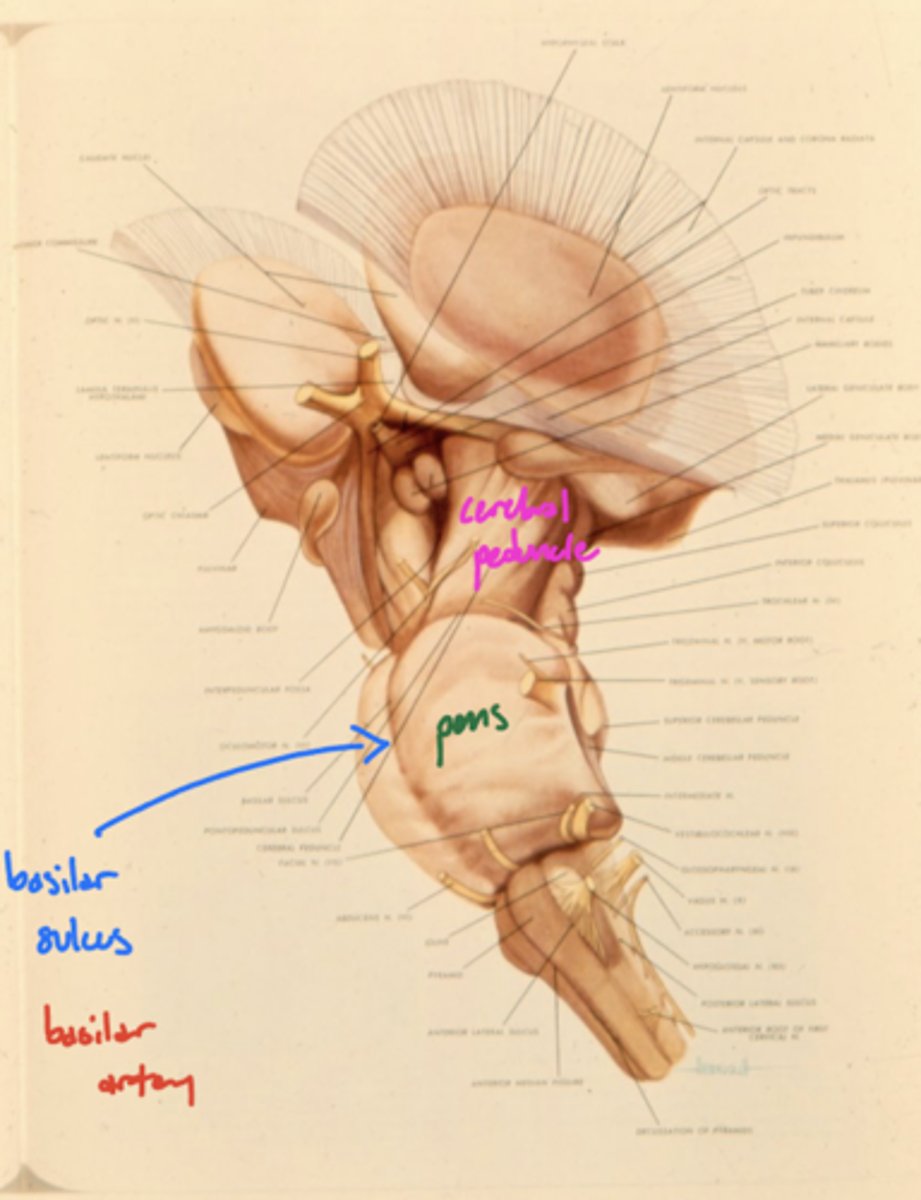
Where is the basilar sulcus?
ventral pons
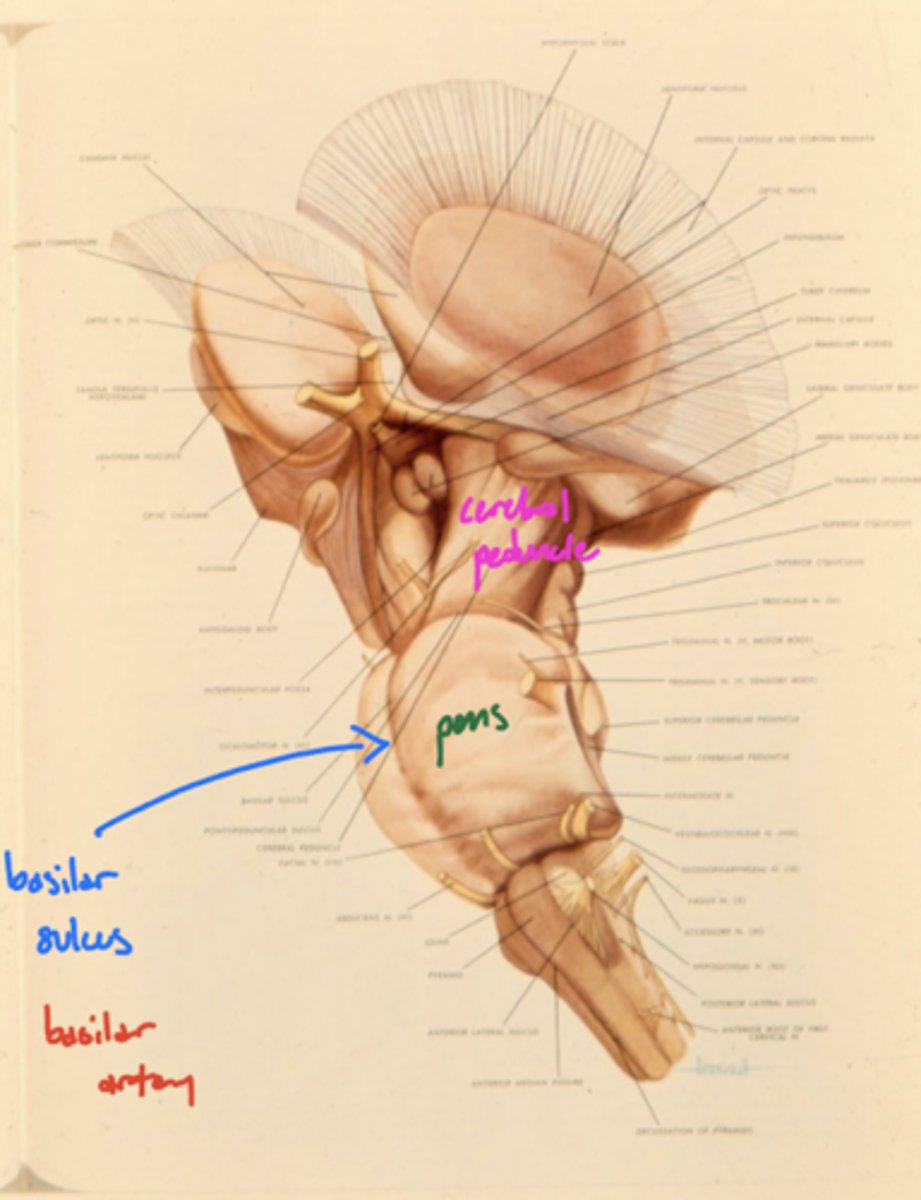
What runs in the basilar sulcus?
basilar artery
What is the floor of the 4th ventricle?
tegmentum pons
image -- green
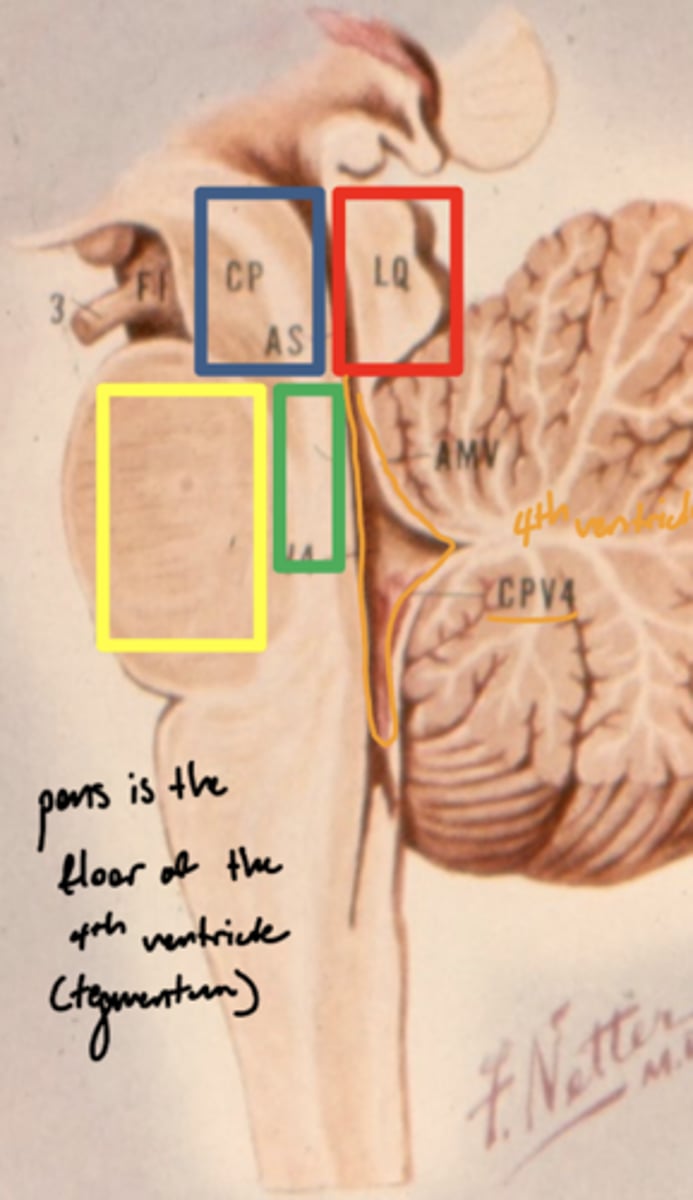
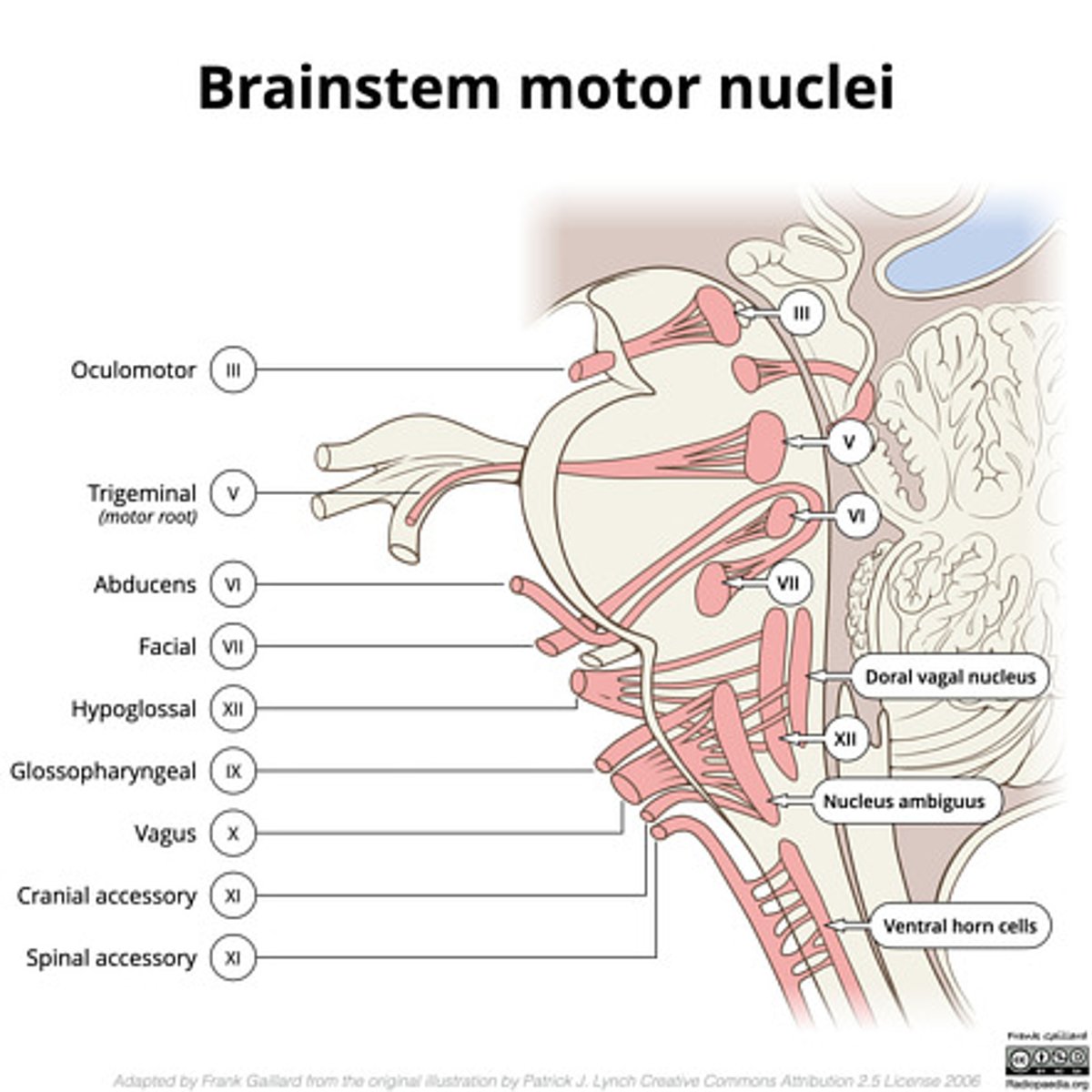
What cranial nerve nuclei are in the tegmentum pons?
1. CN V (5)
2. CN VI (6)
3. CN VII (7)
4. CN VIII (8)
What are the fibers of the tegmentum pons?
ascending sensory pathways
What cranial nerves nuclei are in the base of the pons?
none
What are the fibers of the base of the pons?
descending motor fibers
What nuclei is within the base of the pons?
pontine nuclei
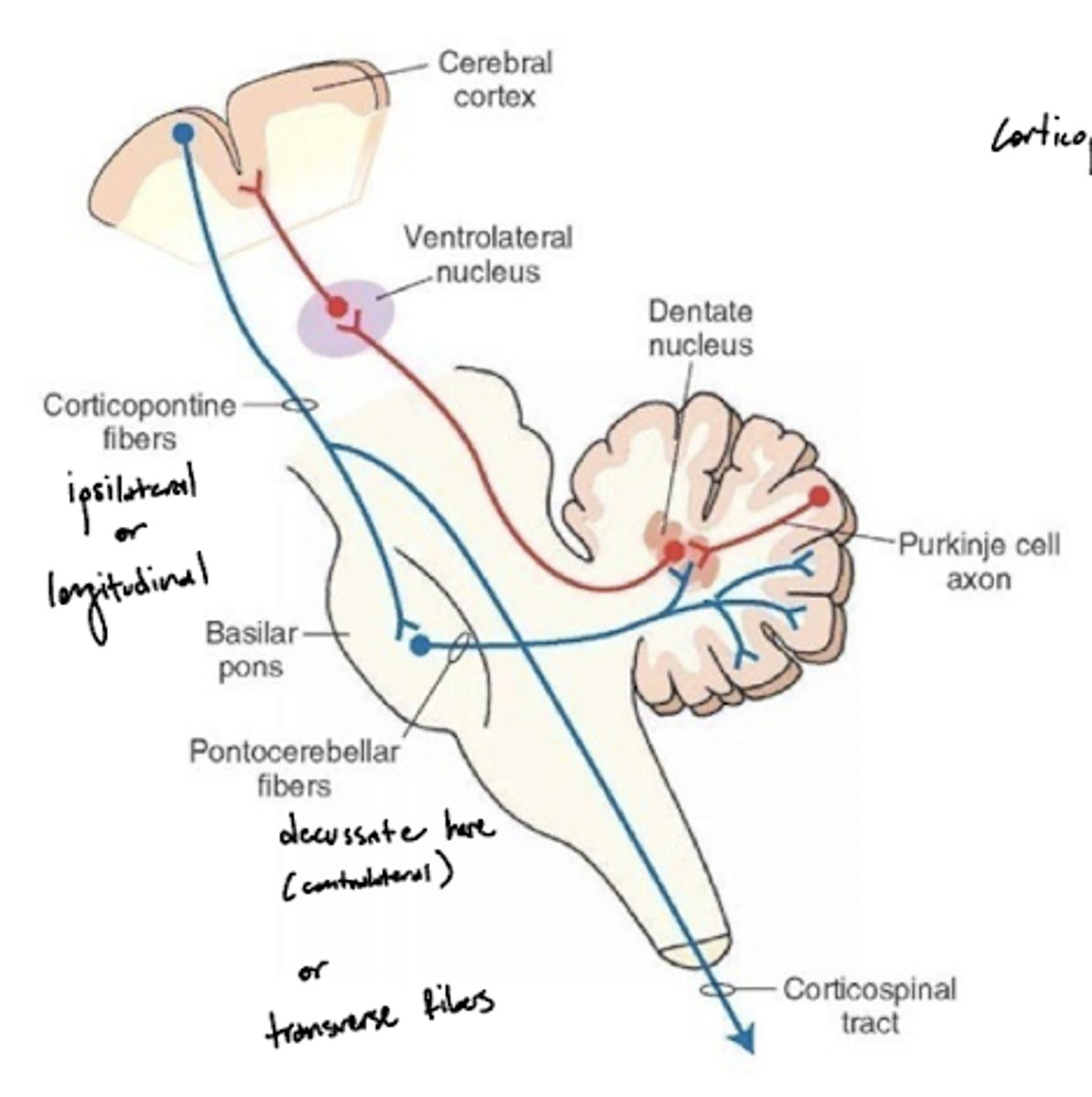
What is the pontine nuclei?
gray matter centers connecting the cerebral cortex and cerebellum -- coordinate voluntary motor output
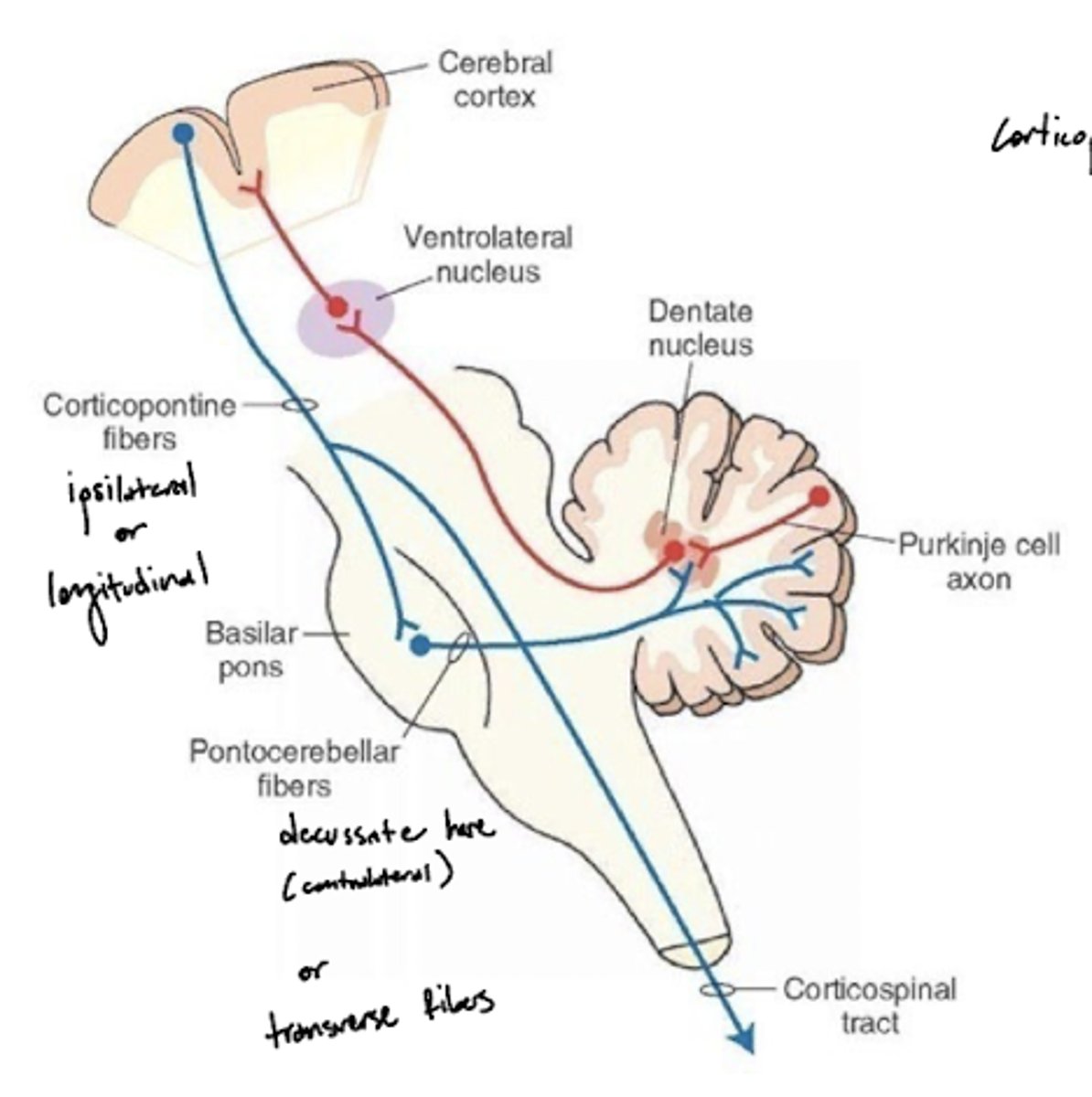
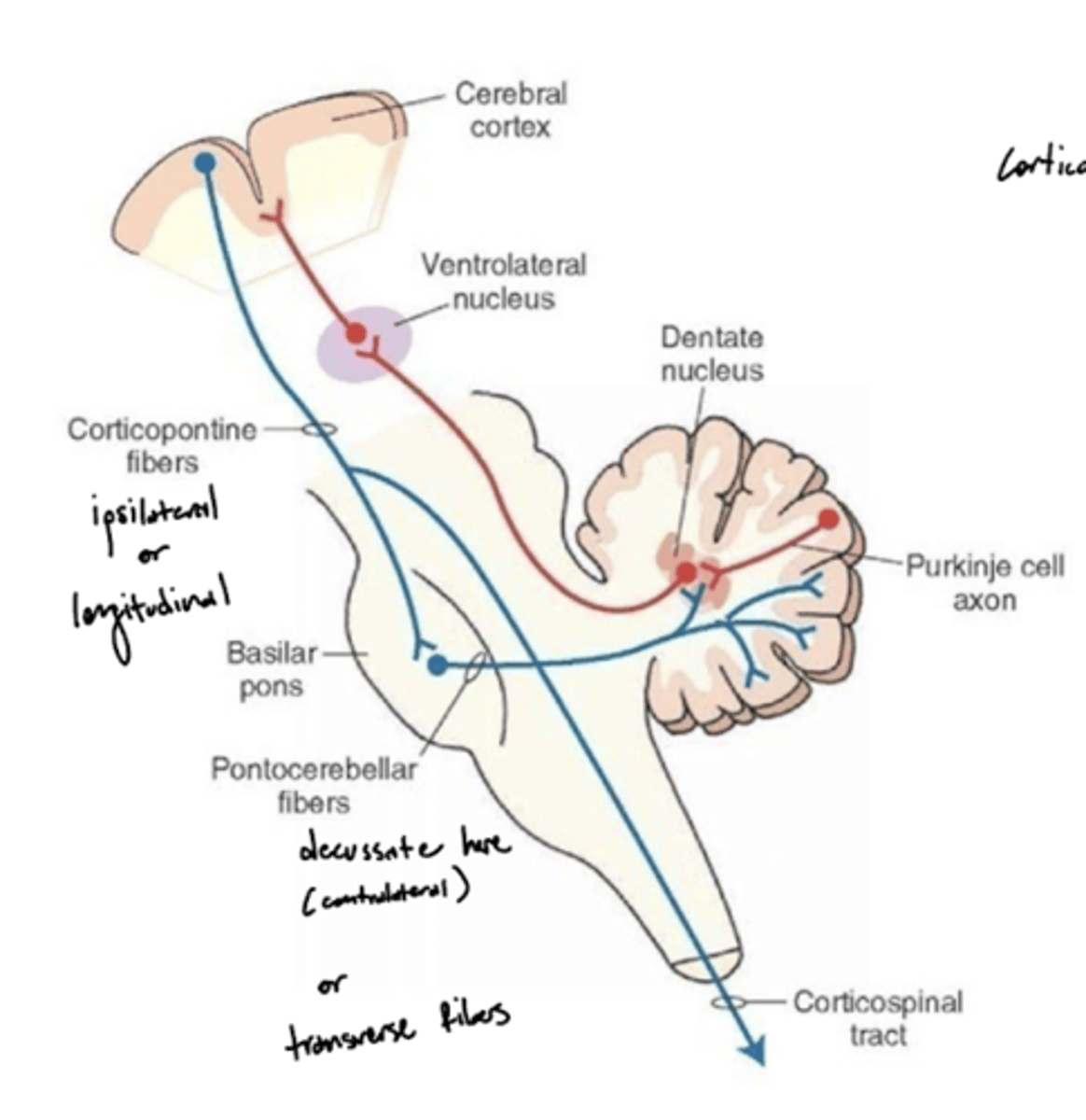
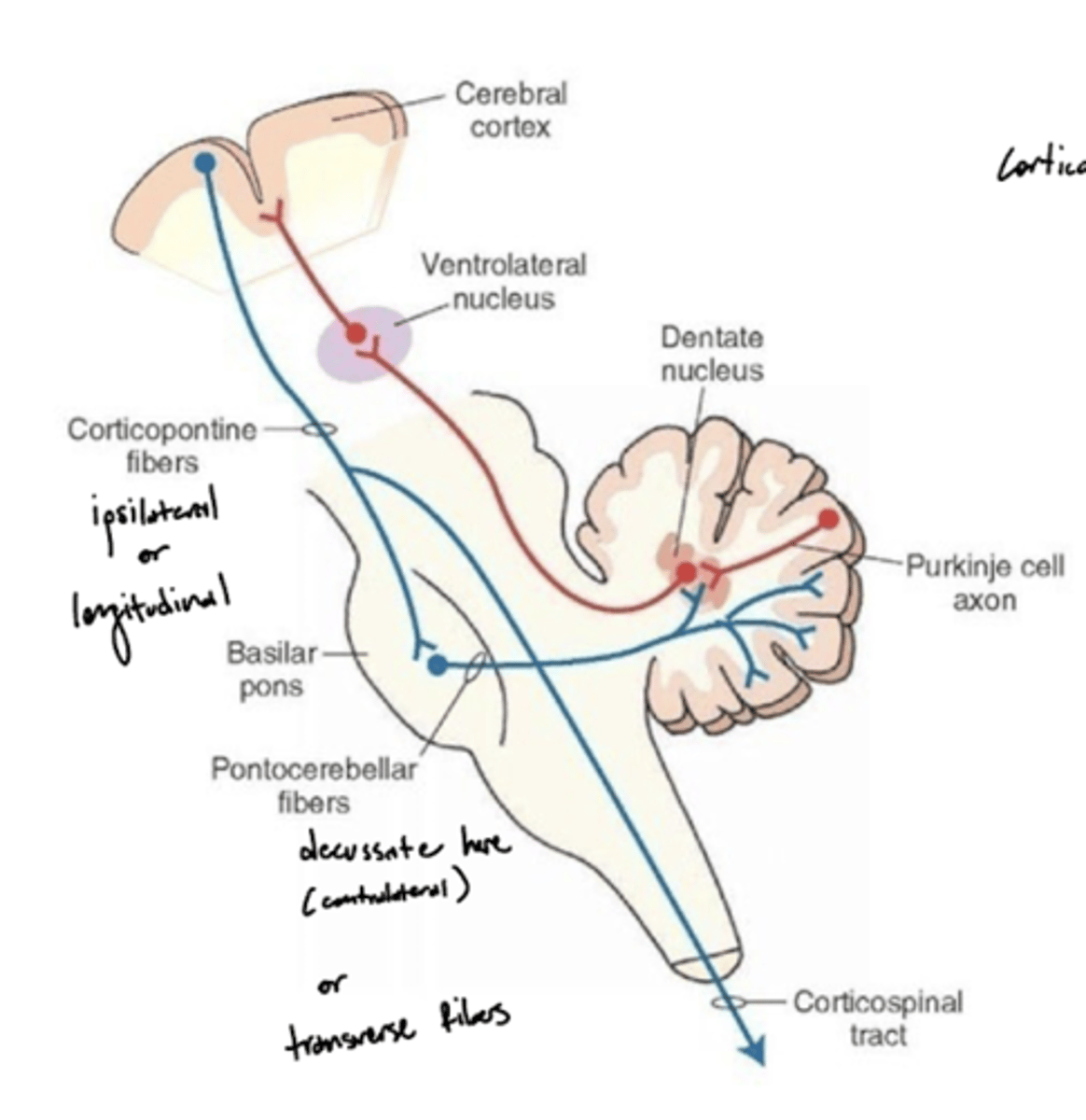
What is the pontocerebellar tract?
a group of second order neuron fibers that run from the pons to the contralateral cerebellum, crossing to the other side of the pons and passing through the middle cerebellar peduncles
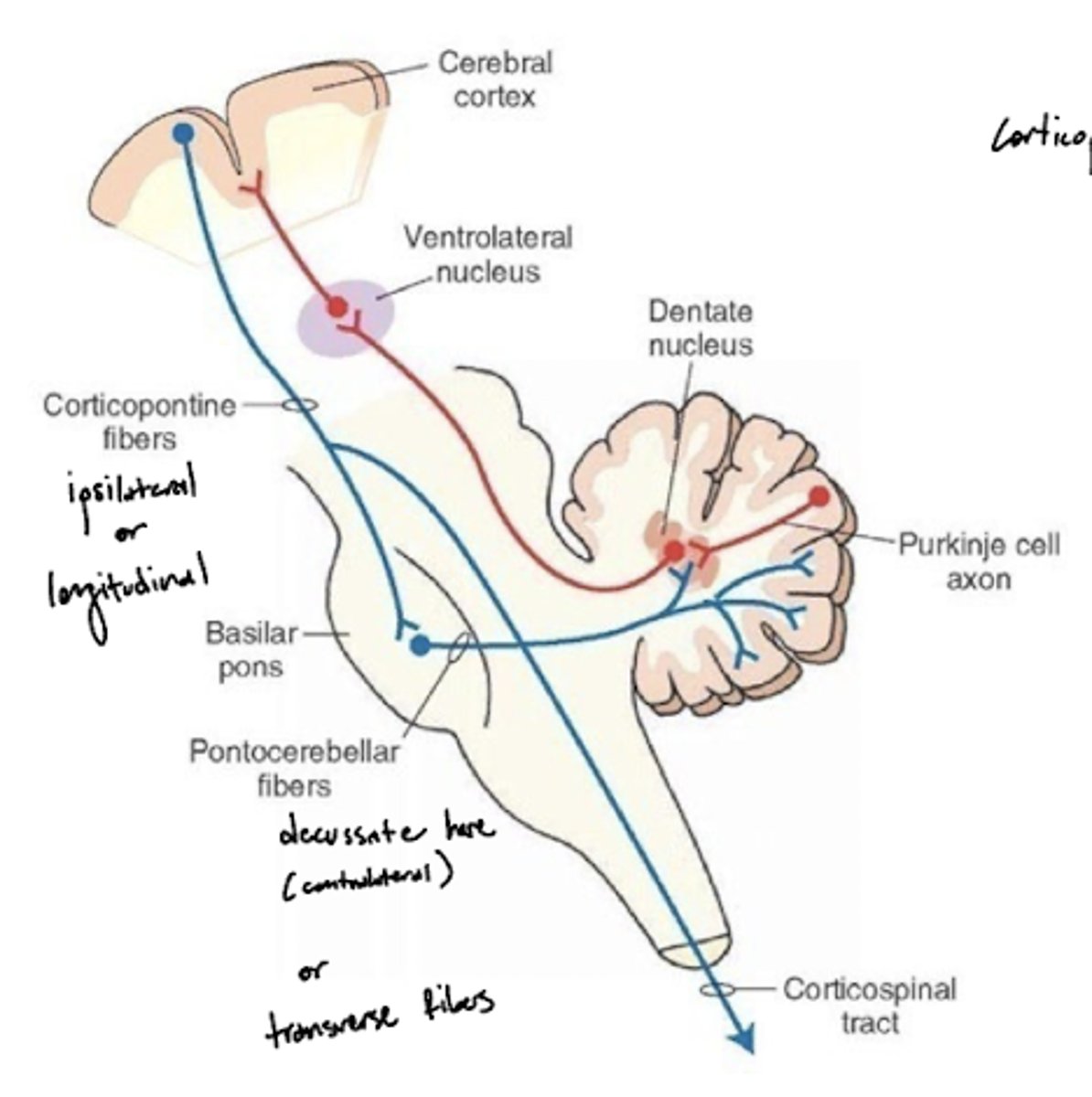
What do the pontocerebellar tract fibers do?
pontocerebellum controls and plans precise dexterous movements of the extremities, especially in the arm, forearm, and hand, and the timing of these movements
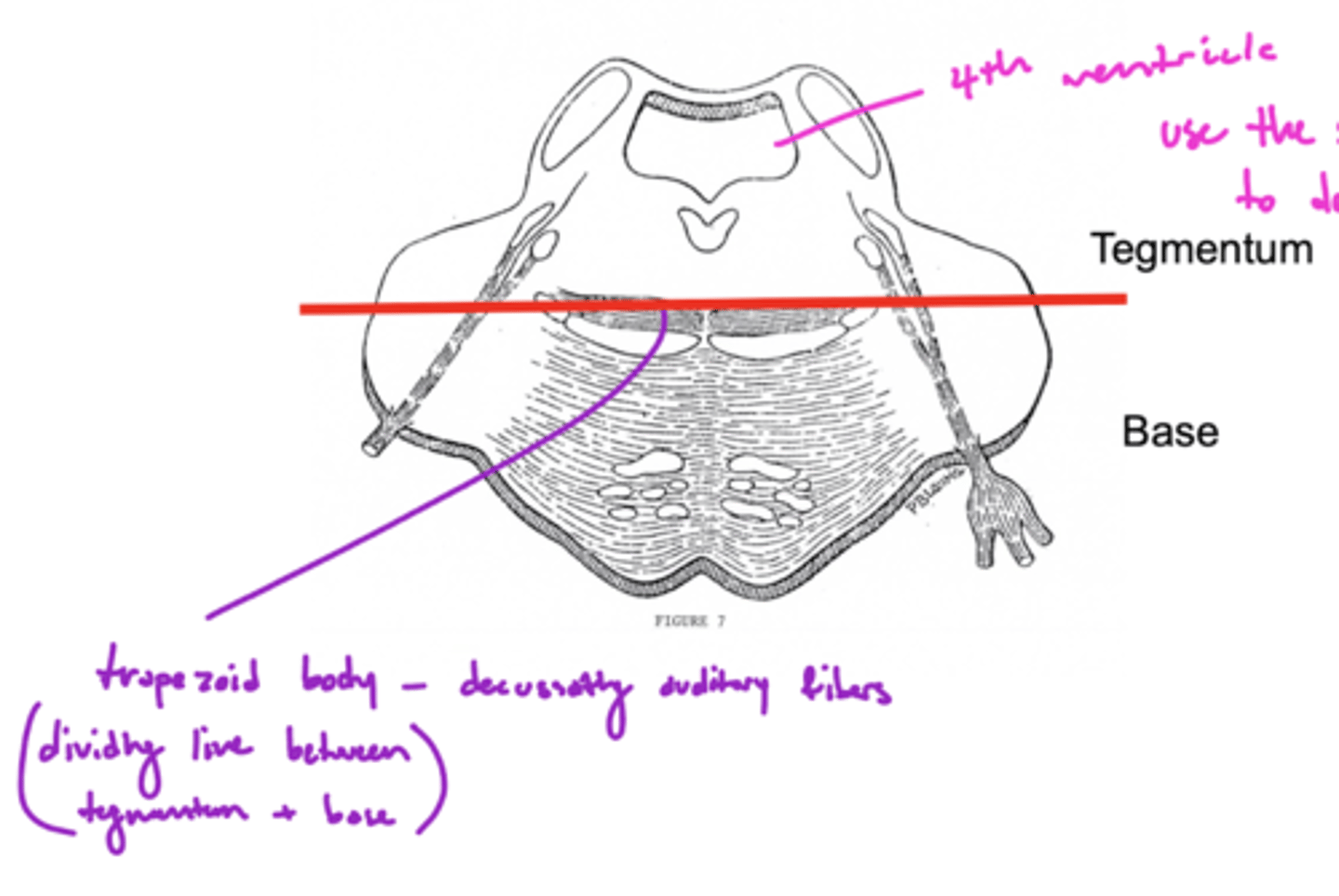
What is the dividing line between the tegmentum pons and the base of the pons?
trapezoid body -- decussating auditory fibers
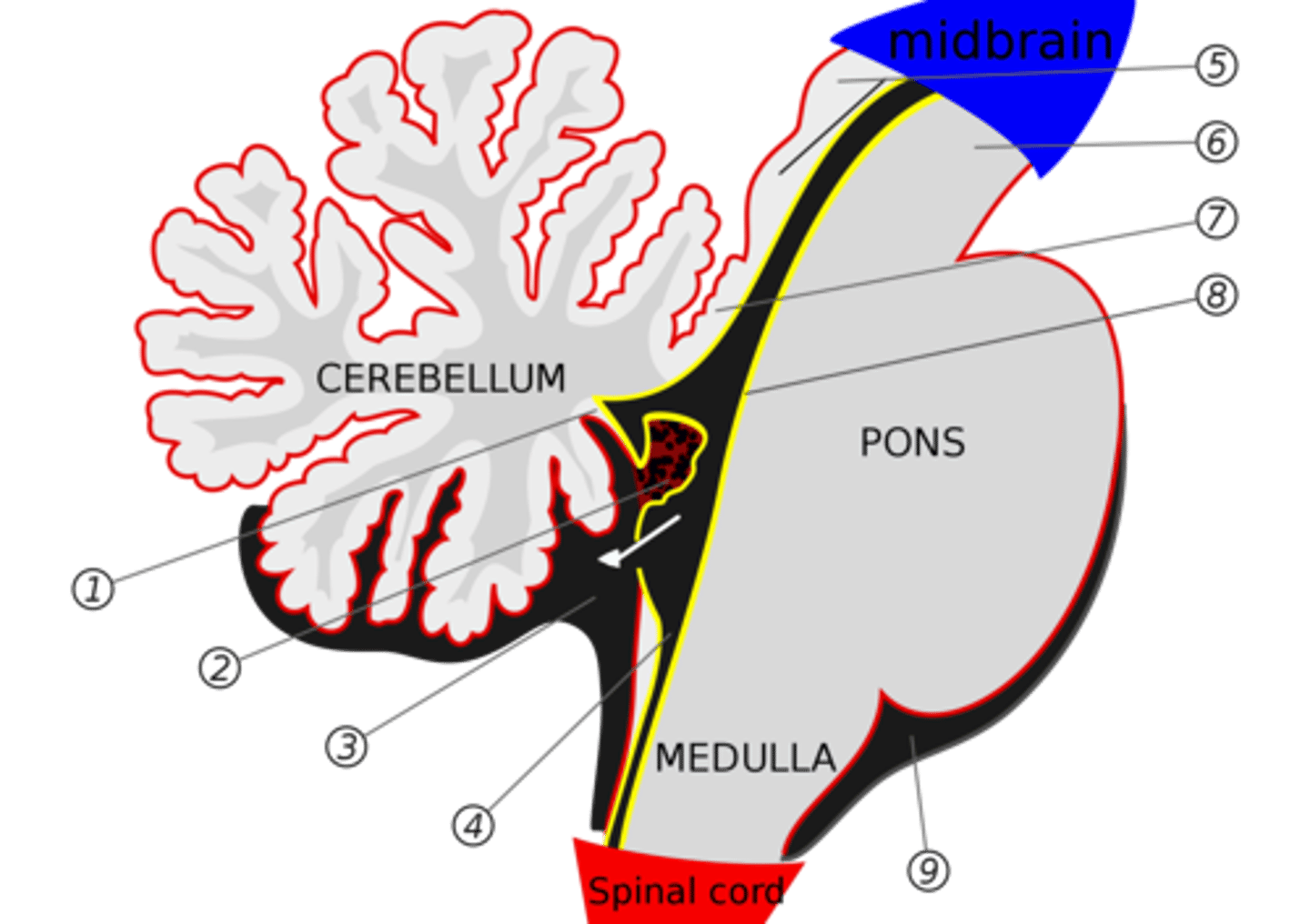
What is the superior medullary velum?
membrane that forms the superior portion of the 4th ventricle roof
image -- 7
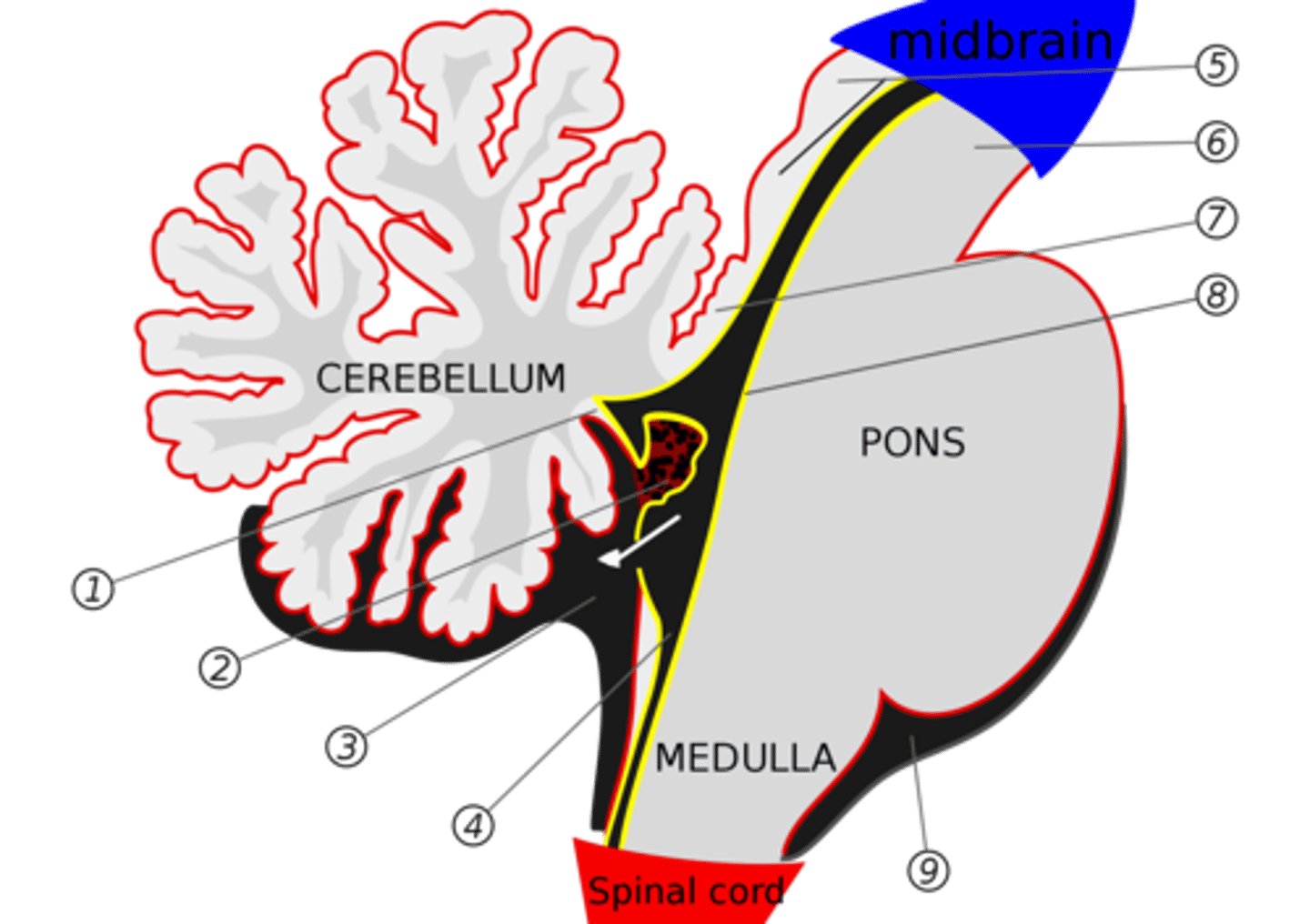
What is the inferior medullary velum?
membrane that forms the inferior portion of the 4th ventricle roof
image -- 1
What structures does CN V divide ventral to dorsal in the pons?
base of pons from middle cerebral peduncle
ventral -- base of pons
dorsal -- middle cerebral peduncle
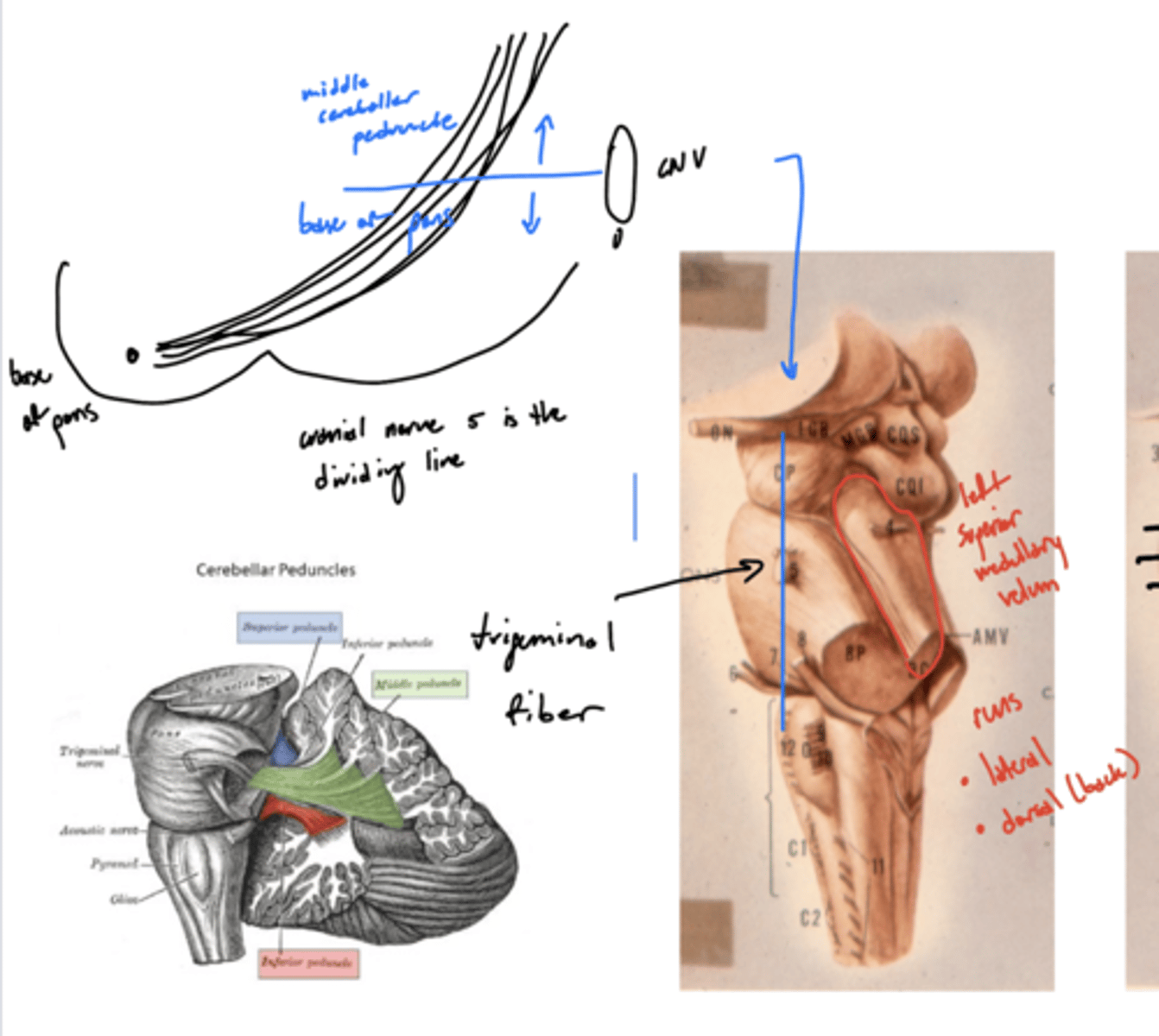
What two things change in size as you descend the pons?
1. size of middle cerebellar peduncle (increase)
2. size of 4th ventricle (increase then decrease)
What structure is visible in the caudal half of the pons, but not the cranial half?
longitudinal (descending) fibers
1. corticobulbar
2. corticospinal
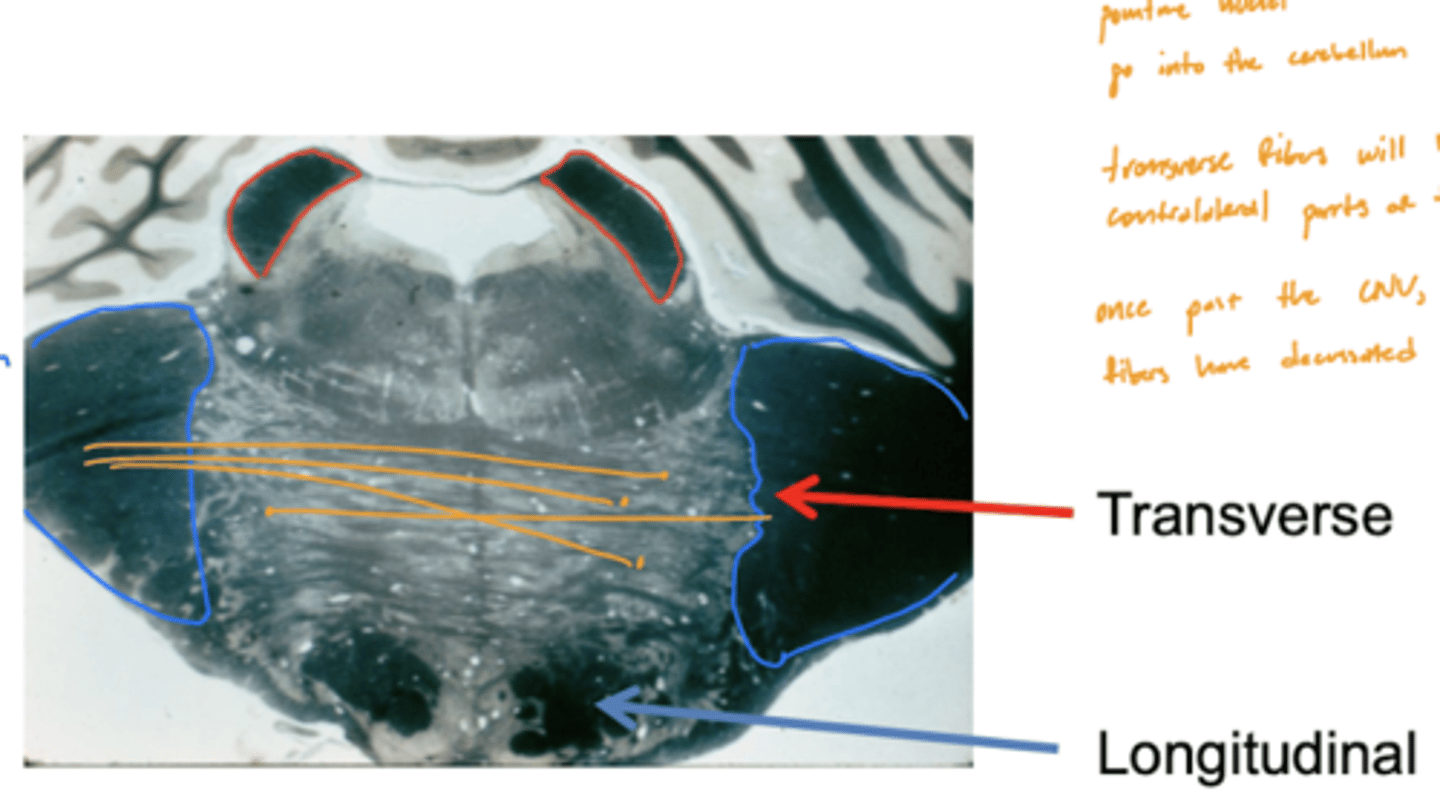
What are the longitudinal fibers of the pons?
1. corticobulbar (facial muscles)
2. corticospinal (limbs and trunks muscles)
3. pontine tract
Are the longitudinal fibers of the pons ipsilateral or contralateral?
ipsilateral
Are the transverse fibers of the pons ipsilateral or contralateral?
contralateral (decussate below CN V exiting)
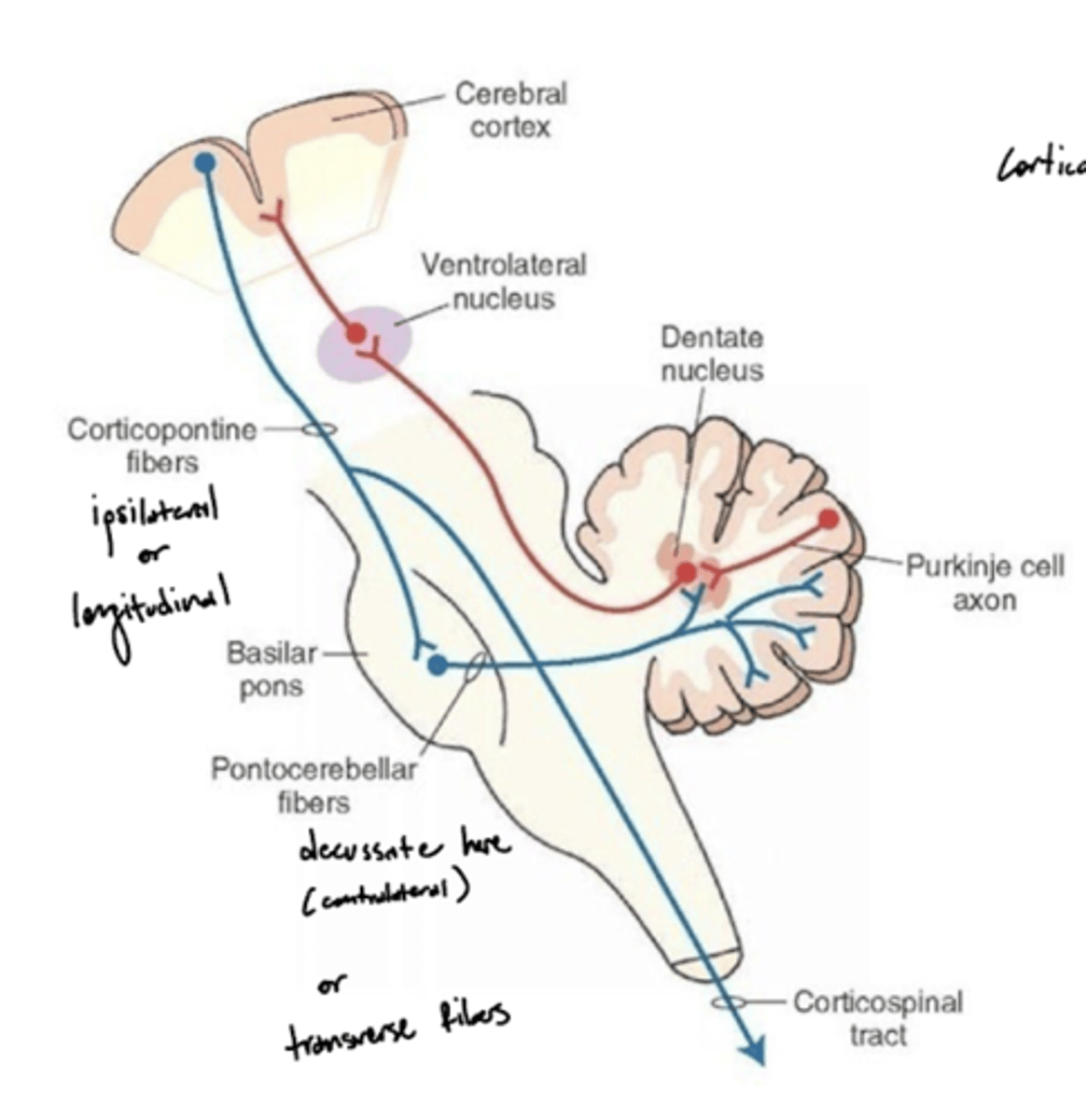
What is the pathway of fibers from the cortex to the cerebellum?
1. Corticopontine fibers (longitudinal fibers)
2. Synapse in the pons
3. Decussation (transverse fibers)
4. Middle cerebellar peduncle
5. Projection to the cerebellum
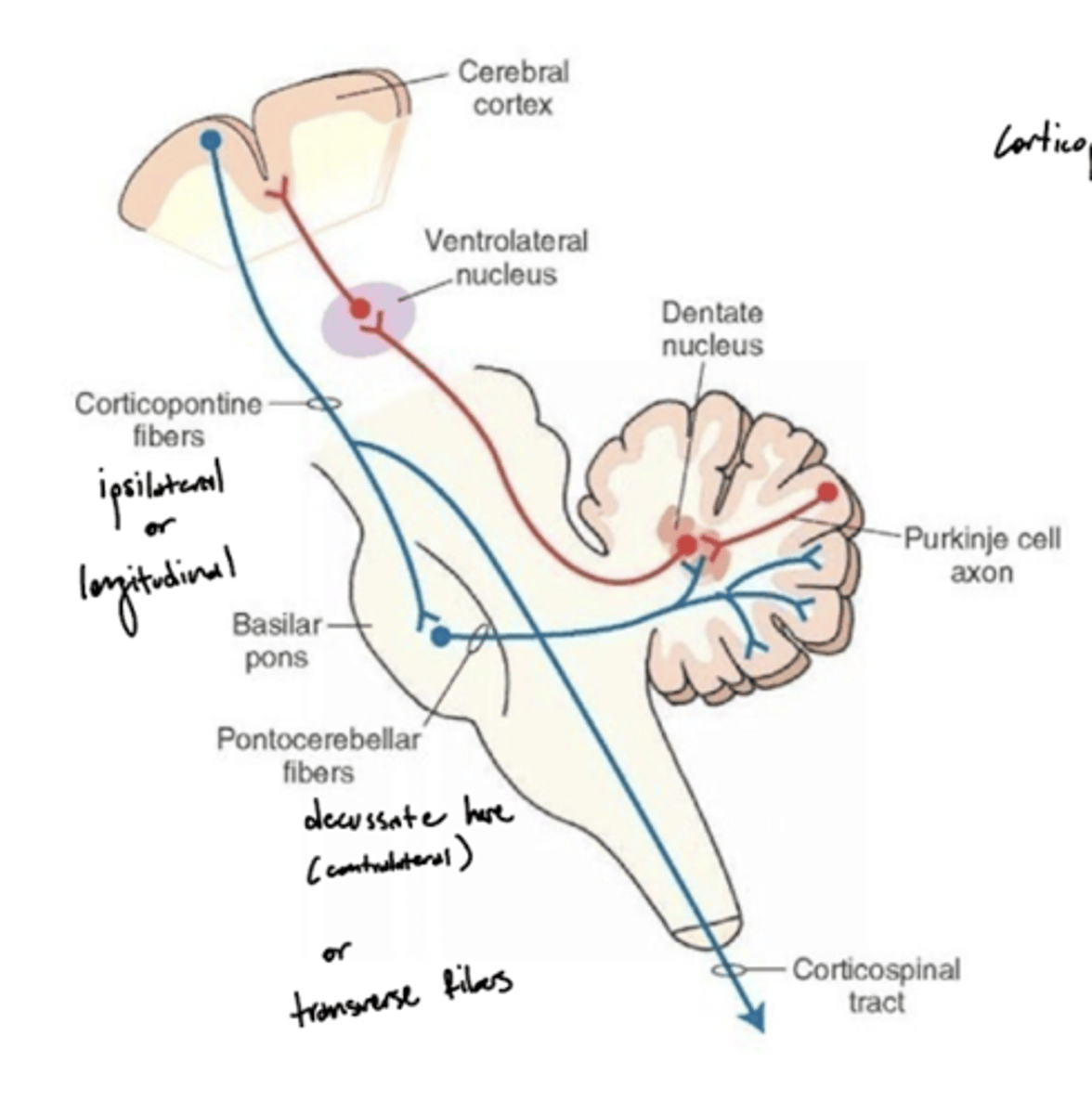
What structures does CN V divide superior to inferior in the pons?
incorrect
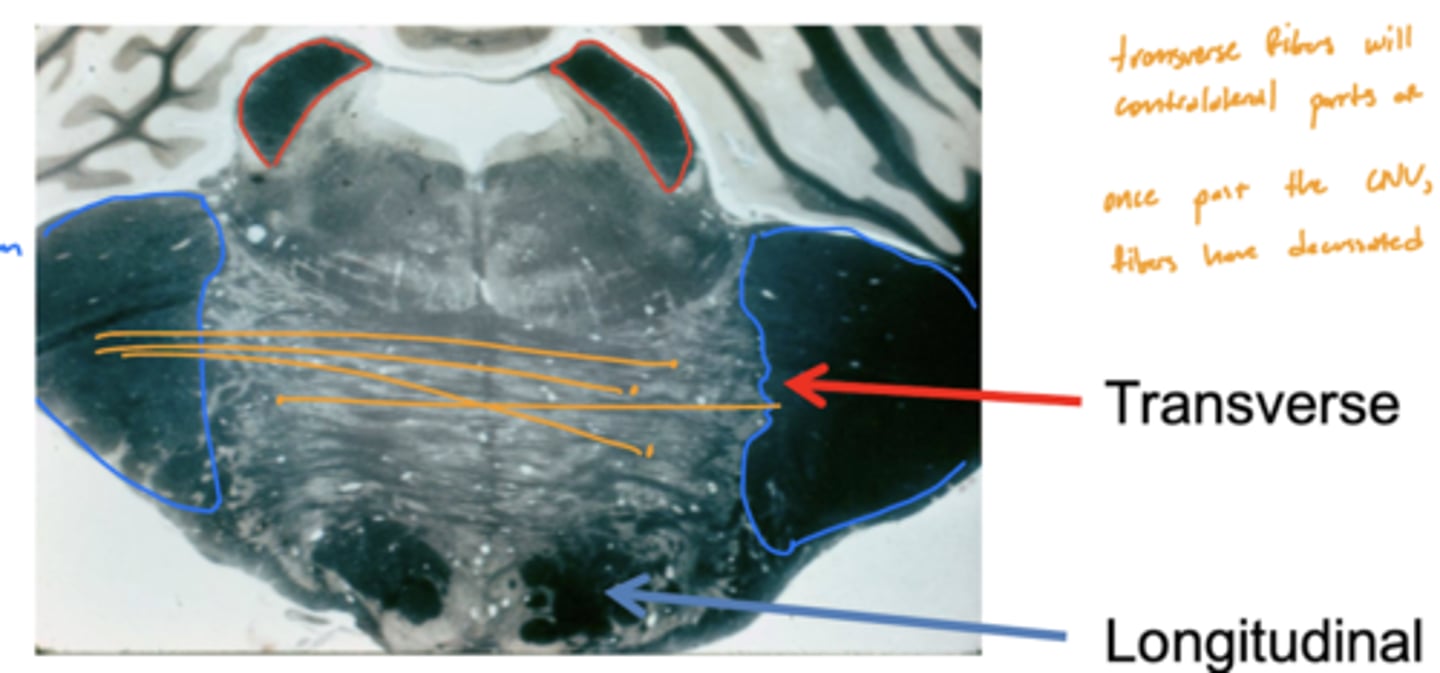
Are the pons and cerebellum connected contralaterally or ipsilaterally?
contralateral -- transverse fibers decussate underneath (inferior) CN V exiting pons
What nuclei are at the pontomedullary junction?
1. SVE of CN VI
2. SVE of CN VII (facial)
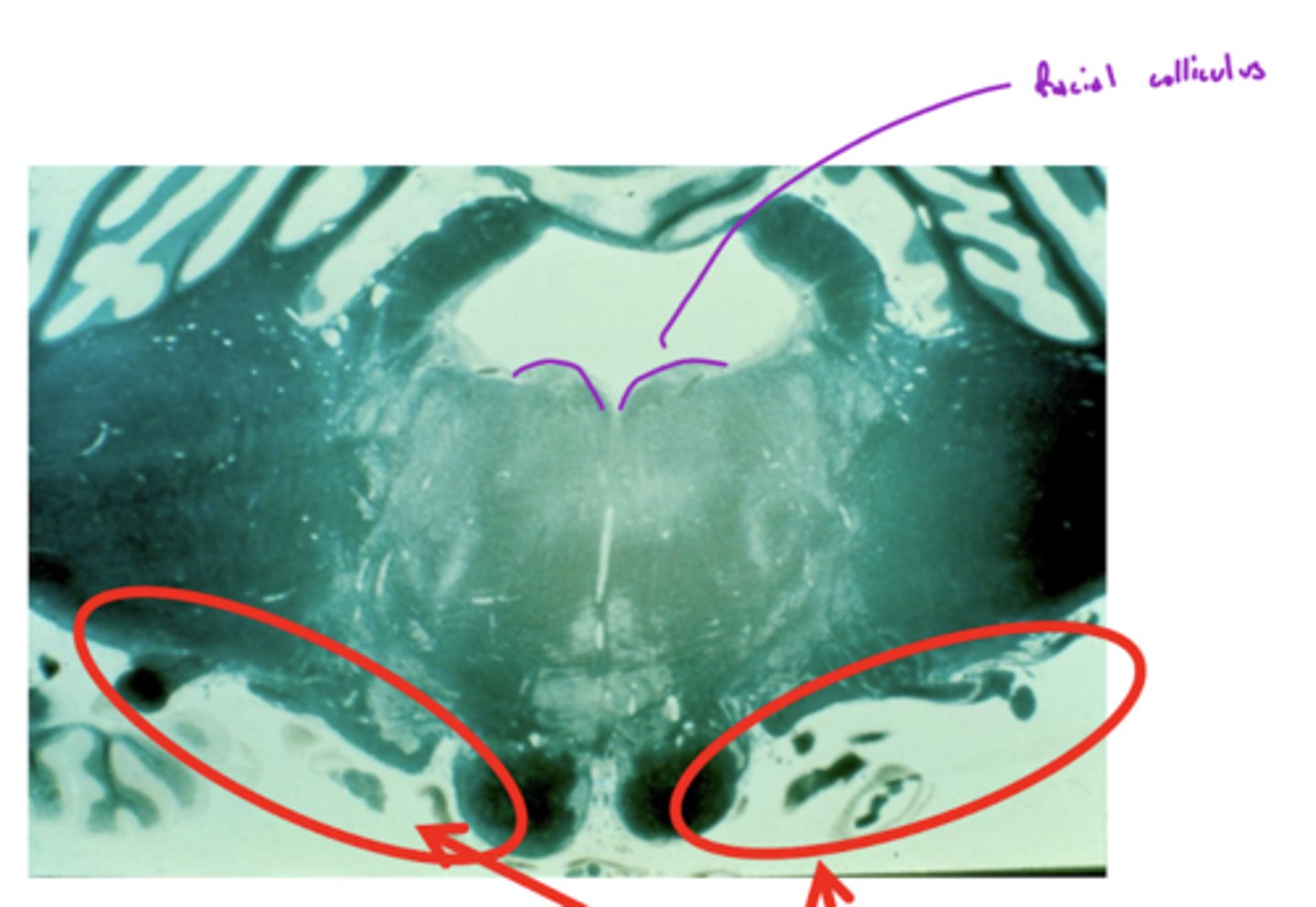
What are the facial colliculi?
bumps (hills) coming out from dorsal pontomedullary junction into the 4th ventricle -- CN VII SVE fibers create this space when they wrap around the abducens nucleus
Where do CN VI, VII, VIII exit the pons?
pontomedullary junction
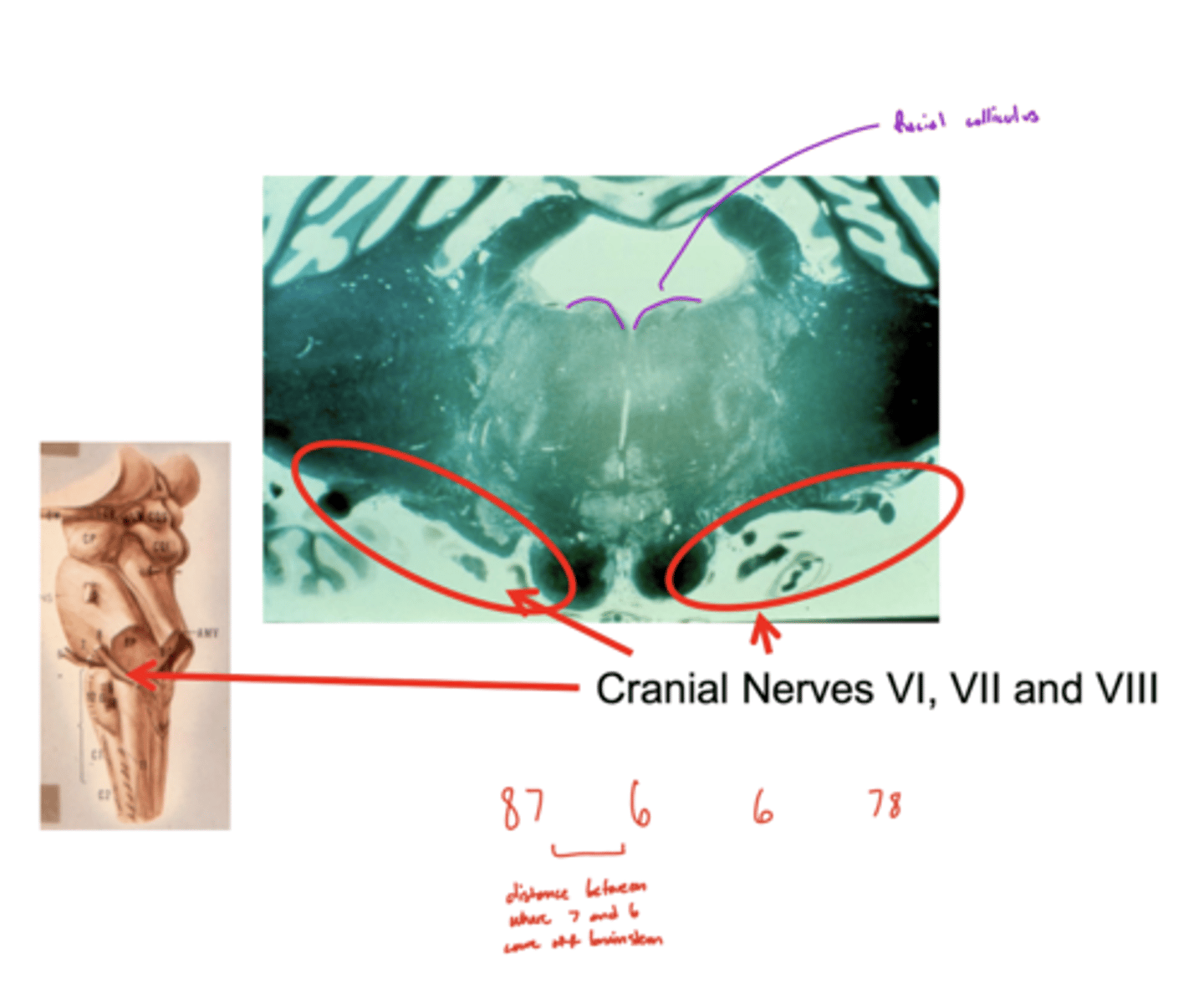
What is the spacing of CN VI, VII, and VIII exiting the pontomedullary junction?
8 & 7 -- lateral and closer together
6 -- medial and far away
image -- look at red font
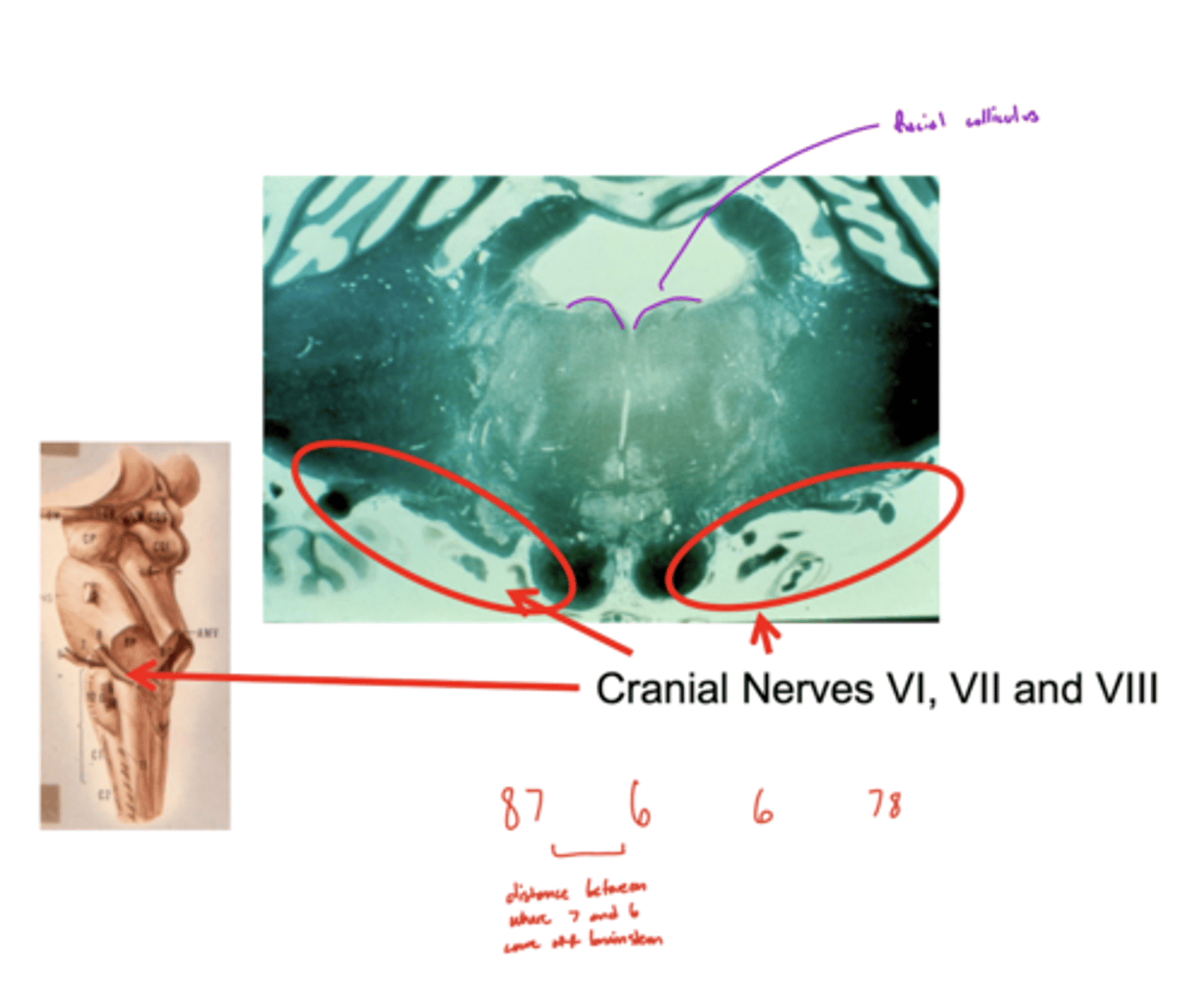
What is the rhombencephalon?
floor of 4th ventricle (for the sake of our class)
dorsal aspect of tegmentum of pons
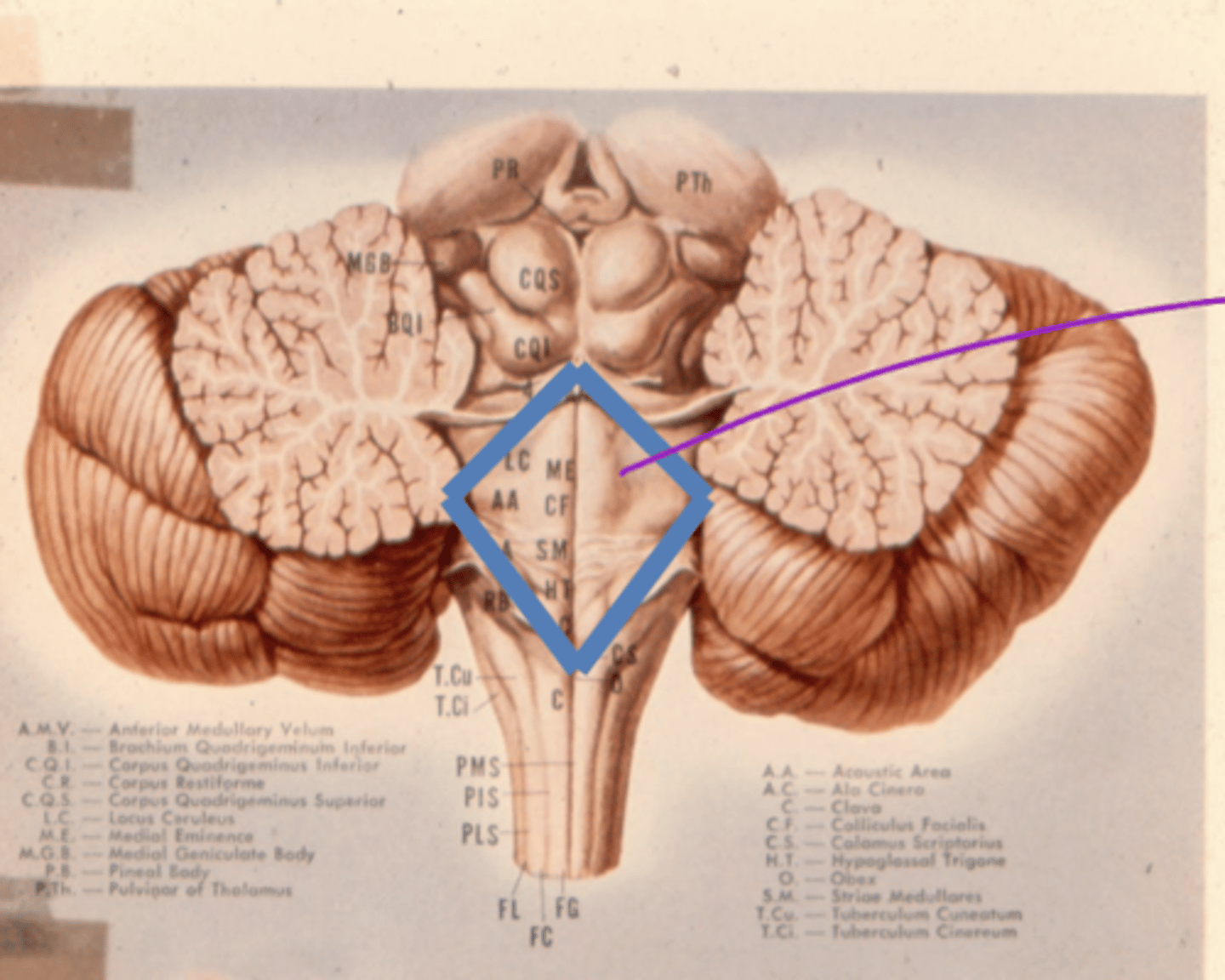
Where does the cerebellum send its copy of voluntional movement corrections?
1. thalamus -- additional processing
2. red nucleus -- projects down spinal cord to limbs for real time corrections
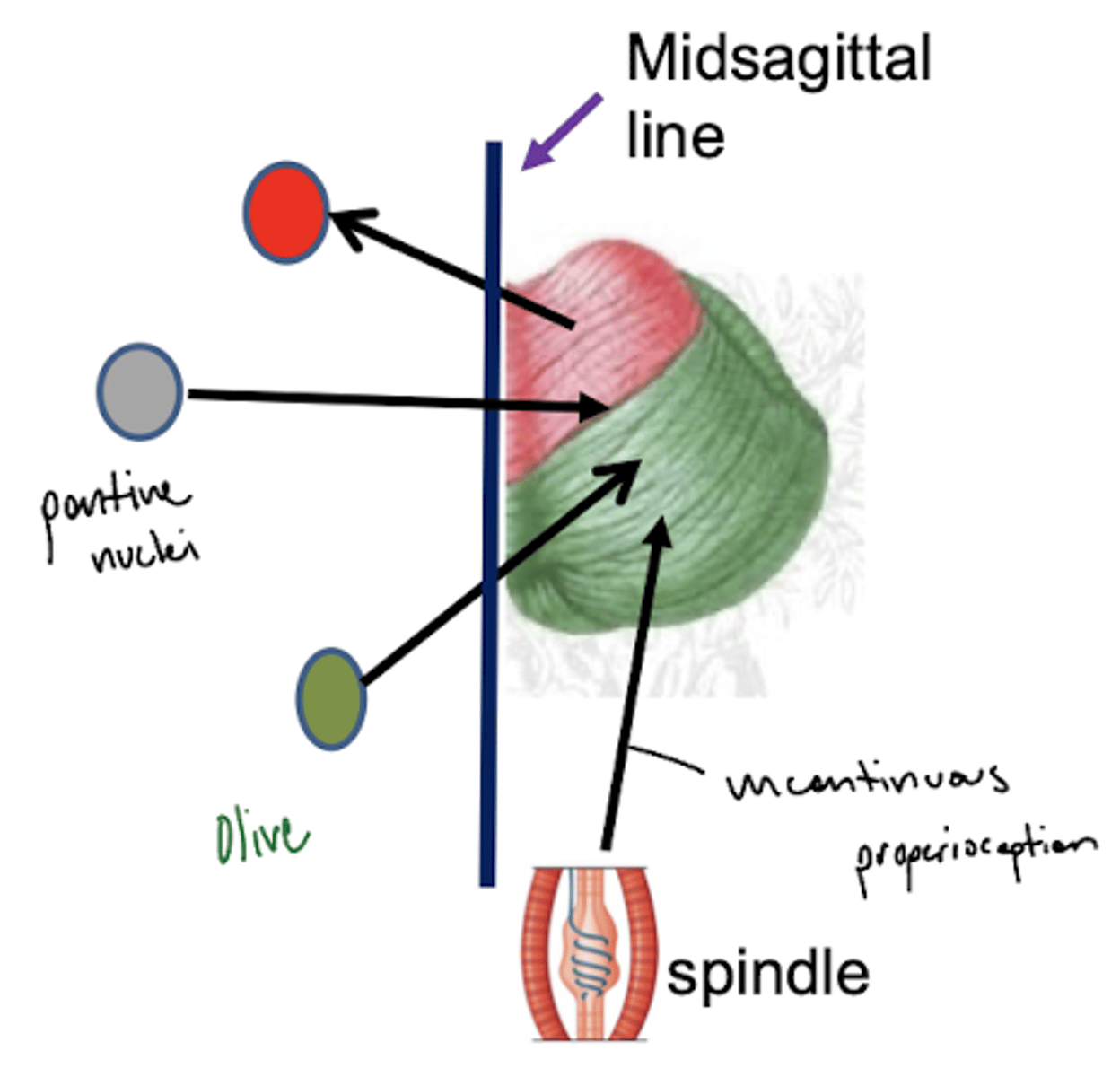
What are the two types of proprioception?
1. conscious -- goes into cortex (3, 1, 2)
2. unconscious -- goes to cerebellum (ipsilateral)
unconscious -- blue line
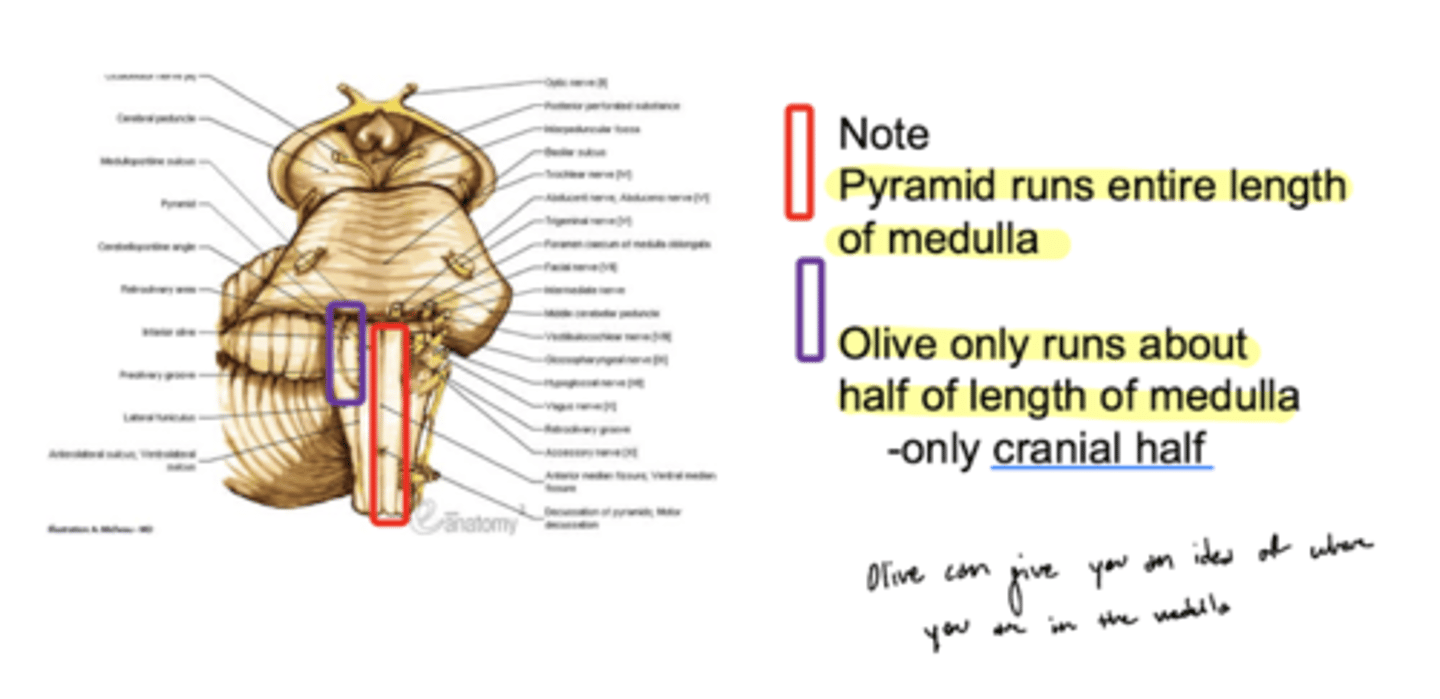
What are the structures of the ventral medulla oblongata (medial to lateral)?
1. pyramid
2. olive
3. lateral funiculus
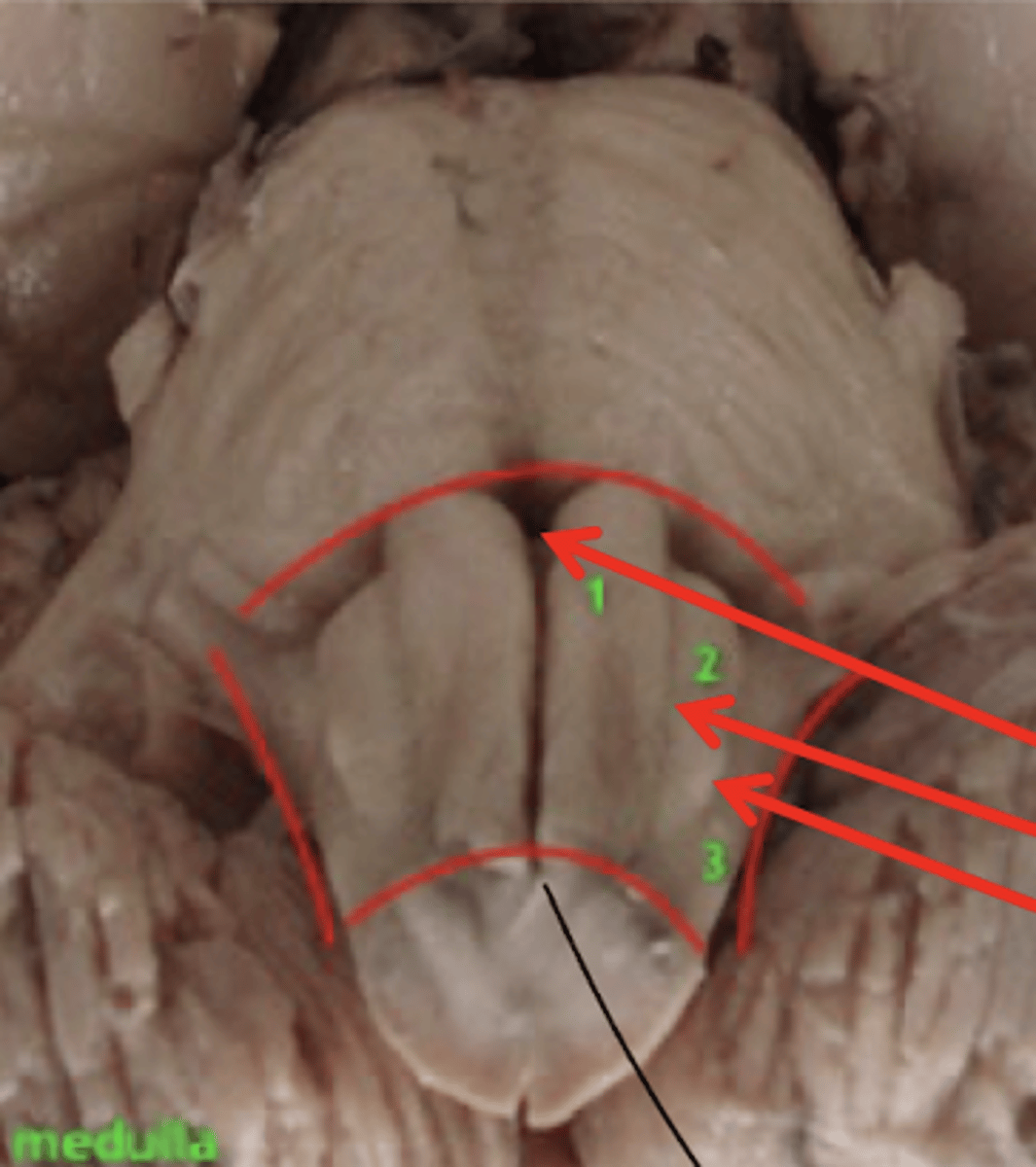
What divides the right and left pyramid of the medulla oblongata?
anterior median fissure
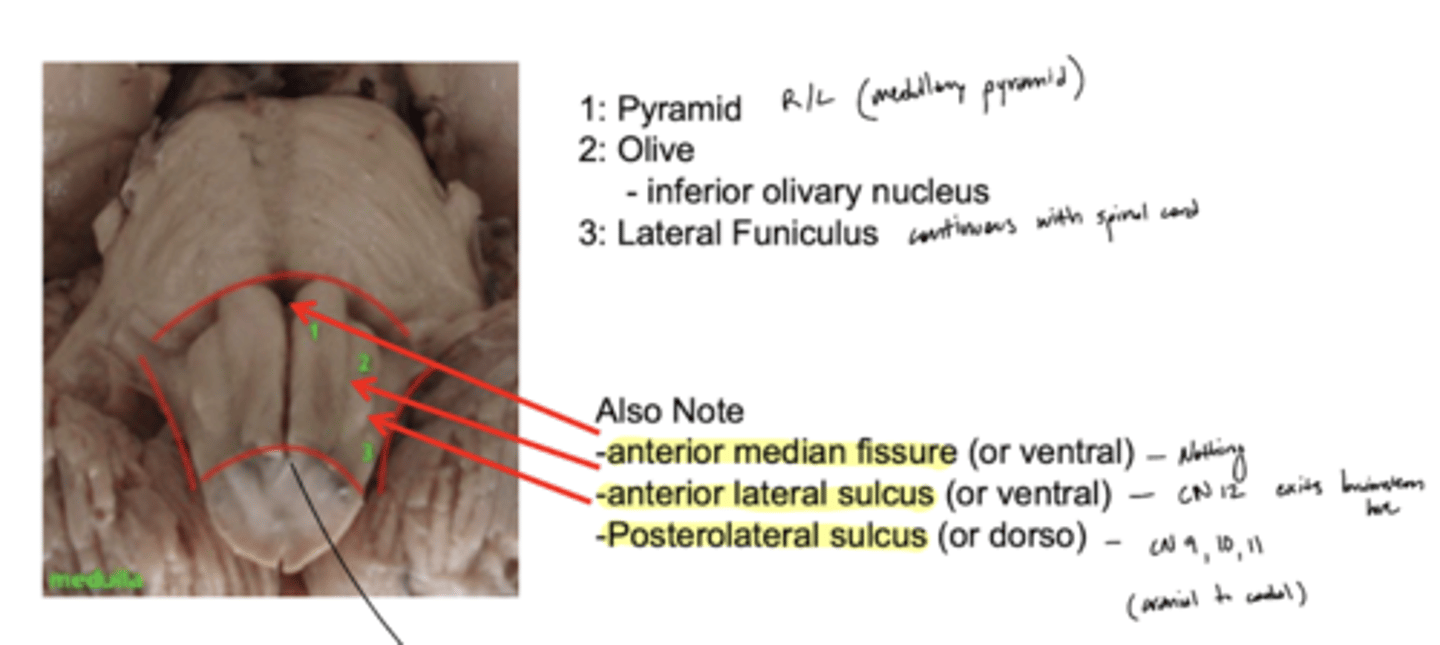
What divides the pyramid from the olive of the medulla oblongata?
anterior lateral sulcus
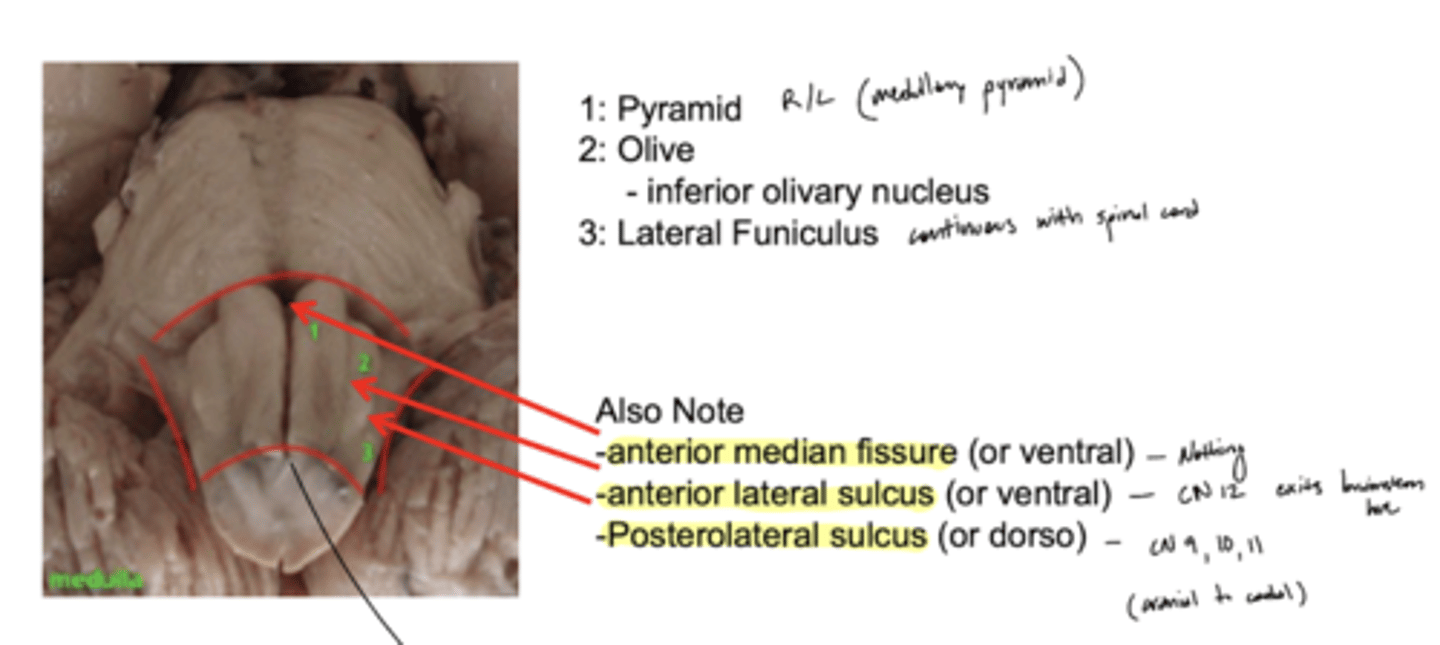
What divides the olive and lateral funiculus?
posterolateral sulcus
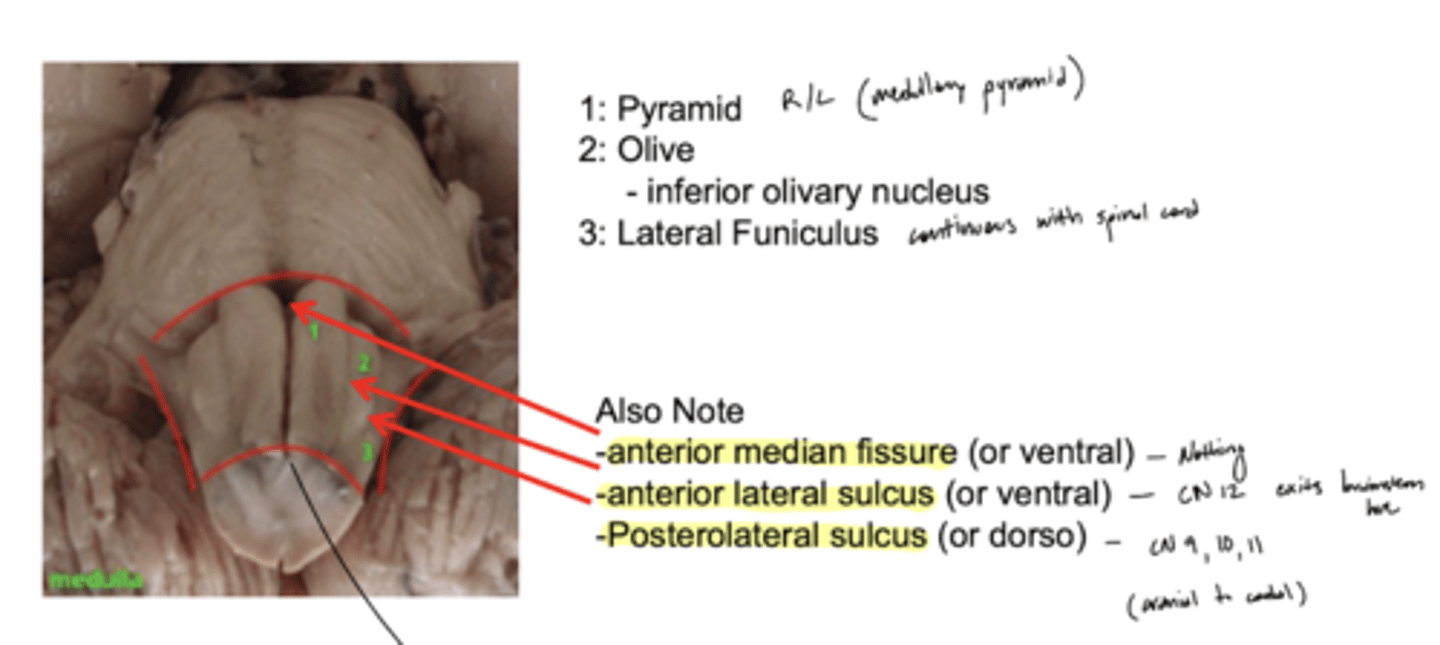
Do the pyramids run the entire length of the medulla oblongata?
yes
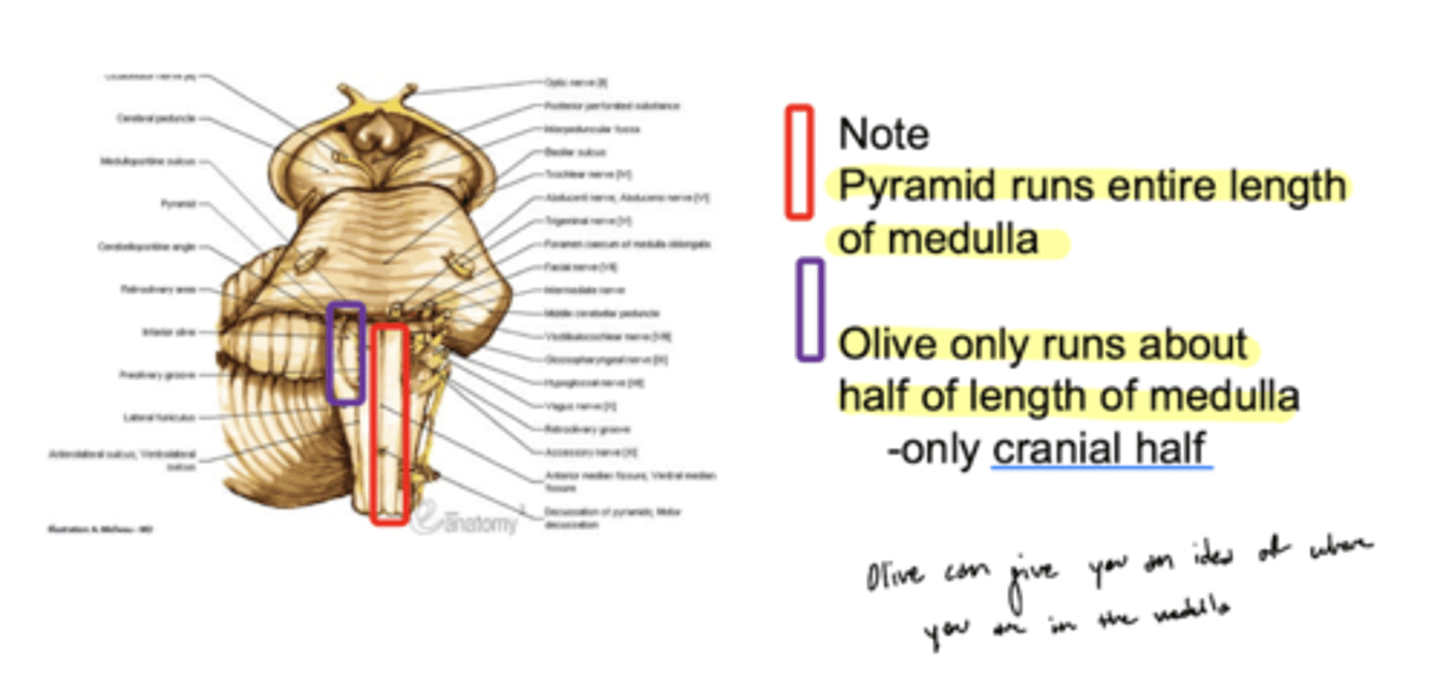
Does the olive (right and left) run the entire length of the medulla oblongata?
no -- only half (cranial)
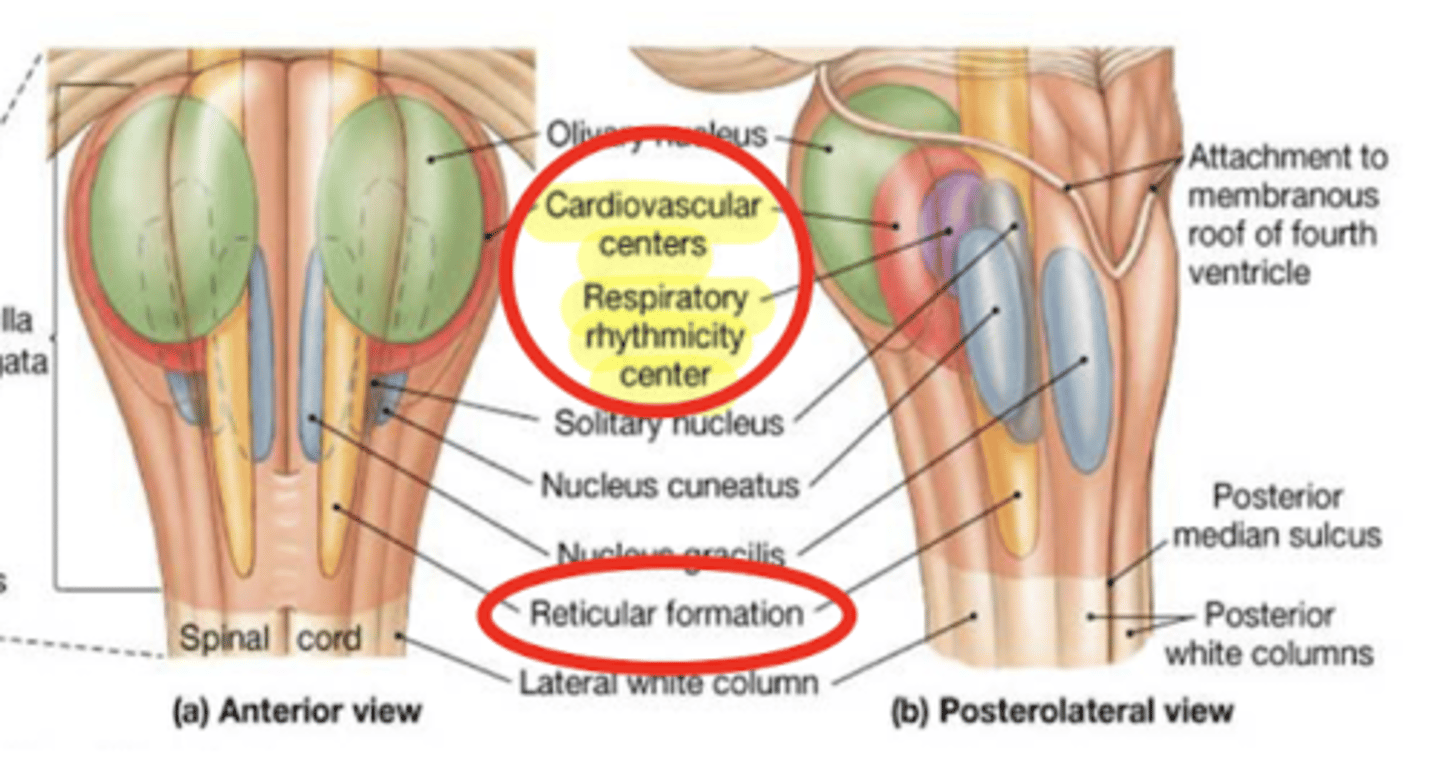
What is the descending phenomenon of comas?
superficial coma -- cortex that is not working (cerebral hemisphere)
deep coma (worst) -- cortex + brain structures
if coma reaches the medulla it can hit the respiratory center, requiring life support
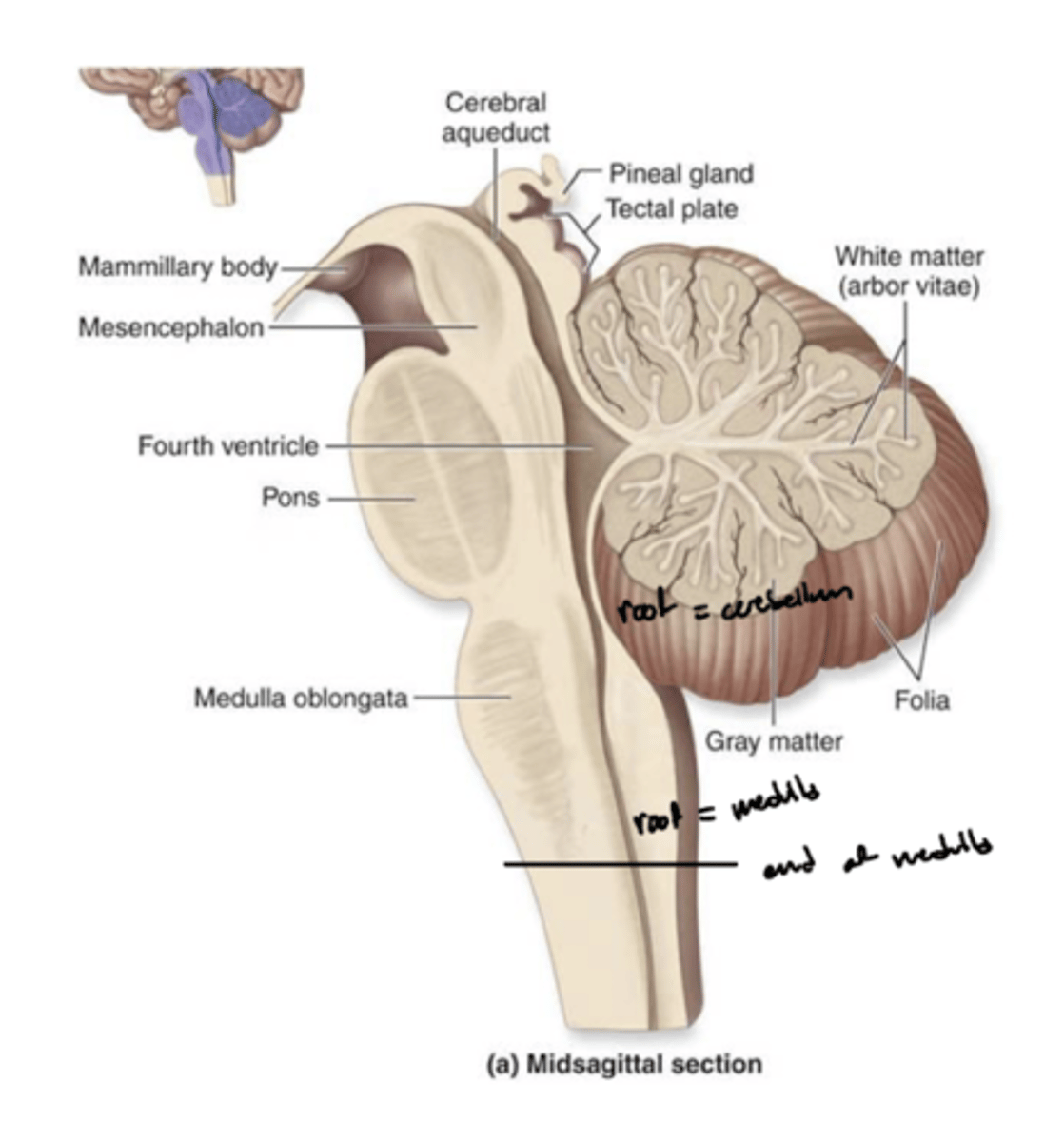
Where does the 4th ventricle end?
medulla
cranial medulla -- "open" half
caudal medulla -- "closed" half
What cranial nerves reside in the medulla?
1. CN IX
2. CN X
3. CN XI
4. CN XII
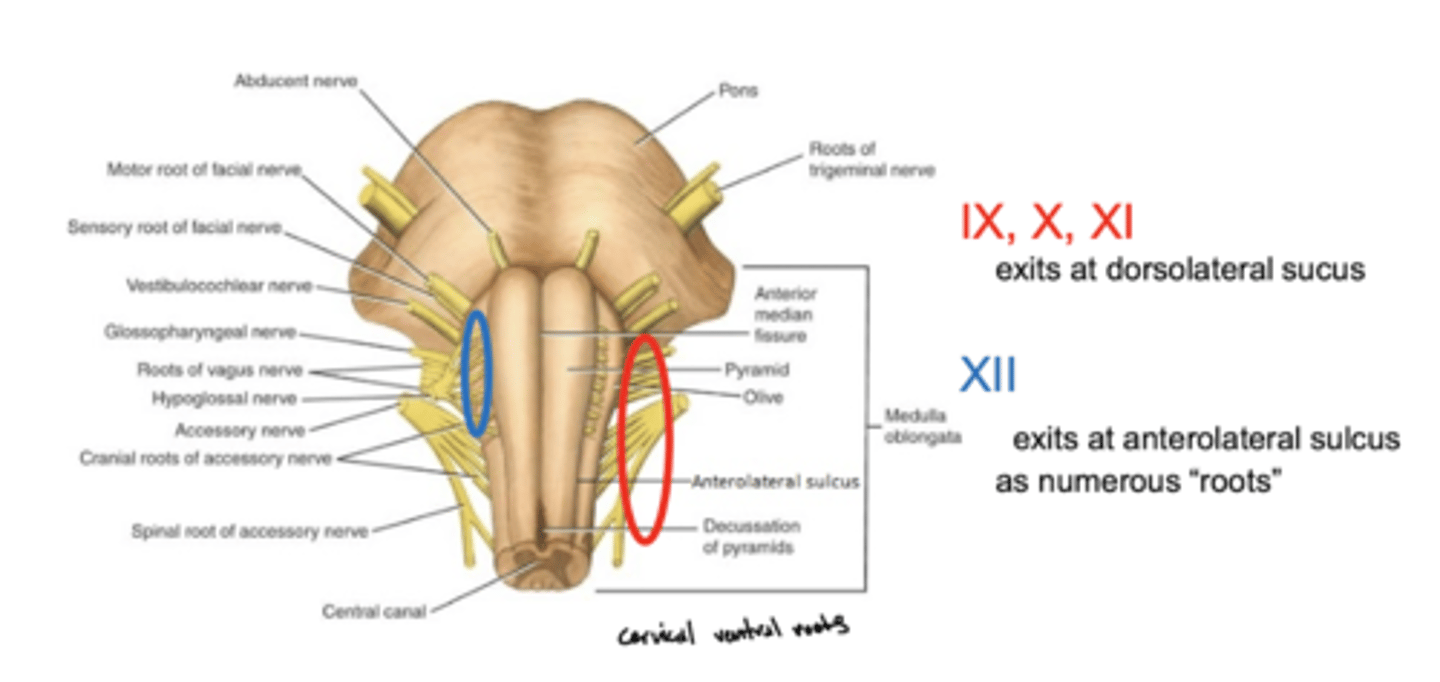
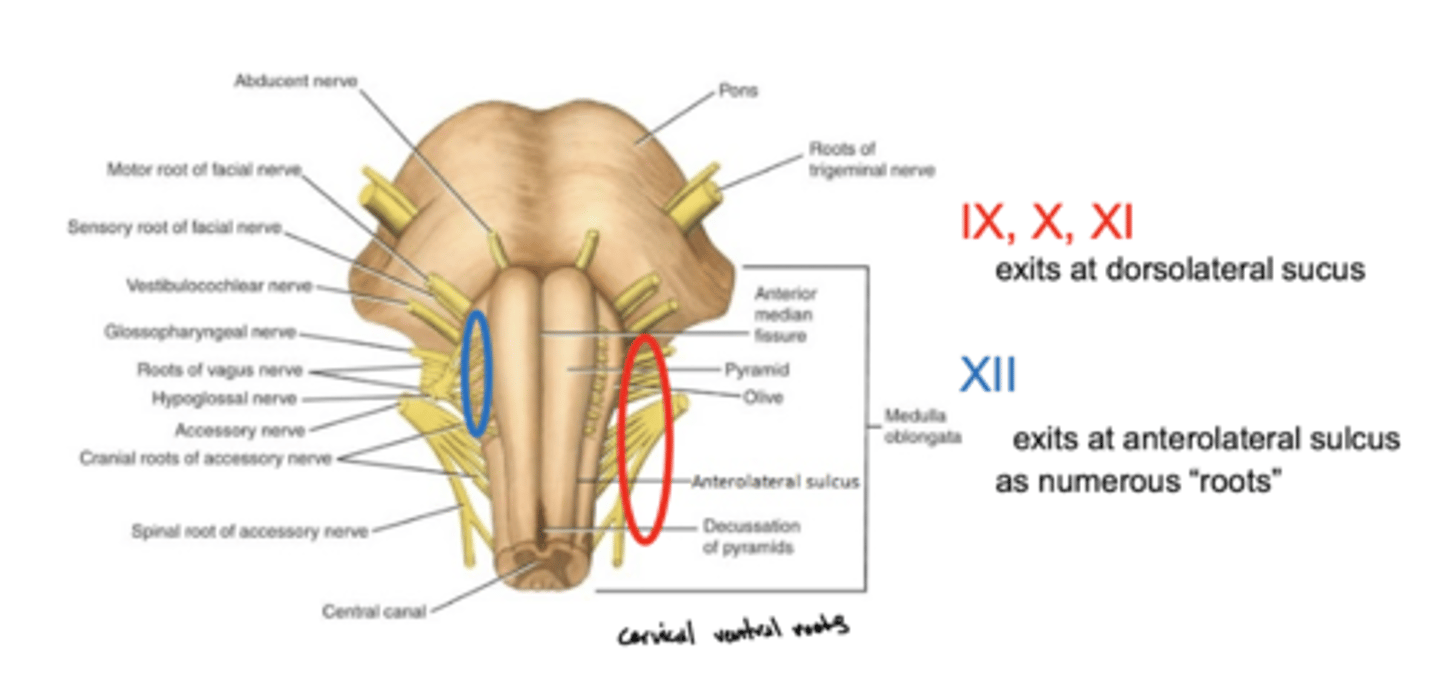
Where do CN IX, X, and XI exit the medulla oblongata?
exit the dorsolateral sulcus (
posterolateral sulcus)
3rd sulcus (counting medial to lateral) -- most lateral
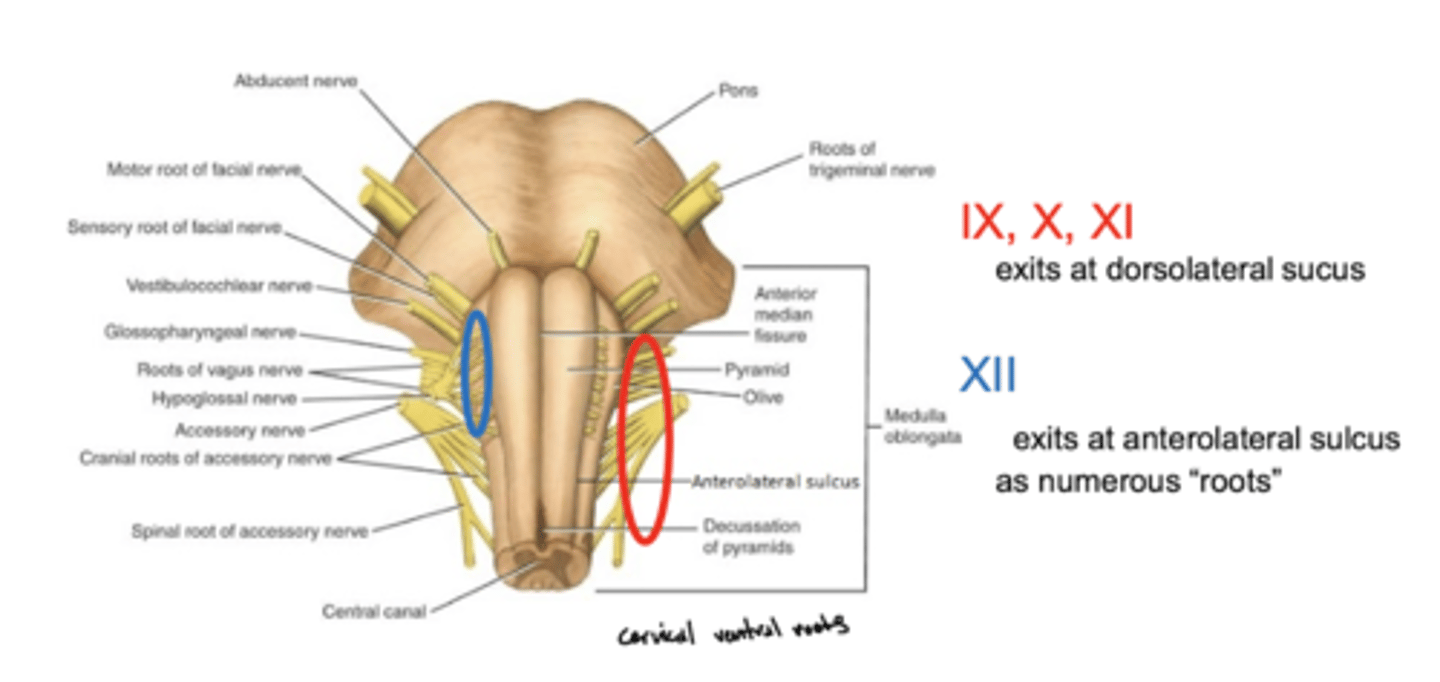
Where does CN XII exit the medulla oblongata?
anterolateral sulcus -- as numerous roots
2nd sulcus (counting medial to lateral)
How do the fibers of the inferior olivary nucleus travel to the inferior cerebellar peduncles?
contralateral -- eventually will reach the (contralateral) cerebellar hemisphere
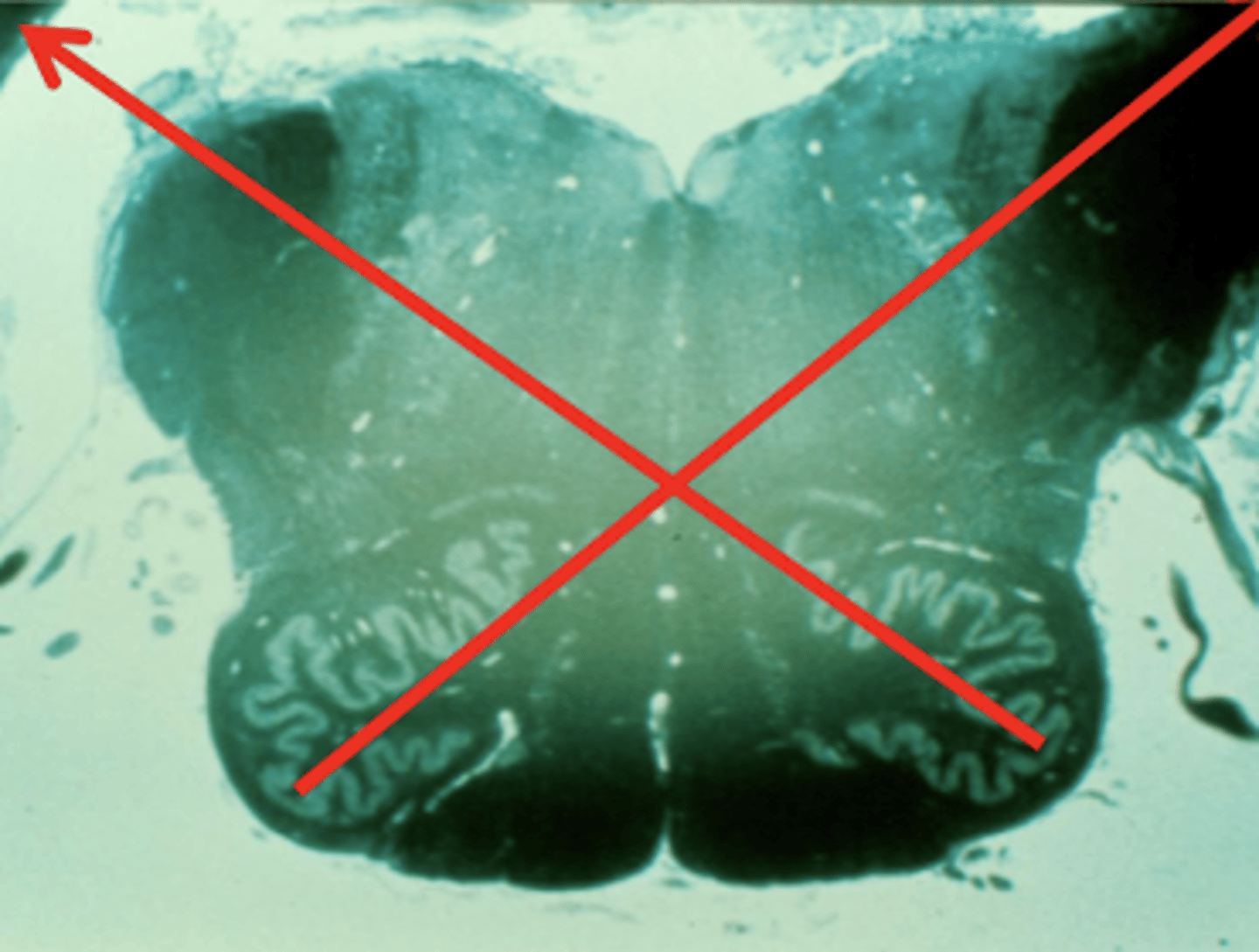
What is the function of the fibers from the inferior olivary nucleus?
error detection for motor movement (amount of force)
What is the function of the superior cerebellar peduncle?
connects the cerebellum to the red nuclei of the mesencephalon (mostly output)
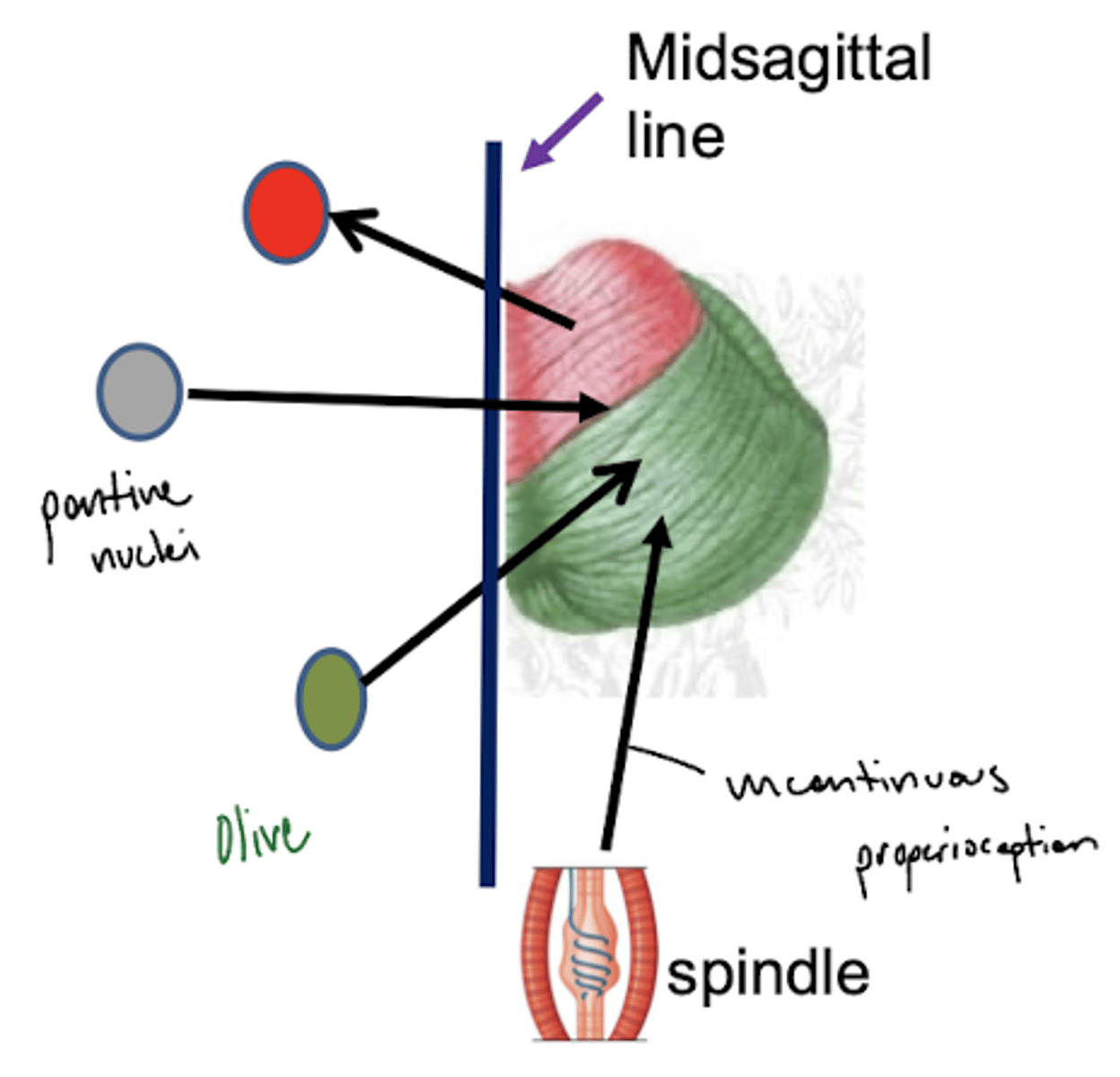
What is the function of the middle cerebellar peduncle?
connects pons to the cerebellum (entirely input)