4.1. Measuring and Reporting Cash Flow
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Common Misunderstanding About Cash
that rapid growth means that your business is doing fine
that a good profit situation equals a good cash situation
that just because your company is “making money“, it will be easy to receive a loan
Profit vs Cash Flow: Accrual Accounting vs Cash Accounting
revenue is recognized when earned rather than when cash is collected
it is possible for a company to have a healthy net income (profits) but not have enough cash to fulfill obligations.
Significance of profit diminished unless earnings translate into cash
there are time lags between profit generation and cash generation
Overview of the Cash Flow Statement
provides information about cash receipts and cash payments during an accounting period
tells how cash was generated and used
Differences Between Income Statement and Cash Flow Statement
Cash flow statement is cash-based as opposed to accrual like in income statement
Cash flow statement reflects when the cash was collected not when the revenue was earned
Cash flow statement specifies where the cash was generated and how they are spent
2 Key Questions Answered by the Cash Flow Statement
Does the company generate enough cash from its operations to pay for its news investment, or is the company relying on new debt issuance to finance them?
Does the company pay its dividends to common stockholders using cash generated from operations, from selling assets, or from issuing debt?
The sources of cash are useful for evaluating liquidity, solvency, financial flexibility, and sustainability
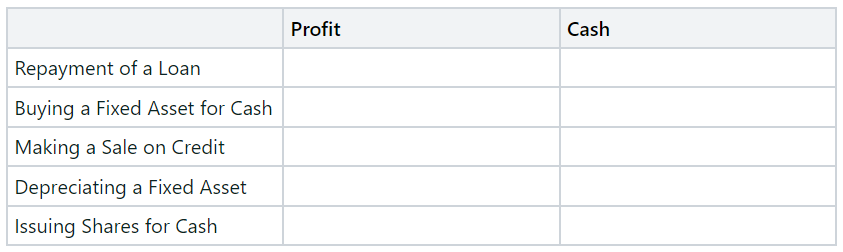
How the Following Scenarios Will Affect the Cash Flow Statement
Layout of Cash Flow Statement
It is important to understand where in the business the cash is being generated and spent, so divided into 3 sections
“+“ in Operating Activities: should be the main source of cash inflow for healthy company
“-” in Investing Activities: as cash is needed to invest in non-current assets to support
“±” in Financing Activities
Cash Flow from Operating Activities
Cash flows for operating activities are cash inflows and outflows directly related to earnings from normal operations
Inflows:
Customers
Dividends and interest on investments (could operation or finance, IFRS is flexible)
Outflows:
Purchase of services (e.g., utilities) and goods for resale
Salaries and wages
Income taxes
Interest on liabilities
Cash Flow from Investing Activities
Cash flows from investing activities are related to the acquisition or sale of long-lived productive assets and investments in the securities of other companies.
Inflows:
Sale or disposal of PP&E
Sale or mutiny of investment in securities
Outflows:
Purchase of PP&E
Purchase of investments in securities
Cash Flow from Financing Activities
Cash flows from financing activities are related to external sources of financing (owners and creditors) for the enterprise
Inflows:
Borrowings on notes, mortgages, bonds from creditors
Issuing stock to owners
Outflows:
Repayment of principal creditors (excluding interest which is an operating activity)
Repurchasing stock from owners
Dividends to owners
2 Formats for Reporting Cash Flow from Operating Activities
Direct Method
reports the net cash effect of each operating activity
more informative as it provides detailed information on cash inflow & outflow, encouraged by both IFRS & GAAP
Indirect Method
starts with accrual net income from income statement, then eliminates noncash items to arrive at net cash flow from operating activities
more popular among companies, as it is deemed easier and less costly
net income (profit) ± adjustments for non items = net cash flow from operating activities