IB BIOLOGY SL - Unit 8: Human Impacts & Conservation | Quizlet
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Negative feedback loop
Returns a system into homeostasis
Positive feedback loop
Amplifies a condition, resulting in more change from homeostasis
Keystone species
A species that has a disproportionately large impact on the ecosystem relative to its population size (removal causes significant biodiversity loss), ex. beaver, wolf, nitrogen-fixing bacteria, etc.
Sustainable resource
Rate at which resources are removed from environment is lower than the rate at which resources naturally replenish themselves
Methods of sustainable resource
- Avoiding use of agro chemicals (use herbivores to eat insects)
- Reduce soil erosion and nutrient loss (avoid drilling, keep plants covered)
- Reduce carbon footprint (use biofuel/energy-powered tractors)
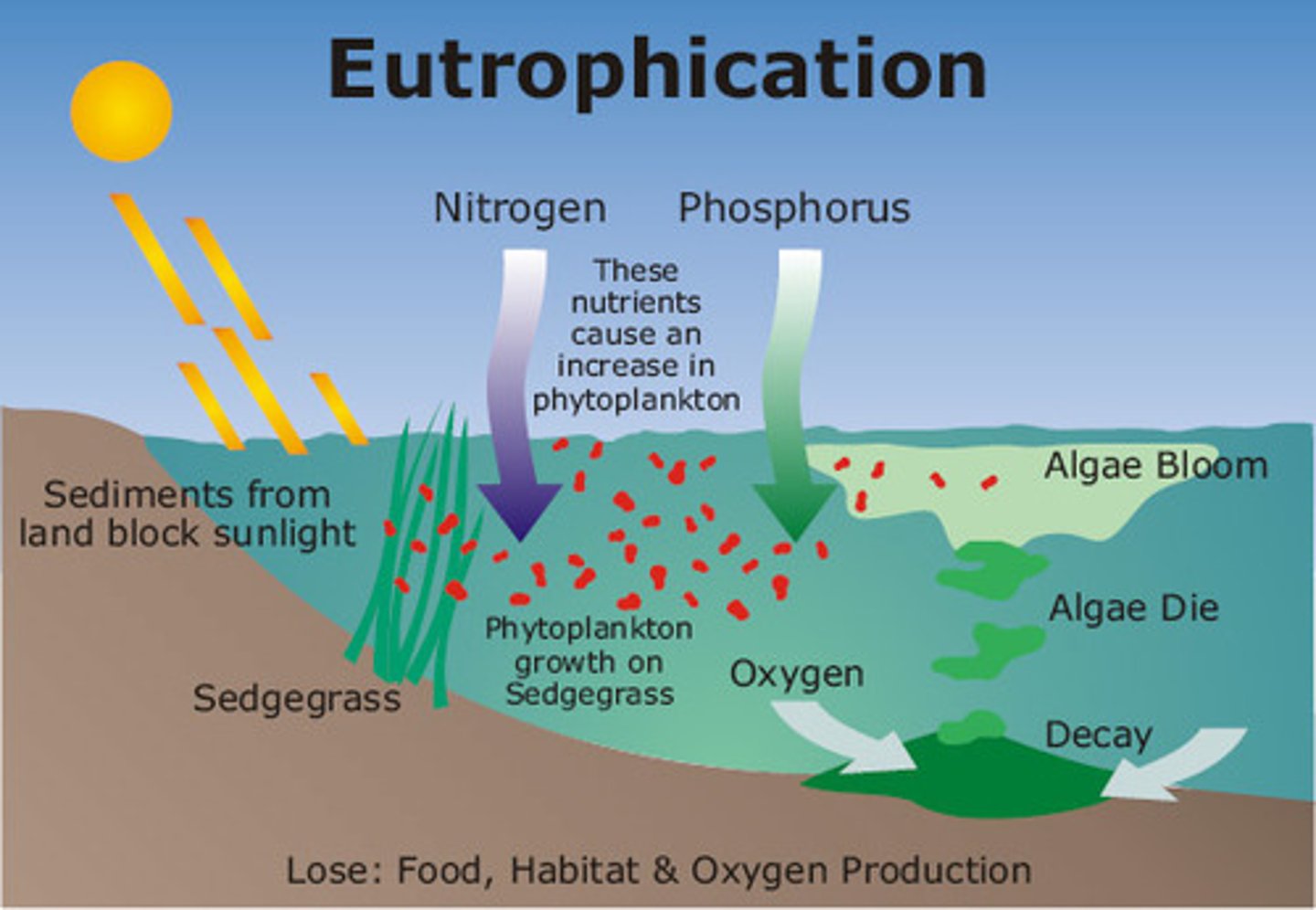
Eutrophication
A process by which nutrients, particularly phosphorus and nitrogen, become highly concentrated in a body of water, leading to increased growth of organisms such as algae or cyanobacteria
Bioaccumulation
Increase in toxin levels throughout an organism's life
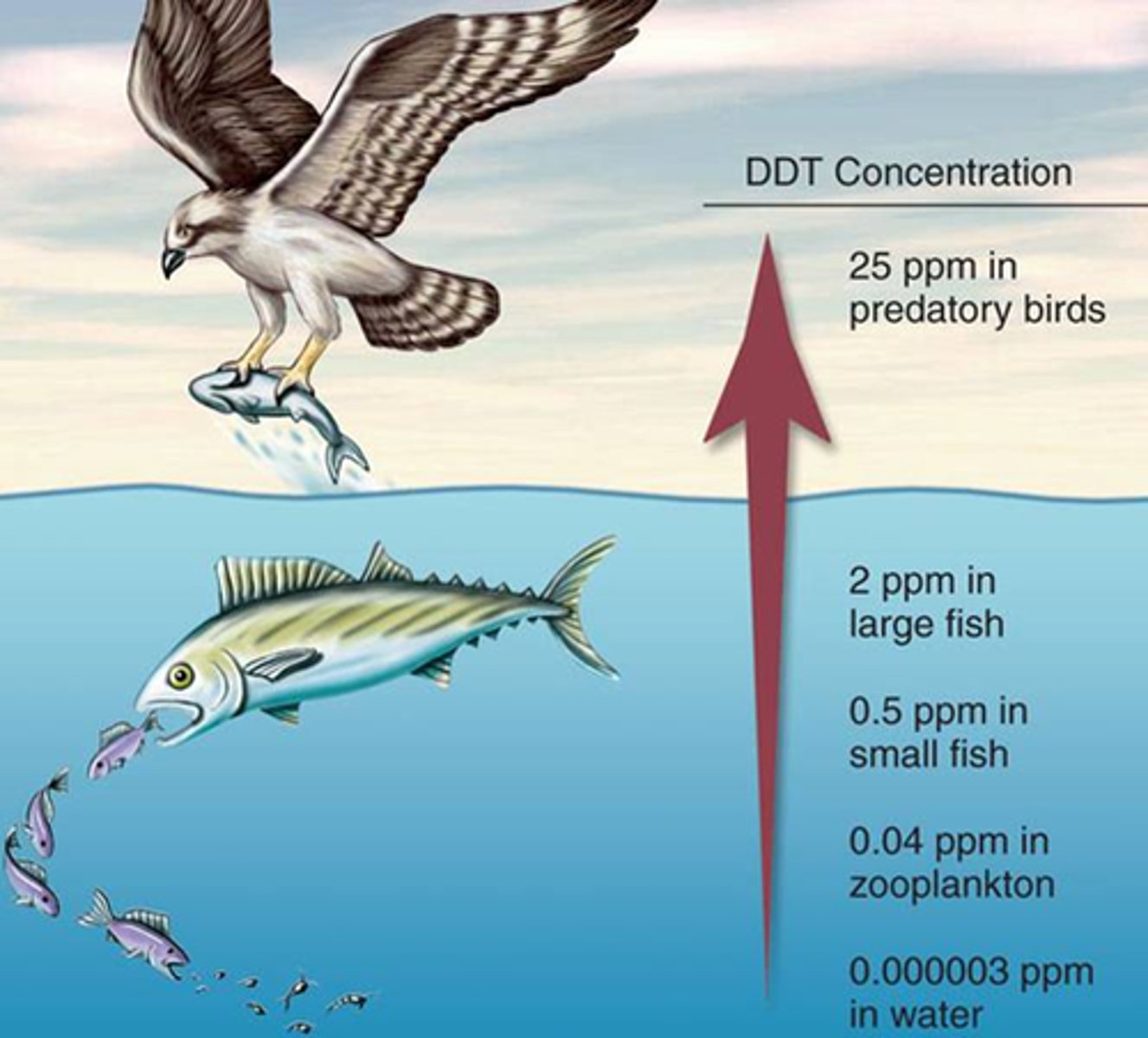
Biomagnification
Increase in toxin levels through the food chain (higher trophic=high toxin)
Rewilding
Encouraging natural ecosystems to return through as few interventions by humans as possible (type of in situ conservation)
Hinewai Reserve
Example of successful rewilding in New Zealand, by adding mammals, returning forest, controlling animals, and lowering interference

Macroplastics
Larger plastics that are known to harm ocean life through entanglement and ingestion
How DDT is accumulated
The inability of natural metabolic processes to break down and remove from system
Short-wave radiation
Form where electromagnetic energy enters the Earth's atmosphere
Long-wave radiation
Form that electromagnetic energy leaves the Earth's atmosphere
Greenhouse gases
Gases in the atmosphere that trap energy, including CO2 (carbon dioxide) and CH4 (methane)
Anthropogenic activities that produce CO2
- Burning forests
- Burning peat/wood
- Combustion of fossil fuels
Anthropogenic activities that produce CH4
- Decay of organic matter in anoxic landfills
- Cattle farming in beef production
- Release of gases by decomposers in a warming wetland/permafrost
Greenhouse effect
Tipping point
Certain threshold that if reached or surpassed can cause massive changes, being irreversible (ex. switch from carbon sink to carbon source of borreal forest, or deforestation in amazon rainforest)
Effects of lack of upwelling due to climate change in oceans
- Less nutrient availability
- Less primary productivity
- Less energy for trophic levels
- Less CO2 taken by ocean
Reasons why species are projected to move up north/higher elevations
- Colder
- Further from equator
- Seeds dispered through north
Effect of increased CO2 in ocean
More acidification (lower pH)
Coral death
Calcium and carbonate levels fall, so calcium pulls hydrogen instead, producing bicarbonate, decreasing calcification
Coral bleaching
Coral expels symbiotes (zooxanthallae) and changes colour to white
Sea ice
Ice that floats on the surface of the sea
Landfast ice
Ice that is attached to the land
Effects of lost of landfast ice on Antartic Emperor penguin
Breeding success decreases as distance from ice edge decreases
Effects of lost of sea ice on Arctic walrus
Decreases survival, leaving offspring unwatched, so young gets eaten
Carbon sequestration
Way to decrease carbon dioxide concentration in atmosphere through capturing and storing in other places (reforestation, afforestation, peat formation)
Advantages of restoring tropical peatland
- Exhibits potential for rapid peat formation
- Sequesters carbon quicker
Advantages of planting non-native species in reforestation efforts
- Grows faster
Advantages of rewilding/planting native species
- Arrive naturally
- Start carbon sequestration
- Supports wildlife
Ecosystem diversity
Variety of habitats (terrestrial/aquatic) found in a geographical area
Species diversity
Number of different species presence, and relative abundance
Genetic diversity
Amount of genetic variation present within a population
Simpson's Reciprocal Index (DI)
N = total, n = for each species
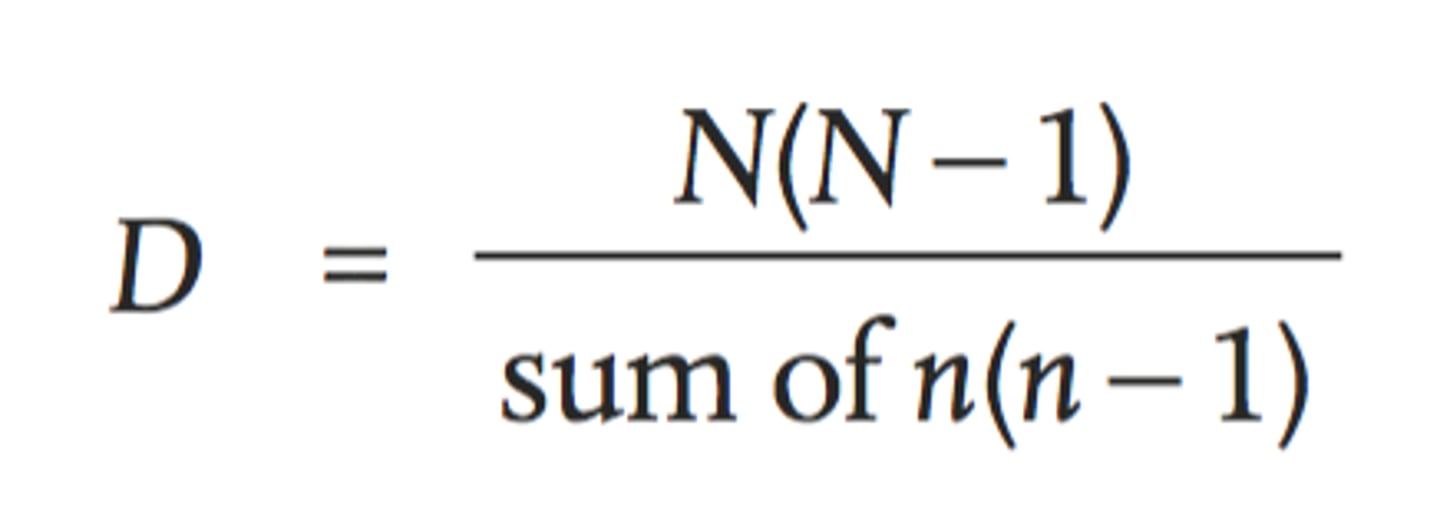
Biodiversity over time
Fluctuated due to evolution
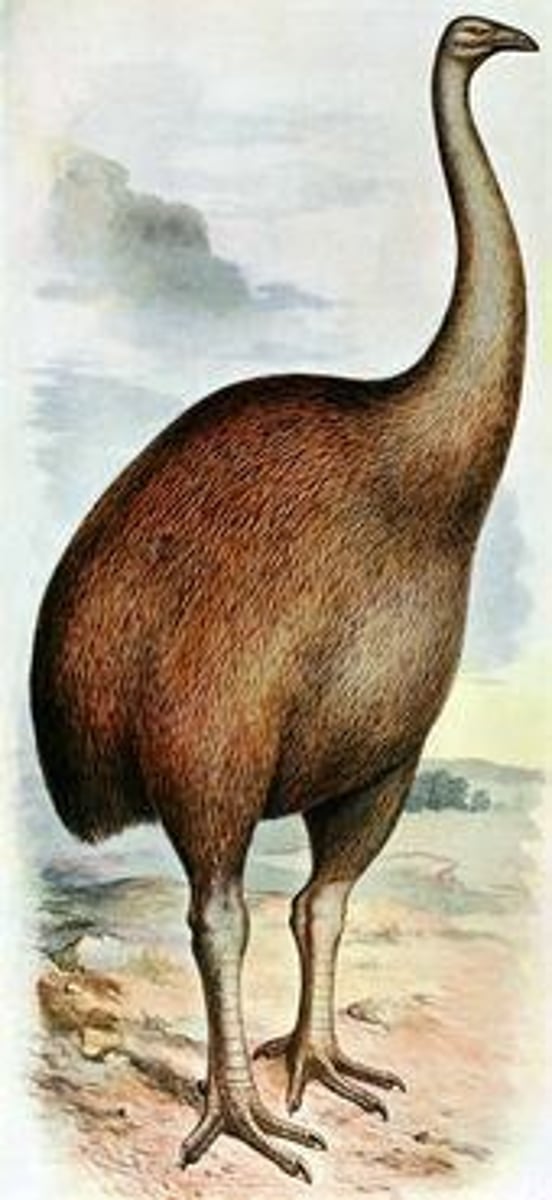
North Island Giant Moa
Anthropogenic species that were hunted by Polynesian people since they were large, couldn't fly, and not fast

Caribbean Monk Seal
Anthropogenic species that European colonists killed for science and food since they were docile, lived near rocks, and approached humans

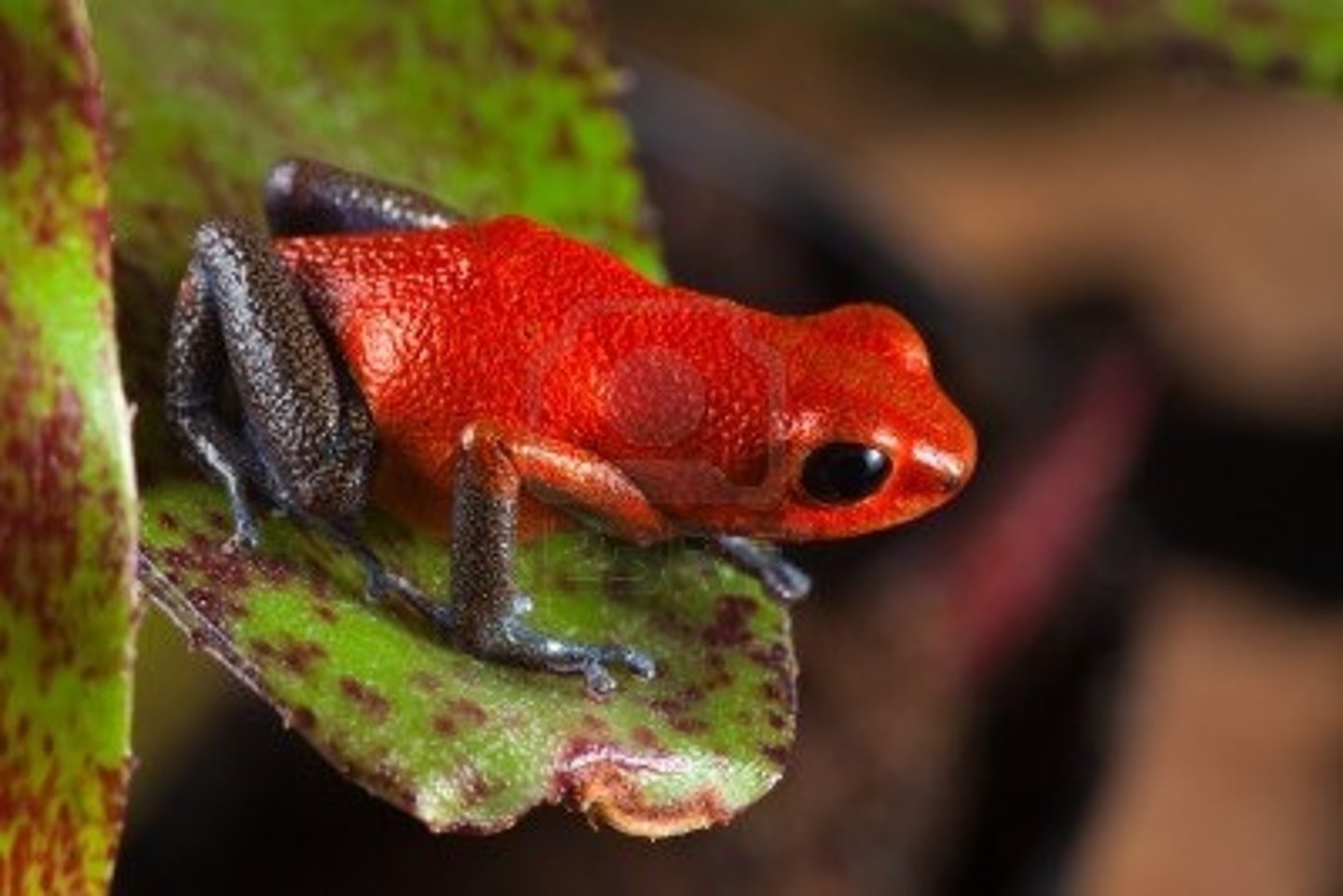
Splendid Poison Frog
Anthropogenic species that were trafficked for pet trade, with their habitats destroyed and caused outbreak of a fungal disease, since they were colourful, attracted people, and relied on the rainforest

Ways that human activity changed ecosystems
Deforestation, pollution, trashing, over-exploitation of resources, logging
Mixed Dipterocarp Forest in Southeast Asia
Lost ecosystem due to deforestation

Coral reefs (worldwide)
Lost ecosystem due to tourism, climate change, and pollution

IPBES (Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services)
Established by the UN for research to strengthen and assess biodiversity and ecosystem services, more reliable as there are more people involved and has peer review process
Causes of biodiversity crisis
Pollution, spread of disease/pests, habitat fragmentation, invasive species, clearance of land for agriculture, urbanization, hunting/ over-exploitation of resources
In situ conservation
Way of conserving animals and plants in their natural habitats while maintaining the original biodiversity of the area (national parks, nature reserves, rewilding, etc.)
Ex situ conservation
Way of conserving animals outside their natural habitats (botanic gardens, animal tissue banks, seed banks, zoos, etc.), easier to study for science reasons
EDGE of existence program
A program that generates a score of a species based on uniqueness and endangerment levels, aims to raise awareness, fund research/conservation, and train local to protect species (Chinese giant salamander, long beaked echinda)