Week 5 Quiz Flashcards
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What is it called when a liquid in which another liquid is dissolved?
Solution
What is it called when a liquid in which insoluble particles are dispersed?
Suspension
What is it called when a liquid in which another insoluble liquid is dispersed?
Emulsion
What is it called when a liquid in which solid particles are all dissolved?
Solution
What is a vehicle?
The main liquid in a liquid medicine
Which type of water is used in the preparation of oral liquid medicines?
Purified Water BP ( British Pharmacopoeia)
A medicine in suspension form has been left to sit and has formed a hard cake at the bottom of the bottle. What will happen to the first and last doses if action is not taken?
The first dose would be underdosed whereas the last dose would be overdosed
Do thickening agents increase or decrease the viscosity of a liquid?
They increase the viscosity of a liquid
Do thickening agents improve the physical stability of suspensions?
YES
Can thickening agents reduce separation in suspensions?
YES
What is methyl hydroxybenzoate?
A preservative
What is a sign of a good quality suspension?
Shaking the bottle disperses the particles evenly in the suspension
Do all cells use DNA that is double-stranded as their genetic carrier?
Yes, except from particular viruses which use single stranded DNA or RNA
How many strands of DNA are there and are they parallel?
DNA is composed of 2 ANTI-PARALLEL strands
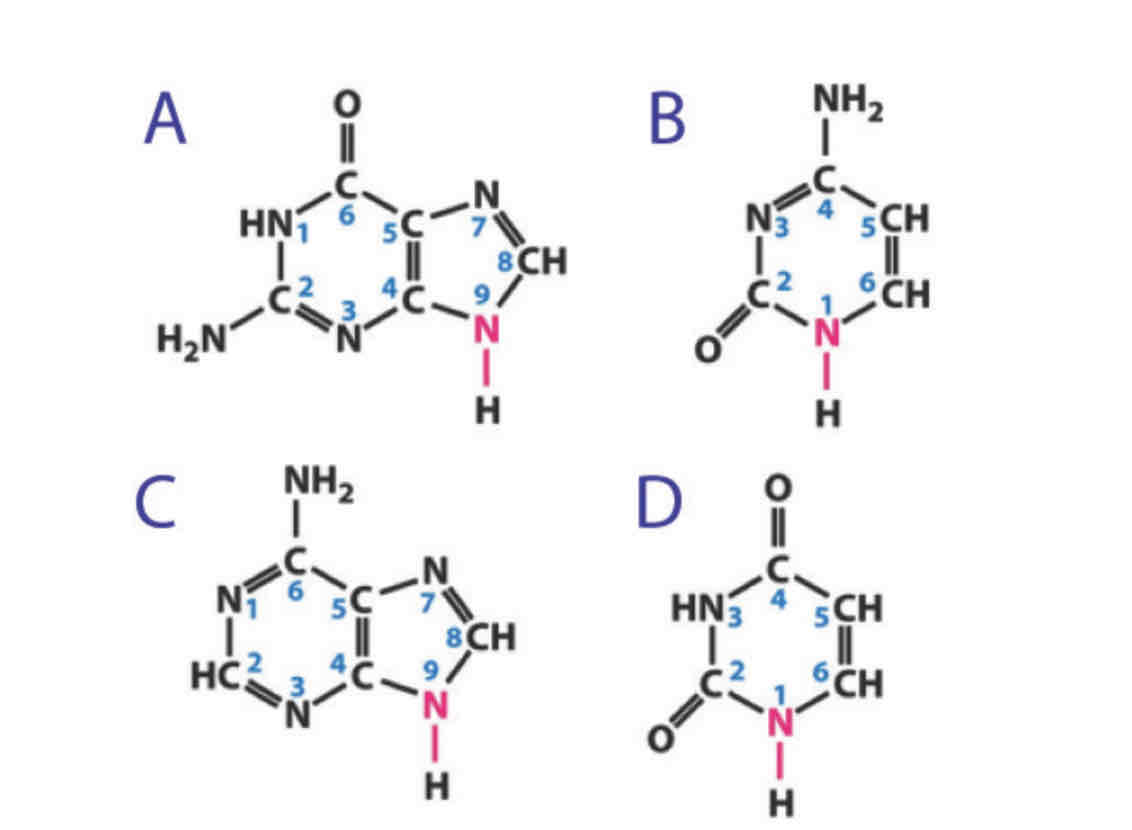
There are 4 nucleotides on the flipside of this card.
A and C are purines which are indicated by the double rings
B and D are pyrmidines which are indicated by the single rings
A is guanosine
D is uracil
There are 3 opportunities for forming hydrogen bonds between these bases . These bases are guanosine and cytosine. N9 does not participate in hydrogen bonding in RNA, because it's linked to the ribose sugar
What are histones ?
The building block of nucleosomes
How many times does DNA lop around each nucleosome?
TWICE
TRUE OR FALSE?
True- The length of DNA looped around nucleosome is 140 base pairs , with a 30-40 base pair linker between nucleosomes
Is DNA in cells always bound by proteins ?
Yes, it is called chromatin (protein-DNA complex)
Is DNA packaged into individual separate chromosomes?
Yes
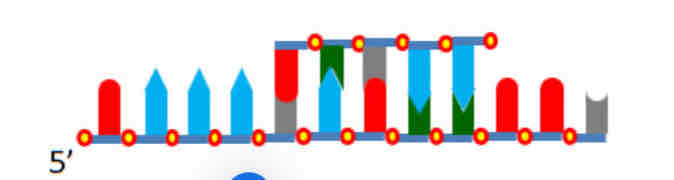
If replication occurs on this complex(in the picture below) , where will new DNA be synthesised?
On the LEFT END of TOP strand
How does DNA replication proceed?
DNA replication proceeds from the 5’-phosphate of the incoming nucleotide to the 3’-hydroxyl of the previously added nucleotide
The sequence for the template DNA strand is 5'-GATATCCATTAGTGAC-3'. What is the sequence of the RNA produced?
5'-GUCACUAAUGGAUAUC-3'
Can chromatin modifications be inherited by the next generation?
Yes
What is methotrexate?
A cancer therapy that affects the synthesis of building blocks of DNA
What is a drug that affects a viral DNA Polymerase?
Azidothymidine
What is an anti-microbial drug that inhibits thymidine monophosphate synthesis in bacteria?
Trimethoprim
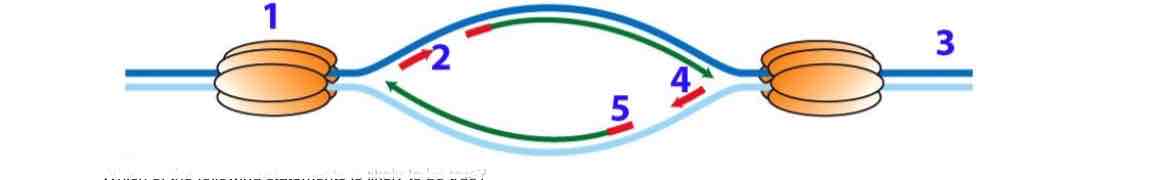
Below you see a depiction of an origin of replication on a chromosome, with DNA synthesis occuring in both directions. 1 indicates a helicase complex that is splitting the DNA, while newly made DNA is shown in green.
Given that the primers take a lot of time to synthesize, the replication above 4 will be faster than that below 4.
2 and 4 are likely to be RNA primers
The DNA end immediately under 3 is a 5’ end
What is true about bonding?
Each orbital can ONLY hold 2 electrons
A pair of electrons in a molecular orbital constitutes to a single bond
When a carbon atom undergoes sp3 hybridisation, there are NO un hybridised orbitals left
The F subshell can hold 14 electrons
Sigma orbitals can be formed from overlap of hybrid orbitals (such as the sp-sp overlap in alkynes), or from p atomic orbitals, provided that they overlap in an end-on, not side-on fashion
Pi orbitals are formed from the unhybridised p orbitals found in sp2 and sp hybridised atoms. The hybridised orbitals take part in sigma, not pi bonding.
There are some oddities in the filling up of atomic orbitals. The 3d orbitals are filled up AFTER the 4s, and silmilarly the 4f are filled in after the 5s, 6s and 5d.
This is most definitely FALSE. Easy counterexamples include the C(sp3)-H(1s) overlap in methane. Other examples might include the C(sp3)-C(sp2) single bond in the molecule propene.
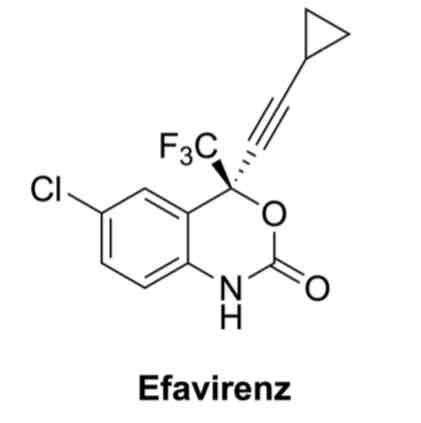
Efavirenz is a drug known as a reverse transcriptase inhibitor used in the treatment of HIV
The chemical structure of Efavirenz contains 5 sp3 hybridised carbon atoms, 7 sp2 carbon atoms, and 2 sp hybridised carbon atoms. Efavirenz contains a single nitrogen atom which is sp2 hyrbrised, the lone pair on this nitrogen sits in the P unhybridised orbital and is in resonance with the adjacent carbonyl group
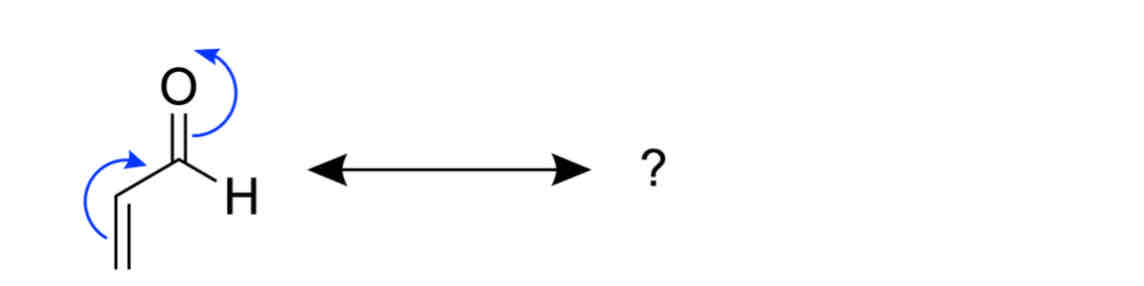
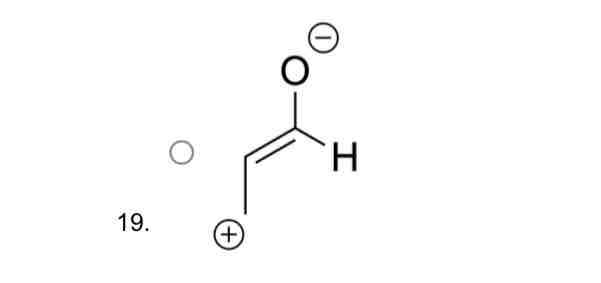
Which of the following structures is the correct outcome of resonace arrows in this diagram ?
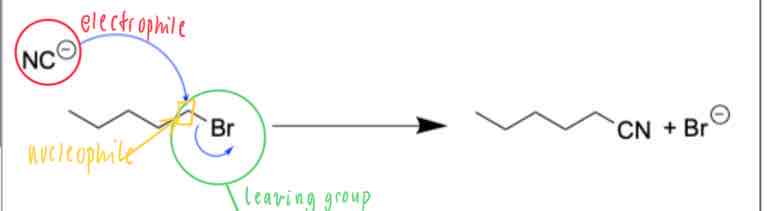
A reaction is shown in the mechanism below:
Identify the components of the reaction scheme
Identify the problem
INCORRECT ARROW USED
Identify the problem
INCORRECT ARROW USED
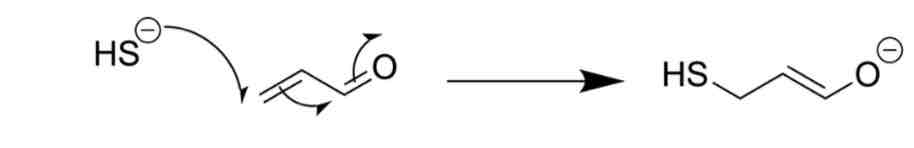
Identify the problem
ELECTRONS TRAVELLING IN THE WRONG DIRECTION

Identify the problem
INCORRECT FORMAL CHARGES
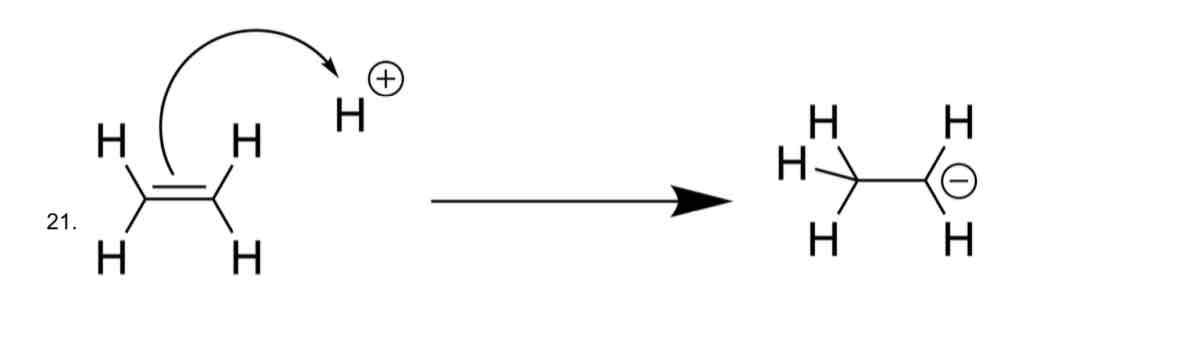
Identify the problem
CHARGE IS NOT CONSERVED
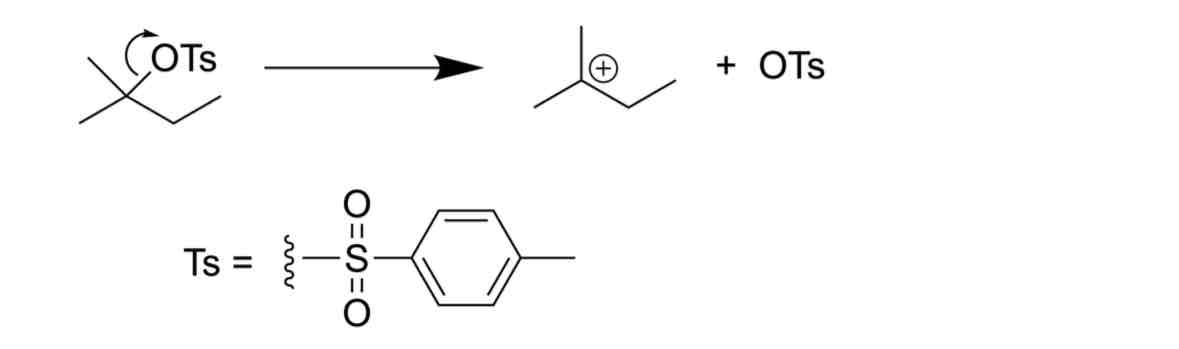
Identify the problem
NON-SPECIFIC CURLY ARROWS
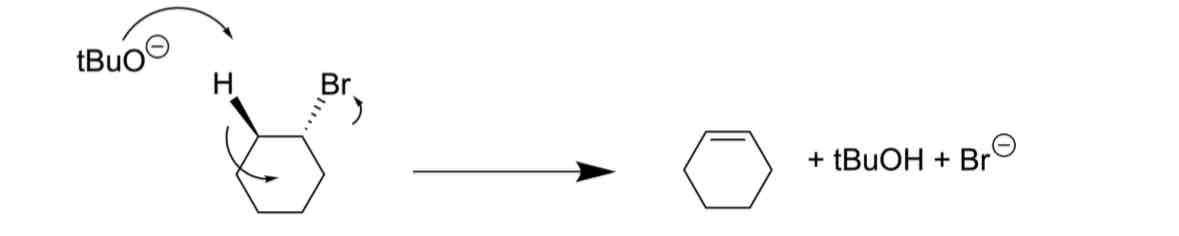
What is Brufen a proprietary name for?
Ibuprofen
Can Adalat® tablets be crushed & why/ why not?
Adalat® LA tablets are modified release, so must not be crushed.
Can Phenoxymethylpenicillin be taken with food?
Phenoxymethylpenicillin takes Cautionary & Advisory label 23 in BNF - take this medicine when your stomach is empty. This means an hour before food or two hours after food.
Does warfarin interact with cimetidine?
Yes, this is because cimetidine is an H2 receptor antangonist
Is erythromycin a macrolide antibiotic?
Yes
What does NSAIDs stand for?
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Which TWO of the following analgesic medicines require additional labelling to warn patients about the maximum dose?
Paracetamol
Cocodamol