Quiz 3: Interest groups, Agenda Setting, Policy Science
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topics: Interest groups, agenda setting, policy science
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What do public interest groups do?
They organize to influence government in order to produce collective goods or services that benefit the general public
What kinds of resources do interest groups need?
Money to have/purchase
staff & professional assistance
to make campaign contributions
etc.
Other than money, what makes an interest group successful?
Leadership
Membership (the size & intensity)
think of National Rifle Association (they are small but very intense so they have somewhat power) etc, etc
Information
What do Pluralists vs Elitists argue about when it comes to interest groups?
Pluralists: that interest groups serve everyone
Elitists: That interest groups skew more towards the wealthy
(they say ppl with resources tend to be more successful, so they’re the only ones we’re going to listen to)
Name at least 3 strategies for congressional lobbying
Personal Contacts (bc they already know each other, it’s easier to speak politics)
Campaign Contributions (PACS: recent regulations and loopholes)
Use of professional lobbyists
What is agenda setting? What do you need on the agenda in order to get anything done?
The agenda is what the most important policy problems are, that need to be addressed and acted
In order to get anything done, you need to get your ideas on thee agenda
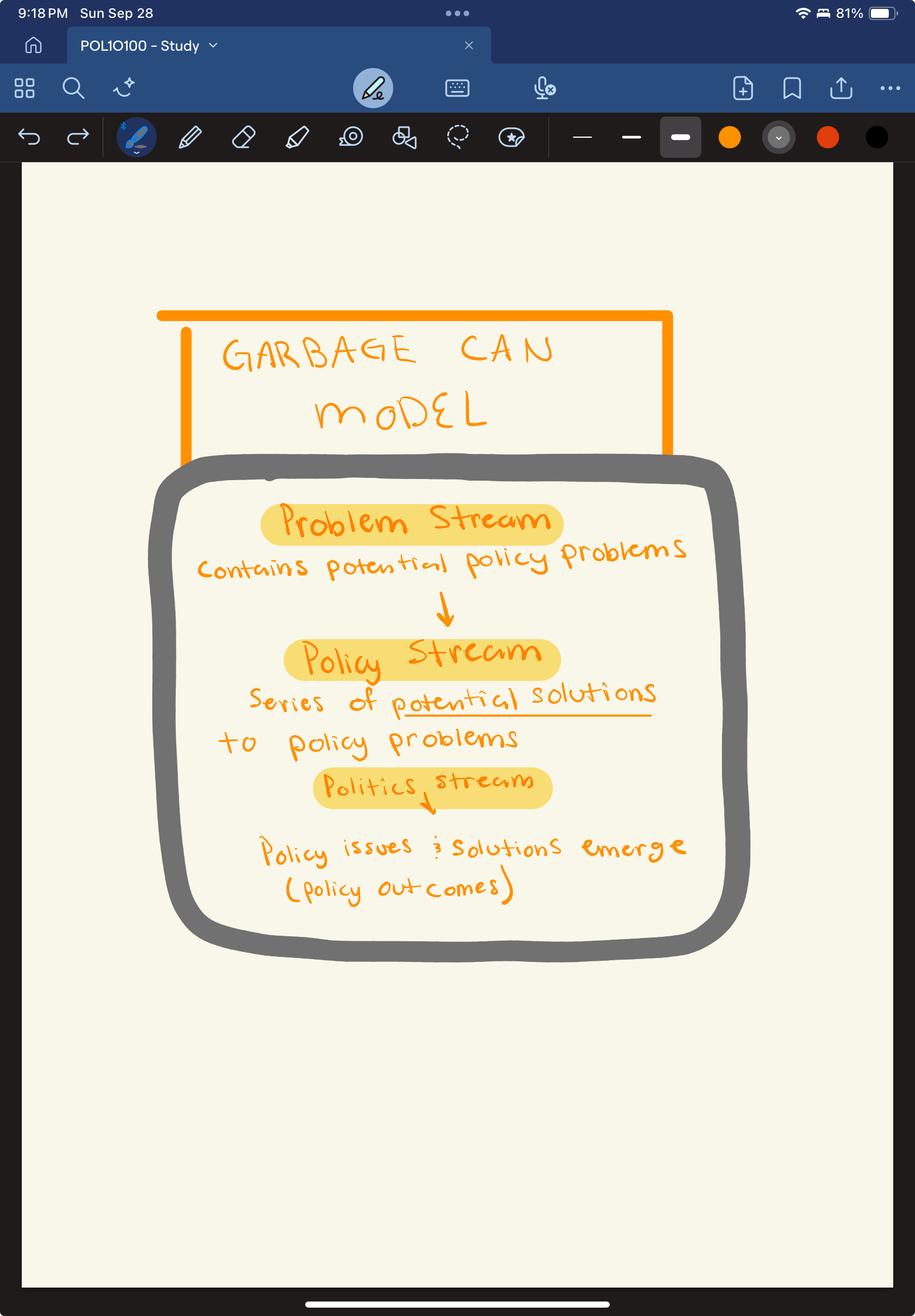
What are the three streams of the garbage can model?
Describe them
Problem Stream
Policy Stream
Politics Stream
What can be the problem with agenda setting / the garbage can model?
You won’t get very high quality thought out solutions because there’s a time constraint, and if theres a lot of publicity on it, the faster the solution— the better
means you’ll get half assed solutions at best
President as Agenda Setter
True or false:
What the president says and does is often important to the agenda (Why?)
True - because whole country is listening to president, so it has attention which gets on the agenda
What term describes the people who interpret the constitution: at what is says and ONLY doing that (not trying to find ways to say the constitution didn’t specifically say or imply something)
Literalists
Before the 20th century, were presidents more literalist? Howcome?
Yes more literalist because now presidential power has expanded in a way that being a literalist is not very easy to do
Since the president approves congressional bills, does this wield them a lot of power for agendas? Why?
Yes because they can pass something that can go on their agenda or even veto something that they would not like on their agenda (my best guess)
How many members in congress? How many senators? How many representatives?
535 members
100 senators
435 representatives
Name at least 3 places where congressional agenda setting can come from
Committee chairs
Parties in majority/minority
Congressional leadership
Caucases ( a group of ppl that’ll have power to agree on one issue together)
Why is it easier for the president to establish their policy agenda when the senate and house (congress) are dominated by the same party?
Easier because their won’t be too many conflicting opinions therefore it is easier to pass things like laws and policies
When the president, and majority of congress represent different political parties, that’s when the agenda setting process becomes complicated
The courts used to operate on the principles of constitutionalism but now what principles do they operate on? Describe it
Judicial Positivism: using legal reasoning to determine substantive meaning and outcomes of policy
Define judicial positivism?
Using legal reasoning to determine the meaning and expected outcomes of policy
Define constitutionalism? Why did it steer the courts away from policy for a time?
1. The idea that government power should be limited by a constitution and the rule of law, ensuring that those in power are subject to legal constraints rather than acting arbitrarily.
2. This legal reasoning was really narrow, which that steered the courts away from policy
(bc only cared about what’s in the constitution/ interpreting w/ the constitution )
Do the courts sometimes reflect on what the public opinion wants?
Yes
What do pressure groups do?
Using what? Name 3 things they do
They seek to influence government policy in a particular direction using cohesiveness and structure
1. Often have well developed organizations designed to aggressively recruit members
2. Capacity to raise a lot of money from their membership and other interested parties
3. Collect and organize information (simplifying decision making process for policy leaders)
Describe policy science
The scientific study of public policy and decision making by the government and governmental agencies
Why can’t policy be based on vibes? Making us use data.
If we pass “the everyone is happy act” it won’t work because some ppl will still be sad, can be ineffective
In policy science we use what two types of analysis?
Quantitative Analysis: using #’s like stats
Qualitative Analysis: like interviews
What is the iron triangle?
Alliance of congressional committees, interest groups, and agencies to work together for mutual benefit (3 of them all work together)
What is the Alliance of congressional committees, interest groups, and agencies to work together for mutual benefit (3 of them all work together)
The Iron Triangle
Other than lobbying what do interest groups do? Name some
Participation; can help people vote, anyone can be part of interest groups (like planned parent hood)
Education
Agenda building
Provision of program alternatives
Program monitoring; means they’re watching programs run by gov.
what are these strategies examples of?
Personal Contacts (bc they already know each other, it’s easier to speak politics)
Campaign Contributions (PACS: recent regulations and loopholes)
Use of professional lobbyists
Strategies used for Congressional Lobbying