Feeds & Feedings Exam 1
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Nutrient
A chemical compound found in feed that is necessary for cellular and physiological functions within animal species
Requirements for Nutrients
-ruminants: 4 compartments; feed microbes
-nonruminant: 1 compartment: feed everything
-production stage: nutrient requirements adjusted based on maintenance; growth/gain; gestation; lactation
6 nutrients
-water (non-organic)
-lipids
-carbohydrates
-vitamins
-minerals (non-organic)
-proteins
Water
-cheapest and most abundant
-majority of body weight: 65-85% at birth, 40-60% at maturity
decreases with age
inverse relationship with body fat b/c water and fats don’t mix
Where is water?
-in blood: 90-95%
-tissue: 70-90%
intracellular: muscle and skin
extracellular: interstitial fluid, blood plasma, lymph, synovial, cerebrospinal
urine and gastrointestinal tract
moves feed throughout the body and carries urea out in liquid form
-know water structure
Function of Water
-transport: nutrients and waste products
-chemical reactions/solvents
-temperature regulation: release of 580 calories from 1 gal water
-cell shape: majority of cell contents
-lubrication/cushion
Effects of water deficiencies
-feed consumption: first to occur- within 24 hours of restriction
decrease productivity
-weight loss due to dehydration
-increased excretion of nitrogen and electrolytes (urine and feces will be more concentrated)
-death within a few days of severe restriction
Factors affecting water consumption
-Environmental temperature and humidity
-Dry matter composition
-Dietary factors
-Access to water
-Animal function
ex-lactating animals are going to drink more to replace what they are losing via bodily function
-Urinary system
-Water quality
Water sources
-drinking water
-water in feed
highly variable
grains: 8-30%
forages: <5%-90+%
silages: 30-50%
-metabolic water: 5-10% of body water; a result of photosynthesis
How is water lost?
-urine
-feces
-insensible losses
vaporization from lungs
dissipation through skin
-sweat
-products
milk and eggs
Vitamins
-organic: distinctive from other organic compounds
-required: small amounts; minute proportion of feed
-necessity: metabolic activity & normal tissue development
-specific deficiency: absence from diet; not absorbed or utilized properly
-synthesis: not made by animal; must be supplied
-know structure
Classification of vitamins
-Fat – soluble: A,D,E,K
Stored in animal
-Water – soluble: B-vitamins & C
Not stored in significant amounts (short-term storage)
Functions of Vitamin A
-vision, bone formation
Function of Vitamin D
bone formation
Functions of Vitamin E
antioxidant, reproduction
Function of Vitamin K
bloodclotting
Function of B vitamins
-energy metabolism
-thiamine
-niacin
-riboflavin
-pantothenic acid
-choline
Function of Vitamin C
-collagen formation
-energy metabolism
Vitamin deficiencies
-vitamin A: xerophthalmia, night blindness
-vitamin D: rickets, osteomalacia, soft eggshells
-vitamin E: muscle dystrophy, encephalomalacia
-vitamin K: spontaneous hemorrhages, increased clotting time
-B vitamins: thiamine, niacine, riboflavin, pantothenic acid, choline
-vitamin C: scurvy (rare)
Vitamin toxicity
-vit A: more likely in nonruminants
-vit D: most likely in supplemented animals; calcification of soft tissue
-vit E: generally nontoxic
-vit K: dicoumarol and warfarin are antagonists'
-b vitamins: general nontoxic
-vit c: nontoxic
Sources of Vitamins
-green forages: less as forage matures; good source for most vitamins
-animal proteins: b vitamins primarily
-grains: mostly fat soluble
Minerals
-inorganic, solid, crystalline
-ash: how we measure mineral content
-approx. 3-5% of body weight
-classified as:
macrominerals: needed in large amounts (Ca, P, Na, Cl, Mg, K, S)
microminerals: needed in small amounts (Co, Cu, F, I, Fe, Mn, Mo, Se, Zn)
Minerals Function: skeletal formation/maintenance
Ca, P, Mg, Cu, Mn
Minerals Function: Protein synthesis
P, S, Zn
Minerals Function: Oxygen Transport
Fe, Cu
Minerals Function: Osmotic pressure
Na, Cl, K
Minerals Function: Acid/Base Balance
Na, Cl, K
Minerals Function: Enzyme activators
Ca, P, K, Mg, Fe, Cu, Mn, Zn
Minerals Function: Relationship with vitamins
-Ca, P, Co, Se
Ca/P deficiencies
-rickets, osteomalacia, thin-shelled eggs
Mg deficiencies
vasodilation (inability to deal with heat), hyperirritability, (grass) tetany
Fe deficiency
anemia
Cu deficiency
fading hair coat, lack of wool, anemia
I deficiency
goiter, hairless pigs or wool-less lambs at birth
Se deficiency
white muscle disease, stiff lamb disease
Sources of Minerals
-natural: forage plants are good; grains are fair
-supplements: rock deposits; many forms
Mineral toxicity
-Ca/P/Mg: high levels affect the absorption of each other
-Na: non ruminants primarily (salt above 8%); staggering, blindness, hypertensions
-Cu: extremely toxic to wool sheep (above 250 ppm)
-Se: blindness, alkali disease
Carbohydrates
-hydrates of carbon formed by combining CO2 and H2O
-general chemical formula: C1H2O1
-compounds: sugar, starch, cellulose, and gums
-very little is stored as carbohydrates in animal body
Carbohydrates as Plants
-major structural component of plants
cell contents: storage carbohydrates
sugar and starch
cell walls: structural carbohydrates
cellulose and hemicellulose
-large fraction of plant dry matter
approx. 75%
largest part of animals’ food supply
-formed by plants in photosynthesis
Carbohydrates structure
-carbons atoms arranged in chains
attached to H and O
-characterized by having a ketone (O double bonded to C with 2 R groups) or an aldehyde (O double bonded to C with 1 R group 1 H)
Classification of Carbohydrates
-monosaccharide: 1 sugar molecule (split into hexoses and pentoses)
-disaccharide: 2 sugar molecules or monosaccharides
-polysaccharide: 3 or more sugar molecules
-non-carbohydrate
Monosaccharides- Hexoses
-6 carbon sugars
-glucose: most important sugar in nutrition; major end product in CHO digestion in non-ruminants
-fructose: 75% of sugars in honey
-galactose: component of milk sugar
-mannose: found in plants like legumes
Monosaccharides- pentoses
-5 carbon sugars
-arabinose and xylose: components of hemicellulose and gums
-ribose: occurs in metabolic compounds
ATP/ADP: energy transfer
riboflavin= b vitamin
RNA: protein synthesis
DNA: genetic coding
Disaccharides
•Sucrose: table sugar
•Maltose: malting of barley
•Lactose: milk sugar
•Cellobiose: fundamental unit of cellulose
•Trehalose: found in mushrooms and insects
Polysaccharides-Homopolysaccharide
Same saccharide units
Starch (glucose & glucose)
Amylose (alpha-1,4 linkages)
14-30% of total plant starch
Amylopectin
70-85% of total plant starch
Glycogen (alpha-1,4 linkages and alpha-1,6 linkages)
Animal stored in liver and muscle
Cellulose (beta-1,4 linkages)
Comprises 25-30% of fibrous plants
Beta-glucans (beta-1,4 linkages and beta-1,3 linkages)
Found primarily in cell walls of barley, oats, and yeast
require microbes to breakdown
Polysaccharides- Heteropolysaccharides
Different saccharide units
Hemicellulose (beta-1,4-linkages)
Principal component of plant cell wall
Non-carbohydrate
lignin:
Polymer which encases cellulose & hemicellulose to enhance rigidity to plant cells
Reduces digestibility by acting as a barrier to CHO
No animal or bacteria enzyme can break lignin
silica:
Physically encrusts plant fiber in some straws
Provides a barrier to digestive enzymes or microbes
Functions of Carbohydrates
-source of energy
-source of heat
-building blocks of other nutrients
-storage energy
Deficiencies/Abnormal Metabolism- Ketosis
-carb or lipid disorder; excess ketones in blood
-high energy demands
lactation-dairy cattle
late pregnancy/parturition-sheep
-symptoms:
breakdown of tissue proteins for energy
loss of body weight
acetone smell on animal breath
Deficiencies/Abnormal Metabolism-Diabetes Mellitus
-more common in humans and pets (dogs)
-type I dependent: insufficient insulin production by pancreas
-type II dependent: tissue resistance to insulin
-often has genetic basis; may be diet related
-symptoms:
high blood glucose
excess urinary loss of glucose
Sources of carbohydrates
-most feedstuffs of plant origin, especially cereal grains
cereal grains = starch
hay and forages = cellulose and hemicellulose
silage = starch, cellulose, and hemicellulose
Lipid Structure
-77% C, 12% H, 11% O
-insoluble in water, soluble in organic solvents
-produce 2.25 times more energy than carbohydrates
Classification of lipids
-simple lipids vs. compound lipids vs. derived lipids
Simple lipids
-true fats: esters of fatty acids with glycerol (TAGs)
-waxes: esters of fatty acids with non glycerol alcohol (found on leaves)
Compound lipids
-phospholipids: contain N and phosphoric acid; make up body cell membranes
-glycolipids: contain N and carbohydrate; make up cerebrosides (myelin sheath and white brain matter)
-lipoproteins: bound to proteins
chylomicron: formed in small intestine; fat absorption (carry fat of S.I and into the body)
VLDL (high in lipids): transport lipids from liver to extra hepatic tissues
LDL (bad lipids): transport cholesterol to cell which use it
HDL (good lipids): carry excess cholesterol back to liver
Derived lipids
-derived from other groups by hydrolysis
-sterols (ring structure)
-cholesterol: found in animal tissues; precursor for other sterols (vit. D, bile salts, hormones, steroids)
-fatty acids:
physical properties: water solubility (inc. chain = less soluble); melting point (FA<10 liquid FA>10 solid); degree of saturation (inc. unsaturation = reduced m.p); susceptible to oxidation (inc. unsaturation = inc oxidation)
essential fatty acids: linoleic acid, lenolenic, arachidonic
Saturated & Unsaturated Structure
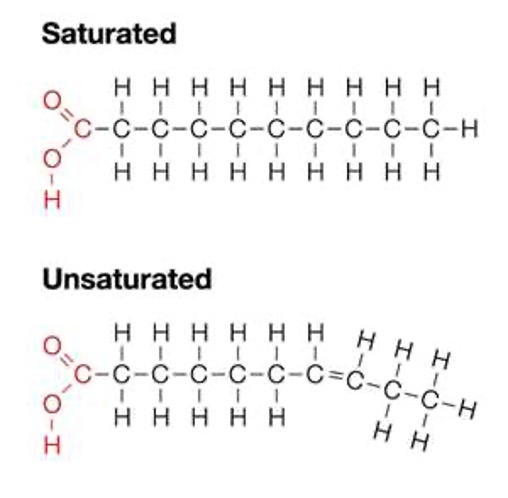
Lipid functions
-dietary energy supply
-heat, insulation, and protection
-source of essential fatty acids
linoleic acid and linolenic: cannot be synthesized by animal tissues; arachidonic: can be synthesized from linoleic acid; required only if linoleic is absent)
-carrier for absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
Lipids deficiency/abnormal metabolism
-monogastric diets: skin lesions, hair loss, poor feather in chicks, reduced growth or reproduction
-ketosis: insufficient energy; catabolize body reserves; toxic levels of ketones produced
-fatty livers: abnormal liver function; high fat/cholesterol diet, increased lipogenesis
Sources & Storage of Lipids
-storage: animal body in subcutaneous, surround organs, marbling or milk; in plant seed germ or embryo
-sources: less than 10% in cereal grains, forages, etc; up to 20% in unprocessed “oil seeds”- soybeans, cottonseed, sunflower
Protein Structure
-only nutrient that has N (16%)
-principle constituent of organs and soft tissue (muscle)
-dietary requirement: highest in young animals, but declines in age
-made up of amino acids- 22 amino acids found in proteins, linked together by peptide bonds
-function of proteins depend on arrangement and length of amino acid chain
Amino Acid Classifications
-neutral
-acidic
-basic
-imino
Neutral amino acids
-aliphatic: glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, isoleucine, serine, threonine
-aromatic: phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan
-sulfur containing: cysteine, cystine, methionine
Acidic amino acids
-aspartic acids, asparagine, glutamine, glutamic acid
Basic amino acids
-histidine, arginine, lysine
Imino
-proline, hydroxyproline
Protein structure
-primary: amino acid sequence; determined by genetic
-secondary: twisting of the peptide chain; alpha helices and beta sheets
-tertiary: coils or folds resulting in rigid structure of layers
-quaternary: several tertiary structures linked together
Protein classification
-simple (globular): yields only amino acids during hydrolysis (albumin, globulins, glutelins, prolamins)
-fibrous: connective tissue (collagens, elastins, keratins)
-conjugated: protein combined with nonprotein radical (glycoproteins, lipoproteins, metalloproteins)
Protein terminology
-true protein: protein composed of only amino acids
-nonprotein nitrogen: contain N; converted to protein by microbes
-crude protein (CP): % N x 6.25
-digestible protein: portion of CP digested; difference between feed and in feces
Essential amino acids
-10 essential amino acids: phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, etc.
-2 for poultry: glycine and proline
Protein function
-basic structural unit of animal body
collagen
elastin
contractile protein
keratin proteins
blood proteins
-body metabolism
enzymes: digestion, degradation, synthesis process
hormones
immune antibodies'
hereditary transmission
-source of energy after deamination: amine group removed
Protein deficiency
-reduced growth
-anorexia
-reduced serum albumin
-anemia
-infertility
-reduced synthesis of enzymes and hormones
Sources of proteins
-most common feedstuffs contain at least some protein
quality and quantity vary
important to provide essential amino acids for non-ruminants
high protein feed stuffs; oilseed meals, grain byproducts, animal byproducts