Cytoskeleton I: Filament structure and regulation
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
cytoskeleton is a complex and highly regulated network of interconnected - (three things) in the cytoplasm
microtubules, actin, and intermediate filaments
cytoskeleton serves as - and -
stable infrastructure, dynamic scaffold
intermediate filaments are - in diameter made of - proteins, providing major support in - and -
~10 nm, fibrous IF, nuclear lamina, axons
microtubules are long hollow tubes - in diameter made of - assembled into a - providing rigid support in a variety of cell structures
~25 nm, tubulin dimers, ringed tube
actin filaments are - assembled from many a - with a diameter of -
helical polymers, actin monomers, ~5-9 nm
microtubules are like the - of the cell
MTs emanate from - within -
bones, MTOC, centrosomes
in pre-mitotic G1 cell, all cytosolic - project from a - outward to the -
MTs, single chromosome, PM
centrosomes duplicate during S-phase and migrate to - poles of the cell during M-phase where specific types of Mts attach to - to align them and pull - apart
opposite, chromosomes, sister chromatids
actin filaments act like the - of the cell
actin filaments are found in all - cells and all throughout their -
muscles, eukaryotic, cytosol
concentrated actin gel forms underneath the plasma membrane called the -
cell cortex
actin fibers can also be bundled into - that impart physical - with -
longer stress fibers, strength, flexibility
reorganization of actin filaments mediates dramatic changes in - (three things)
cell shape, structure, and movement
intermediate filaments act like the - of the cell
nuclear lamins are the - found in all eukaryotic cells that underly the - of the nuclear envelope
ligaments, ancestral intermediate filaments, inner membrane
cytosolic IFs provide structural support to cells, especially those subjected to -
- are specialized IFs that are crucial to the formation of neuronal axons
shearing forces, neurofilaments
all three types of subunits self-assemble into -
helical filaments
intermediate filaments assemble from - proteins winding around each other
two alpha helical fibrous
actin “nucleus” is a trimer of -
MT “nucleus” is a large ringe of more than thirteen -
globular monomers, globular tubulin dimers
nuclear lamins are present in all - cells, the - proteins that line the inner membrane of the nuclear envelope
nuclear lamins are essential for -, serving as anchoring sites
eukaryotic, filamentous, nuclear integrity
cytosolic IFs are found in only certain -, including nematodes, molluscs, and vertebrates
cytosolic IFs are not in all cell types of these animals and are abundant in cells subjected to lots of -
metazoans, mechanical stress
individual IF filamentous proteins assemble into -
the multimers further assemble to create the -
rope-like multimers, intermediate filaments
actin monomer is a - subunit in the cell, a highly conserved - present in all eukaryotic cells
free soluble, ATPase
actin filaments assemble from identical monomers of actin in a - configuration with plus/minus -
head-to-tail, polarity
minus end of monomer contains opening of -, allowing for entry of - and exit of -
ATP binding domain, ATP, ADP
ATP-bound actin subunits have an - (increased/decreased) affinity with each other
filament ends with unhydrolyzed ATP-bound subunits favour - of monomers, resulting in -
filament ends with hydrolyzed ADP-bound subunits favour - of monomers, resulting in -
increased, addition, polymerization, dissociation, de-polymerization
in reality an actin filament grows by stacking two monomers -
side by side
actin filaments are - compared to microtubules; but can be - or - into stronger actin networks
flexible, bundled, cross-linked
actin monomers can associate or dissociate from - (plus/minus/either) end of the filament, if the end - (is/isn’t) capped
either, isn’t
at low concentrations of available actin monomers, there is a net - from either/both ends, resulting in -
at high concentrations of available actin monomers, there is a net - from either/both ends, resulting in -
dissociation, de-polymerization
association, polymerization
due to structural differences between actin plus and minus ends, the - end has greater -, meaning it is more sensitive to changes in -therefore de/polymerization occurs more at the - end
plus, dynamic instability, monomer concentration, plus
at steady state, there is no net - or - of the filament, resulting in treadmilling
growth, shrinkage
formins are a family of - proteins that nucleate the formation of - that can be assembled into parallel bundles
dimeric, straight, unbranched actin filaments
each formin subunit binds to an actin monomer, bringing - together in a ring-like configuration that nucleates growth of a - or joins both monomers to the - end of an -
two monomers, new filament, plus, existing actin filament
formin dimer maintains its association with one of the two actin monomers at the growing - end, allowing a new actin monomer to be added to the available -
plus, formin binding site
profilin bound to actin monomers interact with - and promotes association between - and - to grow the plus end of actin filaments
formin whiskers, actin, formin
free, soluble form of tubulin in the cell is a heterodimer of - and -
alpha, beta tubulin
alpha and beta tubulin monomers are both - and can binds one molecule of - but only beta tubulin has - in the dimer or MT filament
GTP in beta-tubulin is exposed on the - end and can dissociate or be hydrolyzed to GDP by its GTPase activity
GTPases, GTPase activity, GTP
plus
GTP-bound tubulin dimers have - (higher/lower) affinity for each other and for MT ends still containing -
higher, GTP
tubulin dimers self-assemble as helical rings, forming - and - lateral contacts between tubulin subunits in -
result is a stiff microtubule containing 13 parallel protofilaments with a defined polarity: - : -
alpha-alpha, beta-beta, adjacent protofilaments
alpha→beta, minus→plus
a microtubule polymerizes - to - end
because minus end of microtubule is usually -, polymerization and de-polymerization tend to occur at the - end
minus, plus
stabilized, plus
multiple ATP (-) or GTP (-)-bound subunits can form a - at the growing end of a filament
actin, microtubule, T cap
presence of T cap favours - due to the - affinity of incoming ATP or GTP-bound subunits for ATP or GTP-bound ends
polymerization, higher
loss of T cap occurs when hydrolysis of ATP/GTP is - (slower/faster) than subunit addition
faster
kinetics of - and - at one or both filament ends are highly regulated and can result in net filament -
ATP/GTP hydrolysis, subunit addition/loss, de/polymerization
treadmilling results in steady-state balance between addition of - and dissociation of - from filament ends
new ATP-bound subunits, ADP-bound subunits
changes in - of soluble subunits affect the kinetics of subunit association and shift steady-state towards filament polymerization or depolymerization at - or - subunits concentrations, respectively
available concentration, high, low
rate of association and dissociation gives koff/kon = Kd = -
critical subunit concentration
critical subunit concentration (Cc) is the subunit concentration at which - is achieved
equilibrium
Kd for hydrolyzed --bound subunits is higher than for --bound subunits
ADP, ATP
de/polymerization of actin is regulated by -
accessory proteins
what is regulation of actin polymerization is mediated by?
two actin monomer binding proteins: thymosin and profilin
thymosin binds and - actin monomers from associating with either end of the filament, preventing -
inhibits, polymerization
profilin competes with - for binding to actin monomers, promoting - of monomers with filament ends and -
thymosin, association, polymerization
stathmin performs similar inhibitory function in microtubule polymerization by sequestering - and - (decreasing/increasing) the effective concentration of free tubulin in the cell
tubulin subunits, decreasing
phosphorylation of stathmin inhibits its binding to - and favours microtubule -
free tubulin, polymerization
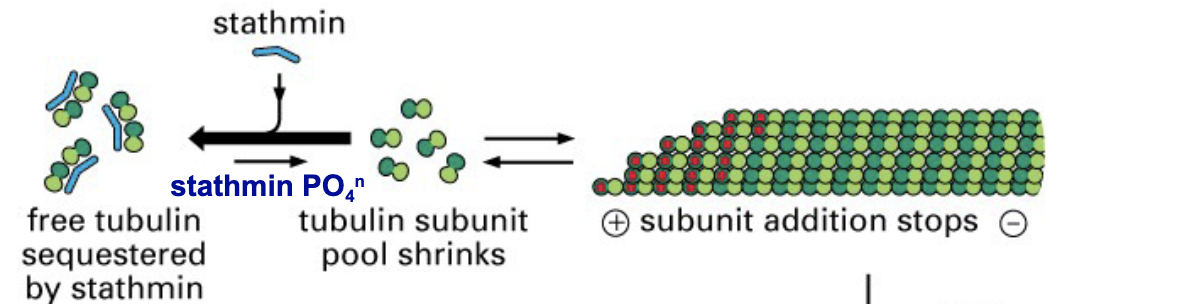
what happens after?
GTP hydrolysis catches up and microtubule shrinks
tropomyosin reduces - with each other
actin filament interactions
cofilin increases -
actin filament turn-over
cofilin is a small protein able to bind to - and -
free actin subunits, filaments
cofilin binds all along the length of actin filament and twists it into a tighter coiled-coil, applying -, weakening the -, resulting in - of actin filaments
mechanical stress, subunit interactions, depolymerization
cofilin preferentially binds - to facilitate filament turn-over for re-organization
older ADP bound actin filaments
MAPs are -
microtubule-associated proteins
MAPs have - or - MT binding domains that laterally link microtubules together into more -
two, three, stable parallel bundles
- of MAP domain that projects and contacts the adjacent MT dictates the - between filaments and thickness of bundle
length, packing distance
short domain of MAP results in - packing (-)
long domain of MAP results in - packing (-)
tighter, tau
looser, MAP2
MAPs are particularly abundant in - (three things)
axons, dendrites and neurites
MAPs are regulated by - in response to signalling
phosphorylation
capping proteins bind to the - of the filaments and have dramatic effects on net - or - of filaments
ends, growth, shrinkage
CapZ binds to the - end of actin filaments and makes it -
plus, inactive
gamma-tubulin nucleates and caps MT - ends and organizes them into a growth center ( - and -)
minus, MTOC, centrosome
MAPs can also bind to MT - and stabilize the -
ends, length
catastrophe factors take microtubule protofilament ends -, resulting in - of MT length
apart, destabilization
severing filaments creates new ends, facilitating - and/or - of filaments
rapid turn-over, reorganization
specialized - (GTPase/ATPase) called - is required to break the 13-protofilament bonds in a microtubule
crucial to - during mitosis
ATPase, katanin
spindle fiber reorganization
severing of actin filaments requires breaking of only - bonds and does not require -
two, ATP
actin severing proteins belong to - superfamily which all respond to high levels of -
gelsolin, Ca2+
gelsolin can also cap -, preventing -
severed ends, depolymerization
cofilin severs both filaments but also promotes their -
depolymerization