C1 - Linear Equations
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Row operations
Alterations to a matrix that maintains the linear equation equivalency
Replace, interchange, scaling
Two row-equivalent matrices have the same solution set
Row echelon form
Each leading entry below the last is to the right of the former’s column
All entries below leading entry are zero
Nonzero rows above zero rows
Reduced row echelon form
All requirements of row echelon form
Each leading entry must be 1
The leading 1 is the only nonzero entry in the column
Uniqueness of echelon forms
Each matrix is row equivalent to only one RREF
Pivot position
Leading 1 in the RREF
Pivot column contains pivot position
Rows w/ no pivot correspond to free variables
Existence and Uniqueness Theorem
Linear system is consistent if and only if row
[0 0 … b]
b = nonzero
does not appear.
Span
All possible combinations of a set of vectors
Matrix equation
Ax = b
Linear combination of columns
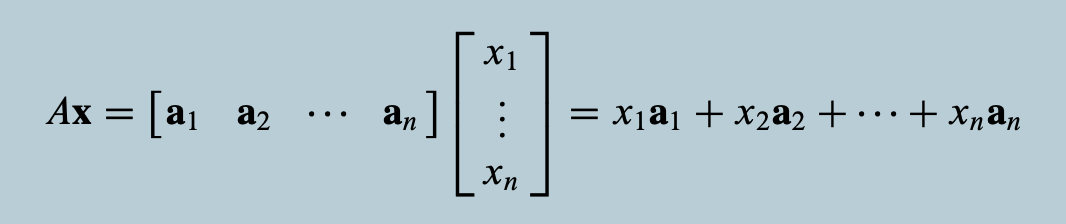
Equivalent statements for matrix equations

*For coefficient matrices
Homogeneous system
Ax = 0
Nontrivial solutions of homogeneous systems
Nontrivial solutions exist if at least one free variable exists
Parametric vector form
x = su + tv
Parameter t
Theorem
Scalar additions of a homogeneous solution correspond to non-homogeneous solutions

Linear independence
When a set of rows in a matrix does not have a free variable
If and only if the only solution to a1x1 + a2x2 + … = 0 is trivial
Each vector adds a unique dimension
Linear dependence of zero vectors
Vector set is linearly dependent if it contains the zero vector
Transformation
Changing of any vector’s position based on how the unit vectors change
Matrix columns can indicate this change
Multiplying by a “transformation matrix” transforms a vector
Change in dimensions is arbitrary
Linear transformation
T(u + v) = T(u) + T(v)
T(cu) = cT(u)
c = scalar
Domain, range, codomain
Domain: input values
Range: output values
Codomain: dimension in which the output values exist