Toxins/ overdoses
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What is the first priority in any toxicology presentation?
ABCs. Airway, breathing, circulation must be stabilized before toxin-specific therapy.
Who should be contacted early in unclear poisoning cases?
Poison Control / Medical Toxicology. Early guidance improves outcomes.
TCA OD primary treatments
Bicarb push/gtt. Increases serum sodium avalible, and makes alkalotic state which release TCA form todium channels.
What is a toxidrome?
A recognizable pattern of signs and symptoms that points to a toxin class.
Activated Charcole indications
With in 1-2 hours of injestions, large volume, and if can swallow. Meds include anticholinergics,
Which toxidrome presents with miosis, salivation, bronchorrhea, and diarrhea?
Cholinergic toxidrome. Classic for organophosphates.
Which toxidrome presents with mydriasis, dry skin, urinary retention, and delirium?
Anticholinergic toxidrome. “Dry as a bone, blind as a bat…”
Which toxidrome presents with diaphoresis, hypertension, agitation, and mydriasis?
Sympathomimetic toxidrome. Seen with cocaine, methamphetamine.
Which toxidrome presents with respiratory depression, pinpoint pupils, and bradycardia?
Opioid toxidrome. Triad: miosis, respiratory depression, AMS.
Which toxidrome presents with bradycardia, hypotension, and hypoglycemia?
Beta-blocker toxicity. Hypoglycemia is a key differentiator.
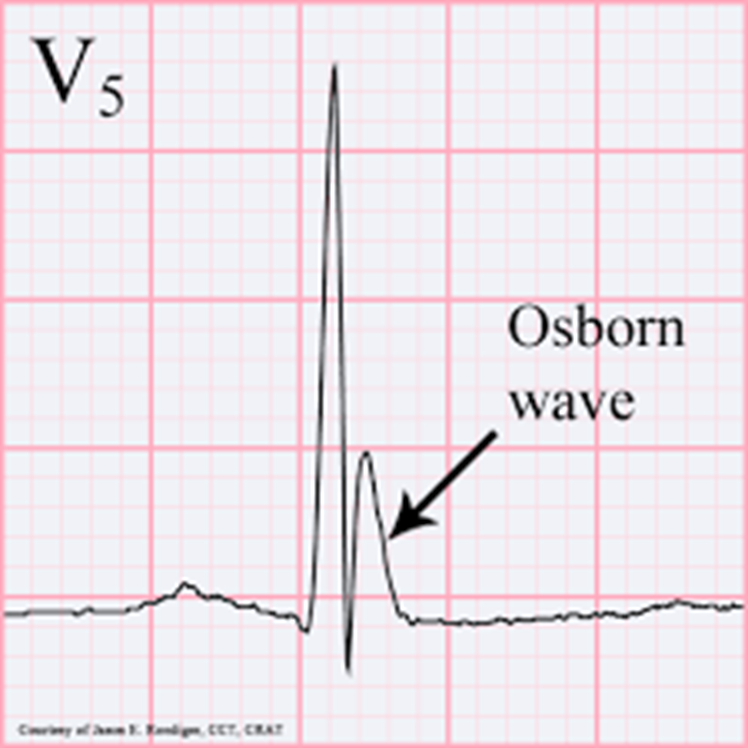
Osborn wave indicates hypothermia
What finding differentiates anticholinergic vs sympathomimetic toxidromes?
Sweating. Sympathomimetics cause sweat; anticholinergics do not.
Within what time window is activated charcoal most effective?
Within 1 hour. Works best before drug leaves stomach.
What tool determines need for treatment in acetaminophen overdose?
Rumack–Matthew nomogram. Used only for single acute ingestions.
CCB OD primary treatments
Calcium, and insulin to push Ca back into cells
N acetylcysteine dose
150mg/kg x 3 doses
What overdose type cannot be assessed with the Rumack–Matthew Nomogram?
Chronic or staggered ingestion. Not validated for repeated doses.
What lab marker rises early in acetaminophen toxicity?
Transaminases. Indicate hepatocellular injury.
S/s of acetmainophein toxicity?
Liver fialure, hypotn, cerbral edema
What is the mechanism of acetaminophen toxicity?
Toxic metabolite causing oxidative liver injury from the CYP 340 system
What prognostic tool helps determine transplant need in acute liver failure?
King’s College Criteria.
What fulfills King’s College Criteria?
pH <7.3 after resuscitation OR all three of: Grade III/IV encephalopathy, INR >6.5, and creatinine >3.4.
Which stage of acetaminophen toxicity presents with RUQ pain?
Hepatic injury phase.
What is the final stage of acetaminophen toxicity?
Liver toxic stage
What antidote prevents acetaminophen hepatotoxicity?
N-acetylcysteine. Replenishes glutathione.
What timing maximizes NAC effectiveness?
Within 8 hours. Early treatment prevents liver injury.
For Tylenol toxicity, when does the liver become most affected?
72-96 hoursafter ingestion of a toxic dose.
Digoxin toxicity S/s
Letherygy, confusion, laxy eye, bradycardia, arrythmiasand gastrointestinal disturbances.
Digoxin toxic levels
> 2.0 mg/dl
Digoxin toxicity treatment
Activated Charcole, hyper K protocol, atropine, DIGIBIND
What lab finding suggests toxic alcohol ingestion?
Elevated osmolar gap.
Which toxic alcohol causes retinal toxicity and blindness?
Methanol.
Which toxic alcohol causes kidney injury from oxalate crystals?
Ethylene glycol.
What is the mechanism of fomepizole in toxic alchool OD?
Inhibits alcohol dehydrogenase, stopping toxic metabolites.
What metabolic pattern is common in toxic alcohol ingestion?
High anion gap metabolic acidosis.
What microscopy finding is classic in ethylene glycol poisoning?
Calcium oxalate crystals.
What symptom strongly suggests methanol toxicity?
Visual disturbances (“snowstorm” vision).
Salicylate OD treatment
Supportive. Vent, bicarb bush/gtt for AGMAand alkaline diuresis. Consider hemodialysis for severe cases.
In which toxic alcohol poisonings may dialysis be required?
Methanol or ethylene glycol.
Primary antidote for beta blocker toxicity?
Glucoagone 5-10 mg IV bolus then 2-5 mg/hr infusion and high-dose insulin therapy even if eglucemic. Not to treat the hyperglycemia, but to shift calcium back into the cell to bolster cardiac function.
What is the hallmark EKG finding in TCA overdose?
QRS widening. Due to sodium channel blockade.
What mechanism causes TCA cardiotoxicity?
Fast sodium channel inhibition.
What symptom cluster reflects anticholinergic effects of TCAs?
Delirium, urinary retention, dry skin.
What major complication results from TCA-induced hypotension?
Cardiogenic shock.
What is the primary treatment goal in TCA toxicity?
Stabilize myocardium and improve conduction.
What neuro complication is common in TCA overdose?
Seizures.
What metabolic finding is classic in beta-blocker overdose, and calcium channel blocker? Why?
Hypoglycemia.
What antidote bypasses beta-receptors to increase cAMP?
Glucagon.
What shared mechanism explains shock in BB and CCB toxicity?
Decreased myocardial contractility.
Why is high-dose insulin used in BB/CCB overdose?
Improves myocardial glucose uptake and contractility.
Which beta-blocker overdose is especially associated with seizures?
Propranolol.
What finding helps distinguish CCB from BB toxicity?
Hyperglycemia suggests CCB overdose.
What exam finding suggests severe CCB toxicity?
Bradycardia with warm extremities.
What symptom may BB toxicity mimic?
Stroke symptoms due to hypoglycemia.
What rhythm is common in severe BB toxicity?
Junctional bradycardia.
What early metabolic pattern occurs in CCB toxicity?
Mild metabolic acidosis.
What tool assesses alcohol withdrawal severity?
CIWA-Ar.
What neurotransmitter imbalance causes alcohol withdrawal?
Decreased GABA and increased glutamate.
Which alcohol withdrawal stage includes hallucinations?
Stage II.
What is the most dangerous alcohol withdrawal complication?
Delirium tremens/ seizures
Which withdrawal resembles alcohol withdrawal?
Benzodiazepine withdrawal.
What symptom suggests benzodiazepine overdose?
Sedation without major respiratory depression. Can have minor resp dep
What drug can precipitate severe withdrawal in chronic benzo users?
Flumazenil.
What finding differentiates opioid from sedative toxidrome?
Pinpoint pupils.
What respiratory pattern is typical in sedative overdose?
Hypoventilation.
What temperature abnormality is more likely in sedative overdose?
Hypothermia.
What acid–base disorder is classic in salicylate poisoning?
Mixed respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis.
What symptom suggests salicylate-induced CNS toxicity?
Tinnitus.
What pulmonary complication occurs in salicylate poisoning?
Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema.
Why do salicylates cause hyperventilation?
Directly stimulate the respiratory center.
What GI symptoms raise suspicion for salicylate toxicity?
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain.
Which antidepressant overdose commonly causes seizures?
Bupropion.
Which OTC drug is the leading cause of acute liver failure?
Acetaminophen.
What skin color is classic in carbon monoxide poisoning?
Cherry red appearance.
What SpO₂ abnormality occurs in carbon monoxide poisoning?
Normal pulse ox despite severe hypoxia.
What symptom differentiates CO poisoning from viral illness?
Multiple family members with headache simultaneously.
Which mushroom causes delayed liver failure?
Amanita phalloides.
What symptom is most distinctive for opioid withdrawal?
Yawning.
What is the most common fatal event in opioid overdose?
Respiratory arrest.
What finding strongly suggests cyanide toxicity?
AMS with severe lactic acidosis.
What blood color suggests methemoglobinemia?
Chocolate-brown blood.